3b93ab02a0a6236a9f69f4ca17d2404f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 NYSAM 2011 Case Presentation Edwin A. Salsitz, M. D. FASAM Beth Israel Medical Center New York City
NYSAM 2011 Case Presentation Edwin A. Salsitz, M. D. FASAM Beth Israel Medical Center New York City
 Physician Clinical Support System PCSS… § answers questions about opioids, including methadone, for treatment of chronic pain § answers questions about use of buprenorphine for treatment of opioid dependence
Physician Clinical Support System PCSS… § answers questions about opioids, including methadone, for treatment of chronic pain § answers questions about use of buprenorphine for treatment of opioid dependence
 Physician Clinical Support System PCSS… § is free, for interested physicians and staff § is supported by SAMHSA through the Center for Substance Abuse Treatment (CSAT) and administered by the American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM)
Physician Clinical Support System PCSS… § is free, for interested physicians and staff § is supported by SAMHSA through the Center for Substance Abuse Treatment (CSAT) and administered by the American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM)
 Physician Clinical Support System Ask a clinical question… • get a response from an expert PCSS mentor – on line by email PCSSproject@asam. org – by phone 877 -630 -8812 From www. PCSSmentor. org. . . • download clinical tools, helpful forms and concise guidance's (like FAQs) on specific questions
Physician Clinical Support System Ask a clinical question… • get a response from an expert PCSS mentor – on line by email PCSSproject@asam. org – by phone 877 -630 -8812 From www. PCSSmentor. org. . . • download clinical tools, helpful forms and concise guidance's (like FAQs) on specific questions
 ADDICTION/PAIN TREATMENT “All Treatments Work For Some People/Patients” “No One Treatment Works for All People/Patients” Alan I. Leshner, Ph. D Former Director NIDA
ADDICTION/PAIN TREATMENT “All Treatments Work For Some People/Patients” “No One Treatment Works for All People/Patients” Alan I. Leshner, Ph. D Former Director NIDA
 CT 2010 Case Presentation 54 y. o. ♀ evaluated on 6/19/09 n Headaches major medical problem n ? Paternal uncle—Et. OH n Lives with husband, has 2 adult stepchildren n Upper level executive in marketing, 250 K n Through H. S. no drugs or Et. OH n
CT 2010 Case Presentation 54 y. o. ♀ evaluated on 6/19/09 n Headaches major medical problem n ? Paternal uncle—Et. OH n Lives with husband, has 2 adult stepchildren n Upper level executive in marketing, 250 K n Through H. S. no drugs or Et. OH n
