4c76ff7b6caf88a05b79926be735278d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 61
 Normalisation des données Oury Monchi, Ph. D. Centre de Recherche, Institut Universitaire de Gériatrie de Montréal & Université de Montréal
Normalisation des données Oury Monchi, Ph. D. Centre de Recherche, Institut Universitaire de Gériatrie de Montréal & Université de Montréal


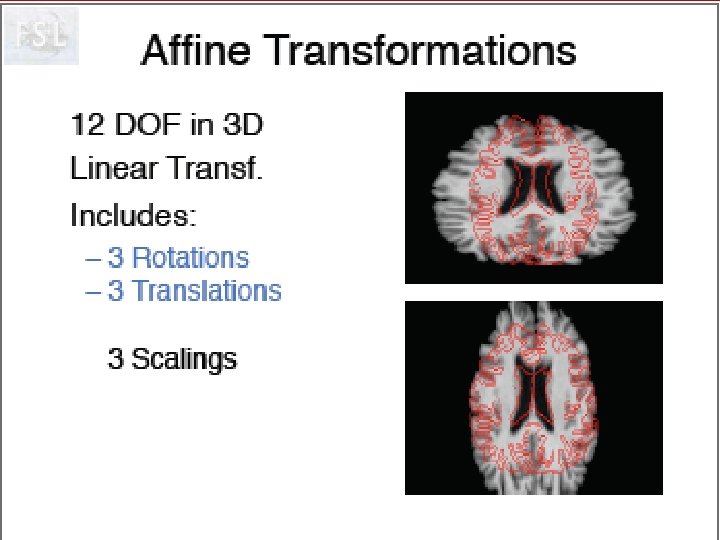
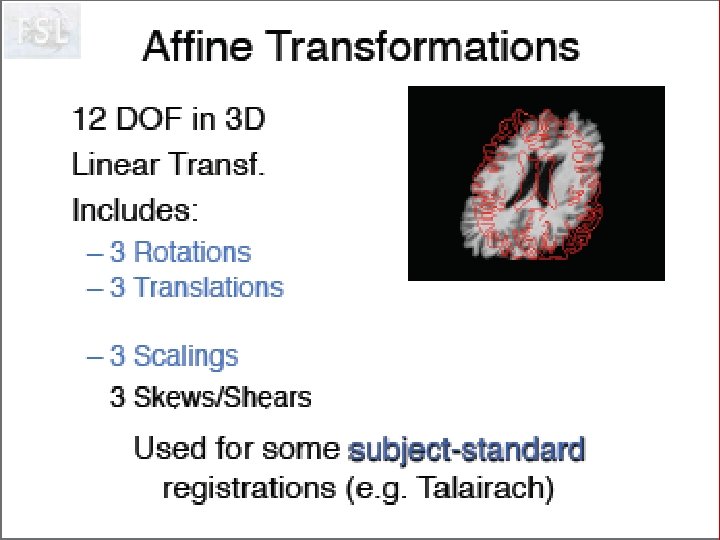
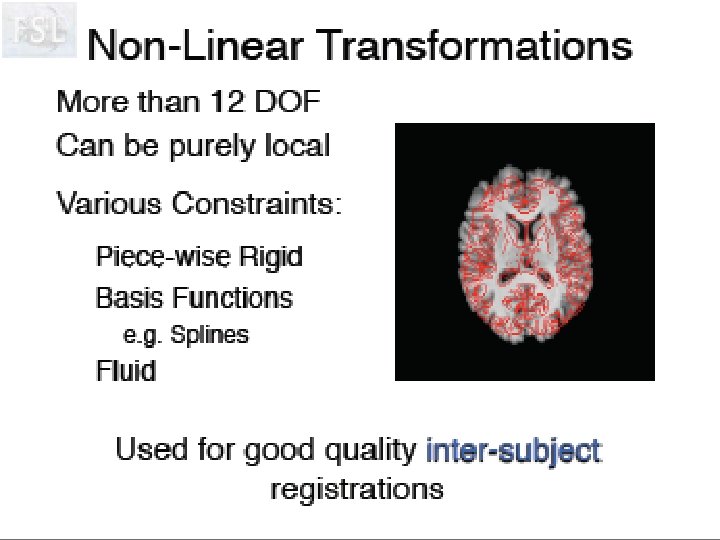
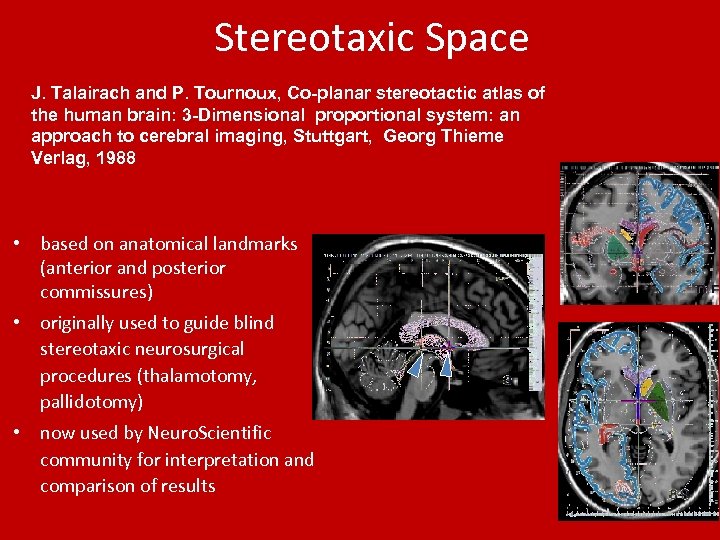 Stereotaxic Space J. Talairach and P. Tournoux, Co-planar stereotactic atlas of the human brain: 3 -Dimensional proportional system: an approach to cerebral imaging, Stuttgart, Georg Thieme Verlag, 1988 • based on anatomical landmarks (anterior and posterior commissures) • originally used to guide blind stereotaxic neurosurgical procedures (thalamotomy, pallidotomy) • now used by Neuro. Scientific community for interpretation and comparison of results
