bb3a4c74ea05ab021355c7268d30154a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 NSI: A Client-Server-Model for PKI Services Wolfgang Schneider
NSI: A Client-Server-Model for PKI Services Wolfgang Schneider
 Public Key Infrastructures • • PKIs setup by companies and organizations Allow certificates to be issued and retrieved May be interconnected through cross-certificates Allows for inter-organizational communication – Authenticated, integrity protected, encrypted • Problem: PKIs not fully deployed nor easy to use Page 2
Public Key Infrastructures • • PKIs setup by companies and organizations Allow certificates to be issued and retrieved May be interconnected through cross-certificates Allows for inter-organizational communication – Authenticated, integrity protected, encrypted • Problem: PKIs not fully deployed nor easy to use Page 2
 Motivation: Slow PKI Deployment • Expensive – Development of applications using PKI security services – Administration cost of configuring and maintaining clients • Complex – Security enabled software is complex to write – Non-user friendly, not transparent • Encryption and digital signatures are not in widespread use Page 3
Motivation: Slow PKI Deployment • Expensive – Development of applications using PKI security services – Administration cost of configuring and maintaining clients • Complex – Security enabled software is complex to write – Non-user friendly, not transparent • Encryption and digital signatures are not in widespread use Page 3
 Motivation II: Complexities of PKI – Trust Path Construction • Initial disjoint PKIs – Communication between arbitrary users not possible – Only useful within single PKI structure • Cross-certificates – Allows communication between separate PKIs – However, makes path building more complicated • PKIs too complicated for user – Validation policies, policy mappings, configuration • Client-Server model Page 4
Motivation II: Complexities of PKI – Trust Path Construction • Initial disjoint PKIs – Communication between arbitrary users not possible – Only useful within single PKI structure • Cross-certificates – Allows communication between separate PKIs – However, makes path building more complicated • PKIs too complicated for user – Validation policies, policy mappings, configuration • Client-Server model Page 4
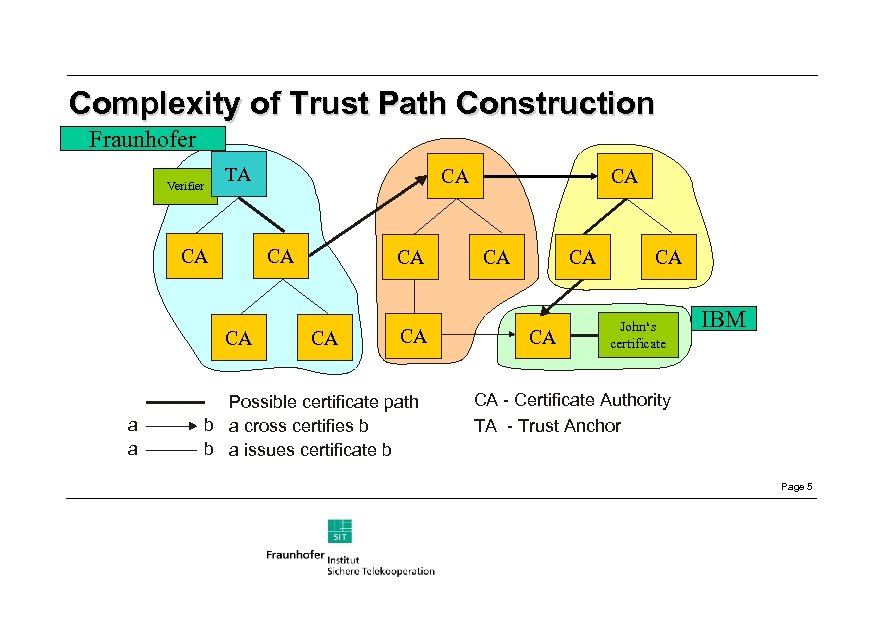 Complexity of Trust Path Construction Fraunhofer Verifier TA CA CA CA a a CA CA Possible certificate path b a cross certifies b b a issues certificate b CA CA CA John‘s certificate IBM CA - Certificate Authority TA - Trust Anchor Page 5
Complexity of Trust Path Construction Fraunhofer Verifier TA CA CA CA a a CA CA Possible certificate path b a cross certifies b b a issues certificate b CA CA CA John‘s certificate IBM CA - Certificate Authority TA - Trust Anchor Page 5
