525511f568f70d067af09df1b9e981ae.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Now What…. . n I want the last remaining orange and so do you
Now What…. . n I want the last remaining orange and so do you
 Focus on interests, not positions: n Behind opposed positions lie shared and/or compatible interests n n n Each side likely has multiple interests that may be valued differently by each party Find these compatible interests and then make trade-offs Complete satisfaction for parties both
Focus on interests, not positions: n Behind opposed positions lie shared and/or compatible interests n n n Each side likely has multiple interests that may be valued differently by each party Find these compatible interests and then make trade-offs Complete satisfaction for parties both
 Mythical Fixed-Pie n Assume that there can only be one winner and one loser (distributive bargaining approach) n n However, only a small percentage of organizational negotiations are purely distributive, involving just one resource or just one issue Consider: n Price, delivery date, financing, service, relationships
Mythical Fixed-Pie n Assume that there can only be one winner and one loser (distributive bargaining approach) n n However, only a small percentage of organizational negotiations are purely distributive, involving just one resource or just one issue Consider: n Price, delivery date, financing, service, relationships
 Continued n Assumption that our interests conflict with the other side n “What’s good for them must be bad for us” n n Terms that appear beneficial when suggested by your side often seem disadvantageous when proposed by the other side The fixed-pie mentality is prevalent
Continued n Assumption that our interests conflict with the other side n “What’s good for them must be bad for us” n n Terms that appear beneficial when suggested by your side often seem disadvantageous when proposed by the other side The fixed-pie mentality is prevalent
 SALT (U. S. & Russia) n “I have had a philosophy for some time in regard to SALT, and it goes like this: the Russians will not accept a SALT treaty that is not in their best interest, and it seems to me that if it is in their best interest, it can’t be in our best interest” n Floyd Spence, U. S. Congress
SALT (U. S. & Russia) n “I have had a philosophy for some time in regard to SALT, and it goes like this: the Russians will not accept a SALT treaty that is not in their best interest, and it seems to me that if it is in their best interest, it can’t be in our best interest” n Floyd Spence, U. S. Congress
 Arms Reduction Proposal n The same proposal was reviewed by two groups of people in the U. S. A. n n Group 1: The arms reduction proposal was offered by Russian President Gorbachev How favorable was it to Russia, the U. S. ? n n n 56% said it strongly favored Russia 16% said it favored the U. S. 28% said it favored both sides equally
Arms Reduction Proposal n The same proposal was reviewed by two groups of people in the U. S. A. n n Group 1: The arms reduction proposal was offered by Russian President Gorbachev How favorable was it to Russia, the U. S. ? n n n 56% said it strongly favored Russia 16% said it favored the U. S. 28% said it favored both sides equally
 n Group 2: The arms reduction proposal was offered by U. S. President Reagan n 27% said it favored the USSR. 27% said it favored the US 46% said it favored both sides equally
n Group 2: The arms reduction proposal was offered by U. S. President Reagan n 27% said it favored the USSR. 27% said it favored the US 46% said it favored both sides equally
 Finding the trade-offs: Easy or not so easy? n Pairs were presented with a negotiation involving multiple issues. On two of these issues, the opposing sides had compatible interests (similar to an interest in the orange peel versus an interest in the fruit) n What percentage of the time did the negotiators fail to trade-off? n n 40% Instead of realizing the gains, they tended to compromise on each one
