2ff39639478e4f50549bd85251981eed.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Northwest Energy: A Look at the Past, Present and Future of Electricity Generation in the Pacific Northwest Jesse Jenkins (RNP) November 7 th, 2006 1
Northwest Energy: A Look at the Past, Present and Future of Electricity Generation in the Pacific Northwest Jesse Jenkins (RNP) November 7 th, 2006 1
 Overview I. Introduction II. Past: where we’re coming from II. Present: where we’re at III. Future: where do we want to go? IV. Conclusions 2
Overview I. Introduction II. Past: where we’re coming from II. Present: where we’re at III. Future: where do we want to go? IV. Conclusions 2
 I. Introduction • Me –recent UO graduate (class of ‘ 06) – now work for the Renewable Northwest Project in Portland (policy research associate) • Renewable Northwest Project (RNP) – founded in 1994 – unique coalition of, consultants, developers, consumer & environmental groups, etc. – seek responsible development of renewable energy in the Pacific Northwest. 3
I. Introduction • Me –recent UO graduate (class of ‘ 06) – now work for the Renewable Northwest Project in Portland (policy research associate) • Renewable Northwest Project (RNP) – founded in 1994 – unique coalition of, consultants, developers, consumer & environmental groups, etc. – seek responsible development of renewable energy in the Pacific Northwest. 3
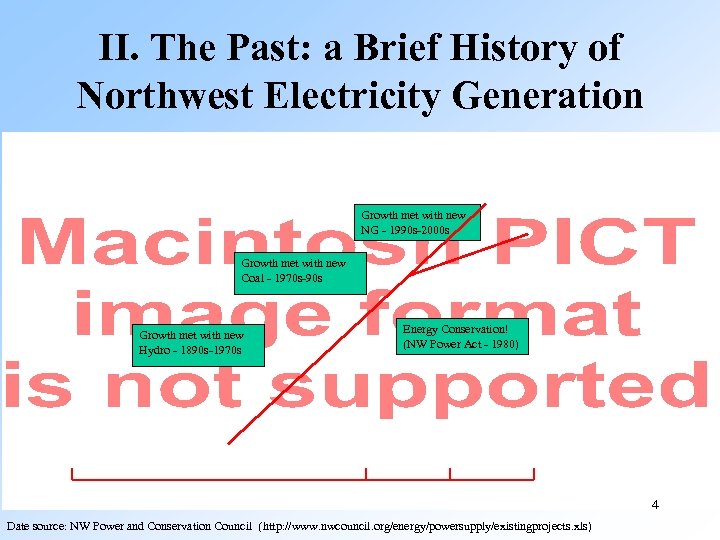 II. The Past: a Brief History of Northwest Electricity Generation Growth met with new NG - 1990 s-2000 s Growth met with new Coal - 1970 s-90 s Growth met with new Hydro - 1890 s-1970 s Energy Conservation! False start with Nukes (NW Power - 1970 s-80 s Act - 1980) 4 Date source: NW Power and Conservation Council (http: //www. nwcouncil. org/energy/powersupply/existingprojects. xls)
II. The Past: a Brief History of Northwest Electricity Generation Growth met with new NG - 1990 s-2000 s Growth met with new Coal - 1970 s-90 s Growth met with new Hydro - 1890 s-1970 s Energy Conservation! False start with Nukes (NW Power - 1970 s-80 s Act - 1980) 4 Date source: NW Power and Conservation Council (http: //www. nwcouncil. org/energy/powersupply/existingprojects. xls)
 II. The Present: Average water & maximum thermal plant availability. September 2006 5
II. The Present: Average water & maximum thermal plant availability. September 2006 5
 6
6
 - Abundant resources - >1, 386 MW currently serving NW Load Source: RNP (http: //www. rnp. org/Projects/projectlist. php) 7
- Abundant resources - >1, 386 MW currently serving NW Load Source: RNP (http: //www. rnp. org/Projects/projectlist. php) 7
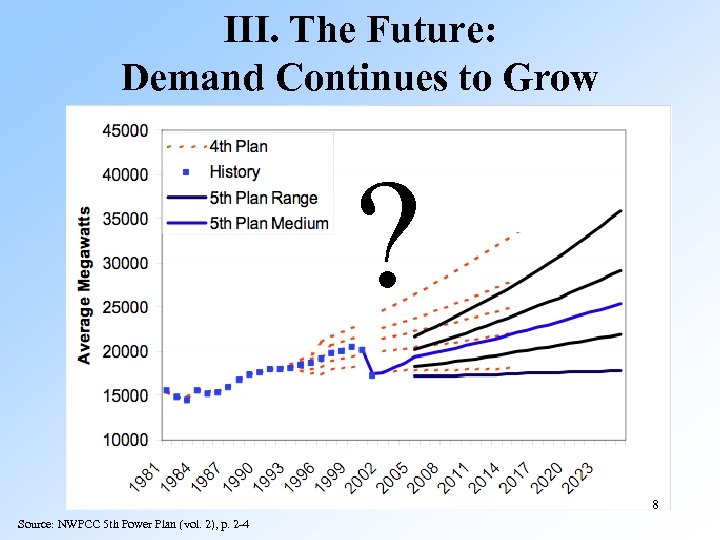 III. The Future: Demand Continues to Grow ? 8 Source: NWPCC 5 th Power Plan (vol. 2), p. 2 -4
III. The Future: Demand Continues to Grow ? 8 Source: NWPCC 5 th Power Plan (vol. 2), p. 2 -4
 III. The Future: Coal? • Coal: – Cheap – Relatively abundant – Dirty! • Utilities love their coal: – cheap baseload (reliable) power – (For the most part) don’t have to pay for public health costs – 150+ coal plants proposed in the West… 9
