7584077869b148ed14b41e130e849020.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 59
 North vs. South A Cultural Divide
North vs. South A Cultural Divide
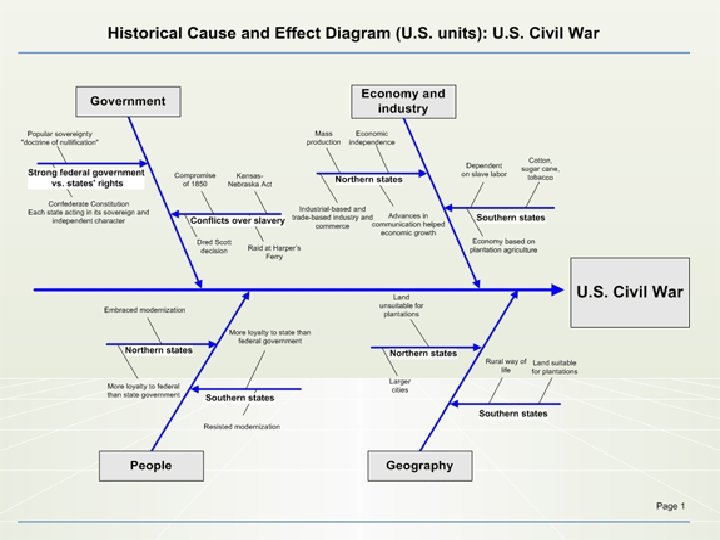
 Goals 19 • Identify differences between North and South in the following areas 1. Geography 2. Transportation 3. Society 4. Economy • Explain how these differences help cause the Civil War
Goals 19 • Identify differences between North and South in the following areas 1. Geography 2. Transportation 3. Society 4. Economy • Explain how these differences help cause the Civil War
 Geography of the North and South • 4 distinct seasons • Jagged NE coast with rocky soil • Thick forests in New England • Wide plains with rich soil in NY, Penn, and NJ • Deforestation • Ohio to IL have rich prairie soils • MD to FL and to LA and TX • Mild winter, hot humid summers • Coastal plains and marshes • Appalachian Mts. , natural resources • Broad flat rivers • Shipping resources
Geography of the North and South • 4 distinct seasons • Jagged NE coast with rocky soil • Thick forests in New England • Wide plains with rich soil in NY, Penn, and NJ • Deforestation • Ohio to IL have rich prairie soils • MD to FL and to LA and TX • Mild winter, hot humid summers • Coastal plains and marshes • Appalachian Mts. , natural resources • Broad flat rivers • Shipping resources


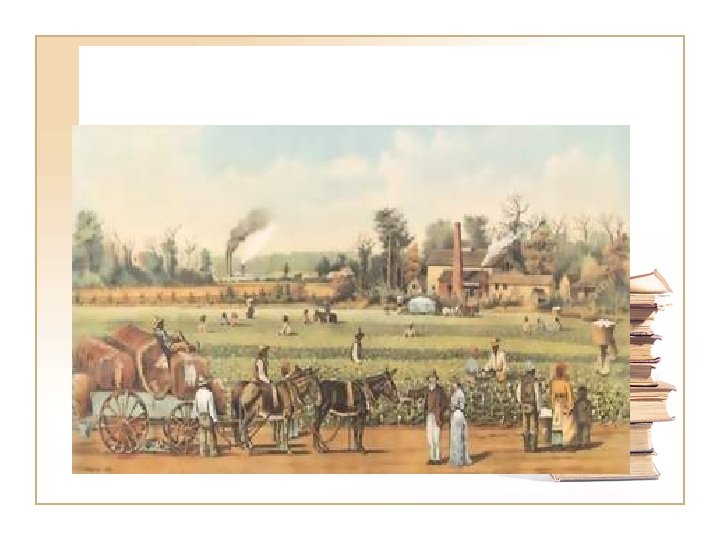
 Economy of the North and South • Industrial Revolution/Indu strialist • Steam powered machinery • Lowell and the Lowell Girls • Unskilled laborers worked in factories • Mc. Cormicks Reaper • Central Plains as the “Bread Basket of America” • Agrarians and Plantations • Cotton Gin • 1860 Cotton was the number one export • Growth of slavery: 1790 500, 000 to 3, 000 in 1850 • Most goods came from the North
Economy of the North and South • Industrial Revolution/Indu strialist • Steam powered machinery • Lowell and the Lowell Girls • Unskilled laborers worked in factories • Mc. Cormicks Reaper • Central Plains as the “Bread Basket of America” • Agrarians and Plantations • Cotton Gin • 1860 Cotton was the number one export • Growth of slavery: 1790 500, 000 to 3, 000 in 1850 • Most goods came from the North

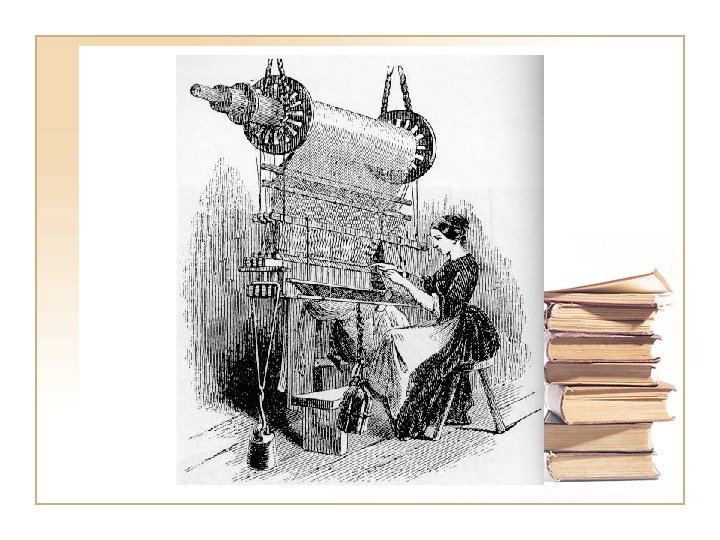

 Inventions of the 1800’s • Factory Conditions
Inventions of the 1800’s • Factory Conditions
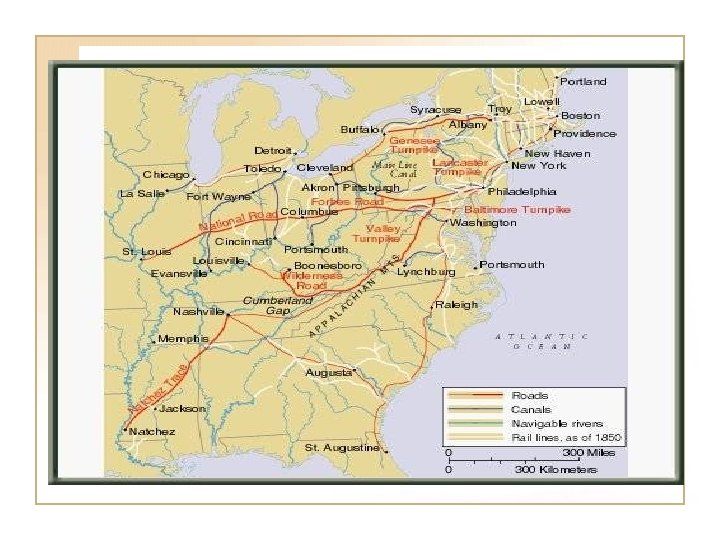
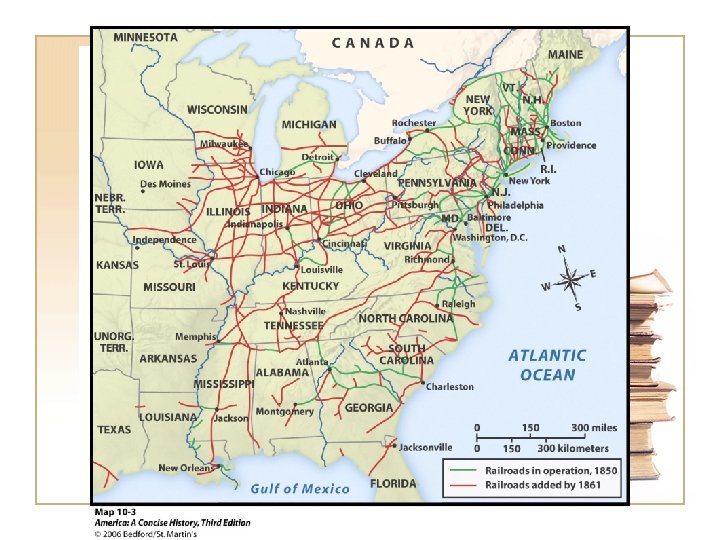
 Transportation • National Roads and the American System • Steamboats and clipper ships • Canals • 20, 000 miles of railroads • Steam powered river boats • Cotton shipped down river • Mississippi River • 10, 000 miles of rail
Transportation • National Roads and the American System • Steamboats and clipper ships • Canals • 20, 000 miles of railroads • Steam powered river boats • Cotton shipped down river • Mississippi River • 10, 000 miles of rail


