6b11594cb785b0a7c09721cc590b53a1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 NOVEL CURRICULA AND TOOLS FOR JAVA IN CS 1 COURSES Glenn D. Blank Computer Science & Engineering Department Lehigh University, Bethlehem, PA, USA With support from the National Science Foundation (Grants No. EIA-0087977 and 0624553) and the Pennsylvania Infrastructure Technology Alliance
NOVEL CURRICULA AND TOOLS FOR JAVA IN CS 1 COURSES Glenn D. Blank Computer Science & Engineering Department Lehigh University, Bethlehem, PA, USA With support from the National Science Foundation (Grants No. EIA-0087977 and 0624553) and the Pennsylvania Infrastructure Technology Alliance
 Outline l A “design-first” approach to the first CS course l l l Elaboration of “objects-first” approach Multimedia introducing classes, methods & attributes Eclipse, Lehigh. UML and Dr. Java tools Intelligent Tutoring System (ITS) support Evaluation results Widening the pipeline of women and minorities from middle school to college
Outline l A “design-first” approach to the first CS course l l l Elaboration of “objects-first” approach Multimedia introducing classes, methods & attributes Eclipse, Lehigh. UML and Dr. Java tools Intelligent Tutoring System (ITS) support Evaluation results Widening the pipeline of women and minorities from middle school to college
 Who’s on first? From syntax to objects to design § § Ongoing debate about how to introduce object-oriented concepts to novices Syntax-driven approach (traditional): § § Objects-first approach § § § Typically starts with “Hello, World” then arithmetic Starts by manipulating classes, objects and methods But objects-first textbooks still tend to emphasize coding and syntax rather than “object think” Design-first approach: § § First learn how to solve a problem Novices need to see the big picture: § § Software development is more than just coding It’s understanding a customer’s problem and designing a solution
Who’s on first? From syntax to objects to design § § Ongoing debate about how to introduce object-oriented concepts to novices Syntax-driven approach (traditional): § § Objects-first approach § § § Typically starts with “Hello, World” then arithmetic Starts by manipulating classes, objects and methods But objects-first textbooks still tend to emphasize coding and syntax rather than “object think” Design-first approach: § § First learn how to solve a problem Novices need to see the big picture: § § Software development is more than just coding It’s understanding a customer’s problem and designing a solution
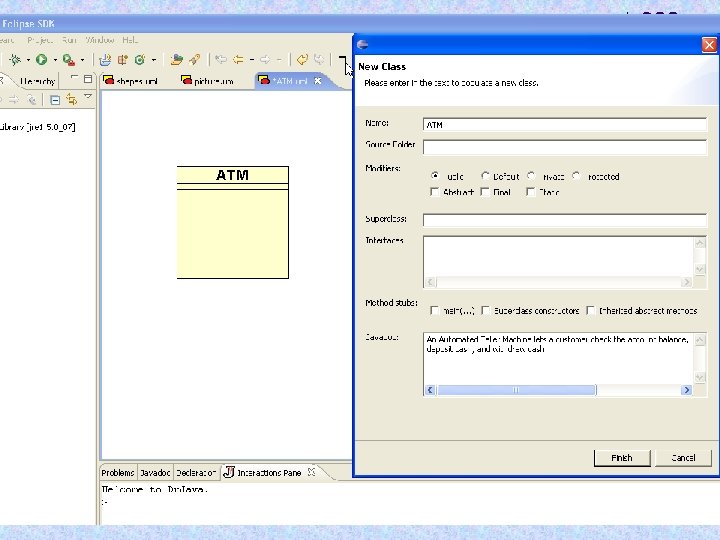
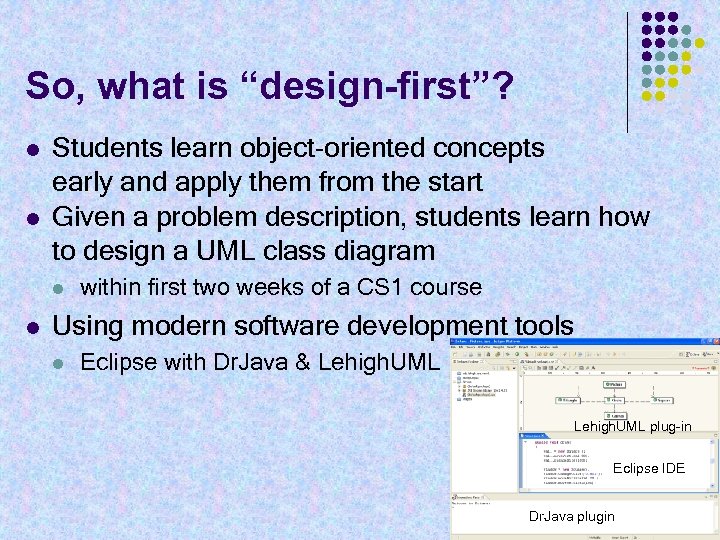 So, what is “design-first”? l l Students learn object-oriented concepts early and apply them from the start Given a problem description, students learn how to design a UML class diagram l l within first two weeks of a CS 1 course Using modern software development tools l Eclipse with Dr. Java & Lehigh. UML plug-in Eclipse IDE Dr. Java plugin
So, what is “design-first”? l l Students learn object-oriented concepts early and apply them from the start Given a problem description, students learn how to design a UML class diagram l l within first two weeks of a CS 1 course Using modern software development tools l Eclipse with Dr. Java & Lehigh. UML plug-in Eclipse IDE Dr. Java plugin
 Four easy lessons 1. “Big picture of software development” l l 2. Objects and classes l 3. Multimedia lesson (preferably in lab, 90 minutes) From problem description to class diagram l 4. Compare building a house to constructing software Discussion and small group work with handout (an hour) Step by step procedure based on OO design principles Design a class, with ITS help l Lab exercise, takes about 90 minutes
Four easy lessons 1. “Big picture of software development” l l 2. Objects and classes l 3. Multimedia lesson (preferably in lab, 90 minutes) From problem description to class diagram l 4. Compare building a house to constructing software Discussion and small group work with handout (an hour) Step by step procedure based on OO design principles Design a class, with ITS help l Lab exercise, takes about 90 minutes
