3ce77e6adaa6bd1e948289cb24d92e25.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38

Nursing at a Crossroads: Is Evidence-based Practice Core … or NOT? Mary Hook, Ph. D, RN-BC Building Bridges Conference 2016 © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

Southeast Wisconsin Research Consortium Alverno College Aurora Health Care Children’s Hospital & Health System Columbia St. Mary’s Concordia University Wisconsin, Froedtert and Medical College of Wisconsin, Community Memorial Hospital St. Joseph’s Hospital Campuses Marquette University Pro. Health Care Sigma Theta Tau Chapters: Delta Gamma , Eta Nu, and Phi Beta; University of Wisconsin Milwaukee, Wheaton Franciscan Healthcare Clement J. Zablocki VA Medical Center © Aurora Health Care, Inc.
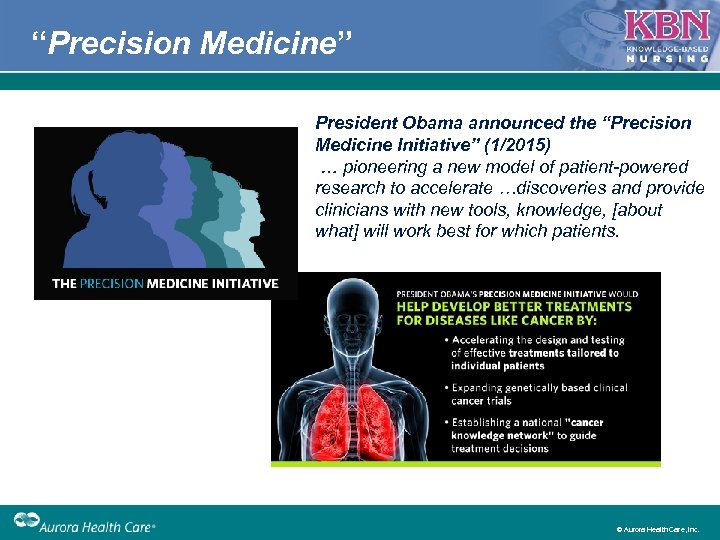
“Precision Medicine” President Obama announced the “Precision Medicine Initiative” (1/2015) … pioneering a new model of patient-powered research to accelerate …discoveries and provide clinicians with new tools, knowledge, [about what] will work best for which patients. © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

What About. . . “Precision Nursing” § Science § Largest § Closest § Technology § Prepared Source: IOM, 2010 Future of Nursing © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

Nursing: Long History of Leadership Link_Nightingale_Notes_on_Nursing. 1869 © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

Learner Objectives 1. Discuss why Nursing is at a Crossroad 2. Define evidence based practice (EBP) and describe the basic competencies for EBP and quality of practice espoused by the ANA Scope and Standards. 3. Describe Implementation Science, an emerging science designed to improve the adoption and use of EBP 4. Identify current research findings about EBP adoption by nurses 5. Identify actions we can take support and sustain EBP as a core competency for nursing © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

Nursing at a Crossroad § Decision making § Move forward § Frozen § Left behind © Aurora Health Care, Inc.
Calls for Health Care Transformation § § Institute of Medicine (IOM) Institute Healthcare Innovation (IHI) – Triple Aim Centers for Medicare and Medicaid – Value Based Purchasing “Meaningful” Use © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

Future of Nursing (IOM, 2011) Institute of Medicine (IOM). 2011. The Future of Nursing: Leading Change, Advancing Health. Washington, DC. , The National Academies Press. © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

