a1ca91dc244d5b10b84a1a55296f49d8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
Object Oriented Analysis and Design System Events & Contracts 1
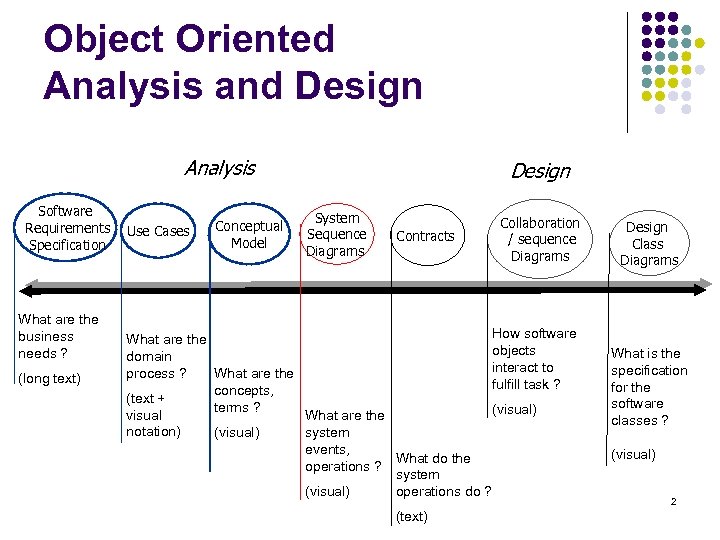
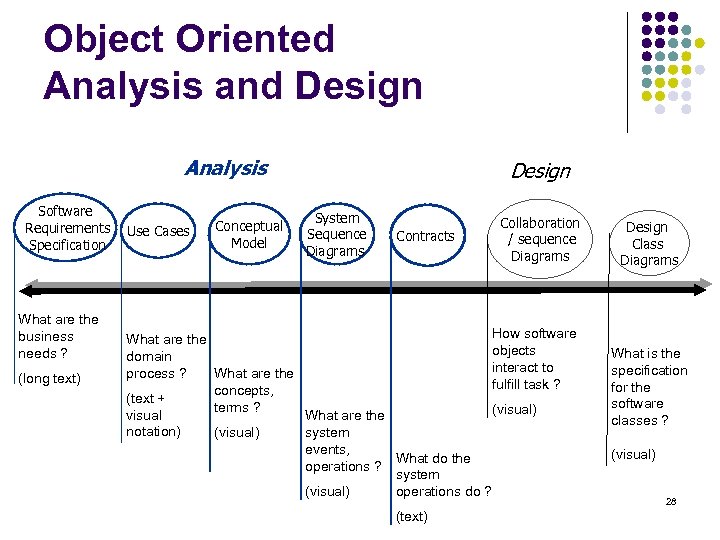
Object Oriented Analysis and Design Analysis Software Requirements Specification What are the business needs ? (long text) Use Cases Conceptual Model Design System Sequence Diagrams Contracts Collaboration / sequence Diagrams How software What are the objects domain interact to process ? What are the fulfill task ? concepts, (text + terms ? (visual) visual What are the notation) (visual) system events, What do the operations ? system (visual) operations do ? (text) Design Class Diagrams What is the specification for the software classes ? (visual) 2
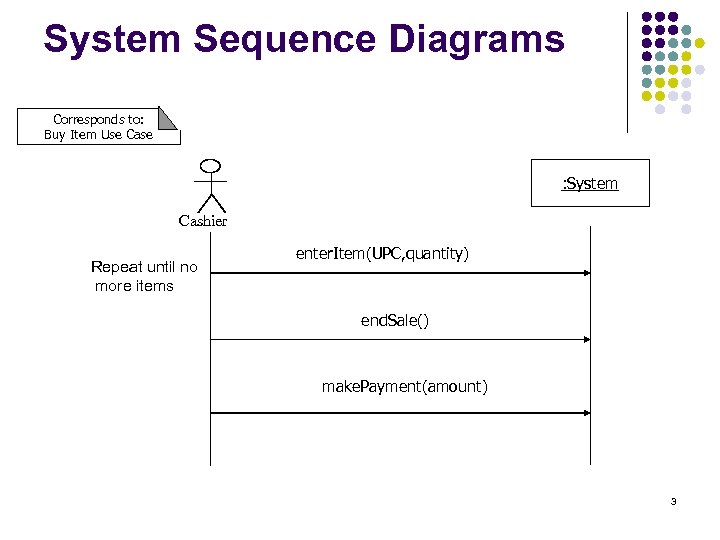
System Sequence Diagrams Corresponds to: Buy Item Use Case : System Cashier Repeat until no more items enter. Item(UPC, quantity) end. Sale() make. Payment(amount) 3
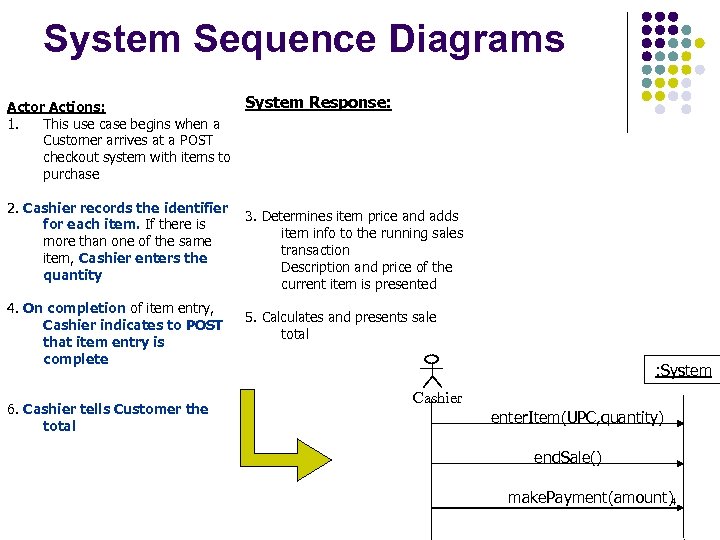
