3f882ebc4da8b37d49acefb463575087.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43
 Notes 8: Predicate logic and inference ICS 271 Fall 2006
Notes 8: Predicate logic and inference ICS 271 Fall 2006
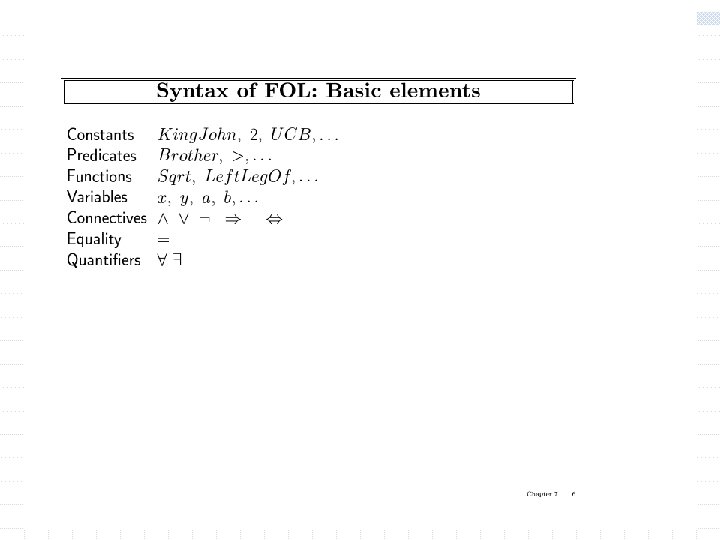
 Outline w New ontology n objects, relations, properties, functions. w New Syntax n Constants, predicates, properties, functions w New semantics n meaning of new syntax w Inference rules for Predicate Logic (FOL) n Resolution n Forward-chaining, Backword-chaining n unification w Readings: Nillson’s Chapters 15 -16, Russel and Norvig Chapter 8, chapter 9
Outline w New ontology n objects, relations, properties, functions. w New Syntax n Constants, predicates, properties, functions w New semantics n meaning of new syntax w Inference rules for Predicate Logic (FOL) n Resolution n Forward-chaining, Backword-chaining n unification w Readings: Nillson’s Chapters 15 -16, Russel and Norvig Chapter 8, chapter 9

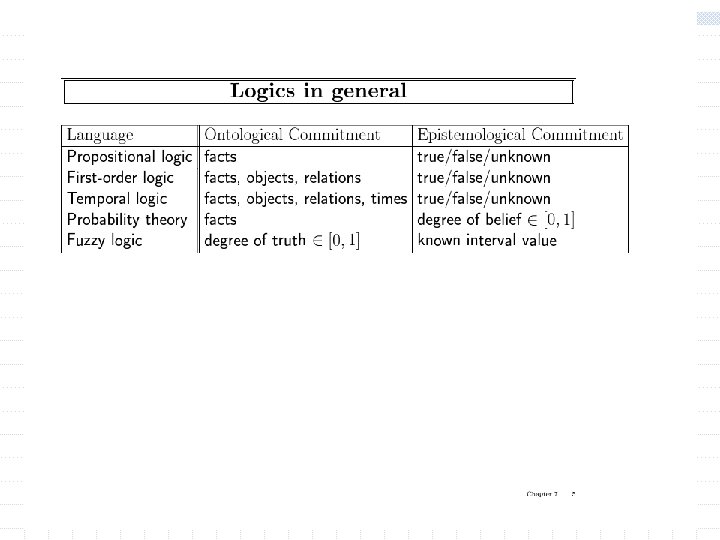
 Propositional logic is not expressive w Needs to refer to objects in the world, w Needs to express general rules n On(x, y) ~ clear(y) n All man are mortal n Everyone who passed age 21 can drink n One student in this class got perfect score n Etc…. w First order logic, also called Predicate calculus allows more expressiveness
Propositional logic is not expressive w Needs to refer to objects in the world, w Needs to express general rules n On(x, y) ~ clear(y) n All man are mortal n Everyone who passed age 21 can drink n One student in this class got perfect score n Etc…. w First order logic, also called Predicate calculus allows more expressiveness



