4c0d145c1480cb87517a3b50b742a9f8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40

Novell ZENworks for Servers 3: ® Distributing Novell Application Launcher Applications through Tiered Electronic Distribution Oscar Sanchez www. novell. com Premium Support Engineer Novell, Inc. Oscar_Sanchez@ novell. com Mark Richards Senior Systems Engineer Novell, Inc. Mark_Richards@novell. com

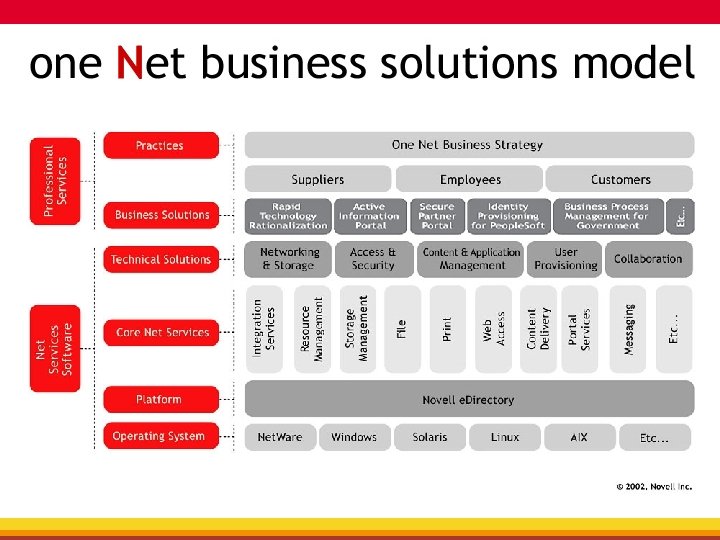
Tiered Electronic Distribution (TED) and Novell Application Launcher (NAL) • Novell vision, mission and one Net model • ZENworks® overview • What is Novell Application Launcher? • What is Tiered Electronic Distribution? • Why do they need each other? • How do you make it work?

Vision…one Net A world where networks of all types—corporate and public, intranets, extranets, and the Internet—work together as one Net and securely connect employees, customers, suppliers, and partners across organizational boundaries Mission To solve complex business and technical challenges with Net business solutions that enable people, processes, and systems to work together and our customers to profit from the opportunities of a networked world

What Is Novell ZENworks? The Novell ZENworks family of products… • Automates and personalizes content and applications to increase productivity for end users and network managers alike • Allows you to minimize costs by reducing redundancies, effectively leveraging your resources and precisely tracking their use
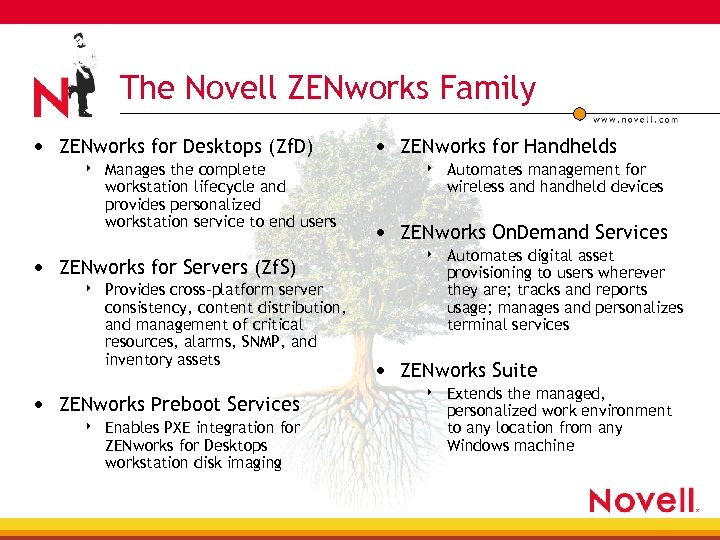
The Novell ZENworks Family • ZENworks for Desktops (Zf. D) 4 Manages the complete workstation lifecycle and provides personalized workstation service to end users • ZENworks for Servers (Zf. S) 4 Provides cross-platform server consistency, content distribution, and management of critical resources, alarms, SNMP, and inventory assets • ZENworks Preboot Services 4 Enables PXE integration for ZENworks for Desktops workstation disk imaging • ZENworks for Handhelds 4 Automates management for wireless and handheld devices • ZENworks On. Demand Services 4 Automates digital asset provisioning to users wherever they are; tracks and reports usage; manages and personalizes terminal services • ZENworks Suite 4 Extends the managed, personalized work environment to any location from any Windows machine