 Society of the North and South • Rich planters lived in large mansions • Some white farmers owned their own small farms • Free African Americans worked as craftspeople, servants, and laborers • Slave culture • Growing number lived in cities • African Americans free but not equal • Immigration movements, especially from Ireland Germany
Society of the North and South • Rich planters lived in large mansions • Some white farmers owned their own small farms • Free African Americans worked as craftspeople, servants, and laborers • Slave culture • Growing number lived in cities • African Americans free but not equal • Immigration movements, especially from Ireland Germany
 A Dividing Nation Chapter 21
A Dividing Nation Chapter 21
 Goals chapter 21 • List the issues that divided the North and South prior to the war. • Describe the provisions of the Missouri Compromise and the Compromise of 1850 • Explain the significance of other key events: Wilmot Proviso, Ostend Manifesto, Kansas-Nebraska Act, John Brown’s war, Dred Scott Decision, and the Lincoln Douglass Debates
Goals chapter 21 • List the issues that divided the North and South prior to the war. • Describe the provisions of the Missouri Compromise and the Compromise of 1850 • Explain the significance of other key events: Wilmot Proviso, Ostend Manifesto, Kansas-Nebraska Act, John Brown’s war, Dred Scott Decision, and the Lincoln Douglass Debates
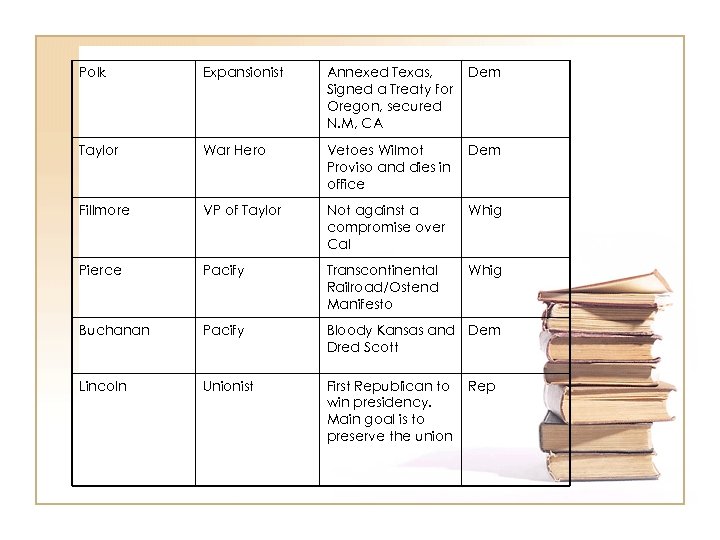 Polk Expansionist Annexed Texas, Signed a Treaty for Oregon, secured N. M, CA Dem Taylor War Hero Vetoes Wilmot Proviso and dies in office Dem Fillmore VP of Taylor Not against a compromise over Cal Whig Pierce Pacify Transcontinental Railroad/Ostend Manifesto Whig Buchanan Pacify Bloody Kansas and Dem Dred Scott Lincoln Unionist First Republican to win presidency. Main goal is to preserve the union Rep
Polk Expansionist Annexed Texas, Signed a Treaty for Oregon, secured N. M, CA Dem Taylor War Hero Vetoes Wilmot Proviso and dies in office Dem Fillmore VP of Taylor Not against a compromise over Cal Whig Pierce Pacify Transcontinental Railroad/Ostend Manifesto Whig Buchanan Pacify Bloody Kansas and Dem Dred Scott Lincoln Unionist First Republican to win presidency. Main goal is to preserve the union Rep
 21. 2 Confronting Slavery • Northwest Ordinance and the balance of slave vs. free • Missouri applies as a slave state • Tallmadge Amendment: Missouri as a free state • States’ rights protests and the balance of Congress
21. 2 Confronting Slavery • Northwest Ordinance and the balance of slave vs. free • Missouri applies as a slave state • Tallmadge Amendment: Missouri as a free state • States’ rights protests and the balance of Congress
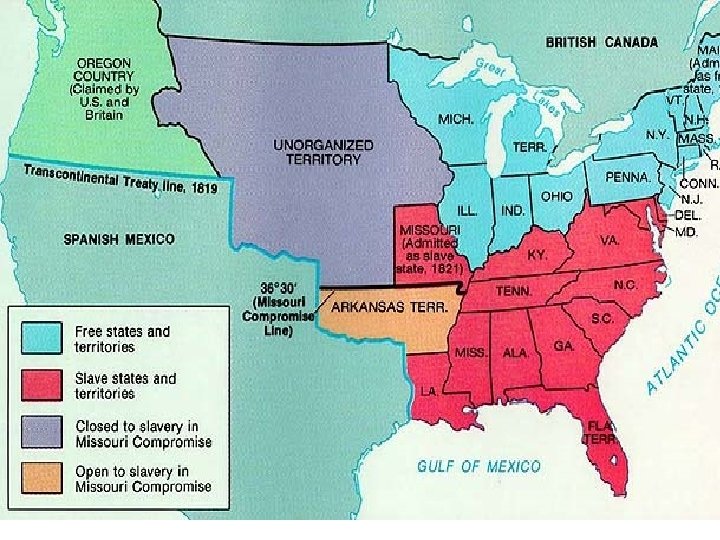
 21. 3 Missouri Compromise • Illinois statehood in 1818 • 1819=11 free states and 11 slave states • House vs. Senate • Henry Clay “The Great Compromiser” • Missouri Compromise and the 36° 30 N • Maine admitted as a free state