 Semantics: Worlds w The world consists of objects that has properties. n n There are relations and functions between these objects Objects in the world, individuals: people, houses, numbers, colors, baseball games, wars, centuries w Clock A, John, 7, the-house in the corner, Tel-Aviv n Functions on individuals: w father-of, best friend, third inning of, one more than n Relations: w brother-of, bigger than, inside, part-of, has color, occurred after n Properties (a relation of arity 1): w red, round, bogus, prime, multistoried, beautiful
Semantics: Worlds w The world consists of objects that has properties. n n There are relations and functions between these objects Objects in the world, individuals: people, houses, numbers, colors, baseball games, wars, centuries w Clock A, John, 7, the-house in the corner, Tel-Aviv n Functions on individuals: w father-of, best friend, third inning of, one more than n Relations: w brother-of, bigger than, inside, part-of, has color, occurred after n Properties (a relation of arity 1): w red, round, bogus, prime, multistoried, beautiful
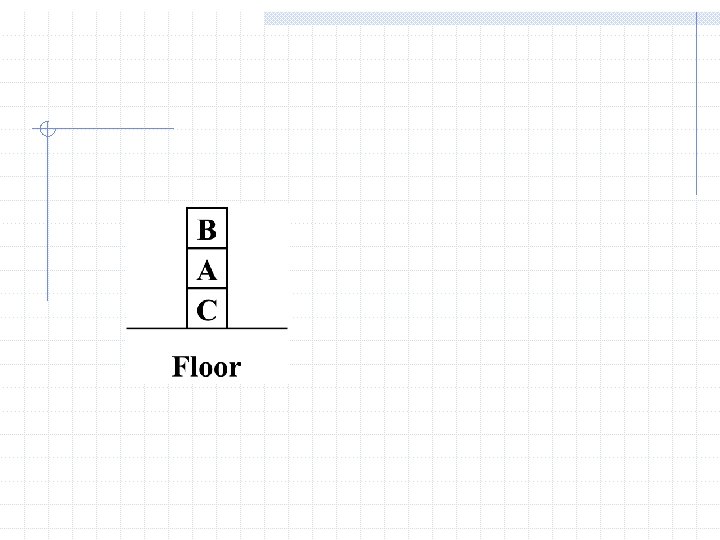
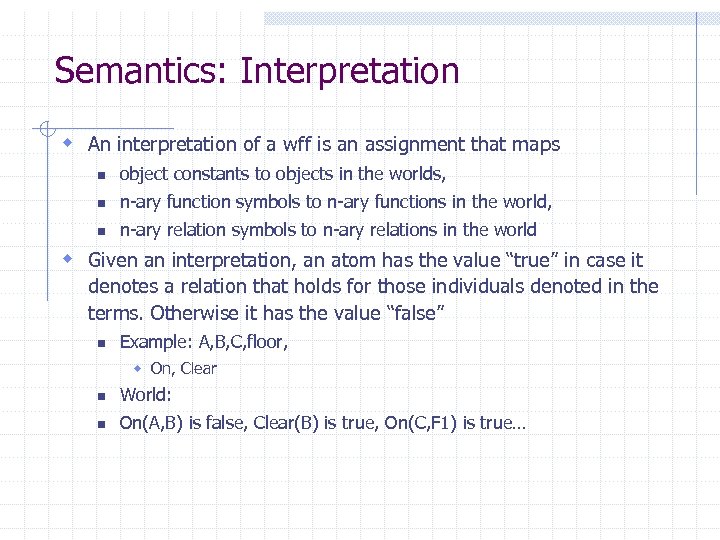 Semantics: Interpretation w An interpretation of a wff is an assignment that maps n object constants to objects in the worlds, n n-ary function symbols to n-ary functions in the world, n n-ary relation symbols to n-ary relations in the world w Given an interpretation, an atom has the value “true” in case it denotes a relation that holds for those individuals denoted in the terms. Otherwise it has the value “false” n Example: A, B, C, floor, w On, Clear n World: n On(A, B) is false, Clear(B) is true, On(C, F 1) is true…
Semantics: Interpretation w An interpretation of a wff is an assignment that maps n object constants to objects in the worlds, n n-ary function symbols to n-ary functions in the world, n n-ary relation symbols to n-ary relations in the world w Given an interpretation, an atom has the value “true” in case it denotes a relation that holds for those individuals denoted in the terms. Otherwise it has the value “false” n Example: A, B, C, floor, w On, Clear n World: n On(A, B) is false, Clear(B) is true, On(C, F 1) is true…
