4a81208a93003ccc2c71d71e5078eff6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
 NSERC - Nano. IP and the Canadian Perspective P. Grutter Physics, Mc. Gill University CIAR Nanoelectronics Program Scientific Director, NSERC Nano. IP grutter@physics. mcgill. ca
NSERC - Nano. IP and the Canadian Perspective P. Grutter Physics, Mc. Gill University CIAR Nanoelectronics Program Scientific Director, NSERC Nano. IP grutter@physics. mcgill. ca
 Science Fiction: 7 of 9 on Star Trek
Science Fiction: 7 of 9 on Star Trek
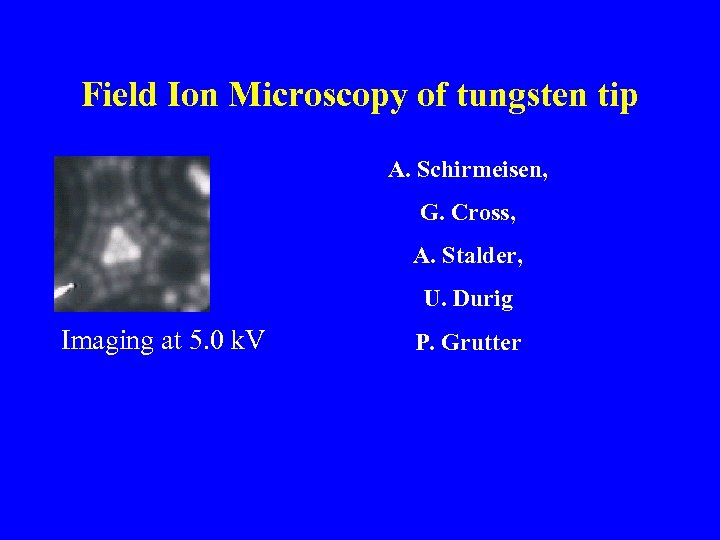 Field Ion Microscopy of tungsten tip A. Schirmeisen, G. Cross, A. Stalder, U. Durig Imaging at 5. 0 k. V P. Grutter
Field Ion Microscopy of tungsten tip A. Schirmeisen, G. Cross, A. Stalder, U. Durig Imaging at 5. 0 k. V P. Grutter
 Field Ion Microscopy of tungsten tip Imaging at 5. 0 k. V Manipulating at 6. 0 k. V
Field Ion Microscopy of tungsten tip Imaging at 5. 0 k. V Manipulating at 6. 0 k. V
 Field Ion Microscopy of tungsten tip Imaging at 5. 0 k. V Manipulating at 6. 0 k. V
Field Ion Microscopy of tungsten tip Imaging at 5. 0 k. V Manipulating at 6. 0 k. V
 Field Ion Microscopy of tungsten tip Imaging at 5. 0 k. V Manipulating at 6. 0 k. V
Field Ion Microscopy of tungsten tip Imaging at 5. 0 k. V Manipulating at 6. 0 k. V
 Single atom on tungsten tip Imaged at 2. 1 KV
Single atom on tungsten tip Imaged at 2. 1 KV
 The Impact of Nano “If I were asked for an area of science and engineering that will most likely produce the breakthroughs of tomorrow, I would point to nanoscale science and engineering. ” (…) “The total societal impact of nanotechnology is expected to be much greater than that of the silicon integrated circuit because it is applicable in many more fields than just electronics. ” Neal Lane, Assistant to former US President Clinton for science and technology
The Impact of Nano “If I were asked for an area of science and engineering that will most likely produce the breakthroughs of tomorrow, I would point to nanoscale science and engineering. ” (…) “The total societal impact of nanotechnology is expected to be much greater than that of the silicon integrated circuit because it is applicable in many more fields than just electronics. ” Neal Lane, Assistant to former US President Clinton for science and technology
 How big is a nanometer?
How big is a nanometer?