Stereotaxic Space J. Talairach and P. Tournoux, Co-planar stereotactic atlas of the human brain: 3 -Dimensional proportional system: an approach to cerebral imaging, Stuttgart, Georg Thieme Verlag, 1988 • based on anatomical landmarks (anterior and posterior commissures) • originally used to guide blind stereotaxic neurosurgical procedures (thalamotomy, pallidotomy) • now used by Neuro. Scientific community for interpretation and comparison of results
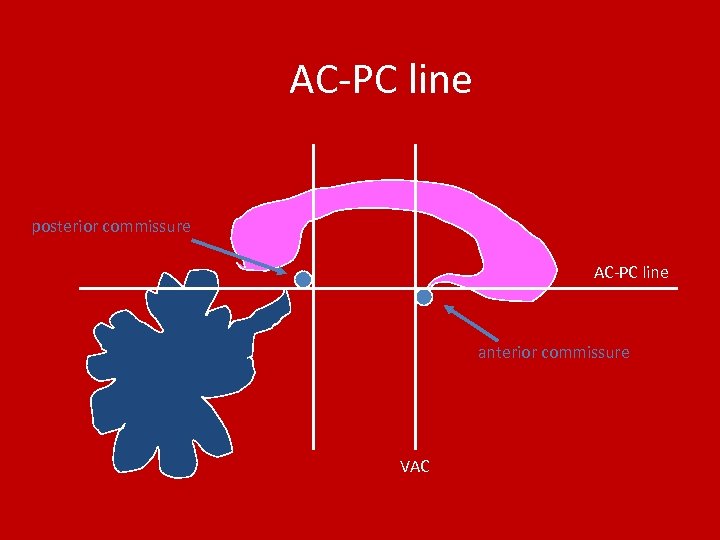 AC-PC line posterior commissure AC-PC line anterior commissure VAC
AC-PC line posterior commissure AC-PC line anterior commissure VAC
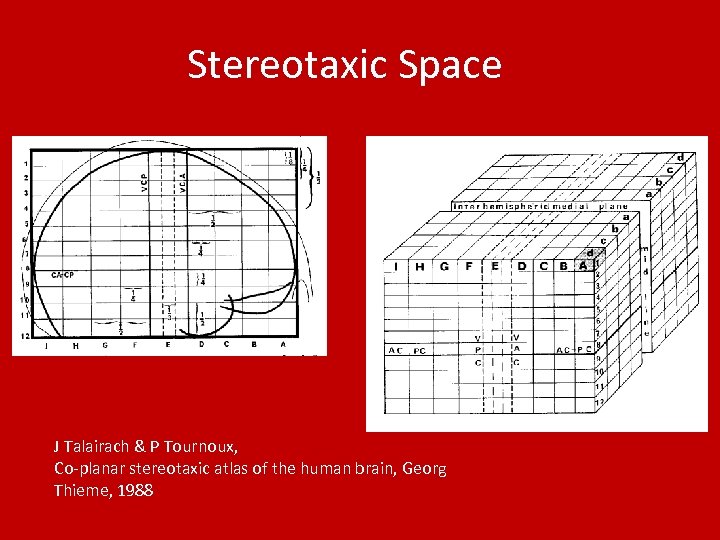 Stereotaxic Space J Talairach & P Tournoux, Co-planar stereotaxic atlas of the human brain, Georg Thieme, 1988
Stereotaxic Space J Talairach & P Tournoux, Co-planar stereotaxic atlas of the human brain, Georg Thieme, 1988
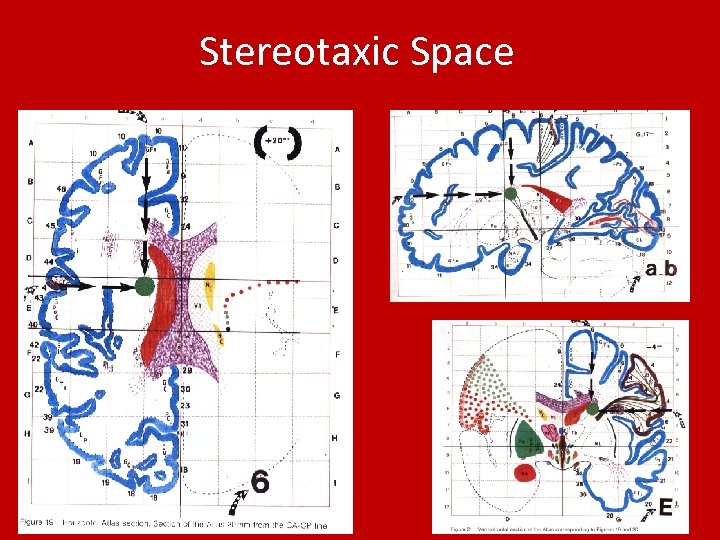 Stereotaxic Space
Stereotaxic Space
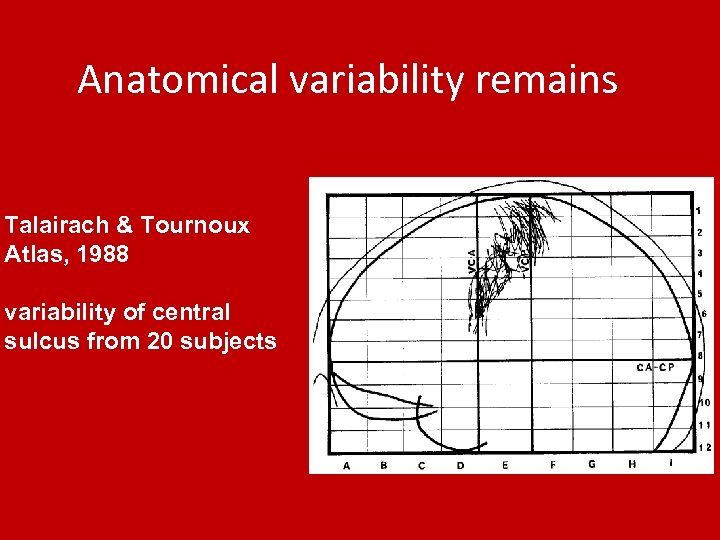 Anatomical variability remains Talairach & Tournoux Atlas, 1988 variability of central sulcus from 20 subjects
