363d295ffe3fd0c4db477deadf4a2c3a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 56
 Normal Pregnancy
Normal Pregnancy
 Pregnancy is a normal physiologic process. . . not a disease!
Pregnancy is a normal physiologic process. . . not a disease!
 Is she pregnant?
Is she pregnant?
 Presumptive symptoms of pregnancy: • • • Cessation of menses Nausea with or without vomiting Frequent urination Fatigue Breast tenderness, fullness, tingling Maternal perception of fetal movement (“Quickening”)
Presumptive symptoms of pregnancy: • • • Cessation of menses Nausea with or without vomiting Frequent urination Fatigue Breast tenderness, fullness, tingling Maternal perception of fetal movement (“Quickening”)
 Presumptive signs of pregnancy: • Breast changes – enlargement, hyperpigmentation, Montgomery’s tubercles • Bluish or purplish coloration of the vaginal mucosa and cervix (Chadwick’s sign) • Increased skin pigmentation – chloasma, linea nigra • Appearance of striae on abdomen and breasts
Presumptive signs of pregnancy: • Breast changes – enlargement, hyperpigmentation, Montgomery’s tubercles • Bluish or purplish coloration of the vaginal mucosa and cervix (Chadwick’s sign) • Increased skin pigmentation – chloasma, linea nigra • Appearance of striae on abdomen and breasts
 Probable signs of pregnancy: • Enlargement of the abdomen • Changes in the size, shape, and consistency of the uterus • Changes in the cervix • Palpation of Braxton-Hicks contractions • Outlining the fetus manually • Endocrine tests of pregnancy
Probable signs of pregnancy: • Enlargement of the abdomen • Changes in the size, shape, and consistency of the uterus • Changes in the cervix • Palpation of Braxton-Hicks contractions • Outlining the fetus manually • Endocrine tests of pregnancy
 Positive signs of pregnancy: • Identification of the fetal heart beat separately and distinctly from that of the mother • Perception of fetal movements by the examiner • Visualization of pregnancy on ultrasound • Fetal recognition on X-ray
Positive signs of pregnancy: • Identification of the fetal heart beat separately and distinctly from that of the mother • Perception of fetal movements by the examiner • Visualization of pregnancy on ultrasound • Fetal recognition on X-ray
 Assessment of Gestational Age • By LMP (last menstrual period) – the mean length of a normal pregnancy is 280 days from the first day of the last normal menstrual period • By physical exam • By ultrasound
Assessment of Gestational Age • By LMP (last menstrual period) – the mean length of a normal pregnancy is 280 days from the first day of the last normal menstrual period • By physical exam • By ultrasound
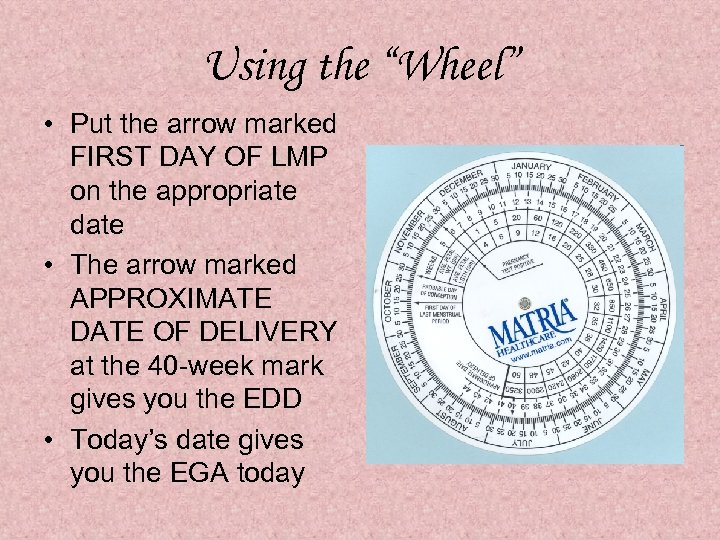 Using the “Wheel” • Put the arrow marked FIRST DAY OF LMP on the appropriate date • The arrow marked APPROXIMATE DATE OF DELIVERY at the 40 -week mark gives you the EDD • Today’s date gives you the EGA today
Using the “Wheel” • Put the arrow marked FIRST DAY OF LMP on the appropriate date • The arrow marked APPROXIMATE DATE OF DELIVERY at the 40 -week mark gives you the EDD • Today’s date gives you the EGA today
 Naegele’s Rule • Add 7 days to the first day of the LMP, then subtract 3 months • EXAMPLE: LMP = October 15 + 7 days = October 22 - 3 months = July 22 = EDD
Naegele’s Rule • Add 7 days to the first day of the LMP, then subtract 3 months • EXAMPLE: LMP = October 15 + 7 days = October 22 - 3 months = July 22 = EDD
