af389df25ca011b11daea0d8b59a75e5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 91
 Nuclear Energy Chapter 15
Nuclear Energy Chapter 15
 15. 1 RADIOACTIVITY
15. 1 RADIOACTIVITY
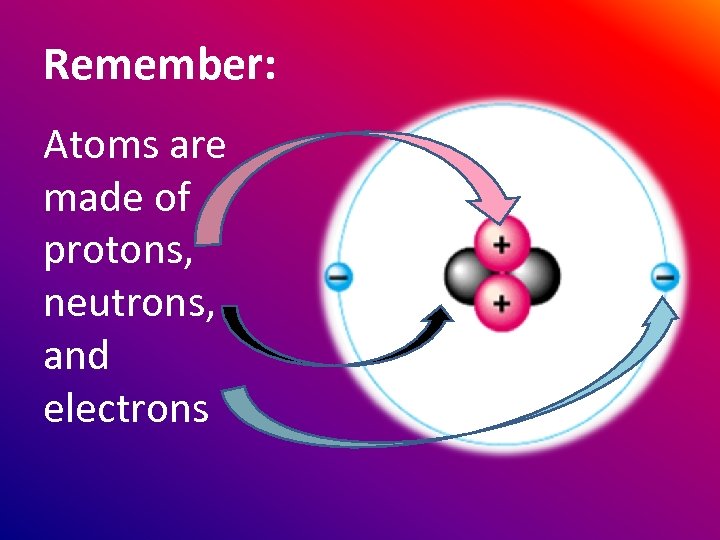 Remember: Atoms are made of protons, neutrons, and electrons
Remember: Atoms are made of protons, neutrons, and electrons
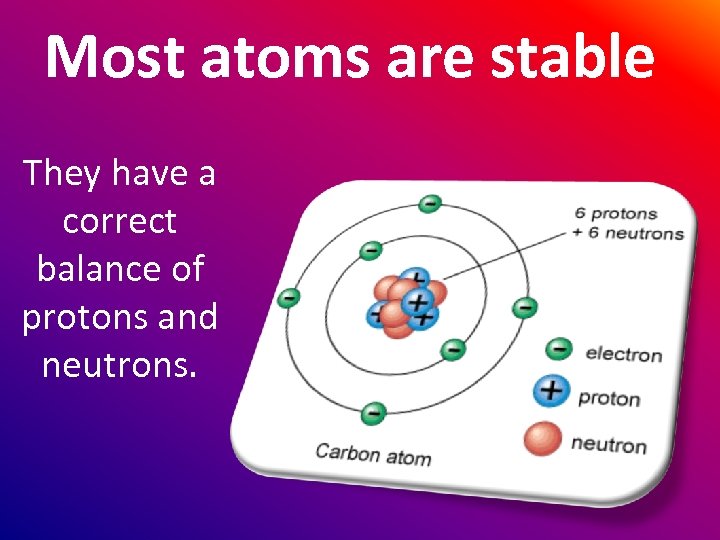 Most atoms are stable They have a correct balance of protons and neutrons.
Most atoms are stable They have a correct balance of protons and neutrons.
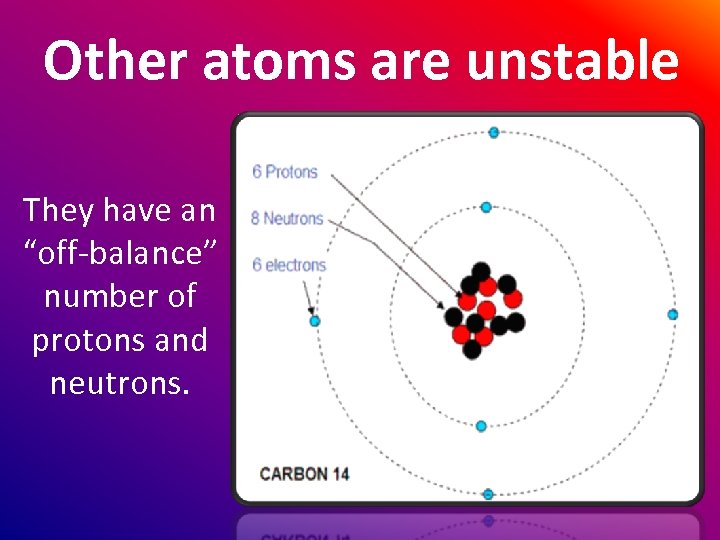 Other atoms are unstable They have an “off-balance” number of protons and neutrons.
Other atoms are unstable They have an “off-balance” number of protons and neutrons.
 Atoms whose nuclei are unstable are said to be radioactive
Atoms whose nuclei are unstable are said to be radioactive
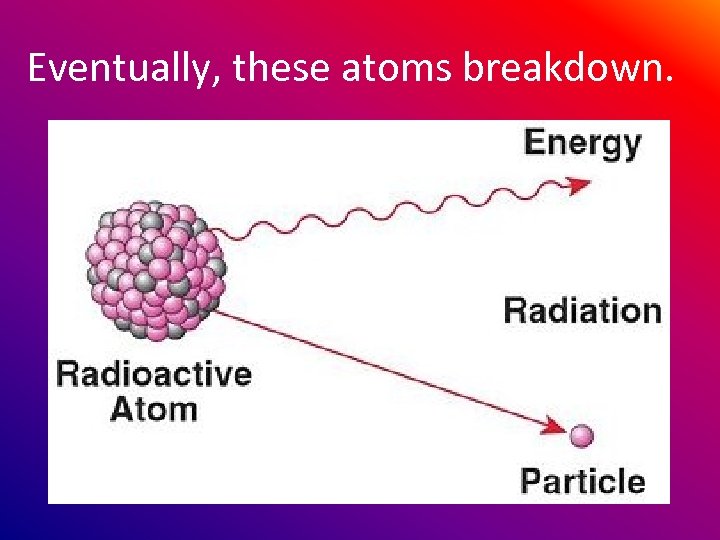 Eventually, these atoms breakdown.