Anatomical variability remains Talairach & Tournoux Atlas, 1988 variability of central sulcus from 20 subjects
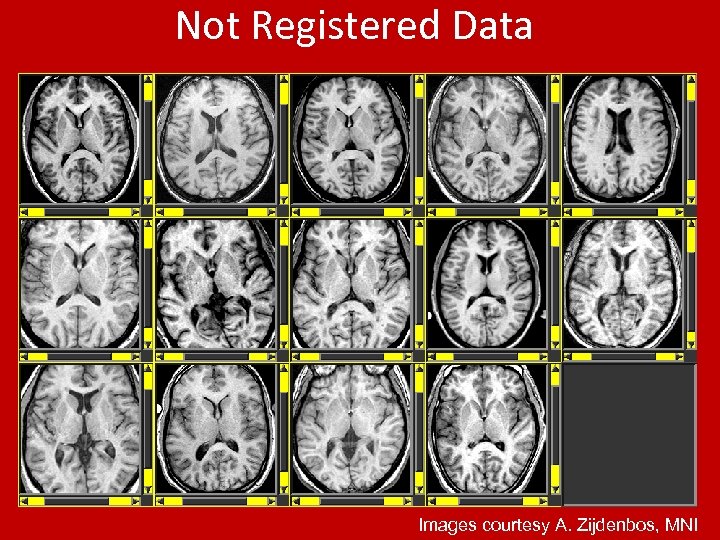 Not Registered Data Images courtesy A. Zijdenbos, MNI
Not Registered Data Images courtesy A. Zijdenbos, MNI
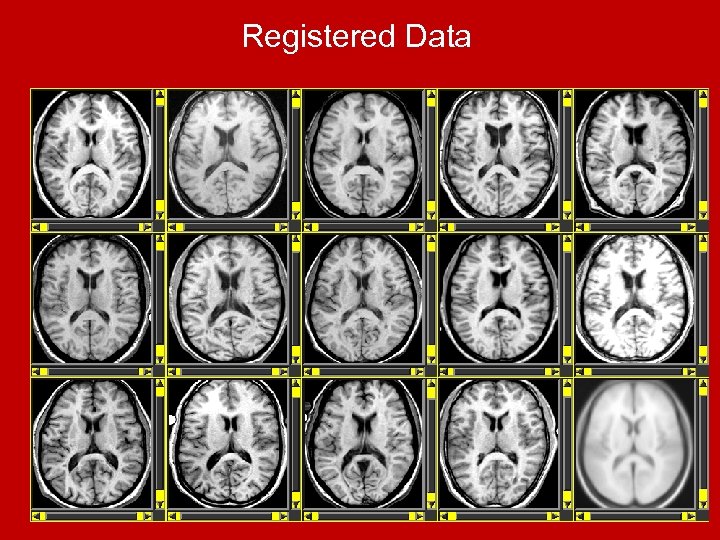 Registered Data
Registered Data
 Registration to Stereotaxic Space Advantages for anatomical/structural imaging: • facilitates comparisons across – time points – subjects – groups – sites • permits averaging between subjects to S/N • Allows the use of spatial masks for post-processing (anatomically driven hypothesis testing) • allows the use of spatial priors (classification) • allows the use of anatomical models (segmentation) • provides a framework for statistical analysis with wellestablished random field models • Allows the rapid re-analysis using different criteria
Registration to Stereotaxic Space Advantages for anatomical/structural imaging: • facilitates comparisons across – time points – subjects – groups – sites • permits averaging between subjects to S/N • Allows the use of spatial masks for post-processing (anatomically driven hypothesis testing) • allows the use of spatial priors (classification) • allows the use of anatomical models (segmentation) • provides a framework for statistical analysis with wellestablished random field models • Allows the rapid re-analysis using different criteria
 Registration to Stereotaxic Space Advantages for functional imaging: • Provides a conceptual framework for the completely automated, 3 D analysis across subjects. • Facilitate intra/inter-subject comparisons across – time points, subjects, groups, sites • Extrapolate findings to the population as a whole • Increase activation signal above that obtained from single subject • Increase number of possible degrees of freedom allowed in statistical model • Enable reporting of activations as co-ordinates within a known standard space – e. g. the space described by Talairach & Tournoux
Registration to Stereotaxic Space Advantages for functional imaging: • Provides a conceptual framework for the completely automated, 3 D analysis across subjects. • Facilitate intra/inter-subject comparisons across – time points, subjects, groups, sites • Extrapolate findings to the population as a whole • Increase activation signal above that obtained from single subject • Increase number of possible degrees of freedom allowed in statistical model • Enable reporting of activations as co-ordinates within a known standard space – e. g. the space described by Talairach & Tournoux
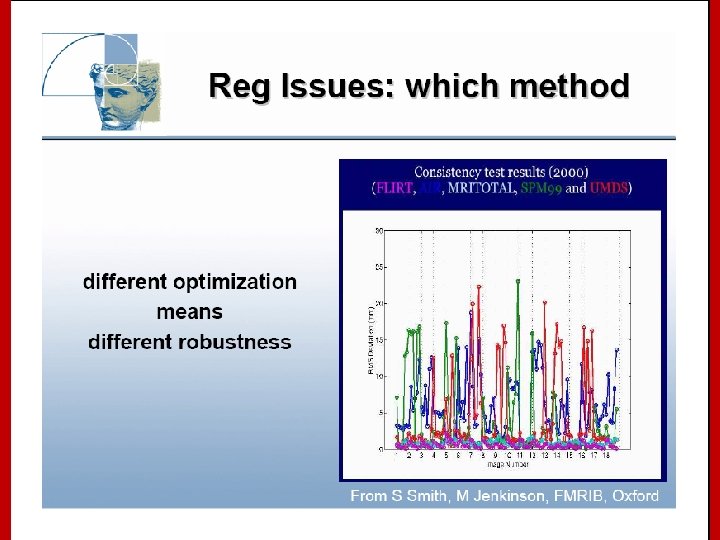
 Talairach Atlas Drawbacks for functional imaging: • is derived from an unrepresentative single 60 -yr old female cadaver brain (when most functional activation studies are done on young living subjects!) • ignores left-right hemispheric differences • has variable slice separation, up to 4 mm • while it contains transverse, coronal and sagittal slices, it is not contiguous in 3 D
Talairach Atlas Drawbacks for functional imaging: • is derived from an unrepresentative single 60 -yr old female cadaver brain (when most functional activation studies are done on young living subjects!) • ignores left-right hemispheric differences • has variable slice separation, up to 4 mm • while it contains transverse, coronal and sagittal slices, it is not contiguous in 3 D