III. The Future: Coal? • Coal: – Cheap – Relatively abundant – Dirty! • Utilities love their coal: – cheap baseload (reliable) power – (For the most part) don’t have to pay for public health costs – 150+ coal plants proposed in the West… 9
 Over 150 Coal-fired Power Plants Proposed in the West Pacific Mountain Lower Columbia 10
Over 150 Coal-fired Power Plants Proposed in the West Pacific Mountain Lower Columbia 10
 III. The Future: Coal = Risky Business • Coal is a risk for everyone: – cheap now, but fuel costs already rising: up 20% from ‘ 03 -’ 05. – Investments in coal now will cost customers later. – Increasing environmental regulations – Carbon restrictions coming soon… • Regional regulations: CA and Northeast • Industry asking Congress to limit carbon emissions - want certainty • Only a matter of time now – Invest in coal = export NW jobs and $$$ to MT, WY for fuel – Moral issue: people in MT, WY bare environmental costs of mining and 11 power plant pollution for our power consumption
III. The Future: Coal = Risky Business • Coal is a risk for everyone: – cheap now, but fuel costs already rising: up 20% from ‘ 03 -’ 05. – Investments in coal now will cost customers later. – Increasing environmental regulations – Carbon restrictions coming soon… • Regional regulations: CA and Northeast • Industry asking Congress to limit carbon emissions - want certainty • Only a matter of time now – Invest in coal = export NW jobs and $$$ to MT, WY for fuel – Moral issue: people in MT, WY bare environmental costs of mining and 11 power plant pollution for our power consumption
 III. The Future: Natural Gas? • Natural Gas: – – Low capital (upfront) costs High fuel costs Cleaner than coal Natural gas prices very volatile 12
III. The Future: Natural Gas? • Natural Gas: – – Low capital (upfront) costs High fuel costs Cleaner than coal Natural gas prices very volatile 12
 III. The Future: Natural Gas? U. S. Historic Natural Gas Prices (Volatile and Unpredictable) 13
III. The Future: Natural Gas? U. S. Historic Natural Gas Prices (Volatile and Unpredictable) 13
 III. The Future: Liquefied Natural Gas • Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG): – Imported from Indonesia, Qatar, Iran, Russia, etc. – More dependence on foreign fossil fuels – Exporting $$$ overseas – Potential security risk (terminals and tankers) – Several LNG terminals proposed for Northwest… 14
III. The Future: Liquefied Natural Gas • Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG): – Imported from Indonesia, Qatar, Iran, Russia, etc. – More dependence on foreign fossil fuels – Exporting $$$ overseas – Potential security risk (terminals and tankers) – Several LNG terminals proposed for Northwest… 14
 III. The Future: Renewables? • NW has abundant renewable energy potential: – Western Governor’s Association developable potential by 2015: • Wind: 2, 310 -7, 735 MW (693 -2, 321 a. MW) • Solar: 325 -500 MW (71. 5 -111 a. MW) • Geothermal: 1, 290 MW (1, 187 a. MW) • Total: 3, 925 -9, 525 MW (1, 951 -3, 617 a. MW) • 72% of 5, 000 a. MW forecasted growth by 2025 15