System Sequence Diagrams Actor Actions: 1. This use case begins when a Customer arrives at a POST checkout system with items to purchase 2. Cashier records the identifier for each item. If there is more than one of the same item, Cashier enters the quantity 4. On completion of item entry, Cashier indicates to POST that item entry is complete 6. Cashier tells Customer the total System Response: 3. Determines item price and adds item info to the running sales transaction Description and price of the current item is presented 5. Calculates and presents sale total : System Cashier enter. Item(UPC, quantity) end. Sale() make. Payment(amount)4
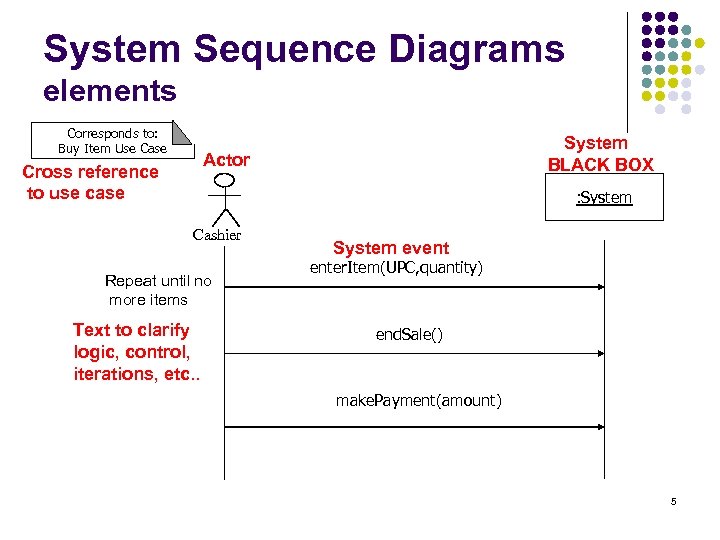
System Sequence Diagrams elements Corresponds to: Buy Item Use Case System BLACK BOX Actor Cross reference to use case : System Cashier Repeat until no more items Text to clarify logic, control, iterations, etc. . System event enter. Item(UPC, quantity) end. Sale() make. Payment(amount) 5
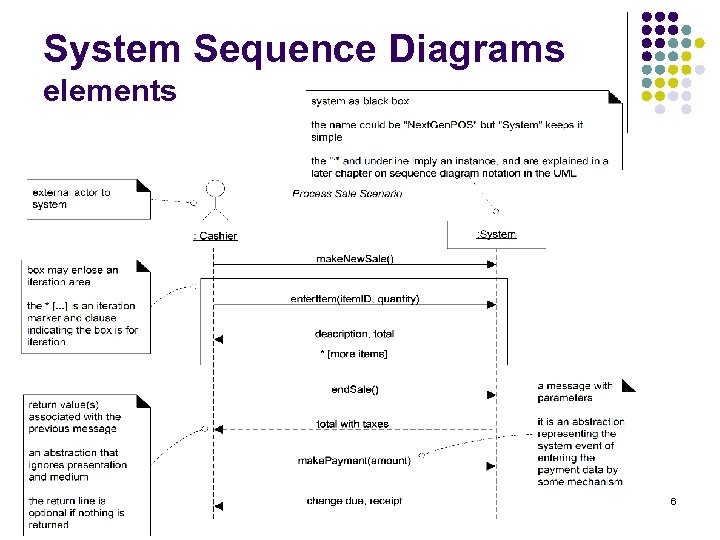
System Sequence Diagrams elements 6