What Does “Top of Scope” Look Like? • • • Enhanced biopsychosocial assessment skills Skilled communication Versatile Sensitive to patient/family needs Able to engage patients in self management © Aurora Health Care, Inc.
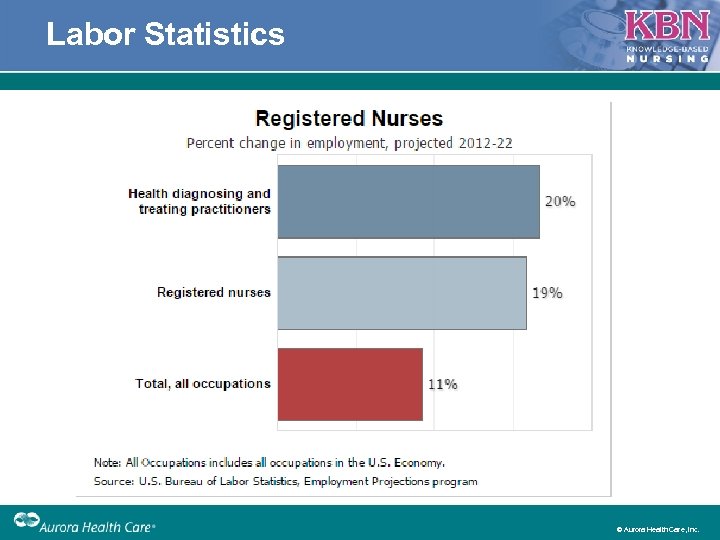
Labor Statistics © Aurora Health Care, Inc.
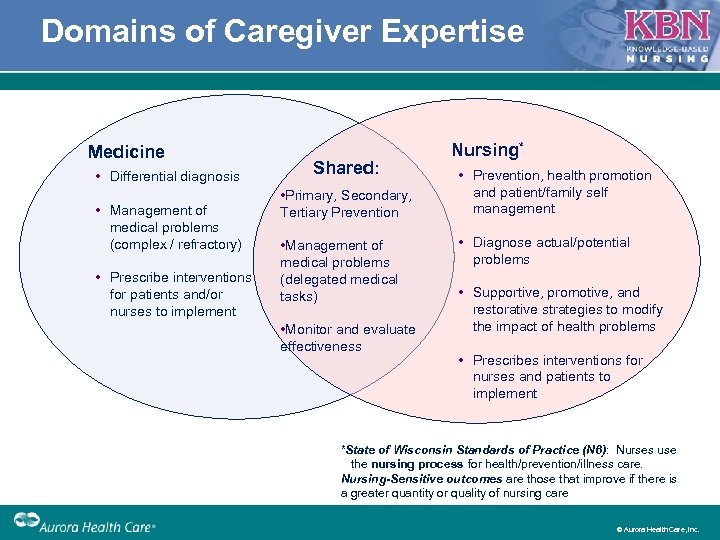
Domains of Caregiver Expertise Medicine • Differential diagnosis • Management of medical problems (complex / refractory) • Prescribe interventions for patients and/or nurses to implement Shared: • Primary, Secondary, Tertiary Prevention • Management of medical problems (delegated medical tasks) • Monitor and evaluate effectiveness Nursing* • Prevention, health promotion and patient/family self management • Diagnose actual/potential problems • Supportive, promotive, and restorative strategies to modify the impact of health problems • Prescribes interventions for nurses and patients to implement *State of Wisconsin Standards of Practice (N 6): Nurses use the nursing process for health/prevention/illness care. Nursing-Sensitive outcomes are those that improve if there is a greater quantity or quality of nursing care © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

Challenging Current Views • Computers are supposed to help you do the right thing without thinking • “Hardwire” things so staff do the same thing every time • Staff don’t have time to think – make things simple! • Mandate assessments (without making sure that the appropriate intervention is done) © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

Technology Must Not Replace Thinking “Worrisome evidence suggests that our own intelligence is withering as we become more dependent on the artificial variety. ” Source: Nicholas Carr, Wall Street Journal, 11/21/14 © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

What if. . . More Automation Happens? § What domain are you focused on? § What happens when technology advances and drugs are titrated by electronic vital sign surveillance? § Rationale for staffing with BSNprepared staff § How do RNs really make a difference in patient care? © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

Nursing Sensitive Patient Outcomes § Outcomes that depend on the quantity or quality of nursing care § Developed in acute care § Based on nursing control processes of key aspects of care delivery © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

“Essential” Practices Definition: • Extremely important and necessary • Integral part of the process (can’t proceed without it) • Embedded into policy as a practice expectation © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

