f594cc81f424a0baa18e1aed8a05eb11.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12
 Not as Easy as E-Mail: Tutors' Perspective of an Online Assignment Submission System Orit Naor-Elaiza (Bar-Ilan University and The Open University of Israel) Nitza Geri (The Open University of Israel)
Not as Easy as E-Mail: Tutors' Perspective of an Online Assignment Submission System Orit Naor-Elaiza (Bar-Ilan University and The Open University of Israel) Nitza Geri (The Open University of Israel)
 Not as Easy as E-Mail: Tutors’ Perspective of an Online Assignment Submission System Orit Naor-Elaiza & Nitza Geri Bar-Ilan University and The Open University of Israel Chais Conference, Raanana, February 18, 2009
Not as Easy as E-Mail: Tutors’ Perspective of an Online Assignment Submission System Orit Naor-Elaiza & Nitza Geri Bar-Ilan University and The Open University of Israel Chais Conference, Raanana, February 18, 2009
 The Puzzle of Continued User acceptance is a necessary condition for realizing information technology innovation potential value (Agarwal & Prasad, 1997) One of the most challenging issues in information systems research is identifying the factors that affect continued use or discontinuance of a system beyond initial adoption (Bhattacherjee, 2001; Delone & Mclean, 1992, 2003) Understanding why people adopt or reject an information system remains one of the most challenging issues (Jeyaraj et al. , 2006; Venkatesh et al. , 2003)
The Puzzle of Continued User acceptance is a necessary condition for realizing information technology innovation potential value (Agarwal & Prasad, 1997) One of the most challenging issues in information systems research is identifying the factors that affect continued use or discontinuance of a system beyond initial adoption (Bhattacherjee, 2001; Delone & Mclean, 1992, 2003) Understanding why people adopt or reject an information system remains one of the most challenging issues (Jeyaraj et al. , 2006; Venkatesh et al. , 2003)
 Why Probing the Assignments System? An online assignment submission system is one of the most valued online activities (Levy, 2006) Apparently, a simple system, similar to e-mail Expected to be valuable especially in a distance or blended learning environment After seven years of implementation, the system handled a marginal part of the assignments After a major management intervention, about half of the assignments were submitted via the system
Why Probing the Assignments System? An online assignment submission system is one of the most valued online activities (Levy, 2006) Apparently, a simple system, similar to e-mail Expected to be valuable especially in a distance or blended learning environment After seven years of implementation, the system handled a marginal part of the assignments After a major management intervention, about half of the assignments were submitted via the system
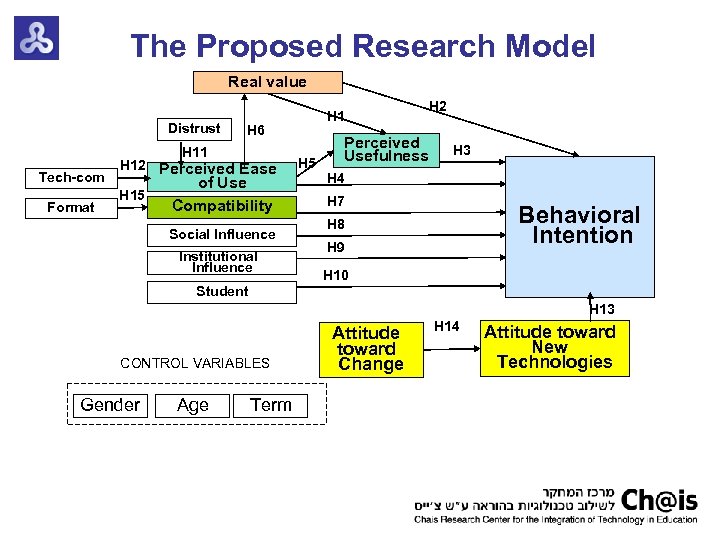 The Proposed Research Model Real value Distrust H 6 H 11 Tech-com Format H 12 Perceived Ease H 15 H 1 of Use Compatibility Social Influence Institutional Influence H 5 H 2 Perceived Usefulness H 3 H 4 H 7 Behavioral Intention H 8 H 9 H 10 Student H 13 CONTROL VARIABLES Gender Age Term Attitude toward Change H 14 Attitude toward New Technologies
