f8a9430a0789d4f84f60c0a854f887df.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 69
November 9, 2015 – A day • Do Now: Pilgrims • Magna Carta • Homework: No Homework!

November 9, 2015 • • Go over missing assignments Go over Test Finish Jamestown Go over colonies sheet

What did England Want? – 104 MEN came on 3 ships after a 4 month journey – Built a fort and lived on the James River – Land was swampy with mosquitoes that spread disease, causing many settlers to die 3

English Ships that sail to Jamestown, Virginia

Inside the Ship

What did England Want? Colonists were so busy looking for gold, they did not plant enough crops Captain John Smith helps save colony by setting up rules to force colonists to work planting food. The Powhatan Indians also saved the colonists from starving by trading corn to them Peaceful friendship between Indians and colonists lasted a short while until there were disagreements over food and land
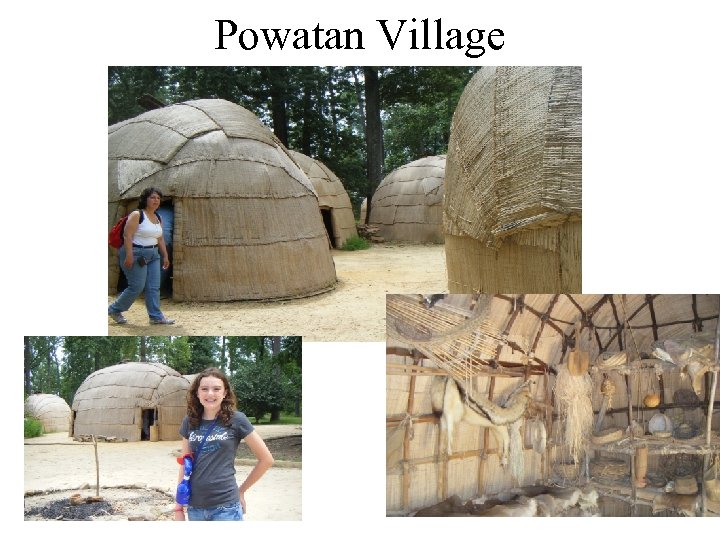

Powatan Village

Making a canoe and leather

Inside the Fort at Jamestown

Inside a home at Jamestown

November 12, 2015 – A Day • Do Now: Representative Government • Homework: Read 100 -105 • Q# 4, 5, and 7 on page 105 • Rewrite Question and answer in • complete sentences • Take out New England Colonies Worksheet • About. com 13 Colonies

• • • Go over Colonies Worksheet In depth on New England Colonies Video on New England Video on Mayflower Video on Pilgrims and Puritans

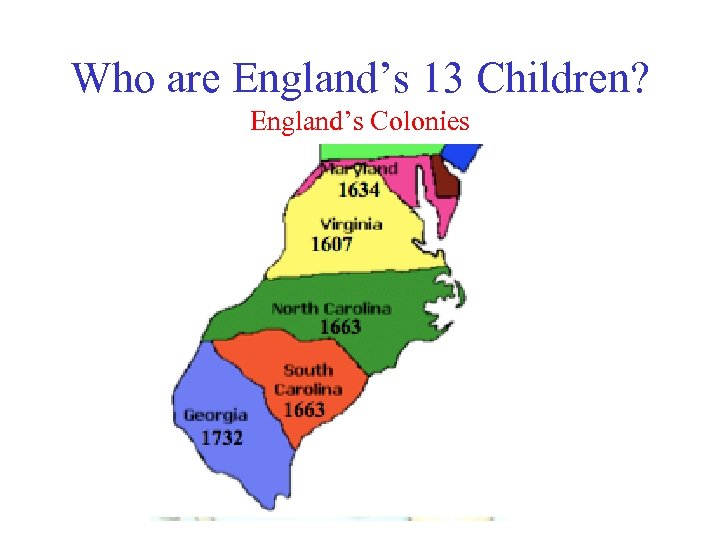
Who are England’s 13 Children? England’s Colonies I) Why do the ppl from England come to America? A) Looking for wealth – gold – cash crops B) Looking for better life – crowded in cities of England – here they can have land farm C) Escaping religious persecution – King did not always let ppl worship as they wanted

