807f162f8dc2bc7533199a6e110188ad.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Nucleus D. K. The Professional Development Service for Teachers is funded by the Department of Education and Skills under the National Development Plan
Nucleus D. K. The Professional Development Service for Teachers is funded by the Department of Education and Skills under the National Development Plan
 Leaving Certificate Physics: Topics § § § § § Mechanics Temperature Heat Waves Vibrations and Sound Light Electricity Modern Physics Option 1: Particle Physics Option 2: Applied Electricity PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 2
Leaving Certificate Physics: Topics § § § § § Mechanics Temperature Heat Waves Vibrations and Sound Light Electricity Modern Physics Option 1: Particle Physics Option 2: Applied Electricity PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 2
 Learning outcomes (1) § Discovery of radioactivity and that three kinds of radiation exist. Know the nature and properties of each type of radiation – Applications: of alpha, beta and gamma rays § Rutherford’s alpha scattering experiment …the significance of the nuclear structure of atoms. – Application: enhanced understanding of chemical bonding § The principle of operation of an ionization chamber and other radiation detectors as well as appreciation of units like the Curie and Becquerel – Application: monitoring levels to ensure safety PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 3
Learning outcomes (1) § Discovery of radioactivity and that three kinds of radiation exist. Know the nature and properties of each type of radiation – Applications: of alpha, beta and gamma rays § Rutherford’s alpha scattering experiment …the significance of the nuclear structure of atoms. – Application: enhanced understanding of chemical bonding § The principle of operation of an ionization chamber and other radiation detectors as well as appreciation of units like the Curie and Becquerel – Application: monitoring levels to ensure safety PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 3
 Learning outcomes (2) § Concept of half-life, decay constant as measurable quantities as well as the random and uncontrolled nature of radioactivity – Application: Radiocarbon dating § Understand how energy may be obtained from nuclear reactions like fission and fusion – Application: Nuclear reactors PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 4
Learning outcomes (2) § Concept of half-life, decay constant as measurable quantities as well as the random and uncontrolled nature of radioactivity – Application: Radiocarbon dating § Understand how energy may be obtained from nuclear reactions like fission and fusion – Application: Nuclear reactors PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 4
 Radioactivity § In 1896 Becquerel found that some materials emitted radiation that blackened photographic plates. It was noticed that the radiation caused ionization and so could be detected by an electroscope § By 1900 it was realised there were three types of radiation. PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 5