21. 3 Missouri Compromise • Illinois statehood in 1818 • 1819=11 free states and 11 slave states • House vs. Senate • Henry Clay “The Great Compromiser” • Missouri Compromise and the 36° 30 N • Maine admitted as a free state
 21. 4 Nat Turner’s Rebellion • 1831 slave rebellion • Large scale revolt • Strict new laws in the south to prevent abolitionist from spreading their ideas • The north harbored runaway slaves • Underground Railroad traffic increases
21. 4 Nat Turner’s Rebellion • 1831 slave rebellion • Large scale revolt • Strict new laws in the south to prevent abolitionist from spreading their ideas • The north harbored runaway slaves • Underground Railroad traffic increases
 21. 4 Expansion and Slavery • 500, 000 square miles newly added after Mexican. American war • Wilmot Proviso and Popular Sovereignty • Free Soil Party: America’s first third party • California and the Compromise of 1850
21. 4 Expansion and Slavery • 500, 000 square miles newly added after Mexican. American war • Wilmot Proviso and Popular Sovereignty • Free Soil Party: America’s first third party • California and the Compromise of 1850
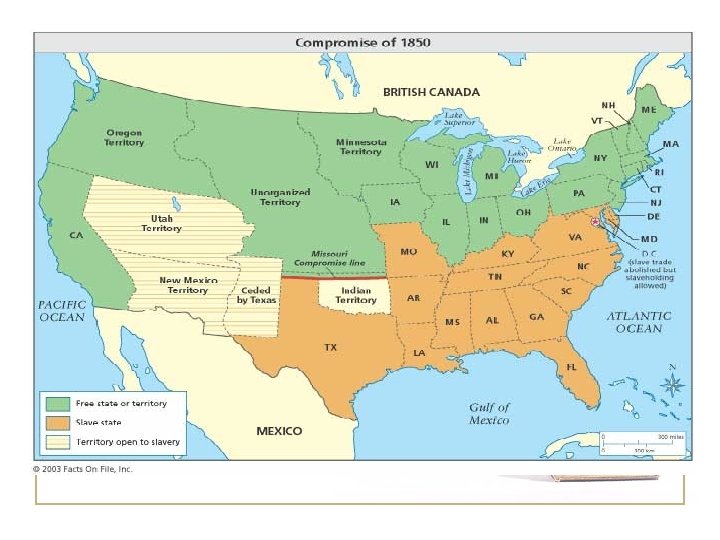
 21. 5 Provisions of the Compromise of 1850 • California free state • Slavery abolished in Washington D. C. • New Mexico territory divided into NM and Utah could become slave states through popular sovereignty • More severe Fugitive Slave act that allowed Federal Marshalls to catch runaways
21. 5 Provisions of the Compromise of 1850 • California free state • Slavery abolished in Washington D. C. • New Mexico territory divided into NM and Utah could become slave states through popular sovereignty • More severe Fugitive Slave act that allowed Federal Marshalls to catch runaways
 21. 5 Fugitive Slave Act 1850 • Most Northerners were not abolitionists • Southerners saw slavery as an economic necessity • All citizens were to enforce the law • Fines up to $1, 000 and prison if you helped a runaway
21. 5 Fugitive Slave Act 1850 • Most Northerners were not abolitionists • Southerners saw slavery as an economic necessity • All citizens were to enforce the law • Fines up to $1, 000 and prison if you helped a runaway
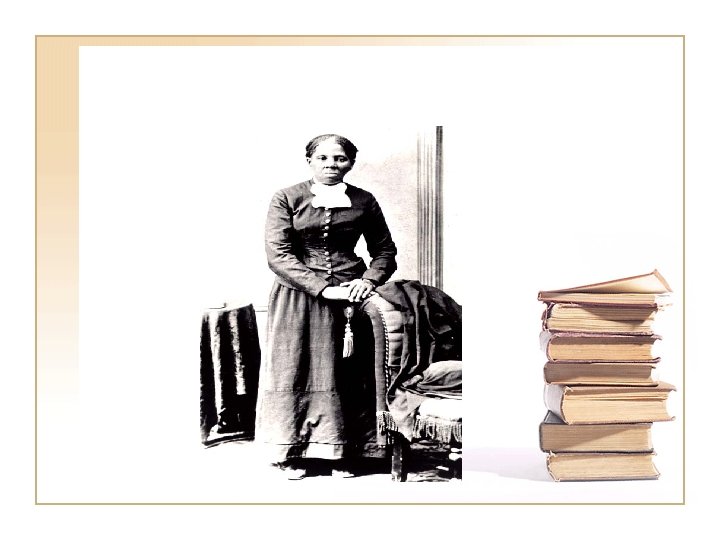
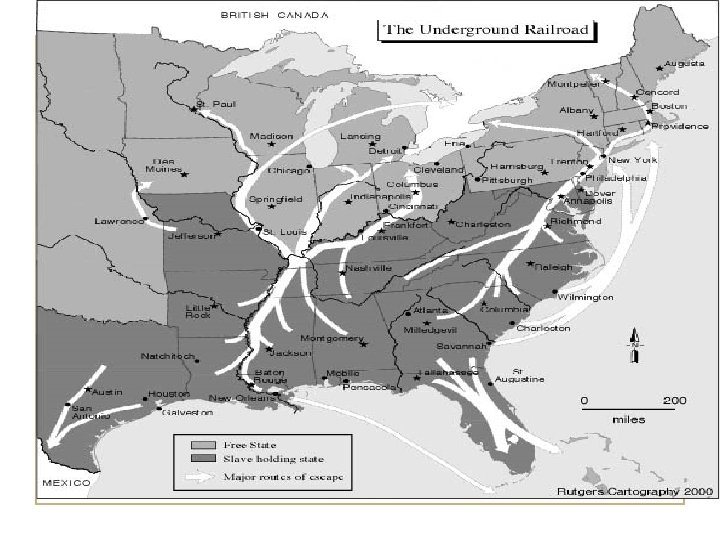
 21. 6 Underground Railroad • Organized system to move slaves to Canada • Series of safe houses and escorts • Harriet Tubman risked her life several times to lead runaways • Large reward for her capture eventually led to her quitting • Possibility that part of the system ran through Williamsville
21. 6 Underground Railroad • Organized system to move slaves to Canada • Series of safe houses and escorts • Harriet Tubman risked her life several times to lead runaways • Large reward for her capture eventually led to her quitting • Possibility that part of the system ran through Williamsville