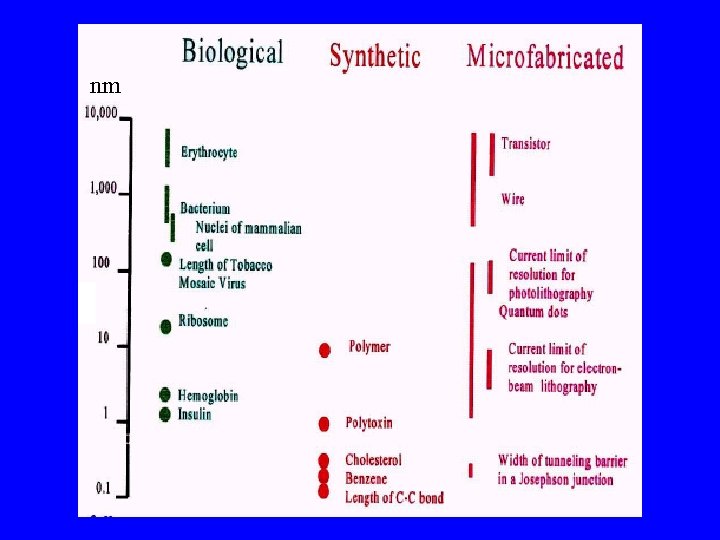 nm
nm
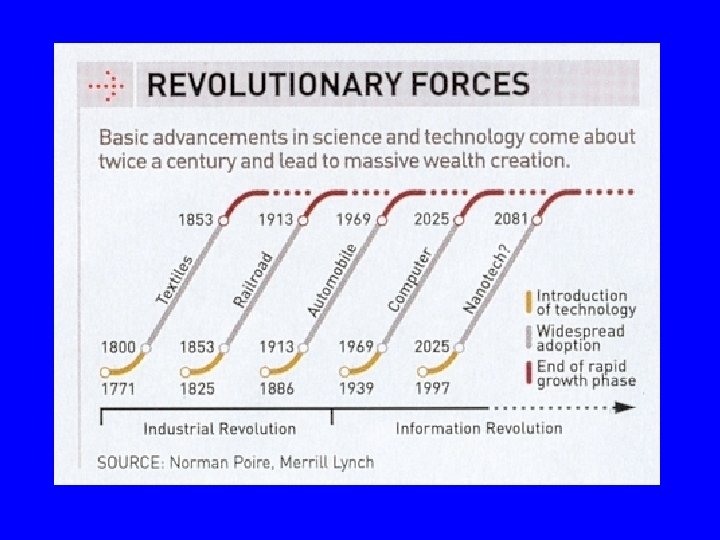
 Definition of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology investigates and applies phenomena, systems and structures where: 1. At least one dimension lc is a few nm 2. The properties are qualitatively different because l < lc Condition 2 distinguishes ‘nano’ from ‘micro’, macromolecular chemistry’ or ‘biology’
Definition of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology investigates and applies phenomena, systems and structures where: 1. At least one dimension lc is a few nm 2. The properties are qualitatively different because l < lc Condition 2 distinguishes ‘nano’ from ‘micro’, macromolecular chemistry’ or ‘biology’
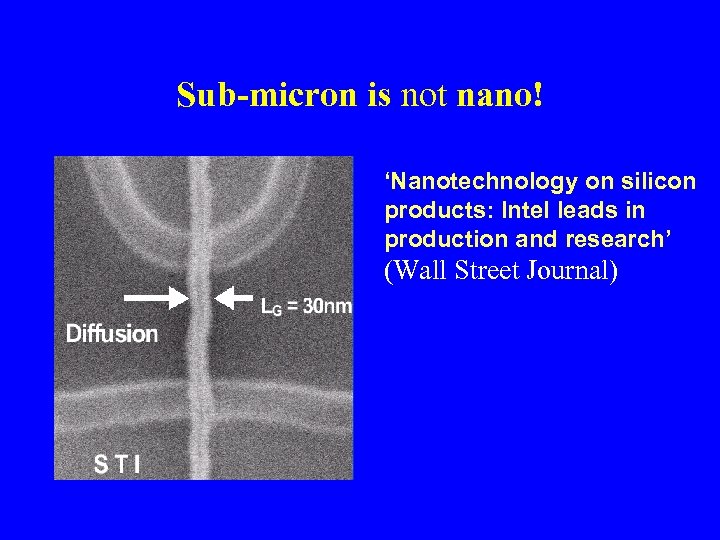 Sub-micron is not nano! ‘Nanotechnology on silicon products: Intel leads in production and research’ (Wall Street Journal)
Sub-micron is not nano! ‘Nanotechnology on silicon products: Intel leads in production and research’ (Wall Street Journal)
 Beware of Power. Point Science or Cartoon Engineering !!!
Beware of Power. Point Science or Cartoon Engineering !!!
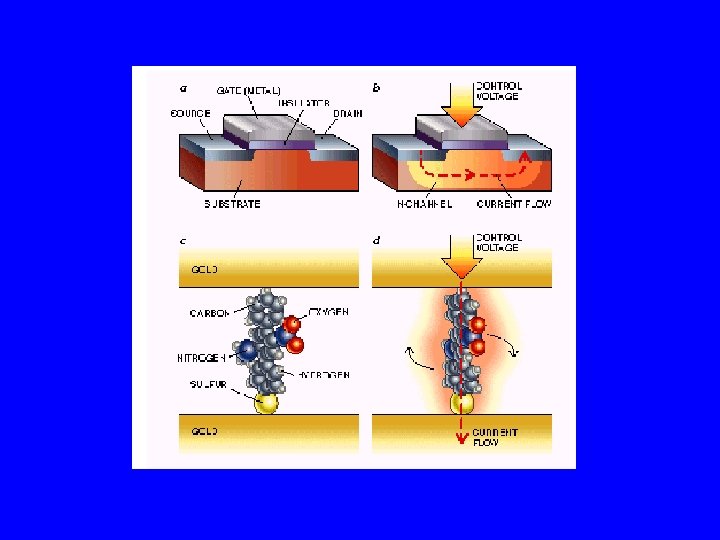
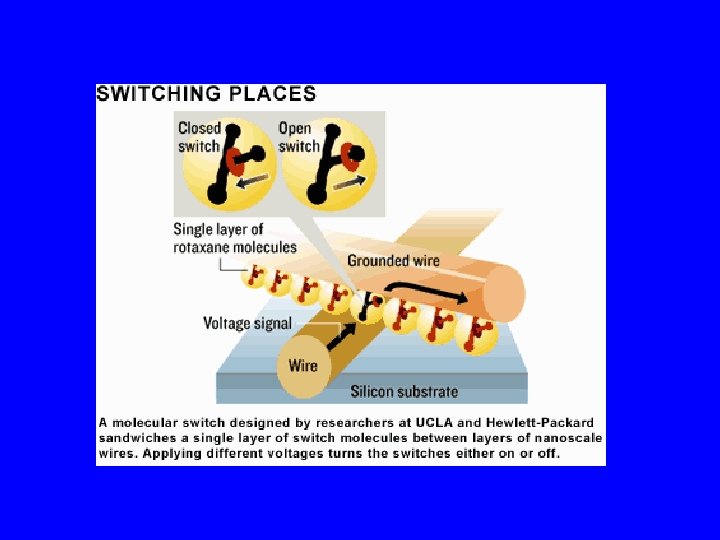
 Where will nano make an impact? • Electronics and photonics – molecular electronics, spintronics – photonics – sensors • Materials – ultra-fine powders, composites – harder, more corrosion resistant, dirt/bacteria repellent – green manufacturing, cost effective • Bio-medical – emerging applications (materials, diagnostics, drug delivery. . . ) – biomedical research tools (labeling, nanotools applied to biomed ) – biotechnology applied to nanoscience & technology
Where will nano make an impact? • Electronics and photonics – molecular electronics, spintronics – photonics – sensors • Materials – ultra-fine powders, composites – harder, more corrosion resistant, dirt/bacteria repellent – green manufacturing, cost effective • Bio-medical – emerging applications (materials, diagnostics, drug delivery. . . ) – biomedical research tools (labeling, nanotools applied to biomed ) – biotechnology applied to nanoscience & technology