 Problems for Security Applications • Support of many protocols is necessary – Certificate and CRL download (HTTP, FTP, LDAP, . . . ) – Certificate Status (OCSP, LDAP) • All applications must – – Support all protocols Know addresses of all needed repositories Have cryptographic functionality Be able to handle the complexities of PKI • Complexity = Bugs = Less security Page 6
Problems for Security Applications • Support of many protocols is necessary – Certificate and CRL download (HTTP, FTP, LDAP, . . . ) – Certificate Status (OCSP, LDAP) • All applications must – – Support all protocols Know addresses of all needed repositories Have cryptographic functionality Be able to handle the complexities of PKI • Complexity = Bugs = Less security Page 6
 Problems for Users • Applications are expensive and large – Small devices cannot support storage and computational requirements • Must configure applications with addresses of repositories – For path construction and encryption key retrieval • Trust path construction is slow Page 7
Problems for Users • Applications are expensive and large – Small devices cannot support storage and computational requirements • Must configure applications with addresses of repositories – For path construction and encryption key retrieval • Trust path construction is slow Page 7
 NSI Solution • Develop a Client-Server based PKI • Reduce complexity on client-side („Thin Client“) by offering server based services such as: – – Signature validation Trust path construction Management of CRLs and Revocation Status‘ Central management of certificate policies • Simple access to non-hierarchical interconnected PKIs Page 8
NSI Solution • Develop a Client-Server based PKI • Reduce complexity on client-side („Thin Client“) by offering server based services such as: – – Signature validation Trust path construction Management of CRLs and Revocation Status‘ Central management of certificate policies • Simple access to non-hierarchical interconnected PKIs Page 8
 Advantages for Clients • Need not support multitude of PKI protocols – Need support only one Client-Server-Protocol • Need not be configured with repository addresses – Application only needs to know 1 or 2 PKI-Servers • Complex tasks delegated to the PKI Server – Signature and certificate validation – Encryption key retrieval • Thus, applications become smaller and simpler • Devices with limited resources can utilize PKI functionality – Examples: Cellular phones, PDAs (Personal Digital Assistants) Page 9
Advantages for Clients • Need not support multitude of PKI protocols – Need support only one Client-Server-Protocol • Need not be configured with repository addresses – Application only needs to know 1 or 2 PKI-Servers • Complex tasks delegated to the PKI Server – Signature and certificate validation – Encryption key retrieval • Thus, applications become smaller and simpler • Devices with limited resources can utilize PKI functionality – Examples: Cellular phones, PDAs (Personal Digital Assistants) Page 9