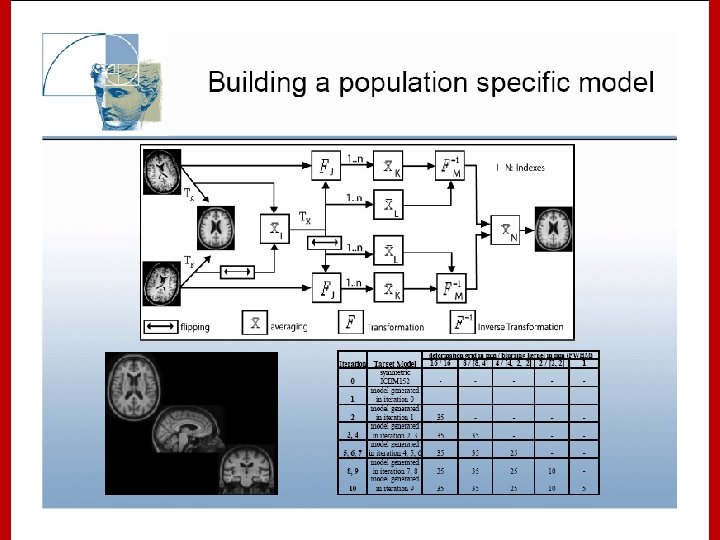
 Stereotaxic Space However, the space and the stereotaxic concept are still worthwhile: • Provides a conceptual framework for the completely automated, 3 D analysis across subjects. • Collins, L. , Evans A. , et al. have created a replacement target volume for stereotaxic mapping to address weaknesses of the Talairach atlas
Stereotaxic Space However, the space and the stereotaxic concept are still worthwhile: • Provides a conceptual framework for the completely automated, 3 D analysis across subjects. • Collins, L. , Evans A. , et al. have created a replacement target volume for stereotaxic mapping to address weaknesses of the Talairach atlas
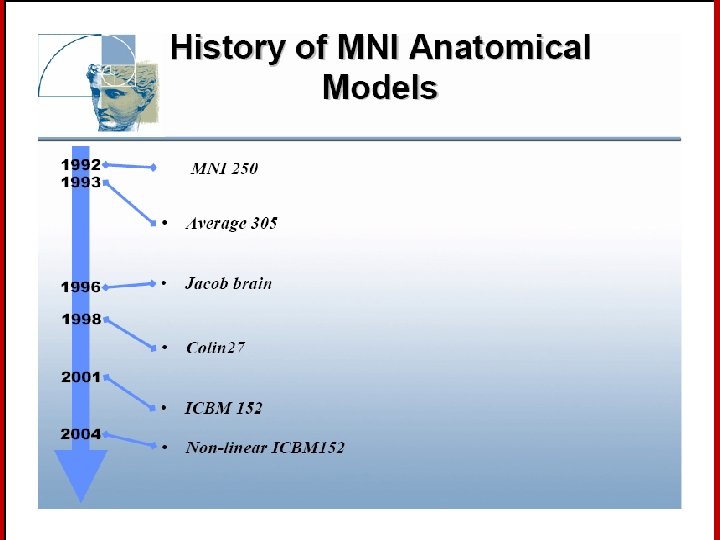
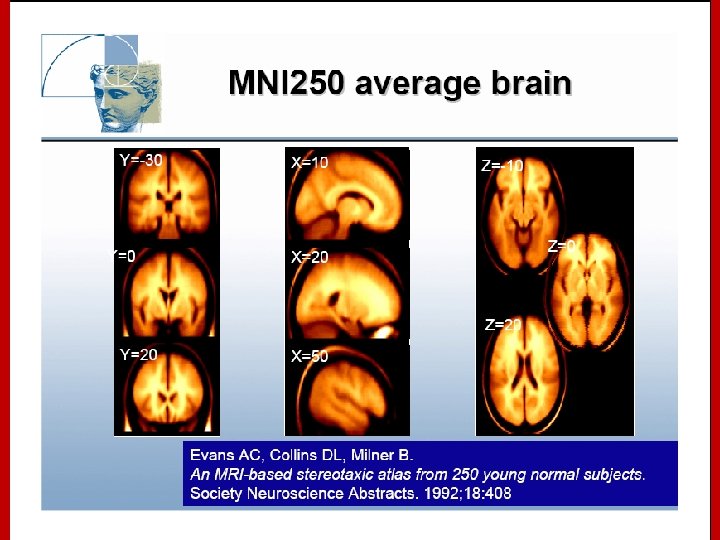
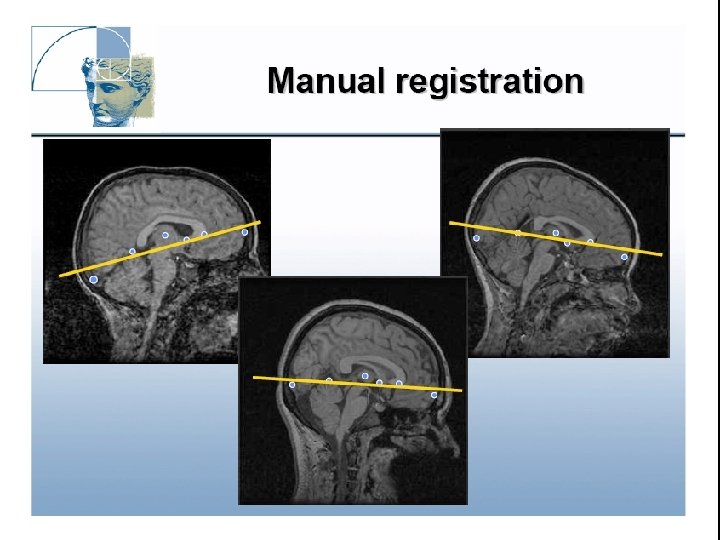
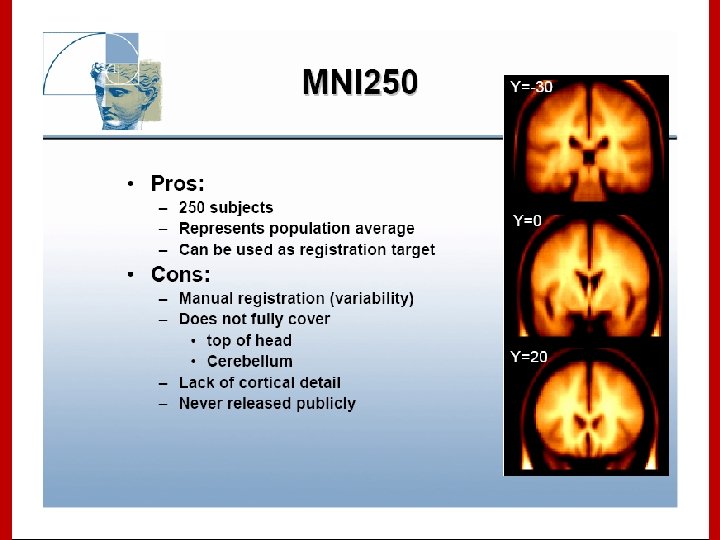
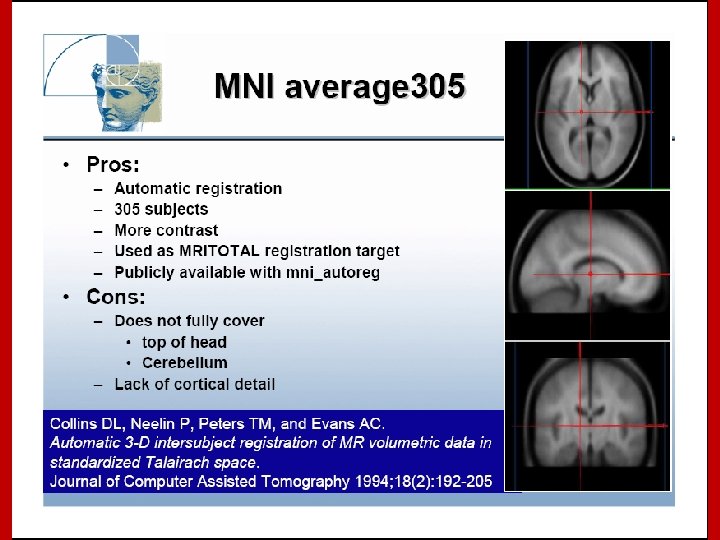
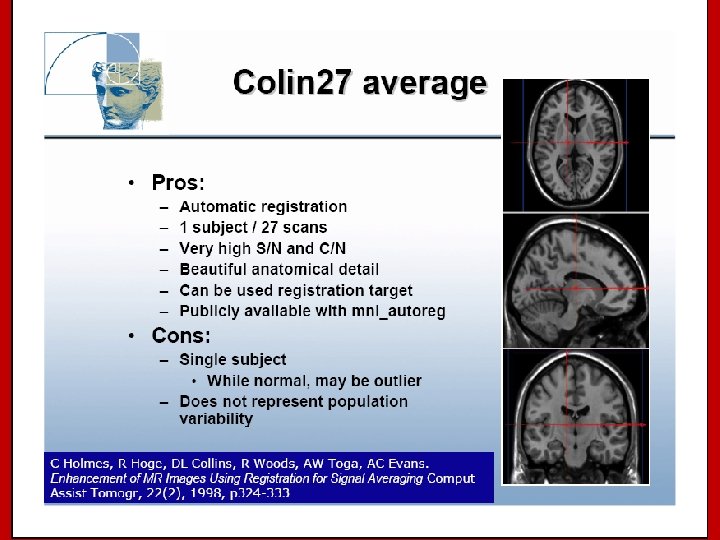
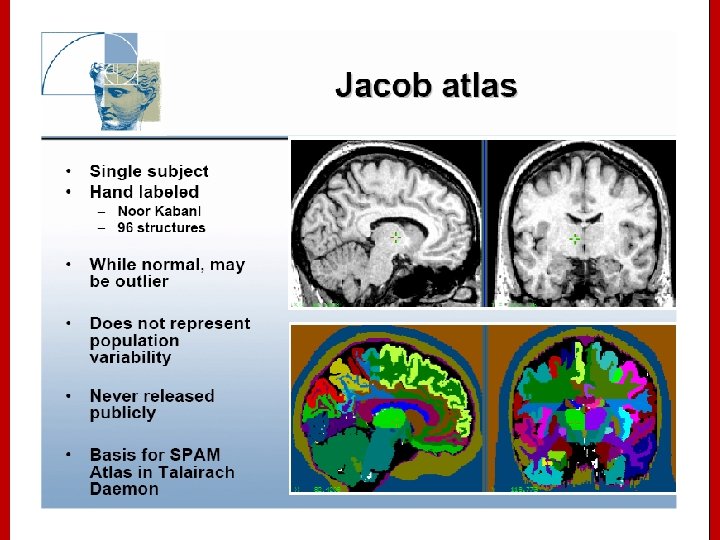