 New materials: non-permeable, selfcleaning, anti-septic, . . . Air-D-Fense (In. Mat, New Jersey): nanoclay/butyl thin film 3000 fold decreased permeability Lotus leaf (artificial): nm sized hydrophobic wax size: water rolls (not slides) -> cleans sol-gel based technique -> on market Self-cleaning plastic, textiles: CNT stabilized enzymes in polymer Textiles with ‘Stain Defender’ Ceramic Coatings: (Inframat) No barnacles on ship hulls: reduced drag
New materials: non-permeable, selfcleaning, anti-septic, . . . Air-D-Fense (In. Mat, New Jersey): nanoclay/butyl thin film 3000 fold decreased permeability Lotus leaf (artificial): nm sized hydrophobic wax size: water rolls (not slides) -> cleans sol-gel based technique -> on market Self-cleaning plastic, textiles: CNT stabilized enzymes in polymer Textiles with ‘Stain Defender’ Ceramic Coatings: (Inframat) No barnacles on ship hulls: reduced drag
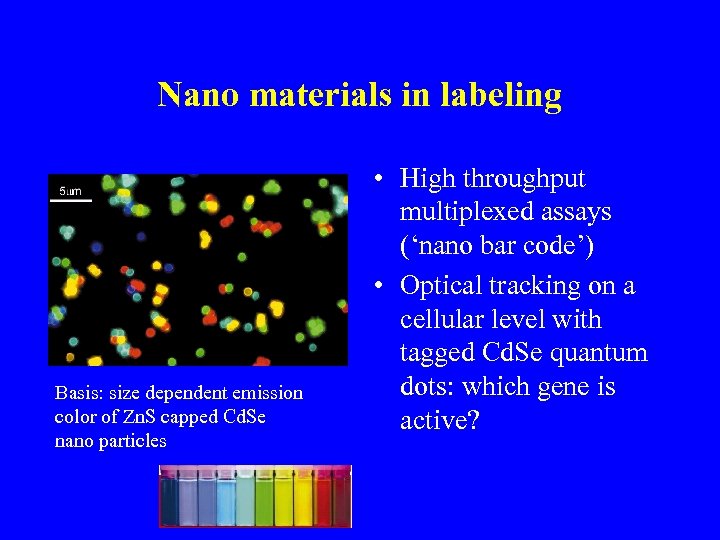 Nano materials in labeling Basis: size dependent emission color of Zn. S capped Cd. Se nano particles • High throughput multiplexed assays (‘nano bar code’) • Optical tracking on a cellular level with tagged Cd. Se quantum dots: which gene is active?
Nano materials in labeling Basis: size dependent emission color of Zn. S capped Cd. Se nano particles • High throughput multiplexed assays (‘nano bar code’) • Optical tracking on a cellular level with tagged Cd. Se quantum dots: which gene is active?
 Nano in Canada • • No national strategy (yet) National Institute of Nanotechnology (Edmonton): 120 M$ $ 3. 15 B Canadian Foundation of Innovation (10 years) $ 900 M Canadian Research Chairs Nano. Quebec $ 10 M operating (since 2001) CIAR Nanoelectronics program (since 1999) Many universities on a hiring spree (baby boomers retiring) Cost structure relevant! 1 C$ = 2 -3 US$
Nano in Canada • • No national strategy (yet) National Institute of Nanotechnology (Edmonton): 120 M$ $ 3. 15 B Canadian Foundation of Innovation (10 years) $ 900 M Canadian Research Chairs Nano. Quebec $ 10 M operating (since 2001) CIAR Nanoelectronics program (since 1999) Many universities on a hiring spree (baby boomers retiring) Cost structure relevant! 1 C$ = 2 -3 US$
 National Science and Engineering Research Council People: support for more than 9, 000 graduate students Discovery: funding of more than 8, 700 researchers p. a. Innovation: encouraging more than 1, 000 Canadian companies to invest in university research. In 2002 -2003, NSERC will invest $678 million in university-based research and training in all the natural sciences and engineering.