The Proposed Research Model Real value Distrust H 6 H 11 Tech-com Format H 12 Perceived Ease H 15 H 1 of Use Compatibility Social Influence Institutional Influence H 5 H 2 Perceived Usefulness H 3 H 4 H 7 Behavioral Intention H 8 H 9 H 10 Student H 13 CONTROL VARIABLES Gender Age Term Attitude toward Change H 14 Attitude toward New Technologies
 The Assignments System Inaugurated in Semester 1999 B – 123 assignments Semester 2006 B – 34, 500 assignments – 19. 2% Students’ use is mainly voluntary The system was not available in all courses As of 2007, management encourages use in all courses Students still have the choice not to use the system This paper focuses on the tutors Part of a comprehensive research examining all parties concerned with the system: students, tutors, course coordinators and management
The Assignments System Inaugurated in Semester 1999 B – 123 assignments Semester 2006 B – 34, 500 assignments – 19. 2% Students’ use is mainly voluntary The system was not available in all courses As of 2007, management encourages use in all courses Students still have the choice not to use the system This paper focuses on the tutors Part of a comprehensive research examining all parties concerned with the system: students, tutors, course coordinators and management
 Methodology Tutors' attitudes toward the assignments system surveyed by the Evaluation Department June 2007 - 475 responses (Alberton, 2007) Pilot Anonymous web survey (July 2008) sent by e-mail to all 275 course coordinators 96 coordinators responses (34. 9%), 89 Tutors Non-response bias (Armstrong & Overton, 1977): 69 “early respondents”; 27 “late” No significant difference
Methodology Tutors' attitudes toward the assignments system surveyed by the Evaluation Department June 2007 - 475 responses (Alberton, 2007) Pilot Anonymous web survey (July 2008) sent by e-mail to all 275 course coordinators 96 coordinators responses (34. 9%), 89 Tutors Non-response bias (Armstrong & Overton, 1977): 69 “early respondents”; 27 “late” No significant difference
 Results Gender: men 33. 3% ; women 66. 7% Age: 30 -39 (23%); 40 -49 (43%); 50 -59 (32%); over 60 (2%) Partial Least Squares (smart. PLS 2. 00) (Ringle et al. , 2005) Structured equation modeling method that analyzes how the items load on their constructs simultaneously with estimating all the paths in the model (Chin, 1998; Chin et al. , 2003; Gefen et al. , 2000; Gefen & Straub, 2005)
Results Gender: men 33. 3% ; women 66. 7% Age: 30 -39 (23%); 40 -49 (43%); 50 -59 (32%); over 60 (2%) Partial Least Squares (smart. PLS 2. 00) (Ringle et al. , 2005) Structured equation modeling method that analyzes how the items load on their constructs simultaneously with estimating all the paths in the model (Chin, 1998; Chin et al. , 2003; Gefen et al. , 2000; Gefen & Straub, 2005)
