e6f58911713f5e7104805fbe4450cd84.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 57

Objective n The learner will determine appropriate measuring tools, units, and scales

The Metric System n Length = Meters n Capacity = Liters n Weight = Grams n King Harry Died Drinking Chocolate Milk Kilo, Hecto, Deka, Deci, Centi, Milli u

The Customary System n Length 12 inches (in) 3 ft 5, 280 ft = = = 1 foot (ft) 1 yard (yd) 1 mile (mi) Capacity 8 fluid ounces (oz) 2 c 2 pt 4 qt n Weight = = 1 cup (c) 1 pint (pt) 1 quart (qt) 1 gallon (gal) 16 dry ounces (oz) 2, 000 lb = = 1 pound (lb) 1 ton (T) n

Measurement Match Tell which metric & customary unit you would use to measure each item Length of house key - centimeter, inch Thickness of nickel - millimeter, inch Width of classroom - meter, feet Length of piece of chalk - centimeter, inch Height of pine tree - meter, feet Distance from Baton Rouge to Shreveport - meters, miles

Choose the Best Estimate Height of an average man A. 18 cm B. 1. 8 m C. 6 km D. 36 mm n Volume of a coffee cup n A. 300 m. L B. 20 L n C. 5 L D. 1 k. L Width of a math book A. 215 mm B. 75 cm C. 2 m D. 1. 5 km n Mass of an average man A. 5 mg n Mass of a dime A. 3 g n B. 15 cg C. 26 g D. 90 kg B. 30 g C. 10 cg D. 1 kg Length of a basketball court A. 1000 mm B. 250 cm C. 28 m D. 2 km

Measurement Match Tell which metric & customary unit you would use to measure each item Length of a book - centimeter, inch Contents of soda can - milliliter, ounces A load of bricks - kilogram, pounds Distance between 2 cities - kilometer, miles Water in a swimming pool - kiloliter, gallons Width of the letter A - millimeter, inch

Customary Conversion Review Decide if you multiply or divide, then complete the conversion 6000 lb = ___ T, divide by 2000 3 8000 ft = ____ mi , divide by 5280 1. 51 80 10 gal = ____ pt , multiply by 8 7 c = ____ pt , divide by 2 3. 5 2 T = 4000 lb, multiply by 2000 ____ 3. 5 ft = ____ in, multiply by 12 42

Worksheet n Choosing best measurement

Objective n The learner will distinguish between precision & accuracy of measurements

Unit 7: Measurement n. Measuring means to compare something with a standard n. Measuring requires an instrument

Measurements n Consists of two parts A Number u. Unit n Must have both parts u. Ex: I have a cat that is 3 u years old? months old? days old?
Ruler (Instrument of Measurement) n. Demonstrate how to use a ruler n. Students measure using Customary Measurements worksheet

What is Accuracy? n What does it mean to be accurate? n Accuracy tells us how CORRECT the measurement is. n Accuracy is how CLOSE a number is to what it should be. n Accuracy is determined by comparing a number to a known or accepted value.

What is Precision? n What does it mean to be precise? n Precision is the degree to which repeated readings agree. n Precision can be the number of decimal places assigned to the measurement. n The precision of an instrument reflects the number of digits in the reading.

Accuracy and Precision n Accuracy and precision can not be considered independently n A number can be accurate and not precise n A number can be precise and not accurate n The use of the number determines the relative need for accuracy and precision