Finding the trade-offs: Easy or not so easy? n Pairs were presented with a negotiation involving multiple issues. On two of these issues, the opposing sides had compatible interests (similar to an interest in the orange peel versus an interest in the fruit) n What percentage of the time did the negotiators fail to trade-off? n n 40% Instead of realizing the gains, they tended to compromise on each one
 n Two students in a library, one wants the window open, the other wants it closed. A loud argument breaks out. n How might this be resolved? n n n Fixed-pie assumptions and Anger closes our minds to alternative solutions Expand the pie n n There may be just ONE way to satisfy a position, but there are MULTIPLE ways to satisfy interests. Inventing options for mutual gain
n Two students in a library, one wants the window open, the other wants it closed. A loud argument breaks out. n How might this be resolved? n n n Fixed-pie assumptions and Anger closes our minds to alternative solutions Expand the pie n n There may be just ONE way to satisfy a position, but there are MULTIPLE ways to satisfy interests. Inventing options for mutual gain
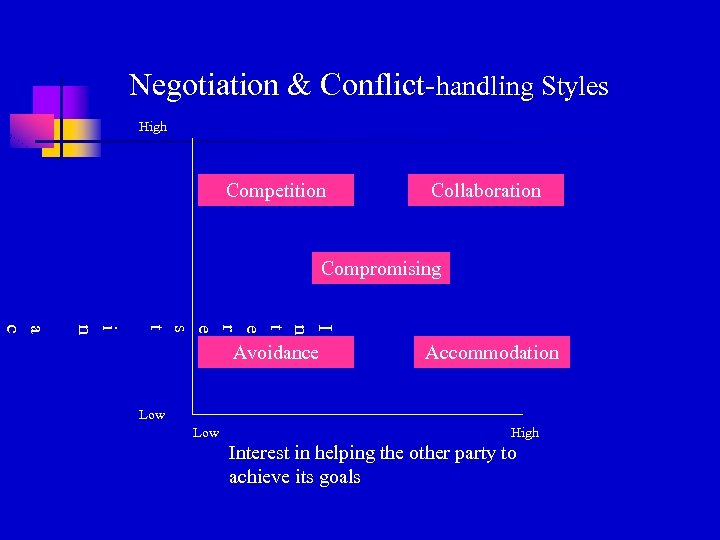 Negotiation & Conflict-handling Styles High Competition Collaboration Compromising I n t e r e s t i n a c Avoidance Accommodation Low High Interest in helping the other party to achieve its goals
Negotiation & Conflict-handling Styles High Competition Collaboration Compromising I n t e r e s t i n a c Avoidance Accommodation Low High Interest in helping the other party to achieve its goals
 Common Negotiation Styles n Competing (distributive mind-set) n n Your gain is my loss Compromising (the middle ground) n “Let’s split the difference” n n Seems like a good strategy: Isn’t it better than no deal at all? However, the middle ground results in incomplete satisfaction for both parties n “Leaving money on the table”
Common Negotiation Styles n Competing (distributive mind-set) n n Your gain is my loss Compromising (the middle ground) n “Let’s split the difference” n n Seems like a good strategy: Isn’t it better than no deal at all? However, the middle ground results in incomplete satisfaction for both parties n “Leaving money on the table”
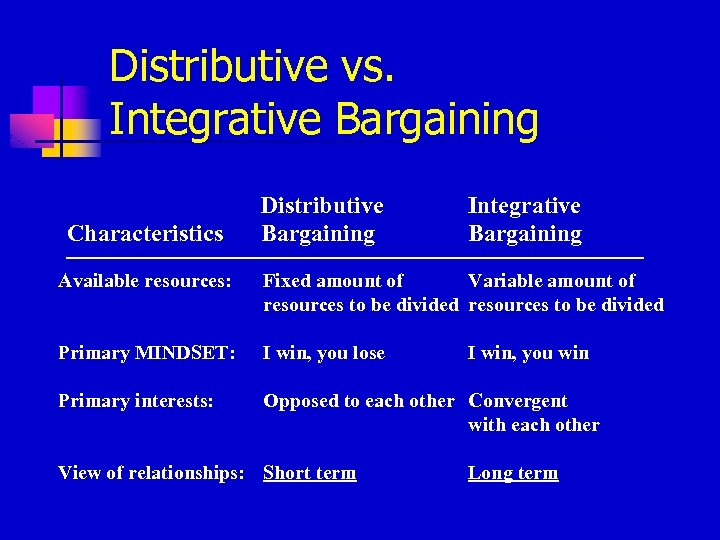 Distributive vs. Integrative Bargaining Characteristics Distributive Bargaining Integrative Bargaining Available resources: Fixed amount of Variable amount of resources to be divided Primary MINDSET: I win, you lose Primary interests: Opposed to each other Convergent with each other View of relationships: Short term I win, you win Long term
Distributive vs. Integrative Bargaining Characteristics Distributive Bargaining Integrative Bargaining Available resources: Fixed amount of Variable amount of resources to be divided Primary MINDSET: I win, you lose Primary interests: Opposed to each other Convergent with each other View of relationships: Short term I win, you win Long term
 Principled Negotiation: Reaching Agreement, Without Giving In n Focus on interests, not positions n Do you know your interests? n Identify and n n value your sides interests Ranking process is one way to start Consult with team to help valuation process
Principled Negotiation: Reaching Agreement, Without Giving In n Focus on interests, not positions n Do you know your interests? n Identify and n n value your sides interests Ranking process is one way to start Consult with team to help valuation process
 Presentation Approaches n n Option 1: “I want that orange because I am interested in baking an orange cake and I need the peel” Option 2: “I am interested in baking an orange cake and I need the peel, that’s why I want that orange” n How are these options the same? Different n Which approach will most effectively convey your interests to the other side? Why?