Nursing Scope and Standards § American Nurses Association (2015) § Public right to professional competence § RN (individual) accountabilities § Employer accountabilities for environment § Evaluation Self assessment Peer assessment Leadership role © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

ANA Standard #13: EBP & Research Integrates evidence/research findings into practice § Articulates value of research/application § Identifies research questions § Uses EB knowledge/research to guide practice § Incorporates evidence for practice change § Participates in formulating EBP through research (revised) § Promotes ethical principles of research § Appraises nursing research for application § Shares peer-reviewed research to integrate knowledge into practice (revised) © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

What We KNOW. . . Evidence-based practice (EBP) is a core nursing competency (ANA, 2010; IOM, 2010) • Nurses generally BELIEVE the use of EBP results in best outcomes. . . but barriers exist. . . Most nurses rely on peers for information Many report limited value/skills for using research (Pravikoff, et al. , 2005) Best Research Evidence Clinical Expertise Patient Values • Nurse managers can influence research use by facilitating and monitoring patient care but this is not a common practice (Gifford et al. , 2012). • Nurse leaders must build organizational cultures that support and sustain EBP (Melynk et al. , 2012; Melynk, 2016) © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

Research to Practice Gap © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

Translating Research into Practice “Studies suggest that it takes an average of 17 years for research evidence to reach clinical practice. ” Balas & Boren (2000, p. 66). Permission requested from Sydney Harris, 2014 © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

Year Ti. DIRH - Host Universities & Organizations 2011 University of North Carolina 2012 University of California, San Francisco 2013 Washington University in St. Louis 2014 Harvard University & Dana-Faber Cancer Institute • 5 Day Institute led by international experts • Competitive/funded workshop (41/289 applicants) • Required to bring feasible D & I projects to work on 2015 Pasadena California
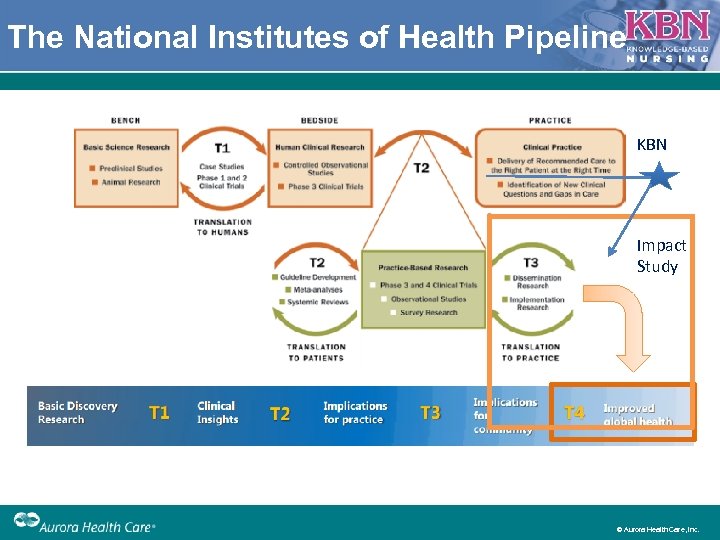
The National Institutes of Health Pipeline KBN Impact Study © Aurora Health Care, Inc.
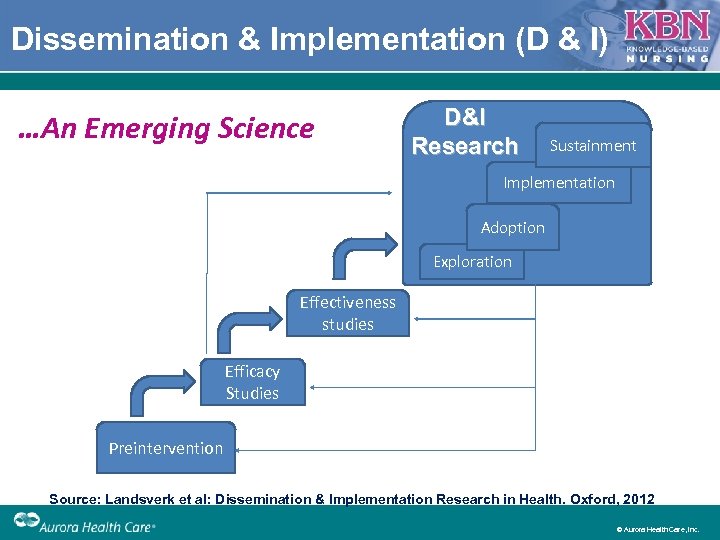
Dissemination & Implementation (D & I) …An Emerging Science D&I Research Sustainment Implementation Adoption Exploration Effectiveness studies Efficacy Studies Preintervention Source: Landsverk et al: Dissemination & Implementation Research in Health. Oxford, 2012 © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