The Golden Triangle of Novell ZENworks for Desktops Three fundamental concepts have made ZENworks for Desktops the industry leader 4 Enabling the Digital Persona 4 Policy-enabled management 4 Managing the complete workstation lifecycle
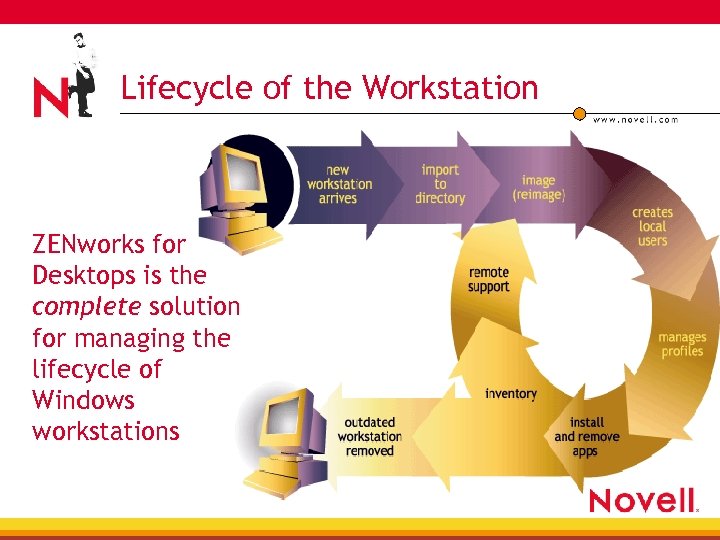
Lifecycle of the Workstation ZENworks for Desktops is the complete solution for managing the lifecycle of Windows workstations
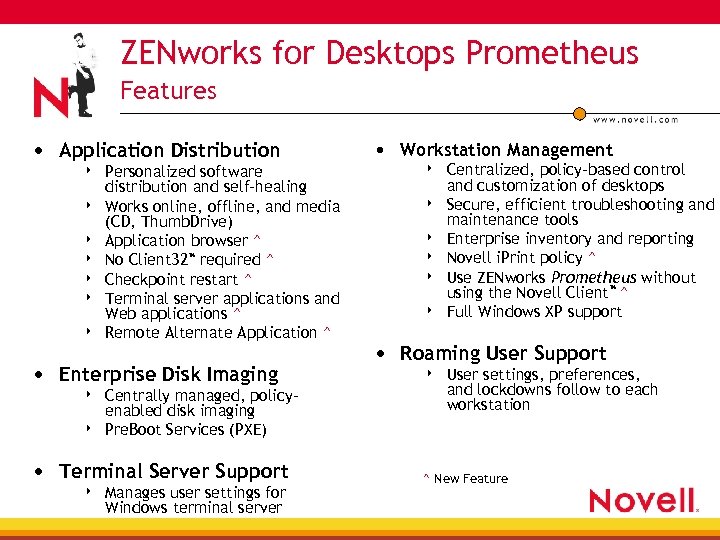
ZENworks for Desktops Prometheus Features • Application Distribution 4 4 4 4 Personalized software distribution and self-healing Works online, offline, and media (CD, Thumb. Drive) Application browser ^ No Client 32™ required ^ Checkpoint restart ^ Terminal server applications and Web applications ^ Remote Alternate Application ^ • Enterprise Disk Imaging 4 4 Centrally managed, policyenabled disk imaging Pre. Boot Services (PXE) • Terminal Server Support 4 Manages user settings for Windows terminal server • Workstation Management 4 4 4 Centralized, policy-based control and customization of desktops Secure, efficient troubleshooting and maintenance tools Enterprise inventory and reporting Novell i. Print policy ^ Use ZENworks Prometheus without using the Novell Client™ ^ Full Windows XP support • Roaming User Support 4 User settings, preferences, and lockdowns follow to each workstation ^ New Feature
The Golden Triangle of Novell ZENworks for Servers Automates 4 Server Policies 4 Server Content Distribution 4 Server and Infrastructure Management

