037ef7d213453cbdf59b1b971fc8a595.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 71
 NOTES ON ENRON Death of a Corporation Idiots v. Crooks
NOTES ON ENRON Death of a Corporation Idiots v. Crooks
 FIRST: • Let’s Discuss BUSINESS ORGANIZATION. – NOTE: This isn’t in the book – but it is a sample of Microeconomics and current events – since ENRON is still in the news. • You will work for one type of organization in your future.
FIRST: • Let’s Discuss BUSINESS ORGANIZATION. – NOTE: This isn’t in the book – but it is a sample of Microeconomics and current events – since ENRON is still in the news. • You will work for one type of organization in your future.
 The Three Types of Business Organization • Sole Proprietorship • Partnerships • Corporations
The Three Types of Business Organization • Sole Proprietorship • Partnerships • Corporations
 Sole Proprietorship • If you alone own and control the service.
Sole Proprietorship • If you alone own and control the service.
 Opportunity Benefits of Sole Proprietorships • Owner has direct control • Small initial investment • Owner receives all profits • Owner can dissolve business when necessary.
Opportunity Benefits of Sole Proprietorships • Owner has direct control • Small initial investment • Owner receives all profits • Owner can dissolve business when necessary.
 Opportunity Costs of Sole Proprietorships • All losses are borne by owner • Difficulty in raising financial capital – Limited growth potential • Only one person in authority • Lack of longevity • Unlimited liability
Opportunity Costs of Sole Proprietorships • All losses are borne by owner • Difficulty in raising financial capital – Limited growth potential • Only one person in authority • Lack of longevity • Unlimited liability
 Partnerships • A business owned and controlled by two or more people. • Ben and Jerry were college buddies that found after certain “experiences” at Berkeley in the 60 s – they were really hungry for ice cream.
Partnerships • A business owned and controlled by two or more people. • Ben and Jerry were college buddies that found after certain “experiences” at Berkeley in the 60 s – they were really hungry for ice cream.
 REMEMBER! • Partnerships don’t have to be just two people. • JC Penney: The man with a thousand partners. • Ben and Jerry today at a “Legalize Hemp” Festival • Essay contest and now their company is part of Borden.
REMEMBER! • Partnerships don’t have to be just two people. • JC Penney: The man with a thousand partners. • Ben and Jerry today at a “Legalize Hemp” Festival • Essay contest and now their company is part of Borden.
 Two forms of partnerships • General Partnerships: Equal decision making. • Limited Partnerships: Partners join as investors, offering capital, but little, if any, role in decision making. – VENTURE CAPITALISTS – Famous Dave made great barbecue – but had no sense of business. – Going broke UNTIL
Two forms of partnerships • General Partnerships: Equal decision making. • Limited Partnerships: Partners join as investors, offering capital, but little, if any, role in decision making. – VENTURE CAPITALISTS – Famous Dave made great barbecue – but had no sense of business. – Going broke UNTIL
 Willy Theisen • Founded Godfather’s Pizza in 1973 and made a fortune – sold out the chain to Pillsbury and now is a Venture Capitalist creating partnerships like Famous Dave
Willy Theisen • Founded Godfather’s Pizza in 1973 and made a fortune – sold out the chain to Pillsbury and now is a Venture Capitalist creating partnerships like Famous Dave
 Advantages of Partnerships • Two or more individuals own the business. – Specialization • Losses are shared by partners. • More money is available to invest in business • Sharing management responsibilities • Taxes are shared by partners
Advantages of Partnerships • Two or more individuals own the business. – Specialization • Losses are shared by partners. • More money is available to invest in business • Sharing management responsibilities • Taxes are shared by partners
 Disadvantages of Partnerships • Division of authority • Unlimited liability. • Difficulty in raising additional capital. • Lack of longevity. • Legal complications when there is a change in ownership.
Disadvantages of Partnerships • Division of authority • Unlimited liability. • Difficulty in raising additional capital. • Lack of longevity. • Legal complications when there is a change in ownership.
