2fba9c6f5c7d5d9a1a98c4e04716f7b9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

NT 1110 Unit 9

Unit 9 Objectives § § § Security Fundamentals – Understand the mindset you should have when securing a computer. – Understand file systems, authentication, and how to protect against malware. Securing Wireless Networks – Explain wireless encryption, and maximizing security on wireless devices. Data and Physical Security – Describe encryption types, the Local Security Policy, backups, password management Access Control Purposes and Principles – Explain User Access Control (UAC), NTFS permissions, and auditing. Installing, Configuring, and Troubleshooting Security Features • Demonstrate how to secure the BIOS, configure a firewall, and set up a secure wireless connection.

Establishing a Security Plan Probability Low Impact Low Medium High
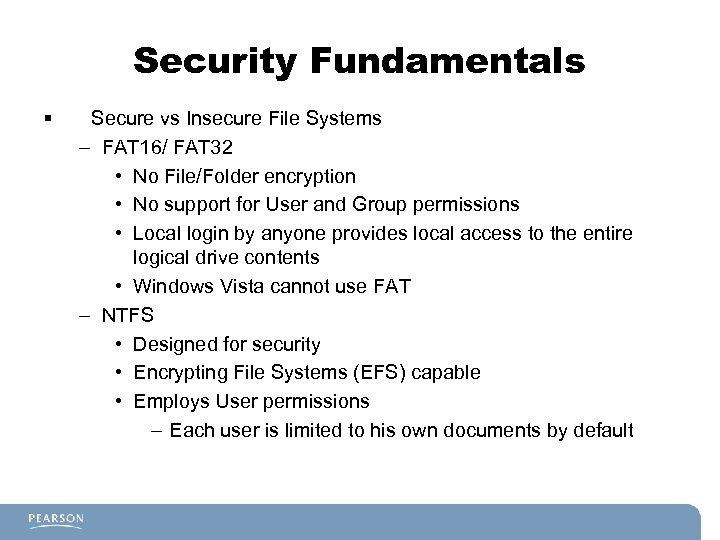
Security Fundamentals § Secure vs Insecure File Systems – FAT 16/ FAT 32 • No File/Folder encryption • No support for User and Group permissions • Local login by anyone provides local access to the entire logical drive contents • Windows Vista cannot use FAT – NTFS • Designed for security • Encrypting File Systems (EFS) capable • Employs User permissions – Each user is limited to his own documents by default

Authentication Technologies § Authentication demands that a user verify his right to access data § Relies on: – Something the user knows • For example a password or Personal Identification Number (PIN) – Something the user has • For example a smart card or other security token – Something the user is • For example the biometric reading of a fingerprint or retina scan – Something the user does • For example, a signature

Username/Password/PIN Authentication § Can be verified locally by the local system – – § PC username/password Access codes on a door lock Can be verified remotely by a server – § Login can be matched to local PC or to a whole domain of PCs Passwords should be complex – – – 6 -8 characters minimum Mix of uppercase/lowercase, numbers & symbols Passphrase • First letters of words in phrase become password characters – Mitigates brute force dictionary attacks by hackers

What a user has or is Things a user might have: § A key § Smart. Card Things a user might be: § Fingerprint – Very effective when combined with username/password – Can be fooled with tape or bubblegum § Retinal Scan Database of fingerprints and retinal scans must be securely maintained to prevent unauthorized access and replication.
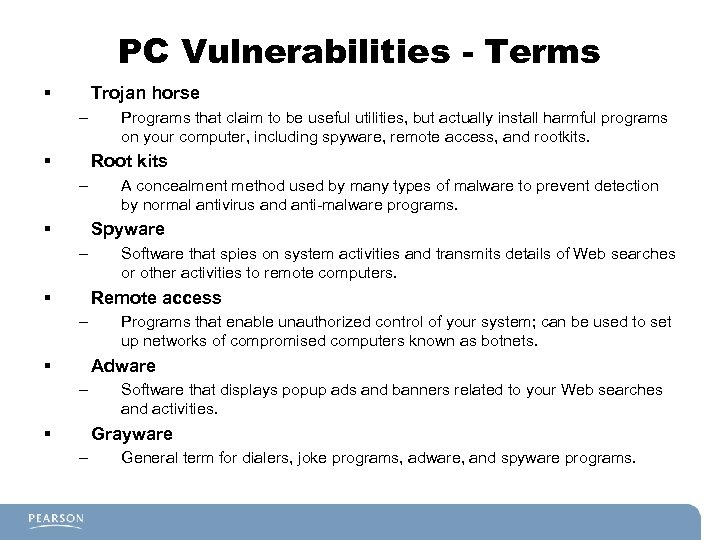
PC Vulnerabilities - Terms § Trojan horse – § Programs that claim to be useful utilities, but actually install harmful programs on your computer, including spyware, remote access, and rootkits. Root kits – § A concealment method used by many types of malware to prevent detection by normal antivirus and anti-malware programs. Spyware – § Software that spies on system activities and transmits details of Web searches or other activities to remote computers. Remote access – § Programs that enable unauthorized control of your system; can be used to set up networks of compromised computers known as botnets. Adware – § Software that displays popup ads and banners related to your Web searches and activities. Grayware – General term for dialers, joke programs, adware, and spyware programs.