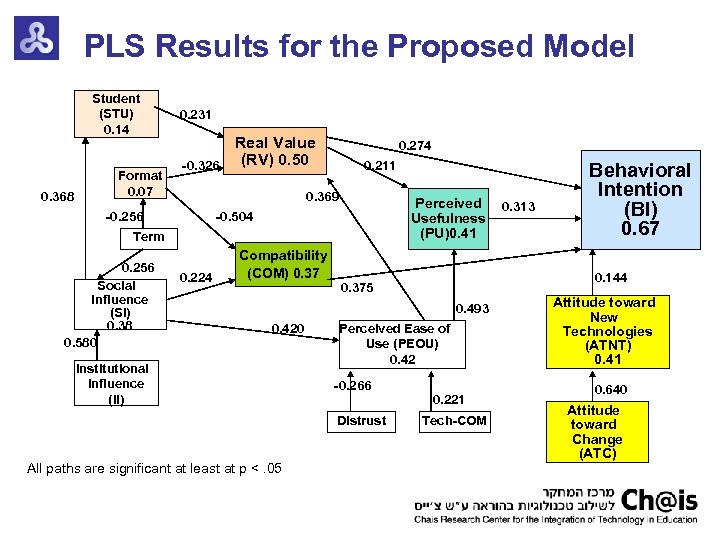 PLS Results for the Proposed Model Student (STU) 0. 14 0. 368 Format 0. 07 0. 231 Real Value (RV) 0. 50 -0. 326 0. 274 0. 211 0. 369 Perceived Usefulness (PU)0. 41 -0. 504 -0. 256 Term 0. 256 Social Influence (SI) 0. 38 0. 580 0. 224 Compatibility (COM) 0. 37 0. 144 0. 375 0. 493 0. 420 Institutional Influence (II) Perceived Ease of Use (PEOU) 0. 42 -0. 266 Distrust All paths are significant at least at p <. 05 0. 313 Behavioral Intention (BI) 0. 67 0. 221 Tech-COM Attitude toward New Technologies (ATNT) 0. 41 0. 640 Attitude toward Change (ATC)
PLS Results for the Proposed Model Student (STU) 0. 14 0. 368 Format 0. 07 0. 231 Real Value (RV) 0. 50 -0. 326 0. 274 0. 211 0. 369 Perceived Usefulness (PU)0. 41 -0. 504 -0. 256 Term 0. 256 Social Influence (SI) 0. 38 0. 580 0. 224 Compatibility (COM) 0. 37 0. 144 0. 375 0. 493 0. 420 Institutional Influence (II) Perceived Ease of Use (PEOU) 0. 42 -0. 266 Distrust All paths are significant at least at p <. 05 0. 313 Behavioral Intention (BI) 0. 67 0. 221 Tech-COM Attitude toward New Technologies (ATNT) 0. 41 0. 640 Attitude toward Change (ATC)
 Discussion and Conclusions Perceived ease of use did not affect behavioral intention of the tutors directly (unlike TAM and student studies) This discrepancy is expected since there is a difference between initial use of an innovation and intentions to continue such use (Agarwal & Prasad, 1997) Tutors consideration of students’ utility positively affected the real value and by that behavioral intention Compatibility, perceived usefulness and real value of the system had the main influence on tutors' behavior
Discussion and Conclusions Perceived ease of use did not affect behavioral intention of the tutors directly (unlike TAM and student studies) This discrepancy is expected since there is a difference between initial use of an innovation and intentions to continue such use (Agarwal & Prasad, 1997) Tutors consideration of students’ utility positively affected the real value and by that behavioral intention Compatibility, perceived usefulness and real value of the system had the main influence on tutors' behavior
 Practical Implications The system and work processes should become more compatible with tutors' needs in order to enhance its use The findings suggest that reluctance to use the system may also be related to tutors' preference for reading from paper rather than a screen Top management involvement in the system adoption resulted in substantial increase of it’s use, but it is not enough as long as the system is not compatible with users’ needs
Practical Implications The system and work processes should become more compatible with tutors' needs in order to enhance its use The findings suggest that reluctance to use the system may also be related to tutors' preference for reading from paper rather than a screen Top management involvement in the system adoption resulted in substantial increase of it’s use, but it is not enough as long as the system is not compatible with users’ needs
 Final Observation "Innovation isn't what innovators do. . . it's what customers and clients adopt" Michael Schrage
Final Observation "Innovation isn't what innovators do. . . it's what customers and clients adopt" Michael Schrage