 Advantages of Corporations Limited liability. Easy to raise needed capital. Business owned by a group of individuals. Responsibilities for running the business divided among many individuals Easy change in ownership and business continues as long as it makes profits. – LONGEVITY.
Advantages of Corporations Limited liability. Easy to raise needed capital. Business owned by a group of individuals. Responsibilities for running the business divided among many individuals Easy change in ownership and business continues as long as it makes profits. – LONGEVITY.
 Disadvantages of Corporations • Corporate charters are $$$ • Federal and state govts. monitor corporations more. • ***Slow process of decision making.
Disadvantages of Corporations • Corporate charters are $$$ • Federal and state govts. monitor corporations more. • ***Slow process of decision making.
 Corporations • Legally distinct from their owners and treated as if individuals. – Corporations can • • • Own property Hire workers Make contracts Pay taxes Sue and be sued Make and sell products.
Corporations • Legally distinct from their owners and treated as if individuals. – Corporations can • • • Own property Hire workers Make contracts Pay taxes Sue and be sued Make and sell products.
 What kind of companies are organized as corporations? • USUALLY – food, steel, oil companies are corporations. • Insurance companies, supermarket chains, major companies.
What kind of companies are organized as corporations? • USUALLY – food, steel, oil companies are corporations. • Insurance companies, supermarket chains, major companies.
 Forming a corporation • When expansion calls for more than adding more partners. • GET A LAWYER!
Forming a corporation • When expansion calls for more than adding more partners. • GET A LAWYER!
 Forming a corporation: • Lawyer applies for a state license: ARTICLES OF INCORPORATION. • Reviewed by state officials. If all in order they grant – CORPORATE CHARTERS
Forming a corporation: • Lawyer applies for a state license: ARTICLES OF INCORPORATION. • Reviewed by state officials. If all in order they grant – CORPORATE CHARTERS
 Corporate Structure • The corporate charter identifies the officers. – Chairman of the board – symbolic head of the corporation. – CEO – Chief Executive Officer – the REAL power. – Martha Stewart – before prison was BOTH Chairman and CEO of her corporation.
Corporate Structure • The corporate charter identifies the officers. – Chairman of the board – symbolic head of the corporation. – CEO – Chief Executive Officer – the REAL power. – Martha Stewart – before prison was BOTH Chairman and CEO of her corporation.
 Corporate Structure • Board of Directors – people from inside or outside the company. – Key decision making body. • Decide on product lines. • Hires / fires corporate officers to do the day-today running of the corporation. – Sees that boards policies are carried out.
Corporate Structure • Board of Directors – people from inside or outside the company. – Key decision making body. • Decide on product lines. • Hires / fires corporate officers to do the day-today running of the corporation. – Sees that boards policies are carried out.
 Corporate Finances • Most common way to raise money is selling STOCK. – STOCK – represents ownership of the firm. – Ownership is issued in portions called SHARES.
Corporate Finances • Most common way to raise money is selling STOCK. – STOCK – represents ownership of the firm. – Ownership is issued in portions called SHARES.
 Corporate finances • If you buy 100 shares of stock in a company, you own 100 pieces of that company. If that company has a total of 10, 000 shares available – you own 1% of the company.
Corporate finances • If you buy 100 shares of stock in a company, you own 100 pieces of that company. If that company has a total of 10, 000 shares available – you own 1% of the company.
 Why own stock? • DIVIDENDS – profits on your investment. – PREFERRED STOCK – guarantees dividends. – COMMON STOCK – potential for dividends.
Why own stock? • DIVIDENDS – profits on your investment. – PREFERRED STOCK – guarantees dividends. – COMMON STOCK – potential for dividends.
 Why own stock? • SOMETIMES can make more money for you. • The “fun” of being involved with a corporation or a product.
Why own stock? • SOMETIMES can make more money for you. • The “fun” of being involved with a corporation or a product.
 Benefits for stockholders • Flexibility of ownership. • Limited liability. – Can’t be sued for corporate problems. – If the corporation folds, you only lose what you invested. – Private assets can’t be seized. – Coors shareholders can’t be sued by a MAD mother.
