Ch. 5 Nouns and Noun Phrases.students .pptx
- Количество слайдов: 35
 Nouns & Noun Phrases
Nouns & Noun Phrases
 N Noun category includes: • physical objects: people, animals, places, things • substances: grapes, horses, Warsaw, mother, water • abstract entities: work, hatred, debt, presence Nouns inflect for: number (singular, plural) case (plain, genitive) Plain : architects Genitive: architect’s architects’
N Noun category includes: • physical objects: people, animals, places, things • substances: grapes, horses, Warsaw, mother, water • abstract entities: work, hatred, debt, presence Nouns inflect for: number (singular, plural) case (plain, genitive) Plain : architects Genitive: architect’s architects’
 What are the functions of the NP? In a clause: • Subject A new book was published • Object They published a new book. • Predicative complement It is a new book. In PP Complement I am talking to students.
What are the functions of the NP? In a clause: • Subject A new book was published • Object They published a new book. • Predicative complement It is a new book. In PP Complement I am talking to students.
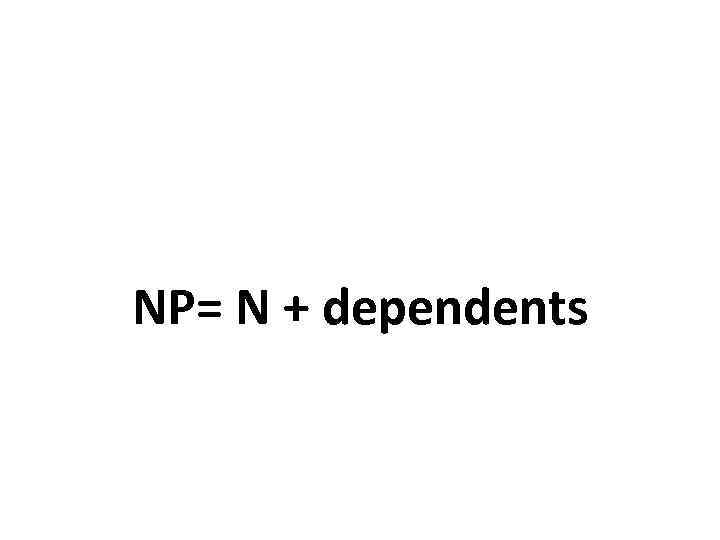 NP= N + dependents
NP= N + dependents
 Dependents They occur exclusively or with nouns as head. Certain determinatives the girl, a month, every child, which firm Pre-head adjectives old people, a big car, recent news Relative clauses the boy who studied, the slides I’m presenting
Dependents They occur exclusively or with nouns as head. Certain determinatives the girl, a month, every child, which firm Pre-head adjectives old people, a big car, recent news Relative clauses the boy who studied, the slides I’m presenting
 Dependents cd determiners some books, the girls, three boys, no reason complements the loss of blood, a ban on smoking, the fact that she’s alive modifiers a young teacher, a student from Ukraine, patients who complained Determiners – obligatory with certain types of singular noun. I saw a girl. *I saw girl. Complements are licensed by the head noun his loss of patience/He is losing patience Modifiers – no limit to the number of modifiers in a NP. a young student from Ukraine who complained
Dependents cd determiners some books, the girls, three boys, no reason complements the loss of blood, a ban on smoking, the fact that she’s alive modifiers a young teacher, a student from Ukraine, patients who complained Determiners – obligatory with certain types of singular noun. I saw a girl. *I saw girl. Complements are licensed by the head noun his loss of patience/He is losing patience Modifiers – no limit to the number of modifiers in a NP. a young student from Ukraine who complained
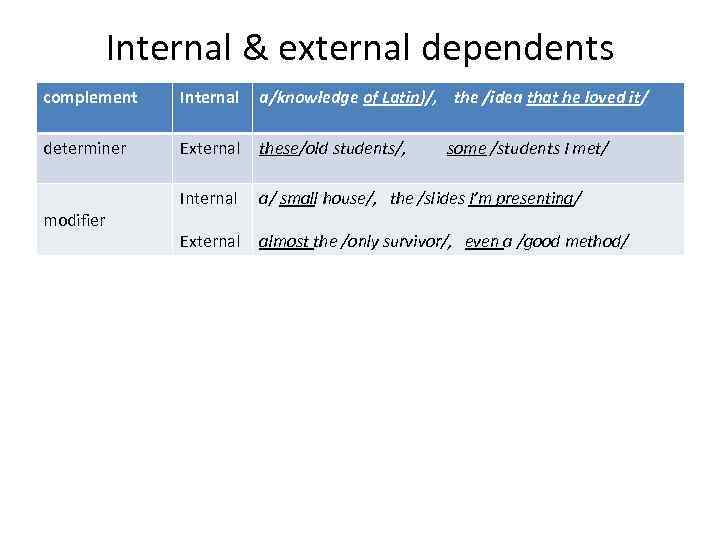 Internal & external dependents complement Internal a/knowledge of Latin)/, the /idea that he loved it/ determiner External these/old students/, Internal a/ small house/, the /slides I’m presenting/ External almost the /only survivor/, even a /good method/ modifier some /students I met/
Internal & external dependents complement Internal a/knowledge of Latin)/, the /idea that he loved it/ determiner External these/old students/, Internal a/ small house/, the /slides I’m presenting/ External almost the /only survivor/, even a /good method/ modifier some /students I met/
 Underline nouns and put NP in brackets: I have never met a person who is not interested in languages. It is the guy who fainted. Look at the book he’s reading.