 Semantics: Models w An interpretation satisfies a wff (sentence) if the wff has the value “true” under the interpretation. w An interpretation that satisfies a wff is a model of that wff w Any wff that has the value “true” under all interpretations is valid w Any wff that does not have a model is inconsistent or unsatisfiable w If a wff w has a value true under all the models of a set of sentences KB then KB logically entails w
Semantics: Models w An interpretation satisfies a wff (sentence) if the wff has the value “true” under the interpretation. w An interpretation that satisfies a wff is a model of that wff w Any wff that has the value “true” under all interpretations is valid w Any wff that does not have a model is inconsistent or unsatisfiable w If a wff w has a value true under all the models of a set of sentences KB then KB logically entails w
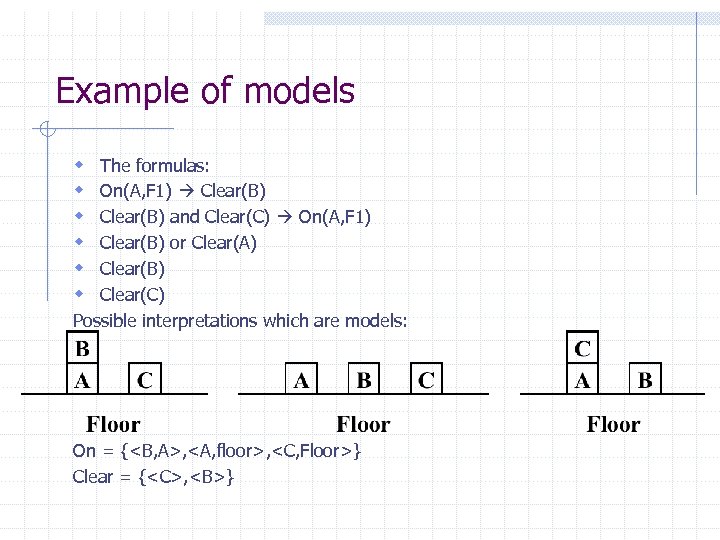 Example of models w w w The formulas: On(A, F 1) Clear(B) and Clear(C) On(A, F 1) Clear(B) or Clear(A) Clear(B) Clear(C) Possible interpretations which are models: On = {
Example of models w w w The formulas: On(A, F 1) Clear(B) and Clear(C) On(A, F 1) Clear(B) or Clear(A) Clear(B) Clear(C) Possible interpretations which are models: On = {
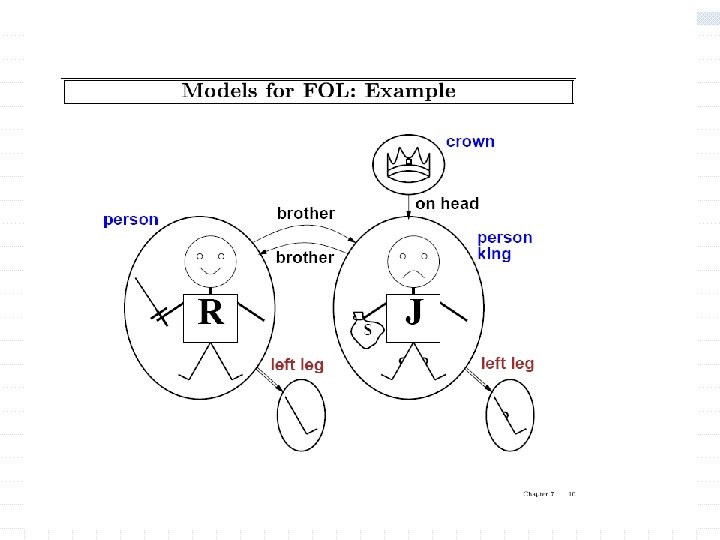
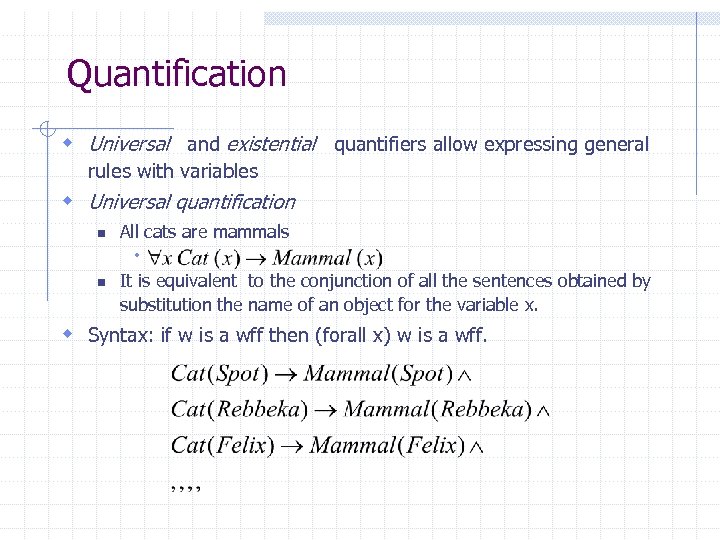 Quantification w Universal and existential quantifiers allow expressing general rules with variables w Universal quantification n All cats are mammals w n It is equivalent to the conjunction of all the sentences obtained by substitution the name of an object for the variable x. w Syntax: if w is a wff then (forall x) w is a wff.