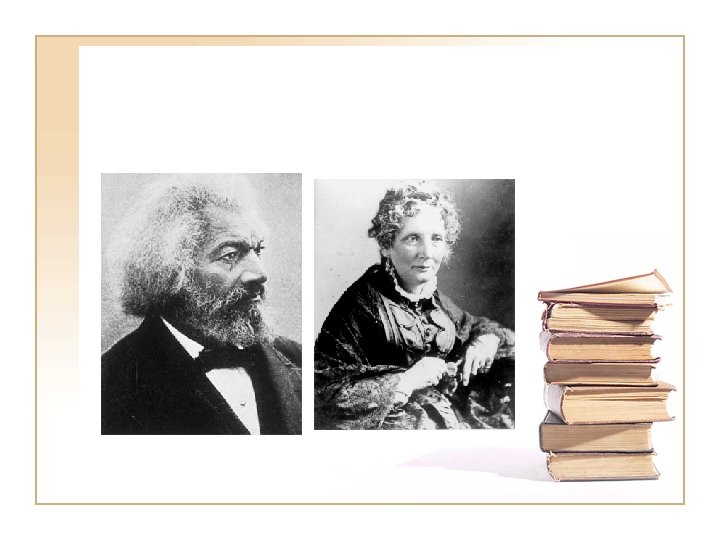
 21. 6 Antislavery Literature Frederick Douglass • Slave narratives • Spoke as an abolitionist Harriett Beecher Stowe • Uncle Tom’s Cabin • Between 1852 -1862 2, 000 copies sold
21. 6 Antislavery Literature Frederick Douglass • Slave narratives • Spoke as an abolitionist Harriett Beecher Stowe • Uncle Tom’s Cabin • Between 1852 -1862 2, 000 copies sold

 21. 6 Kansas-Nebraska Act • Milliard Fillmore then Franklin Pierce • Stephen Douglas and the transcontinental railroad through Illinois • Kansas-Nebraska Act: organized the rest of the Louisiana Territory into two. Kansas and Nebraska that would decide slavery by popular sovereignty • In exchange, southern congressmen would vote for the railroad to go through Chicago and not through the south • Ostend Manifesto: attempt to buy Cuba leaked out
21. 6 Kansas-Nebraska Act • Milliard Fillmore then Franklin Pierce • Stephen Douglas and the transcontinental railroad through Illinois • Kansas-Nebraska Act: organized the rest of the Louisiana Territory into two. Kansas and Nebraska that would decide slavery by popular sovereignty • In exchange, southern congressmen would vote for the railroad to go through Chicago and not through the south • Ostend Manifesto: attempt to buy Cuba leaked out
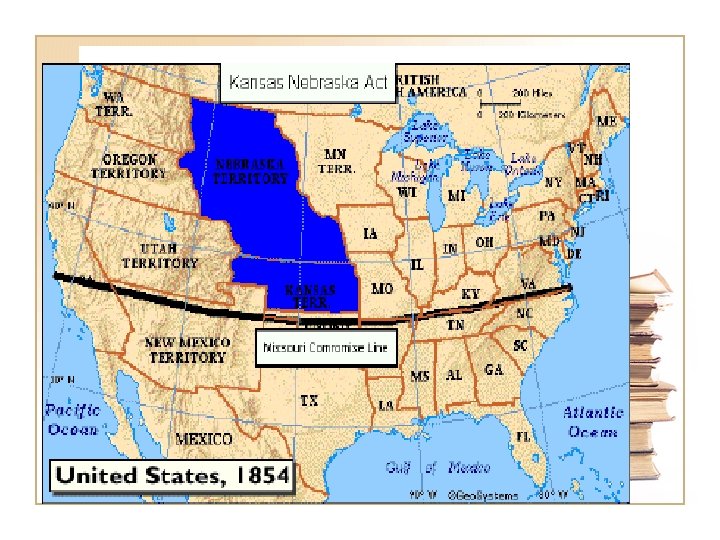
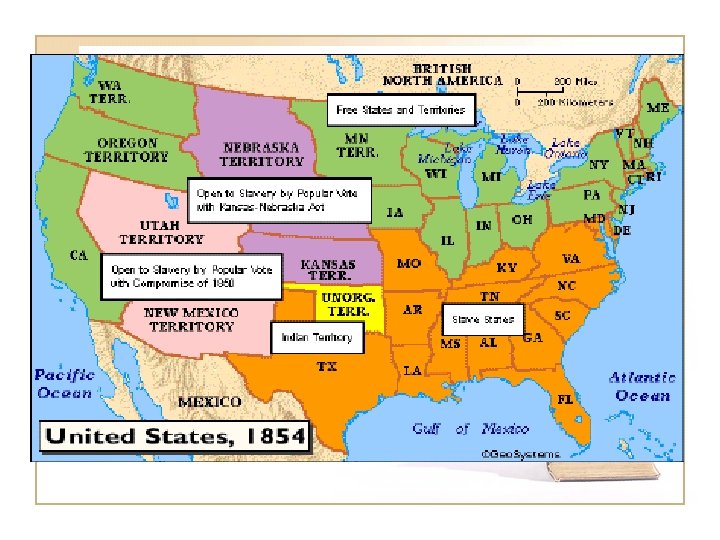
 21. 6 Bleeding Kansas • Two separate governments with two hostile sets of people with weapons • May 1856 violence with border ruffians and retaliation by John Brown at Potawatomie Creek • The attack on Charles Sumner in the Senate
21. 6 Bleeding Kansas • Two separate governments with two hostile sets of people with weapons • May 1856 violence with border ruffians and retaliation by John Brown at Potawatomie Creek • The attack on Charles Sumner in the Senate

 Biographies John Brown • Abolitionist who vowed to purge the nation of slavery • Led retaliatory massacre of proslavery settlers in Kansas Stephen Douglas • Struck a deal in congress to organize the Kansas and Nebraska territories • Wanted popular sovereignty there in exchange for a transcontinental railroad to go through Chicago
Biographies John Brown • Abolitionist who vowed to purge the nation of slavery • Led retaliatory massacre of proslavery settlers in Kansas Stephen Douglas • Struck a deal in congress to organize the Kansas and Nebraska territories • Wanted popular sovereignty there in exchange for a transcontinental railroad to go through Chicago
 21. 7 Politics and Slavery • • 1. 2. 3. Republican Party: combination of Whigs, Dem, and free soilers Election of 1856 is Buchanan vs. Fremont Dred Scott sued for his freedom in 1856 Taney ruled that: No rights for Africans as citizens Missouri compromise unconstitutional (5 th Amendment) Citizenship depended on the color of your skin
