7d7a72b05cd670775831d65e904f146a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37

Objectives 1. How should Gemini respond in terms of scientific effectiveness the current to the competition from Subaru, ESO and perhaps even Keck? 2. What does the Gemini Science Staff want to see discussed and proposed at Aspen 2003 • What is our vision of the Future?

The Gemini telescopes are designed to compete by exploiting D/q For background or sky noise limited observations: S N Telescope Diameter (D) . Delivered Image Diameter (q) Speed = Time to given S/N D 2 q . B B Where: is the product of the system throughput and detector QE B is the instantaneous background flux
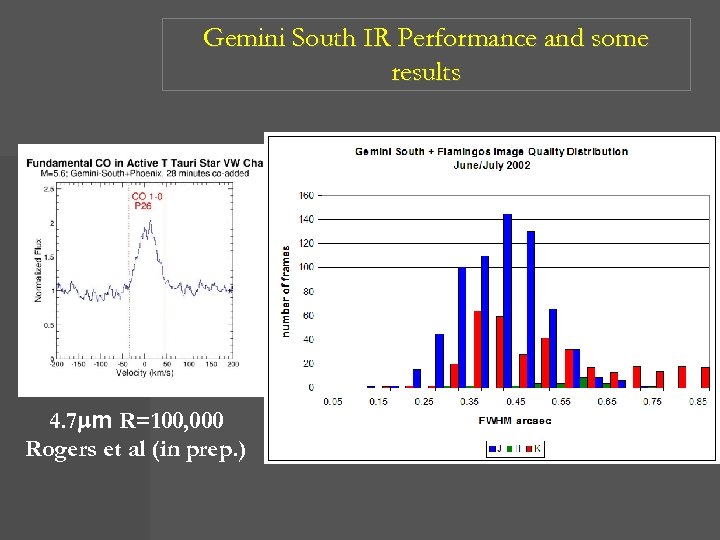
Gemini South IR Performance and some results 4. 7 mm R=100, 000 Rogers et al (in prep. )
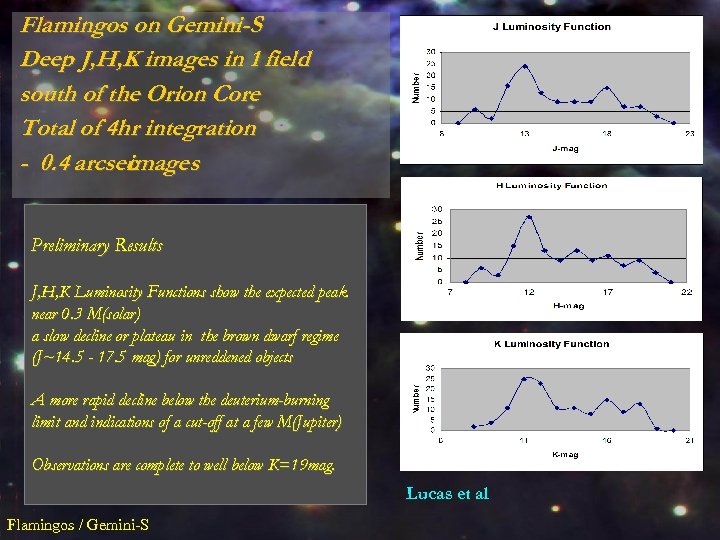
Flamingos on Gemini-S Deep J, H, K images in 1 field south of the Orion Core Total of 4 hr integration - 0. 4 arcsec images Preliminary Results J, H, K Luminosity Functions show the expected peak near 0. 