Eventually, these atoms breakdown.
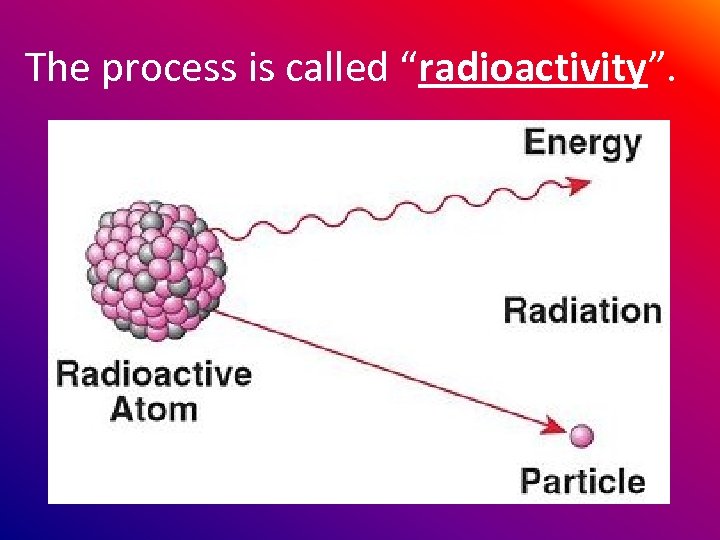 The process is called “radioactivity”.
The process is called “radioactivity”.
 Radioactivity is not new. Radioactivity is not caused by man.
Radioactivity is not new. Radioactivity is not caused by man.

 Radioactive decay in Earth’s interior heats the water for geysers
Radioactive decay in Earth’s interior heats the water for geysers
 Radioactive decay in Earth’s interior heats the water for hot springs
Radioactive decay in Earth’s interior heats the water for hot springs
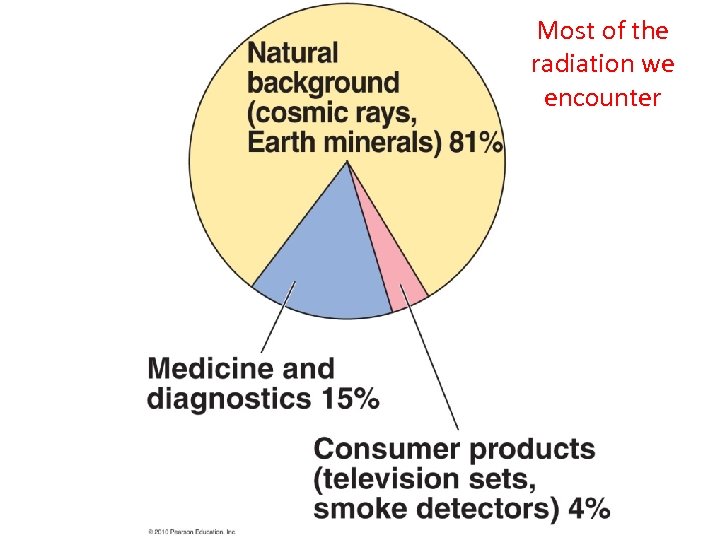 Most of the radiation we encounter
Most of the radiation we encounter
 Nuclear Technology - Pros • Medical X-rays & Anti Cancer Treatments
Nuclear Technology - Pros • Medical X-rays & Anti Cancer Treatments
 Nuclear Technology - Pros • Smoke detectors
Nuclear Technology - Pros • Smoke detectors
 Nuclear Technology - Pros • Nuclear Energy
Nuclear Technology - Pros • Nuclear Energy
 Nuclear Technology - Cons • Nuclear Disaster
Nuclear Technology - Cons • Nuclear Disaster
 Nuclear Technology - Cons • Nuclear Weapons
Nuclear Technology - Cons • Nuclear Weapons
 Nuclear Technology - Cons • Nuclear Weapons
Nuclear Technology - Cons • Nuclear Weapons
 Nuclear Technology Demands Responsibility • Safeguard nuclear material • Safe, clean disposal • Protect the environment for future generations
Nuclear Technology Demands Responsibility • Safeguard nuclear material • Safe, clean disposal • Protect the environment for future generations
 It’s up to you to make the decisions for the future!
It’s up to you to make the decisions for the future!