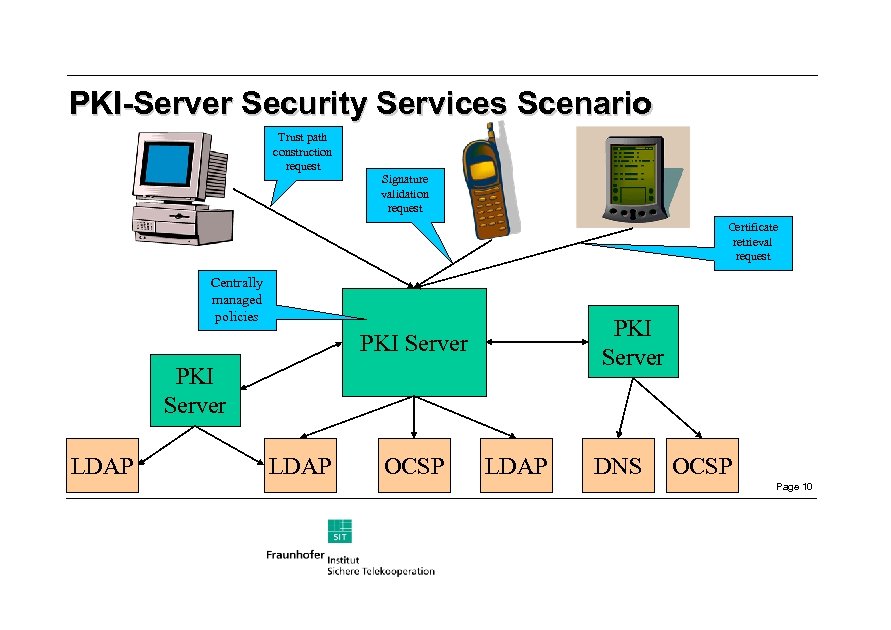 PKI-Server Security Services Scenario Trust path construction request Signature validation request Certificate retrieval request Centrally managed policies PKI Server LDAP OCSP LDAP DNS OCSP Page 10
PKI-Server Security Services Scenario Trust path construction request Signature validation request Certificate retrieval request Centrally managed policies PKI Server LDAP OCSP LDAP DNS OCSP Page 10
 Who will benefit from the PKI Server? • Companies – Central management of Security Policies – No longer need to reconfigure every client when PKI or policy changes • Developers for small devices – API on client side has low resource requirements – More devices able to use PKI services • Security application developers – Decreased development time and costs – More robust security code • Trust. Centre may provide PKI services Page 11
Who will benefit from the PKI Server? • Companies – Central management of Security Policies – No longer need to reconfigure every client when PKI or policy changes • Developers for small devices – API on client side has low resource requirements – More devices able to use PKI services • Security application developers – Decreased development time and costs – More robust security code • Trust. Centre may provide PKI services Page 11
 NSI Goals • Develop concrete protocols • Develop client library such that clients with limited resources may use it • Develop a working PKI Server that is deployable • Run field tests Page 12
NSI Goals • Develop concrete protocols • Develop client library such that clients with limited resources may use it • Develop a working PKI Server that is deployable • Run field tests Page 12
 Issues with NSI approach • What is the architecture? • Interconnection within existing PKIs • What trust relationships are needed? Page 13
Issues with NSI approach • What is the architecture? • Interconnection within existing PKIs • What trust relationships are needed? Page 13
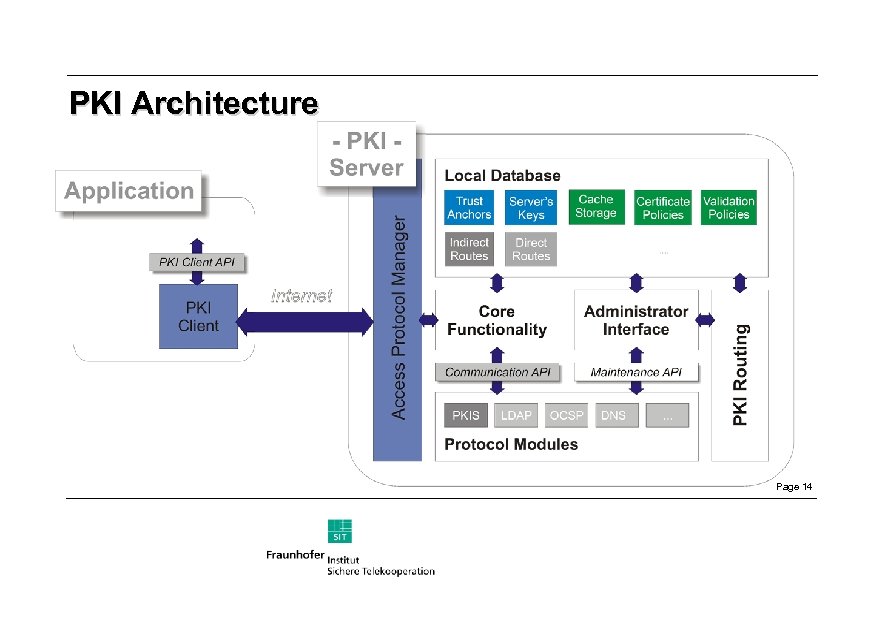 PKI Architecture Page 14
PKI Architecture Page 14
 Comparison: Internet Routing <-> PKI • IP Routing – – Cooperation of many IP routers No computer knows every IP Address in the Internet Network changes are known only to routers, not clients Personal computer knows 1 to n DNS servers • PKI – Little cooperation between PKIs – Application must know all repositories (incl. PKI meshes) – Every client must be updated for every PKI change Page 15
Comparison: Internet Routing <-> PKI • IP Routing – – Cooperation of many IP routers No computer knows every IP Address in the Internet Network changes are known only to routers, not clients Personal computer knows 1 to n DNS servers • PKI – Little cooperation between PKIs – Application must know all repositories (incl. PKI meshes) – Every client must be updated for every PKI change Page 15
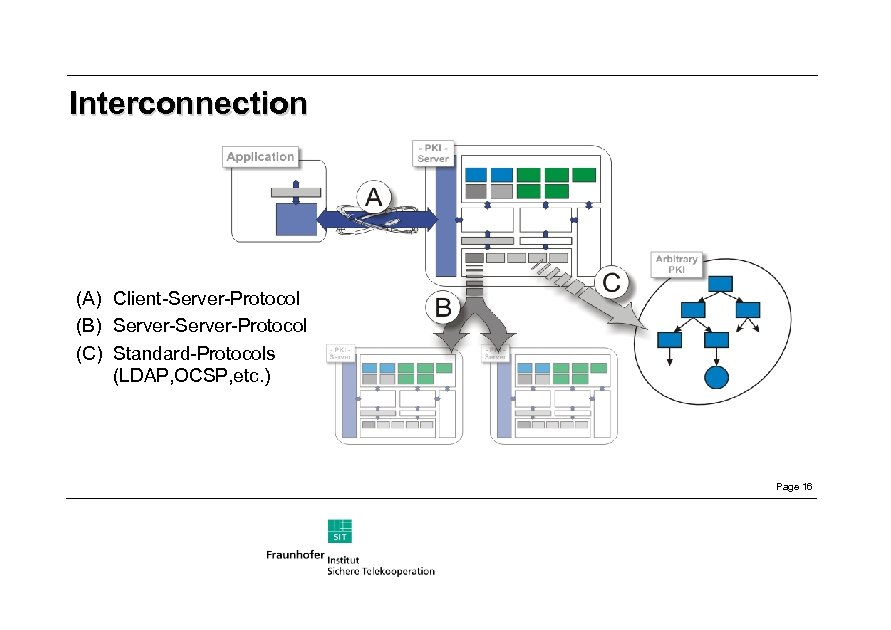 Interconnection (A) Client-Server-Protocol (B) Server-Protocol (C) Standard-Protocols (LDAP, OCSP, etc. ) Page 16