National Science and Engineering Research Council People: support for more than 9, 000 graduate students Discovery: funding of more than 8, 700 researchers p. a. Innovation: encouraging more than 1, 000 Canadian companies to invest in university research. In 2002 -2003, NSERC will invest $678 million in university-based research and training in all the natural sciences and engineering.
 NSERC 2002 Total: $ 10, 433 k
NSERC 2002 Total: $ 10, 433 k
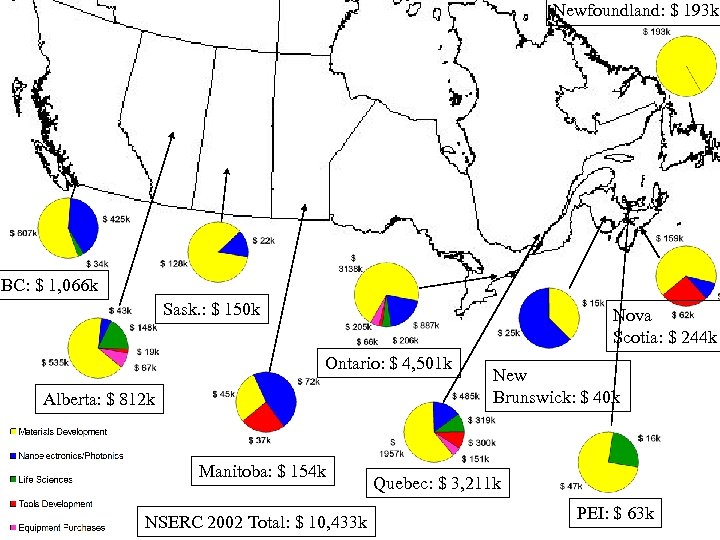 Newfoundland: $ 193 k BC: $ 1, 066 k Sask. : $ 150 k Nova Scotia: $ 244 k Ontario: $ 4, 501 k Alberta: $ 812 k Manitoba: $ 154 k NSERC 2002 Total: $ 10, 433 k New Brunswick: $ 40 k Quebec: $ 3, 211 k PEI: $ 63 k
Newfoundland: $ 193 k BC: $ 1, 066 k Sask. : $ 150 k Nova Scotia: $ 244 k Ontario: $ 4, 501 k Alberta: $ 812 k Manitoba: $ 154 k NSERC 2002 Total: $ 10, 433 k New Brunswick: $ 40 k Quebec: $ 3, 211 k PEI: $ 63 k
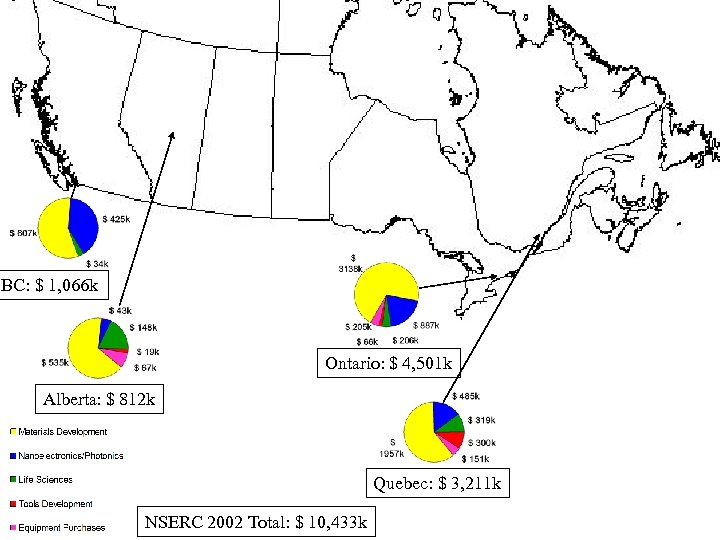 BC: $ 1, 066 k Ontario: $ 4, 501 k Alberta: $ 812 k Quebec: $ 3, 211 k NSERC 2002 Total: $ 10, 433 k
BC: $ 1, 066 k Ontario: $ 4, 501 k Alberta: $ 812 k Quebec: $ 3, 211 k NSERC 2002 Total: $ 10, 433 k
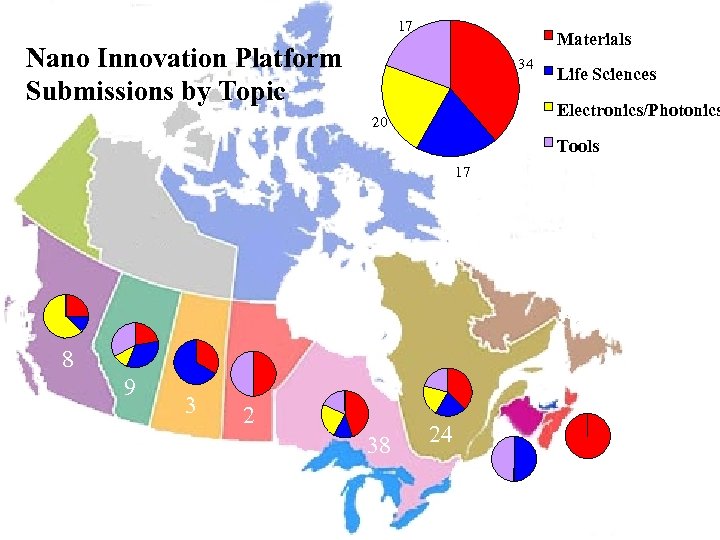 17 Materials Nano Innovation Platform Submissions by Topic 34 Life Sciences Electronics/Photonics 20 Tools 17 8 9 3 2 38 24 2 2
17 Materials Nano Innovation Platform Submissions by Topic 34 Life Sciences Electronics/Photonics 20 Tools 17 8 9 3 2 38 24 2 2
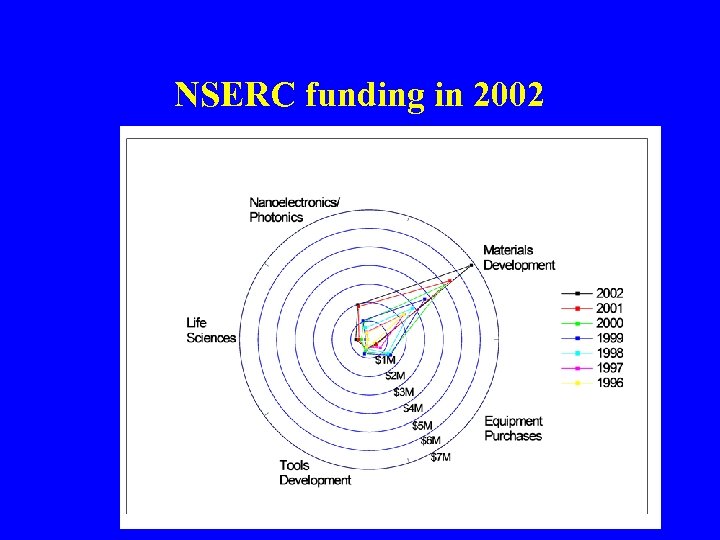 NSERC funding in 2002
NSERC funding in 2002
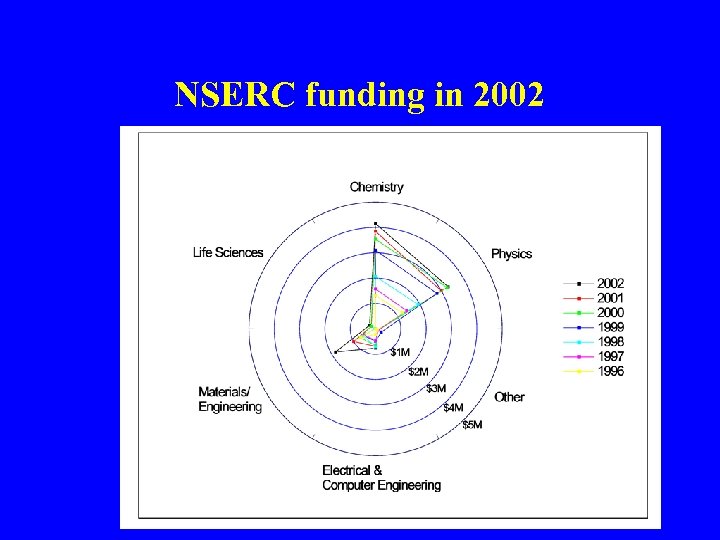 NSERC funding in 2002
NSERC funding in 2002
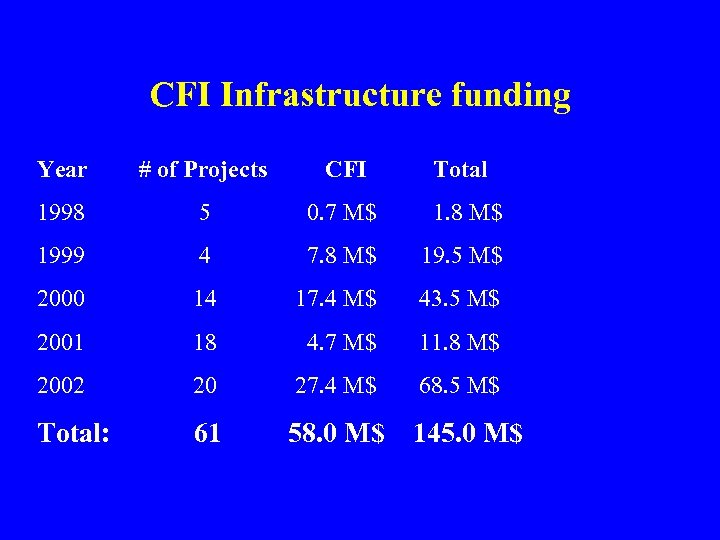 CFI Infrastructure funding Year # of Projects CFI Total 1998 5 0. 7 M$ 1. 8 M$ 1999 4 7. 8 M$ 19. 5 M$ 2000 14 17. 4 M$ 43. 5 M$ 2001 18 4. 7 M$ 11. 8 M$ 2002 20 27. 4 M$ 68. 5 M$ Total: 61 58. 0 M$ 145. 0 M$