 CT 2010 Case Boyfriend 1 st year of college introduced to heroin IN n 1 st use may have led to gang rape? Uncontrollable crying over story n 1 st “migraine” around this time, frequent & severe n “nervous breakdown” after boyfriend ends relationship in 2 nd year college n Heroin IN IV x 2 yrs illicit methadone TC Abstinent age 25 n
CT 2010 Case Boyfriend 1 st year of college introduced to heroin IN n 1 st use may have led to gang rape? Uncontrollable crying over story n 1 st “migraine” around this time, frequent & severe n “nervous breakdown” after boyfriend ends relationship in 2 nd year college n Heroin IN IV x 2 yrs illicit methadone TC Abstinent age 25 n
 CT 2010 Case Migraines lessened in 30’s and 40’s n frequency and severity post-menopause n Opioids X 4 years—oxy. CR & oxy. IR n Nationally known HA clinic—weaned off opioids 2 yrs ago—severe HAs opioids(1 mo. ) n Neuro and Pain Specialist—ran out of meds 1 week early ? Inpatient “detox”--? work n Current meds. Oxy CR 30 mg tid Oxy. IR 5 mg qid(NSAID, ondansetron, prednisone, venlafaxine, topiramate) n
CT 2010 Case Migraines lessened in 30’s and 40’s n frequency and severity post-menopause n Opioids X 4 years—oxy. CR & oxy. IR n Nationally known HA clinic—weaned off opioids 2 yrs ago—severe HAs opioids(1 mo. ) n Neuro and Pain Specialist—ran out of meds 1 week early ? Inpatient “detox”--? work n Current meds. Oxy CR 30 mg tid Oxy. IR 5 mg qid(NSAID, ondansetron, prednisone, venlafaxine, topiramate) n
 CT 2010 Case Age 17—appendectomy— 1 st opioid— “felt good, ” “took away my insecurities” n Subsequent heroin--- “energized” n Sobbing and Crying at mention of mother who died 9 mos ago at age 93 n Felt she was a terrible disappointment to mother n Saw therapist on and off for many years— currently not in psychotherapy n
CT 2010 Case Age 17—appendectomy— 1 st opioid— “felt good, ” “took away my insecurities” n Subsequent heroin--- “energized” n Sobbing and Crying at mention of mother who died 9 mos ago at age 93 n Felt she was a terrible disappointment to mother n Saw therapist on and off for many years— currently not in psychotherapy n
 Diagnosis and Plan After Initial Consultation Opioid Physical Dependence n Pain Paradigm n Husband to Dispense Opioids n Attempt to taper opioids n Rx Oxy CR 30 mg—attempt bid n One week later 1. Oxy CR bid 2. D/C venlafaxine, start duloxetine 3. Oxy IR 5 q 6 h prn n
Diagnosis and Plan After Initial Consultation Opioid Physical Dependence n Pain Paradigm n Husband to Dispense Opioids n Attempt to taper opioids n Rx Oxy CR 30 mg—attempt bid n One week later 1. Oxy CR bid 2. D/C venlafaxine, start duloxetine 3. Oxy IR 5 q 6 h prn n