ZENworks for Servers 3 Policy and Distribution Services * Provides software, configuration, and behavioral management system for servers* 4 Allows you to control the versions of software installed on servers throughout the network —Define and enforce a standard configuration on any given set of servers and control the behavior of servers in given situations, such as downing a server, backing up volumes, managing thresholds exceeded, and so on • Tiered Electronic Distribution (TED) 4 NAL Application delivery, data delivery and server policy implementation • Server Policies • Server Software Packages • Web-based Management 4 Plugs into Novell i. Manager web management console *Supported server platforms: Net. Ware® 5. 1 and Net. Ware 6, Windows NT 4. 0 and Windows 2000, Linux (Red Hat 7 and above), and Solaris 8

The Novell Application Launcher • What is the Novell Application Launcher (NAL)? 4 4 4 Component of Zf. D that allows you install applications to Windows desktops Can leverage Windows Installer (MSI) or traditional applications (SETUP. EXE) Supports all Win 32 platforms, including XP • Features 4 4 4 On demand install Lights-out pre-install Disconnected support Application self-healing (online and offline) Source server fail-over Load balancing Closest-on-WAN source sensitivity Application personalization DLL management Checkpoint Restart Remote Alternate Application Rogue Process Management
Tiered Electronic Distribution (TED) • What is TED? 4 Overview 4 TED components 4 Flow through the components 4 What’s new 4 TED features 4 NAL and TED, Why do they need each other? • NAL Application Distribution features
What Is TED? Overview • Tiered Electronic Distribution, or TED, enables you to automatically deploy applications, software updates, system patches, and data files to your enterprise servers without leaving your desk 4 ZENworks for Servers uses TED to automatically distribute software and data files to Net. Ware, Windows NT/2000, Solaris and Linux servers throughout your network and is designed for optimal management efficiency, which allows you can schedule distributions for off-peak hours to minimize the impact on overall network performance 4 Some of these servers host TED components such as distributors and subscribers that are used for more effective software distribution
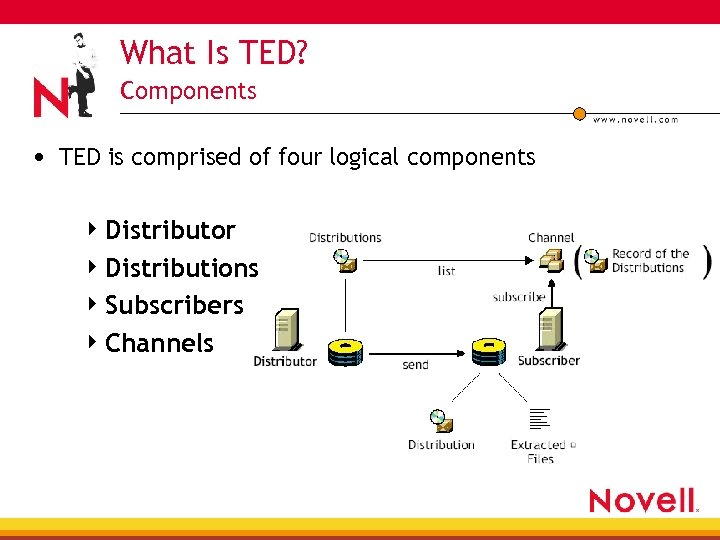