Radioactivity § In 1896 Becquerel found that some materials emitted radiation that blackened photographic plates. It was noticed that the radiation caused ionization and so could be detected by an electroscope § By 1900 it was realised there were three types of radiation. PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 5
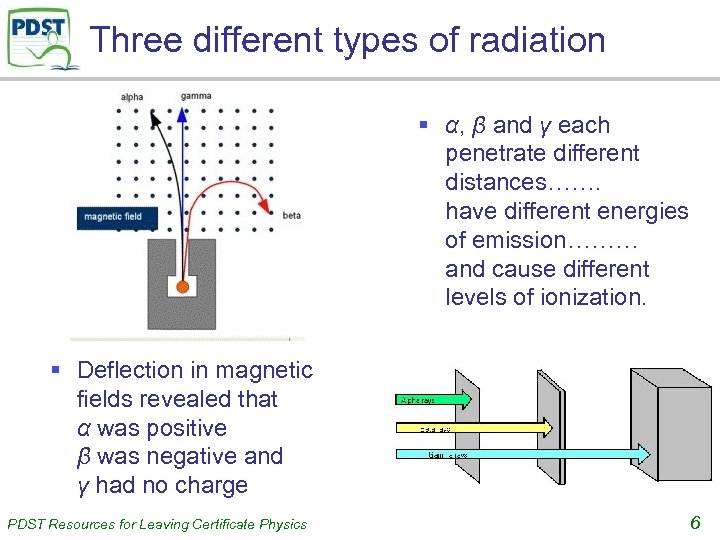 Three different types of radiation § α, β and γ each penetrate different distances……. have different energies of emission……… and cause different levels of ionization. § Deflection in magnetic fields revealed that α was positive β was negative and γ had no charge PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 6
Three different types of radiation § α, β and γ each penetrate different distances……. have different energies of emission……… and cause different levels of ionization. § Deflection in magnetic fields revealed that α was positive β was negative and γ had no charge PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 6
 Radioactive decay § The rate of decay of a radioactive source is proportional to the number of radioactive atoms (N) present: – λ is the decay constant. It is constant for a given isotope. § The solution of this equation is an exponential one, where N 0 is the initial number of atoms present: § While radioactivity is a random and uncontrolled phenomenon, it is found that the time for half the nuclei in a sample to decay is constant. This is known as the “half life” PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 7
Radioactive decay § The rate of decay of a radioactive source is proportional to the number of radioactive atoms (N) present: – λ is the decay constant. It is constant for a given isotope. § The solution of this equation is an exponential one, where N 0 is the initial number of atoms present: § While radioactivity is a random and uncontrolled phenomenon, it is found that the time for half the nuclei in a sample to decay is constant. This is known as the “half life” PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 7
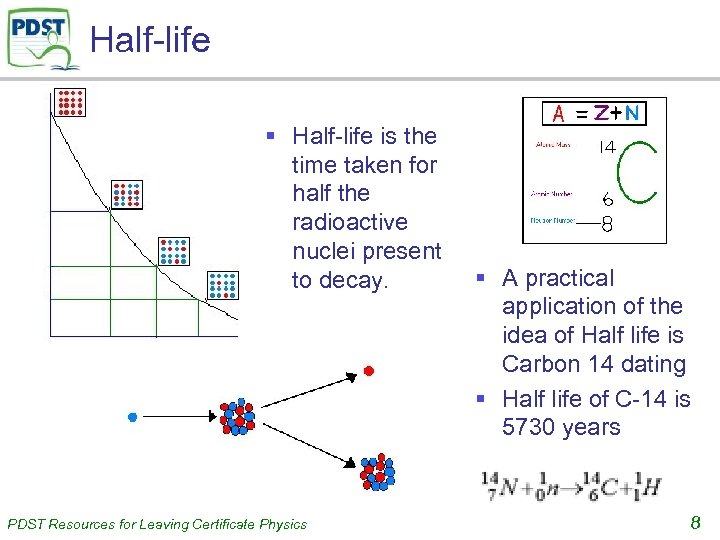 Half-life § Half-life is the time taken for half the radioactive nuclei present to decay. PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics § A practical application of the idea of Half life is Carbon 14 dating § Half life of C-14 is 5730 years 8
Half-life § Half-life is the time taken for half the radioactive nuclei present to decay. PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics § A practical application of the idea of Half life is Carbon 14 dating § Half life of C-14 is 5730 years 8
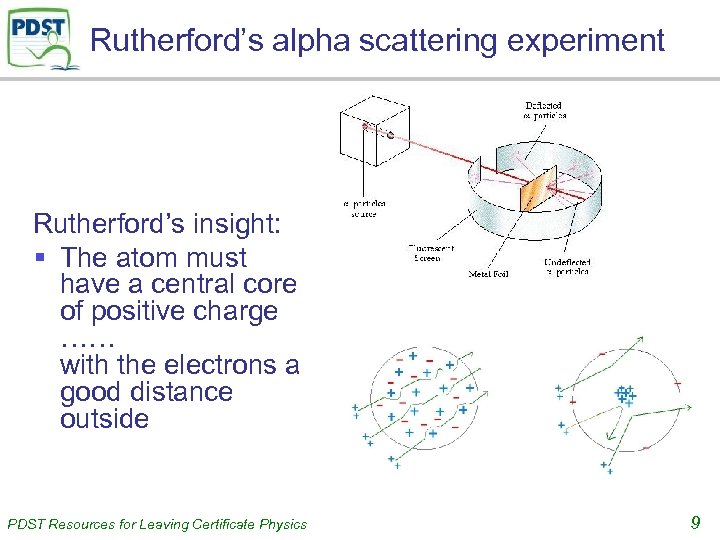 Rutherford’s alpha scattering experiment Rutherford’s insight: § The atom must have a central core of positive charge …… with the electrons a good distance outside PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 9