 3 Weeks later Headaches have markedly increased while on vacation—husband not in agreement on chronic opioid paradigm n Neurologist adds gabapentin 300 mg tid and topiramate(now 100 mg. qd) n Continued attempts to taper opioids not successful n
3 Weeks later Headaches have markedly increased while on vacation—husband not in agreement on chronic opioid paradigm n Neurologist adds gabapentin 300 mg tid and topiramate(now 100 mg. qd) n Continued attempts to taper opioids not successful n
 4 Weeks Later Husband no longer coming in with patient n Headaches daily—making work and home difficult n After long discussion, OXY CR d/c’d and methadone low dose started and titrated upwards n
4 Weeks Later Husband no longer coming in with patient n Headaches daily—making work and home difficult n After long discussion, OXY CR d/c’d and methadone low dose started and titrated upwards n
 After 7 months Stable methadone dose 30 mg tid n Infrequent short acting opioids n Significant improvement in headache frequency, severity, n Improved function at work n Stopped therapy, and refuses new therapy n Marital issues difficult to discuss n All urines, pill counts, appts. , etc reveal no problematic behavior n Overall patient rating 9 3(as of 4/13/10) n
After 7 months Stable methadone dose 30 mg tid n Infrequent short acting opioids n Significant improvement in headache frequency, severity, n Improved function at work n Stopped therapy, and refuses new therapy n Marital issues difficult to discuss n All urines, pill counts, appts. , etc reveal no problematic behavior n Overall patient rating 9 3(as of 4/13/10) n
 April 2010 Present June 2010— 2 Rxs given for methadone n October 2010 ---Short Acting Opioids D/C’d n October 2010 ---Methadone 30 mg bid n Headaches present, but intensity/frequency n Stigma issue around methadone continues n Marital issue, no psychosocial n Random urines negative n
April 2010 Present June 2010— 2 Rxs given for methadone n October 2010 ---Short Acting Opioids D/C’d n October 2010 ---Methadone 30 mg bid n Headaches present, but intensity/frequency n Stigma issue around methadone continues n Marital issue, no psychosocial n Random urines negative n
 NEUROLOGY 2004; 62: 1687 -1694 160 enrolled 70 remained on daily scheduled opioids X 4 yrs 74% LA, 26% SA 41(59%) Responders by 50% in SHI—freq x duration severe headache/week
NEUROLOGY 2004; 62: 1687 -1694 160 enrolled 70 remained on daily scheduled opioids X 4 yrs 74% LA, 26% SA 41(59%) Responders by 50% in SHI—freq x duration severe headache/week
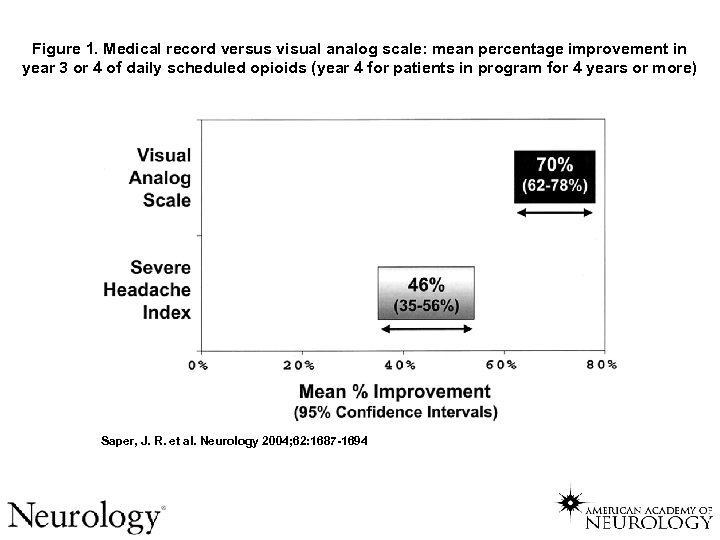 Figure 1. Medical record versus visual analog scale: mean percentage improvement in year 3 or 4 of daily scheduled opioids (year 4 for patients in program for 4 years or more) Saper, J. R. et al. Neurology 2004; 62: 1687 -1694