Example 1: n How old are you? I am 16 years old u. I am 15 years and 8 months old u. I am 15 years, 8 months, and 5 days old u. I am 15 years, 8 months, 5 days, and 10 hours old u
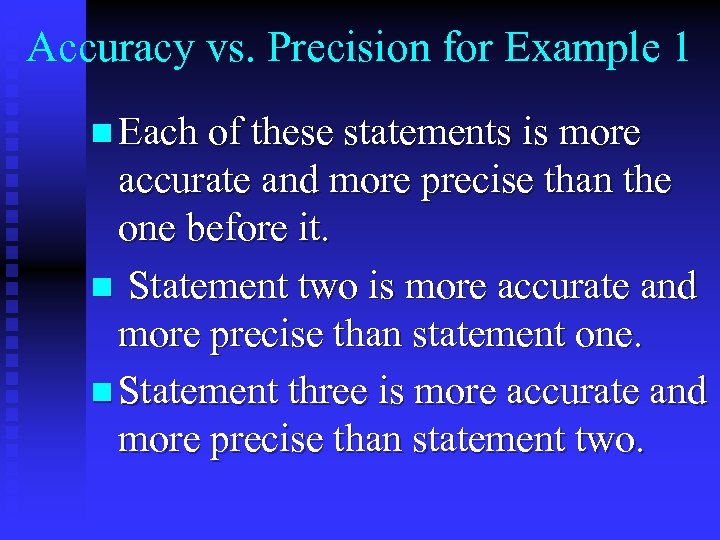
Accuracy vs. Precision for Example 1 n Each of these statements is more accurate and more precise than the one before it. n Statement two is more accurate and more precise than statement one. n Statement three is more accurate and more precise than statement two.

Example 2: n How long is a piece of string? Johnny measures the string at 2. 63 cm. u Using the same ruler, Fred measures the string at 1. 98 cm. u Who is most precise? u Who is most accurate? u

Accuracy vs. Precision for Example 2 n The actual measurement is 2. 65 cm. n Johnny is fairly accurate and also very precise. n Fred is very precise, however, he is not very accurate. His lack of accuracy is due to using the ruler incorrectly.

ACCURACY/PRECISION n You can tell the precision of a number simply by looking at it. The number of decimal places gives the precision. n Accuracy on the other hand, depends on comparing a number to a known value. Therefore, you cannot simply look at a number and tell if it is accurate.

Activity n Lesson 1: Linear Measurement n Unit 7: Activity 4

When Do We Need to Be Accurate & Precise? ? n Making Accurate Measurements n Accuracy (Actual) & Precision (Predict)

Target Examples Were we accurate or precise? This is a random-like pattern, neither precise nor accurate. The darts are not clustered together and are not near the bull’s eye.

Target Examples Were we accurate or precise? This is a precise pattern, but not accurate. The darts are clustered together but did not hit the intended mark.

Target Examples Were we accurate or precise? This is an accurate pattern, but not precise. The darts are not clustered, but their average position is the center of the bull’s eye.

Target Examples Were we accurate or precise? This pattern is both precise and accurate. The darts are tightly clustered and their average position is the center of the bull's eye.

Objective n. The learner will use significant digits in computational problems.

REMEMBER: Scientific Notation • Used to deal with very small or very large numbers as powers of 10 Examples: 0. 00002 is written as 2 x 10 -5 4, 000 is written as 4 x 106 Note: a negative exponent just means it’s a number less than 1

Significant Digits • Not every number your calculator gives you can be believed • Every measurement has error in it so the calculations do too

Significant Digits - all digits in a number representing data or results that are known with certainty plus one uncertain digit.

The measuring device determines the number of significant digits a measurement has. n In this section you will learn u to determine the correct number of significant digits to record in a measurement u to count the number of significant digits in a recorded value u to determine the number of significant digits that should be retained in a calculation. Significant Digits n

For example, if you measured the length, width, and height of a block you could calculate the volume of a block: Length: 0. 11 cm Volume = lwh Width: 3. 47 cm Height: 22. 70 cm Volume = 0. 11 cm x 3. 47 cm x 22. 70 cm = 8. 66459 cm 3 Where do you round off? = 8. 66? = 8. 7? 8. 66459? n

RECOGNITION OF SIGNIFICANT DIGITS Significant Digits • All nonzero digits are significant. • 3. 51 has 3 significant digits • The number of significant digits is independent of the position of the decimal point • Zeros located between nonzero digits are significant • 4055 has 4 significant digits

