73f162d04c74fc0ce1950ea96d21732b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

Objective 2. 03 Analyze financial and legal aspects of home ownership

So you want to buy a house… • Most people need to borrow money called a mortgage • Mortgages are contracts outlining terms of a loan between lenders and borrowers • Loans are repaid monthly over a term of 15 -30 years.

Fixed Rate Mortgages (interest rate and monthly payment are constant) 1. Conventional 2. FHA-insured: (Federal Housing Administration) guarantees mortgages made to those with lowmedium credit 3. VA loan: loan guaranteed by the Veterans Administration.

Estimating What You Can Afford • Gross income X 2. 5 = price of house you can afford • Buyers must also have a down payment that must be paid in cash!

Down Payment Calculation • Example: $72, 000 with 10% down payment • Cost of house = $72, 000. 00 • 10% down payment = $7200 • Amount to finance = $64, 800 • Example: $72, 000 with 20% down payment • Cost of house = $72, 000. 00 • 20% down payment = $14, 400. 00 • Amount to finance = $57, 600. 00 • Larger the down payment, the smaller the mortgage!

Qualifying for a Loan 1. Housing to Income Ratio: ALL of your housing Ratio costs should equal no more than 28% of your gross monthly income 2. Debt to Income Ratio: Monthly housing costs plus long-term debts total no more than 36% of your gross monthly income 3. BOTH ratios must be met to qualify for a loan!

Stop here and complete “Calculating Housing Costs”

The Purchasing Process 1. Agreement of sale or purchase agreement: States all the conditions of the sale 2. Earnest Money: – Shows you are serious – Applied to cost of house or refunded if buyer cannot get a loan.

3. Abstract of title or title search: – Makes sure the seller is the true owner of the house – Makes sure there are no debts on the house 4. Survey: – Makes sure property lines are accurate.
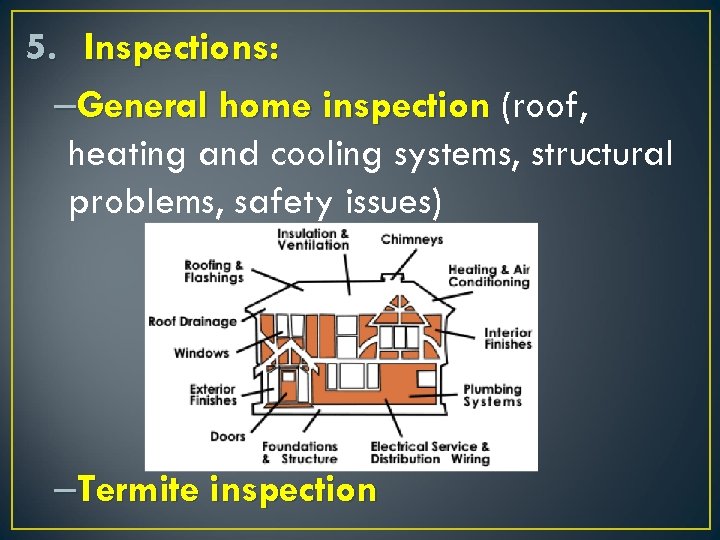
5. Inspections: –General home inspection (roof, heating and cooling systems, structural problems, safety issues) –Termite inspection

6. Have house appraised • Determines the real worth of the house

7. Secure a mortgage

8. Closing: The day you get the keys! Closing costs are paid: – Origination fees: paid to lender fees for processing loan – Fees for lawyers, real estate agents, etc – Escrow: money held for taxes and insurance.

Pros and Cons of Owning a Home • Strain on finances • Sense of freedom property taxes, • Helps establish insurance, and good credit maintenance • Interest and taxes • Uses up lots of free are deductible time • Foreclosure if you get • Houses usually behind on monthly increase in value – this is called equity. payments • Limited mobility.

Equity Example • Mary owns a house. She currently owes $90, 000 on her mortgage. She has decided to sell her house and buy a new one • Mary’s real estate agent sells Mary’s house for $140, 000 (market value) • Mary paid off her mortgage of $90, 000 • How much money did Mary make when she sold her house? • Mary made $50, 000. This is called equity. • Mary used her equity as a down payment on a new home.

Watch “Rent or Buy”
73f162d04c74fc0ce1950ea96d21732b.ppt