III. The Future: Renewables? • NW has abundant renewable energy potential: – Western Governor’s Association developable potential by 2015: • Wind: 2, 310 -7, 735 MW (693 -2, 321 a. MW) • Solar: 325 -500 MW (71. 5 -111 a. MW) • Geothermal: 1, 290 MW (1, 187 a. MW) • Total: 3, 925 -9, 525 MW (1, 951 -3, 617 a. MW) • 72% of 5, 000 a. MW forecasted growth by 2025 15
 III. The Future: Conservation + Renewables = More than Enough • Expected demand growth by 2025: 5, 000 a. MW • Conservation and Efficiency: 2, 800 a. MW (NWPCC) • Renewables: ~2, 000 -3, 600 a. MW (WGA) • Total: 4, 800 -6, 400 a. MW • So who needs coal or natural gas? 16
III. The Future: Conservation + Renewables = More than Enough • Expected demand growth by 2025: 5, 000 a. MW • Conservation and Efficiency: 2, 800 a. MW (NWPCC) • Renewables: ~2, 000 -3, 600 a. MW (WGA) • Total: 4, 800 -6, 400 a. MW • So who needs coal or natural gas? 16
 III. The Future: Benefits of Renewables · Provides power at stable, predictable price for many years - (Fossil fuel prices volatile & unpredictable. ) · Helps fight global warming: no/low emissions, offsets fossil fuels · Economic Development: it creates jobs & tax revenue · Domestic resources: Keep jobs and $ local instead of sending elsewhere to buy their fuels (e. g. . coal from WY, gas from Canada). · Minimal water use · Public Health Benefits Doesn’t have air & water pollution impacts of fossil fuels ·Customers want it: PGE poll: 75% customers want RE and efficiency, <10% want coal. 17
III. The Future: Benefits of Renewables · Provides power at stable, predictable price for many years - (Fossil fuel prices volatile & unpredictable. ) · Helps fight global warming: no/low emissions, offsets fossil fuels · Economic Development: it creates jobs & tax revenue · Domestic resources: Keep jobs and $ local instead of sending elsewhere to buy their fuels (e. g. . coal from WY, gas from Canada). · Minimal water use · Public Health Benefits Doesn’t have air & water pollution impacts of fossil fuels ·Customers want it: PGE poll: 75% customers want RE and efficiency, <10% want coal. 17
 III. The Future: So Where Do We Want to Go? • Coal? • Natural Gas? • Conservation + Renewables? • It’s our energy future: what do we want it to look like? 18
III. The Future: So Where Do We Want to Go? • Coal? • Natural Gas? • Conservation + Renewables? • It’s our energy future: what do we want it to look like? 18
 A Clean Energy Future is Possible: It’s up to us to make it happen! 19
A Clean Energy Future is Possible: It’s up to us to make it happen! 19
 20
20
 Policy Solutions • Renewable Energy Standard / Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS) • Purpose – have electric utilities gradually increase amount of new RE in electricity supply to certain % by certain year. – Gov. Kulongoski: 25% by 2025 proposed for Oregon – Washington ballot initiative (I-937): 15% by 2020 – Create a stable market for renewables, encourage siting of domestic manufacturing, create jobs, economic development, health benefits 21
