1b529500ab1625fbe279d2068df6cbff.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 95

Object:Master of Grade 2015 Lecturer :赵巍(zhao wei) Time: 2 nd Semester of 2015 -2016 Total period : 36(24+12) office:Mechanical Manufacturing Dep. E-MAIL:zhaowei@tju. edu. cn 1

Unit 1: Introduction to Numerical Control (数控技术介绍) 1. 1 History of Numerical Control(数控发展史) 1. 2 Concept of NC and CNC(数控和计算机数控的定义) 1. 3 Basic Components of NC Machine Tools(数控机床 的基本组成) 1. 4 Classification of NC Machine Tools(数控机床的分类) 1. 5 NC Features and Applications(数控的特点及应用) 1. 6 Development of CNC machine (数控机床的发展趋势)

1. 1 History of Numerical Control.
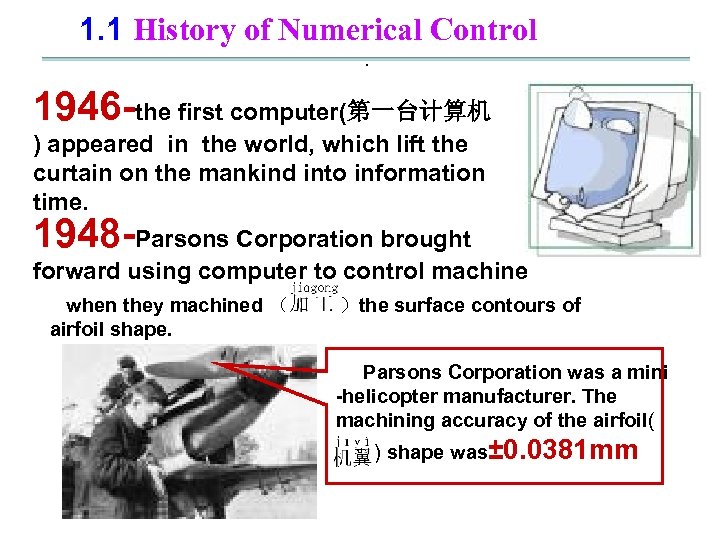
1. 1 History of Numerical Control. 1946 -the first computer(第一台计算机 ) appeared in the world, which lift the curtain on the mankind into information time. 1948 -Parsons Corporation brought forward using computer to control machine when they machined ( )the surface contours of airfoil shape. Parsons Corporation was a mini -helicopter manufacturer. The machining accuracy of the airfoil( ) shape was± 0. 0381 mm

1. 1 History of Numerical Control. Under the support by the U. S Air Force Responsed by the Servomechanisms Laboratory MIT at the (Massachusetts Institute of Technology)(麻省理 学院)

1. 1 History of Numerical Control. Three years later, in 1952 MIT Parsons Corporation cooperated with and each other, and developed the first NC Cincinnati Hydrotel milling machine which named Background, time and place? ?

1. 1 History of Numerical Control. (1) Concept for NC → 1940 s United States Air Force and aerospace( )industry complex parts: manual machining + inspected by templates ↓ manual methods ↓↓ time consuming and inaccurate

1. 1 History of Numerical Control. John Parsons: inspection templates for helicopter rotor( ) blades ( )
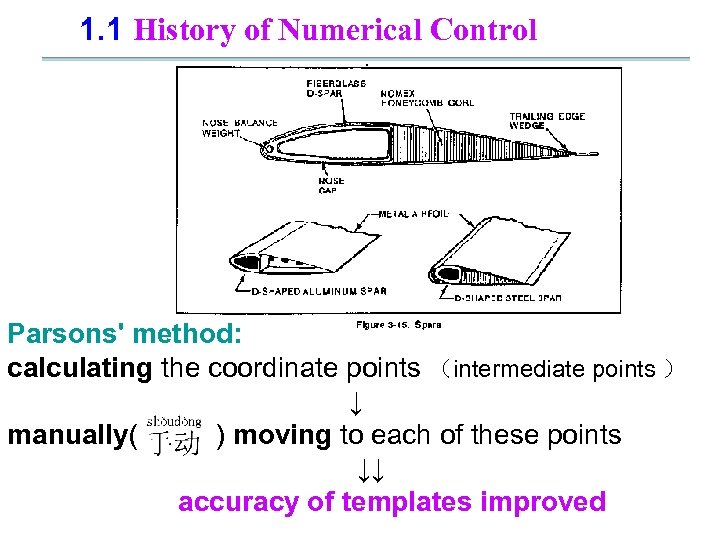
1. 1 History of Numerical Control. Parsons' method: calculating the coordinate points (intermediate points ) ↓ manually( ) moving to each of these points ↓↓ accuracy of templates improved
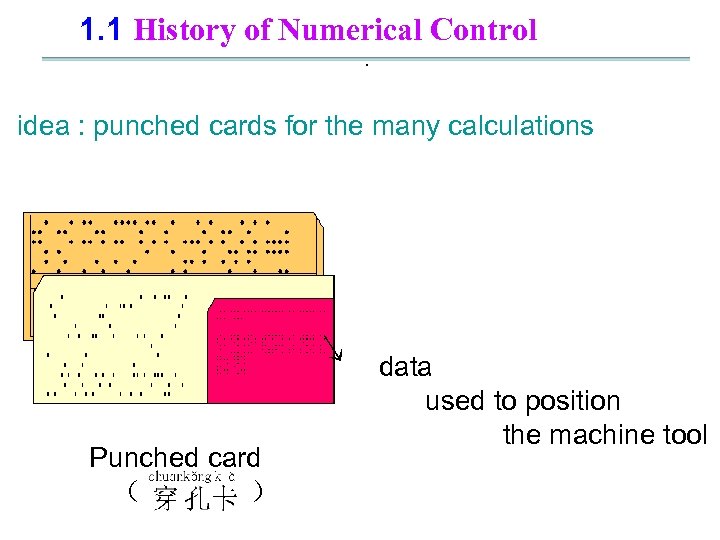
1. 1 History of Numerical Control. idea : punched cards for the many calculations ↘ Punched card ( ) data used to position the machine tool
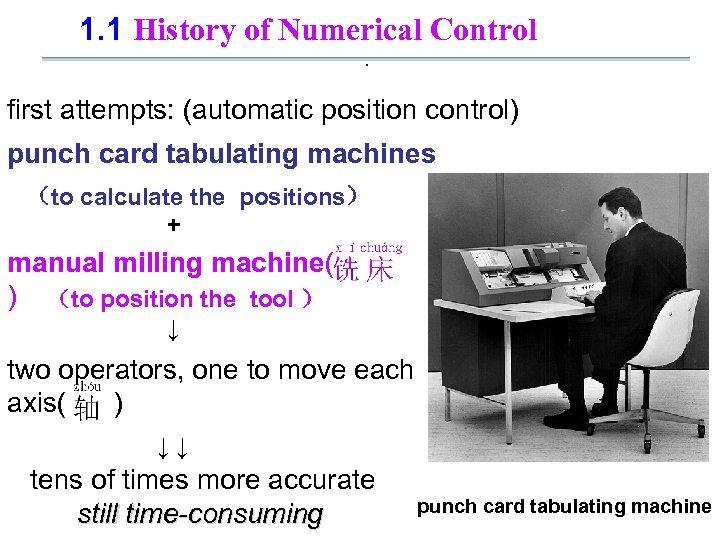
1. 1 History of Numerical Control. first attempts: (automatic position control) punch card tabulating machines (to calculate the positions) + manual milling machine( ) (to position the tool ) ↓ two operators, one to move each axis( ) ↓ ↓ tens of times more accurate still time-consuming punch card tabulating machine
1. 1 History of Numerical Control. Parsons envisioned the following system: a computer (calculate the path) + punched cards (store information) + a reader ( read cards) + the machine control (control motors( ) attached to each axis) ↓ ↓ • In 1952, a three-axis milling machine was demonstrated( )
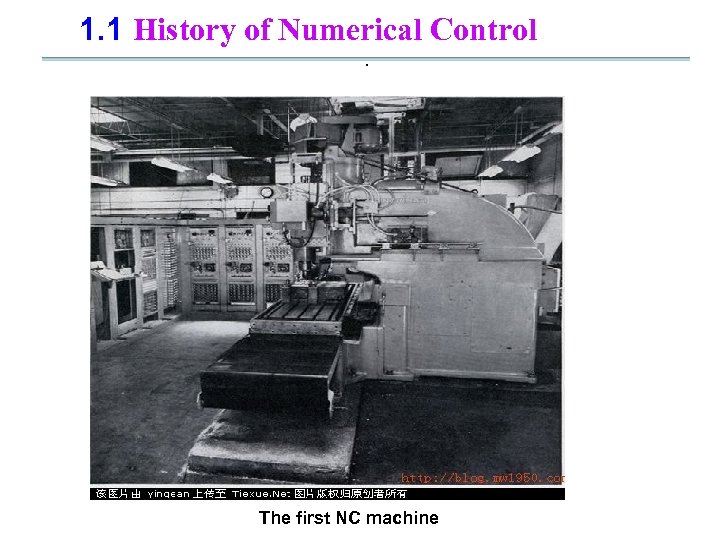
1. 1 History of Numerical Control . The first NC machine