• Zeros at the end of a number (trailing zeros) are significant if the number contains a decimal point. Significant Digits • 5. 7000 has 5 sig figs • Trailing zeros are not significant if the number does not contain a decimal point • 2000. versus 2000 • Zeros to the left of the first nonzero integer are not significant. • 0. 00045 (note: 4. 5 x 10 -4)

Significant Digits How many significant figures are in the following? 4 7. 500 4 2009 3 600. 4 0. 003050 6 80. 0330

Significant Digits 6 2. 30900 2 0. 00040 4 30. 07 1 300 2 0. 033

Significant Digits SCIENTIFIC NOTATION & SIGNIFICANT DIGITS • Often used to clarify the number of significant digits in a number. • Example: 4, 300 = 4. 3 x 1, 000 = 4. 3 x 103 0. 070 = 7. 0 x 0. 01 = 7. 0 x 10 -2

SIGNIFICANT DIGITS IN CALCULATION OF RESULTS Significant Digits I. Rules for Addition and Subtraction • The answer in a calculation cannot have greater significance than any of the quantities that produced the answer. • example: 54. 4 cm + 2. 02 cm 54. 4 cm 2. 02 cm 56. 42 cm correct answer 56. 4 cm

Significant Digits II. Rules for Multiplication and Division • The answer can be no more precise than the least precise number from which the answer is derived. • The least precise number is the one with the fewest significant digits Which number has the fewest sig figs? The answer is therefore, 3. 0 x 10 -8

For example, if you measured the length, width, and height of a block you could calculate the volume of a block: Length: 0. 11 cm Volume = lwh Width: 3. 47 cm Height: 22. 70 cm Volume = 0. 11 cm x 3. 47 cm x 22. 70 cm = 8. 66459 cm 3 Where do you round off? = 8. 66? = 8. 7? 8. 66459? n

Significant Digits Rules for Rounding Off Numbers • When the number to be dropped is less than 5 the preceding number is not changed. • When the number to be dropped is 5 or larger, the preceding number is increased by one unit. • Round the following number to 3 sig figs: 3. 34966 x 104 =3. 35 x 104