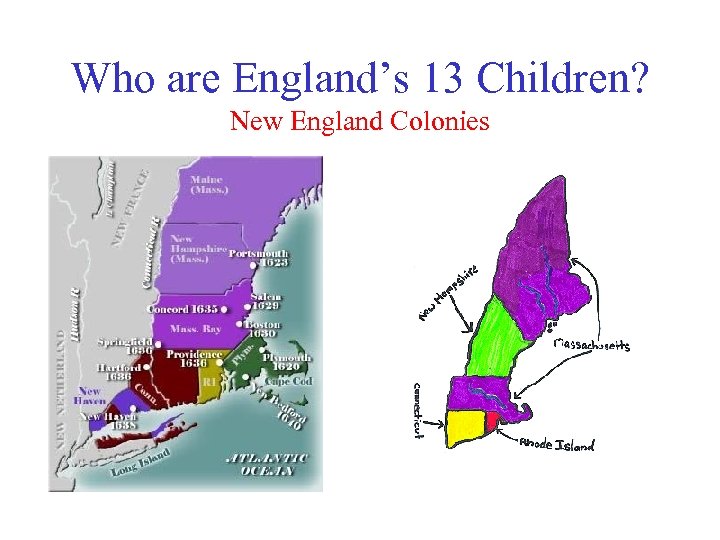
Who are England’s 13 Children? New England Colonies • The 13 Colonies (Notice Maine and Massachusetts are the same colony)

Who are England’s 13 Children? New England Colonies II) New England Colonies (Northeast) Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, New Hampshire A) Massachusetts 1. Pilgrims left England a) Left England to worship God as they wanted (religious reasons) 1)King James was attacking them for believing in their own religion
Who are England’s 13 Children? New England Colonies

Who are England’s 13 Children? New England Colonies 2. Pilgrims ask Virginia Company for land to settle on (April Showers…) a) They travel on the Mayflower 1. 3 month journey 2. 100 men and women 3. Land north of Virginia Company’s land in Plymouth, Massachusetts (History Channel … Deconstructing the Mayflower)

Who are England’s Children? New England Colonies 3. Mayflower Compact a) Agreement made on the Mayflower as to what laws would be when they got off ship – “Power to the People”! 4. Puritans – also left England for religious reasons 5. Puritans mixed religion and gov’t when they passed laws saying ppl had to live by their religion (God’s Will).

Who are England’s Children? New England Colonies 5. Like Jamestown, Pilgrims built a fort at Plymouth, but life is hard a) During the first winter cold and disease killed half the ppl b) Had to steal corn from the Natives c) A Native American named Squanto (spoke English) and helped the Pilgrims with a peace treaty between the Pilgrims and Natives

Who are England’s Children? New England Colonies

Who are England’s Children? New England Colonies d) Taught them to grow three sisters, hunt, fish, and traded for furs e) In the fall the Natives and Pilgrims celebrated their time of peace and harvest with a three-day feast - Thanksgiving

Who are England’s Children? New England Colonies • The First Thanksgiving » »

Who are England’s Children? New England Colonies

Who are England’s Children? New England Colonies » Plymouth Village and Fort

Who are England’s Children? New England Colonies

Who are England’s Children? New England Colonies • Inside the colonist’s homes Bed with curtain keeps cold out

Who are England’s Children? New England Colonies • Inside homes at Plymouth

Who are England’s Children? New England Colonies B) Rhode Island 1. Settled on the basis of religious freedom for Puritans a) disagreed with some of the New England church’s rules b) Believed in religious toleration = allowing ppl to have their own beliefs c) Did not believe the colony’s church and government should be mixed together – should be separate.