3 M(solar) a slow decline or plateau in the brown dwarf regime (J~14. 5 - 17. 5 mag) for unreddened objects A more rapid decline below the deuterium-burning limit and indications of a cut-off at a few M(Jupiter) Observations are complete to well below K=19 mag. Lucas et al Flamingos / Gemini-S
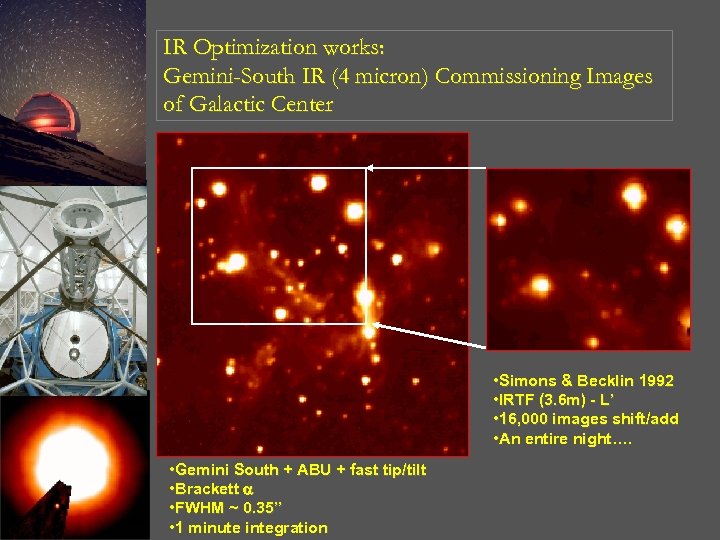
IR Optimization works: Gemini-South IR (4 micron) Commissioning Images of Galactic Center • Simons & Becklin 1992 • IRTF (3. 6 m) - L’ • 16, 000 images shift/add • An entire night…. • Gemini South + ABU + fast tip/tilt • Brackett • FWHM ~ 0. 35” • 1 minute integration
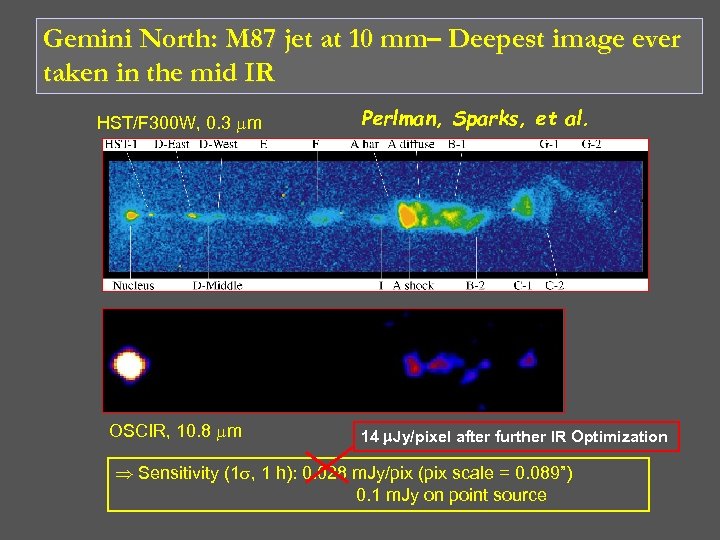
Gemini North: M 87 jet at 10 mm– Deepest image ever taken in the mid IR HST/F 300 W, 0. 3 m OSCIR, 10. 8 m Perlman, Sparks, et al. 14 m. Jy/pixel after further IR Optimization Þ Sensitivity (1 , 1 h): 0. 028 m. Jy/pix (pix scale = 0. 089”) 0. 1 m. Jy on point source
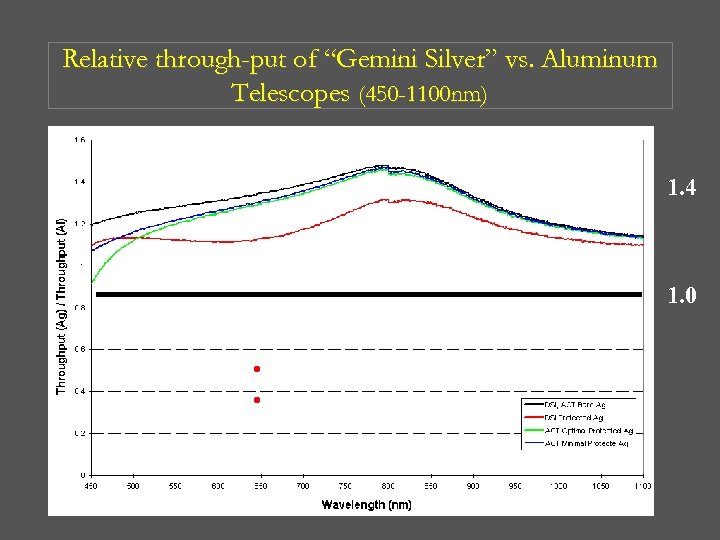
Relative through-put of “Gemini Silver” vs. Aluminum Telescopes (450 -1100 nm) 1. 4 1. 0 • Ratio of System Transmission • Three Reflecting Surfaces