CFI Infrastructure funding Year # of Projects CFI Total 1998 5 0. 7 M$ 1. 8 M$ 1999 4 7. 8 M$ 19. 5 M$ 2000 14 17. 4 M$ 43. 5 M$ 2001 18 4. 7 M$ 11. 8 M$ 2002 20 27. 4 M$ 68. 5 M$ Total: 61 58. 0 M$ 145. 0 M$
 Nanotools Facility: 9. 4 M$, part of Nano. Quebec Network
Nanotools Facility: 9. 4 M$, part of Nano. Quebec Network
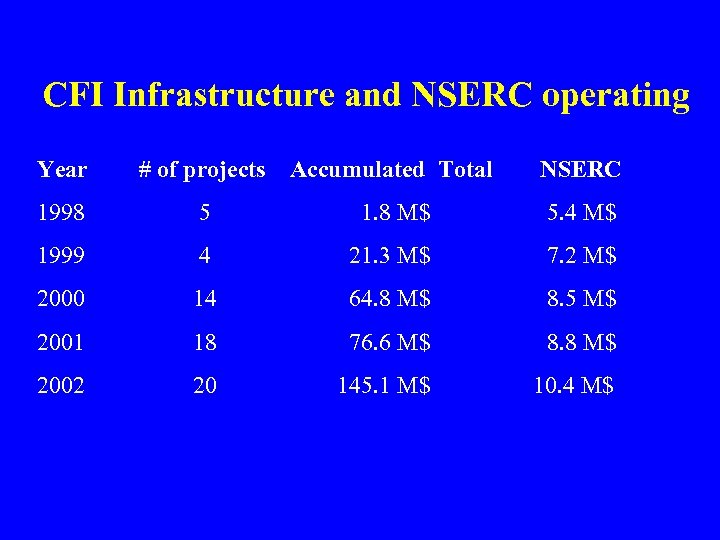 CFI Infrastructure and NSERC operating Year # of projects Accumulated Total NSERC 1998 5 1. 8 M$ 5. 4 M$ 1999 4 21. 3 M$ 7. 2 M$ 2000 14 64. 8 M$ 8. 5 M$ 2001 18 76. 6 M$ 8. 8 M$ 2002 20 145. 1 M$ 10. 4 M$
CFI Infrastructure and NSERC operating Year # of projects Accumulated Total NSERC 1998 5 1. 8 M$ 5. 4 M$ 1999 4 21. 3 M$ 7. 2 M$ 2000 14 64. 8 M$ 8. 5 M$ 2001 18 76. 6 M$ 8. 8 M$ 2002 20 145. 1 M$ 10. 4 M$
 A few observations • Some world class nano research in Canada • Spread out over 6000 km • Current funding structure does not encourage risk taking • Researchers have grant writing fatigue • No strategic coordination or science policy • Commercialization a problem in Canada
A few observations • Some world class nano research in Canada • Spread out over 6000 km • Current funding structure does not encourage risk taking • Researchers have grant writing fatigue • No strategic coordination or science policy • Commercialization a problem in Canada
 Canada is World Class in Nanoscience Patents as strength indicators:
Canada is World Class in Nanoscience Patents as strength indicators:
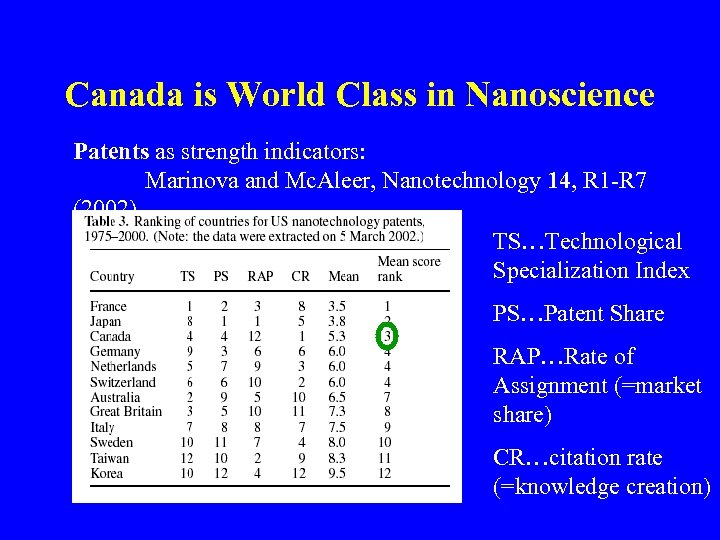 Canada is World Class in Nanoscience Patents as strength indicators: Marinova and Mc. Aleer, Nanotechnology 14, R 1 -R 7 (2002) TS…Technological Specialization Index PS…Patent Share RAP…Rate of Assignment (=market share) CR…citation rate (=knowledge creation)