1. 1 History of Numerical Control. Noticed: Since the 1980 s, no hardwired NCs have been produced. Today, when the term NC is mentioned, it normally means CNC
1. 2 Concept of NC and CNC(数控与计算机数控) NC: Numerical Control(数字控制) ↓ ( 1970's ) CNC: Computer Numerical Control (计算机数字控制)
1. 2 Concept of NC and CNC. (1) NC: a form of programmable automation( ) in which the mechanical actions of a machine tool or other equipment are controlled by a program containing coded alphanumeric data ( ). • alphanumeric data: relative positions between a workhead ( ) and a workpart( ) + instructions needed to operate the machine ↓↓ suitable for low and medium production
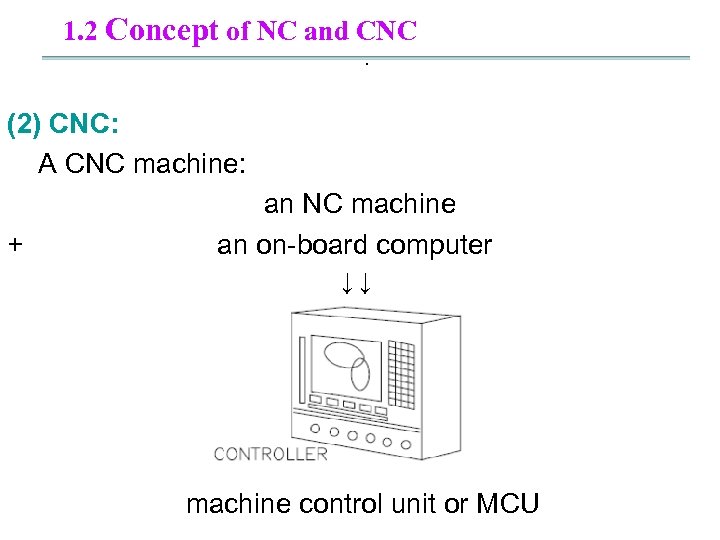
1. 2 Concept of NC and CNC . (2) CNC: A CNC machine: an NC machine + an on-board computer ↓ ↓ machine control unit or MCU
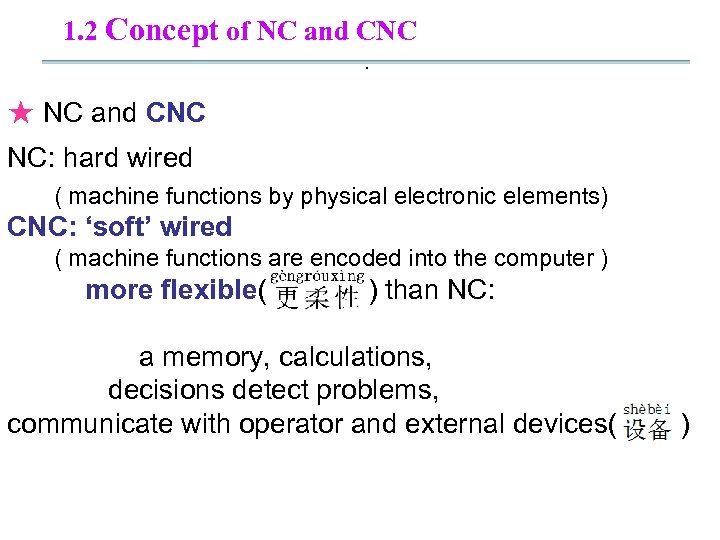
1. 2 Concept of NC and CNC. ★ NC and CNC NC: hard wired ( machine functions by physical electronic elements) CNC: ‘soft’ wired ( machine functions are encoded into the computer ) more flexible( ) than NC: a memory, calculations, decisions detect problems, communicate with operator and external devices( )

• C 1. 2 Concept of NC and CNC. N C m a c h i n e t o
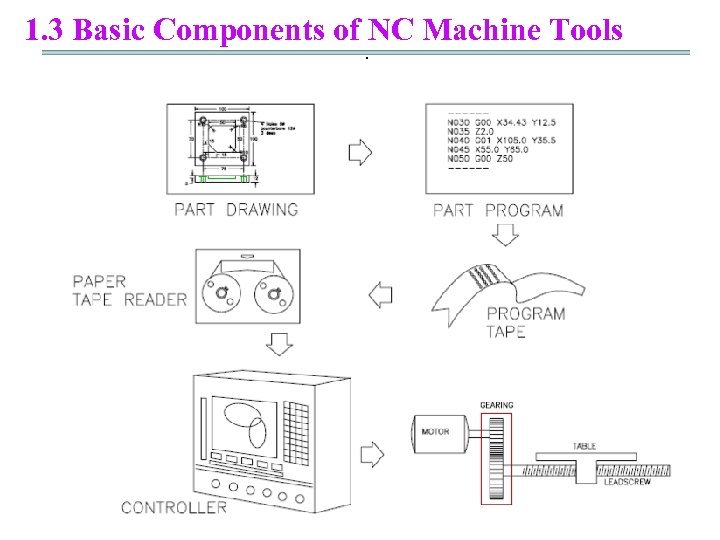
1. 3 Basic Components of NC Machine Tools.

1. 3 Basic Components of NC Machine Tools. five fundamental units of typical NC machine tool • (1)the input media( ); • (2)the machine control unit( ); • (3)the servo-drive unit( ); • (4)the feedback transducer( ); • (5)the mechanical machine tool unit( ).
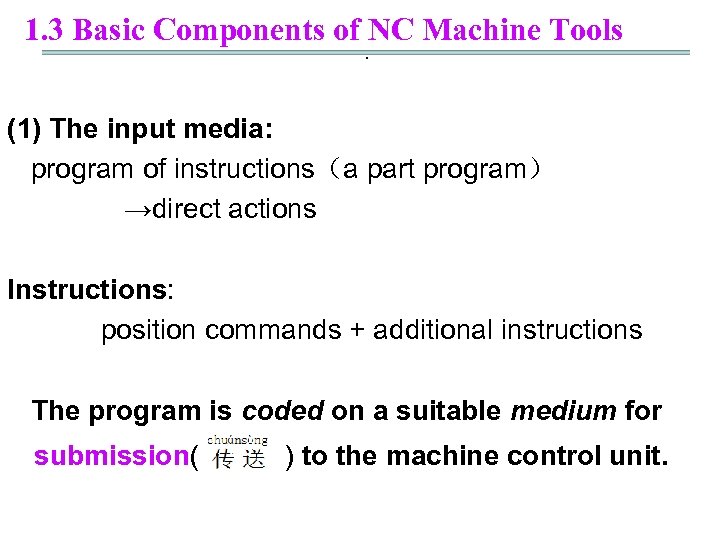
1. 3 Basic Components of NC Machine Tools. (1) The input media: program of instructions(a part program) →direct actions Instructions: position commands + additional instructions The program is coded on a suitable medium for submission( ) to the machine control unit.