 Chapter 15. 2 Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Rays
Chapter 15. 2 Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Rays
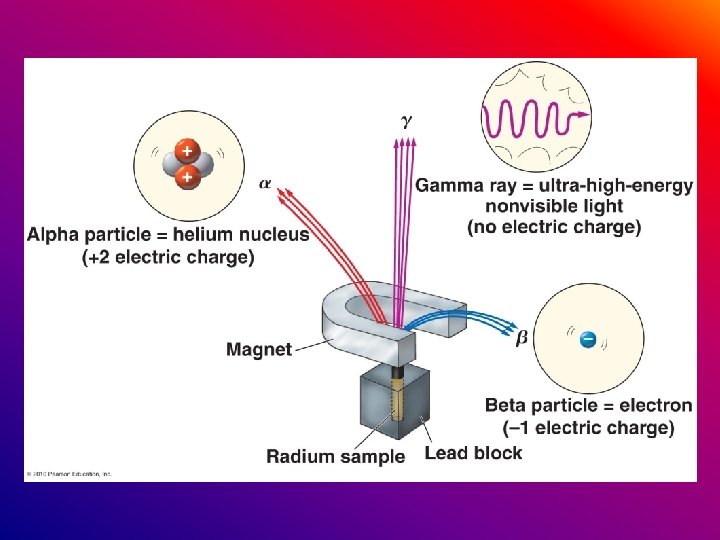
 Radioactive elements emit 3 different types of particles α alpha β beta γ gamma
Radioactive elements emit 3 different types of particles α alpha β beta γ gamma
 α particles are positively charged β particles are negatively charged γ particles are neutral
α particles are positively charged β particles are negatively charged γ particles are neutral
 • http: //www. youtube. co m/watch? v=o 9 yt 7 OAYm. E
• http: //www. youtube. co m/watch? v=o 9 yt 7 OAYm. E
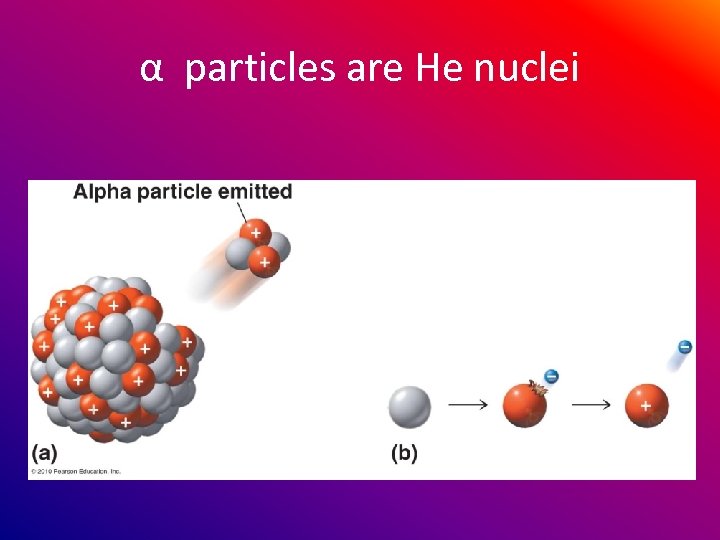 α particles are He nuclei
α particles are He nuclei
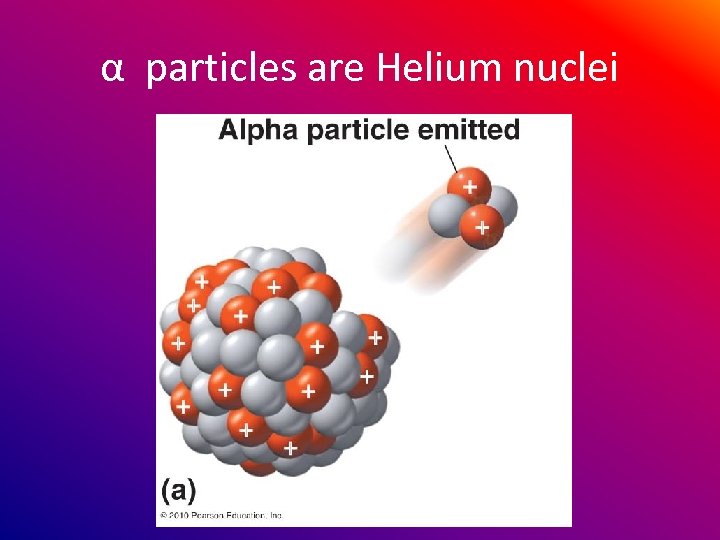 α particles are Helium nuclei
α particles are Helium nuclei
 α particles • Relatively low speed • Eventually become HE • Easy to shield against • Can’t go through paper or clothing
α particles • Relatively low speed • Eventually become HE • Easy to shield against • Can’t go through paper or clothing
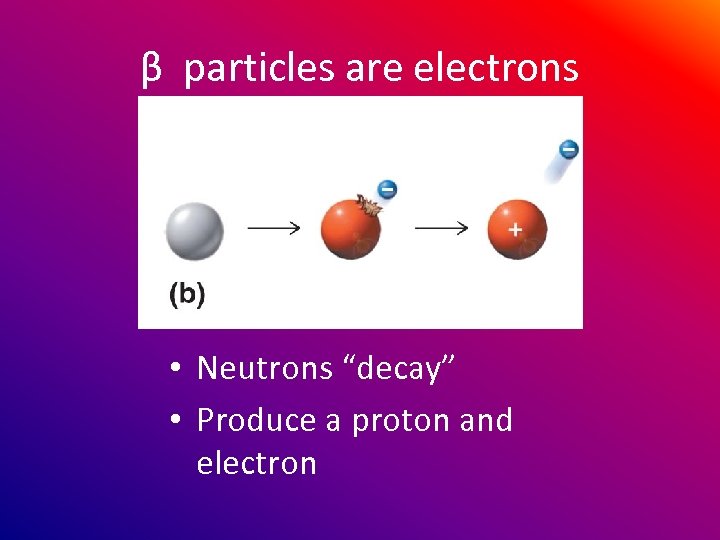 β particles are electrons • Neutrons “decay” • Produce a proton and electron
β particles are electrons • Neutrons “decay” • Produce a proton and electron
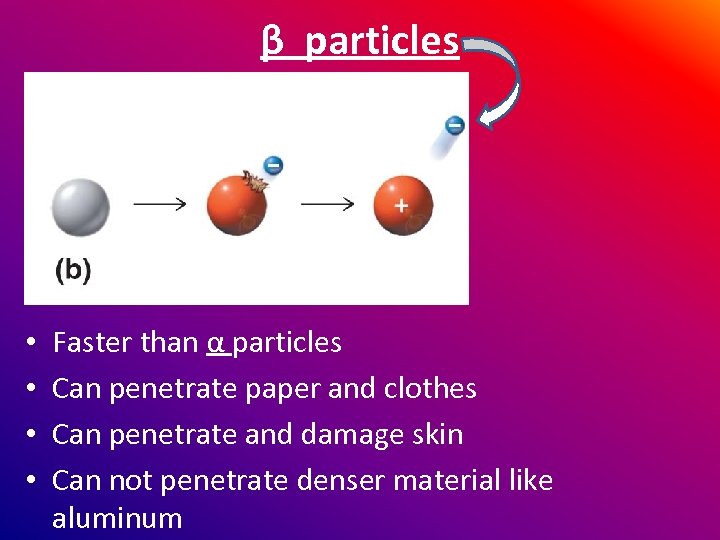 β particles • • Faster than α particles Can penetrate paper and clothes Can penetrate and damage skin Can not penetrate denser material like aluminum
β particles • • Faster than α particles Can penetrate paper and clothes Can penetrate and damage skin Can not penetrate denser material like aluminum
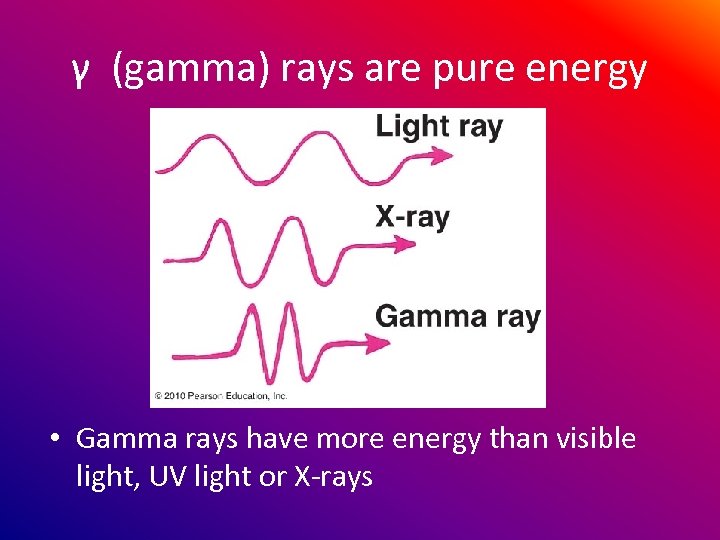 γ (gamma) rays are pure energy • Gamma rays have more energy than visible light, UV light or X-rays
γ (gamma) rays are pure energy • Gamma rays have more energy than visible light, UV light or X-rays
 γ (gamma) rays • Can easily penetrate and damage living tissue • Can penetrate most materials – except lead
γ (gamma) rays • Can easily penetrate and damage living tissue • Can penetrate most materials – except lead