Canada is World Class in Nanoscience Patents as strength indicators: Marinova and Mc. Aleer, Nanotechnology 14, R 1 -R 7 (2002) TS…Technological Specialization Index PS…Patent Share RAP…Rate of Assignment (=market share) CR…citation rate (=knowledge creation)
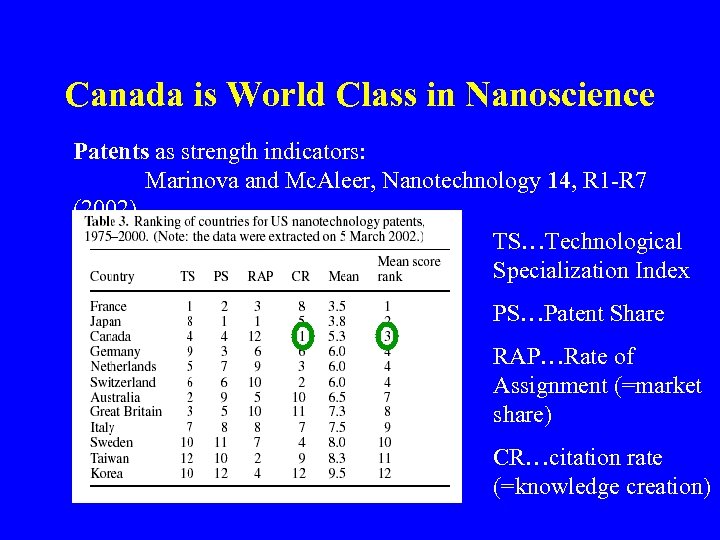 Canada is World Class in Nanoscience Patents as strength indicators: Marinova and Mc. Aleer, Nanotechnology 14, R 1 -R 7 (2002) TS…Technological Specialization Index PS…Patent Share RAP…Rate of Assignment (=market share) CR…citation rate (=knowledge creation)
Canada is World Class in Nanoscience Patents as strength indicators: Marinova and Mc. Aleer, Nanotechnology 14, R 1 -R 7 (2002) TS…Technological Specialization Index PS…Patent Share RAP…Rate of Assignment (=market share) CR…citation rate (=knowledge creation)
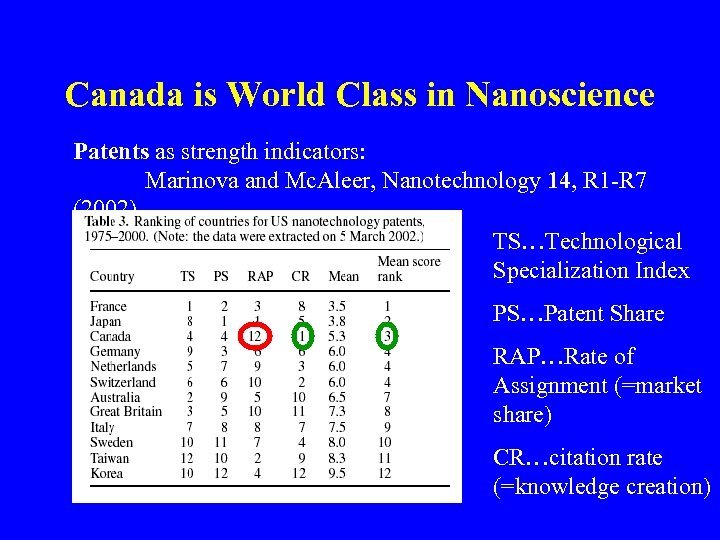 Canada is World Class in Nanoscience Patents as strength indicators: Marinova and Mc. Aleer, Nanotechnology 14, R 1 -R 7 (2002) TS…Technological Specialization Index PS…Patent Share RAP…Rate of Assignment (=market share) CR…citation rate (=knowledge creation)
Canada is World Class in Nanoscience Patents as strength indicators: Marinova and Mc. Aleer, Nanotechnology 14, R 1 -R 7 (2002) TS…Technological Specialization Index PS…Patent Share RAP…Rate of Assignment (=market share) CR…citation rate (=knowledge creation)
 NSERC Nano Innovation Platform: “The NSERC Nano Innovation Platform is a multidisciplinary national network of university researchers from many fields of science and engineering created to accelerate and intensify research and education of HQP in nanoscience and nanotechnology in Canada. ”
NSERC Nano Innovation Platform: “The NSERC Nano Innovation Platform is a multidisciplinary national network of university researchers from many fields of science and engineering created to accelerate and intensify research and education of HQP in nanoscience and nanotechnology in Canada. ”