1. 3 Basic Components of NC Machine Tools. Types of medium : punched tape, magnetic tape, diskette( ), electronic transfer from computer. punched tape diskette magnetic tape
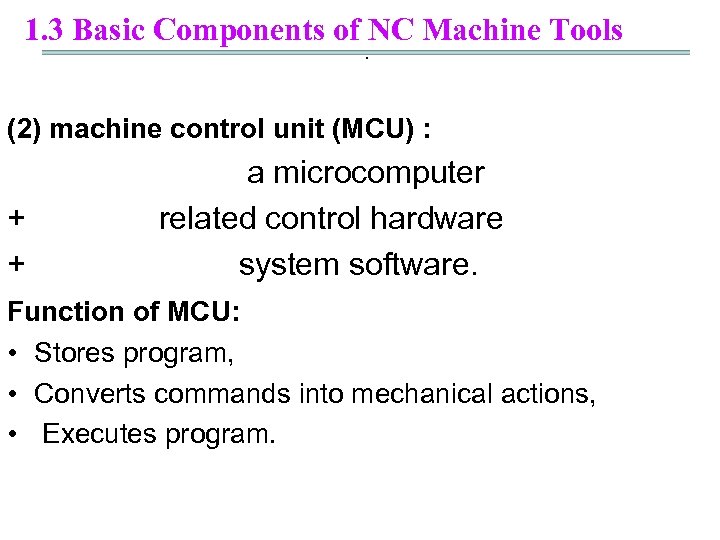
1. 3 Basic Components of NC Machine Tools. (2) machine control unit (MCU) : a microcomputer + related control hardware + system software. Function of MCU: • Stores program, • Converts commands into mechanical actions, • Executes program.
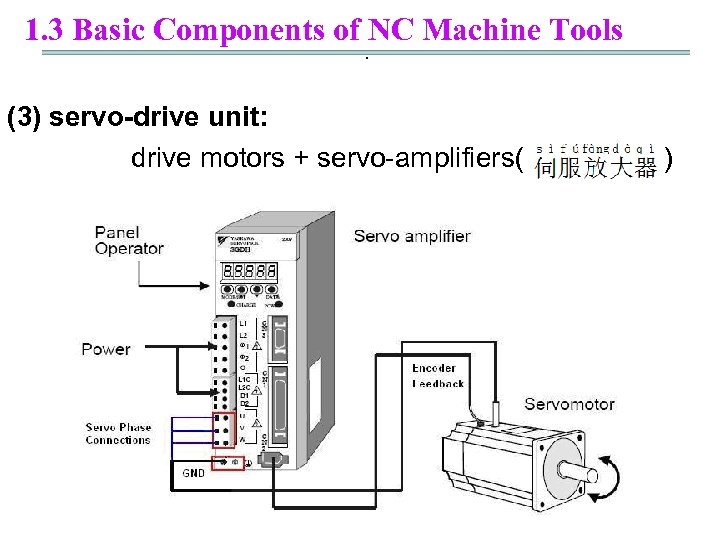
1. 3 Basic Components of NC Machine Tools. (3) servo-drive unit: drive motors + servo-amplifiers( )
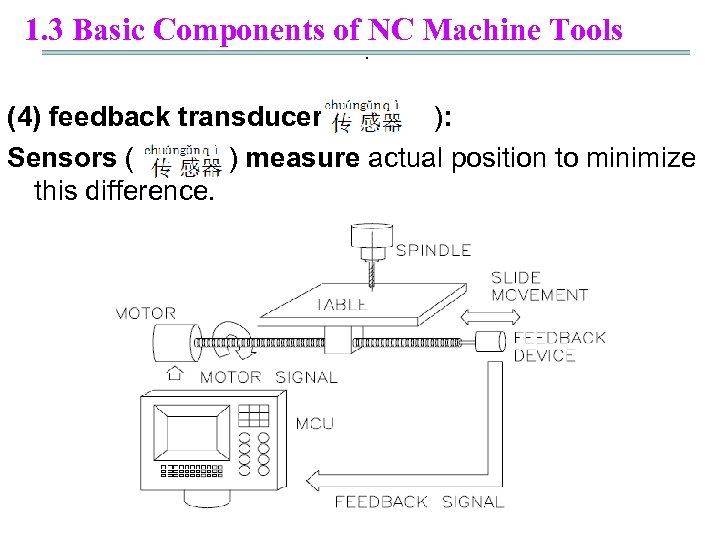
1. 3 Basic Components of NC Machine Tools. (4) feedback transducer( ): Sensors ( ) measure actual position to minimize this difference.

1. 3 Basic Components of NC Machine Tools. (5) the machine tool : performs useful work worktable and spindle ( )

1. 3 Basic Components of NC Machine Tools. Review( ) • In 1952, a three-axis milling machine was demonstrated( ) • NC, alphanumeric datum are used to control the action(motion) of machine tool or other equipment • CNC, with the development of electric, computer, automation technology, computer is used in NC (more flexible) • Basic Components of NC Machine Tools
1. 4 CLASSIFICATIONS OF CNC MACHNINES. NC machines are classified in different way: (1) the types of NC motion system, (2) the type of control system, (3) application of NC. (1) Types of CNC Motion( ) System two types: 1) point-to-point ( ) 2) continuous path( )
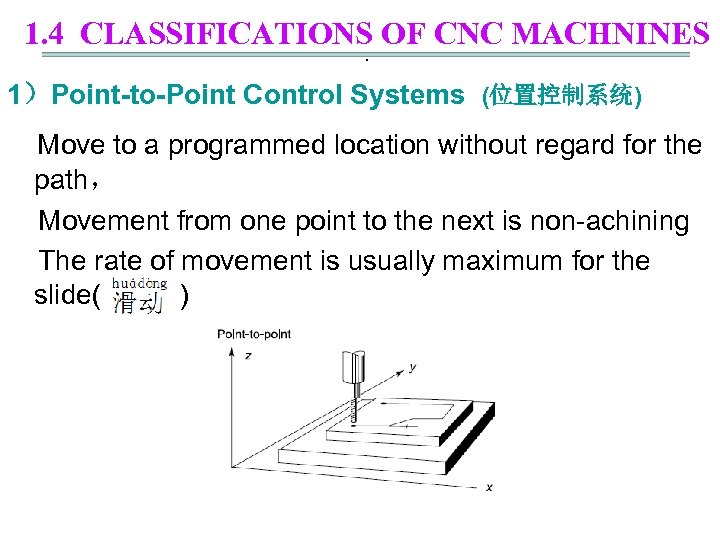
1. 4 CLASSIFICATIONS OF CNC MACHNINES. 1)Point-to-Point Control Systems (位置控制系统) Move to a programmed location without regard for the path, Movement from one point to the next is non-achining The rate of movement is usually maximum for the slide( )
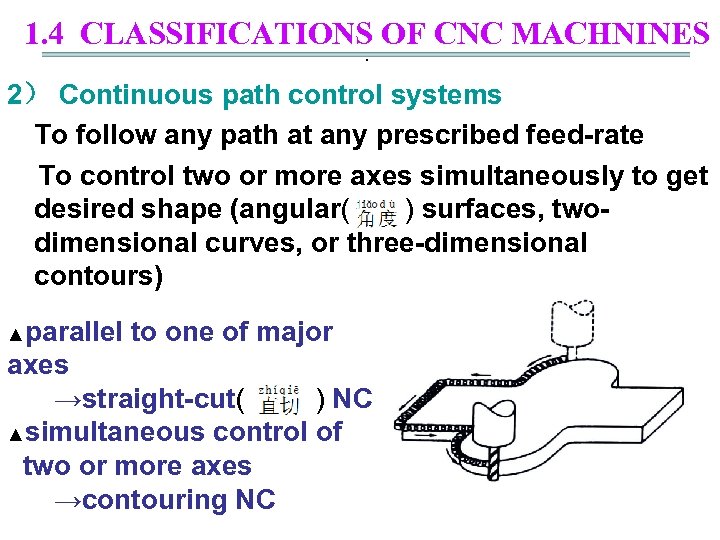
1. 4 CLASSIFICATIONS OF CNC MACHNINES. 2) Continuous path control systems To follow any path at any prescribed feed-rate To control two or more axes simultaneously to get desired shape (angular( ) surfaces, twodimensional curves, or three-dimensional contours) ▲parallel to one of major axes →straight-cut( ) NC ▲simultaneous control of two or more axes →contouring NC