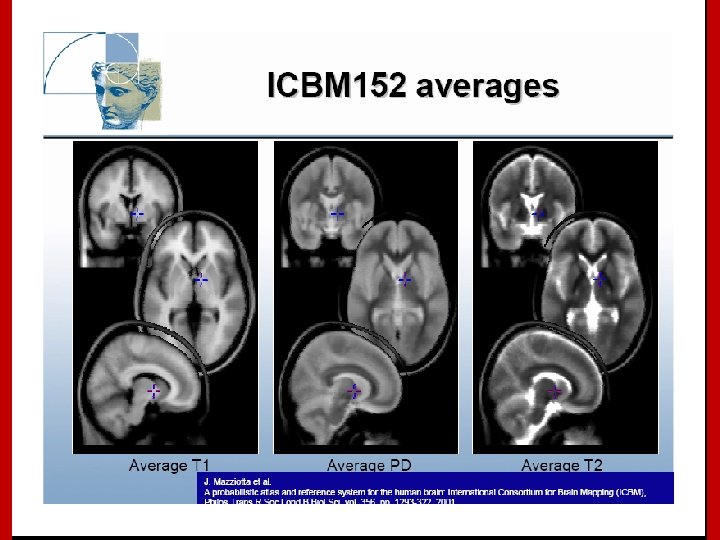
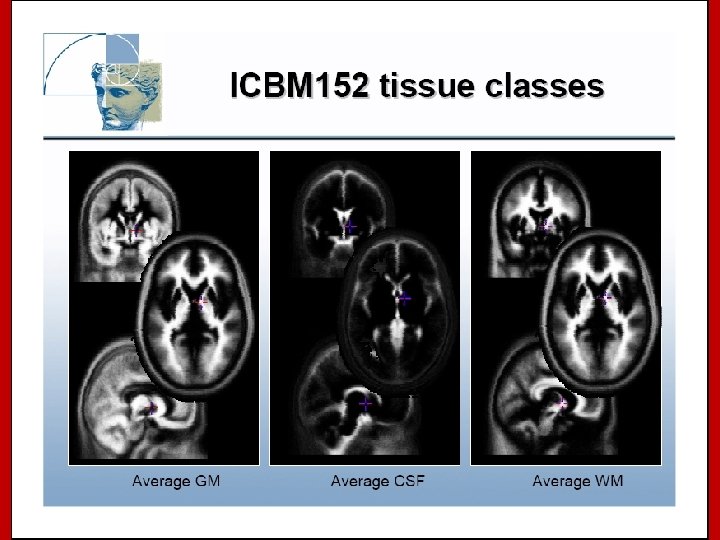
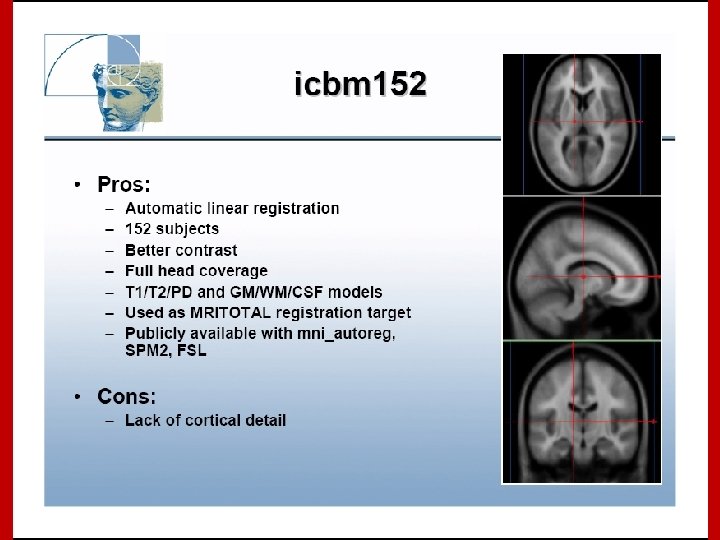
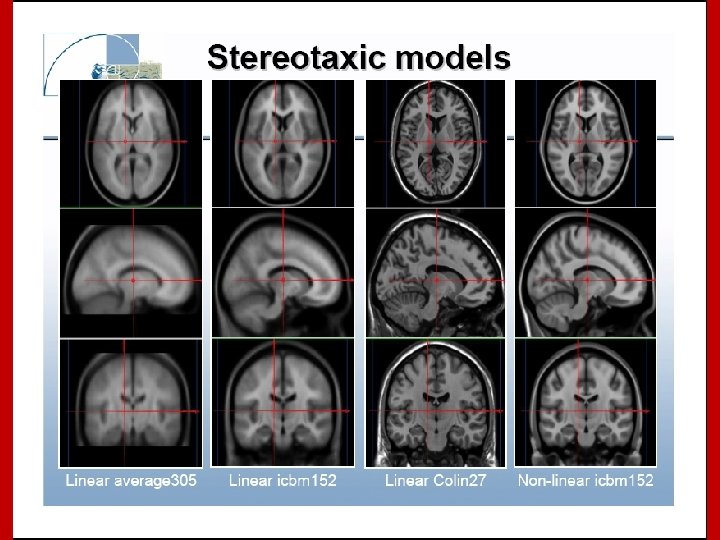
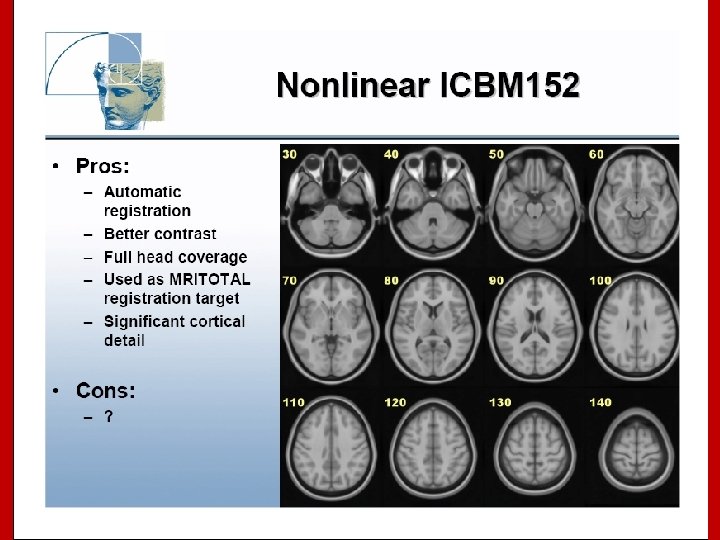
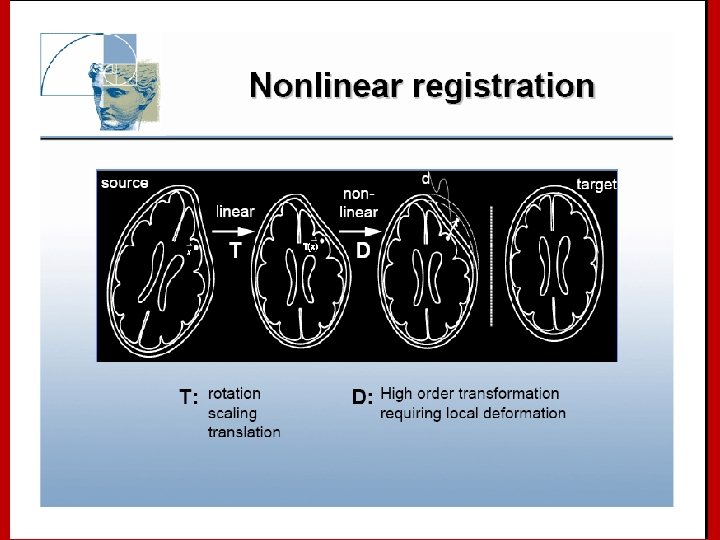
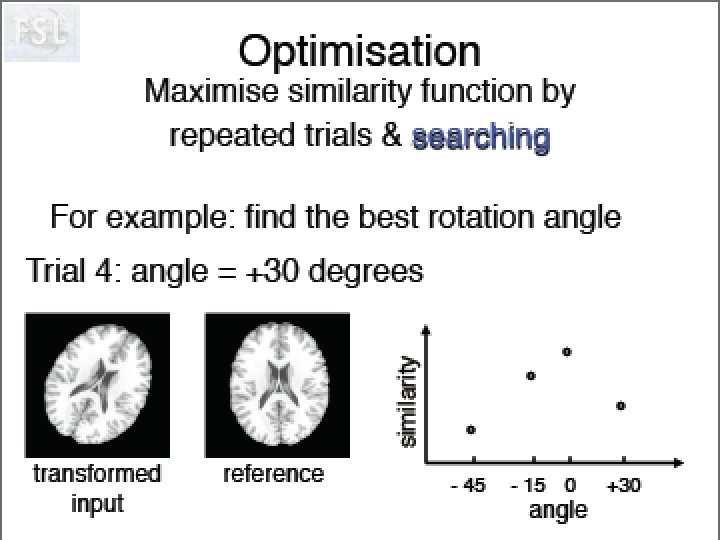
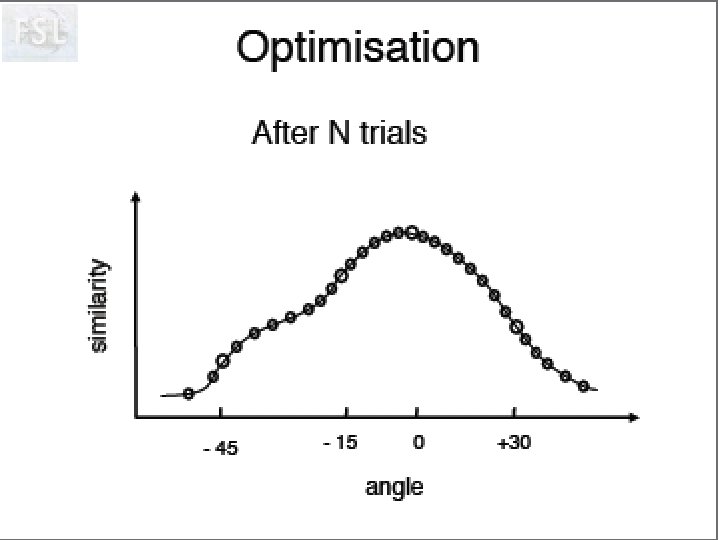
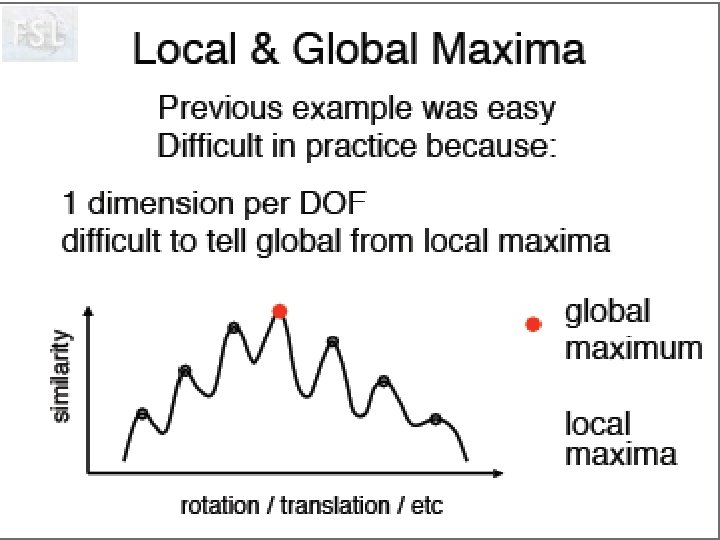
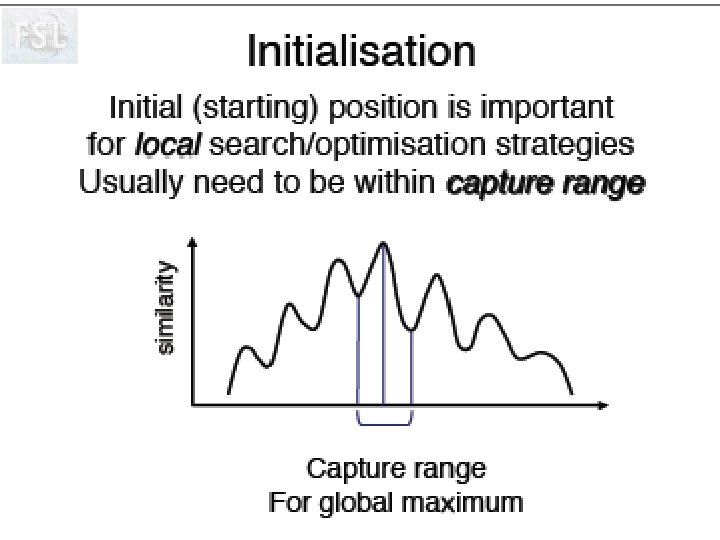
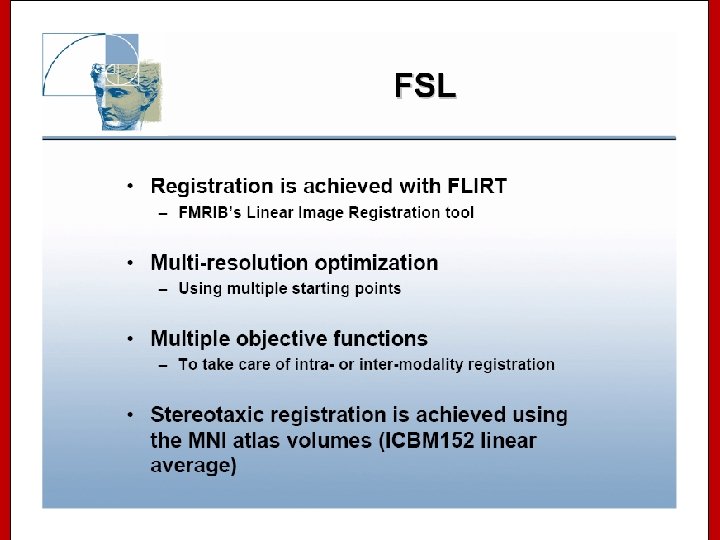
 Image Registration • Registration - i. e. Optimise the parameters that describe a spatial transformation between the source and reference (template) images mritotal: créer la matrice de transformation. xfm • Transformation - i. e. Re-sample according to the determined transformation parameters p. ex: mincresample ou resample_tal: appliquer la transformation aux données
Image Registration • Registration - i. e. Optimise the parameters that describe a spatial transformation between the source and reference (template) images mritotal: créer la matrice de transformation. xfm • Transformation - i. e. Re-sample according to the determined transformation parameters p. ex: mincresample ou resample_tal: appliquer la transformation aux données