Policy Solutions • Renewable Energy Standard / Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS) • Purpose – have electric utilities gradually increase amount of new RE in electricity supply to certain % by certain year. – Gov. Kulongoski: 25% by 2025 proposed for Oregon – Washington ballot initiative (I-937): 15% by 2020 – Create a stable market for renewables, encourage siting of domestic manufacturing, create jobs, economic development, health benefits 21
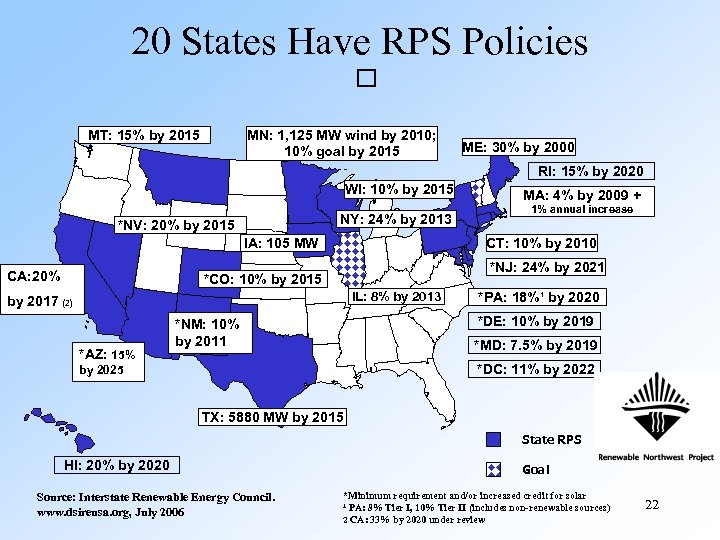 20 States Have RPS Policies MT: 15% by 2015 MN: 1, 125 MW wind by 2010; 10% goal by 2015 ME: 30% by 2000 RI: 15% by 2020 WI: 10% by 2015 NY: 24% by 2013 *NV: 20% by 2015 IA: 105 MW CA: 20% 1% annual increase CT: 10% by 2010 *NJ: 24% by 2021 *CO: 10% by 2015 IL: 8% by 2013 by 2017 (2) *AZ: 15% MA: 4% by 2009 + *PA: 18%¹ by 2020 *DE: 10% by 2019 *NM: 10% by 2011 *MD: 7. 5% by 2019 *DC: 11% by 2022 by 2025 TX: 5880 MW by 2015 State RPS HI: 20% by 2020 Source: Interstate Renewable Energy Council. www. dsireusa. org, July 2006 Goal *Minimum requirement and/or increased credit for solar ¹ PA: 8% Tier I, 10% Tier II (includes non-renewable sources) 2 CA: 33% by 2020 under review 22
20 States Have RPS Policies MT: 15% by 2015 MN: 1, 125 MW wind by 2010; 10% goal by 2015 ME: 30% by 2000 RI: 15% by 2020 WI: 10% by 2015 NY: 24% by 2013 *NV: 20% by 2015 IA: 105 MW CA: 20% 1% annual increase CT: 10% by 2010 *NJ: 24% by 2021 *CO: 10% by 2015 IL: 8% by 2013 by 2017 (2) *AZ: 15% MA: 4% by 2009 + *PA: 18%¹ by 2020 *DE: 10% by 2019 *NM: 10% by 2011 *MD: 7. 5% by 2019 *DC: 11% by 2022 by 2025 TX: 5880 MW by 2015 State RPS HI: 20% by 2020 Source: Interstate Renewable Energy Council. www. dsireusa. org, July 2006 Goal *Minimum requirement and/or increased credit for solar ¹ PA: 8% Tier I, 10% Tier II (includes non-renewable sources) 2 CA: 33% by 2020 under review 22
 Policy Solutions • Incentives – Public health, energy security and economic development benefits of renewables all warrant incentives – Federal Production Tax Credit is biggest factor – State incentives too (OR and WA offer strong package of incentives) • Environmental Regulations / Carbon Cap – Stricter environmental regulations force polluters to pay – Renewables have no emissions so more competitive – Cost of carbon needs to be included (carbon cap or tax) 23
Policy Solutions • Incentives – Public health, energy security and economic development benefits of renewables all warrant incentives – Federal Production Tax Credit is biggest factor – State incentives too (OR and WA offer strong package of incentives) • Environmental Regulations / Carbon Cap – Stricter environmental regulations force polluters to pay – Renewables have no emissions so more competitive – Cost of carbon needs to be included (carbon cap or tax) 23