What Is TED? Components • TED is comprised of four logical components 4 Distributor 4 Distributions 4 Subscribers 4 Channels
What Is TED? Components • A Distributor builds a distribution from the information you provide • A Distribution contains a list of data packages or data grouping information Compilation of software and/or files, or a policy package 4 Distribution types 4 • File, FTP, HTTP, RPM*, NAL Application, Policy Package*, Software Package * New
What Is TED? Components • A Subscriber is a server that receives and extracts Distributions 4 Any server where you want to distribute applications, files, or policy packages must be a Subscriber • An External Subscriber is an object that represents a Subscriber in another tree • A Channel contains a list of Distributions associated with it and Subscribers that are subscribed to it
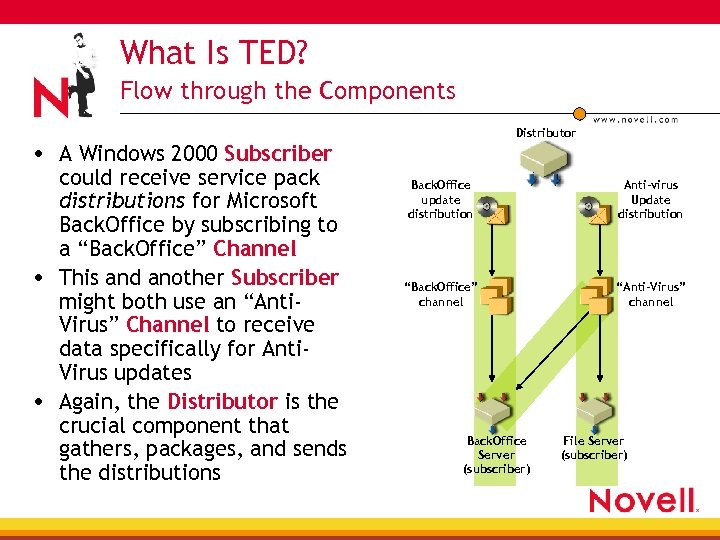
What Is TED? Flow through the Components Distributor • A Windows 2000 Subscriber could receive service pack distributions for Microsoft Back. Office by subscribing to a “Back. Office” Channel • This and another Subscriber might both use an “Anti. Virus” Channel to receive data specifically for Anti. Virus updates • Again, the Distributor is the crucial component that gathers, packages, and sends the distributions Back. Office update distribution Anti-virus Update distribution “Back. Office” channel “Anti-Virus” channel Back. Office Server (subscriber) File Server (subscriber)
What Is New • Supports the following platforms 4 4 Net. Ware 5. 1 and Net. Ware 6 Windows NT 4. 0 and Windows 2000 Linux (Red Hat 7 and above) Solaris 8 • Server Inventory and Remote control 4 Net. Ware, NT/2000 platforms only • TED and Policies will now be referred to as PDS (Policy and Distribution Services)
What Is New TED Enhancements • New TED Startup commands • Distribution patching 4 Removed 4 Send Queue and I/O Rate • New distribution types • Prioritizing distributions • Distribution security • File type distributions • Backwards compatibility with TED 2 • NAL application distribution 4 No more Site Distribution object • • • Windows NT/2000 support Linux/UNIX support New platform restrictions Cluster support DNS and NAT support Downstream schedule control 4 Parents Subscribers • Linking the Gather and Send processes • Distribution space limitation 4 Amount of disk space that you require to be free above the size of any Distribution