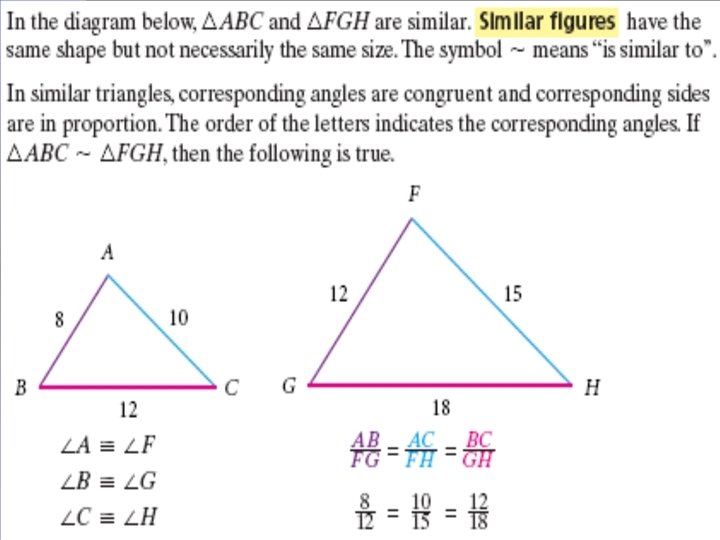
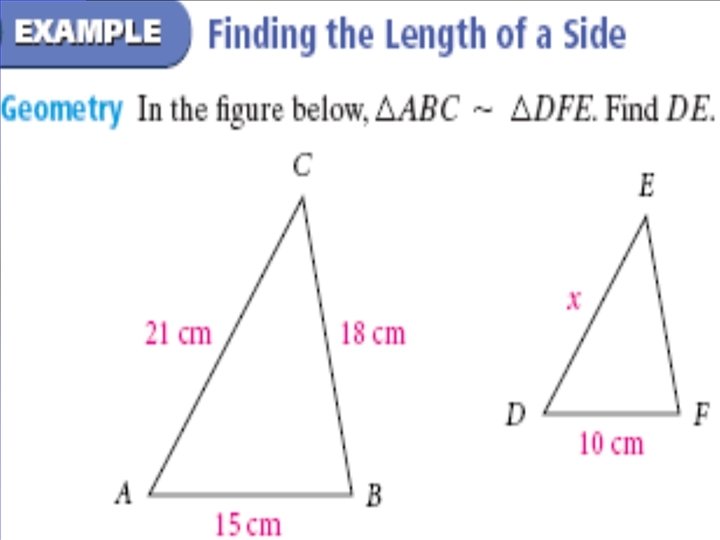
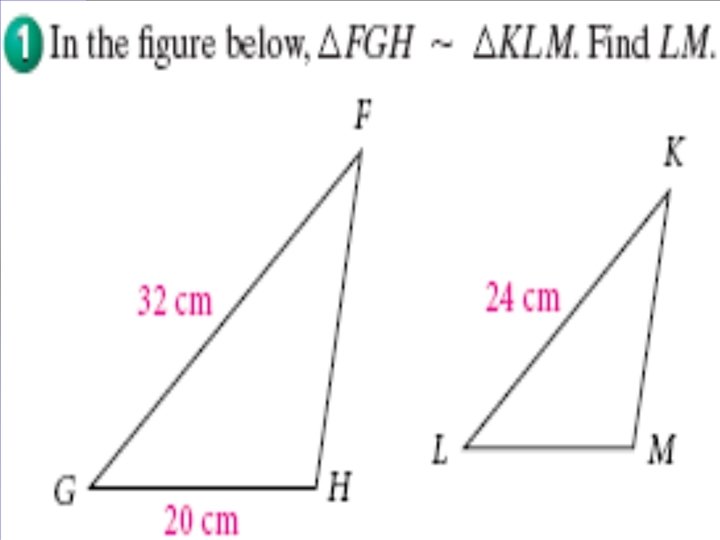
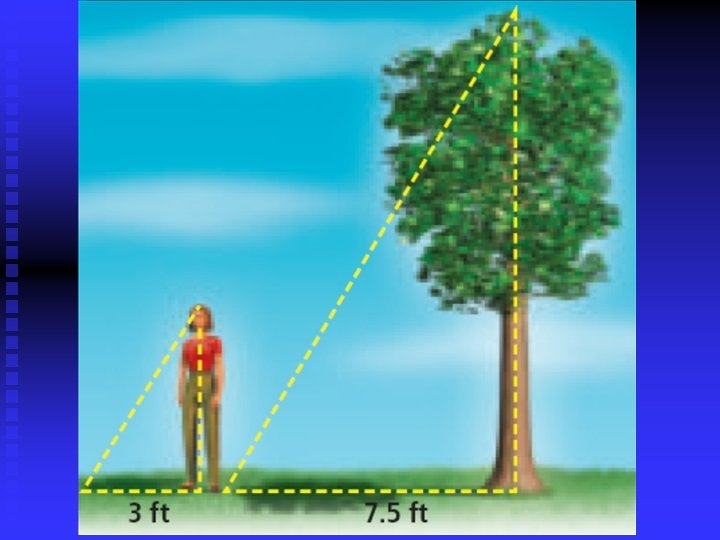
Objective n. The learner will solve problems using indirect measurement & similar triangles (Lesson 4 -2)

Think – Pair - Share n. How thick is a sheet of paper? n. How much does a grain of rice weigh?

