dfb78a7be2edc73326319ce07c69d570.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13
 Nouns, Determiners and Pronouns
Nouns, Determiners and Pronouns
 Definitions of “Noun” • Classic “A person, place, or thing” • Sanskrit grammarians - does not have a time axis, like frozen time • Formal definition - takes nominal affixes: noun derivational affix (e. g. , government), can take plural, can occur with possessive suffix • Functional definition - can be preceded by an article (the/a house), can appear in a frame sentence ((The) _____ seem(s) nice. )
Definitions of “Noun” • Classic “A person, place, or thing” • Sanskrit grammarians - does not have a time axis, like frozen time • Formal definition - takes nominal affixes: noun derivational affix (e. g. , government), can take plural, can occur with possessive suffix • Functional definition - can be preceded by an article (the/a house), can appear in a frame sentence ((The) _____ seem(s) nice. )
 Number • Types of plural: normal, internal change, zero plural, foreign plurals (syllabi, curricula, indices, data) • Nouns of quantity - three dozen, hundred, pound (in British English), mile (in some dialects) • Nouns resitant to singular/plural contrast – Proper nouns – Some words ending in -s (news, physics, mumps, billiards, dominoes) – Noncount (mass) nouns - cheese, instability – Binary nouns - scissors, pants, trousers, glasses, binoculars, shorts – Aggregate nouns - people, cattle, clergy, police, offspring, series, barracks, committee (British English)
Number • Types of plural: normal, internal change, zero plural, foreign plurals (syllabi, curricula, indices, data) • Nouns of quantity - three dozen, hundred, pound (in British English), mile (in some dialects) • Nouns resitant to singular/plural contrast – Proper nouns – Some words ending in -s (news, physics, mumps, billiards, dominoes) – Noncount (mass) nouns - cheese, instability – Binary nouns - scissors, pants, trousers, glasses, binoculars, shorts – Aggregate nouns - people, cattle, clergy, police, offspring, series, barracks, committee (British English)
 Gender • Generally not a significant grammatical distinction in English, except for with pronouns • Animals - Familiar animals often have a gender distinction and use male/female pronouns (e. g. , horse/stallion/mare (he, she), but spider (it) • Gender with other nouns – Gendered nouns (bachelor, usherette, king, princess…) - he, she – Dual nouns (doctor, student, participant, customer) - he, she – Plural nouns - “he or she”, “they”
Gender • Generally not a significant grammatical distinction in English, except for with pronouns • Animals - Familiar animals often have a gender distinction and use male/female pronouns (e. g. , horse/stallion/mare (he, she), but spider (it) • Gender with other nouns – Gendered nouns (bachelor, usherette, king, princess…) - he, she – Dual nouns (doctor, student, participant, customer) - he, she – Plural nouns - “he or she”, “they”
 Common/Proper Nouns • Common Nouns do not refer to a specific person, place, event, or thing – E. g. , shoe, house, day, car • Proper Nouns refer to specific person, place, event, or thing – E. g. , Pat, the Queen, Chicago, Christmas, Lucille, General Motors – Do not usually follow articles: on (*the) Christmas Day, in (*the) Chicago, *the Shakespeare – Do not usually take plurals – Exceptions: • Referring to a real or imagined unique proper noun: “the Christmas of 1942”, “Are you the Howard Dean? ”, “That’s not the Chicago I remember. ” • Certain place names: the Missippi River, the Great Lakes, the Rocky Mountains, the Atlantic Ocean, the White House • Certain institutions: the New York Times, the Lincoln Museum,
Common/Proper Nouns • Common Nouns do not refer to a specific person, place, event, or thing – E. g. , shoe, house, day, car • Proper Nouns refer to specific person, place, event, or thing – E. g. , Pat, the Queen, Chicago, Christmas, Lucille, General Motors – Do not usually follow articles: on (*the) Christmas Day, in (*the) Chicago, *the Shakespeare – Do not usually take plurals – Exceptions: • Referring to a real or imagined unique proper noun: “the Christmas of 1942”, “Are you the Howard Dean? ”, “That’s not the Chicago I remember. ” • Certain place names: the Missippi River, the Great Lakes, the Rocky Mountains, the Atlantic Ocean, the White House • Certain institutions: the New York Times, the Lincoln Museum,