Quantification w Universal and existential quantifiers allow expressing general rules with variables w Universal quantification n All cats are mammals w n It is equivalent to the conjunction of all the sentences obtained by substitution the name of an object for the variable x. w Syntax: if w is a wff then (forall x) w is a wff.


 Quantification: Existential w Existential quantification : an existentially quantified sentence is true in case one of the disjunct is true w Equivalent to disjunction: w We can mix existential and universal quantification.
Quantification: Existential w Existential quantification : an existentially quantified sentence is true in case one of the disjunct is true w Equivalent to disjunction: w We can mix existential and universal quantification.









 Using FOL w The kinship domain: n n object are people Properties include gender and they are related by relations such as parenthood, brotherhood, marriage predicates: Male, Female (unary) Parent, Sibling, Daughter, Son. . . Function: Mother Father w Brothers are siblings x, y Brother(x, y) Sibling(x, y) w One's mother is one's female parent m, c Mother(c) = m (Female(m) Parent(m, c)) w “Sibling” is symmetric
Using FOL w The kinship domain: n n object are people Properties include gender and they are related by relations such as parenthood, brotherhood, marriage predicates: Male, Female (unary) Parent, Sibling, Daughter, Son. . . Function: Mother Father w Brothers are siblings x, y Brother(x, y) Sibling(x, y) w One's mother is one's female parent m, c Mother(c) = m (Female(m) Parent(m, c)) w “Sibling” is symmetric
 Using FOL The set domain: w s Set(s) (s = {} ) ( x, s 2 Set(s 2) s = {x|s 2}) w x, s {x|s} = {} w x, s x s s = {x|s} w (the only members of a set are the elements that were adjoint into it) w x, s x s [ y, s 2} (s = {y|s 2} (x = y x s 2))] w s 1, s 2 s 1 s 2 ( x x s 1 x s 2) Objects are (s w s 1, s 2 (s 1 = s 2) sets 1 s 2 s 1) Predicates: unary predicate “set: , binary predicate membership (x is a member of set), (x s subset of s 2) w x, s 1, s 2 x (s 1 s 2) “subset” 1 (s 1 is a 2) Functions: intersections, union, adjoining an eleiment to a set. w x, s 1, s 2 x (s 1 s 2) (x s 1 x s 2)