Gemini in the Optical – GMOS North comes on-line 60 min – 140 min per filter GMOS on Gemini 5. 5’ x 5. 5’ Seeing (FWHM) 0. 5 – 0. 7 arcsec 5 sigma detection limits : g'=27. 5 mag r'=27. 2 mag i'=26. 3 mag PMN 2314+0201 Quasar at z=4. 11 Gemini SV PI: Isobel Hook

GMOS Queue Observing 2002 A Summary of the completion rates as fraction of programs ============================= Band 1 2 3 4 Completion rate >90% >50% <50% --------------------10/14=0. 71 11/14=0. 79 3/14=0. 21 2/8 =0. 25 3/8 =0. 38 5/8 =0. 63 2/8 =0. 25 4/8 =0. 50 1/11=0. 09 2/11 =0. 18 9/11=0. 82 Many observations in band 3 and 4 were taken in poor observing conditions, and the programs in these bands with significant data were programs that could tolerate CC=70% or worse, and seeing of 1 arcsec or worse. Gemini North reliability GMOS Observing efficiency (shutter open/elapsed) >90% (<10% down time) ~ 70%
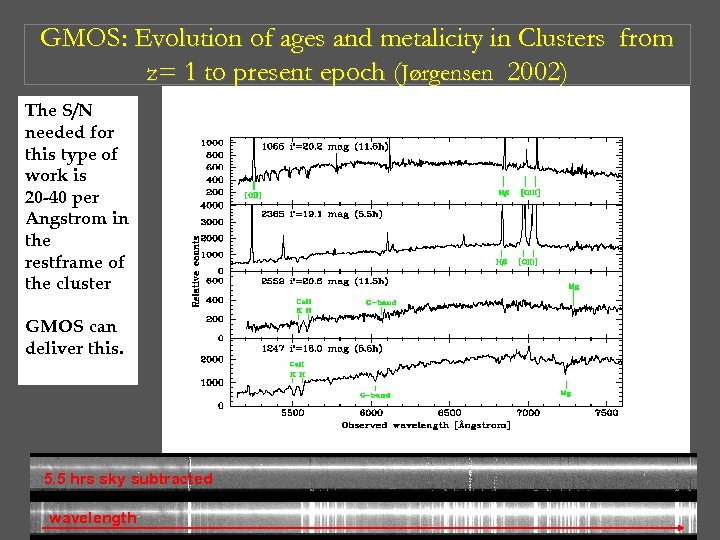
GMOS: Evolution of ages and metalicity in Clusters from z= 1 to present epoch (Jørgensen 2002) The S/N needed for this type of work is 20 -40 per Angstrom in the restframe of the cluster GMOS can deliver this. 5. 5 hrs sky subtracted wavelength
![Example object: N&S subtracted I=23. 8 z=1. 07 [OII] 3727 at 7700Å The GDDS Example object: N&S subtracted I=23. 8 z=1. 07 [OII] 3727 at 7700Å The GDDS](https://present5.com/presentation/7d7a72b05cd670775831d65e904f146a/image-11.jpg)
Example object: N&S subtracted I=23. 8 z=1. 07 [OII] 3727 at 7700Å The GDDS team
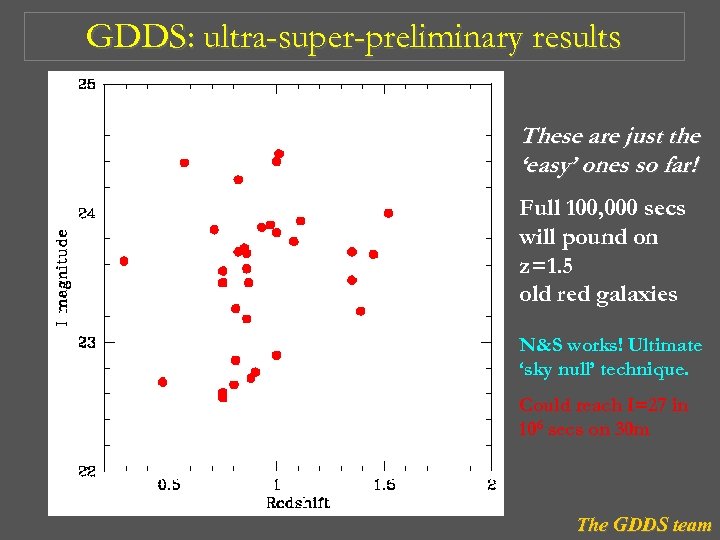
GDDS: ultra-super-preliminary results These are just the ‘easy’ ones so far! Full 100, 000 secs will pound on z=1. 5 old red galaxies N&S works! Ultimate ‘sky null’ technique. Could reach I=27 in 106 secs on 30 m The GDDS team

Y ( 5 arcsec ) 3 C 324 3 -D data cube at z = 1. 2 X (7 arcsec) [OII]3727 structure has two velocity components at +/-400 km/s Wavelength/velocity Bunker et al (2002)