Underline nouns and put NP in brackets: I have never met a person who is not interested in languages. It is the guy who fainted. Look at the book he’s reading.
 I have never met (a person who is not interested in languages. ) It is (the guy who fainted). Look at (the book he’s reading).
I have never met (a person who is not interested in languages. ) It is (the guy who fainted). Look at (the book he’s reading).
 Number: singular & plural; inflectional forms: cat, cats Nouns with fixed number • some nouns are invariably singular: - footwear, harm, nonsense, information, furniture, money italics, linguistics, physics, news, phonetics *Informations are. *Linguistics are boring. *Money are • or invariably plural - clothes, belongings, scissors, trousers cattle, vermin *This cattle.
Number: singular & plural; inflectional forms: cat, cats Nouns with fixed number • some nouns are invariably singular: - footwear, harm, nonsense, information, furniture, money italics, linguistics, physics, news, phonetics *Informations are. *Linguistics are boring. *Money are • or invariably plural - clothes, belongings, scissors, trousers cattle, vermin *This cattle.
 Count and non-count nouns are in minority • Count nouns take cardinal numerals as dependents. Count noun: one chair two chairs. Non-count noun: *one furniture, *two furnitures Invariably singular: furniture, clothing, equipment, eagerness, wetness Count noun: Non-count noun: one chair two chairs. *one remain, *two remains Invariably plural: remains, credentials, proceeds, genitals Furniture , remains cannot combine with any numerals.
Count and non-count nouns are in minority • Count nouns take cardinal numerals as dependents. Count noun: one chair two chairs. Non-count noun: *one furniture, *two furnitures Invariably singular: furniture, clothing, equipment, eagerness, wetness Count noun: Non-count noun: one chair two chairs. *one remain, *two remains Invariably plural: remains, credentials, proceeds, genitals Furniture , remains cannot combine with any numerals.
 Nouns with count and non-count uses Most nouns can be used with either kind of interpretation. • Would you like a cake? Would you like some more cake? • I’ve bought a new football. Let’s play football. • I’ve suggested a few improvements. There’s been little improvement.
Nouns with count and non-count uses Most nouns can be used with either kind of interpretation. • Would you like a cake? Would you like some more cake? • I’ve bought a new football. Let’s play football. • I’ve suggested a few improvements. There’s been little improvement.
 Which nouns are plural-only? Give 2 examples in an appropriate context: - one where it has plural-one sense, - one where it is an ordinary plural with a contrasting singular form. e. g. spectacles, people, holidays, bread, customs, wood spectacles – eyeglasses There are many impressive public spectacles. The coronation was a lavish spectacle. A spectacle - a public show
Which nouns are plural-only? Give 2 examples in an appropriate context: - one where it has plural-one sense, - one where it is an ordinary plural with a contrasting singular form. e. g. spectacles, people, holidays, bread, customs, wood spectacles – eyeglasses There are many impressive public spectacles. The coronation was a lavish spectacle. A spectacle - a public show
 Subject-verb agreement The verb agrees with the subject; inflectional forms of the verb; agreement involves person and number. 4 special cases: 1. Measure expressions Ten days, thirty dollars, five kilometers are plural in form but the quantity and the measure they denote can be treated as a single entity; it determines the form of the verb. Fifty days is a long time to stay abroad. Thirty dollars seems far too much for a pizza. That ten days we spent together in Spain was wonderful. Another three days is all we need.