21. 7 Politics and Slavery • • 1. 2. 3. Republican Party: combination of Whigs, Dem, and free soilers Election of 1856 is Buchanan vs. Fremont Dred Scott sued for his freedom in 1856 Taney ruled that: No rights for Africans as citizens Missouri compromise unconstitutional (5 th Amendment) Citizenship depended on the color of your skin
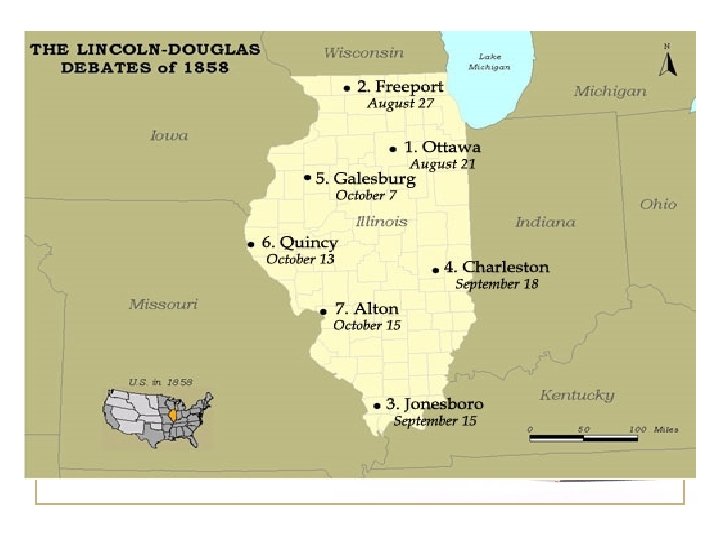
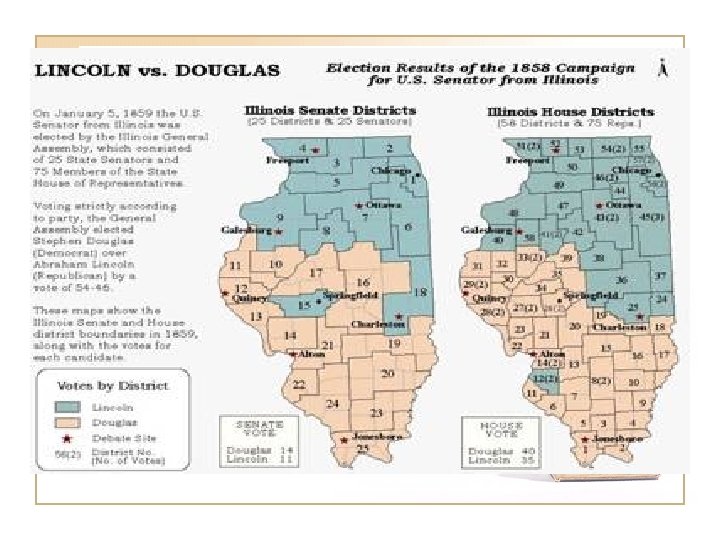
 21. 8 Lincoln-Douglas Debates • 1858 Race for the Senate • Lincoln, a Republican, argues that a house divided against itself cannot stand that slavery is a moral issue not a legal one • Douglas, a Democrat, argues that the Dred Scott decision ended the slavery debate that it was legal and was maintained by the Constitution. • Douglas also says that slavery should be decided by the people • Douglas wins but Lincoln makes a case for slavery being wrong as a moral issue and becomes a national name
21. 8 Lincoln-Douglas Debates • 1858 Race for the Senate • Lincoln, a Republican, argues that a house divided against itself cannot stand that slavery is a moral issue not a legal one • Douglas, a Democrat, argues that the Dred Scott decision ended the slavery debate that it was legal and was maintained by the Constitution. • Douglas also says that slavery should be decided by the people • Douglas wins but Lincoln makes a case for slavery being wrong as a moral issue and becomes a national name

 21. 8 John Brown’s Raid on Harpers Ferry • The Plan (22 men to raid the federal arsenal) • October 16 th 1859 raided the arsenal and urged slaves to join him • Federal troops surround and capture him • Brown is executed • Reactions in Europe
21. 8 John Brown’s Raid on Harpers Ferry • The Plan (22 men to raid the federal arsenal) • October 16 th 1859 raided the arsenal and urged slaves to join him • Federal troops surround and capture him • Brown is executed • Reactions in Europe
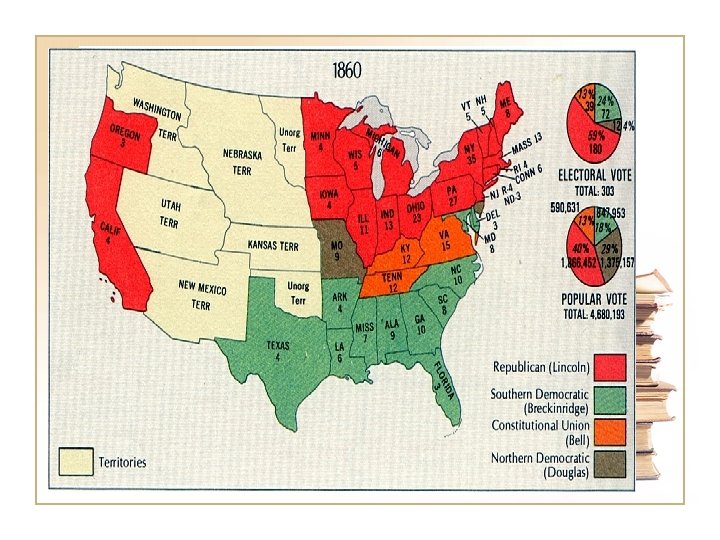
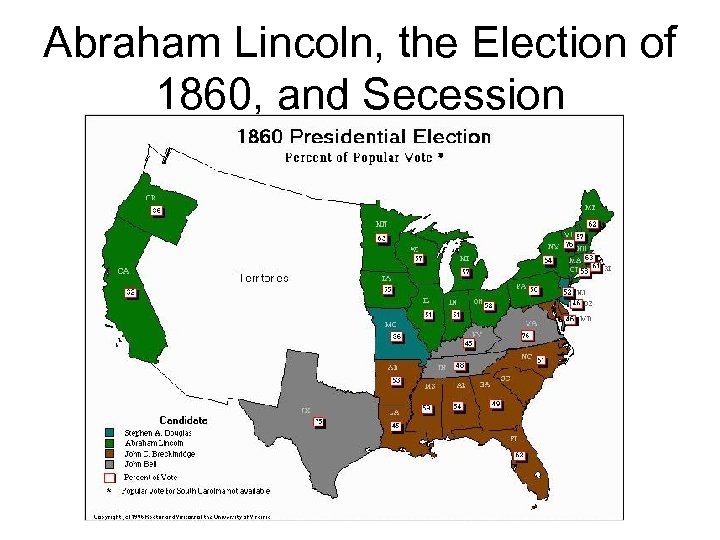
 21. 8 Election of 1860 • Lincoln for the Republicans, Douglas for the N. Dem, Breckinridge for S. Dem and John Bell for the Constitutional Union Party • Lincoln wins despite not carrying a single southern state • Dec. 17 th 1860 S. Carolina votes to secede • Crittenden compromise fails
21. 8 Election of 1860 • Lincoln for the Republicans, Douglas for the N. Dem, Breckinridge for S. Dem and John Bell for the Constitutional Union Party • Lincoln wins despite not carrying a single southern state • Dec. 17 th 1860 S. Carolina votes to secede • Crittenden compromise fails
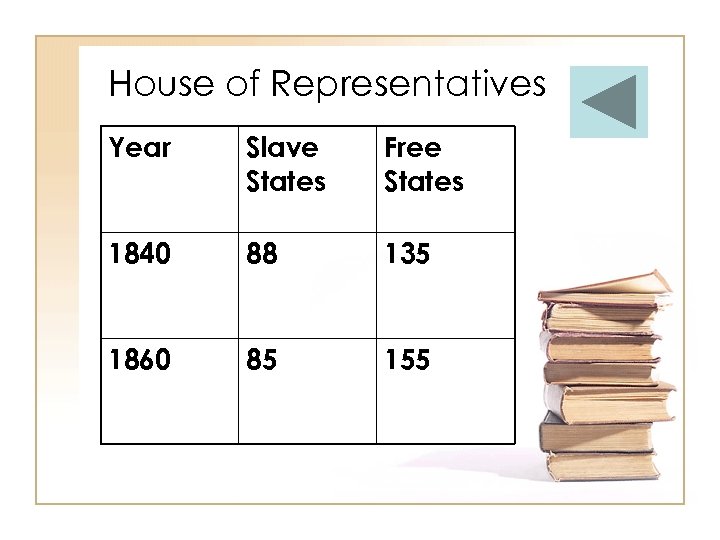 House of Representatives Year Slave States Free States 1840 88 135 1860 85 155
House of Representatives Year Slave States Free States 1840 88 135 1860 85 155
 Abraham Lincoln, the Election of 1860, and Secession
Abraham Lincoln, the Election of 1860, and Secession