CIRPASS early results – first use of a near-IR IFU on an 8 m-class telescope. The example from the z=1. 2 radio galaxy 3 C 324. Dispersion runs horizontally, spatial direction is vertical; each of the 500 IFU lenslets produces a spectrum 2 pixels high. The preliminary processing (basic sky subtraction and cosmic ray rejection) of this single 20 minute exposure shows a very clear detection of the redshifted [OIII] 500. 7 nm emission line (centre of the frame). http: //www. gemini. edu/sciops/instruments/cirpass. Demo. Science. html GMOS – IFU now available on Gemini North CIRPASS – IR IFU will be available on Gemini South in Service Mode in 2003 A
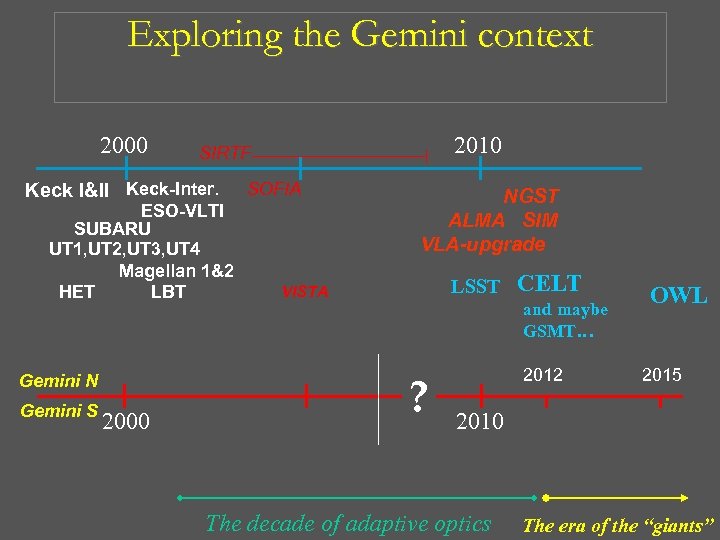
Exploring the Gemini context 2000 Keck I&II Keck-Inter. ESO-VLTI SUBARU UT 1, UT 2, UT 3, UT 4 Magellan 1&2 HET LBT Gemini N Gemini S 2000 2010 SIRTF SOFIA NGST ALMA SIM VLA-upgrade LSST VISTA CELT and maybe GSMT… ? 2012 OWL 2015 2010 The decade of adaptive optics The era of the “giants”
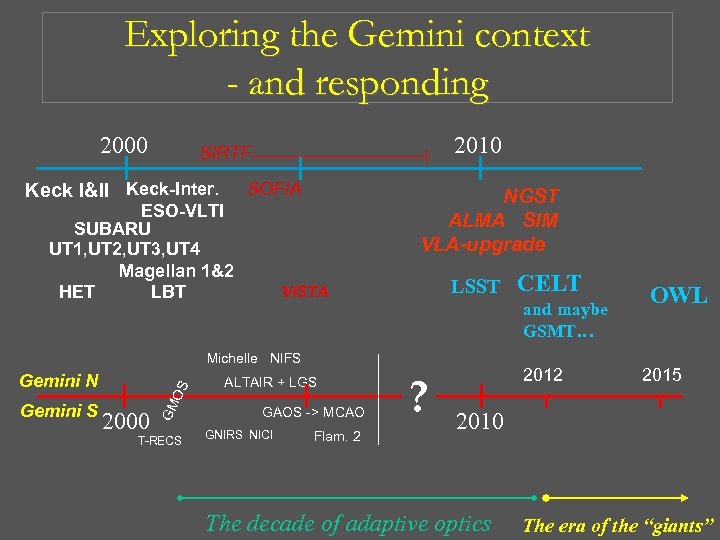