Subject-verb agreement The verb agrees with the subject; inflectional forms of the verb; agreement involves person and number. 4 special cases: 1. Measure expressions Ten days, thirty dollars, five kilometers are plural in form but the quantity and the measure they denote can be treated as a single entity; it determines the form of the verb. Fifty days is a long time to stay abroad. Thirty dollars seems far too much for a pizza. That ten days we spent together in Spain was wonderful. Another three days is all we need.
 Quantificational nouns 2. Quantificational nouns: lot, rest, number A lot= NP singular (A lot of money) wasted. plural (A lot of things) were wasted. (The rest of meat) is over there. (The rest of the eggs) are over there. (Not possible) (A number of errors) were found. The meaning of number is such that the NP must be plural.
Quantificational nouns 2. Quantificational nouns: lot, rest, number A lot= NP singular (A lot of money) wasted. plural (A lot of things) were wasted. (The rest of meat) is over there. (The rest of the eggs) are over there. (Not possible) (A number of errors) were found. The meaning of number is such that the NP must be plural.
 Collective nouns 3. Collective nouns, groups of people In British English singular words which refer to groups of people can be used either as singular or plural. Singular- group as an impersonal unit Plural - group as a collection of people doing some things. bank, choir, class, club, government, jury, ministry, orchestra, party, public, school, staff, team, union. My family have decided to move to England. The average Polish family has 2, 1 members. It is smaller than 50 years ago. My firm are wonderful. They do all they can for me. My firm was established 20 years ago.
Collective nouns 3. Collective nouns, groups of people In British English singular words which refer to groups of people can be used either as singular or plural. Singular- group as an impersonal unit Plural - group as a collection of people doing some things. bank, choir, class, club, government, jury, ministry, orchestra, party, public, school, staff, team, union. My family have decided to move to England. The average Polish family has 2, 1 members. It is smaller than 50 years ago. My firm are wonderful. They do all they can for me. My firm was established 20 years ago.
 Any, no, neither, none 4. Any, no, neither, none • Any, no occur with both singulars and plurals. No objection is valid. No objections are valid. • Neither & either occur only with singulars. Neither objection is valid. • None occurs with both singulars and plurals None of my friends is interested. (formal) None of my friends are interested. (informal)
Any, no, neither, none 4. Any, no, neither, none • Any, no occur with both singulars and plurals. No objection is valid. No objections are valid. • Neither & either occur only with singulars. Neither objection is valid. • None occurs with both singulars and plurals None of my friends is interested. (formal) None of my friends are interested. (informal)
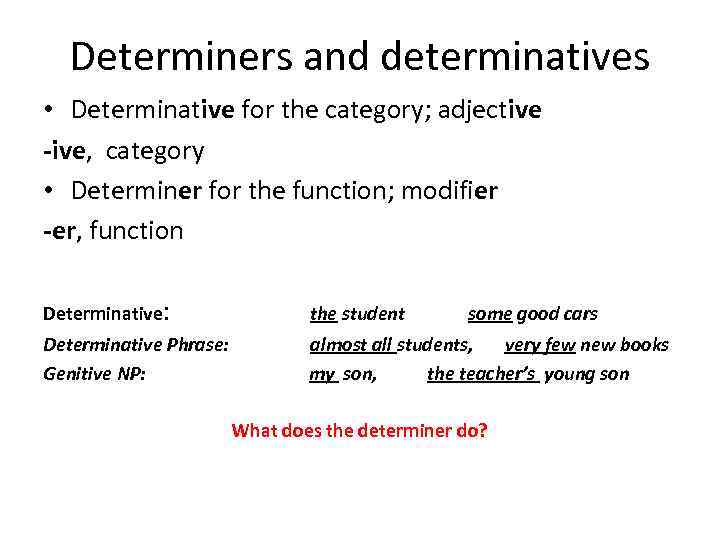 Determiners and determinatives • Determinative for the category; adjective -ive, category • Determiner for the function; modifier -er, function Determinative: the student Determinative Phrase: Genitive NP: almost all students, very few new books my son, the teacher’s young son some good cars What does the determiner do?