Who are England’s Children? New England Colonies d) Roger Williams and Anne Hutchinson started the R. I. colony after being thrown out of Massachusetts for their religious beliefs

November 13 – B Day • Do Now: House of Burgesses • Indentured Servants • Homework: Complete graphic organizer • Write and type (if possible) paragraph

November 13 – B day • • Pass up Homework Notes on Middle Colony SAS William Penn HW Southern Colonies Notes Chart in pairs Go over chart Hand out homework
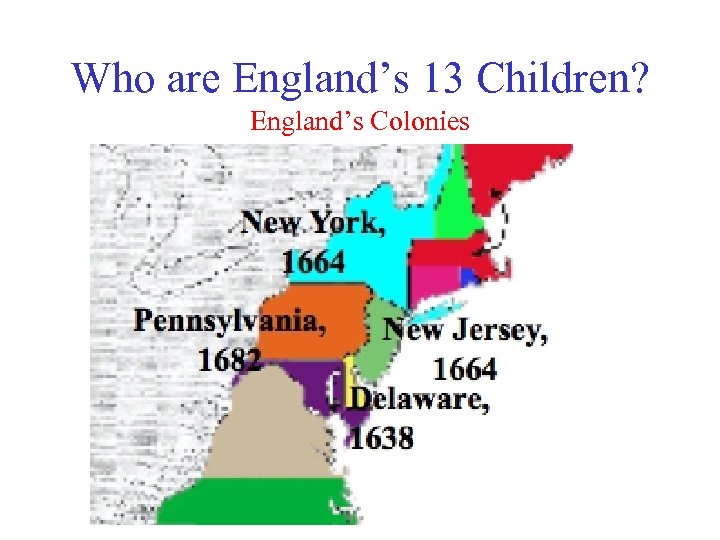
Who are England’s 13 Children? England’s Colonies

Who else came to the colonies? Middle Colonies = The Bread Colonies New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware III) New York – Henry Hudson helped discover A) Dutch (Dutch West India Company) settled Hudson River Valley and NYC 1. Dutch colony named New Netherland a) Governor: Peter Stuyvestant (Old Silvernails – had wooden peg leg w/nails on it) b) New Amsterdam = NYC (bought for $24 from Indians)

Who else came to the colonies? Middle Colonies c) Put up a wall at end of Manhattan Island to protect them from wolves = Wall Street d) Farms and trading were big business. NY Harbor brought ppl and goods from around the world. e) British took colony from Dutch, renamed it New York and added land for the New Jersey colony
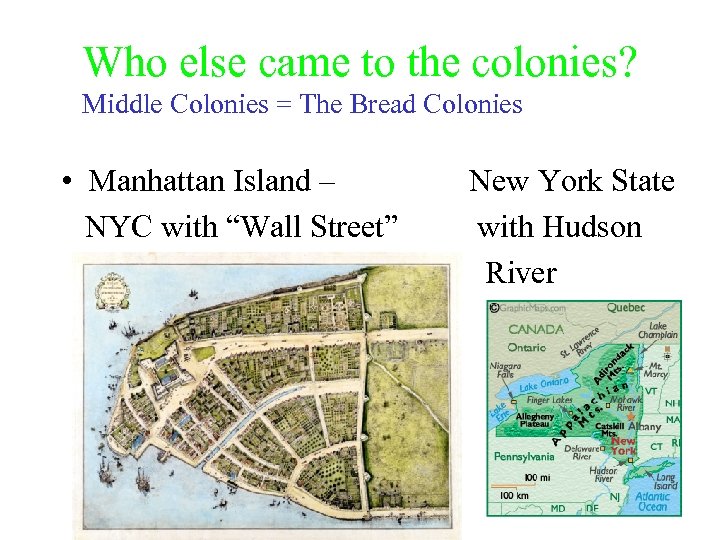
Who else came to the colonies? Middle Colonies = The Bread Colonies • Manhattan Island – NYC with “Wall Street” New York State with Hudson River