Benefits for stockholders • Flexibility of ownership. • Limited liability. – Can’t be sued for corporate problems. – If the corporation folds, you only lose what you invested. – Private assets can’t be seized. – Coors shareholders can’t be sued by a MAD mother.
 The trade-off • Common stock ownership allows a “voice” on how the company is run. • Preferred stock does not. • ATT, DISNEY have had their CEOs replaced by the majority shareholders voting.
The trade-off • Common stock ownership allows a “voice” on how the company is run. • Preferred stock does not. • ATT, DISNEY have had their CEOs replaced by the majority shareholders voting.
 IMPORTANT ADVICE TO FUTURE CORPORATE HEADS!!! • ALWAYS hold or directly control 51% of your company’s stock. • OR have a lack of control at annual shareholder meetings. • You can lose your job! • As Steve Jobs found out!
IMPORTANT ADVICE TO FUTURE CORPORATE HEADS!!! • ALWAYS hold or directly control 51% of your company’s stock. • OR have a lack of control at annual shareholder meetings. • You can lose your job! • As Steve Jobs found out!
 The corporation raises money • If there are thousands of shareholders, there is enormous amounts of money through the sale of stock. • e. Bay has 6, 643, 058 shares available.
The corporation raises money • If there are thousands of shareholders, there is enormous amounts of money through the sale of stock. • e. Bay has 6, 643, 058 shares available.
 Other ways corporations raise $$. • Corporate bonds. – You loan your money to the company. – You DO NOT own the company. – Repaid the principal and the interest. • Principal – the actual money borrowed. • Interest – the price you gave to that principal.
Other ways corporations raise $$. • Corporate bonds. – You loan your money to the company. – You DO NOT own the company. – Repaid the principal and the interest. • Principal – the actual money borrowed. • Interest – the price you gave to that principal.
 Example of Corporate Bonds • You hold a 1 year $1, 000 bond. • At the end of the year you are paid back the $1, 000 principal AND the 5% ($50) interest.
Example of Corporate Bonds • You hold a 1 year $1, 000 bond. • At the end of the year you are paid back the $1, 000 principal AND the 5% ($50) interest.
 Corporate Combinations • Most corporations seek to expand. – Build new facilities – Legally combines with another enterprise. • MERGERS!
Corporate Combinations • Most corporations seek to expand. – Build new facilities – Legally combines with another enterprise. • MERGERS!
 Three types of Mergers (corporate combinations) • Horizontal • Vertical • Conglomerate
Three types of Mergers (corporate combinations) • Horizontal • Vertical • Conglomerate
 Horizontal Combination • Buying up companies involved in the same industry. • THINK STANDARD OIL – John D. Rockefeller. • IF on any future test there is a Standard Oil question – just skip to the horizontal answer.
Horizontal Combination • Buying up companies involved in the same industry. • THINK STANDARD OIL – John D. Rockefeller. • IF on any future test there is a Standard Oil question – just skip to the horizontal answer.
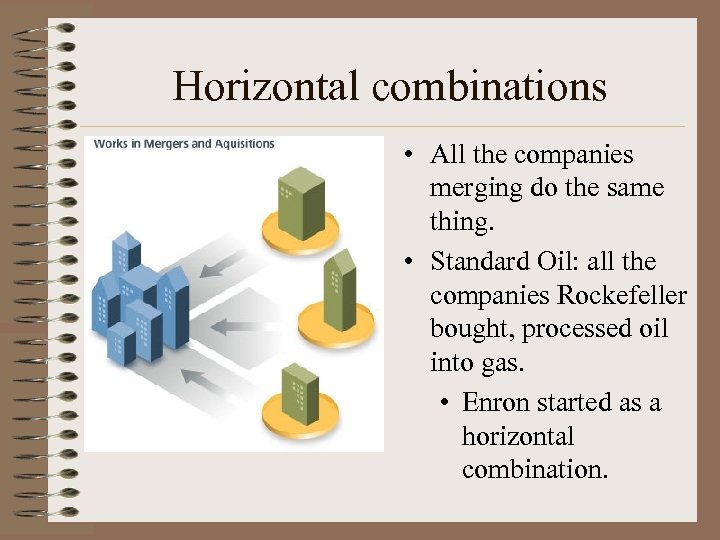 Horizontal combinations • All the companies merging do the same thing. • Standard Oil: all the companies Rockefeller bought, processed oil into gas. • Enron started as a horizontal combination.