Figure 1. Medical record versus visual analog scale: mean percentage improvement in year 3 or 4 of daily scheduled opioids (year 4 for patients in program for 4 years or more) Saper, J. R. et al. Neurology 2004; 62: 1687 -1694
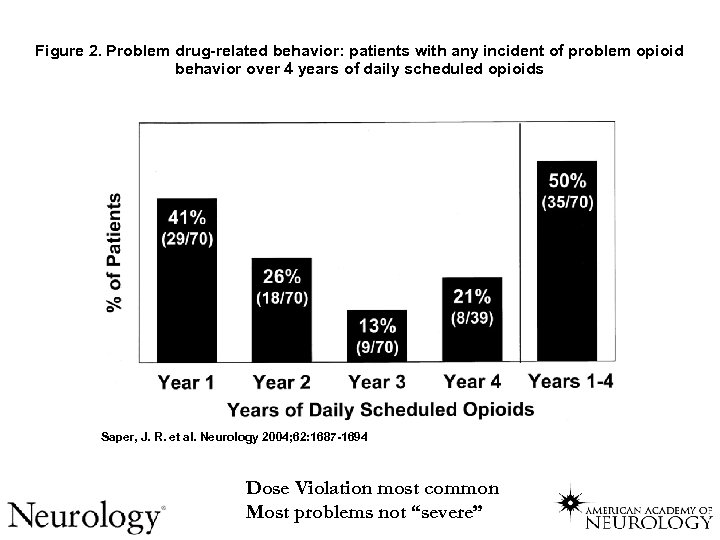 Figure 2. Problem drug-related behavior: patients with any incident of problem opioid behavior over 4 years of daily scheduled opioids Saper, J. R. et al. Neurology 2004; 62: 1687 -1694 Dose Violation most common Most problems not “severe”
Figure 2. Problem drug-related behavior: patients with any incident of problem opioid behavior over 4 years of daily scheduled opioids Saper, J. R. et al. Neurology 2004; 62: 1687 -1694 Dose Violation most common Most problems not “severe”
 Chronic Pain S U B S E T Addiction ê Hedonic Tone Somatic Sxs OPIOIDS ? Endorphin Deficiency Pain Medicine Prescriptions Pharmacies Legitimate Anti-Depressants Anti-Convulsants Mood Stabilizers Addiction Treatment Methadone Clinics Regulations
Chronic Pain S U B S E T Addiction ê Hedonic Tone Somatic Sxs OPIOIDS ? Endorphin Deficiency Pain Medicine Prescriptions Pharmacies Legitimate Anti-Depressants Anti-Convulsants Mood Stabilizers Addiction Treatment Methadone Clinics Regulations
 ** * *Anterior Cingulate Gyrus
** * *Anterior Cingulate Gyrus
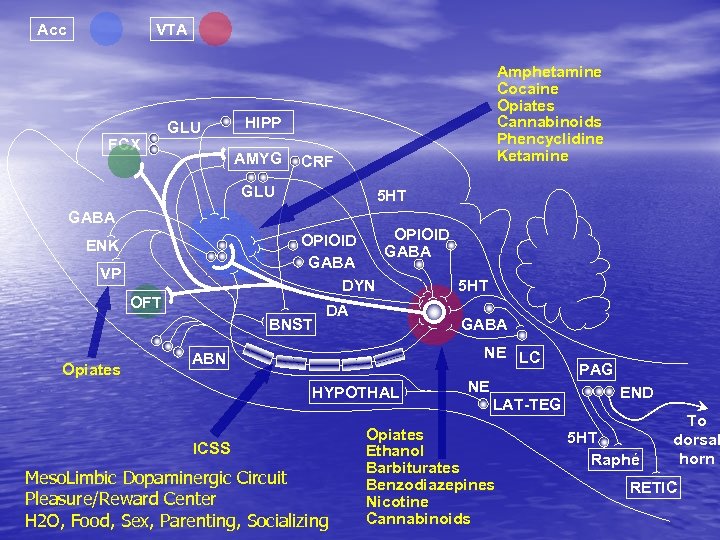 Acc VTA FCX GLU HIPP AMYG CRF GLU GABA 5 HT OPIOID GABA DYN 5 HT ENK VP OFT BNST Opiates Amphetamine Cocaine Opiates Cannabinoids Phencyclidine Ketamine DA GABA NE LC ABN HYPOTHAL ICSS Meso. Limbic Dopaminergic Circuit Pleasure/Reward Center H 2 O, Food, Sex, Parenting, Socializing NE LAT-TEG Opiates Ethanol Barbiturates Benzodiazepines Nicotine Cannabinoids PAG END 5 HT Raphé To dorsal horn RETIC
Acc VTA FCX GLU HIPP AMYG CRF GLU GABA 5 HT OPIOID GABA DYN 5 HT ENK VP OFT BNST Opiates Amphetamine Cocaine Opiates Cannabinoids Phencyclidine Ketamine DA GABA NE LC ABN HYPOTHAL ICSS Meso. Limbic Dopaminergic Circuit Pleasure/Reward Center H 2 O, Food, Sex, Parenting, Socializing NE LAT-TEG Opiates Ethanol Barbiturates Benzodiazepines Nicotine Cannabinoids PAG END 5 HT Raphé To dorsal horn RETIC
 HCC=Healthcare for Communities 1998, 2001
HCC=Healthcare for Communities 1998, 2001
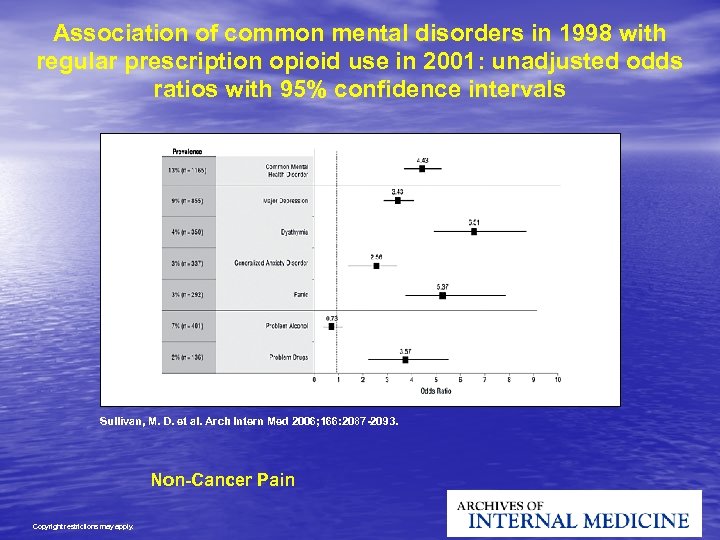 Association of common mental disorders in 1998 with regular prescription opioid use in 2001: unadjusted odds ratios with 95% confidence intervals Sullivan, M. D. et al. Arch Intern Med 2006; 166: 2087 -2093. Non-Cancer Pain Copyright restrictions may apply.