Using FOL The set domain: w s Set(s) (s = {} ) ( x, s 2 Set(s 2) s = {x|s 2}) w x, s {x|s} = {} w x, s x s s = {x|s} w (the only members of a set are the elements that were adjoint into it) w x, s x s [ y, s 2} (s = {y|s 2} (x = y x s 2))] w s 1, s 2 s 1 s 2 ( x x s 1 x s 2) Objects are (s w s 1, s 2 (s 1 = s 2) sets 1 s 2 s 1) Predicates: unary predicate “set: , binary predicate membership (x is a member of set), (x s subset of s 2) w x, s 1, s 2 x (s 1 s 2) “subset” 1 (s 1 is a 2) Functions: intersections, union, adjoining an eleiment to a set. w x, s 1, s 2 x (s 1 s 2) (x s 1 x s 2)
 Knowledge engineering in FOL 1. Identify the task 1. Assemble the relevant knowledge 1. Decide on a vocabulary of predicates, functions, and constants 1. Encode general knowledge about the domain 1. Encode a description of the specific problem instance 1. Pose queries to the inference procedure and get answers 1. Debug the knowledge base
Knowledge engineering in FOL 1. Identify the task 1. Assemble the relevant knowledge 1. Decide on a vocabulary of predicates, functions, and constants 1. Encode general knowledge about the domain 1. Encode a description of the specific problem instance 1. Pose queries to the inference procedure and get answers 1. Debug the knowledge base
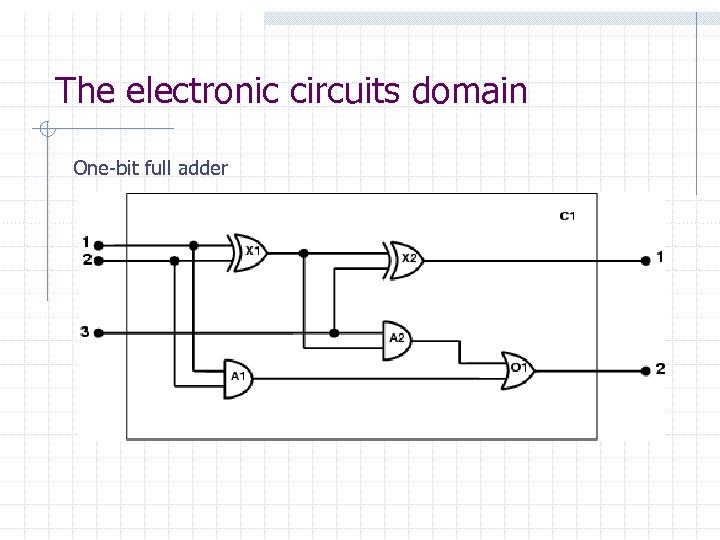 The electronic circuits domain One-bit full adder
The electronic circuits domain One-bit full adder
 The electronic circuits domain 1. Identify the task n 1. Does the circuit actually add properly? (circuit verification) Assemble the relevant knowledge n n 1. Composed of wires and gates; Types of gates (AND, OR, XOR, NOT) Irrelevant: size, shape, color, cost of gates Decide on a vocabulary n Alternatives: Type(X 1) = XOR Type(X 1, XOR) XOR(X 1)