Determiners and determinatives • Determinative for the category; adjective -ive, category • Determiner for the function; modifier -er, function Determinative: the student Determinative Phrase: Genitive NP: almost all students, very few new books my son, the teacher’s young son some good cars What does the determiner do?
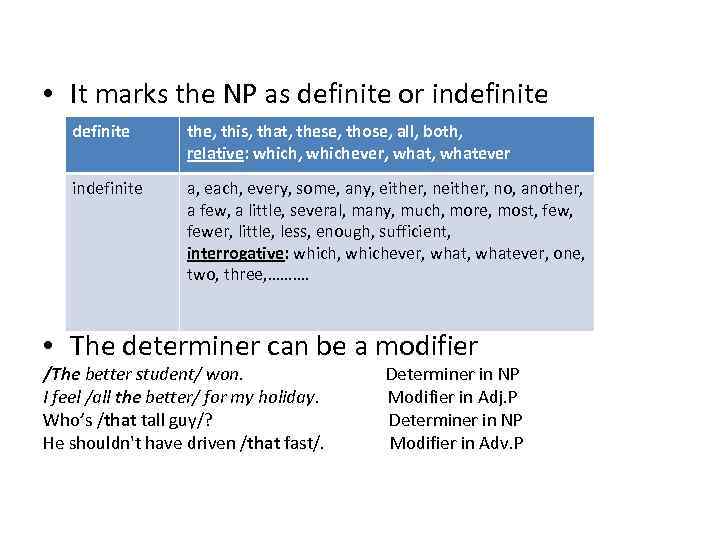 • It marks the NP as definite or indefinite the, this, that, these, those, all, both, relative: which, whichever, whatever indefinite a, each, every, some, any, either, no, another, a few, a little, several, many, much, more, most, fewer, little, less, enough, sufficient, interrogative: which, whichever, whatever, one, two, three, ………. • The determiner can be a modifier /The better student/ won. I feel /all the better/ for my holiday. Who’s /that tall guy/? He shouldn't have driven /that fast/. Determiner in NP Modifier in Adj. P Determiner in NP Modifier in Adv. P
• It marks the NP as definite or indefinite the, this, that, these, those, all, both, relative: which, whichever, whatever indefinite a, each, every, some, any, either, no, another, a few, a little, several, many, much, more, most, fewer, little, less, enough, sufficient, interrogative: which, whichever, whatever, one, two, three, ………. • The determiner can be a modifier /The better student/ won. I feel /all the better/ for my holiday. Who’s /that tall guy/? He shouldn't have driven /that fast/. Determiner in NP Modifier in Adj. P Determiner in NP Modifier in Adv. P
 Complements Nouns do not take objects, they take complements I criticised her decision. My criticism of her decision … object complement Complements: Preposition Phrase, subordinate clause N + PP the return of the warriors an attack by a hooligan the removal of the files by the secretary N + subordinate clause the people who need help things you forgot to say your ability to complete the task the rumour that he is ill
Complements Nouns do not take objects, they take complements I criticised her decision. My criticism of her decision … object complement Complements: Preposition Phrase, subordinate clause N + PP the return of the warriors an attack by a hooligan the removal of the files by the secretary N + subordinate clause the people who need help things you forgot to say your ability to complete the task the rumour that he is ill
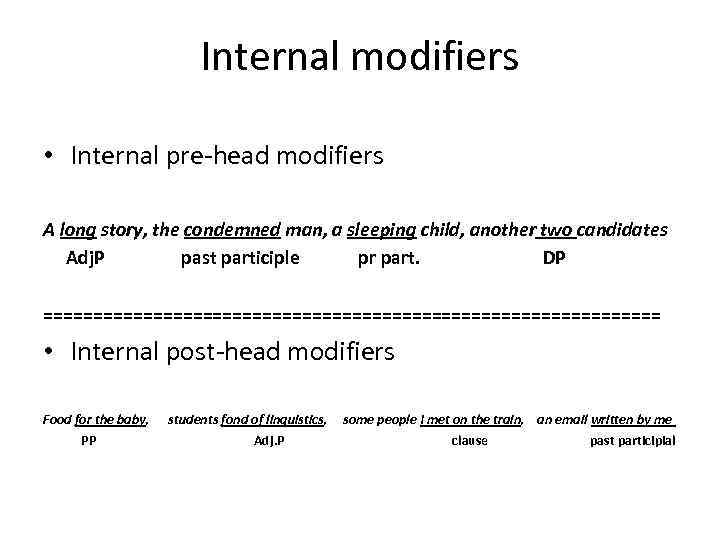 Internal modifiers • Internal pre-head modifiers A long story, the condemned man, a sleeping child, another two candidates Adj. P past participle pr part. DP =============================== • Internal post-head modifiers Food for the baby, PP students fond of linguistics, Adj. P some people I met on the train, an email written by me clause past participial
Internal modifiers • Internal pre-head modifiers A long story, the condemned man, a sleeping child, another two candidates Adj. P past participle pr part. DP =============================== • Internal post-head modifiers Food for the baby, PP students fond of linguistics, Adj. P some people I met on the train, an email written by me clause past participial
 External modifiers • are within the NP but outside the head nominal Both her sons, Even a young woman, all the mistakes I made, All the children Such a disaster ,