Protection Against Viruses and Malware Computer protection needs specialized software to perform: § Real-time protection to block infection § Automatic periodic scans for known/suspected threats § Automatic updating on a frequent (usually daily) basis § Renewable subscriptions to obtain updated threat signatures § Links to virus and threat encyclopedias § Inoculation of system files § Permissions-based access to the Internet § Scanning of downloaded files and sent/received emails

Software Firewalls § § Program designed to examines data packets – Criteria in headers are monitored • Destination source IP addresses • Application ports and data • Protocols – Can filter packets coming in or going out • Windows XP & Vista use a one way firewall – Allows ping out, but not in – Vista can be modified for two way use Hardware firewalls are dedicated devices with specially designed operating systems

Troubleshooting Software Firewalls § § Your firewall is configured to block all connections – Clear ‘no exceptions’ checkbox Your firewall does not have an exception set up for the program – Click ‘unblock’ to permit access You might have two firewalls (Windows Firewall and a third-party firewall) You did not open the correct TCP or UDP ports for a program

Hardware Recycling and Deconstruction § What do you do with an old PC that is no longer needed? – Hard disks should be destroyed • Many data recovery programs can read deleted files – Exception is when the disk is intended for a second life as a donated computer • Remove data with DOD 5220. 22 -M compliant program – CDs, DVDs, Floppy disks should be physically destroyed

Securing Wireless Networks § § Air is insecure, data in transit must be encrypted. Both the access point and the end host must use the same encryption. – Common encryption types • WEP – Not considered very secure • WPA – Secure but should still be protected further by using strong passwords – TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) • WPA 2 – AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) – Preferred when available – Availability is determined by all hosts being able to support a common standard
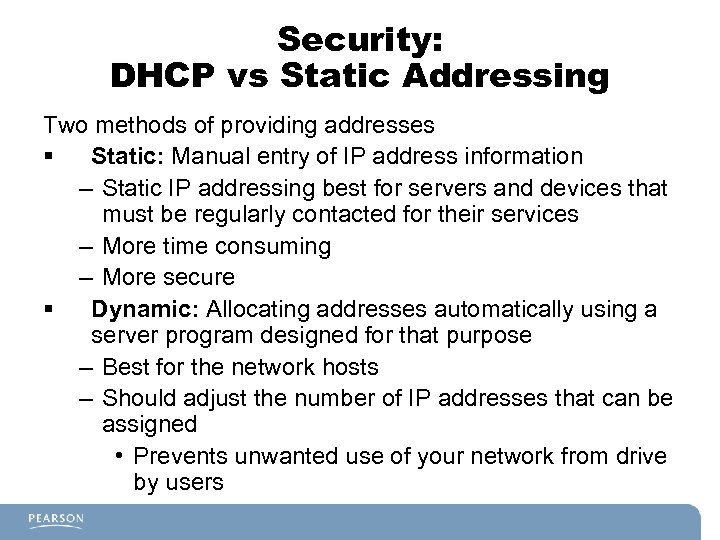
Security: DHCP vs Static Addressing Two methods of providing addresses § Static: Manual entry of IP address information – Static IP addressing best for servers and devices that must be regularly contacted for their services – More time consuming – More secure § Dynamic: Allocating addresses automatically using a server program designed for that purpose – Best for the network hosts – Should adjust the number of IP addresses that can be assigned • Prevents unwanted use of your network from drive by users

SSID – Security Set Identifier § § § Default is easily seen by unwanted intruders – Often means there is no administrative password in place • Most Wireless Access Points (WAP) use a generic password • Must be changed to ensure protection of the WAP – Can be confusing if more than one WAP of the same manufacturer/model is in the same locality Change name – Do not use: Family name, company name, location Disable the SSID Broadcast – This prevents the access point from announcing its presence – Caution: XP will go looking for previously known networks by seeking for them using the SSID…hackers can use this

Additional WAP Firewall Features § § § MAC Address is ‘burned into Network Card” – Can be allowed or denied access to Wireless Access Point (WAP) • Blocks casual Internet surfers from using your network • Serious hackers can get around this Network Address Translation – Hides the internal network numbers from external users Access Logs – A list of traffic denied or permitted Traffic Filtering – IP addresses, websites, or ports can be specifically filtered Support for Virtual Private Networking (VPN)

Troubleshooting Wireless Clients § § Selected the wrong SSID – Often happens when default SSID is used Selected the wrong encryption type – WAP and client must use the same Specified the wrong channel – In ad-hoc (direct) connection, both must use same channel – WAP and clients automatically ‘discover’ the right channel Incorrect adapter for the network. – Use of 802. 11 a for 802. 11 b/g network