Rutherford’s alpha scattering experiment Rutherford’s insight: § The atom must have a central core of positive charge …… with the electrons a good distance outside PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 9
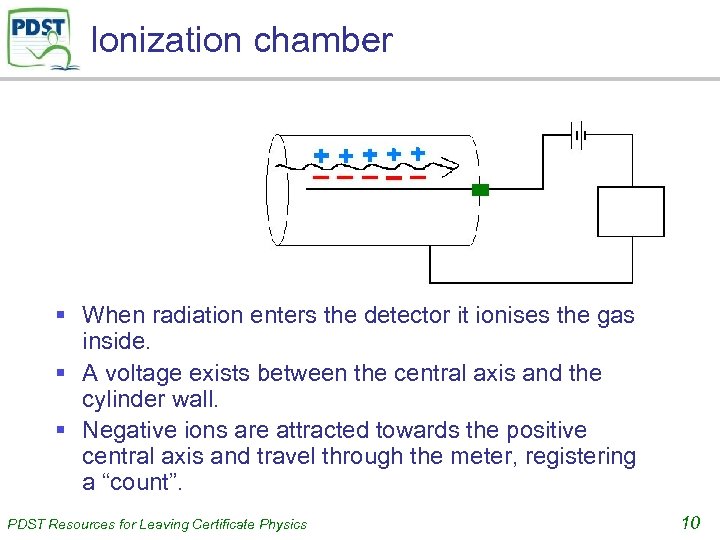 Ionization chamber § When radiation enters the detector it ionises the gas inside. § A voltage exists between the central axis and the cylinder wall. § Negative ions are attracted towards the positive central axis and travel through the meter, registering a “count”. PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 10
Ionization chamber § When radiation enters the detector it ionises the gas inside. § A voltage exists between the central axis and the cylinder wall. § Negative ions are attracted towards the positive central axis and travel through the meter, registering a “count”. PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 10
 Recap questions § Who discovered radioactivity? § How was it recognised that there were 3 types of radiation? § What did Rutherford conclude from the alpha scattering experiment? § What is the principle on which most radiation detectors work? § What does the symbol mean? PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 11
Recap questions § Who discovered radioactivity? § How was it recognised that there were 3 types of radiation? § What did Rutherford conclude from the alpha scattering experiment? § What is the principle on which most radiation detectors work? § What does the symbol mean? PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 11
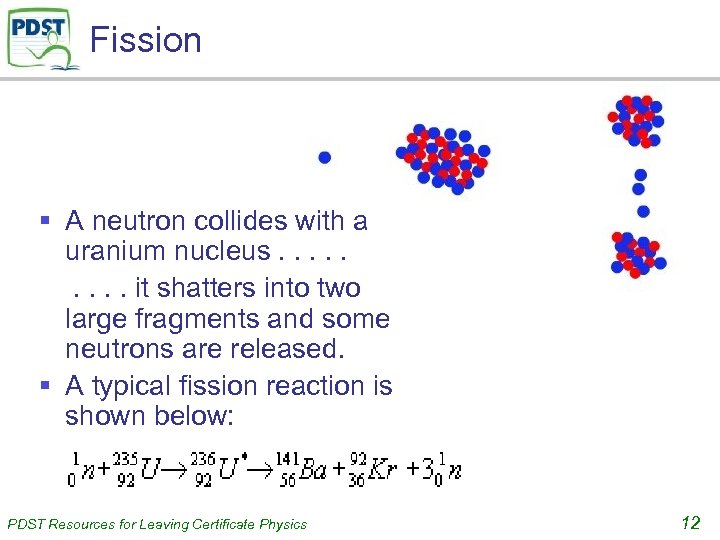 Fission § A neutron collides with a uranium nucleus. . it shatters into two large fragments and some neutrons are released. § A typical fission reaction is shown below: PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 12
Fission § A neutron collides with a uranium nucleus. . it shatters into two large fragments and some neutrons are released. § A typical fission reaction is shown below: PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 12
 Nuclear reactors § The fuel rods contain uranium, whose nuclei undergo fission, releasing energy. § The control rods absorb neutrons to reduce the rate of production of energy. § If water is used as the coolant, it can also serve as a moderator. § The moderator slows down the neutrons released by fission to the sort of speeds at which they are more likely to cause further fission. § The coolant removes energy to a heat exchanger, where steam is generated to turn turbines as in a conventional power station. PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 13
Nuclear reactors § The fuel rods contain uranium, whose nuclei undergo fission, releasing energy. § The control rods absorb neutrons to reduce the rate of production of energy. § If water is used as the coolant, it can also serve as a moderator. § The moderator slows down the neutrons released by fission to the sort of speeds at which they are more likely to cause further fission. § The coolant removes energy to a heat exchanger, where steam is generated to turn turbines as in a conventional power station. PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 13