The electronic circuits domain 1. Identify the task n 1. Does the circuit actually add properly? (circuit verification) Assemble the relevant knowledge n n 1. Composed of wires and gates; Types of gates (AND, OR, XOR, NOT) Irrelevant: size, shape, color, cost of gates Decide on a vocabulary n Alternatives: Type(X 1) = XOR Type(X 1, XOR) XOR(X 1)
 The electronic circuits domain 4. Encode general knowledge of the domain n t 1, t 2 Connected(t 1, t 2) Signal(t 1) = Signal(t 2) t Signal(t) = 1 Signal(t) = 0 n 1≠ 0 n t 1, t 2 Connected(t 1, t 2) Connected(t 2, t 1) n g Type(g) = OR Signal(Out(1, g)) = 1 n Signal(In(n, g)) = 1 n g Type(g) = AND Signal(Out(1, g)) = 0 n Signal(In(n, g)) = 0 n g Type(g) = XOR Signal(Out(1, g)) = 1 Signal(In(1, g)) ≠ Signal(In(2, g)) n g Type(g) = NOT Signal(Out(1, g)) ≠ Signal(In(1, g)) n
The electronic circuits domain 4. Encode general knowledge of the domain n t 1, t 2 Connected(t 1, t 2) Signal(t 1) = Signal(t 2) t Signal(t) = 1 Signal(t) = 0 n 1≠ 0 n t 1, t 2 Connected(t 1, t 2) Connected(t 2, t 1) n g Type(g) = OR Signal(Out(1, g)) = 1 n Signal(In(n, g)) = 1 n g Type(g) = AND Signal(Out(1, g)) = 0 n Signal(In(n, g)) = 0 n g Type(g) = XOR Signal(Out(1, g)) = 1 Signal(In(1, g)) ≠ Signal(In(2, g)) n g Type(g) = NOT Signal(Out(1, g)) ≠ Signal(In(1, g)) n
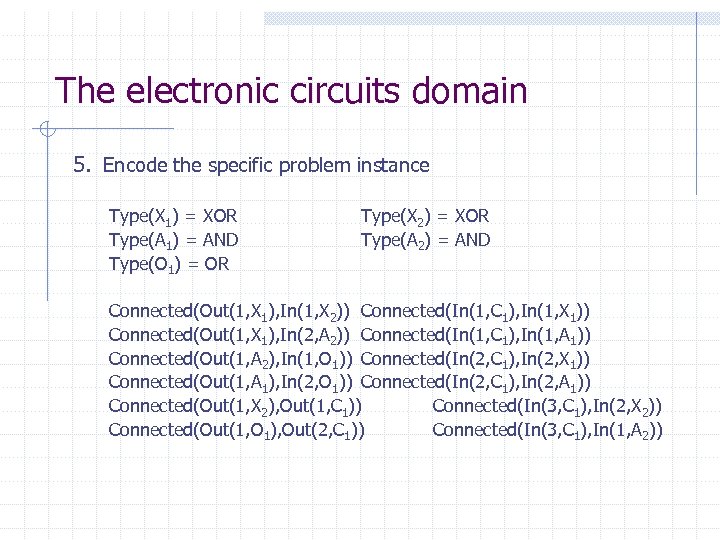 The electronic circuits domain 5. Encode the specific problem instance Type(X 1) = XOR Type(A 1) = AND Type(O 1) = OR Type(X 2) = XOR Type(A 2) = AND Connected(Out(1, X 1), In(1, X 2)) Connected(In(1, C 1), In(1, X 1)) Connected(Out(1, X 1), In(2, A 2)) Connected(In(1, C 1), In(1, A 1)) Connected(Out(1, A 2), In(1, O 1)) Connected(In(2, C 1), In(2, X 1)) Connected(Out(1, A 1), In(2, O 1)) Connected(In(2, C 1), In(2, A 1)) Connected(Out(1, X 2), Out(1, C 1)) Connected(In(3, C 1), In(2, X 2)) Connected(Out(1, O 1), Out(2, C 1)) Connected(In(3, C 1), In(1, A 2))