Association of common mental disorders in 1998 with regular prescription opioid use in 2001: unadjusted odds ratios with 95% confidence intervals Sullivan, M. D. et al. Arch Intern Med 2006; 166: 2087 -2093. Non-Cancer Pain Copyright restrictions may apply.
 Journal of Addictive Diseases, Vol. 27(3) 2008
Journal of Addictive Diseases, Vol. 27(3) 2008
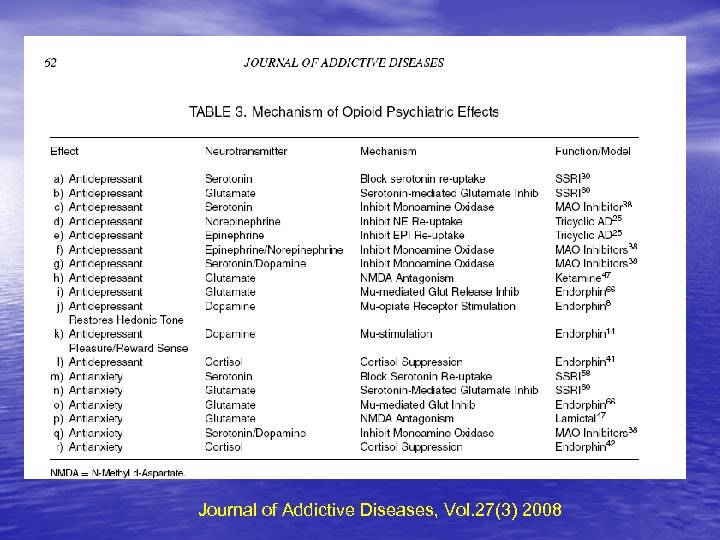 Journal of Addictive Diseases, Vol. 27(3) 2008
Journal of Addictive Diseases, Vol. 27(3) 2008
 Problematic (Aberrant) Behaviors • Probably more predictive – – – – Selling prescription drugs Prescription forgery Stealing or borrowing another patient’s drugs Injecting oral formulation Obtaining prescription drugs from non-medical sources Concurrent abuse of related illicit drugs Multiple unsanctioned dose escalations Recurrent prescription losses Passik and Portenoy, 1998 • Probably less predictive – Aggressive complaining about need for higher doses – Drug hoarding during periods of reduced symptoms – Requesting specific drugs – Acquisition of similar drugs from other medical sources – Unsanctioned dose escalation 1 -2 times – Unapproved use of the drug to treat another symptom – Reporting psychic effects not intended by the clinician
Problematic (Aberrant) Behaviors • Probably more predictive – – – – Selling prescription drugs Prescription forgery Stealing or borrowing another patient’s drugs Injecting oral formulation Obtaining prescription drugs from non-medical sources Concurrent abuse of related illicit drugs Multiple unsanctioned dose escalations Recurrent prescription losses Passik and Portenoy, 1998 • Probably less predictive – Aggressive complaining about need for higher doses – Drug hoarding during periods of reduced symptoms – Requesting specific drugs – Acquisition of similar drugs from other medical sources – Unsanctioned dose escalation 1 -2 times – Unapproved use of the drug to treat another symptom – Reporting psychic effects not intended by the clinician
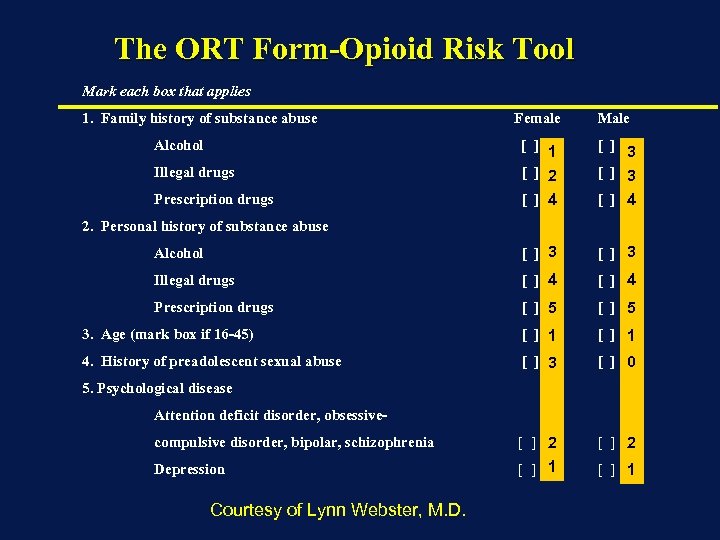 The ORT Form-Opioid Risk Tool Mark each box that applies 1. Family history of substance abuse Female Male Illegal drugs [ ] 1 [ ] 2 [ ] 3 Prescription drugs [ ] 4 Alcohol [ ] 3 Illegal drugs [ ] 4 Prescription drugs [ ] 5 3. Age (mark box if 16 -45) [ ] 1 4. History of preadolescent sexual abuse [ ] 3 [ ] 0 compulsive disorder, bipolar, schizophrenia [ ] 2 Depression [ ] 1 Alcohol 2. Personal history of substance abuse 5. Psychological disease Attention deficit disorder, obsessive- Courtesy of Lynn Webster, M. D.