What Is New Web-Based Management 4 Zf. S 3 adds web management via Novell i. Manager 4 You can manage • • Distributors Subscribers Distributions Policies
TED Features WAN Optimization Features • Distribution hierarchies (parent subscribers) 4 4 Allows multiple-level distribution Enterprise-to-Region-to-District-to-Site • Compression 4 4 Compresses distributions before sending Uses less bandwidth for larger distributions • Scheduling 4 4 Controls when TED actions occur so data transmission occurs exactly when it is needed, or during off hours to reduce WAN traffic Send stops at the end of the time window and resumes when schedule allows • Checkpoint/Restart 4 Restarts interrupted distributions at the point of failure, does not require a complete resend
TED Features WAN Optimization Features • Throttling 4 On distributors to aggregate outbound flow 4 On subscribers for inbound flow 4 Prevents software distribution from dominating a WAN link and slowing network service 4 I/O Rate • Sending and receiving distributions • You can set the maximum bytes per second 4 Maximum Number of Concurrent Distributions • how many simultaneous distributions the Distributor Agent or Subscriber Agent will send 4 Send Queue • You can prioritize the order distributions are sent – High, medium, or low
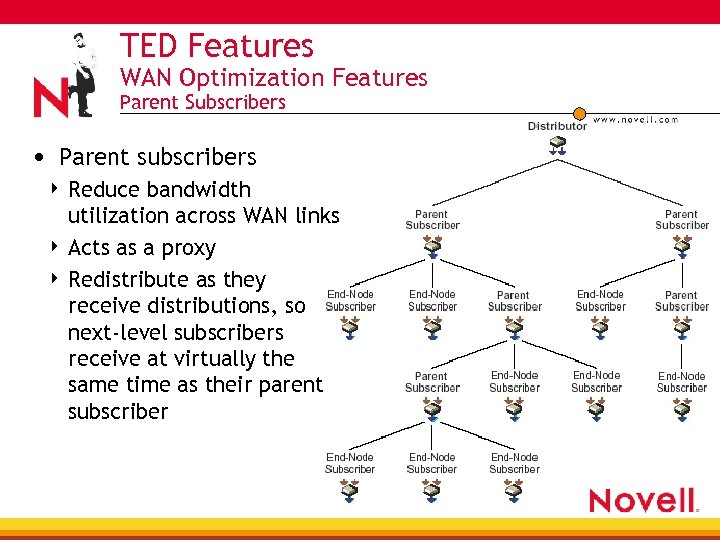
TED Features WAN Optimization Features Parent Subscribers • Parent subscribers Reduce bandwidth utilization across WAN links 4 Acts as a proxy 4 Redistribute as they receive distributions, so next-level subscribers receive at virtually the same time as their parent subscriber 4
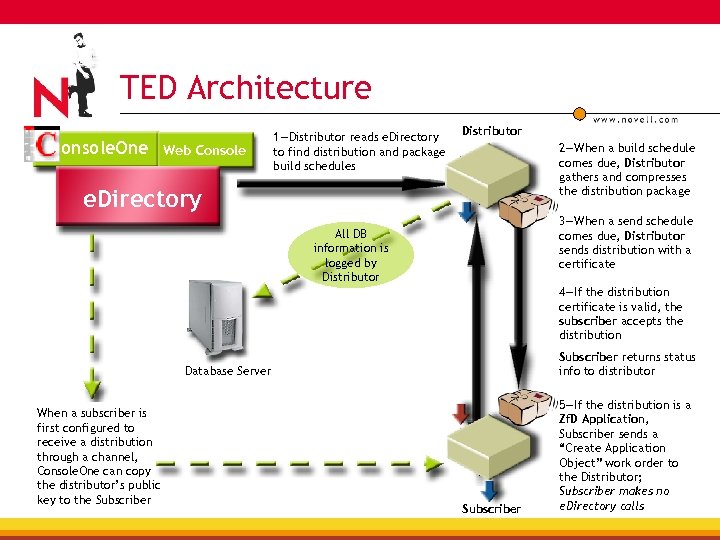
TED Architecture onsole. One Web Console 1—Distributor reads e. Directory to find distribution and package build schedules Distributor 2—When a build schedule comes due, Distributor gathers and compresses the distribution package e. Directory 3—When a send schedule comes due, Distributor sends distribution with a certificate All DB information is logged by Distributor 4—If the distribution certificate is valid, the subscriber accepts the distribution Subscriber returns status info to distributor Database Server When a subscriber is first configured to receive a distribution through a channel, Console. One can copy the distributor’s public key to the Subscriber 5—If the distribution is a Zf. D Application, Subscriber sends a “Create Application Object” work order to the Distributor; Subscriber makes no e. Directory calls
Summary of TED • TED provides a data distribution solution for the enterprise 4 Extensively scalable 4 Multiplatform 4 Extremely WAN-efficient • • • Tiered Secured Compressed Scheduled I/O throttled Resumed by checkpoint restart
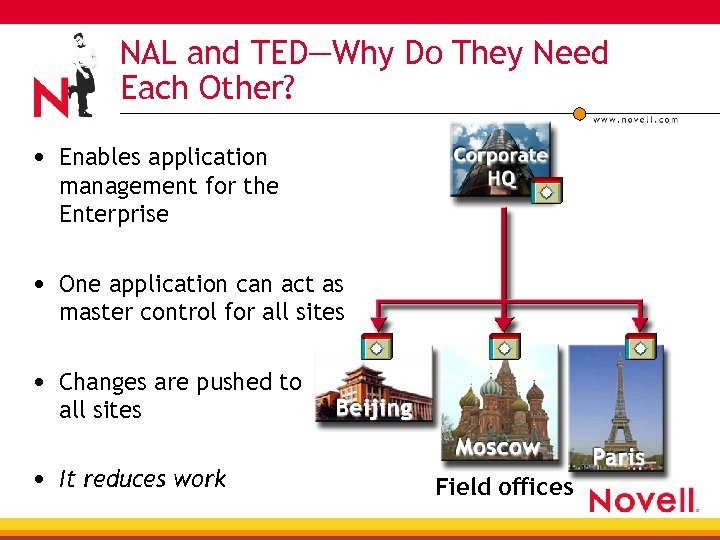
NAL and TED—Why Do They Need Each Other? • Enables application management for the Enterprise • One application can act as master control for all sites • Changes are pushed to all sites • It reduces work Field offices