1. 4 CLASSIFICATIONS OF CNC MACHNINES. (2) Types of NC Control Systems Based on how the NC system accomplishes positioning, Three types of drives: 1) open-loop( ) drive system, 2) closed-loop( ) drive system, 3) half closed-loop( ) drive system.
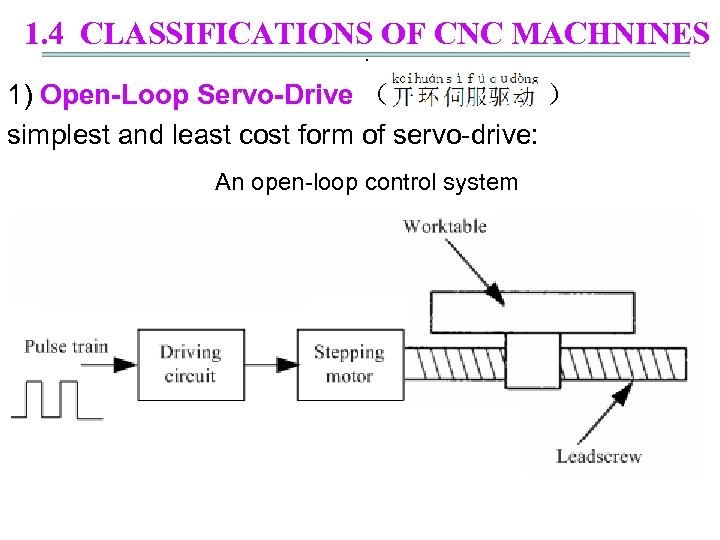
1. 4 CLASSIFICATIONS OF CNC MACHNINES. 1) Open-Loop Servo-Drive ( ) simplest and least cost form of servo-drive: An open-loop control system
1. 4 CLASSIFICATIONS OF CNC MACHNINES. Feature of open-Loop Servo-Drive : lacks feedback( ) ( no sensing device to confirm the action ) actuator will not have the intended effect motor : stepping motor ( ) Advantages: high accuracy, easy implementation, compatible with digital signals; 1 2 3 4 disadvantages: low torque ( ) limited speed and risk of missed pulse( ) under overload ( )
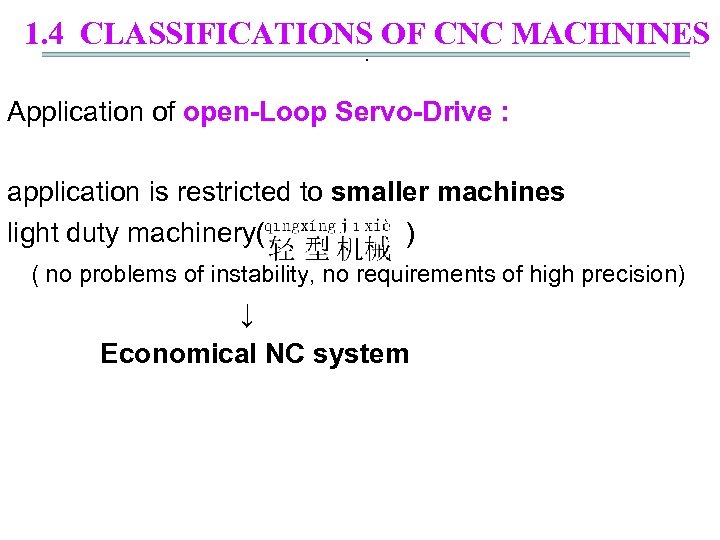
1. 4 CLASSIFICATIONS OF CNC MACHNINES. Application of open-Loop Servo-Drive : application is restricted to smaller machines light duty machinery( ) ( no problems of instability, no requirements of high precision) ↓ Economical NC system
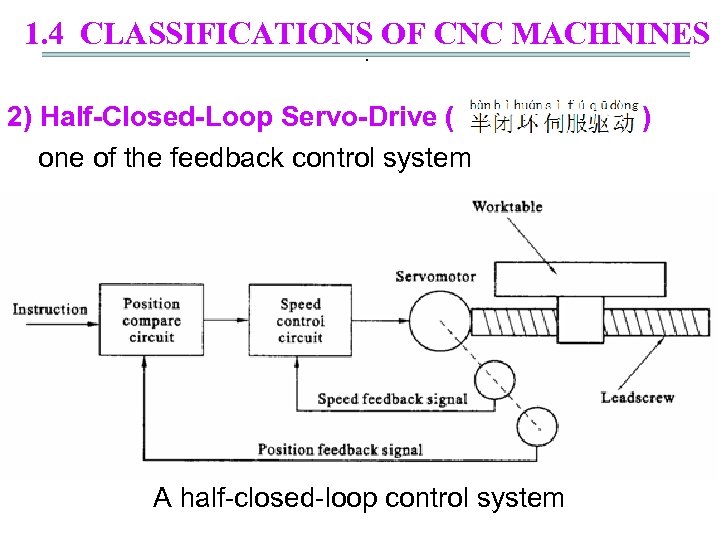
1. 4 CLASSIFICATIONS OF CNC MACHNINES. 2) Half-Closed-Loop Servo-Drive ( ) one of the feedback control system A half-closed-loop control system

1. 4 CLASSIFICATIONS OF CNC MACHNINES. Feature: indirect feedback ( )monitors the output of servomotor ( ) a feedback sensor is attached to servomotor axis or lead -screw( ) (measures the rotary angle ( ) of motor or leadscrew) Disadvantage: unable to sense backlash( ) or lead-screw windup Advantage: convenient to adjust , a good stability motor : Servo motor (DC or AC) (直流或交流伺服电机)
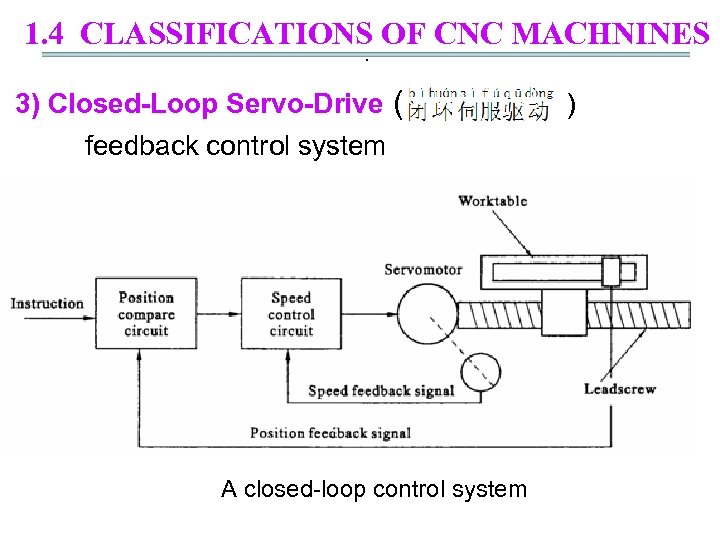
1. 4 CLASSIFICATIONS OF CNC MACHNINES. 3) Closed-Loop Servo-Drive ( ) feedback control system A closed-loop control system
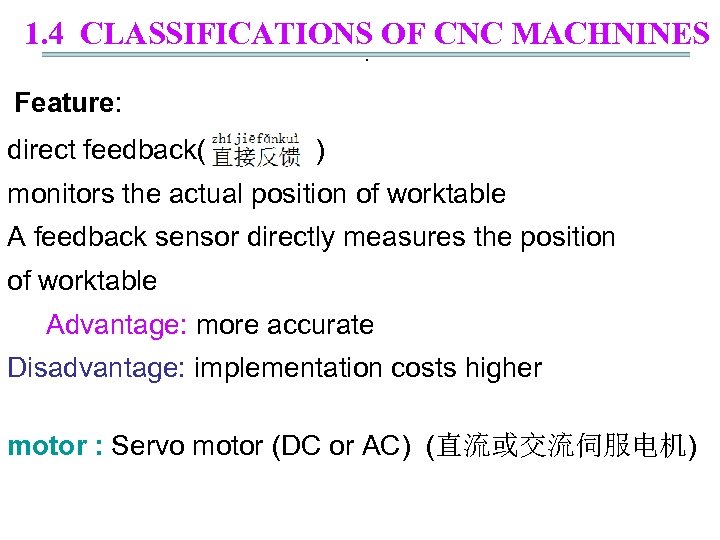
1. 4 CLASSIFICATIONS OF CNC MACHNINES. Feature: direct feedback( ) monitors the actual position of worktable A feedback sensor directly measures the position of worktable Advantage: more accurate Disadvantage: implementation costs higher motor : Servo motor (DC or AC) (直流或交流伺服电机)

1. 4 CLASSIFICATIONS OF CNC MACHNINES. Applications divided into two categories: (1) machine tool applications (2) non-machine tool applications Machine tool applications are those usually associated with the metalworking industries. Non-machine tool applications comprise a diverse group of operations in other industries. The most common applications of NC are in machine tool control, machining was the first application of NC.
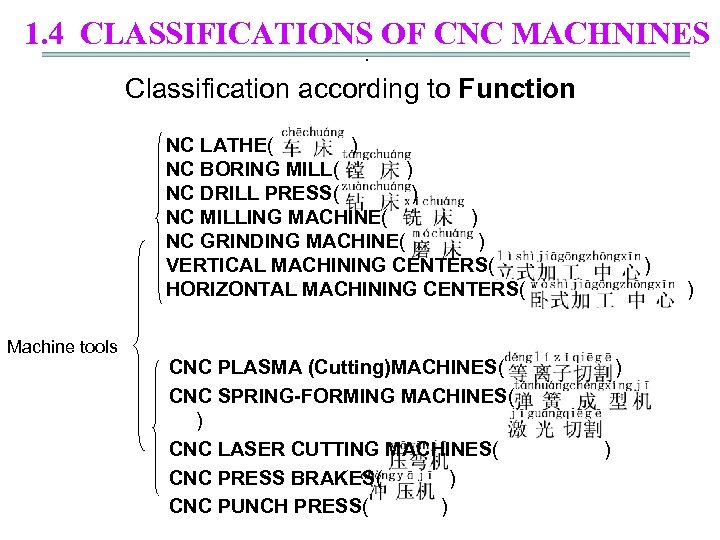
1. 4 CLASSIFICATIONS OF CNC MACHNINES. Classification according to Function NC LATHE( ) NC BORING MILL( ) NC DRILL PRESS( ) NC MILLING MACHINE( ) NC GRINDING MACHINE( ) VERTICAL MACHINING CENTERS( ) HORIZONTAL MACHINING CENTERS( ) Machine tools CNC PLASMA (Cutting)MACHINES( ) CNC SPRING-FORMING MACHINES( ) CNC LASER CUTTING MACHINES( ) CNC PRESS BRAKES( ) CNC PUNCH PRESS( )

1. 4 CLASSIFICATIONS OF CNC MACHNINES. (1) Machine Tool Applications (Machining : manufacturing process, in which the geometry of work is produced by removing excess material. ) Four common types of machining operations: 1) turning( ) (performed on a lathe), 2) drilling( ) (on a drilling press), 3) milling( )(on a milling machine), 4) grinding( ) (on a grinding machine).