Horizontal combinations • All the companies merging do the same thing. • Standard Oil: all the companies Rockefeller bought, processed oil into gas. • Enron started as a horizontal combination.
 Vertical Combination • A merger between two or more companies involved in different production phases of the same good or service. • THINK US STEEL / Andrew Carnegie.
Vertical Combination • A merger between two or more companies involved in different production phases of the same good or service. • THINK US STEEL / Andrew Carnegie.
 Conglomerates • Merger of companies producing unrelated products. • Subsidiaries. • Started in the 1960 s. – Kind of started by Warren Buffet
Conglomerates • Merger of companies producing unrelated products. • Subsidiaries. • Started in the 1960 s. – Kind of started by Warren Buffet
 BERKSHIRE HATHAWAY INC. Acme Brick Company Johns Manville Ben Bridge Jeweler Jordan's Furniture Benjamin Moore & Co. Justin Brands Berkshire Hathaway Group Larson-Juhl Berkshire Hathaway Homestates Companies Mc. Lane Company Borsheim's Fine Jewelry Mid. American Energy Holdings Company Buffalo NEWS, Buffalo NY Mi. Tek Inc.
BERKSHIRE HATHAWAY INC. Acme Brick Company Johns Manville Ben Bridge Jeweler Jordan's Furniture Benjamin Moore & Co. Justin Brands Berkshire Hathaway Group Larson-Juhl Berkshire Hathaway Homestates Companies Mc. Lane Company Borsheim's Fine Jewelry Mid. American Energy Holdings Company Buffalo NEWS, Buffalo NY Mi. Tek Inc.
 Borsheim's Fine Jewelry Mid. American Energy Holdings Company Buffalo NEWS, Buffalo NY Mi. Tek Inc. Central States Indemnity Company National Indemnity Company Clayton Homes Nebraska Furniture Mart CORT Business Services Net. Jets® CTB Inc. The Pampered Chef®
Borsheim's Fine Jewelry Mid. American Energy Holdings Company Buffalo NEWS, Buffalo NY Mi. Tek Inc. Central States Indemnity Company National Indemnity Company Clayton Homes Nebraska Furniture Mart CORT Business Services Net. Jets® CTB Inc. The Pampered Chef®
 And. . • GEICO! • There is a lot more – but I don’t have room!
And. . • GEICO! • There is a lot more – but I don’t have room!
 Opportunity Benefits of Combinations • Efficiency – centralized decision making. • Potential lower costs. • Easier to acquire financial capital.
Opportunity Benefits of Combinations • Efficiency – centralized decision making. • Potential lower costs. • Easier to acquire financial capital.
 Opportunity Costs of Combinations • Can lead to unemployment (don’t need to double the jobs) • Reduced competition in the market place. – MONOPOLIES.
Opportunity Costs of Combinations • Can lead to unemployment (don’t need to double the jobs) • Reduced competition in the market place. – MONOPOLIES.
 Franchises • One company agrees – for a fee – to let another person or group set up a FRANCHISE. – Have to uphold the reputation of the parent company. – Get training and advertising.
Franchises • One company agrees – for a fee – to let another person or group set up a FRANCHISE. – Have to uphold the reputation of the parent company. – Get training and advertising.
 Cooperatives • Co-ops – businesses owned by their members. – Membership gives privileges.
Cooperatives • Co-ops – businesses owned by their members. – Membership gives privileges.
 Cooperatives
Cooperatives
 Nonprofit Organizations • Does not focus on financial gain and profits. • Business organization but pursues other goals. • Income isn’t taxed.