Life in the Middle Colonies New York • Throughout all of the colonies, people farmed

Life in the Middle Colonies New York • Philipsburg Manor

Life in the Middle Colonies New York • Philipsburg Manor

Who else came to the colonies? Middle Colonies – The Bread Colonies IV) Pennsylvania and Delaware A) English Quakers settled Pennsylvania 1. Quakers = looking for religious freedom a) did not believe in war –wouldn’t fight for King of England b) William Penn (Quaker) offered his land to them – colony was set up c) Philadelphia set up with no walls or forts because ppl were expected to behave w/ peace –CITY OF BROTHERLY LOVE

Who else came to the colonies? The Middle Colonies – The Bread Colonies * Middle Colonies called: The Bread Colonies A) Immigrants came to farm – GOOD SOIL 1. Came from England, France, Germany, Sweden 2. Grew wheat, rye, oats, corn, indigo (blue dye) – ingredients for making bread 3. Cash crop = sold grain for money
Who are England’s 13 Children? England’s Colonies

Who else came to the colonies? Southern Colonies Maryland, Virginia, No. Carolina, So. Carolina, Georgia V) Maryland 1. Proprietary Colony: Colony owned by businessmen and taxed the settlers a. Owned by Lord Baltimore 1. Allowed religious freedom and toleration to Catholics and Protestants 2. Grew tobacco – required slaves

Who else came to the colonies? Southern Colonies VI) Carolina Colony - Plantations 1. Split into North and South VII) Georgia-Plantations 1. Set up as a place where England’s poor could make a new life-ppl in debt a) not a lot of ppl came VIII) Virginia-Plantations 1. Jamestown/Williamsburg 2. Cash Crops – Tobacco •

3. House of Burgesses – First representative gov’t in the colonies! Followed the British idea of the Magna Carta – limited the king’s power and gave ppl representative government

Williamsburg, Virginia • Colonial Soldiers

Williamsburg, Virginia • Governor’s Palace – Chosen by the King

Williamsburg, Virginia • The Entrance Hall of the Governor’s Palace

Williamsburg, Virginia Colonial Life • Street in Williamsburg with businesses (trades)

Williamsburg, Virginia • Trades (Businesses) Shoemaker Butcher

Williamsburg, Virginia Colonial Life • Brick making

Williamsburg, Virginia • The next time you do not do your homework, you’ll be put in the stocks!

Who else came to the colonies? Southern Colonies IX) Plantations – large farms A) Grew cash crops = grown to be sold 1. Tobacco 2. Indigo – plant used to make blue dye 3. Cotton B) Needed large amount of workers to plant and pick crops C) INDENTURED SERVANTS AND SLAVES

• Southern colonies – about. com

• 13 Colonies Chart • Paragraph for homework

Who else came to the colonies? Southern Colonies 1. Indentured Servants a) most came from Europe b) Plantation owners paid the cost of their trip to America c) workers agreed to work as servants for a number of years

Who else came to the colonies? Southern Colonies 2. Slaves a) permanent workers b) sent from Africa in chains on slave ships c) many died of disease on ships d) legal to sell as property e) gave up their names, had no rights

Slavery • First Passage: Inside Africa to shore where ships were waiting • For weeks, months, sometimes as long as a year, they waited in the dungeons of the slave factories scattered along Africa's western coast. • Out of the roughly 20 million who were taken from their homes and sold into slavery, half didn't complete the journey to the African coast, most of those dying along the way. And the worst was yet to come.

Slavery Middle Passage • The captives were about to embark on the infamous Middle Passage, so called because it was the middle trip of a threepart voyage. The last part was the sale of slave in America.