 Organization of Nano IP • Scientific Director (P. Grutter) • Assoc. Scientific Director (M. Roseman) • Advisory Committee (9 members) • Admin. and other support staff • International Panel (6 members) • NSERC Steering Committee
Organization of Nano IP • Scientific Director (P. Grutter) • Assoc. Scientific Director (M. Roseman) • Advisory Committee (9 members) • Admin. and other support staff • International Panel (6 members) • NSERC Steering Committee
 Aim of NSERC Nano IP • Develop and implement a national strategy together with all stake holders • Support a few high risk projects at a high funding level • Facilitate and build local nano communities • Increase NSERC budget with and for nano
Aim of NSERC Nano IP • Develop and implement a national strategy together with all stake holders • Support a few high risk projects at a high funding level • Facilitate and build local nano communities • Increase NSERC budget with and for nano
 The Canadian Nano Vision: answers to the following questions • What is Canada’s position and strength in this field? • By the end of 2003 as a community of stakeholders we will have made some strategic choices both in terms of topics as well as where these efforts should geographically be concentrated. • We will also have a clearer understanding of what the required funding is and what it will be used for.
The Canadian Nano Vision: answers to the following questions • What is Canada’s position and strength in this field? • By the end of 2003 as a community of stakeholders we will have made some strategic choices both in terms of topics as well as where these efforts should geographically be concentrated. • We will also have a clearer understanding of what the required funding is and what it will be used for.