Nonprofit Organizations • Does not focus on financial gain and profits. • Business organization but pursues other goals. • Income isn’t taxed.
 So What About ENRON?
So What About ENRON?
 Enron History Created in 1985 with a merger between two companies Houston Natural Gas and Inter. North in Omaha, NE. Horizontal merger between two gas pipeline companies.
Enron History Created in 1985 with a merger between two companies Houston Natural Gas and Inter. North in Omaha, NE. Horizontal merger between two gas pipeline companies.
 BTW: • BAD feelings about Enron in Omaha! • Ken Lay of Enron promised to keep Omaha as a central headquarters for Enron. – Broke the promise in six months and moved everything to Houston.
BTW: • BAD feelings about Enron in Omaha! • Ken Lay of Enron promised to keep Omaha as a central headquarters for Enron. – Broke the promise in six months and moved everything to Houston.
 Enron History • Branched out of the natural gas business into power plants, pipelines for gas and energy. • Ken Lay CEO and later Chairman • Jeff Skilling came in and took the company into conglomerate enterprises.
Enron History • Branched out of the natural gas business into power plants, pipelines for gas and energy. • Ken Lay CEO and later Chairman • Jeff Skilling came in and took the company into conglomerate enterprises.
 Enron • By 2000, Enron was the SEVENTH largest corporation in the country and a darling of Wall Street with great earnings report. – They sell energy – so how could they go wrong? • A needed good!
Enron • By 2000, Enron was the SEVENTH largest corporation in the country and a darling of Wall Street with great earnings report. – They sell energy – so how could they go wrong? • A needed good!
 So, what went wrong? • It is still being sorted out. • Problems with people not talking. • Evidence was destroyed. • Political pressure not to investigate too much? ?
So, what went wrong? • It is still being sorted out. • Problems with people not talking. • Evidence was destroyed. • Political pressure not to investigate too much? ?
 So, what went wrong? • Primary question: Were they idiots or crooks? • Brian Cruver’s story is about his time at Enron – about the last six months of the company and his observations.
So, what went wrong? • Primary question: Were they idiots or crooks? • Brian Cruver’s story is about his time at Enron – about the last six months of the company and his observations.
 What happened at ENRON? • Enron branched into operations they didn’t really “know” about. – Didn’t have a corporate board that was based on knowing the business world.
What happened at ENRON? • Enron branched into operations they didn’t really “know” about. – Didn’t have a corporate board that was based on knowing the business world.
 In just 5 years Enron branched into fields like: • • • • Oil & LNG Transportation Broadband Petrochemicals* Plastics* Power* Principal Investments Pulp & Paper* Risk Management for Commodities Shipping / Freight Steel* Streaming Media Water & Wastewater Computer Chips Weather Risk Management
In just 5 years Enron branched into fields like: • • • • Oil & LNG Transportation Broadband Petrochemicals* Plastics* Power* Principal Investments Pulp & Paper* Risk Management for Commodities Shipping / Freight Steel* Streaming Media Water & Wastewater Computer Chips Weather Risk Management
 No one really was an expert in any of these fields … • If mistakes were made – they simply went to find another business to get into.
No one really was an expert in any of these fields … • If mistakes were made – they simply went to find another business to get into.
 Management Problems • Managers that weren’t managing their people. • Personnel afraid of the reviews that “automatically deployed” the lowest 15% based on peer reviews. – No one wanted to make anyone mad at them! – Lack of accountability.
Management Problems • Managers that weren’t managing their people. • Personnel afraid of the reviews that “automatically deployed” the lowest 15% based on peer reviews. – No one wanted to make anyone mad at them! – Lack of accountability.
 Management Problems • “No bad news” the Enron motto. • Falsifying reports that might make “unfavorable” news about the people or company. • Enron = power + success
Management Problems • “No bad news” the Enron motto. • Falsifying reports that might make “unfavorable” news about the people or company. • Enron = power + success
 Yes! It is True! • Enron employed a number of people solely on their looks. • People think beauty = success. • STRIPPERS were hired to work in the offices.