NAL and TED—Why Do They Need Each Other? • Zf. D can use TED to distribute application objects to other locations in the same tree or other trees—the distribution includes copying the original files associated with the applications to the appropriate server locations, where they can be used to service user groups and workstation groups associated with the distributed application objects • The Desktop Application Distribution Wizard configures your Distribution 4 4 Determining the destination’s tree structure, and/or whether to maintain the associations between user/workstation groups or containers and the applications, and/or whether to have automated load balancing or fault tolerance Selects your applications and determines your file copying paths

NAL and TED—Why Do They Need Each Other? • Once you have created the Desktop Application Distribution and it has been built on the Distributor, sent through a Channel, and extracted on the Subscriber, objects in your user groups, workstation groups, and containers at the destination location can use the distributed applications through Zf. D • If the target destination does not have the groups or containers to be replicated, the wizard will help the distribution create them
NAL and TED: Application Distribution Agent • Totally rewritten code for the TED/NAL agent new • No Site Distribution Objects (SDO) • • In Zf. S 2, This object was responsible for holding configuration data that was used in constructing and updating any applications that were created during the TED distribution process Each SDO had a “location list” of which sites would receive the distributed application, that you manually had to update

NAL and TED: Application Distribution Agent • The Application Distribution Agent can • • • Distribute an application to any site by associating the target Subscriber to the distribution Auto associate the target application object to OUs and groups, if the distribution has been defined to do so Create OUs and groups in the target site based on the distribution • Application Linked Site lists support* • Allows users who travel from site to have similar local access to their applications * New feature to Zf. D Prometheus
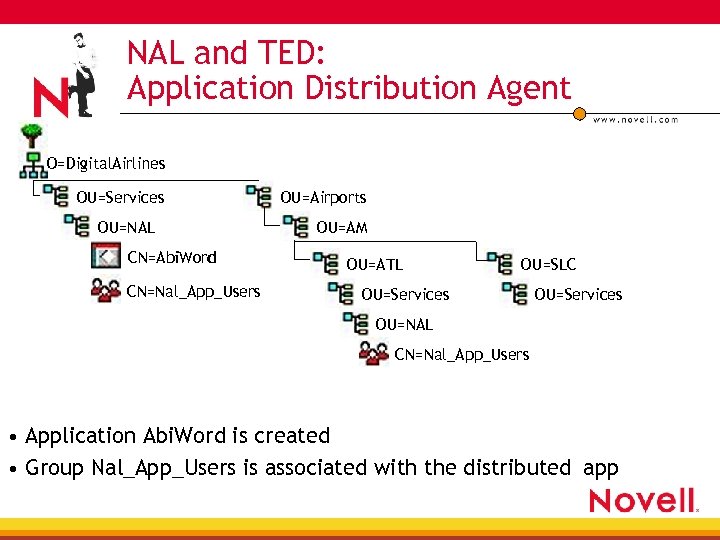
NAL and TED: Application Distribution Agent O=Digital. Airlines OU=Services OU=NAL CN=Abi. Word CN=Nal_App_Users OU=Airports OU=AM OU=ATL OU=SLC OU=Services OU=NAL CN=Nal_App_Users • Application Abi. Word is created • Group Nal_App_Users is associated with the distributed app