Machine Tool Applications. 1)NC lathe: (horizontal or vertical )( ) two-axis continuous path control

Machine Tool Applications. 1) CNC lathe (数控车床) Turning requires two-axis continuous path control, either to produce a straight cylindrical( ) geometry or to create a profile.

Machine Tool Applications. 2) CNC boring mill : horizontal or vertical spindle Operation: continuous path, two-axis control
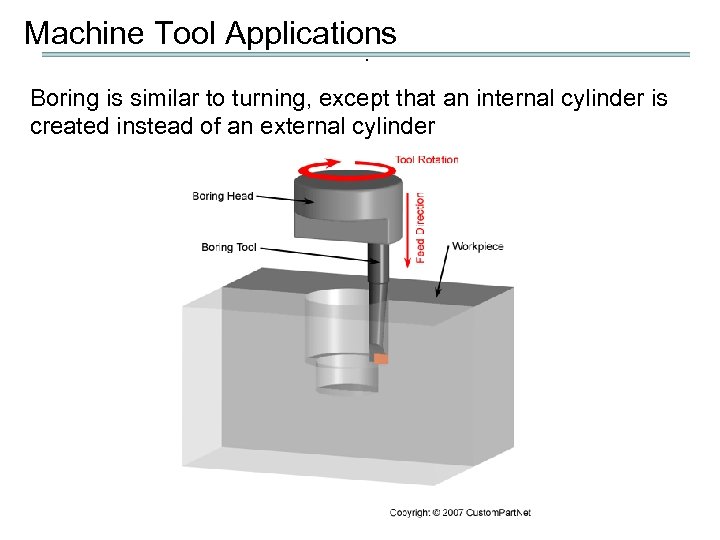
Machine Tool Applications. Boring is similar to turning, except that an internal cylinder is created instead of an external cylinder

Machine Tool Applications.
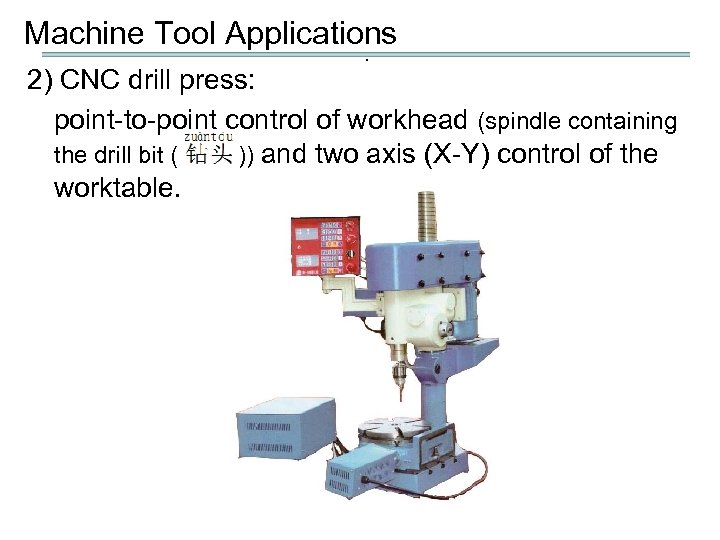
Machine Tool Applications. 2) CNC drill press: point-to-point control of workhead (spindle containing the drill bit ( )) and two axis (X-Y) control of the worktable.

Machine Tool Applications. 3) NC milling machine: require continuous path control to perform straight cut or contouring operations
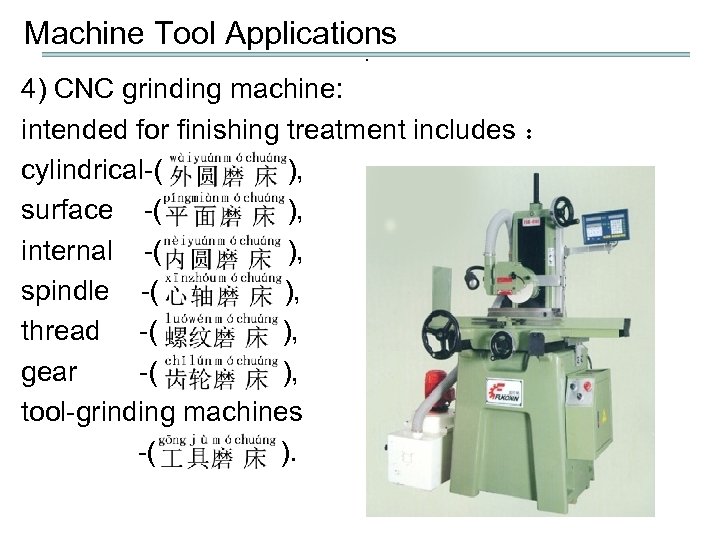
Machine Tool Applications. 4) CNC grinding machine: intended for finishing treatment includes : cylindrical-( ), surface -( ), internal -( ), spindle -( ), thread -( ), gear -( ), tool-grinding machines -( ).

Machine Tool Applications. Tool grinding machine
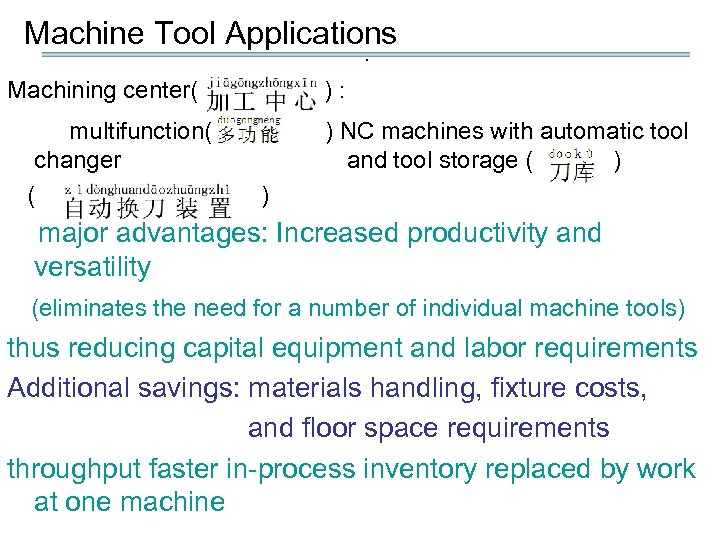
Machine Tool Applications. Machining center( ) : multifunction( ) NC machines with automatic tool changer and tool storage ( ) ( ) major advantages: Increased productivity and versatility (eliminates the need for a number of individual machine tools) thus reducing capital equipment and labor requirements Additional savings: materials handling, fixture costs, and floor space requirements throughput faster in-process inventory replaced by work at one machine
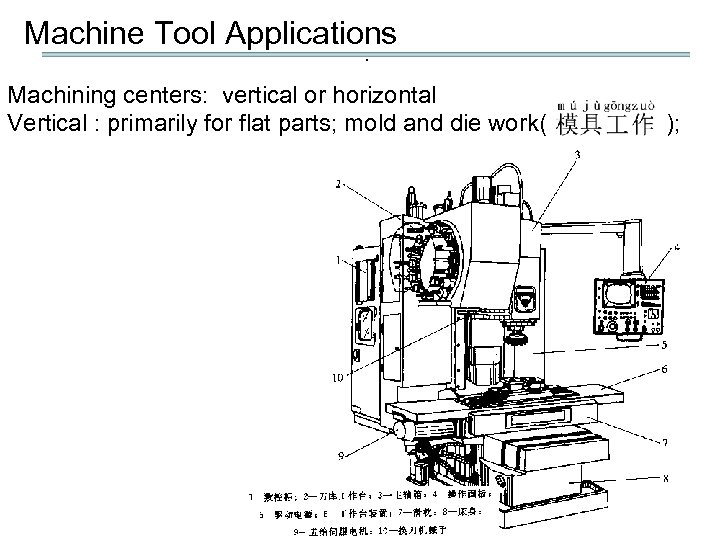
Machine Tool Applications. Machining centers: vertical or horizontal Vertical : primarily for flat parts; mold and die work( );
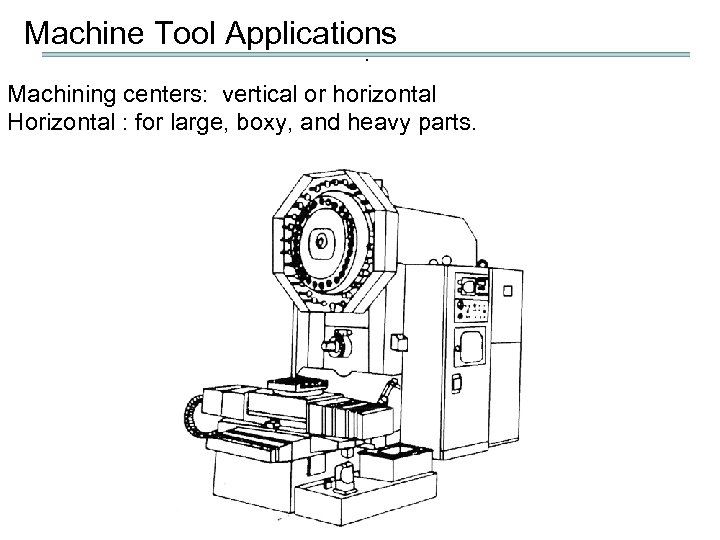
Machine Tool Applications. Machining centers: vertical or horizontal Horizontal : for large, boxy, and heavy parts.
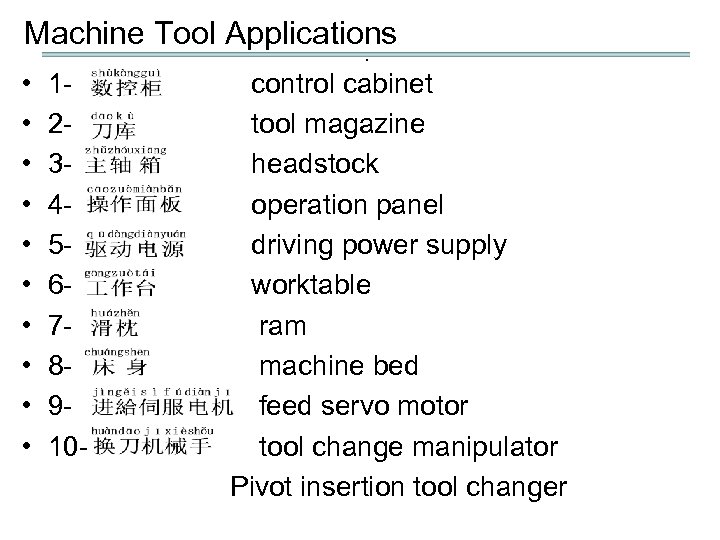
Machine Tool Applications. • 1 - control cabinet • 2 - tool magazine • 3 - headstock • 4 - operation panel • 5 - driving power supply • 6 - worktable • 7 - ram • 8 - machine bed • 9 - feed servo motor • 10 - tool change manipulator Pivot insertion tool changer