External modifiers • are within the NP but outside the head nominal Both her sons, Even a young woman, all the mistakes I made, All the children Such a disaster ,
 Combination of modifiers the grammar book we have to study that handsome, tall, young student in the room with a book an old English tutor with 50 angry students who are complaining bitterly
Combination of modifiers the grammar book we have to study that handsome, tall, young student in the room with a book an old English tutor with 50 angry students who are complaining bitterly
 The fused-head construction A single word is at the same time a determiner/modifier and the head. /Noun Phrases are in brackets/ Fused heads are undrelined Simple I have lots of grammar books but you don’t seem to have /any/. They sent three exams though I ordered /ten/. Partitive /Some of your notes/ are quite good. They sent twenty copies but /several/ were damaged. Special /Many/ would disagree with me on that point. I don’t think /much/ has happened while you’ve been away. /This/ is amusing. Any can be replaed wtih any books Part rather than the whole thing Actual meaning is not retrievable from the text
The fused-head construction A single word is at the same time a determiner/modifier and the head. /Noun Phrases are in brackets/ Fused heads are undrelined Simple I have lots of grammar books but you don’t seem to have /any/. They sent three exams though I ordered /ten/. Partitive /Some of your notes/ are quite good. They sent twenty copies but /several/ were damaged. Special /Many/ would disagree with me on that point. I don’t think /much/ has happened while you’ve been away. /This/ is amusing. Any can be replaed wtih any books Part rather than the whole thing Actual meaning is not retrievable from the text
 The, a, every in fused structures • the > that The impact of war is more serious than that of flood. • a > one I need a book but I haven’t got one. • every > every one I inspected a dozen cars but every one was defective. No > none, none is the inflected form of no I have no money and you also have none. Compund forms: Some famous person > somebody famous No harmful thing > nothing harmful
The, a, every in fused structures • the > that The impact of war is more serious than that of flood. • a > one I need a book but I haven’t got one. • every > every one I inspected a dozen cars but every one was defective. No > none, none is the inflected form of no I have no money and you also have none. Compund forms: Some famous person > somebody famous No harmful thing > nothing harmful
 Classify the fused heads as: simple, partitive, special 1 Mary has two exams and Mark four. 2 Lots of students understood it and most thought it was easy. 3 You’ve made progress, but much still remains to be done. 4 There are foreigners out there; I saw several. 5 Many are called but few are chosen. 6 There were several options, and as usual he took the best. 7 Which of the topics did you find the most interesting?
Classify the fused heads as: simple, partitive, special 1 Mary has two exams and Mark four. 2 Lots of students understood it and most thought it was easy. 3 You’ve made progress, but much still remains to be done. 4 There are foreigners out there; I saw several. 5 Many are called but few are chosen. 6 There were several options, and as usual he took the best. 7 Which of the topics did you find the most interesting?