 "A House Divided" • In his “House Divided” speech, Abraham Lincoln addresses how the election of President Buchanan, the Nebraska Bill, and the Dred Scott decision will affect the unity of the Nation. • “In my opinion, it will not cease, until a crisis shall have been reached, and passed. ``A house divided against itself cannot stand. '' I believe this government cannot endure; permanently half slave and half free. I do not expect the Union to be dissolved ---I do not expect the house to fall ---but I do expect it will cease to be divided. It will become all one thing, or all the other. ” “Either the opponents of slavery, will arrest the further spread of it, and place it where the public mind shall rest in the belief that it is in course of ultimate extinction; or its advocates will push it forward, till it shall become alike lawful in all the States, old as well as new--North as well as South. Have we no tendency to the latter condition? ” •
"A House Divided" • In his “House Divided” speech, Abraham Lincoln addresses how the election of President Buchanan, the Nebraska Bill, and the Dred Scott decision will affect the unity of the Nation. • “In my opinion, it will not cease, until a crisis shall have been reached, and passed. ``A house divided against itself cannot stand. '' I believe this government cannot endure; permanently half slave and half free. I do not expect the Union to be dissolved ---I do not expect the house to fall ---but I do expect it will cease to be divided. It will become all one thing, or all the other. ” “Either the opponents of slavery, will arrest the further spread of it, and place it where the public mind shall rest in the belief that it is in course of ultimate extinction; or its advocates will push it forward, till it shall become alike lawful in all the States, old as well as new--North as well as South. Have we no tendency to the latter condition? ” •
 1860 Election Banners
1860 Election Banners
 South Carolina's Causes for Secession from the Union • • The election of 1860 has left many on edge in the South, particularly South Carolina. The fear that a Republican President would take actions to limit states' rights has led them to take drastic action. In this declaration, South Carolina outlines there reasons for secession from the Union. “The people of the State of South Carolina…. declared that the frequent violations of the Constitution of the United States, by the Federal Government, and its encroachments upon the reserved rights of the States, fully justified this State in then withdrawing from the Federal Union; but in deference to the opinions and wishes of the other slaveholding States, she forbore at that time to exercise this right. Since that time, these encroachments have continued to increase, and further forbearance ceases to be a virtue. ”