1. 4 CLASSIFICATIONS OF CNC MACHNINES. (2) Non-Machine Tool Applications 1) Punch presses for sheet metal hole punching ( ) 2) Presses for sheet metal bending( ) 3) Welding machine ( ) 4) Thermal cutting machine( ) 5) Tube bending machine( )

Non-Machine Tool Applications. 1) Punch presses for sheet metal hole punching (数控冲床) The two-axis NC operation is similar to that of a drill press except that holes are produced by punching rather than by drilling.

Non-Machine Tool Applications. 2) Presses for sheet metal bending (数控折弯机) Instead of cutting sheet metal, these systems bend sheet metal according to programmed commands.

Non-Machine Tool Applications. 3) Welding machine (数控焊接机) Both spot welding and continuous arc welding ( )machines are available with automatic controls based on NC.

Non-Machine Tool Applications. 4) Thermal cutting machine (数控热切割机 ) Such as oxyfuel cutting( ), laser cutting( ), and plasma arc cutting( ). The stock is usually flat; thus two-axis control is adequate. Some laser cutting machines can cut holes in preformed sheet metal stock ( ), requiring four or five axis control.
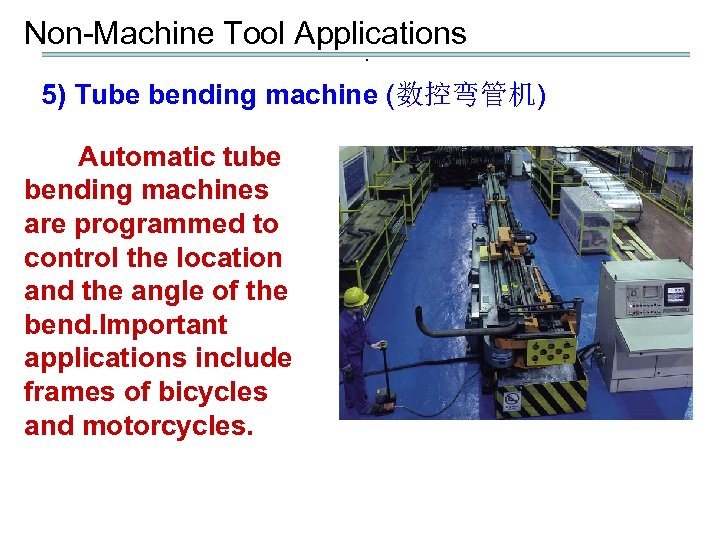
Non-Machine Tool Applications. 5) Tube bending machine (数控弯管机) Automatic tube bending machines are programmed to control the location and the angle of the bend. Important applications include frames of bicycles and motorcycles.

Non-Machine Tool Applications. Automated 6 -Axis Screw Driver( )

Non-Machine Tool Applications. Robots bend large heavy metal plates
1. 5 NC Features and Applications. Characteristics: (1) batch( ) production in small or medium lot sizes; (2) repeat orders at random or periodic intervals; (3) complex part geometry; (4) Much metal needs to be removed from part; (5) many separate machining operations on the part (6) the part is expensive. ↓ NC benefits and advantages (economic savings for the user company)

1. 5 NC Features and Applications. Advantages and Disadvantages of NC NC has many benefits and advantages over manual production methods, but NC is more sophisticated technology than conventional production methods.

1. 5 NC Features and Applications. Advantages of NC: Greater accuracy and repeatability(duplication); flexibility More complex part geometries are possible ; Nonproductive time is reduced Lower scrap rates( ) Inspection requirements are reduced Engineering changes can be accommodated more gracefully Simpler fixtures are needed Shorter manufacturing lead times ( ) Reduced parts inventory ( ) Less floor space ( )required Operator skill-level requirements are reduced
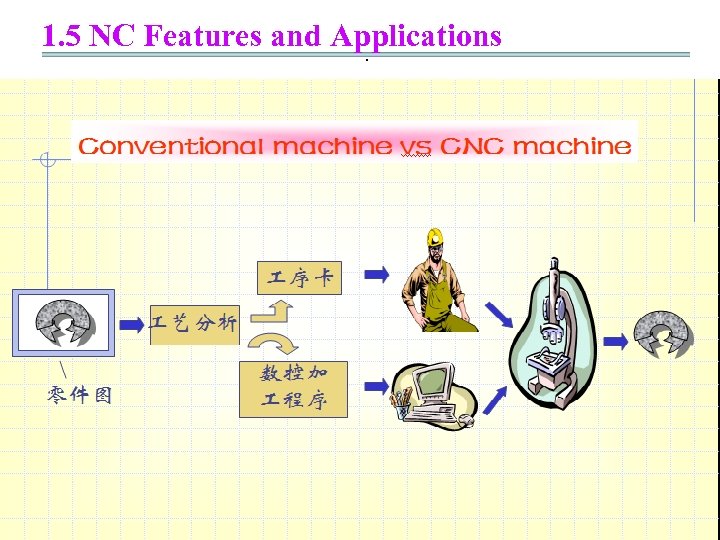
1. 5 NC Features and Applications.
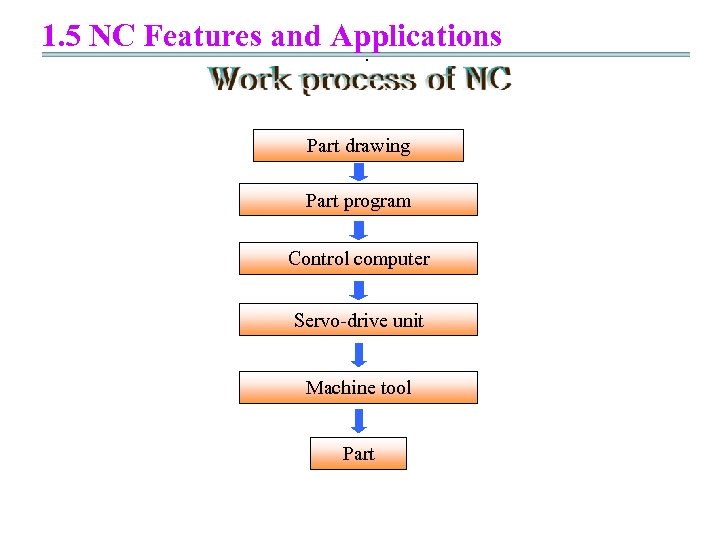
1. 5 NC Features and Applications. Part drawing Part program Control computer Servo-drive unit Machine tool Part
1. 5 NC Features and Applications. Disadvantages of NC : Higher investment cost Higher maintenance( )effort Part program Higher utilization( ) of NC equipment