 Pronouns • Personal: I like them. • Reciprocal: They dislike each other. • Interrogative: Who saw them? What do you want? • Relative: the guy who helped us the book which you recommend
Pronouns • Personal: I like them. • Reciprocal: They dislike each other. • Interrogative: Who saw them? What do you want? • Relative: the guy who helped us the book which you recommend
 Gender • Masculine; he is used for males-humans or animals • Feminine; she is used for females, political entities, ships • Neutral, it is used for inanimates or for male or female animals, human infants
Gender • Masculine; he is used for males-humans or animals • Feminine; she is used for females, political entities, ships • Neutral, it is used for inanimates or for male or female animals, human infants
 Cases • • • Nominative ‘the man’ Genitive ‘of the man’ Dative ‘to the man’ Accusative ‘the man’ Ablative ‘by the man’ Vocative ‘O man!’ No locative case
Cases • • • Nominative ‘the man’ Genitive ‘of the man’ Dative ‘to the man’ Accusative ‘the man’ Ablative ‘by the man’ Vocative ‘O man!’ No locative case
 The nominative-accusative contrast of case • • They wrote the examinations. subject: nominative They finished them in room 102. object of verb: accusative I talked to them yesterday. object of prep. : accusative It was they/them who complained. Predicative Complement (PC) : nominative or accusative Verbless constructions: She is a year older than I. She is a year older than me. Style: nominative - formal style accusative - informal style
The nominative-accusative contrast of case • • They wrote the examinations. subject: nominative They finished them in room 102. object of verb: accusative I talked to them yesterday. object of prep. : accusative It was they/them who complained. Predicative Complement (PC) : nominative or accusative Verbless constructions: She is a year older than I. She is a year older than me. Style: nominative - formal style accusative - informal style
 Select an appropriate case form of the pronoun I. 1. Your father and ………. . have been considering the matter. 2. In the other photo the guy in the middle is ………. 3. They’ve arranged for you and … to meet with Dr Jackson in the evening.
Select an appropriate case form of the pronoun I. 1. Your father and ………. . have been considering the matter. 2. In the other photo the guy in the middle is ………. 3. They’ve arranged for you and … to meet with Dr Jackson in the evening.
 The Genitive is marked by the apostrophe and the suffix ‘s – cat’s or by the apostrophe alone cats’. The teacher’s car was stolen. The teachers’ car was stolen. These people’s fate is unknown. • The ‘s suffix occurs at the end of the genitive NP someone else’s responsibility the guy next door’s voice • Dual function of the genitive as a definite determiner the patient’s condition and a clause subject the condition of the patient is serious
The Genitive is marked by the apostrophe and the suffix ‘s – cat’s or by the apostrophe alone cats’. The teacher’s car was stolen. The teachers’ car was stolen. These people’s fate is unknown. • The ‘s suffix occurs at the end of the genitive NP someone else’s responsibility the guy next door’s voice • Dual function of the genitive as a definite determiner the patient’s condition and a clause subject the condition of the patient is serious
 The genitive constructions 1 Subject of a gerund participial clause She didn’t approve of /his being given a second chance/. 2 Fused head They accepted Mary’s proposal but not Mark’s. 3 Oblique The argument was caused by a stupid remark of Mark’s. 4 Predicative Everything in this room is John’s. 5 Attributive They’ve moved on to a new students’ dormitory.
The genitive constructions 1 Subject of a gerund participial clause She didn’t approve of /his being given a second chance/. 2 Fused head They accepted Mary’s proposal but not Mark’s. 3 Oblique The argument was caused by a stupid remark of Mark’s. 4 Predicative Everything in this room is John’s. 5 Attributive They’ve moved on to a new students’ dormitory.
 What kind of genitives are in the following sentences? 1. Subject of a gerund participial clause She didn’t approve of /his being given a second chance/. 2. Fused head They accepted Mary’s proposal but not Mark’s. 1. A friend of mine told me the truth. 2. Your application has been approved but Jill’s is still being considered. 3. This book belongs to Pat but the rest are yours. 3. Oblique The argument was caused by a stupid remark of Mark’s. 4. Do you know if there’s a men’s toilet around here? 4. Predicative Everything in this room is John’s. 5. He objects to your being paid more than everybody else. 5. Attributive They’ve moved on to a new students’ dormitory.
What kind of genitives are in the following sentences? 1. Subject of a gerund participial clause She didn’t approve of /his being given a second chance/. 2. Fused head They accepted Mary’s proposal but not Mark’s. 1. A friend of mine told me the truth. 2. Your application has been approved but Jill’s is still being considered. 3. This book belongs to Pat but the rest are yours. 3. Oblique The argument was caused by a stupid remark of Mark’s. 4. Do you know if there’s a men’s toilet around here? 4. Predicative Everything in this room is John’s. 5. He objects to your being paid more than everybody else. 5. Attributive They’ve moved on to a new students’ dormitory.
 Thank you
Thank you