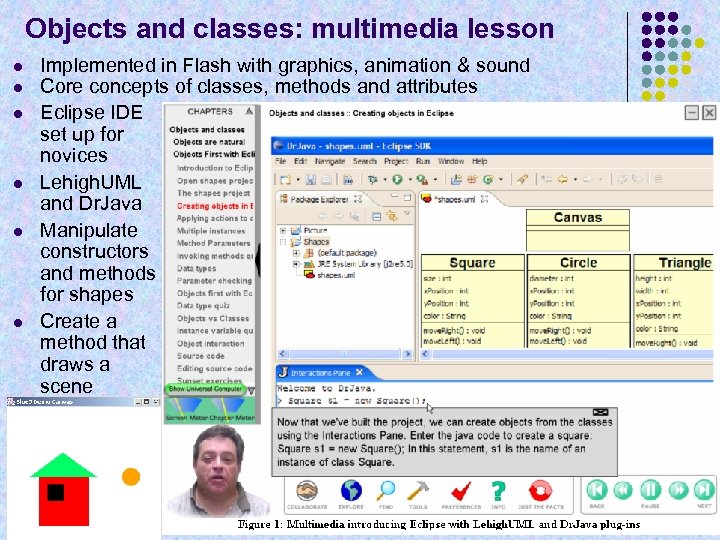 Objects and classes: multimedia lesson l l l Implemented in Flash with graphics, animation & sound Core concepts of classes, methods and attributes Eclipse IDE set up for novices Lehigh. UML and Dr. Java Manipulate constructors and methods for shapes Create a method that draws a scene
Objects and classes: multimedia lesson l l l Implemented in Flash with graphics, animation & sound Core concepts of classes, methods and attributes Eclipse IDE set up for novices Lehigh. UML and Dr. Java Manipulate constructors and methods for shapes Create a method that draws a scene
 Demo the multimedia l l l Plug in a head set for sound Start Microsoft Internet Explorer http: //cimel. cse. lehigh. edu login: evb 209 password: beit*8 The Universal Computer – breadth-first intro to Computer Science (with a textbook: see www. cse. lehigh. edu/~glennb/um) Design First with Java: Objects and Classes
Demo the multimedia l l l Plug in a head set for sound Start Microsoft Internet Explorer http: //cimel. cse. lehigh. edu login: evb 209 password: beit*8 The Universal Computer – breadth-first intro to Computer Science (with a textbook: see www. cse. lehigh. edu/~glennb/um) Design First with Java: Objects and Classes
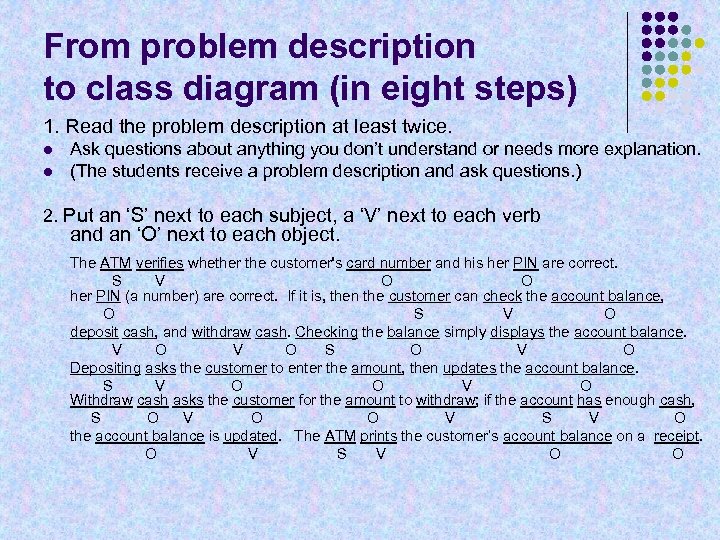 From problem description to class diagram (in eight steps) 1. Read the problem description at least twice. l l Ask questions about anything you don’t understand or needs more explanation. (The students receive a problem description and ask questions. ) 2. Put an ‘S’ next to each subject, a ‘V’ next to each verb and an ‘O’ next to each object. The ATM verifies whether the customer's card number and his her PIN are correct. S V O O her PIN (a number) are correct. If it is, then the customer can check the account balance, O S V O deposit cash, and withdraw cash. Checking the balance simply displays the account balance. V O S O V O Depositing asks the customer to enter the amount, then updates the account balance. S V O O V O Withdraw cash asks the customer for the amount to withdraw; if the account has enough cash, S O V O O V S V O the account balance is updated. The ATM prints the customer’s account balance on a receipt. O V S V O O
From problem description to class diagram (in eight steps) 1. Read the problem description at least twice. l l Ask questions about anything you don’t understand or needs more explanation. (The students receive a problem description and ask questions. ) 2. Put an ‘S’ next to each subject, a ‘V’ next to each verb and an ‘O’ next to each object. The ATM verifies whether the customer's card number and his her PIN are correct. S V O O her PIN (a number) are correct. If it is, then the customer can check the account balance, O S V O deposit cash, and withdraw cash. Checking the balance simply displays the account balance. V O S O V O Depositing asks the customer to enter the amount, then updates the account balance. S V O O V O Withdraw cash asks the customer for the amount to withdraw; if the account has enough cash, S O V O O V S V O the account balance is updated. The ATM prints the customer’s account balance on a receipt. O V S V O O
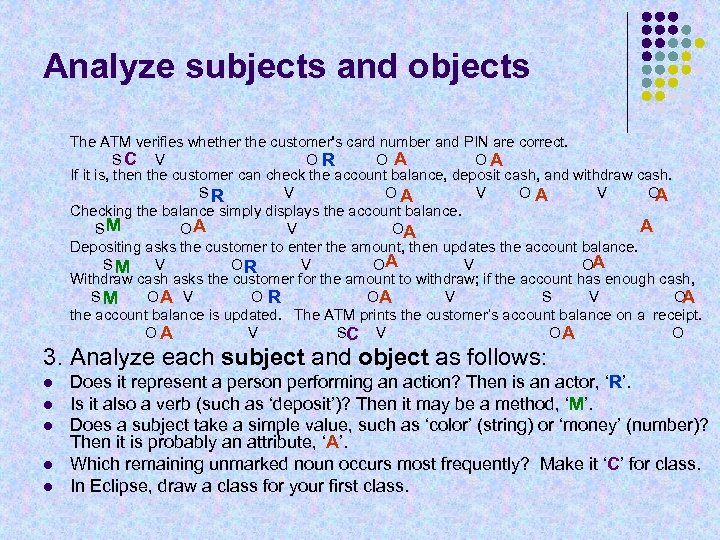 Analyze subjects and objects The ATM verifies whether the customer's card number and PIN are correct. SC V OR OA OA If it is, then the customer can check the account balance, deposit cash, and withdraw cash. SR V OA V O A Checking the balance simply displays the account balance. A SM OA V OA Depositing asks the customer to enter the amount, then updates the account balance. SM V OR V OA Withdraw cash asks the customer for the amount to withdraw; if the account has enough cash, SM OA V OR OA V S V O A the account balance is updated. The ATM prints the customer’s account balance on a receipt. OA V SC V OA O 3. Analyze each subject and object as follows: l l l Does it represent a person performing an action? Then is an actor, ‘R’. Is it also a verb (such as ‘deposit’)? Then it may be a method, ‘M’. Does a subject take a simple value, such as ‘color’ (string) or ‘money’ (number)? Then it is probably an attribute, ‘A’. Which remaining unmarked noun occurs most frequently? Make it ‘C’ for class. In Eclipse, draw a class for your first class.