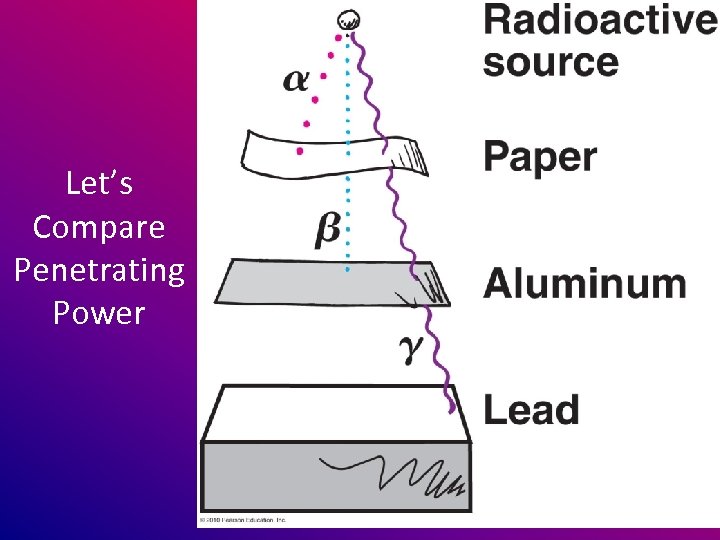 Let’s Compare Penetrating Power
Let’s Compare Penetrating Power
 γ (gamma) rays can help preserve food
γ (gamma) rays can help preserve food
 Question • Pretend you are given three radioactive rocks. • One is an alpha emitter, one is a beta emitter and one is a gamma emitter and you know which is which.
Question • Pretend you are given three radioactive rocks. • One is an alpha emitter, one is a beta emitter and one is a gamma emitter and you know which is which.
 Question • You can throw one away. • Of the other two, you must hold one in your hand place one in your shirt pocket.
Question • You can throw one away. • Of the other two, you must hold one in your hand place one in your shirt pocket.
 Question • What can you do to minimize your exposure?
Question • What can you do to minimize your exposure?
 Answer • Hold the alpha emitter in your hand. • The skin on your hand will shield you.
Answer • Hold the alpha emitter in your hand. • The skin on your hand will shield you.
 Answer • Put the beta emitter in your pocket. • The combined thickness of you skin and clothing should shield you from the beta emissions.
Answer • Put the beta emitter in your pocket. • The combined thickness of you skin and clothing should shield you from the beta emissions.
 Answer • THROW AWAY THE GAMMA EMITTER! • Because it would penetrate your body from any of these locations.
Answer • THROW AWAY THE GAMMA EMITTER! • Because it would penetrate your body from any of these locations.
 Answer • In a perfect world…… • Distance yourself from all the rocks!.
Answer • In a perfect world…… • Distance yourself from all the rocks!.
 Chapter 15. 3 Environmental Radiation
Chapter 15. 3 Environmental Radiation
 Most radiation we encounter originates in nature • Common rocks and minerals
Most radiation we encounter originates in nature • Common rocks and minerals
 Which family is exposed to more radiation? The one living in a Brick house? Or the one living in a wooden house?