1. 6 Development of CNC machine. Since 1990 s, with the rapid development of the computer technology, numerical control technology using the latest technology achievements of computer, control theory and other fields, towards the direction of the development of several.
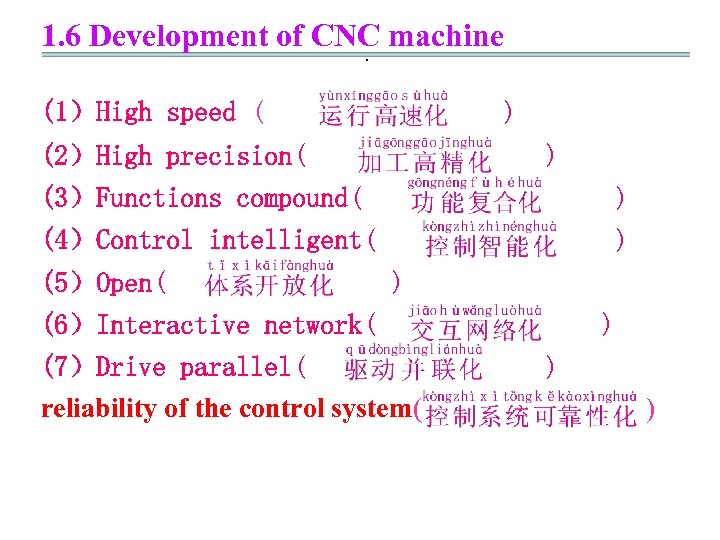
1. 6 Development of CNC machine. (1)High speed ( ) (2)High precision( ) (3)Functions compound( ) (4)Control intelligent( ) (5)Open( ) (6)Interactive network( (7)Drive parallel( reliability of the control system( ) ) )
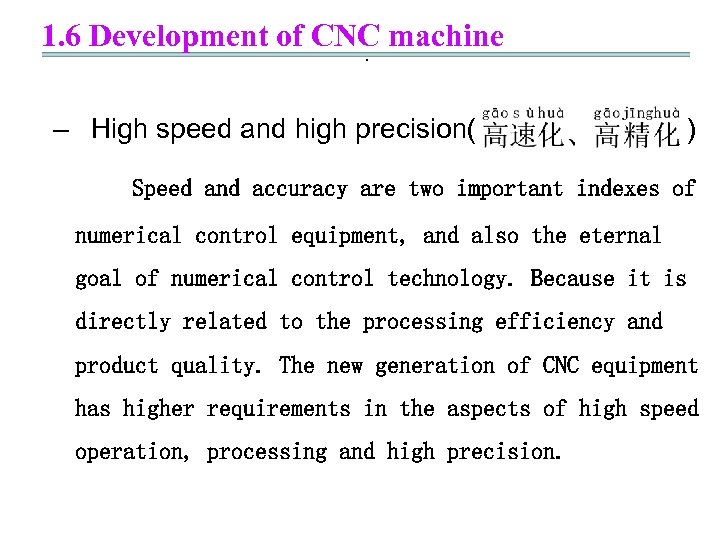
1. 6 Development of CNC machine. – High speed and high precision( ) Speed and accuracy are two important indexes of numerical control equipment, and also the eternal goal of numerical control technology. Because it is directly related to the processing efficiency and product quality. The new generation of CNC equipment has higher requirements in the aspects of high speed operation, processing and high precision.

1. 6 Development of CNC machine. (1) High speed(运行高速化) Definition: make feedrate , spindle speed , rate of tool switching( ) , rate of tray switching( ) own high speed and acceleration/deceleration. • high feedrate : – When the resolution of workpiece surface is 1 m , Fmax=240 m/min, can get precision machining of complex surface; – When the program segment size is 1 mm,Fmax=60 m/min, can get the acceleration/deceleration of 1. 5 g
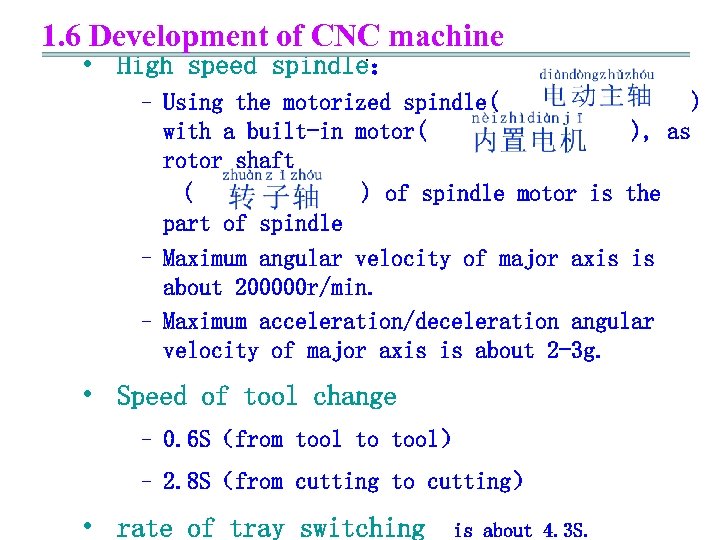
1. 6 Development of CNC machine. • High speed spindle: – Using the motorized spindle( ) with a built-in motor( ), as rotor shaft ( ) of spindle motor is the part of spindle – Maximum angular velocity of major axis is about 200000 r/min. – Maximum acceleration/deceleration angular velocity of major axis is about 2 -3 g. • Speed of tool change – 0. 6 S(from tool to tool) – 2. 8 S(from cutting to cutting) • rate of tray switching is about 4. 3 S.
1. 6 Development of CNC machine. (2)High-precision Method of getting high-precision 1) Improving the mechanical equipment’s precision in manufacture and assembly; 2) Increasing control precision of CNC system; 3) Using error compensation technique ( ).
1. 6 Development of CNC machine. 2) Increasing control precision of CNC system - Make the control unit of CNC refine through highspeed interpolation( )techniques achieve continuous feeding according to tiny program blocks. - Improving the detection accuracy of position with position detection equipment of high resolution (impulse per rotate insided position detector have been equipped in Janpanese ac servo motor ( ) , its position detection precision can up to 0. 01 m per impulse); - Ways of feedforward control and nolinear( ) control are also used by positional servosystem.
1. 6 Development of CNC machine. 3) Using error compensation technique - Techniques , such as backlash( ) compensation , screw pitch( ) error compensation , tool compensation are used; - The technique of thermal deformation error compensation and space errors synthetic compensation( ) for equipment. - The study indicates that application of synthetic error compensation technique can decrease the machining error by 60%~ 80%. - The positioning accuracy of ultraprecise horizontal( ) machining center made in Mitsui Seiki is ± 0. 1 m.
1. 6 Development of CNC machine. (3)Functions compound Compound( ) is a method that can achieve a variety of technological means to machine in a device. • Boring , milling and drilling composite-machining center(ATC) , five-face machining center(ATC, spindle horizontalvertical conversion( )); • Turing and milling composite—turning center ( )(ATC,Power head); • Milling , boring , drilling and turning composite— composite machining centers(ATC,automatic load and unload tool holder); • Milling , boring , drilling and grinding composite—compound machining center(ATC,power grinding wheel( )); • Headstock changing N/C machine—Combined machining center.
1. 6 Development of CNC machine. (4)Control intelligent With the constantly development of artificial intelligence tech -nology ( )for gratifing the development needs of manufacturing flexibility and manufacturing automation, the level of intellect for NC technique continue to improve , the detailed contents are as follows: 1) Adaptive control technology for machining process 2) The intelligent optimization and choice of machining parameters 3) Intelligent fault diagnosis and self-repairing technology 4) Intelligent AC servo driving equipment

1. 6 Development of CNC machine. 1) Adaptive control technology for machining process By monitoring the information , such as cutting force( ), spindle and feed motor power, current, voltage( ) in the processing , recognising with algorithms of traditional or modern to confirm stress , wear , states of disrepair of tool and stability of machining process; Make the machine in the best operation state according to these real-time status to trim machining parameters( ) ( spindle speed , feedrate ) and processing orders , in order to improve machining accuracy , reduce work surface roughness( ) and equipment safety.
1. 6 Development of CNC machine. – “Miracle Fuzzy”based on fuzzy logic adaptive controller is used to NC spark-erosion sinking machine ( ) can automatic control and optimization of machining parameters ; – Makino adopt expert system instead of the human to supervision during machining process in the Makino_Mce 20 of NC spark-erosion system. – Israel adaptive controller with external force ( ). – Italian’ company of Mandelli apply self-adaptation control function of programmable power to NC system. – The university such as Tsinghua have achieved fruit in the technology of adaptation control and commercial development is being carried out.

1. 6 Development of CNC machine. 2) The intelligent optimization and choice of machining parameters Construct the device of intelligent optimization of machin -ing parameters and selection based on expert system and model with special and general regulation of process experts or mechanics’experience, machining parts and modern intelligent method , using this device to optimize ( ) the machining parameters , then achieve to improve the efficiency of programs and process technic level , shorten the time of production preparing. The mach -ining system always in the working state of more reason -able and economical with the process programs have been prepared by the optimized machining parameters.
1. 6 Development of CNC machine. – So far , The expert system of neural network for EDM with the function of self-learning have been developed. – 7000 serious CNC of Okulma company have automatic programming function with artificial intelligence. – Tsinghua has made some achievements in intelligent optimization of machining parameters and research on CAPP.