Exploring the Gemini context - and responding 2000 2010 SIRTF Keck I&II Keck-Inter. SOFIA ESO-VLTI SUBARU UT 1, UT 2, UT 3, UT 4 Magellan 1&2 HET LBT NGST ALMA SIM VLA-upgrade LSST VISTA and maybe GSMT… Michelle NIFS 2000 GM Gemini S OS Gemini N T-RECS ALTAIR + LGS GAOS -> MCAO GNIRS NICI Flam. 2 CELT ? 2012 OWL 2015 2010 The decade of adaptive optics The era of the “giants”
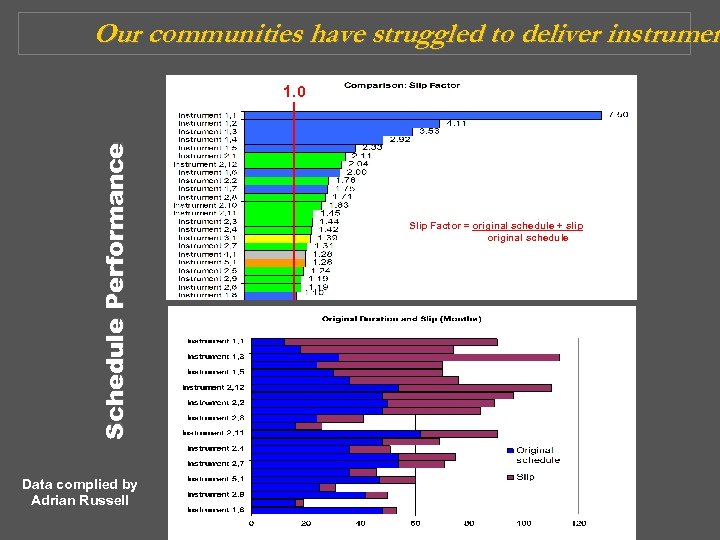
Our communities have struggled to deliver instrumen Schedule Performance 1. 0 Data complied by Adrian Russell Slip Factor = original schedule + slip original schedule
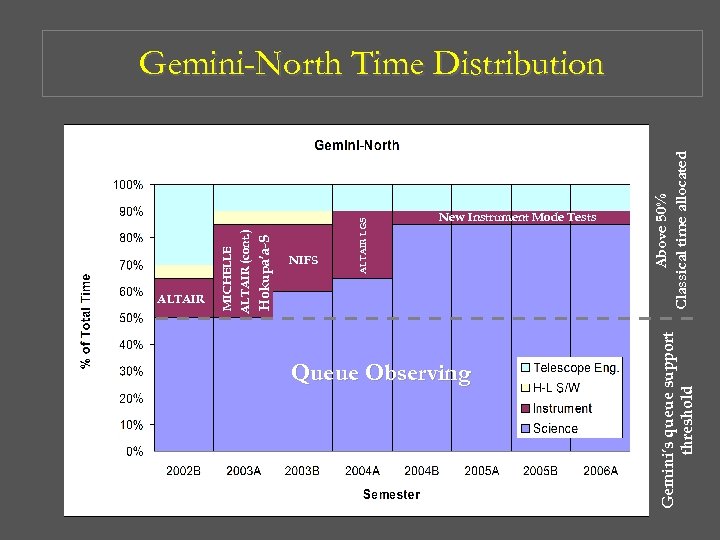
Hokupa’a-S ALTAIR LGS NIFS Queue Observing Above 50% Classical time allocated New Instrument Mode Tests Gemini’s queue support threshold ALTAIR MICHELLE ALTAIR (cont. ) Gemini-North Time Distribution
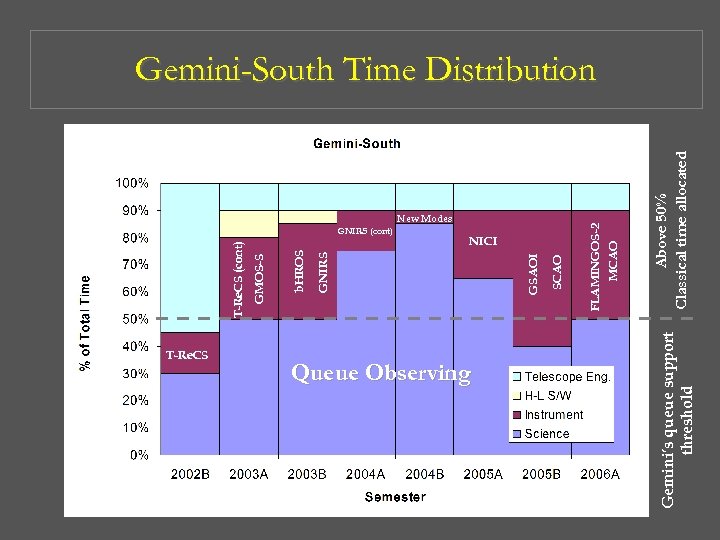
T-Re. CS NICI Above 50% Classical time allocated FLAMINGOS-2 MCAO New Modes Gemini’s queue support threshold Queue Observing SCAO GNIRS (cont) GSAOI GNIRS b. HROS GMOS-S T-Re. CS (cont) Gemini-South Time Distribution