Which family is exposed to more radiation? The one living in a Brick house? Or the one living in a wooden house?
 • More radiation exposure • Naturally Occurring
• More radiation exposure • Naturally Occurring
 • Radon A Common Source of Radiation
• Radon A Common Source of Radiation
 • Heavy, inert gas • Arises from uranium deposits
• Heavy, inert gas • Arises from uranium deposits
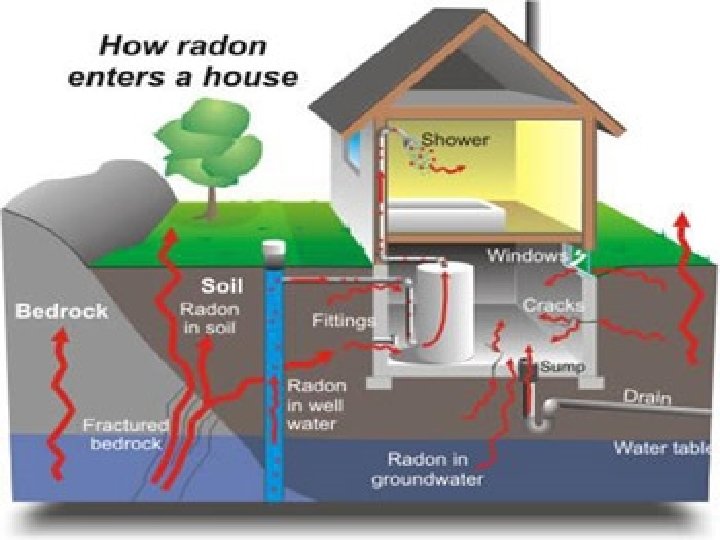
 Is Radon Dangerous? • According to the EPA, radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer. • It is the leading cause of lung cancer in non-smokers.
Is Radon Dangerous? • According to the EPA, radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer. • It is the leading cause of lung cancer in non-smokers.
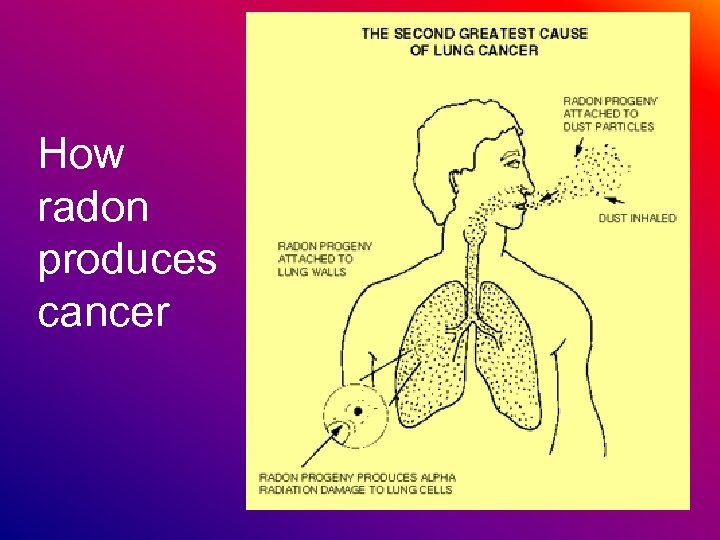 How radon produces cancer
How radon produces cancer
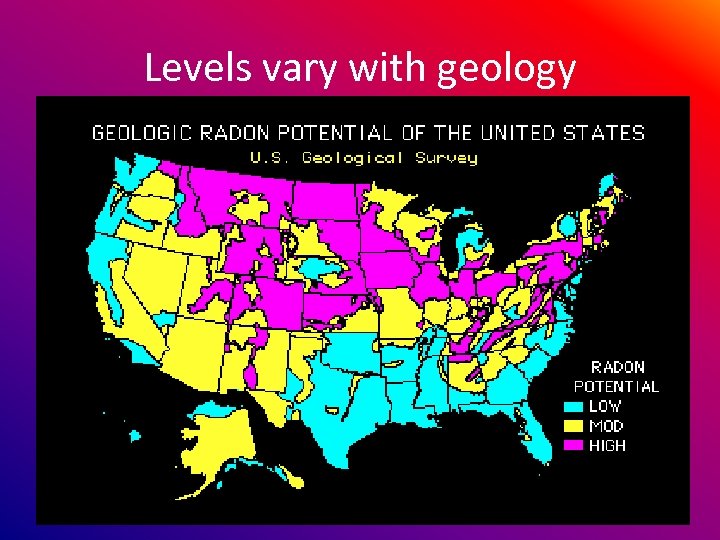 Levels vary with geology
Levels vary with geology
 You can check radon levels with a test kit
You can check radon levels with a test kit
 High levels require action
High levels require action
 Here’s another interesting question….
Here’s another interesting question….
 Which is a greater source of radiation? Coal Combustion Nuclear power
Which is a greater source of radiation? Coal Combustion Nuclear power
 The Coal Industry! • Global combustion of coal releases about 13, 000 tons of radioactive thorium and uranium into the atmosphere. • In addition to other polluting molecules released into the air.
The Coal Industry! • Global combustion of coal releases about 13, 000 tons of radioactive thorium and uranium into the atmosphere. • In addition to other polluting molecules released into the air.
 • Worldwide they generate about 10, 000 tons of radioactive waste each year Nuclear plants • Almost all the waste is contained and not released into the atmosphere.
• Worldwide they generate about 10, 000 tons of radioactive waste each year Nuclear plants • Almost all the waste is contained and not released into the atmosphere.