NAL and TED: Application Distribution Agent How did it do that? You can configure your associations during the desktop application distribution wizard setup Maintain Associations • Maintains the associations established in the source tree between the distributed applications and the trusted user/workstation groups and containers • This is done by replicating the associated groups or containers at the target location if they do not exist
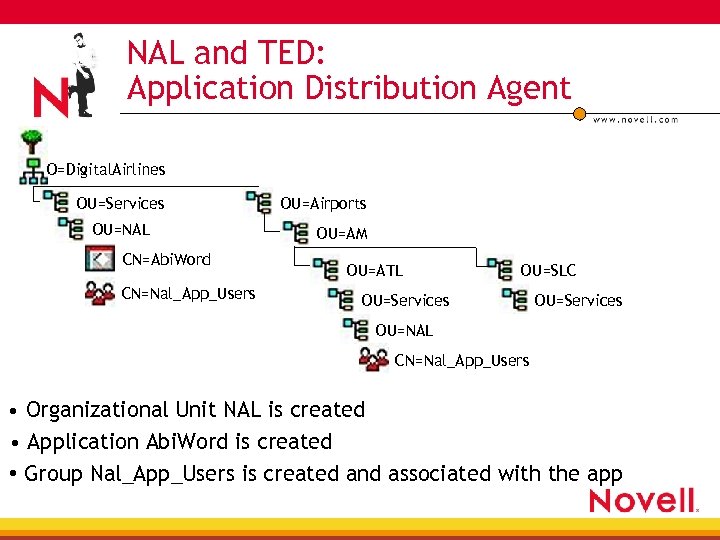
NAL and TED: Application Distribution Agent O=Digital. Airlines OU=Services OU=NAL CN=Abi. Word CN=Nal_App_Users OU=Airports OU=AM OU=ATL OU=SLC OU=Services OU=NAL CN=Nal_App_Users • Organizational Unit NAL is created • Application Abi. Word is created • Group Nal_App_Users is created and associated with the app

NAL and TED: Application Distribution Agent How did it do that? You can configure the target directory structure during the desktop application distribution wizard setup Maintain Source Tree Structure • Duplicates the source tree’s structure at the destination’s location for placing the Zf. D application objects

NAL and TED: Linked Site Lists Feature Using the Linking Site Lists feature allows users who travel from site to have similar local access to their applications Example 1. You create the App 1 application object at Site. A 2. You replicate App 1 to Site. B and Site. C 3. You click Link Up Site Lists on the Distributions tab in the App 1 application object’s properties 4. Users who had access to App 1 at Site. A will also have the same local access to App 1 when they travel to Site. B or Site. C Therefore, no matter which site the user is visiting, the application will be available in the same way that they are used to

Making It Happen (Step-by-Step) • The part we won’t show 1. Install Zf. D Prometheus 2. Create new applications, or use previous Zf. Dx applications 3. Install Zf. S 3 Policy and Distribution Services to create distributor— subscriber hierarchies • The part we’ll show 1. Creating TED Channels 2. Creating TED distributions a. Desktop Application distributions 3. Configure distribution hierarchies 4. Configure Site Link Lists


Summary • The combination of Novell Application Launcher (NAL) and Tiered Electronic Distribution (TED) allows you to minimize costs by reducing redundancies, effectively leveraging your existing resources and precisely tracking their use in the enterprise

4c0d145c1480cb87517a3b50b742a9f8.ppt