Using Proportions n. Rates (miles/gallon, words/minute) n. Indirect Measurement (shadow, similar triangles) n. Scale Drawings (maps, scales, floor plans)


A ratio is the comparison of two numbers by division. A ratio can be written as a fraction. For example: Your school’s volleyball team has won 7 games and lost 3 games. What is the ratio of wins to losses? Because we are comparing wins to losses the first number in our ratio should be the number of wins and the second number is the number of losses. The ratio is games won games lost = 7 games 3 games = 7 3

In a ratio, if the numerator and denominator are measured in different units then the ratio is called a rate. A unit rate is a rate per one given unit, like 60 miles per 1 hour. Example: You can travel 120 miles on 60 gallons of gas. What is your fuel efficiency in miles per gallon? Rate = ____ 120 miles 60 gallons ____ 20 miles = 1 gallon Your fuel efficiency is 20 miles per gallon.

Example The table at right gives several prices for different sizes of the same brand of apple juice. Find the unit rate (cost per ounce) for the 16 -oz size.
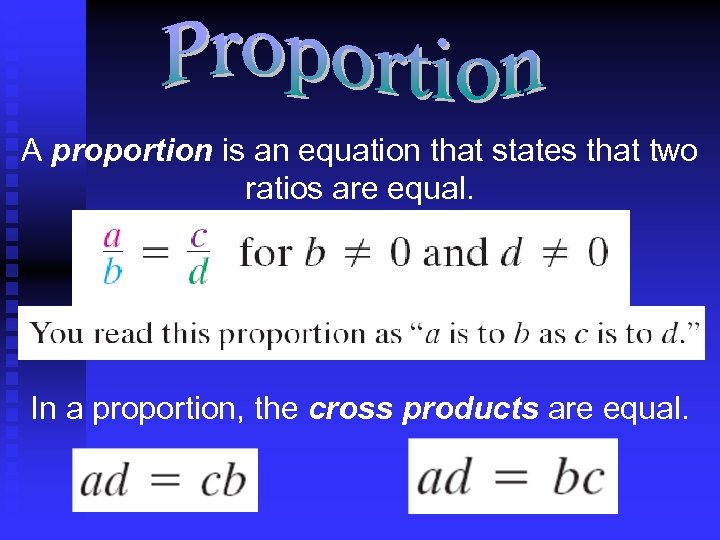
A proportion is an equation that states that two ratios are equal. In a proportion, the cross products are equal.

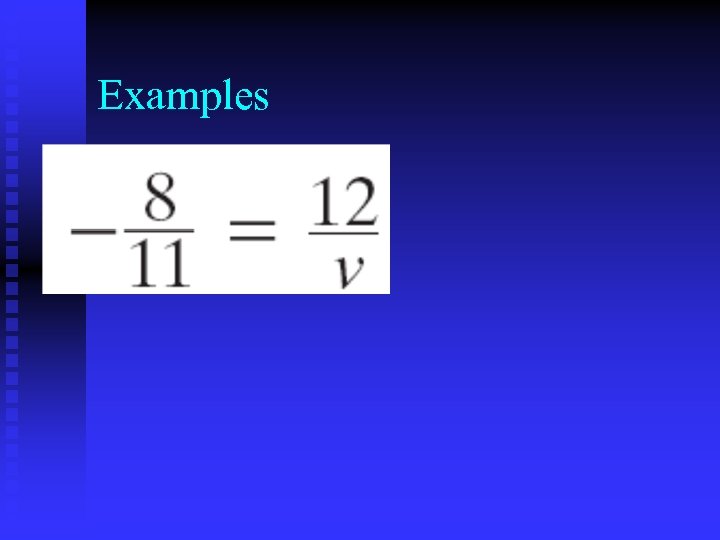
Examples


The scale of the map at the left is 1 inch : 10 miles. Approximately how far is it from Valkaria to Wabasso?
e6f58911713f5e7104805fbe4450cd84.ppt