Slavery Voyage of Death • The African slave boarding the ship had no idea what lay ahead. Africans who had made the Middle Passage to the plantations of the New World did not return to their homeland to tell what happened to those people who suddenly disappeared.

Slavery Voyage of Death • The slaves were branded with hot irons and restrained with shackles. Their "living quarters" was often a deck within the ship that had less than five feet of headroom • an area with little ventilation and, in some cases, not even enough space to place buckets for human waste -- disease spread quickly.

Slavery No Hope! • Faced with the nightmarish conditions of the voyage and the unknown future that lay beyond, many Africans preferred to die. But even the choice of suicide was taken away from these persons. From the captain's point of view, his human cargo was extremely valuable and had to be kept alive and, if possible, uninjured. A slave who tried to starve him or herself was tortured. If torture didn't work, the slave was force fed
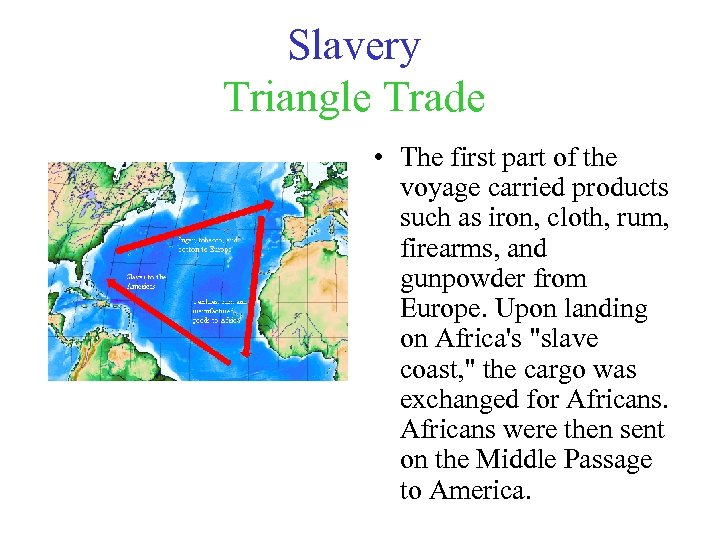
Slavery Triangle Trade • The first part of the voyage carried products such as iron, cloth, rum, firearms, and gunpowder from Europe. Upon landing on Africa's "slave coast, " the cargo was exchanged for Africans were then sent on the Middle Passage to America.
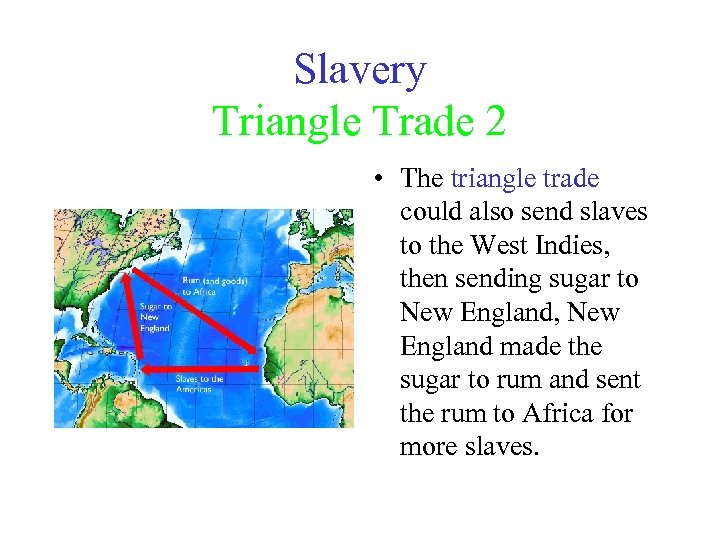
Slavery Triangle Trade 2 • The triangle trade could also send slaves to the West Indies, then sending sugar to New England, New England made the sugar to rum and sent the rum to Africa for more slaves.