The ORT Form-Opioid Risk Tool Mark each box that applies 1. Family history of substance abuse Female Male Illegal drugs [ ] 1 [ ] 2 [ ] 3 Prescription drugs [ ] 4 Alcohol [ ] 3 Illegal drugs [ ] 4 Prescription drugs [ ] 5 3. Age (mark box if 16 -45) [ ] 1 4. History of preadolescent sexual abuse [ ] 3 [ ] 0 compulsive disorder, bipolar, schizophrenia [ ] 2 Depression [ ] 1 Alcohol 2. Personal history of substance abuse 5. Psychological disease Attention deficit disorder, obsessive- Courtesy of Lynn Webster, M. D.
 Total score risk category Low risk: 0– 3 Moderate risk: 4– 7 High risk: ≥ 8 Aberrant Behavior Displayed (%) Validation Study Results 100 ORT Total Score Risk Category 90. 9 80 60 40 28 20 5. 6 0 Low Moderate High Webster LR and Webster RM. Predicting aberrant behaviors in opioid-treated patients: validation of the Opioid Risk Tool. Pain Med. 2005; 6: 432 -442. Non-Cancer Pain
Total score risk category Low risk: 0– 3 Moderate risk: 4– 7 High risk: ≥ 8 Aberrant Behavior Displayed (%) Validation Study Results 100 ORT Total Score Risk Category 90. 9 80 60 40 28 20 5. 6 0 Low Moderate High Webster LR and Webster RM. Predicting aberrant behaviors in opioid-treated patients: validation of the Opioid Risk Tool. Pain Med. 2005; 6: 432 -442. Non-Cancer Pain
 Russell Portenoy, M. D.
Russell Portenoy, M. D.
 “…as we know, there are knowns, there are things we know. We also know there are known unknowns; that is to say we know there are some things we do not know. But there also unknowns – the ones we don’t know. ” – Donald Rumsfeld
“…as we know, there are knowns, there are things we know. We also know there are known unknowns; that is to say we know there are some things we do not know. But there also unknowns – the ones we don’t know. ” – Donald Rumsfeld
 “MORPHINE IS GOD’S OWN MEDICINE” Sir William Osler
“MORPHINE IS GOD’S OWN MEDICINE” Sir William Osler
 ADDICTION/PAIN TREATMENT “All Treatments Work For Some People/Patients” “No One Treatment Works for All People/Patients” Alan I. Leshner, Ph. D Former Director NIDA
ADDICTION/PAIN TREATMENT “All Treatments Work For Some People/Patients” “No One Treatment Works for All People/Patients” Alan I. Leshner, Ph. D Former Director NIDA
 SUPPORT ASAM!!
SUPPORT ASAM!!