 RADIATION DAMAGE TO THE BODY
RADIATION DAMAGE TO THE BODY
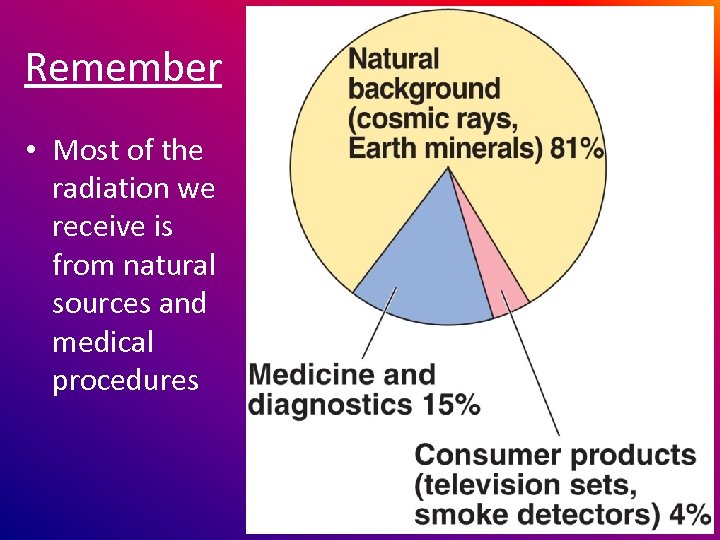 Remember • Most of the radiation we receive is from natural sources and medical procedures
Remember • Most of the radiation we receive is from natural sources and medical procedures
 The human body itself is a source of radiation!
The human body itself is a source of radiation!
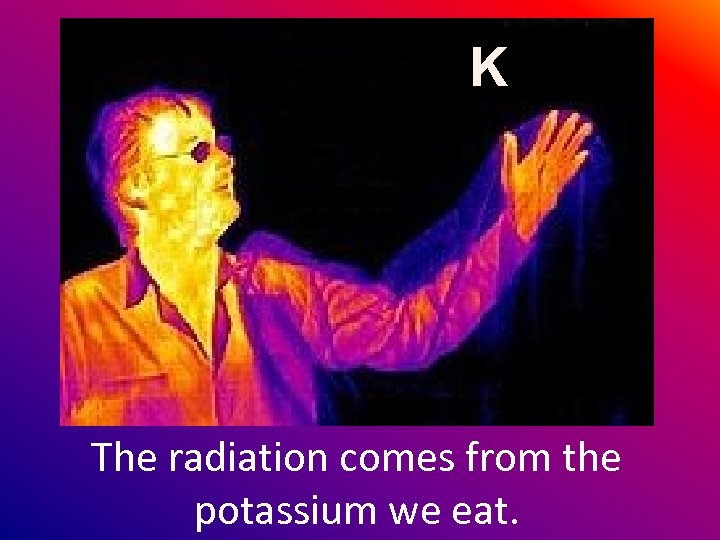 K The radiation comes from the potassium we eat.
K The radiation comes from the potassium we eat.
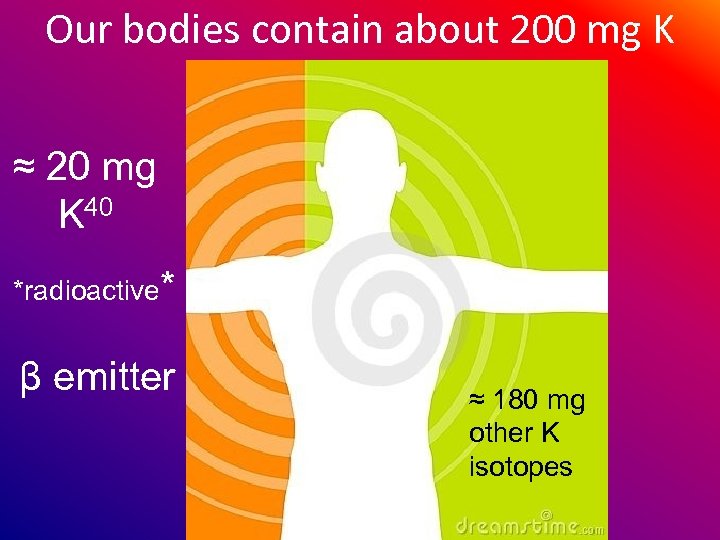 Our bodies contain about 200 mg K ≈ 20 mg K 40 *radioactive* β emitter ≈ 180 mg other K isotopes
Our bodies contain about 200 mg K ≈ 20 mg K 40 *radioactive* β emitter ≈ 180 mg other K isotopes
 Between every heartbeat… ≈ 5000 K 40 undergo spontaneous radioactive decay!
Between every heartbeat… ≈ 5000 K 40 undergo spontaneous radioactive decay!
 Radiation is everywhere!
Radiation is everywhere!