Analyze subjects and objects The ATM verifies whether the customer's card number and PIN are correct. SC V OR OA OA If it is, then the customer can check the account balance, deposit cash, and withdraw cash. SR V OA V O A Checking the balance simply displays the account balance. A SM OA V OA Depositing asks the customer to enter the amount, then updates the account balance. SM V OR V OA Withdraw cash asks the customer for the amount to withdraw; if the account has enough cash, SM OA V OR OA V S V O A the account balance is updated. The ATM prints the customer’s account balance on a receipt. OA V SC V OA O 3. Analyze each subject and object as follows: l l l Does it represent a person performing an action? Then is an actor, ‘R’. Is it also a verb (such as ‘deposit’)? Then it may be a method, ‘M’. Does a subject take a simple value, such as ‘color’ (string) or ‘money’ (number)? Then it is probably an attribute, ‘A’. Which remaining unmarked noun occurs most frequently? Make it ‘C’ for class. In Eclipse, draw a class for your first class.
 Analyze methods and attributes 4. If a verb has a non-actor object it’s a method, M 5. Distinguish attributes, A, and parameters, P: l If it doesn’t distinguish instances of a class or store information about objects, it’s probably a parameter, not an attribute l Add attributes to a class in the UML class diagram Add methods in the class diagram While adding methods, include the parameters See the return type of your methods: l l l l “get” methods take the type of the attribute returned “set” methods take “void” return type compute methods take the type of the computed value Methods that answer true/false questions take boolean type Constructor(s)
Analyze methods and attributes 4. If a verb has a non-actor object it’s a method, M 5. Distinguish attributes, A, and parameters, P: l If it doesn’t distinguish instances of a class or store information about objects, it’s probably a parameter, not an attribute l Add attributes to a class in the UML class diagram Add methods in the class diagram While adding methods, include the parameters See the return type of your methods: l l l l “get” methods take the type of the attribute returned “set” methods take “void” return type compute methods take the type of the computed value Methods that answer true/false questions take boolean type Constructor(s)
 Any more classes? 6. If any remaining classes has no attributes, it’s probably an attribute of another class 7. Otherwise, add another class to the diagram and go back to step 4 (analyze its methods and attributes) 8. Draw association links between the classes Check your design to make sure it makes sense!
Any more classes? 6. If any remaining classes has no attributes, it’s probably an attribute of another class 7. Otherwise, add another class to the diagram and go back to step 4 (analyze its methods and attributes) 8. Draw association links between the classes Check your design to make sure it makes sense!
 Eclipse setup for novices l Eclipse l l l l Dr. Java plug-in (www. drjava. org) l l l Open source, so it’s free! Widely used in academia and industry Students learn one IDE; learn features as needed Good error messages and syntax support Caveat: it’s complicated for novices to set up and learn! Multimedia explains how to set it up and get started using it Interprets Java expressions from compiled code Supports test-driven programming Lehigh. UML plug-in l l l Students enter class diagram Generates code stubs for class automatically Instead of syntax, students focus on design
Eclipse setup for novices l Eclipse l l l l Dr. Java plug-in (www. drjava. org) l l l Open source, so it’s free! Widely used in academia and industry Students learn one IDE; learn features as needed Good error messages and syntax support Caveat: it’s complicated for novices to set up and learn! Multimedia explains how to set it up and get started using it Interprets Java expressions from compiled code Supports test-driven programming Lehigh. UML plug-in l l l Students enter class diagram Generates code stubs for class automatically Instead of syntax, students focus on design
 Eclipse for novices demo l l Eclipse: incremental compiler, debugger, plugins Dr. Java interprets any Java expression from byte -compiled code l l Lehigh. UML creates UML class diagrams l l l Supports test-driven development of methods With or without intelligent tutoring support Right click on class diagram > Properties for details Check it out: l l Login as cscc 1, cscc 2, … cscc 15 Login connects to a server which provides intelligent tutoring system support
Eclipse for novices demo l l Eclipse: incremental compiler, debugger, plugins Dr. Java interprets any Java expression from byte -compiled code l l Lehigh. UML creates UML class diagrams l l l Supports test-driven development of methods With or without intelligent tutoring support Right click on class diagram > Properties for details Check it out: l l Login as cscc 1, cscc 2, … cscc 15 Login connects to a server which provides intelligent tutoring system support
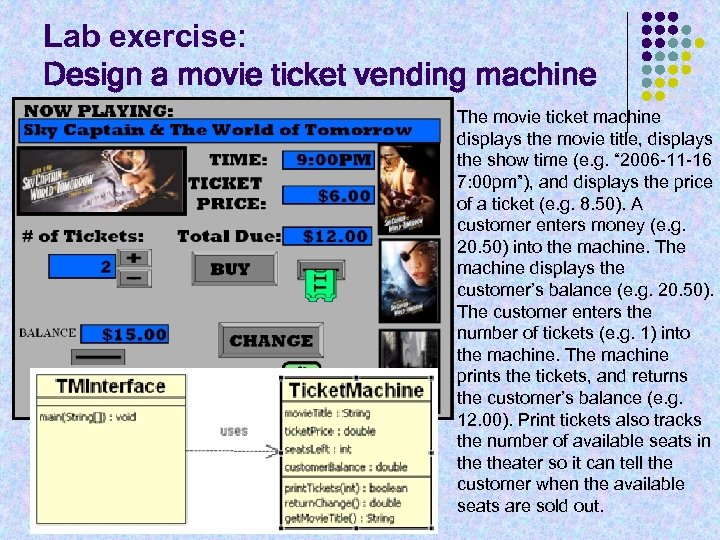 Lab exercise: Design a movie ticket vending machine The movie ticket machine displays the movie title, displays the show time (e. g. “ 2006 -11 -16 7: 00 pm”), and displays the price of a ticket (e. g. 8. 50). A customer enters money (e. g. 20. 50) into the machine. The machine displays the customer’s balance (e. g. 20. 50). The customer enters the number of tickets (e. g. 1) into the machine. The machine prints the tickets, and returns the customer’s balance (e. g. 12. 00). Print tickets also tracks the number of available seats in theater so it can tell the customer when the available seats are sold out.
