f3f6e5e247ac443af6b8098b0f11331c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY By Mr M

Radiation n All elements after bismuth are radioactive • Some others are, but only in certain forms like carbon 14 • Being radioactive means that the element is naturally unstable and wants to fall apart into smaller elements and radiation n There are three main types of nuclear radiation…

Alpha Radiation n n α or Helium nuclei Can be stopped by a piece of paper or a layer of skin Not very dangerous for external contact, must be consumed to do harm

Beta n n β or Electron Can be stopped by a piece of metal or wood beam Can cause damage from external exposure

Gamma n n γ or Piece of the electromagnetic spectrum Takes a few feet of concrete to stop it Will rip through the human body

Fission/Fusion n Fission = the splitting of an atom • Ex. Uranium splits into barium and krypton n Fusion = the combining of atoms • ex. Hydrogen fuse into helium
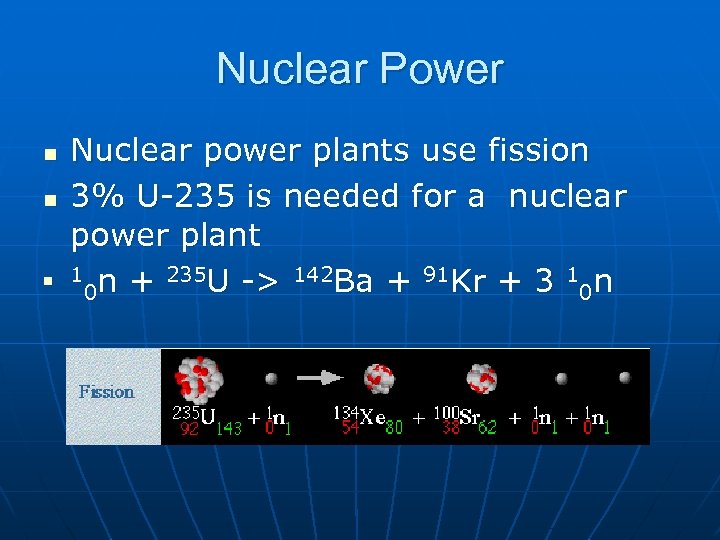
Nuclear Power n n n Nuclear power plants use fission 3% U-235 is needed for a nuclear power plant 1 n + 235 U -> 142 Ba + 91 Kr + 3 1 n 0 0

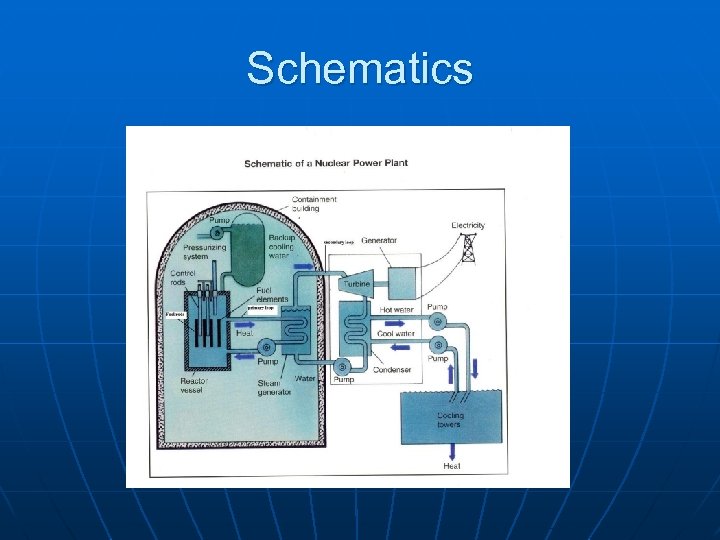
Schematics

n n Control rods absorb neutrons The heat of the reactions turns water to steam • The steam turns a turbine which makes the power that goes to your house
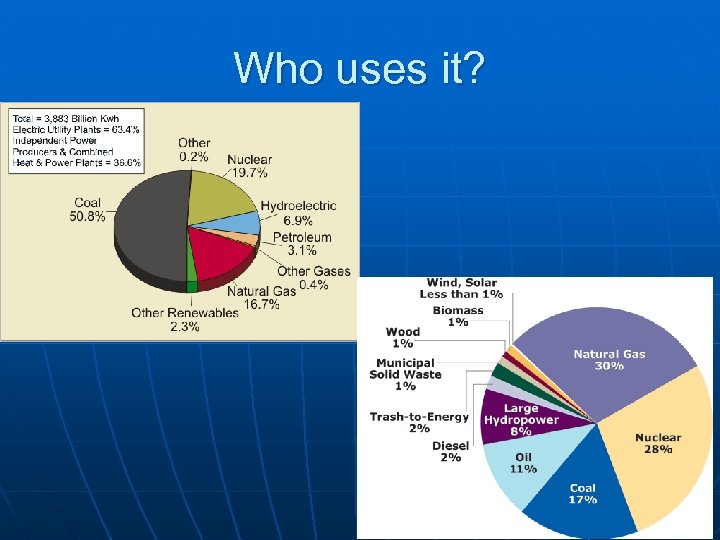
Who uses it?