Interconnection (A) Client-Server-Protocol (B) Server-Protocol (C) Standard-Protocols (LDAP, OCSP, etc. ) Page 16
 NSI‘s role within PKI • PKI Server is separate from CA – Accesses available repositories to build paths – Does not need to be certified by CA • Trust in PKI Server is through PKI Server‘s certificate – Must be configured on each client – Revocation check of certificate not defined Page 17
NSI‘s role within PKI • PKI Server is separate from CA – Accesses available repositories to build paths – Does not need to be certified by CA • Trust in PKI Server is through PKI Server‘s certificate – Must be configured on each client – Revocation check of certificate not defined Page 17
 Trust Relationships • Client trust in PKI Server – – Certificate validation: complete trust Signature validation: complete trust Path construction: no trust Certificate retrieval: no trust • PKI Servers deployed within organizations – Clients use organization validation policy and trust server Page 18
Trust Relationships • Client trust in PKI Server – – Certificate validation: complete trust Signature validation: complete trust Path construction: no trust Certificate retrieval: no trust • PKI Servers deployed within organizations – Clients use organization validation policy and trust server Page 18
 Validity of PKI Server Responses • All responses are authenticated – Secure connection (eg. SSL, IPsec) or – Digitally signed response • Integrity of all requests and responses verifiable – Hashes, signatures, encryption • Replay attacks detectable – nonces Page 19
Validity of PKI Server Responses • All responses are authenticated – Secure connection (eg. SSL, IPsec) or – Digitally signed response • Integrity of all requests and responses verifiable – Hashes, signatures, encryption • Replay attacks detectable – nonces Page 19
 NSI comparison with XKMS • Certificate retrieval and validation services supported • NSI needs no connection with an RA or CA – XKMS offers registration and revocation services • Size of sent and stored responses – XKMS uses XML tags – NSI uses ASN. 1 (support embedded within client library) • Small storage requirements for audits Page 20
NSI comparison with XKMS • Certificate retrieval and validation services supported • NSI needs no connection with an RA or CA – XKMS offers registration and revocation services • Size of sent and stored responses – XKMS uses XML tags – NSI uses ASN. 1 (support embedded within client library) • Small storage requirements for audits Page 20
 NSI: A Client-Server-Model for PKI Services Wolfgang Schneider wolfgang. schneider@sit. fhg. de Fraunhofer-Institute for Secure Telecooperation http: //www. sit. fhg. de/NSI/ Page 21
NSI: A Client-Server-Model for PKI Services Wolfgang Schneider wolfgang. schneider@sit. fhg. de Fraunhofer-Institute for Secure Telecooperation http: //www. sit. fhg. de/NSI/ Page 21