South Carolina's Causes for Secession from the Union • • The election of 1860 has left many on edge in the South, particularly South Carolina. The fear that a Republican President would take actions to limit states' rights has led them to take drastic action. In this declaration, South Carolina outlines there reasons for secession from the Union. “The people of the State of South Carolina…. declared that the frequent violations of the Constitution of the United States, by the Federal Government, and its encroachments upon the reserved rights of the States, fully justified this State in then withdrawing from the Federal Union; but in deference to the opinions and wishes of the other slaveholding States, she forbore at that time to exercise this right. Since that time, these encroachments have continued to increase, and further forbearance ceases to be a virtue. ”
 Constitution of the Confederate States of America • When the framers of the Confederate Constitution set out to draft the document they were set on forming a document that was fundamentally different form the one they opposed. • The framers wanted a document that not only represented their ideological differences, but their governing differences as well. • Ironically, in the end, the only difference that can be found between the two documents is in the ideology.
Constitution of the Confederate States of America • When the framers of the Confederate Constitution set out to draft the document they were set on forming a document that was fundamentally different form the one they opposed. • The framers wanted a document that not only represented their ideological differences, but their governing differences as well. • Ironically, in the end, the only difference that can be found between the two documents is in the ideology.
 Confederate President - Jefferson Davis • Jefferson Davis served as the provisional president of the Confederacy until elections could be held. • On February 18, 1861 he delivered his inaugural address. • In this address, the causes for southern secession and the differences between their government and that of the Union are explained. • “We have changed the constituent parts, but not the system of our Government. The Constitution formed by our fathers is that of these Confederate States, in their exposition of it, and in the judicial construction it has received, we have a light which reveals its true meaning. ”
Confederate President - Jefferson Davis • Jefferson Davis served as the provisional president of the Confederacy until elections could be held. • On February 18, 1861 he delivered his inaugural address. • In this address, the causes for southern secession and the differences between their government and that of the Union are explained. • “We have changed the constituent parts, but not the system of our Government. The Constitution formed by our fathers is that of these Confederate States, in their exposition of it, and in the judicial construction it has received, we have a light which reveals its true meaning. ”