Challenges • Instruments, instruments…… • Gemini South will be without facility instruments until mid 2003 from the user perspective • And instrument delivery schedules constrain science availability of Gemini Telescopes • How do we maximize our science effectiveness? • Should we commission everything we get?

Responding to the Future • MCAO Ø Building a system • Aspen 2003 Instrumentation Workshop Ø Planning Gemini instruments for 2007+ • The competition in the next decade (post 2012) ØExploring our “market place”
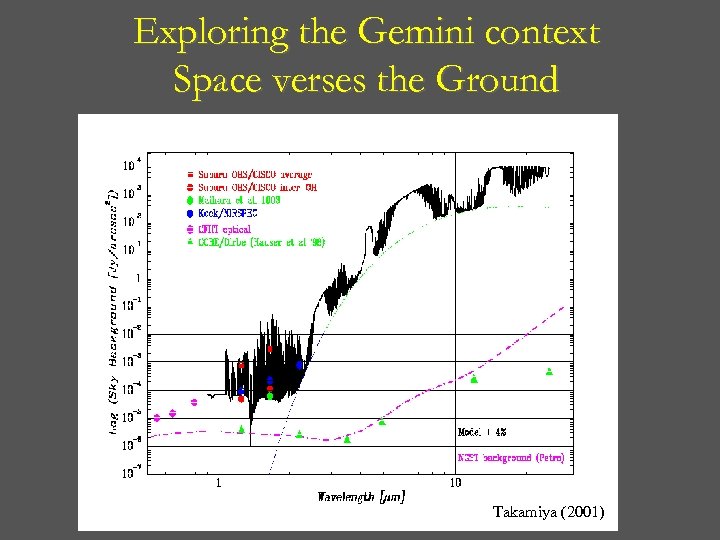
Exploring the Gemini context Space verses the Ground Takamiya (2001)
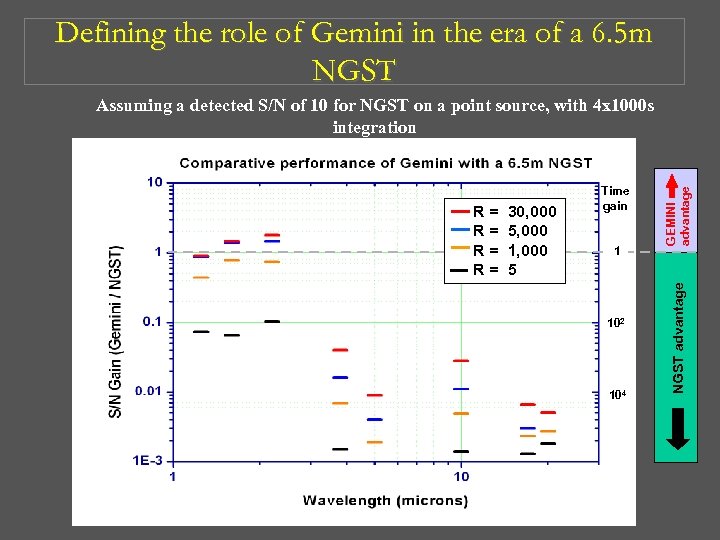
Defining the role of Gemini in the era of a 6. 5 m NGST 30, 000 5, 000 1, 000 5 1 102 104 NGST advantage R= R= Time gain GEMINI advantage Assuming a detected S/N of 10 for NGST on a point source, with 4 x 1000 s integration

Redefining “wide field” in the 8 – 10 m era NICMOS HDF 49”x 49” GMOS on Gemini 5. 5’ x 5. 5’ PMN 2314+0201 Quasar at z=4. 11 5 sigma detection limits : g'=27. 5 mag r'=27. 2 mag i'=26. 3 mag 235 Objects down to AB mag 28. 8 at 1. 6 mm >1000 objects

The Future and Exploiting our strengths Image quality • Diffraction limited, near IR AO, thermal IR • Optical – exploiting queue scheduling -- AO enhanced seeing Efficiency • Minimizing emissivity -- Maximizing through-put • Highly multiplexed spectroscopy • The “automated queue” Innovation • How do we sustain innovation is such a competitive environment? But let’s look a little further ahead……

Entering the Era of Giants - the Challengers in the post 2012 World ALMA

Entering the Era of Giants - the Challengers in the post 2012 World The 30 m challengers The ~6 -8 m challenger CELT NGST The 100 m challenger GSMT OWL
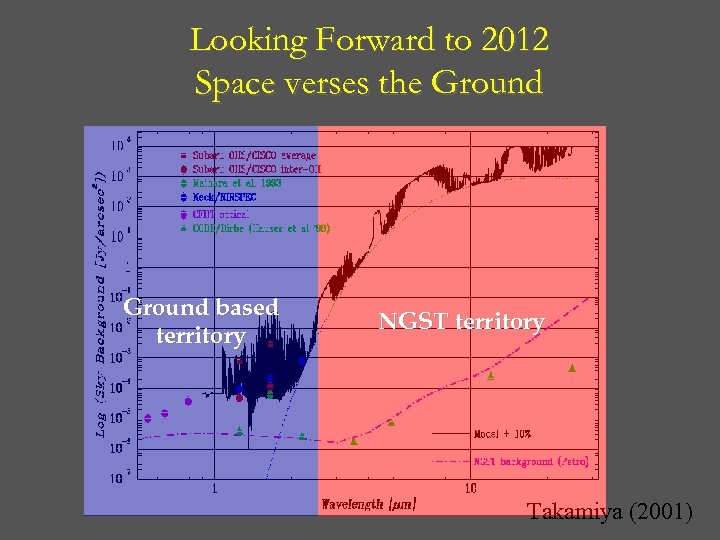
Looking Forward to 2012 Space verses the Ground based territory NGST territory Takamiya (2001)
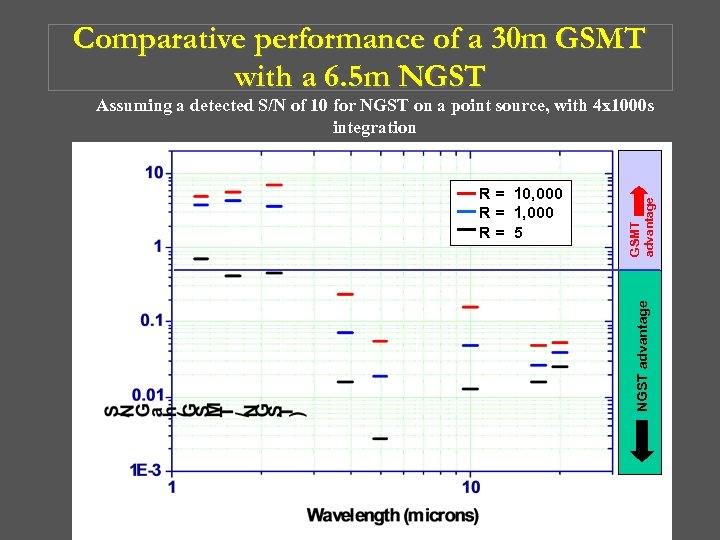
Comparative performance of a 30 m GSMT with a 6. 5 m NGST advantage R = 10, 000 R = 1, 000 R= 5 GSMT advantage Assuming a detected S/N of 10 for NGST on a point source, with 4 x 1000 s integration