Lab exercise: Design a movie ticket vending machine The movie ticket machine displays the movie title, displays the show time (e. g. “ 2006 -11 -16 7: 00 pm”), and displays the price of a ticket (e. g. 8. 50). A customer enters money (e. g. 20. 50) into the machine. The machine displays the customer’s balance (e. g. 20. 50). The customer enters the number of tickets (e. g. 1) into the machine. The machine prints the tickets, and returns the customer’s balance (e. g. 12. 00). Print tickets also tracks the number of available seats in theater so it can tell the customer when the available seats are sold out.
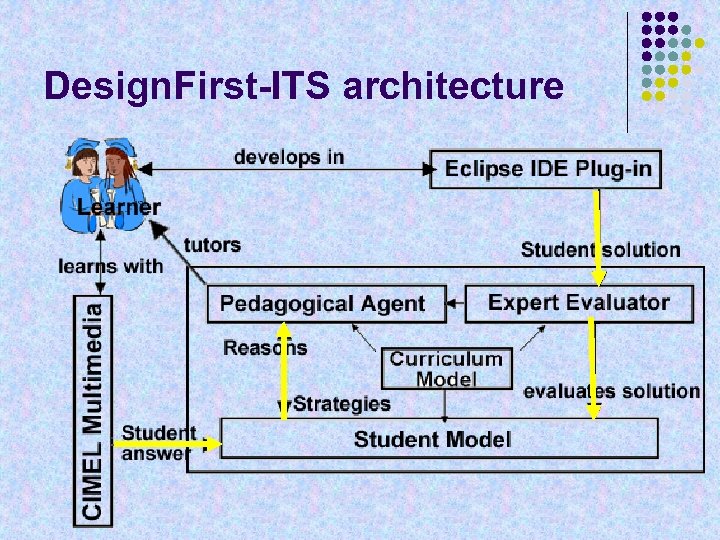 Design. First-ITS architecture
Design. First-ITS architecture
 Expert Evaluator – Sally Moritz § Interprets each step of a student’s solution § § Allows variations from expert solutions § § § Matches student step with pieces of expert solutions Applies concepts in Curriculum Information Network Produces info packets for rest of ITS Matches synonyms and abbreviations An attribute in expert solution can also be defined as a class (e. g. class “Time” with Ticket. Machine’s attribute show. Time) “Unknown” elements (can’t be matched to anything in problem description or solution) are the most problematic § Pedagogical advisor encourages student to use terms related to the problem description
Expert Evaluator – Sally Moritz § Interprets each step of a student’s solution § § Allows variations from expert solutions § § § Matches student step with pieces of expert solutions Applies concepts in Curriculum Information Network Produces info packets for rest of ITS Matches synonyms and abbreviations An attribute in expert solution can also be defined as a class (e. g. class “Time” with Ticket. Machine’s attribute show. Time) “Unknown” elements (can’t be matched to anything in problem description or solution) are the most problematic § Pedagogical advisor encourages student to use terms related to the problem description
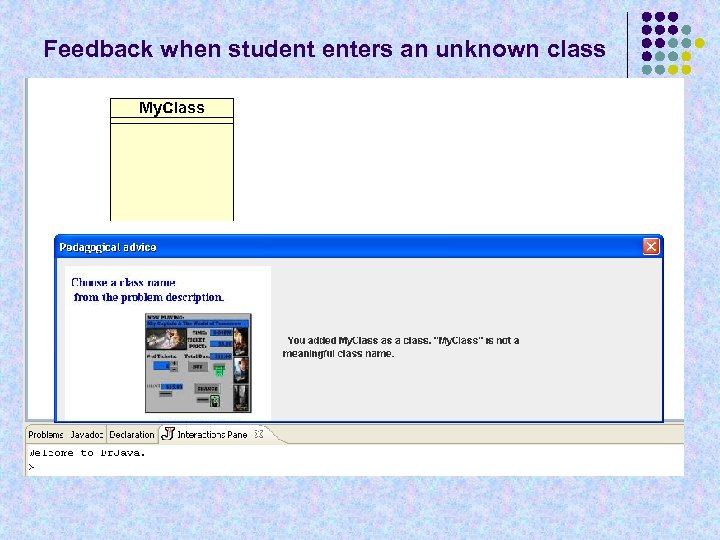 Feedback when student enters an unknown class
Feedback when student enters an unknown class
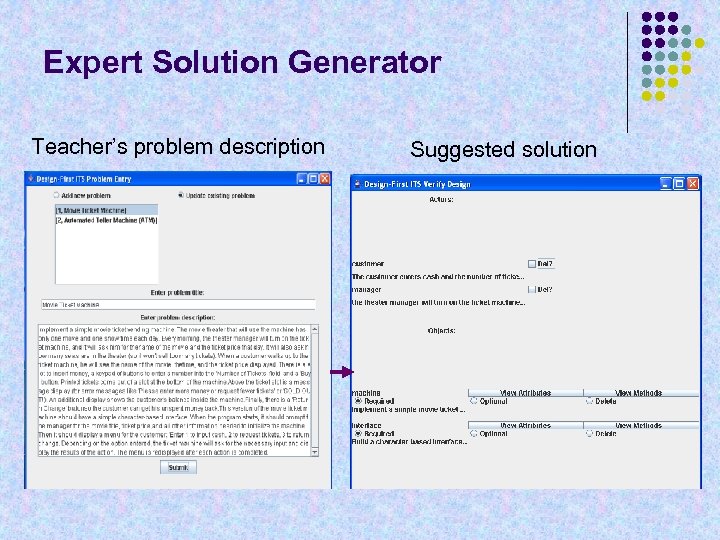 Expert Solution Generator Teacher’s problem description Suggested solution
Expert Solution Generator Teacher’s problem description Suggested solution
 Expert Solution Generator § Generates multiple possible “expert” solutions § § § Analyzes natural language problem description Algorithm similar to what we now teach novices Uses Monty. Lingua NL parser to tag parts of speech
Expert Solution Generator § Generates multiple possible “expert” solutions § § § Analyzes natural language problem description Algorithm similar to what we now teach novices Uses Monty. Lingua NL parser to tag parts of speech
 Student Model – Fang Wei Challenges: l OO design requires understanding of concepts (not just procedural rules) l l Student works in an open-ended environment l l l E. g. , class, method, attribute, data type, etc. Concepts depend on prerequisites E. g. , attribute vs. parameter attribute, parameter Lehigh. UML plug-in provides some scaffolding Students learn how to apply concepts in design Limited time for updating the Student Model l l EE+SM+PA must respond in real student time Bayesian networks can take exponential time
Student Model – Fang Wei Challenges: l OO design requires understanding of concepts (not just procedural rules) l l Student works in an open-ended environment l l l E. g. , class, method, attribute, data type, etc. Concepts depend on prerequisites E. g. , attribute vs. parameter attribute, parameter Lehigh. UML plug-in provides some scaffolding Students learn how to apply concepts in design Limited time for updating the Student Model l l EE+SM+PA must respond in real student time Bayesian networks can take exponential time