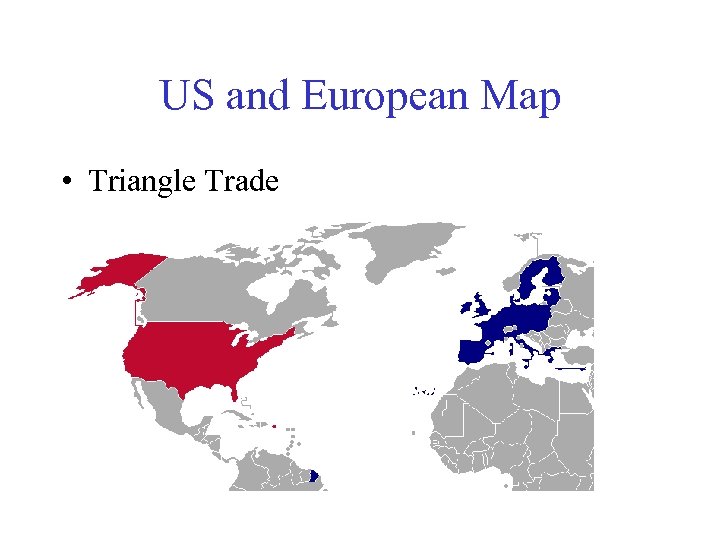
US and European Map • Triangle Trade
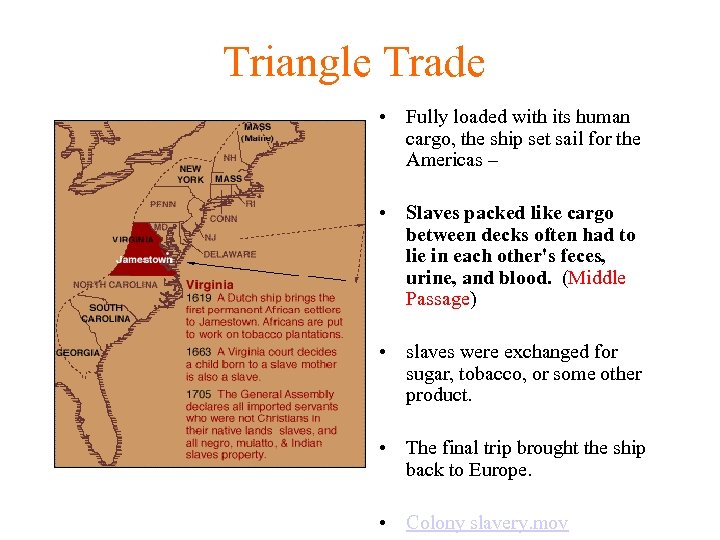
Triangle Trade • Fully loaded with its human cargo, the ship set sail for the Americas – • Slaves packed like cargo between decks often had to lie in each other's feces, urine, and blood. (Middle Passage) • slaves were exchanged for sugar, tobacco, or some other product. • The final trip brought the ship back to Europe. • Colony slavery. mov

Who are England’s 13 Colonies? Review • Why did people come to the colonies? I) Religion (pilgrims) – escape persecution II) Profit – Looking to make money (Virginia Company) – trade or farming – most ppl were farmers III) Get out of England • Crowded • Not as many jobs IV) Hope for a better life – new opportunities – own land V) Slaves – did not come by choice

Who are England’s Children? The Beginnings of a New Government - Democracy A) Democracy and Self-government 1. Democracy – Ppl choose their own leaders 2. Self-government – Ppl rule themselves instead of ruled by a king 3. Held town meetings to discuss ideas

Who are England’s 13 Colonies? Review 4. House of Burgesses – Ppl in Virginia elected representatives to make laws (Legislature) 5. Mayflower Compact – Pilgrims agreed to laws they made for Plymouth 6. America is starting to want to rule itself instead of having England do it

Williamsburg, Virginia • House of Burgesses – Legislature (makes laws)
f8a9430a0789d4f84f60c0a854f887df.ppt