 Count/Mass (Noncount) Nouns • Count Nouns are nouns that can be counted and take a plural – E. g. , shoe, horse, boy, inconsistency, universe – Occur with “many” - “How many ____? ”, “There were many ___” – Occur with “few” - “too few ____”, “We only have a few _____” • Mass Nouns (Noncount Nouns) are nouns that cannot be counted – E. g. , sugar, water, rice, wheat, mud, milk, music, laziness – Occur with “much” - “How much __”, “There is much ____” – Occurs with “little” instead of “few”: “too little ____”, “We only have a little ____” – Occur with partitive constructions to indicate units - grain of sand/rice, cup of water/milk, piece of music/leather, clump of mud, blade of grass, slice of meat/pie, item of clothing • Some nouns can be both – E. g. , pie, cake, brick, stone, love
Count/Mass (Noncount) Nouns • Count Nouns are nouns that can be counted and take a plural – E. g. , shoe, horse, boy, inconsistency, universe – Occur with “many” - “How many ____? ”, “There were many ___” – Occur with “few” - “too few ____”, “We only have a few _____” • Mass Nouns (Noncount Nouns) are nouns that cannot be counted – E. g. , sugar, water, rice, wheat, mud, milk, music, laziness – Occur with “much” - “How much __”, “There is much ____” – Occurs with “little” instead of “few”: “too little ____”, “We only have a little ____” – Occur with partitive constructions to indicate units - grain of sand/rice, cup of water/milk, piece of music/leather, clump of mud, blade of grass, slice of meat/pie, item of clothing • Some nouns can be both – E. g. , pie, cake, brick, stone, love
 Types of Nouns
Types of Nouns
 Determiners • • Articles – Definite (the), indefinite (a/an) Demonstratives – this, these, that, those Possessives – my, our, your… Indefinites (Quantifiers) – some, any, no, every, other, another, many, more, most, enough, few, less, much, either, neither, several, all, both, each, half… • Cardinal Numbers – one, two, three, four… • Ordinal Numbers – first, second, third…
Determiners • • Articles – Definite (the), indefinite (a/an) Demonstratives – this, these, that, those Possessives – my, our, your… Indefinites (Quantifiers) – some, any, no, every, other, another, many, more, most, enough, few, less, much, either, neither, several, all, both, each, half… • Cardinal Numbers – one, two, three, four… • Ordinal Numbers – first, second, third…
 Definite and Indefinite Articles • Definite Article – the – Refers to something predictable – E. g. , from a the narrative context – Once upon a time there was a king…Now the king had three daughters. – E. g. , from the cultural context – What do you think of the President? ; Do you watch the news on television? – E. g. , from the situational context – We went to a restaurant and liked the menu (waiter, service, food, *teller, *nurse); We were in a house, in the dining room, when we heard a knock at the door. • Indefinite Articles – a/an, this (very informal) – Refer to something unpredictable – E. g. , I met an interesting man; Once upon a time there was a king. ; I know this man and he says…
Definite and Indefinite Articles • Definite Article – the – Refers to something predictable – E. g. , from a the narrative context – Once upon a time there was a king…Now the king had three daughters. – E. g. , from the cultural context – What do you think of the President? ; Do you watch the news on television? – E. g. , from the situational context – We went to a restaurant and liked the menu (waiter, service, food, *teller, *nurse); We were in a house, in the dining room, when we heard a knock at the door. • Indefinite Articles – a/an, this (very informal) – Refer to something unpredictable – E. g. , I met an interesting man; Once upon a time there was a king. ; I know this man and he says…
 Generic vs. Specific Reference • Specific refers to a specific person or thing – E. g. , Look at that elephant; Yesterday I met a man. • Generic refers to any one of a group – Generic pronouns – one, they, you, s/he – Nouns can also have generic reference – A good man is hard to find; The bald eagle is back for near extinction. • Some sentences are ambiguous in terms of generic or specific reference – E. g. , My sister wants to marry a rich man; The lion is dangerous.