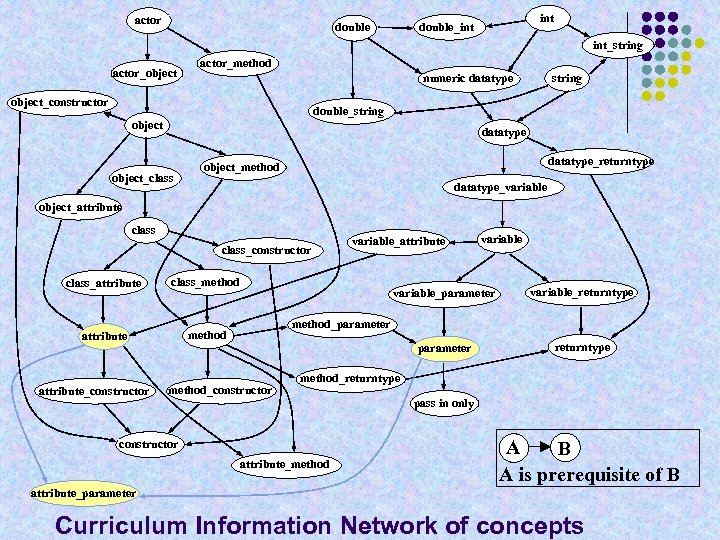 actor int double_int double int_string actor_object actor_method string numeric datatype object_constructor double_string object datatype object_class datatype_returntype object_method datatype_variable object_attribute class_constructor class_attribute class_method attribute method variable_attribute_constructor variable_parameter variable_returntype parameter returntype method_parameter method_constructor method_returntype constructor attribute_method pass in only A B A is prerequisite of B attribute_parameter Curriculum Information Network of concepts
actor int double_int double int_string actor_object actor_method string numeric datatype object_constructor double_string object datatype object_class datatype_returntype object_method datatype_variable object_attribute class_constructor class_attribute class_method attribute method variable_attribute_constructor variable_parameter variable_returntype parameter returntype method_parameter method_constructor method_returntype constructor attribute_method pass in only A B A is prerequisite of B attribute_parameter Curriculum Information Network of concepts
 Two kinds of concepts (KU) l l Unique concept, such as attribute or parameter Relationship concept, such as attribute_parameter Relationships emerge because of student confusions between concepts E. g. , student defines movie. Title as a parameter when he has already defined movie. Title as an attribute
Two kinds of concepts (KU) l l Unique concept, such as attribute or parameter Relationship concept, such as attribute_parameter Relationships emerge because of student confusions between concepts E. g. , student defines movie. Title as a parameter when he has already defined movie. Title as an attribute
 Two kinds of concepts (KU) l l Unique concept, such as attribute or parameter Relationship concept, such as attribute_parameter Relationships emerge because of student confusions between concepts E. g. , student defines movie. Title as a parameter when he has already defined movie. Title as an attribute
Two kinds of concepts (KU) l l Unique concept, such as attribute or parameter Relationship concept, such as attribute_parameter Relationships emerge because of student confusions between concepts E. g. , student defines movie. Title as a parameter when he has already defined movie. Title as an attribute
 Prerequisite relationships l Prerequisite is relationship between concepts or knowledge units: l l l The concepts a learner needs to understand before understanding a concept E. g. , one needs to under int and double in order to understand numeric_datatype Relationship concepts are prerequisites of unique concepts and vice versa l l E. g. , class_constructor -> constructor Understanding constructor doesn’t imply understanding of class, just how to define a constructor for a class
Prerequisite relationships l Prerequisite is relationship between concepts or knowledge units: l l l The concepts a learner needs to understand before understanding a concept E. g. , one needs to under int and double in order to understand numeric_datatype Relationship concepts are prerequisites of unique concepts and vice versa l l E. g. , class_constructor -> constructor Understanding constructor doesn’t imply understanding of class, just how to define a constructor for a class