System Sequence Diagrams Identifying system events l It is necessary to be clear about the system boundary l Actors to be considered are those who trigger the system l l Costumer is not an actor ! From use case typical course of events, identify system (external) events 7
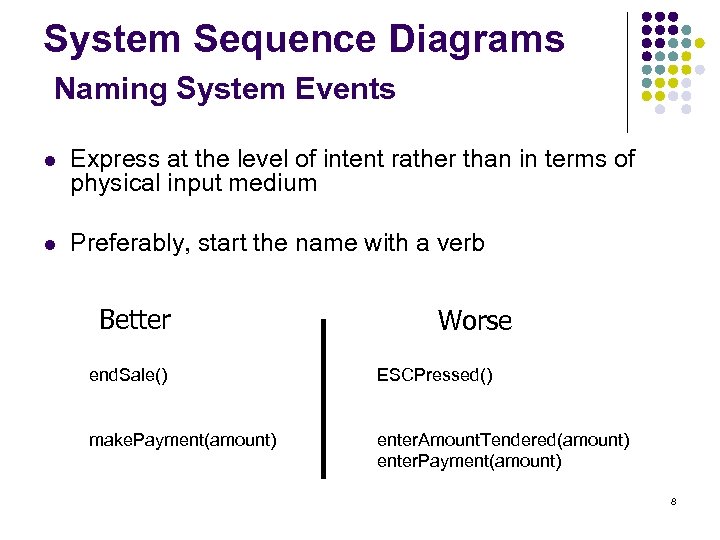
System Sequence Diagrams Naming System Events l Express at the level of intent rather than in terms of physical input medium l Preferably, start the name with a verb Better Worse end. Sale() ESCPressed() make. Payment(amount) enter. Amount. Tendered(amount) enter. Payment(amount) 8
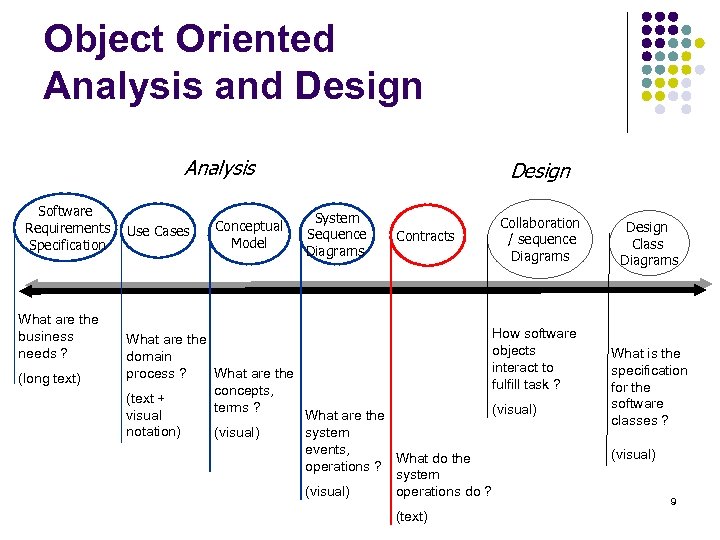
Object Oriented Analysis and Design Analysis Software Requirements Specification What are the business needs ? (long text) Use Cases Conceptual Model Design System Sequence Diagrams Contracts Collaboration / sequence Diagrams How software What are the objects domain interact to process ? What are the fulfill task ? concepts, (text + terms ? (visual) visual What are the notation) (visual) system events, What do the operations ? system (visual) operations do ? (text) Design Class Diagrams What is the specification for the software classes ? (visual) 9