 ADVANTAGES of FISSION § It releases a huge amount of energy per kilogram of fuel. It causes less pollution of the environment than fossil fuels PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 14
ADVANTAGES of FISSION § It releases a huge amount of energy per kilogram of fuel. It causes less pollution of the environment than fossil fuels PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 14
 DISADVANTAGES of FISSION § Reactors produce waste which emit dangerous radiation, that is difficult to dispose of, store, or recycle, safely. If nuclear radiation escaped it could cause serious illness or even death. § A reactor meltdown could occur. § In a meltdown, the fission chain reaction goes out of control, leading to an explosion, releasing great amounts of radiation. – Three Mile Island (USA) 1979. – Chernobyl (Russia) 1986. PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 15
DISADVANTAGES of FISSION § Reactors produce waste which emit dangerous radiation, that is difficult to dispose of, store, or recycle, safely. If nuclear radiation escaped it could cause serious illness or even death. § A reactor meltdown could occur. § In a meltdown, the fission chain reaction goes out of control, leading to an explosion, releasing great amounts of radiation. – Three Mile Island (USA) 1979. – Chernobyl (Russia) 1986. PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 15
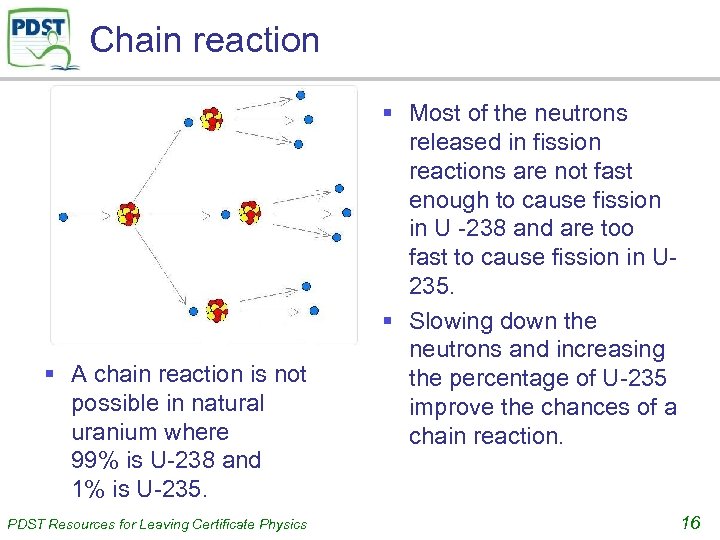 Chain reaction § A chain reaction is not possible in natural uranium where 99% is U-238 and 1% is U-235. PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics § Most of the neutrons released in fission reactions are not fast enough to cause fission in U -238 and are too fast to cause fission in U 235. § Slowing down the neutrons and increasing the percentage of U-235 improve the chances of a chain reaction. 16
Chain reaction § A chain reaction is not possible in natural uranium where 99% is U-238 and 1% is U-235. PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics § Most of the neutrons released in fission reactions are not fast enough to cause fission in U -238 and are too fast to cause fission in U 235. § Slowing down the neutrons and increasing the percentage of U-235 improve the chances of a chain reaction. 16
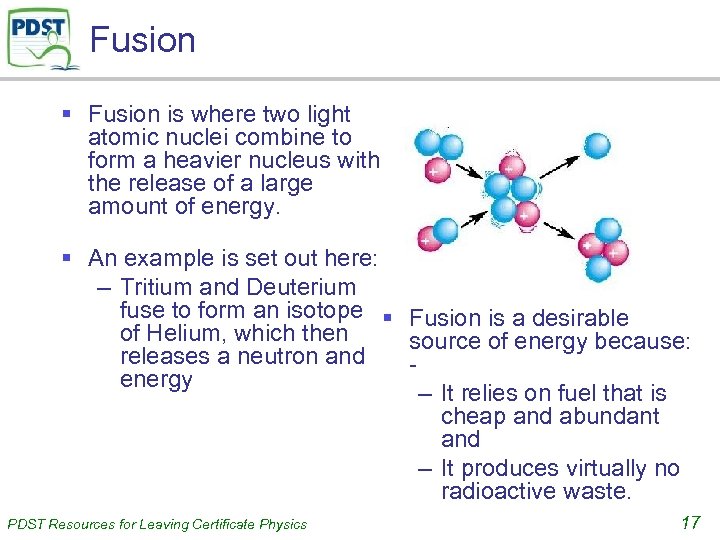 Fusion § Fusion is where two light atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus with the release of a large amount of energy. § An example is set out here: – Tritium and Deuterium fuse to form an isotope § Fusion is a desirable of Helium, which then source of energy because: releases a neutron and energy – It relies on fuel that is cheap and abundant and – It produces virtually no radioactive waste. PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 17