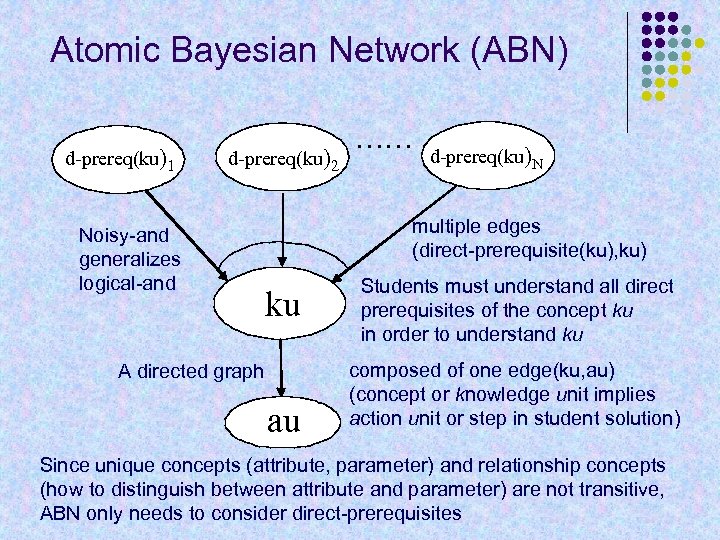 Atomic Bayesian Network (ABN) d-prereq(ku)1 d-prereq(ku)2 Noisy-and generalizes logical-and …… d-prereq(ku)N multiple edges (direct-prerequisite(ku), ku) ku A directed graph au Students must understand all direct prerequisites of the concept ku in order to understand ku composed of one edge(ku, au) (concept or knowledge unit implies action unit or step in student solution) Since unique concepts (attribute, parameter) and relationship concepts (how to distinguish between attribute and parameter) are not transitive, ABN only needs to consider direct-prerequisites
Atomic Bayesian Network (ABN) d-prereq(ku)1 d-prereq(ku)2 Noisy-and generalizes logical-and …… d-prereq(ku)N multiple edges (direct-prerequisite(ku), ku) ku A directed graph au Students must understand all direct prerequisites of the concept ku in order to understand ku composed of one edge(ku, au) (concept or knowledge unit implies action unit or step in student solution) Since unique concepts (attribute, parameter) and relationship concepts (how to distinguish between attribute and parameter) are not transitive, ABN only needs to consider direct-prerequisites
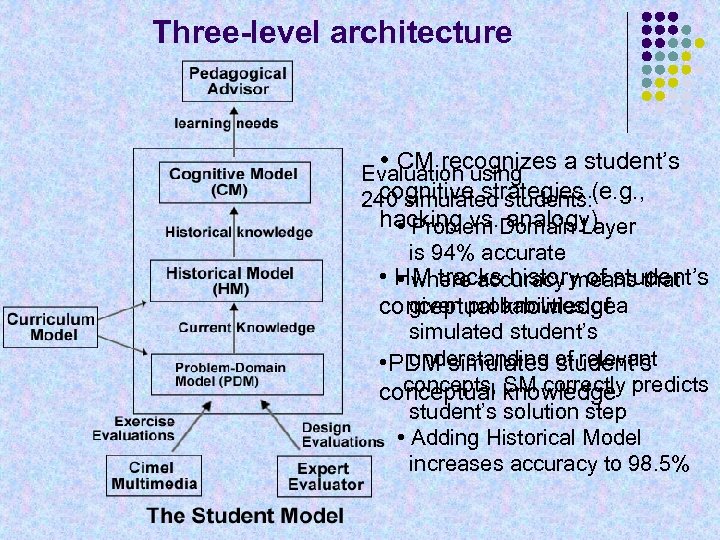 Three-level architecture • CM recognizes a student’s Evaluation using cognitive strategies 240 simulated students: (e. g. , hacking vs. Domain Layer • Problem analogy) is 94% accurate • HM tracks history of student’s • where accuracy means that given probabilities of conceptual knowledgea simulated student’s understanding student’s • PDM simulates of relevant concepts, SM correctly conceptual knowledge predicts student’s solution step • Adding Historical Model increases accuracy to 98. 5%
Three-level architecture • CM recognizes a student’s Evaluation using cognitive strategies 240 simulated students: (e. g. , hacking vs. Domain Layer • Problem analogy) is 94% accurate • HM tracks history of student’s • where accuracy means that given probabilities of conceptual knowledgea simulated student’s understanding student’s • PDM simulates of relevant concepts, SM correctly conceptual knowledge predicts student’s solution step • Adding Historical Model increases accuracy to 98. 5%
 Atomic Dynamic Bayesian Networks l ADBNs extend ABNs to account for knowledge states over successive time slices l l Evaluated of student model l l Each time slice is an ABN connected to next ABN 71 college and high school students in CS 1 courses Compared diagnosed knowledge state for each student with the ones reflected from posttest. l l l Average correct diagnostic rate is 81. 8% Improves to 89. 5% by adding multimedia observations Average response time after a student enters the solution step is 0. 63 seconds, comfortably real time for the students
Atomic Dynamic Bayesian Networks l ADBNs extend ABNs to account for knowledge states over successive time slices l l Evaluated of student model l l Each time slice is an ABN connected to next ABN 71 college and high school students in CS 1 courses Compared diagnosed knowledge state for each student with the ones reflected from posttest. l l l Average correct diagnostic rate is 81. 8% Improves to 89. 5% by adding multimedia observations Average response time after a student enters the solution step is 0. 63 seconds, comfortably real time for the students
 Pedagogical Advisor with Learning Styles Shahida Parvez What is an individual learning style? The way a learner perceives and interacts with an environment. Some people like information in the form of pictures / images, while others like it in written form. Some like to work alone while others like to work in groups. Some prefer concept and theory while others like facts and concrete experience. Visual Learner Auditory Active Learner