Contracts l Describes what an operation commits to achieve l What will happen rather than l l how it will be achieved Depends on l l l conceptual model system sequence diagrams identification of system operations 10

Contracts example: enter. Item l Name: enter. Item(upc: number, quantity: integer) l Responsibility: Enter (record) sale of an item and add it to sale. Display item description and price. l Type: System l Cross References: System Functions: R 1. 1, R 1. 3, R 1. 9. Use Cases: Buy Items l Notes: Use fast dbase access l Exceptions: If UPC is invalid, indicate an error l Pre-Conditions: UPC is known to system 11

Contracts example: enter. Item l Post-Conditions: l If new sale, a Sale was created (instance creation) l If new sale, new Sale was associated with POST (association formed) l A Sales. Line. Item was created (instance created) l Sales. Line. Item was associated with Sale (association formed) l Sale. Line. Item. quantity was set to quantity (attribute modification) l Sale. Line. Item was associated with Product. Specification based on UPC match (association formed) 12

Contracts Contract Sections l Name: Name of operation, and parameters l Responsibilities: An informal description of responsibilities this operation must fulfill l Type: Name of type (concept, software class, interface) l Cross References: System function reference numbers, use cases, etc. l Notes: Design notes, algorithms, etc. l Exceptions: Exceptional cases 13

Contracts Contract Sections l Output: Non-UI outputs such as messages or records that are sent outside of system l Pre-Conditions: Assumptions about the state of system before execution of operation l Post-Conditions: l The state of system after completion of operation 14

Contracts How to make Contracts l Identify system operations from system sequence diagrams l For each system operation, construct a contract l Start by writing responsibilities section l Then complete post conditions section l Then move to pre-conditions section 15

Contracts How to make Contracts l Writing post conditions l It should describe the state changes that occur to objects in the conceptual model (rather than actions) l Possible state changes: Instance creation or deletion l Attribute modification l Association formed or broken l 16

Contracts How to make Contracts l Writing post conditions l Use past passive tense form (was. . ) l Establish memory between existing objects: l The most common mistake: not forming associations l Association to several objects is very likely l Think of the system and its object like a stage in a theatre 17 Craig Larman

Contracts More on Contracts l Generating complete and accurate set of postconditions is not likely and not necessary l Following pre-conditions worth capturing: l l Things that are important to test in software Things that affect the success of operation l Use notes section to capture known design statements l Use exceptions section to discuss reaction to exceptional situations 18
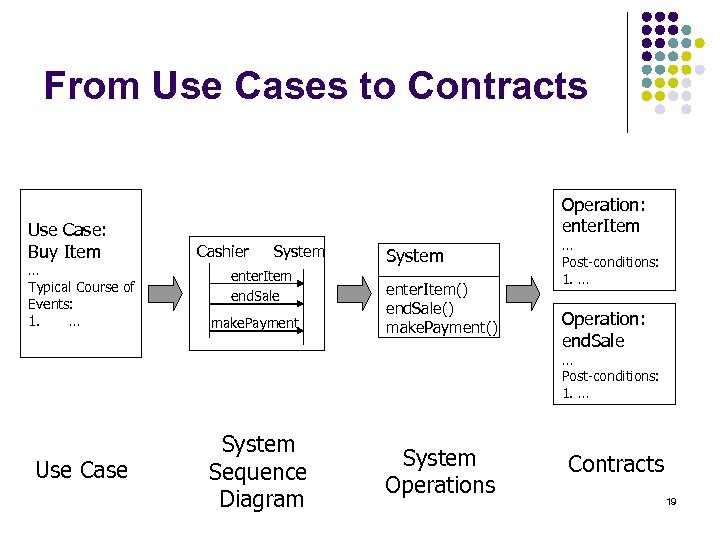
From Use Cases to Contracts Use Case: Buy Item … Typical Course of Events: 1. … Operation: enter. Item Cashier System enter. Item end. Sale make. Payment System enter. Item() end. Sale() make. Payment() … Post-conditions: 1. … Operation: end. Sale … Post-conditions: 1. … Use Case System Sequence Diagram System Operations Contracts 19

Contracts More example (from larman’s book) 20

21

22

23

Contracts More example login use case contract 24

Use Case Description 25

26

27
Object Oriented Analysis and Design Analysis Software Requirements Specification What are the business needs ? (long text) Use Cases Conceptual Model Design System Sequence Diagrams Contracts Collaboration / sequence Diagrams How software What are the objects domain interact to process ? What are the fulfill task ? concepts, (text + terms ? (visual) visual What are the notation) (visual) system events, What do the operations ? system (visual) operations do ? (text) Design Class Diagrams What is the specification for the software classes ? (visual) 28
a1ca91dc244d5b10b84a1a55296f49d8.ppt