1. 6 Development of CNC machine. 3) Intelligent fault diagnosis( ) and selfrepairing technology –Technology of intelligent fault diagnosis : According to the information have been got and applying modern intelligent method , such as AI , EX , ANN , to achieve technology that fault can be located quickly and exactly. –Technology of intelligent fault self-repairing : According to diagnosis to make sure the reason and position of fault for troubleshooting( ) automatically or leading eliminate fault. Technology of intelligent fault selfrepairing integrates fault self-diagnosis , fault selfeliminating , fault self-repairing , fault self-adjusting and through whole lifecycle of machining process. –Technology of intelligent fault diagnosis has been applied in CNC system produced by Japan and America , bacially this

1. 6 Development of CNC machine. 4) Intelligent AC servo driving equipment (智能化交流伺服驱动装置) So far, intelligent servo system that can automatic diagnosis load and adjust parameters is developing , it includes equipment of intelligent spindle AC driving and intelligent feed servo. This driving equipment makes driving system run best , because it can diagnosis automatically moment of inertia( ) of motor and load , can optimize and adjust the parameters of control system automatically.

1. 6 Development of CNC machine. 5) Intelligent 4 M NC system(智能 4 M数控系统) Integration( ) of processing and measure-ment is an effective way to achieve rapid machining , rapid detection and fast response in the manufactur-ing process. Integrating Measurement , Modeling , Manufacturing , Manipulator( ) into one sys -tem for information sharing to promote 4 M intelli -gent system of integration of measurement , model -ing , manufacturing , clamping( , operating. )
1. 6 Development of CNC machine. (5) Opening of system (体系开放化) Definition(IEEE):A system that can achieve sys -tem function in the different working platforms and interoperate with other system. Characteristic of open CNC system: –System component( ) includes software and hard- ware has features of Standardization , Diversification( ) and Interchangeability( ) –Achieving system integration of cordwood through construction system that can fluctuat component. Construction should be portable and transparent.
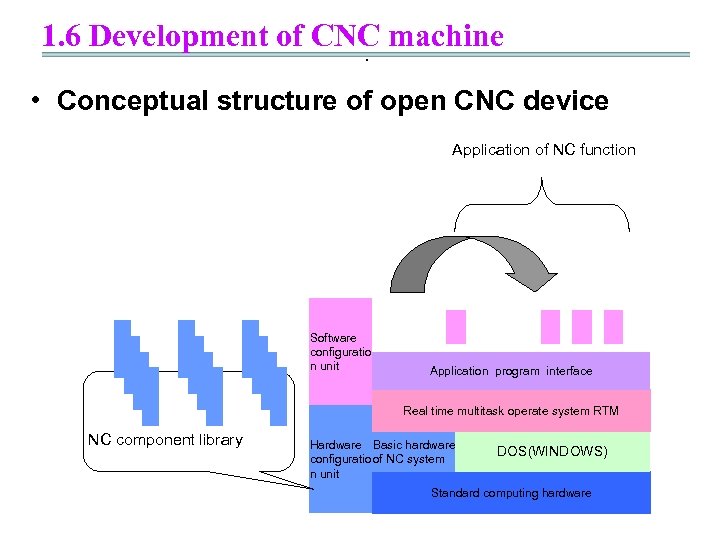
1. 6 Development of CNC machine. • Conceptual structure of open CNC device Application of NC function Software configuratio n unit Application program interface Real time multitask operate system RTM NC component library Hardware Basic hardware configuratio of NC system n unit DOS(WINDOWS) Standard computing hardware
1. 6 Development of CNC machine. Advantage of open system structure CNC: - Open to new technology: Due to the interface of software and hardware follow accepted standard protocols, only a small amount of redesign and adjustment, a new generation of general software and hardware resources can be adopted , be absor -bed , be compatible in the existing system, this means that the system development costs will be greatly reduced and the system performance and reliability will continue to improve in the long life cycle. - Standard man-machine interface:standard programming language available for users , lower labour consumption related directly with operational efficiency(
1. 6 Development of CNC machine. - Open to users' special requirements : Update products, expand capacity, provide the various combinations of hard software products available to meet specific application requirements, provide users with a method, starting from the low-level controller, gradually increase until it reaches the required performance. In addition the user's own technical knack( ) can be easily integrated into and create their own brand products. - Can decrease products, convenient for mass production, improve reliability and reduce cost, increase market supplies ability and competition ability.
1. 6 Development of CNC machine. Research progress of open CNC system at home and abroad – America:NGC(The Next Generation Workstation/ Machine Controller) and OMAC(Open Modular( ) Architecture Controller)plan – EEC:OSACA(Open System Architecture for Control within Automation Systems)plan – Japan:OSEC(Open System Environment for Controller) plan – China:ONC (Open Numerical Control System)project Huazhong I type——CNC open system structure based on IPC – Aerospace I type CNC system——multi-machine open system structure based on PC

1. 6 Development of CNC machine. (6)Interaction networked The system is base unit of forming globle manufacturing , it supports network communication protocol , Both meet the needs of the stand-alone requirements, and can satisfy the FMC, FMS, CIMS for numerical control system of the basic equipment integration requirements • Network resources sharing • Remote network control of NC machine tools • Digital service based on network, such as remote monitoring of CNC machine tools , fault diagnosis , remote network training and teaching, ecommerce
1. 6 Development of CNC machine. (7) Driven parallel Parallel machining center Virtual Axis Machine. Tools is an important breakthrough in the structure of CNC machine tools. Parallel machine tool is considered to be the most meaningful progress since the invention of numerical control technology in machine tool industry, the 21 st century a new generation of numerical control processing equipment
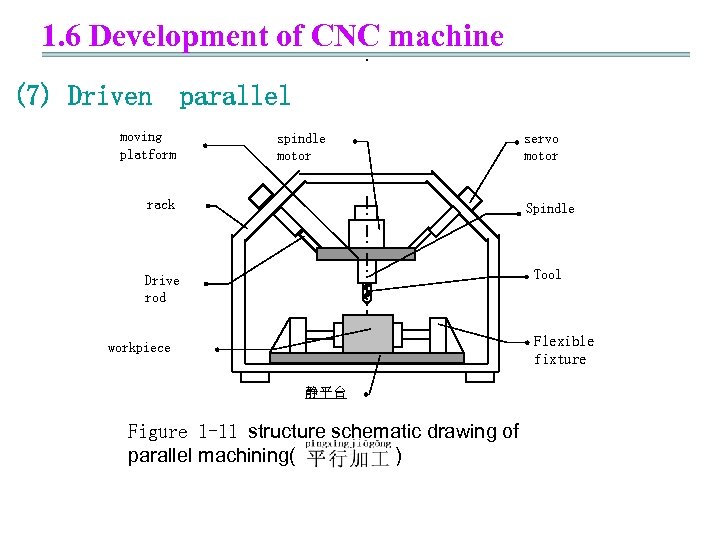
1. 6 Development of CNC machine. (7) Driven parallel moving platform spindle motor servo motor rack Spindle Drive rod Tool Flexible fixture workpiece 静平台 Figure 1 -11 structure schematic drawing of parallel machining( )
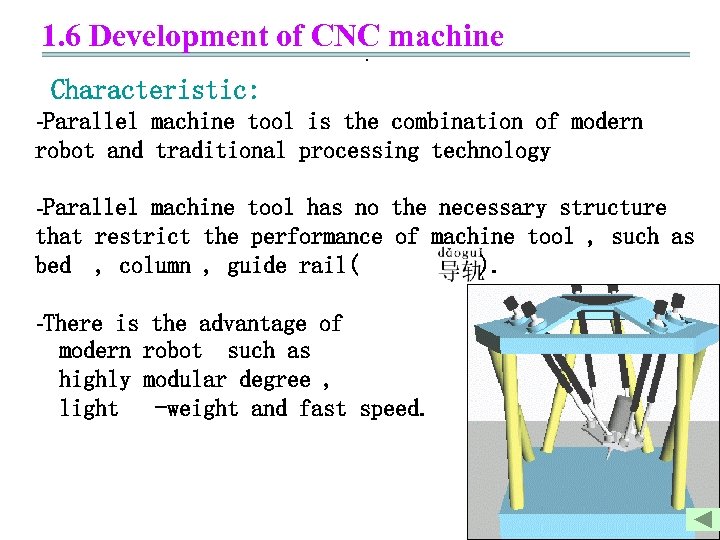
1. 6 Development of CNC machine. Characteristic: -Parallel machine tool is the combination of modern robot and traditional processing technology -Parallel machine tool has no the necessary structure that restrict the performance of machine tool , such as bed , column , guide rail( ). -There is the advantage of modern robot such as highly modular degree , light -weight and fast speed.
1b529500ab1625fbe279d2068df6cbff.ppt