D & I Concepts Dissemination: active approach for spreading EBP interventions to target audiences via determined channels and planned strategies. Implementation: an active process of integrating core components of an EBP intervention within specific setting – Adoption: deciding to make full use of an innovation. – Implementation: carrying out innovation with completeness and fidelity using behavioral expectations to improve adopter skills. – Maintenance: embedding innovation into normal operation and maintaining with policy enforcement. © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

A Tale of Two Worlds… How do practitioners learn about research findings? How do researchers perceive they most effectively reach practitioners? 1. Professional associations 1. Journal articles 2. Seminars/workshops 2. Face to face meetings 3. Email alerts 3. Media interviews 4. Journal articles 4. Press releases © Aurora Health Care, Inc.
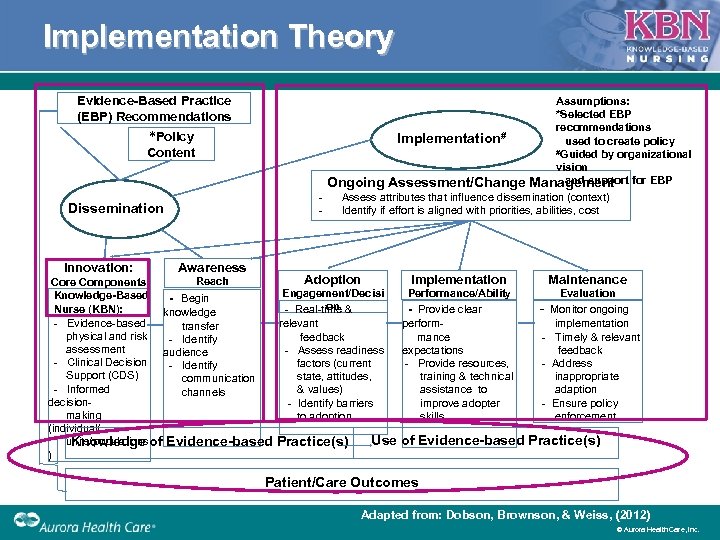
Implementation Theory Evidence-Based Practice (EBP) Recommendations Assumptions: *Selected EBP recommendations Implementation# used to create policy #Guided by organizational vision and support for EBP Ongoing Assessment/Change Management *Policy Content Dissemination Innovation: Assess attributes that influence dissemination (context) Identify if effort is aligned with priorities, abilities, cost Awareness Adoption Implementation Maintenance Reach Core Components Engagement/Decisi Performance/Ability Evaluation Knowledge-Based - Begin on - Real time & - Provide clear - Monitor ongoing Nurse (KBN): knowledge Evidence based relevant perform implementation transfer physical and risk Identify feedback mance Timely & relevant assessment Assess readiness expectations feedback audience Clinical Decision Identify factors (current Provide resources, Address Support (CDS) state, attitudes, training & technical inappropriate communication Informed & values) assistance to adaption channels decision Identify barriers improve adopter Ensure policy making to adoption skills enforcement (individual/ Use of Evidence-based Practice(s) units/populations Knowledge of Evidence-based Practice(s) ) Patient/Care Outcomes Adapted from: Dobson, Brownson, & Weiss, (2012) © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