The electronic circuits domain 5. Encode the specific problem instance Type(X 1) = XOR Type(A 1) = AND Type(O 1) = OR Type(X 2) = XOR Type(A 2) = AND Connected(Out(1, X 1), In(1, X 2)) Connected(In(1, C 1), In(1, X 1)) Connected(Out(1, X 1), In(2, A 2)) Connected(In(1, C 1), In(1, A 1)) Connected(Out(1, A 2), In(1, O 1)) Connected(In(2, C 1), In(2, X 1)) Connected(Out(1, A 1), In(2, O 1)) Connected(In(2, C 1), In(2, A 1)) Connected(Out(1, X 2), Out(1, C 1)) Connected(In(3, C 1), In(2, X 2)) Connected(Out(1, O 1), Out(2, C 1)) Connected(In(3, C 1), In(1, A 2))
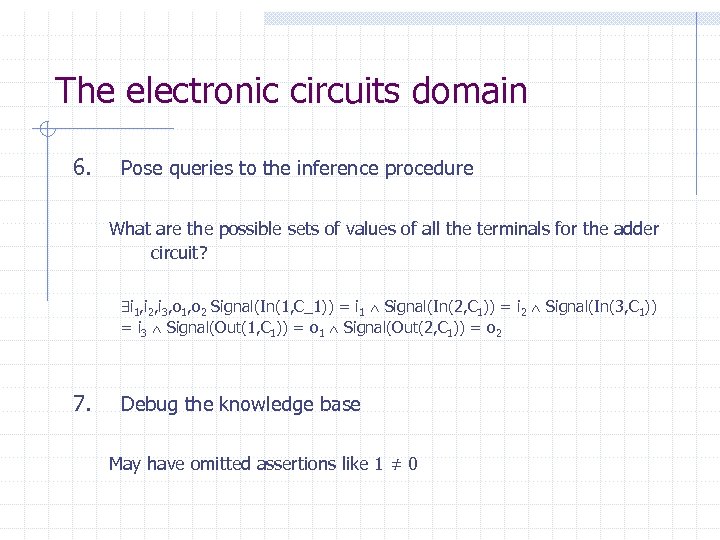 The electronic circuits domain 6. Pose queries to the inference procedure What are the possible sets of values of all the terminals for the adder circuit? i 1, i 2, i 3, o 1, o 2 Signal(In(1, C_1)) = i 1 Signal(In(2, C 1)) = i 2 Signal(In(3, C 1)) = i 3 Signal(Out(1, C 1)) = o 1 Signal(Out(2, C 1)) = o 2 7. Debug the knowledge base May have omitted assertions like 1 ≠ 0
The electronic circuits domain 6. Pose queries to the inference procedure What are the possible sets of values of all the terminals for the adder circuit? i 1, i 2, i 3, o 1, o 2 Signal(In(1, C_1)) = i 1 Signal(In(2, C 1)) = i 2 Signal(In(3, C 1)) = i 3 Signal(Out(1, C 1)) = o 1 Signal(Out(2, C 1)) = o 2 7. Debug the knowledge base May have omitted assertions like 1 ≠ 0



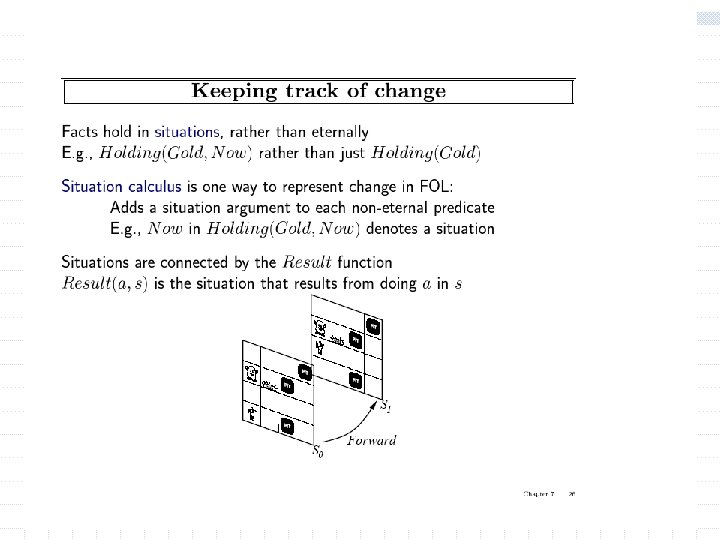


 Summary w First-order logic: n objects and relations are semantic primitives n syntax: constants, functions, predicates, equality, quantifiers w Increased expressive power: sufficient to define wumpus world
Summary w First-order logic: n objects and relations are semantic primitives n syntax: constants, functions, predicates, equality, quantifiers w Increased expressive power: sufficient to define wumpus world