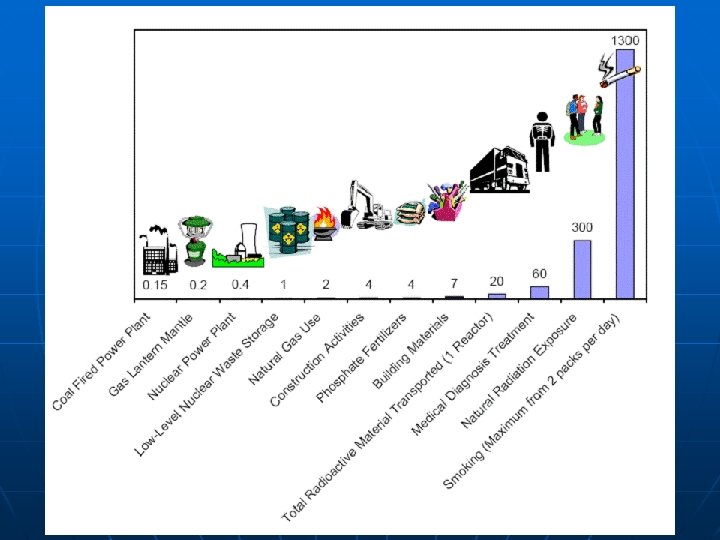
Is it safe? n Used fuel rods must be stored after use • Pu-239 is a radioactive waste product • It has a half life of 24, 000 years n n n Shielding = radiation absorbing material Moderator = slow down fast neutrons Nuclear waste is stored deep under ground

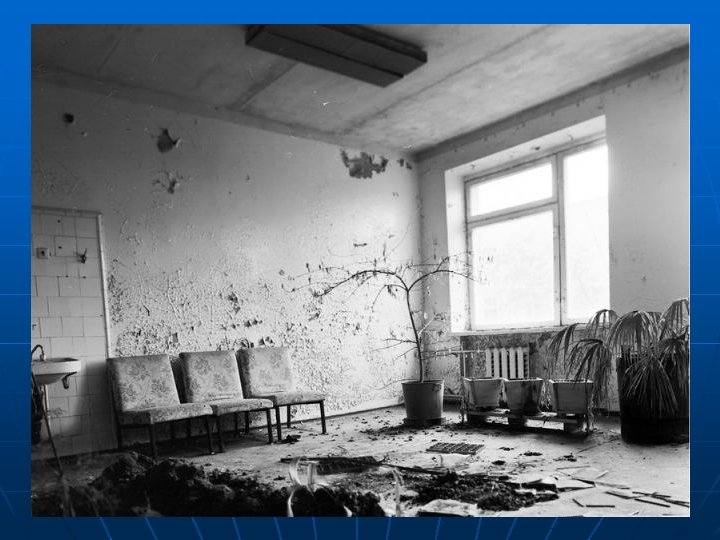
What if something does go wrong? n Chernobyl • 1985, Chernobyl Ukraine • Engineers lost control of the plant during a routine test by overriding the plant’s safety mechanisms and withdrew most of the control rods from the reactor core • The reactor overheated and broke out into a fire, this resulted in an explosion…

Chernobyl


Thyroid Cancer n n n The explosion released radioactive iodine KI pills are given out to dilute the amount of radioactive iodine in the body The beta radiation from the radioactive I initiates thyroid cancer

Three Mile Island n n n 1979, Harrisburg Pennsylvania Failures in the water based cooling system The core heated to over 2200°C • Half of it melted • The plant was thirty minutes from complete meltdown

Waste n n n The waste from a nuclear power plant is still radioactive and will be for hundreds of years. It can be reused in the newest power plants It can be stored in salt mines

Fusion Plants n n 2 H + 23 He -> 4 He +2 protons Produces almost a million times as much energy as regular exothermic chemical reactions Requires higher temperatures and confinement Best source of 3 He is the moon

Harnessing Nuclear Energy: The Bomb n n n Atomic bombs use 97% U-235 This high of a concentration can be detected by flying over a weapon plant Missiles are stored underground or under water


Critical Mass n The minimum amount of nuclide that provides the number of neutrons needed to sustain a chain reaction • 52 kg for U-235
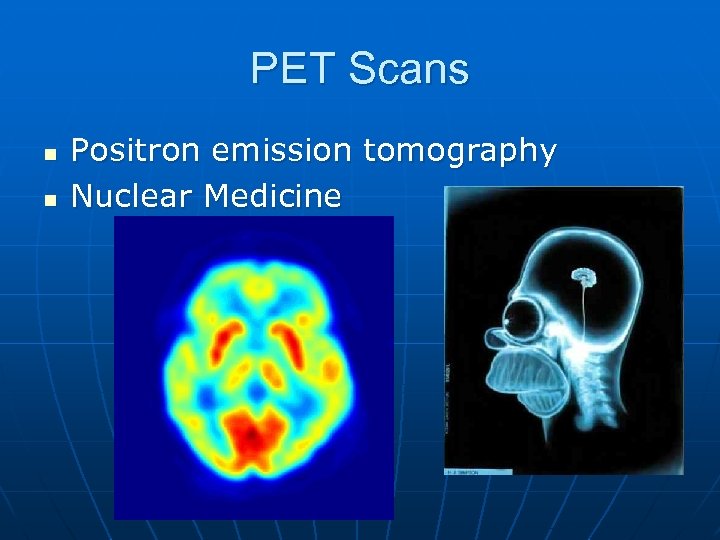
PET Scans n n Positron emission tomography Nuclear Medicine

Medical Scans n n MRI = magnetic Resonance Imaging CAT Scan = Computer Aided Tomography

Radon n Radon is an elemental gas It is in the air we breath, but does not react or dissolve well so posses little threat Radon loses alpha particles which do not go much more than 10 cm

Daughter Elements n n Radon decomposes in lead, polonium, and bismuth They attach to dust particles and can cause radiation damage to bronchial cells • This leads to lung cancer • It is the second leading cause of lung cancer

Other Applications n n n Sterilizing medical equipment Dating fossils Teflon pots and pans Smoke detectors Exit signs Radium paint for watches
f3f6e5e247ac443af6b8098b0f11331c.ppt