Presentation Approaches n n Option 1: “I want that orange because I am interested in baking an orange cake and I need the peel” Option 2: “I am interested in baking an orange cake and I need the peel, that’s why I want that orange” n How are these options the same? Different n Which approach will most effectively convey your interests to the other side? Why?
 Find out the other party’s interests and preferences n Ask questions n Listen to the response!
Find out the other party’s interests and preferences n Ask questions n Listen to the response!
 n Concessions n Find an issue of lower value to you and offer a concession on that issue n n Other party will typically reciprocate Contingent concessions n I can give here if you can work with me on another issue
n Concessions n Find an issue of lower value to you and offer a concession on that issue n n Other party will typically reciprocate Contingent concessions n I can give here if you can work with me on another issue
 n Make multiple offers simultaneously n Each is different, yet results in the same level of profitability for you
n Make multiple offers simultaneously n Each is different, yet results in the same level of profitability for you
 Emotional Strategy n Benefits of a good mood More creative, more ideas n Found most trade-offs for joint gain n Highest level of value Detriments of anger Found fewest trade-offs n Least value n
Emotional Strategy n Benefits of a good mood More creative, more ideas n Found most trade-offs for joint gain n Highest level of value Detriments of anger Found fewest trade-offs n Least value n
 n Expressed emotion “Put on a happy face” n Your smile is often reciprocated by the other side n Positive feelings and behaviors n Finding trade-offs n Offering concessions n
n Expressed emotion “Put on a happy face” n Your smile is often reciprocated by the other side n Positive feelings and behaviors n Finding trade-offs n Offering concessions n
 Where do we start? A. Start with the easy issues first! B. Start with the most difficult ones first! C. Either A or B: It depends D. None of the above
Where do we start? A. Start with the easy issues first! B. Start with the most difficult ones first! C. Either A or B: It depends D. None of the above
 Principled Negotiation: “Getting to Yes” n Separate the people from the problem n n n Perceive yourself working side by side with the other party to resolve the issue Resist the temptation to “attack” people Physically/actually sit on the same side of the table n Together we can attack this problem
Principled Negotiation: “Getting to Yes” n Separate the people from the problem n n n Perceive yourself working side by side with the other party to resolve the issue Resist the temptation to “attack” people Physically/actually sit on the same side of the table n Together we can attack this problem
 n Insist on objective criteria n Search for a standard such as market value, expert opinion, law This way, neither party is “giving in” to the other and a fair agreement is possible n We are asking for $200, 000 in fees n n n How did you arrive at that figure? Is it supported by market data?
n Insist on objective criteria n Search for a standard such as market value, expert opinion, law This way, neither party is “giving in” to the other and a fair agreement is possible n We are asking for $200, 000 in fees n n n How did you arrive at that figure? Is it supported by market data?
 n “It’s company policy – there is nothing I can do”
n “It’s company policy – there is nothing I can do”
 Where do we start? A. Start with the easy issues first! B. Start with the most difficult ones first! C. Either A or B: It depends D. None of the above
Where do we start? A. Start with the easy issues first! B. Start with the most difficult ones first! C. Either A or B: It depends D. None of the above
 Issues in Negotiation n Anchoring n Putting too much weight on an initial offer
Issues in Negotiation n Anchoring n Putting too much weight on an initial offer