 Radiation cause damage to cells
Radiation cause damage to cells
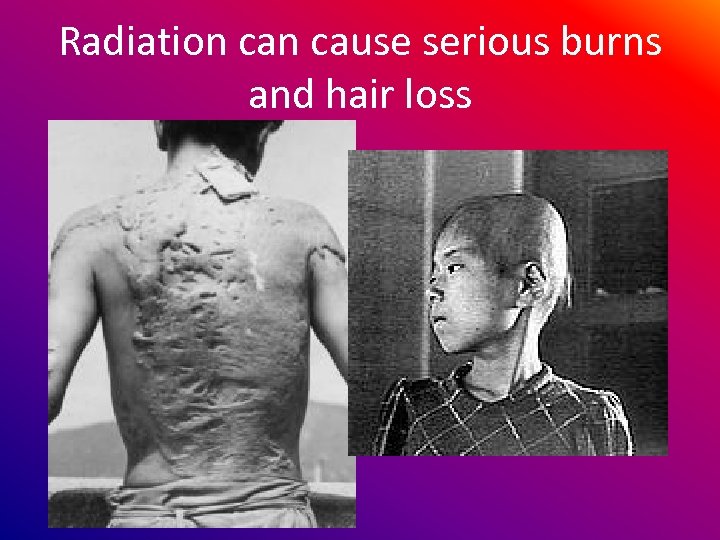 Radiation cause serious burns and hair loss
Radiation cause serious burns and hair loss
 Cells can repair radiation damage if it is not too severe
Cells can repair radiation damage if it is not too severe
 Radiation can damage DNA
Radiation can damage DNA
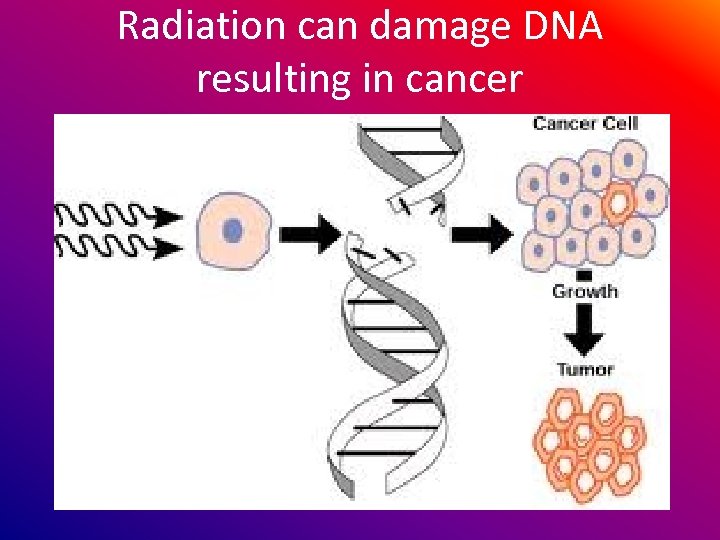 Radiation can damage DNA resulting in cancer
Radiation can damage DNA resulting in cancer
 High doses of radiation can damage DNA resulting hereditary birth defects
High doses of radiation can damage DNA resulting hereditary birth defects
 • Avoid radiation when possible • All radiation can not be avoided • Most is simply part of nature Common sense
• Avoid radiation when possible • All radiation can not be avoided • Most is simply part of nature Common sense
 Chapter 15. 5 HALF- LIFE
Chapter 15. 5 HALF- LIFE
 Radioactive isotopes decay at different rates • Measured in terms of a characteristic time • “Half-life”
Radioactive isotopes decay at different rates • Measured in terms of a characteristic time • “Half-life”
 Half-life The time needed for half the radioactive atoms of a radioactive material to decay
Half-life The time needed for half the radioactive atoms of a radioactive material to decay
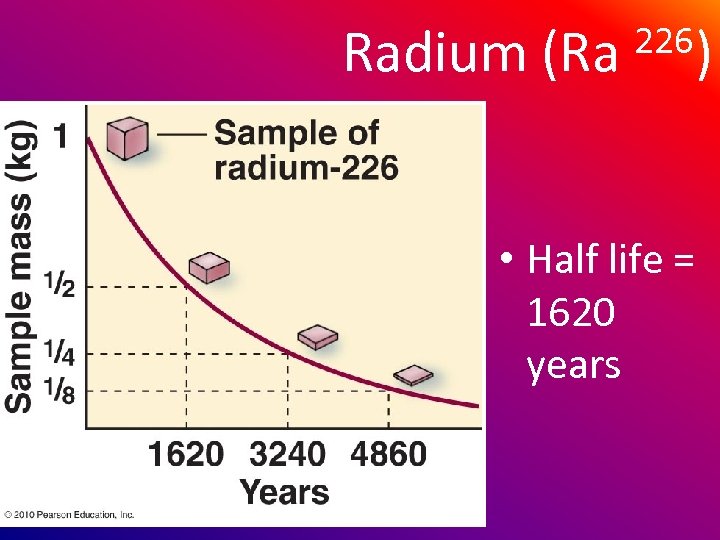 Radium (Ra 226) • Half life = 1620 years
Radium (Ra 226) • Half life = 1620 years
 Half lives are constant • Not affected by external conditions • Some are less than 1/1, 000 sec • Some are much longer
Half lives are constant • Not affected by external conditions • Some are less than 1/1, 000 sec • Some are much longer

 Uranium - 238 • Half life = 4. 5 billion years • In 4. 5 billion years, half the uranium on earth will be lead!
Uranium - 238 • Half life = 4. 5 billion years • In 4. 5 billion years, half the uranium on earth will be lead!
 ISOTOPIC DATING
ISOTOPIC DATING
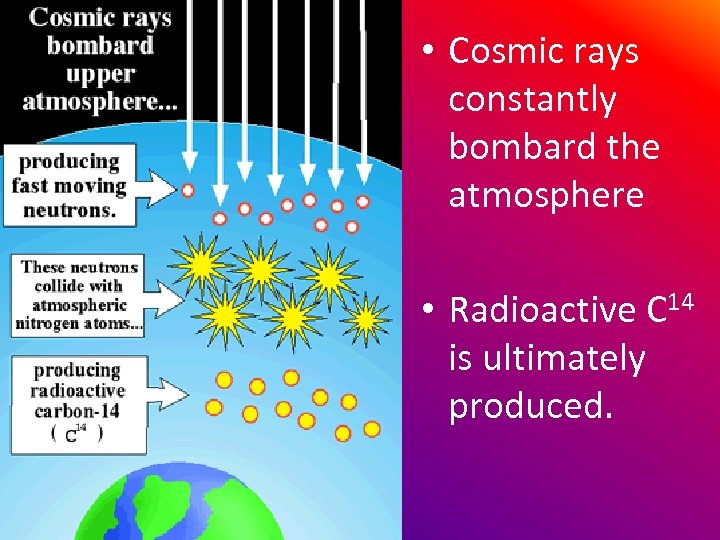 • Cosmic rays constantly bombard the atmosphere • Radioactive C 14 is ultimately produced.