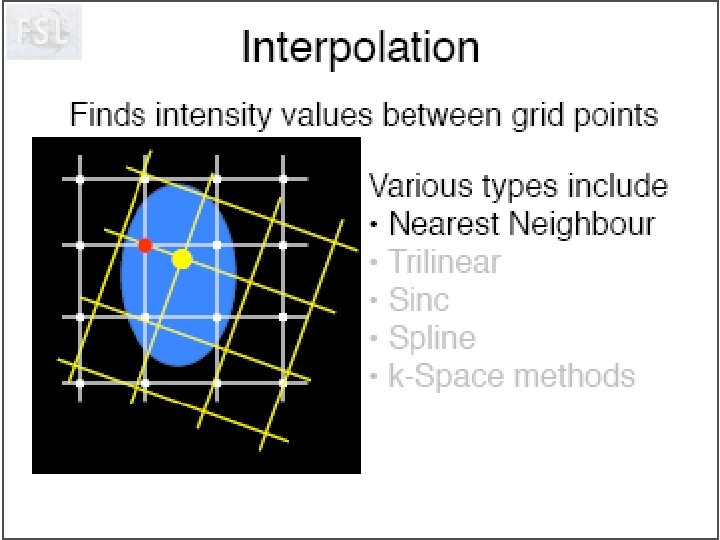
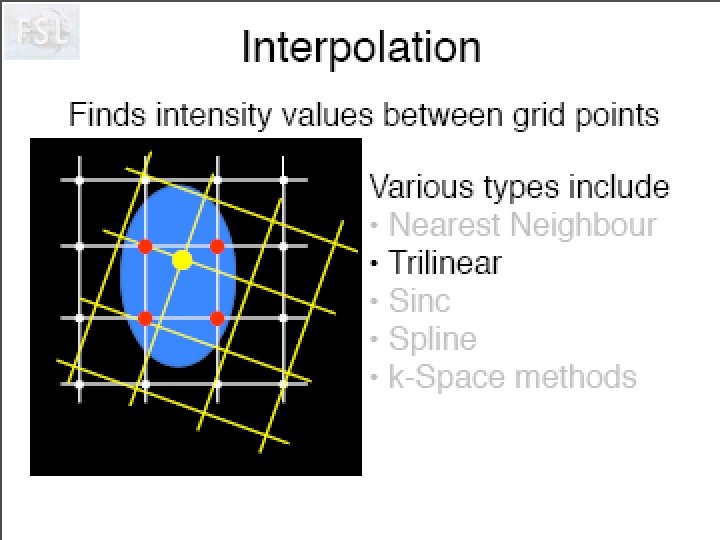
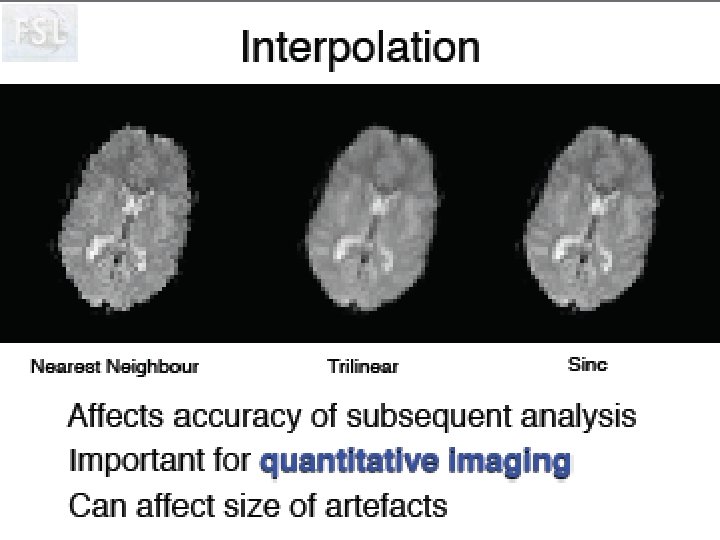
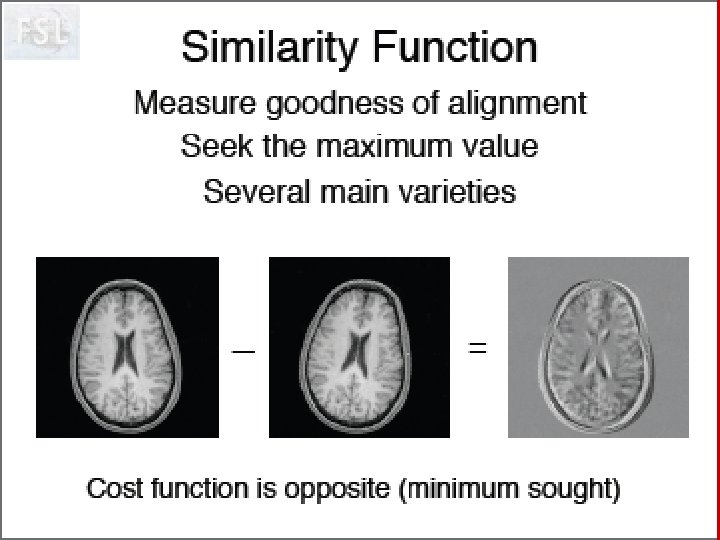
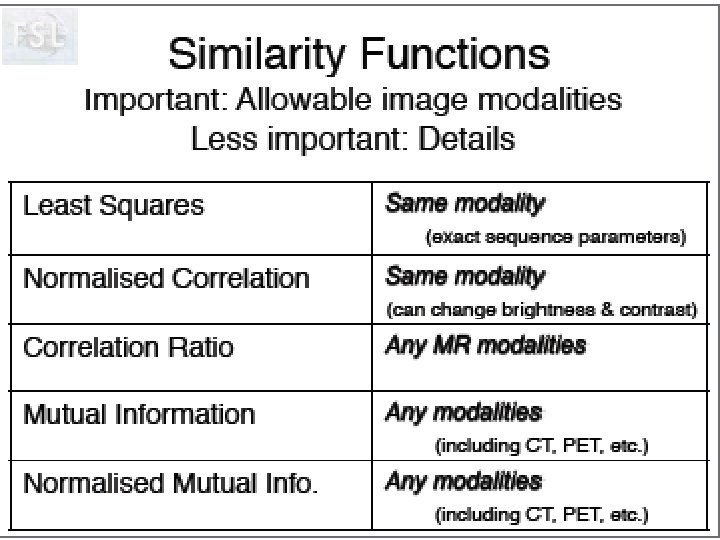
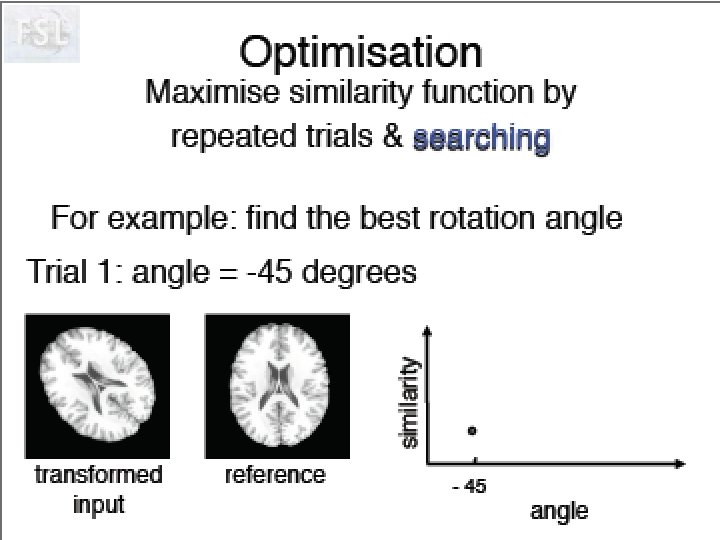
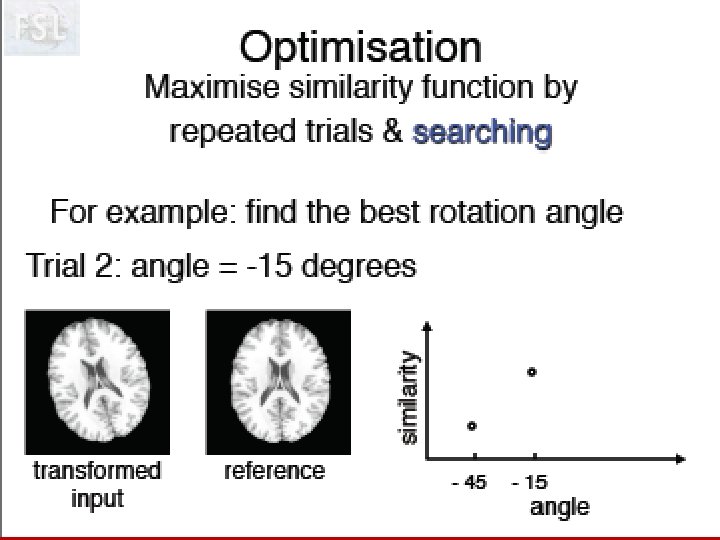
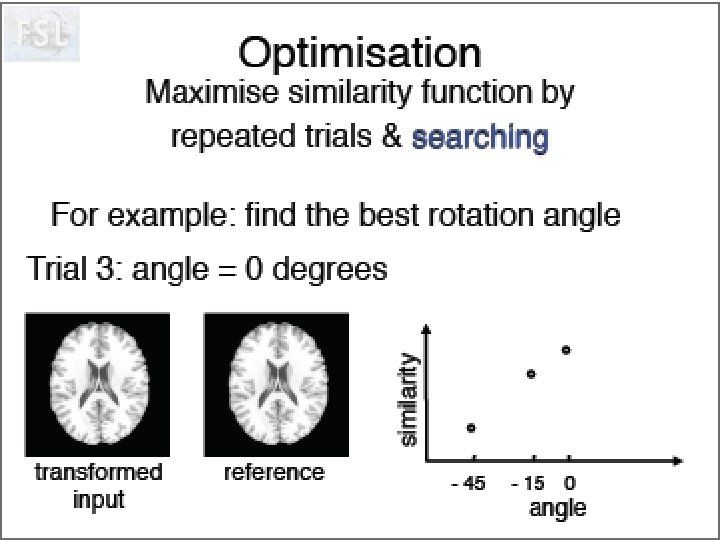


 Idée de Neurolens Pourquoi normaliser des données fonctionnelles sur un ‘template’ anatomique. Création d’un template T 2* Visualisation du processus d’optimisation!
Idée de Neurolens Pourquoi normaliser des données fonctionnelles sur un ‘template’ anatomique. Création d’un template T 2* Visualisation du processus d’optimisation!
 Slides Aknowledgements Louis Collins, Montreal Neurological Institute Andrew Janke, Montreal Neurological Institute FSL & Free. Surfer Course, f. MRIb, Oxford
Slides Aknowledgements Louis Collins, Montreal Neurological Institute Andrew Janke, Montreal Neurological Institute FSL & Free. Surfer Course, f. MRIb, Oxford