Fusion § Fusion is where two light atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus with the release of a large amount of energy. § An example is set out here: – Tritium and Deuterium fuse to form an isotope § Fusion is a desirable of Helium, which then source of energy because: releases a neutron and energy – It relies on fuel that is cheap and abundant and – It produces virtually no radioactive waste. PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 17
 Applications of Radioactive Isotopes § used in industry in quality control, for measuring thickness (by absorption). § used in the irradiation of food to kill parasites, bacteria. (The food itself does not become radioactive). § used to sterilize medical equipment. § used as tracers in medicine, to locate blockages in the circulatory system. § used as tracers in water and gas pipes, to locate leaks. § used in smoke alarms § Carbon-14 dating used by archaelogists PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 18
Applications of Radioactive Isotopes § used in industry in quality control, for measuring thickness (by absorption). § used in the irradiation of food to kill parasites, bacteria. (The food itself does not become radioactive). § used to sterilize medical equipment. § used as tracers in medicine, to locate blockages in the circulatory system. § used as tracers in water and gas pipes, to locate leaks. § used in smoke alarms § Carbon-14 dating used by archaelogists PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics 18
 Summary § Radioactivity is a natural phenomenon § Nuclear radiation is ionising § A Geiger counter is used to detect radiation § Fission is the splitting of a heavy nucleus yielding energy § Fusion is the combining of two light nuclei yielding energy § The core of a nuclear reactor contains fuel rods, control rods, moderator and coolant. PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics § A chain reaction is selfsustaining if sufficient neutrons from early fission events result in successful fission later. § There are many uses of radioactive isotopes in industry and medicine § Carbon-14 dating is a valuable technique for archaeologists and historians § Radon gas could be a hazard to health 19
Summary § Radioactivity is a natural phenomenon § Nuclear radiation is ionising § A Geiger counter is used to detect radiation § Fission is the splitting of a heavy nucleus yielding energy § Fusion is the combining of two light nuclei yielding energy § The core of a nuclear reactor contains fuel rods, control rods, moderator and coolant. PDST Resources for Leaving Certificate Physics § A chain reaction is selfsustaining if sufficient neutrons from early fission events result in successful fission later. § There are many uses of radioactive isotopes in industry and medicine § Carbon-14 dating is a valuable technique for archaeologists and historians § Radon gas could be a hazard to health 19