Pedagogical Advisor with Learning Styles Shahida Parvez What is an individual learning style? The way a learner perceives and interacts with an environment. Some people like information in the form of pictures / images, while others like it in written form. Some like to work alone while others like to work in groups. Some prefer concept and theory while others like facts and concrete experience. Visual Learner Auditory Active Learner
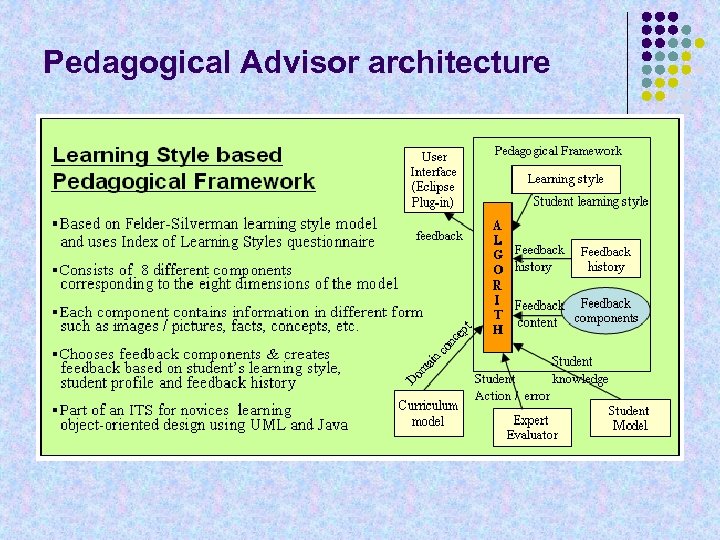 Pedagogical Advisor architecture
Pedagogical Advisor architecture
 Felder-Silverman learning style survey l l l http: //designfirstui. cse. lehigh. edu: 8080/servletsexamples/servlet/Learning. Style Survey has been validated 44 questions determine learning styles along 8 dimensions
Felder-Silverman learning style survey l l l http: //designfirstui. cse. lehigh. edu: 8080/servletsexamples/servlet/Learning. Style Survey has been validated 44 questions determine learning styles along 8 dimensions
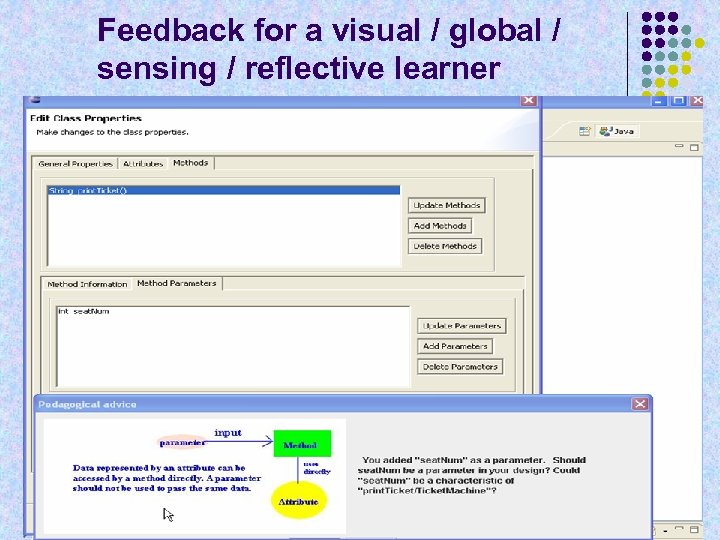 Feedback for a visual / global / sensing / reflective learner
Feedback for a visual / global / sensing / reflective learner
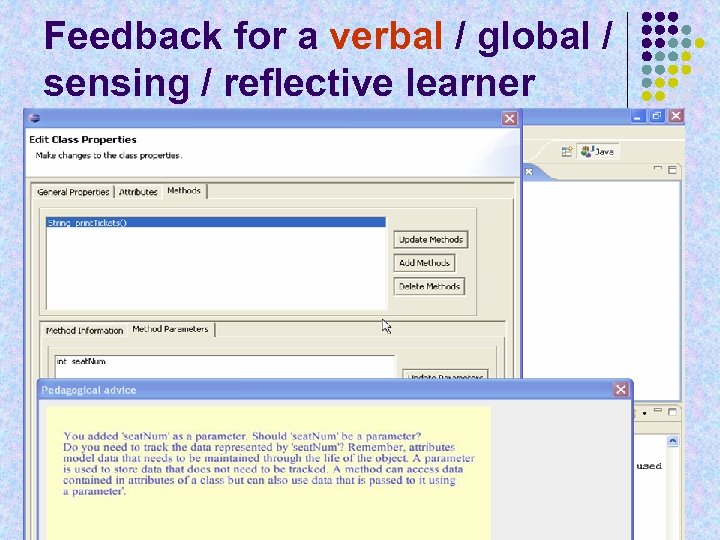 Feedback for a verbal / global / sensing / reflective learner
Feedback for a verbal / global / sensing / reflective learner
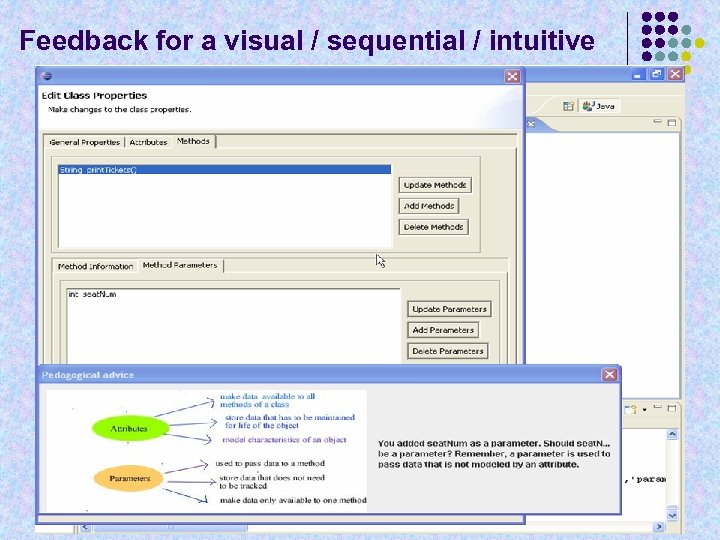 Feedback for a visual / sequential / intuitive
Feedback for a visual / sequential / intuitive
 Evaluation l l l 49 CS 1 students completed four lesson introduction to object-oriented design After multimedia, students took a multiple choice test on object-oriented concepts l Out of 31 questions, mean of 5. 5 errors l Confirms previous pre-test/post-test results demonstrating effectiveness of multimedia (Blank et all 2003, 2005) All students completed Ticket. Machine design l Average graded score of 96. 9/100 (1 point per error) l Out of 31 questions, mean of 2. 3 errors l Lab exercise with ITS help had a significant effect l Using paired-samples t test, the T value is 10. 2111, p<. 001
Evaluation l l l 49 CS 1 students completed four lesson introduction to object-oriented design After multimedia, students took a multiple choice test on object-oriented concepts l Out of 31 questions, mean of 5. 5 errors l Confirms previous pre-test/post-test results demonstrating effectiveness of multimedia (Blank et all 2003, 2005) All students completed Ticket. Machine design l Average graded score of 96. 9/100 (1 point per error) l Out of 31 questions, mean of 2. 3 errors l Lab exercise with ITS help had a significant effect l Using paired-samples t test, the T value is 10. 2111, p<. 001
 Standalone Dr. Java and Lehigh. UML l l Eclipse is popular for large-scale software development, but has a steep learning curve Dr. Java (Blue. J, etc. ) more suitable for novices? Dr. Java. exe (from www. drjava. org) New: standalone version of Lehigh. UML
Standalone Dr. Java and Lehigh. UML l l Eclipse is popular for large-scale software development, but has a steep learning curve Dr. Java (Blue. J, etc. ) more suitable for novices? Dr. Java. exe (from www. drjava. org) New: standalone version of Lehigh. UML
 Widening the pipeline l The pipeline for women and minorities entering computer science (CS) and information technology (IT) is shrinking, at a time when the projected demand for IT professionals is growing l l Camp, 1997, 1999, Cohoon, 2002 “We must take direct action to attract and retain more women to computing at all points in the pipeline (i. e. , K-12, undergraduate, faculty and industry). ” l Camp 1999
Widening the pipeline l The pipeline for women and minorities entering computer science (CS) and information technology (IT) is shrinking, at a time when the projected demand for IT professionals is growing l l Camp, 1997, 1999, Cohoon, 2002 “We must take direct action to attract and retain more women to computing at all points in the pipeline (i. e. , K-12, undergraduate, faculty and industry). ” l Camp 1999