 Crittenden Compromise • On March 4, 1861, a Peace Convention was held in Washington. • This convention was called to order by the state of Virginia. • Virginia, on the verge of secession, was looking for a way they could compromise with the federal government before making the final decision. • The outcome of the Peace Convention was the Crittenden Compromise. • This compromise proposed six amendments to the Constitution and four resolutions. The amendments and resolutions were centered around slavery, slave trade, and fugitive slave laws.
Crittenden Compromise • On March 4, 1861, a Peace Convention was held in Washington. • This convention was called to order by the state of Virginia. • Virginia, on the verge of secession, was looking for a way they could compromise with the federal government before making the final decision. • The outcome of the Peace Convention was the Crittenden Compromise. • This compromise proposed six amendments to the Constitution and four resolutions. The amendments and resolutions were centered around slavery, slave trade, and fugitive slave laws.
 A Cure for Republican Lock-Jaw • This cartoon depicts congressional efforts to pass the Crittenden Compromise.
A Cure for Republican Lock-Jaw • This cartoon depicts congressional efforts to pass the Crittenden Compromise.
 Abraham Lincoln's First Inaugural Address • In his first Inaugural Address, Abraham Lincoln, addresses the issue of South Carolina seceding from the Union. • In doing so, he also outlines how he will handle the situation as President of the United States. • The picture is of the crowd gathered to see Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln's First Inaugural Address • In his first Inaugural Address, Abraham Lincoln, addresses the issue of South Carolina seceding from the Union. • In doing so, he also outlines how he will handle the situation as President of the United States. • The picture is of the crowd gathered to see Abraham Lincoln
 Lincoln's July 4 Message to Congress • On July 4, 1861, President Abraham Lincoln addressed a special session of Congress. • In this address, he announced that a war has been declared on the states that seceded from the Union. • He also calls on Congress to make available the funds and man power needed for a short war. • “It is now recommended that you give the legal means for making this contest a short, and a decisive one; that you place at
Lincoln's July 4 Message to Congress • On July 4, 1861, President Abraham Lincoln addressed a special session of Congress. • In this address, he announced that a war has been declared on the states that seceded from the Union. • He also calls on Congress to make available the funds and man power needed for a short war. • “It is now recommended that you give the legal means for making this contest a short, and a decisive one; that you place at