GSMT: Galaxy Evolution Courtesy of M. Bolte
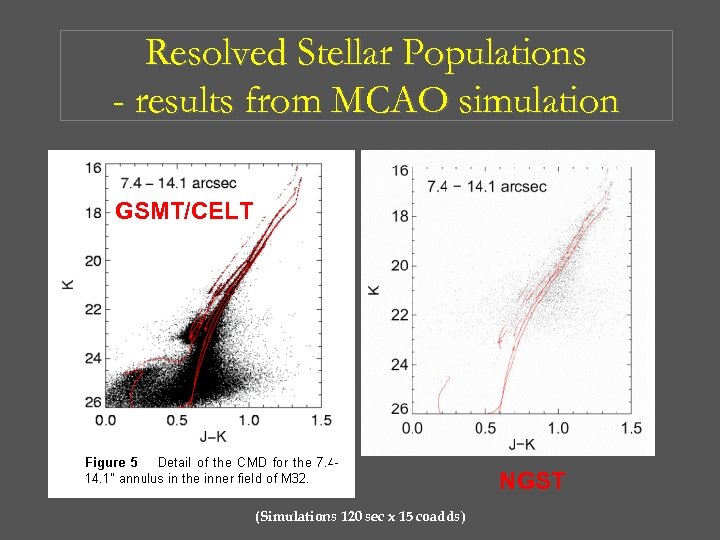
Resolved Stellar Populations - results from MCAO simulation GSMT/CELT NGST (Simulations 120 sec x 15 coadds)
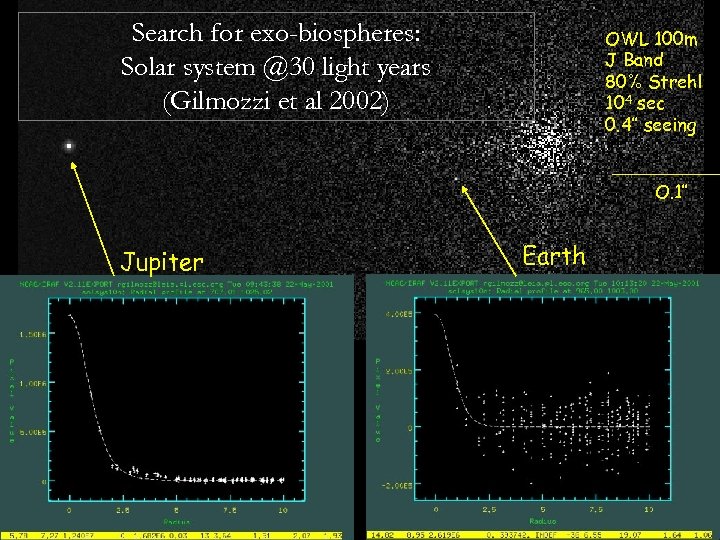
Search for exo-biospheres: Solar system @30 light years (Gilmozzi et al 2002) OWL 100 m J Band 80% Strehl 104 sec 0. 4’’ seeing O. 1’’ Jupiter Earth
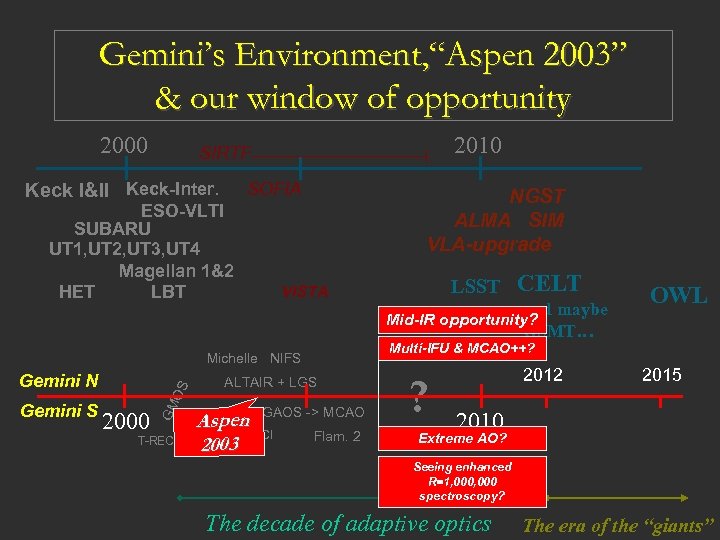
Gemini’s Environment, “Aspen 2003” & our window of opportunity 2000 2010 SIRTF Keck I&II Keck-Inter. SOFIA ESO-VLTI SUBARU UT 1, UT 2, UT 3, UT 4 Magellan 1&2 HET LBT NGST ALMA SIM VLA-upgrade VISTA OS 2000 GM Gemini S T-RECS ALTAIR + LGS GAOS -> MCAO Aspen GNIRS NICI 2003 CELT and maybe Mid-IR opportunity? GSMT… OWL Multi-IFU & MCAO++? Michelle NIFS Gemini N LSST Flam. 2 ? 2012 2015 2010 Extreme AO? Seeing enhanced R=1, 000 spectroscopy? The decade of adaptive optics The era of the “giants”
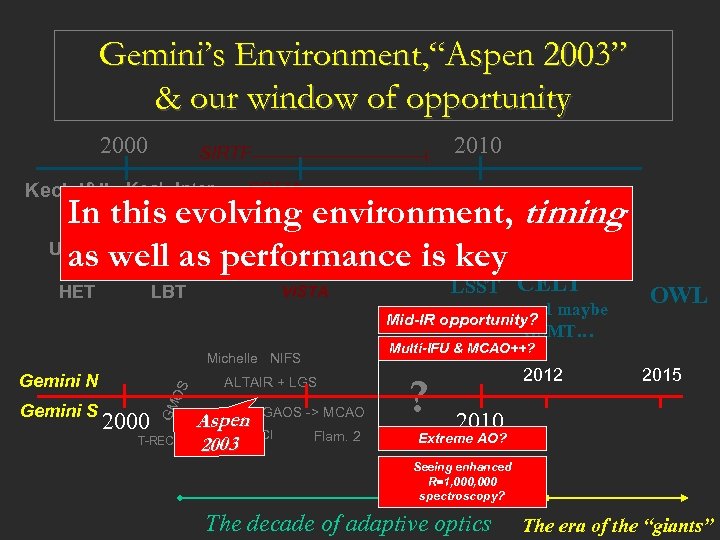
Gemini’s Environment, “Aspen 2003” & our window of opportunity 2000 2010 SIRTF Keck I&II Keck-Inter. SOFIA NGST ALMA SIM VLA-upgrade ESO-VLTI In this evolving environment, timing SUBARU UT 1, UT 2, UT 3, UT 4 as well as performance is key Magellan 1&2 HET LBT VISTA OS 2000 GM Gemini S T-RECS ALTAIR + LGS GAOS -> MCAO Aspen GNIRS NICI 2003 CELT and maybe Mid-IR opportunity? GSMT… OWL Multi-IFU & MCAO++? Michelle NIFS Gemini N LSST Flam. 2 ? 2012 2015 2010 Extreme AO? Seeing enhanced R=1, 000 spectroscopy? The decade of adaptive optics The era of the “giants”

Conclusions and thoughts • Staying competitive in the 2010 decade is going to be challenging: • We will have to [very thoughtfully] play to our strengths • Gemini: IR performance, image quality • • Mauna Kea and Cerro Pachon SUBARU: Extremely versatile high-performance telescope, unprecedented wide field performance, Mauna Kea ESO……. . ? ? ? • By 2012, in the era of, ALMA, NGST and “the emerging Giants must ” we be globally acknowledged, world-class science machines Ø But probably quite specialized ‘queue based’ machines Ø And ‘classical’ time will be allocated to Project Teams (and their instruments), not individuals…. . Ø optimum use of “remote observing” to create “virtual teams”

Challenges • Instruments, instruments…… • Gemini South will be without facility instruments until mid 2003 from the user perspective • And instrument delivery schedules constrain science availability of Gemini Telescopes • Should we commission everything we get?

Conclusions and thoughts • We must understand our respective “market places” – starting today • Can we continue to duplicate facility instruments at $7 M - $15 M each? • Should we begin to explore time exchange models?
7d7a72b05cd670775831d65e904f146a.ppt