Data and Physical Security § Data Access Local Security Policy – In Control Panel Administrative Tools Local Security Policy § Policies that can be enabled/configured: – Enable Auditing – Shutdown: Clear Virtual Memory Pagefile – Take ownership of files/objects in system – Enable/Disable “Ctrl+Alt+Del” for login purposes
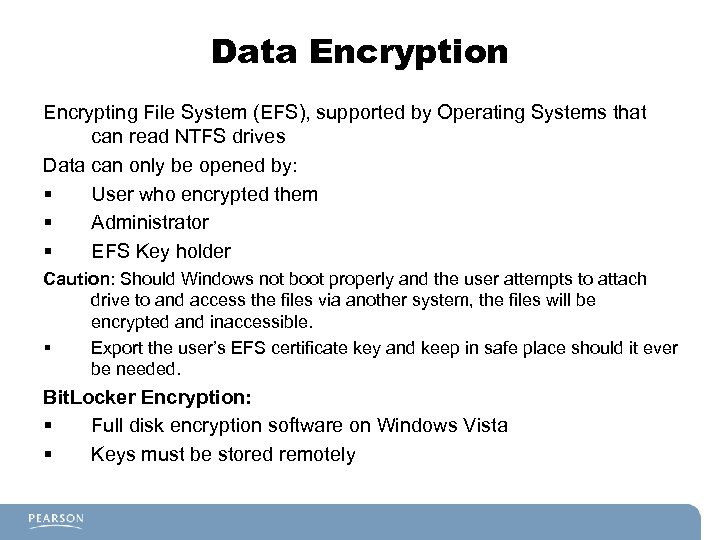
Data Encryption Encrypting File System (EFS), supported by Operating Systems that can read NTFS drives Data can only be opened by: § User who encrypted them § Administrator § EFS Key holder Caution: Should Windows not boot properly and the user attempts to attach drive to and access the files via another system, the files will be encrypted and inaccessible. § Export the user’s EFS certificate key and keep in safe place should it ever be needed. Bit. Locker Encryption: § Full disk encryption software on Windows Vista § Keys must be stored remotely
Data Backups § § Backups necessary because: – Mechanical devices eventually fail Backup can be subject to hacking/tampering – Backup data drive/media should be password protected Data Migration: § Direct connection is best § Network connections offer opportunity for data retrieval by unauthorized parties – ‘Files and Settings Transfer Wizard’ offers password protected transfer of files across network connection

Other Vulnerabilities § Social Engineering Techniques – Pretexting: Pretending to be authorized to perform security functions – Phishing: Setting up websites to obtain secure information through fraudulent means • Fake bank account solicitation – Trojan Horse • Baiting the user with a ‘free’ program • Obtains user information through monitoring of keystrokes – Baiting • Leaving USB memory behind in hopes that someone will insert it to see what is on it. It then executes a program to install Malware (Malicious software)

Access Control Purposes and Principles § Control access to the following user accounts: – User – only has control over created folders/files – Administrator – has full control – Guest – disabled by default § User Access Control (UAC) – Automatically makes all accounts standard users – Prompts administrator when system changes are being made – Reduces risk of malware using the administrator account – Can be turned off if necessary: • Control Panel User Accounts Family Safety User Accounts. – System must be restarted

Groups and Permissions § ‘Groups’ allows control of resources through grouping users together who need the same access levels to files and objects on the system – Installed groups include: Administrators, Users, Power Users, Guest – Permissions that can be assigned to Groups/Users • Full Control • Modify: Change file or folder contents • Read & Execute • List Folder Contents • Read • Write: Add a new file or folder – Each permission can either be allowed or denied

Permissions: Important Details § § Permission Inheritance – Creating Folders • Default is to inherit the permissions granted to parent folder • Can extend to subfolders of the newly created folder – Call Permissions Propagation • Default permission can be altered in folder properties Moving and Copying Folders and files – Copy causes a folder to inherit permissions of new parent – Moving causes the folder to retain original permissions if on the same volume

Reflection A well-trusted and loyal employee asked to be able to use a color printer instead of the black and white laser printer for some documents he is preparing for an A+ presentation this afternoon. His permission set only allows him to print to the black and white laser printer. What do you do?

What have you learned? – – – What is Malware? Why is WEP considered insecure? Name three things must be known/configured for the WAP and client to connect securely? What is the encryption available to NTFS file systems? How is a passphrase superior to most passwords?

Unit 9 Summary § § § Security Fundamentals – Understand file systems, authentication, and how to protect against malware. Securing Wireless Networks – Explain wireless encryption, and maximizing security on wireless devices. Data and Physical Security – Describe encryption types, the Local Security Policy, backups, password management Access Control Purposes and Principles – Explain User Access Control (UAC), NTFS permissions, and auditing. Installing, Configuring, and Troubleshooting Security Features – Demonstrate how to secure the BIOS, configure a firewall, and set up a secure wireless connection.
2fba9c6f5c7d5d9a1a98c4e04716f7b9.ppt