What’s the Evidence for EBP by Nurses? § Beliefs about the value of EBP is high § Implementation of EBP is relatively low (Sanders & Vehvilainen Julkunen, 2016; Eaton, et al. , 2015) § Low implementation associated with not achieving national core measures and performance benchmarks (Melynk, et al. 2016) § Large body of evidence about barriers § Little evidence regarding effective interventions © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

New Barrier to EBP: Leader Resistance § EBP is tied to improved outcomes § EBP is direct pathway to achieving the Triple AIM § CNEs rate EBP as low priority with little budgeted resources (Melynk, 2016) § Nurse Leaders and Managers must demonstrate EBP competency (Melynk & Gallagher Ford, 2014) § Treatment fidelity © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

What’s the Evidence re: Nursing Research? • Vast majority of nursing research studies are descriptive • Small, nonprobabilility samples • Modest quality • More focus on intervention research Source: Sanders & Vehvilainen Julkunen (2016) © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

Call to ACTION! • Our window of opportunity is open © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

Ask the Right Questions § § § § Who do we want to be? What are we great at? What are we uniquely advantaged at doing? ” Are you aligned with patient/customer needs? (create value) Invest strategic focus Efficient Competitively differentiated © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

What Can We Do? § Work within Your Culture to be more Strategic Way of thinking belief system The way members behave every day in the workplace § Dissemination vs. Implementation Tendency to see education as primary intervention Engagement Accountability © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

What Can We Do? Dr. Larry Green (2006) “If we want evidencebased practice, we need more practice based evidence” © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

Conclusions § Nursing is at a Crossroad § Evidence based Practice is core but barriers limit use in practice § Implementation Science is an emerging science that provides direction for how to accelerate the adoption of research § Positive beliefs in EBP does not ensure use § Action is needed More research to test interventions and demonstrate value of nursing based approaches Strategic use of nurses and nursing evidence More focus on implementation and maintenance of EBP behaviors © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

Questions? For more information: Mary Hook Ph. D, RN-BC mary. hook@aurora. org © Aurora Health Care, Inc.

References • • • American Nurses Association. (2015). Nursing: Scope and Standards of Practice (3 rd ed. ) (pp. 4– 5). Silver Spring, MD: ANA. Brownson, R. C et al. (2012) Dissemination and implementation research in health: Translating science to practice (pp. 437 458). NY: Oxford Press. Carr, N. (2014, 11/21/2014). Automation makes us dumb. Wall Street Journal. Eaton, L. H, , Meins, A. R. , Mitchell, P. H. , Voss, J. , Doorenbos, A. Z. (2015). Evidence based Practice Behaviors of Nurses Providing Cancer Pain Management. Oncol Nurs Forum 42(2), 165 173 Gifford, W. A. , et al. (2013). Developing leadership capacity for guideline use: A pilot cluster randomized control trial. Worldviews on Evidence-Based Nursing, 10(1), 51 65. Institute of Medicine. (2010). Transforming Education: Defining core competencies. In Future of nursing: leading change, advancing health Retrieved www. thefutureofnursing. org/IOM Report Melnyk, B. M. , et al. , (2012). The state of evidence based practice in US nurses: Critical implications for nurse leaders and educators. Journal of Nursing Administration, 42(9), 410 417. Melnyk, B. M. , et al. . (2016). A Study of Chief Nurse Executives Indicates Low Prioritization of Evidence Based Practice and Shortcomings in Hospital Performance Metrics Across the United States. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs, 13(1), 6 -14. Melnyk Editor, B. M. (2016). An Urgent Call to Action for Nurse Leaders to Establish Sustainable Evidence Based Practice Cultures and Implement Evidence Based Interventions to Improve Healthcare Quality. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs, 13(1), 3 -5. Saunders, H. , & Vehvilainen Julkunen, K. (2016). The state of readiness for evidence based practice among nurses: An integrative review. Int J Nurs Stud, 56, 128 -140. © Aurora Health Care, Inc.
3ce77e6adaa6bd1e948289cb24d92e25.ppt