• Cosmic rays constantly bombard the atmosphere • Radioactive C 14 is ultimately produced.
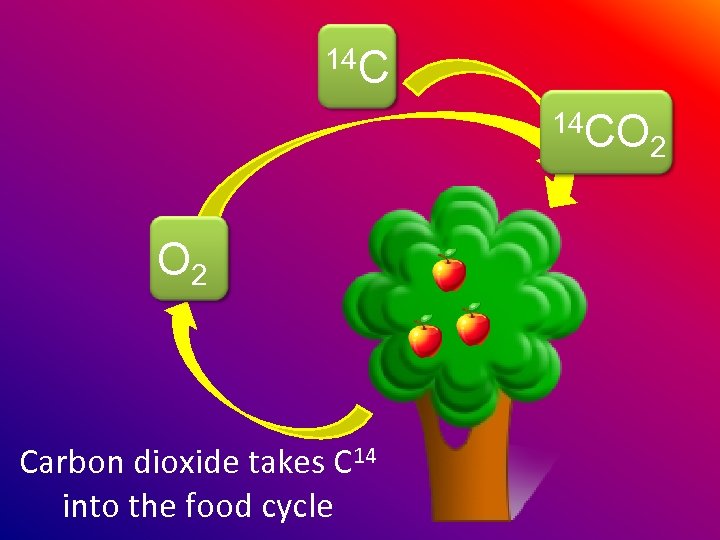 14 C 14 CO O 2 Carbon dioxide takes C 14 into the food cycle 2
14 C 14 CO O 2 Carbon dioxide takes C 14 into the food cycle 2
 Animals eat the plants so all animals have some C 14 in them
Animals eat the plants so all animals have some C 14 in them
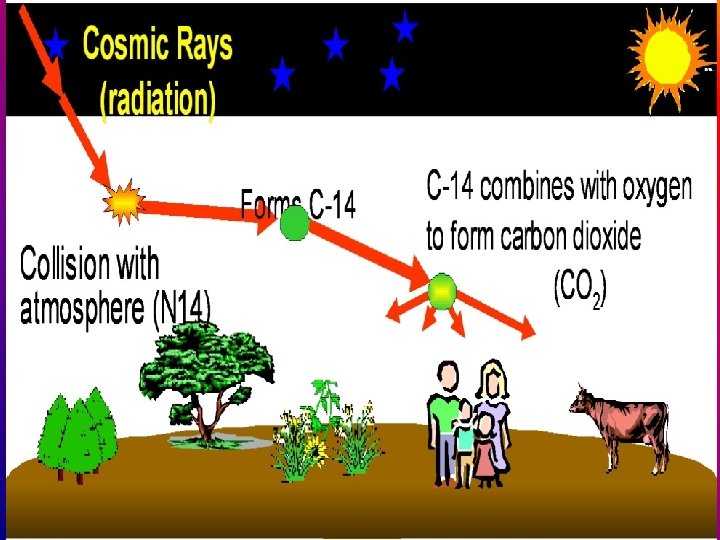
 …. . so all living things on Earth contain some C 14
…. . so all living things on Earth contain some C 14
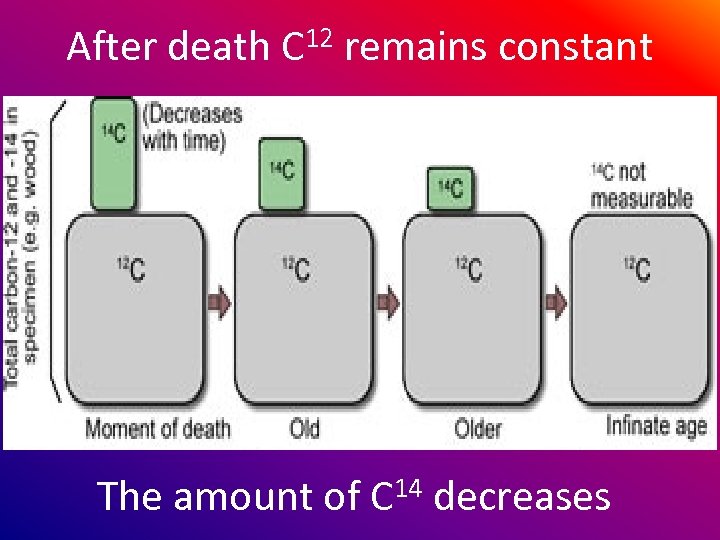 After death C 12 remains constant The amount of C 14 decreases
After death C 12 remains constant The amount of C 14 decreases
 Scientists can use this information to determine the age of carbon containing artifacts • Carbon-14 Dating
Scientists can use this information to determine the age of carbon containing artifacts • Carbon-14 Dating
 C-14 dating can only be used on something that was previously alive
C-14 dating can only be used on something that was previously alive
 Scientists use the elements lead (Pb) and Uranium (U) to date rocks samples.
Scientists use the elements lead (Pb) and Uranium (U) to date rocks samples.

 Meteor crater, Arizona Meteor Crater Video -- Killer Asteroid -National Geographic
Meteor crater, Arizona Meteor Crater Video -- Killer Asteroid -National Geographic