 LV (Lehigh Valley) STEM www. lehigh. edu/stem l l An NSF-sponsored GK-12 project Faculty and Graduate Fellows lead outreach teams Work with K-12 teachers to develop new curricula l Martian landscape with remotely controlled robot “rovers” created in the basement of an Allentown middle school (now a NASA Explorer school) l Flash introduced in a Bethlehem middle school l Design-first curriculum in an Allentown high school NSF program manager has indicated likely recommendation for a continuing GK-12 project l New project also feature smaller Outreach supplements for grads or undergrads to implement curricula developed by Graduate Fellow teams
LV (Lehigh Valley) STEM www. lehigh. edu/stem l l An NSF-sponsored GK-12 project Faculty and Graduate Fellows lead outreach teams Work with K-12 teachers to develop new curricula l Martian landscape with remotely controlled robot “rovers” created in the basement of an Allentown middle school (now a NASA Explorer school) l Flash introduced in a Bethlehem middle school l Design-first curriculum in an Allentown high school NSF program manager has indicated likely recommendation for a continuing GK-12 project l New project also feature smaller Outreach supplements for grads or undergrads to implement curricula developed by Graduate Fellow teams
 Launch-IT (NSF ITEST) www. lehigh. edu/launchit l l l Build on success of LV STEM and S. T. A. R. Academies l Promote academic achievement for at-risk middle & high school students in the Lehigh Valley l 98% of S. T. A. R. students go to college (now in 18 th year) l Saturdays (once a month) and summer (three weeks) l Corporate partners, regional colleges & schools, and parents Focus on Information Technology (IT) l Connect & widen pipeline laid that STEM laid in schools l Self-directed multimedia, intelligent tutoring, and one-on-one mentoring by college undergraduate and graduate students Three teams led by IT faculty and Graduate Fellows l 6 th and 7 th graders: science, math and IT ‘missions’ using remotely controlled robots in a simulated Martian landscape l 8 th and 9 th graders: create web-based juke box or i. Pod™ as an interactive, animated web site using Flash™ l 10 th through 12 th graders: learn Java “design first” with goal of getting AP Java college credit
Launch-IT (NSF ITEST) www. lehigh. edu/launchit l l l Build on success of LV STEM and S. T. A. R. Academies l Promote academic achievement for at-risk middle & high school students in the Lehigh Valley l 98% of S. T. A. R. students go to college (now in 18 th year) l Saturdays (once a month) and summer (three weeks) l Corporate partners, regional colleges & schools, and parents Focus on Information Technology (IT) l Connect & widen pipeline laid that STEM laid in schools l Self-directed multimedia, intelligent tutoring, and one-on-one mentoring by college undergraduate and graduate students Three teams led by IT faculty and Graduate Fellows l 6 th and 7 th graders: science, math and IT ‘missions’ using remotely controlled robots in a simulated Martian landscape l 8 th and 9 th graders: create web-based juke box or i. Pod™ as an interactive, animated web site using Flash™ l 10 th through 12 th graders: learn Java “design first” with goal of getting AP Java college credit
 Thank you! glennblank@gmail. com www. cse. lehigh. edu/~glennb designfirst. cse. lehigh. edu Questions?
Thank you! glennblank@gmail. com www. cse. lehigh. edu/~glennb designfirst. cse. lehigh. edu Questions?