Yes! It is True! • Enron employed a number of people solely on their looks. • People think beauty = success. • STRIPPERS were hired to work in the offices.
 Cooking the Books • Andy Fastow CFO (Chief Financial Officer) cooked the books. • As bad deals kept happening a corporation has two choices:
Cooking the Books • Andy Fastow CFO (Chief Financial Officer) cooked the books. • As bad deals kept happening a corporation has two choices:
 Cooking the Books • Revealing the bad deals. – Makes the value of the stock go down. – People lose their jobs. • Hide the debt – Keep the stock price up. – People keep their jobs.
Cooking the Books • Revealing the bad deals. – Makes the value of the stock go down. – People lose their jobs. • Hide the debt – Keep the stock price up. – People keep their jobs.
 Virtual Assets • Fastow’s creation. • What does VIRTUAL mean? • What does assets mean?
Virtual Assets • Fastow’s creation. • What does VIRTUAL mean? • What does assets mean?
 Virtual Assets • For years, no one questioned the term. • They were counting on deals to pay off before they actually paid off. – Example: Living like you already have a million dollars because you know someday you will win the lottery, since you buy a ticket a week.
Virtual Assets • For years, no one questioned the term. • They were counting on deals to pay off before they actually paid off. – Example: Living like you already have a million dollars because you know someday you will win the lottery, since you buy a ticket a week.
 Virtual Assets • The SEC and Wall Street demand a balance sheet that when a company says “We made 100 -billion in profits” – that it is true. – Arthur Andersen Auditors come in.
Virtual Assets • The SEC and Wall Street demand a balance sheet that when a company says “We made 100 -billion in profits” – that it is true. – Arthur Andersen Auditors come in.
 Buying off the auditors • Enron executives “bought off” the Arthur Andersen Company to keep the lie of profits based on “virtual assets” going. – Note how that info is just “slipped in” to Brian Cruver’s training. – They also helped shred evidence about who knew what and when.
Buying off the auditors • Enron executives “bought off” the Arthur Andersen Company to keep the lie of profits based on “virtual assets” going. – Note how that info is just “slipped in” to Brian Cruver’s training. – They also helped shred evidence about who knew what and when.
 Enron Image • If people saw Enron employees living well – it gave the impression that the company was doing great. – Encouraged employees to live beyond their means? ? ?
Enron Image • If people saw Enron employees living well – it gave the impression that the company was doing great. – Encouraged employees to live beyond their means? ? ?
 Political Influences? • The movie brings up the connections to George Bush and Dick Cheney – and there are legitimate questions there. • But Enron was also contributing to both sides of the aisle. – Note Mr. Blue’s insider trading. – Note the news flashes of helping politicians.
Political Influences? • The movie brings up the connections to George Bush and Dick Cheney – and there are legitimate questions there. • But Enron was also contributing to both sides of the aisle. – Note Mr. Blue’s insider trading. – Note the news flashes of helping politicians.
 Ken Lay’s Role in Enron • He encouraged the employees to buy the stock. – Creating demand to bring the price up. – But he sold his stock when the price went up. – His son was short-selling Enron. • Betting the stock would go down in value and collecting a payoff.
Ken Lay’s Role in Enron • He encouraged the employees to buy the stock. – Creating demand to bring the price up. – But he sold his stock when the price went up. – His son was short-selling Enron. • Betting the stock would go down in value and collecting a payoff.
 Characters to know: • Ken Lay – Founder of Enron – Chairman and CEO
Characters to know: • Ken Lay – Founder of Enron – Chairman and CEO
 Jeff Skilling • CEO of Enron • ARROGANCE in his management style and encouraged it in the company.
Jeff Skilling • CEO of Enron • ARROGANCE in his management style and encouraged it in the company.
 Andy Fastow • CFO
Andy Fastow • CFO
 “Mr. Blue” • Real life name: J. Clifford Baxter.
“Mr. Blue” • Real life name: J. Clifford Baxter.