Generic vs. Specific Reference • Specific refers to a specific person or thing – E. g. , Look at that elephant; Yesterday I met a man. • Generic refers to any one of a group – Generic pronouns – one, they, you, s/he – Nouns can also have generic reference – A good man is hard to find; The bald eagle is back for near extinction. • Some sentences are ambiguous in terms of generic or specific reference – E. g. , My sister wants to marry a rich man; The lion is dangerous.
 Pronoun Types • Central – Personal – e. g. , I, me, they, them – Reflexive – e. g. , myself, themselves – Reciprocal – each other, one another – Possessive – e. g. , my/mine, their/theirs • Relative – which, whose, whom, that • Interrogative – who, whom, which, whose, what • Demonstrative – this, these, that, those • Indefinite – e. g. , both, each, nobody, everything
Pronoun Types • Central – Personal – e. g. , I, me, they, them – Reflexive – e. g. , myself, themselves – Reciprocal – each other, one another – Possessive – e. g. , my/mine, their/theirs • Relative – which, whose, whom, that • Interrogative – who, whom, which, whose, what • Demonstrative – this, these, that, those • Indefinite – e. g. , both, each, nobody, everything
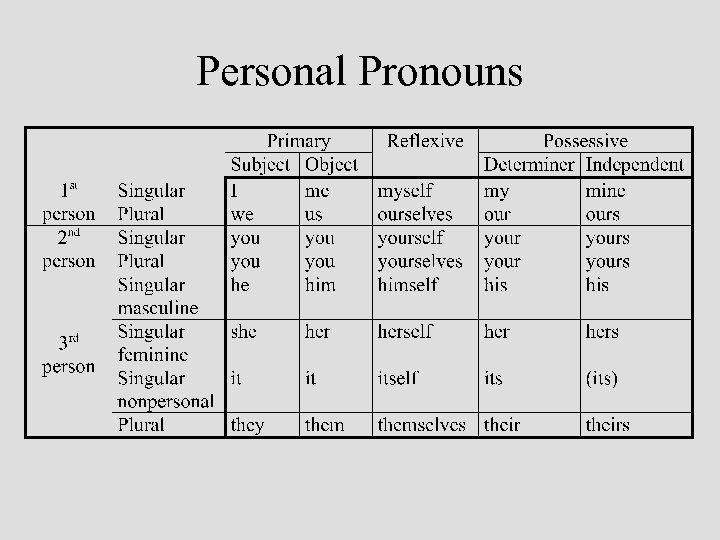 Personal Pronouns
Personal Pronouns
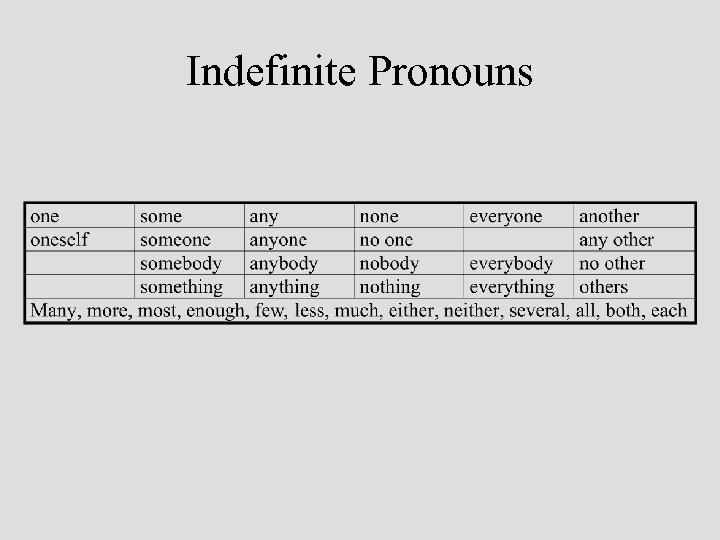 Indefinite Pronouns
Indefinite Pronouns