 Summary Nano. IP • Nine high risk = high visibility projects: NSERC is doing something innovative and visionary in Nano • Workshops help build a community with students, researchers across all disciplines and sectors • Strategic coordination of Nano in Canada with all stake holders
Summary Nano. IP • Nine high risk = high visibility projects: NSERC is doing something innovative and visionary in Nano • Workshops help build a community with students, researchers across all disciplines and sectors • Strategic coordination of Nano in Canada with all stake holders
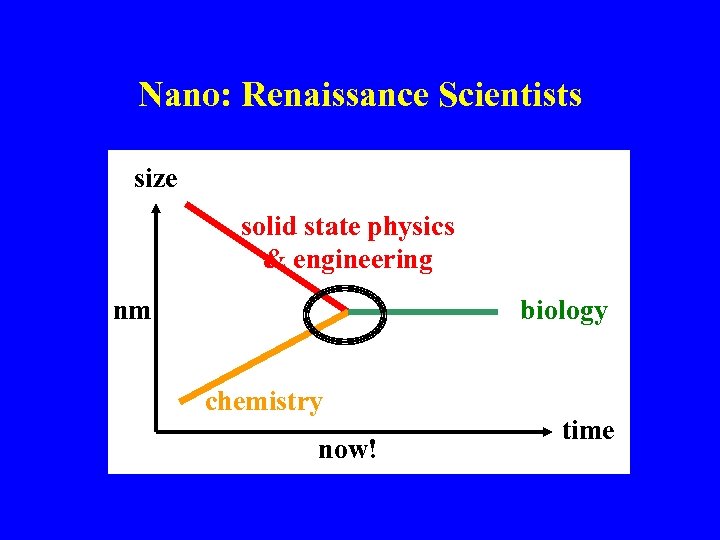 Nano: Renaissance Scientists size solid state physics & engineering nm nm biology chemistry now! time
Nano: Renaissance Scientists size solid state physics & engineering nm nm biology chemistry now! time
 Nano Technology Nanotechnology is at its infancy, still rather quite primitive! some of the issues: • • • Science! Scaling Laws? Statistics? Better function? Throughput? • Cost? • Systems integration? • Environmental impact? • Social acceptance? • Ethics?
Nano Technology Nanotechnology is at its infancy, still rather quite primitive! some of the issues: • • • Science! Scaling Laws? Statistics? Better function? Throughput? • Cost? • Systems integration? • Environmental impact? • Social acceptance? • Ethics?


 Nano. IP Awards: Philosophy • • Excellence, quality, innovation and need for funds. 'The risk taker is the best decision-maker. ’ Being first is important. Is it ‘nano’ or a tool for nanoscience? Minimize overhead/workload on applicant(s). International refereeing committee. For first round no selection based on strategic themes.
Nano. IP Awards: Philosophy • • Excellence, quality, innovation and need for funds. 'The risk taker is the best decision-maker. ’ Being first is important. Is it ‘nano’ or a tool for nanoscience? Minimize overhead/workload on applicant(s). International refereeing committee. For first round no selection based on strategic themes.
 Nano. IP Awards: evaluation criteria • • • Is it 'Nano'? Or is it a new tool for nano research? Excellence of proposal. Originality. Track record/potential of applicant(s). Justification of why $100, 000 will make an impact. Reasonable to expect significant progress and impact with overall funding?
Nano. IP Awards: evaluation criteria • • • Is it 'Nano'? Or is it a new tool for nano research? Excellence of proposal. Originality. Track record/potential of applicant(s). Justification of why $100, 000 will make an impact. Reasonable to expect significant progress and impact with overall funding?
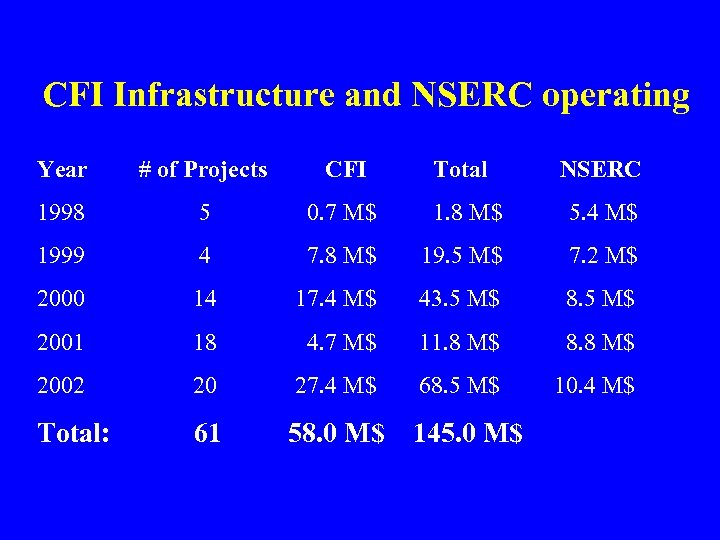 CFI Infrastructure and NSERC operating Year # of Projects CFI Total NSERC 1998 5 0. 7 M$ 1. 8 M$ 5. 4 M$ 1999 4 7. 8 M$ 19. 5 M$ 7. 2 M$ 2000 14 17. 4 M$ 43. 5 M$ 8. 5 M$ 2001 18 4. 7 M$ 11. 8 M$ 8. 8 M$ 2002 20 27. 4 M$ 68. 5 M$ 10. 4 M$ Total: 61 58. 0 M$ 145. 0 M$
CFI Infrastructure and NSERC operating Year # of Projects CFI Total NSERC 1998 5 0. 7 M$ 1. 8 M$ 5. 4 M$ 1999 4 7. 8 M$ 19. 5 M$ 7. 2 M$ 2000 14 17. 4 M$ 43. 5 M$ 8. 5 M$ 2001 18 4. 7 M$ 11. 8 M$ 8. 8 M$ 2002 20 27. 4 M$ 68. 5 M$ 10. 4 M$ Total: 61 58. 0 M$ 145. 0 M$