 Uterine Sizing • 6 weeks – globular with softening of the isthmus, size of a tangerine • 8 weeks – globular, size of a baseball • 10 weeks – globular with irregularity around one cornua (Piskacek’s sign), size of a softball • 12 weeks – globular, size of a grapefruit
Uterine Sizing • 6 weeks – globular with softening of the isthmus, size of a tangerine • 8 weeks – globular, size of a baseball • 10 weeks – globular with irregularity around one cornua (Piskacek’s sign), size of a softball • 12 weeks – globular, size of a grapefruit
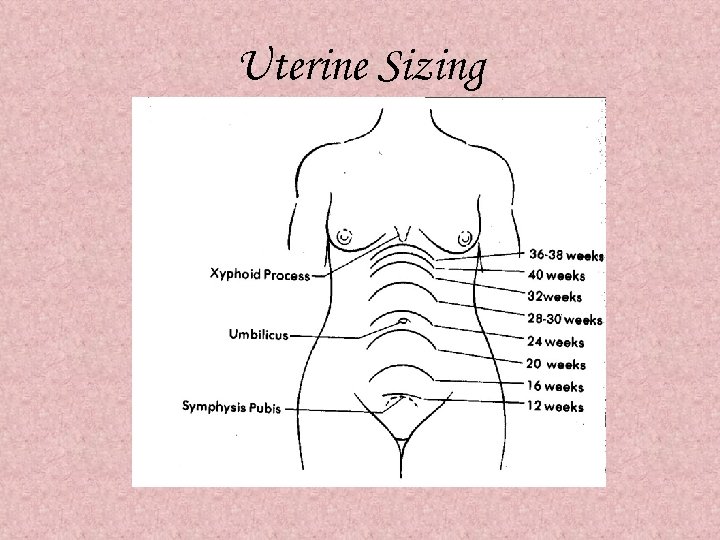 Uterine Sizing
Uterine Sizing
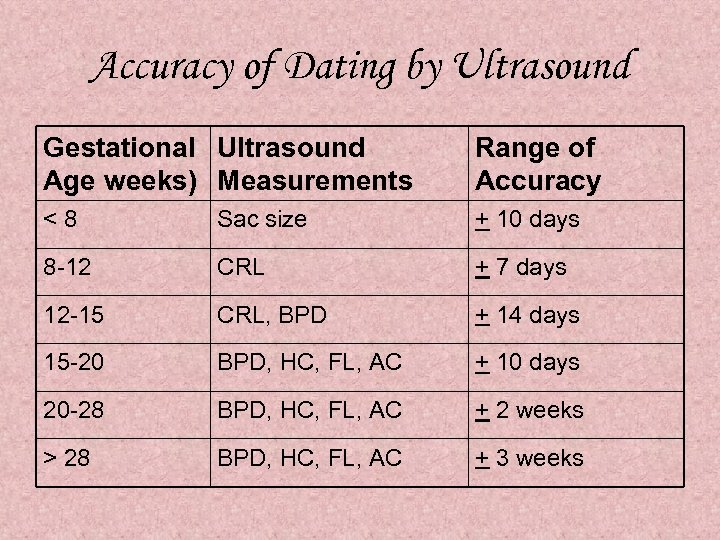 Accuracy of Dating by Ultrasound Gestational Ultrasound Age weeks) Measurements Range of Accuracy <8 Sac size + 10 days 8 -12 CRL + 7 days 12 -15 CRL, BPD + 14 days 15 -20 BPD, HC, FL, AC + 10 days 20 -28 BPD, HC, FL, AC + 2 weeks > 28 BPD, HC, FL, AC + 3 weeks
Accuracy of Dating by Ultrasound Gestational Ultrasound Age weeks) Measurements Range of Accuracy <8 Sac size + 10 days 8 -12 CRL + 7 days 12 -15 CRL, BPD + 14 days 15 -20 BPD, HC, FL, AC + 10 days 20 -28 BPD, HC, FL, AC + 2 weeks > 28 BPD, HC, FL, AC + 3 weeks
 The Trimesters • The “trimesters” are three periods of 14 weeks each • 1 st trimester = through completion of 14 weeks • 2 nd trimester = through completion of 28 weeks • 3 rd trimester = 29 th through 42 nd weeks
The Trimesters • The “trimesters” are three periods of 14 weeks each • 1 st trimester = through completion of 14 weeks • 2 nd trimester = through completion of 28 weeks • 3 rd trimester = 29 th through 42 nd weeks
 Gravida and Para • Gravida means a woman who has been, or currently is, pregnant • Para means a woman who has given birth • • Nulligravida – never been pregnant Primigravida – pregnant for the first time Primipara – has delivered once Multipara – has delivered more than once
Gravida and Para • Gravida means a woman who has been, or currently is, pregnant • Para means a woman who has given birth • • Nulligravida – never been pregnant Primigravida – pregnant for the first time Primipara – has delivered once Multipara – has delivered more than once
 GTPAL • G – GRAVIDA (how many pregnancies) • T – TERM (how many term deliveries) • P – PRETERM (how many preterm deliveries) • A – ABORTIONS (how many abortions, spontaneous or induced) • L – LIVING – how many children currently living
GTPAL • G – GRAVIDA (how many pregnancies) • T – TERM (how many term deliveries) • P – PRETERM (how many preterm deliveries) • A – ABORTIONS (how many abortions, spontaneous or induced) • L – LIVING – how many children currently living
 Term, Preterm, Abortion • TERM means delivery occurring in weeks 38 -42 • PRETERM means delivery occurring in weeks 20 -37 • ABORTION means delivery occurring before 20 weeks • POSTTERM means delivery occurring after week 42
Term, Preterm, Abortion • TERM means delivery occurring in weeks 38 -42 • PRETERM means delivery occurring in weeks 20 -37 • ABORTION means delivery occurring before 20 weeks • POSTTERM means delivery occurring after week 42
 Psychological Adaptation and Developmental Tasks of Pregnancy • 1 st Trimester – Accepting reality of pregnancy • 2 nd Trimester – Resolving feelings about her own mother; defining herself as a mother • 3 rd Trimester – Active preparation for childbirth and baby
Psychological Adaptation and Developmental Tasks of Pregnancy • 1 st Trimester – Accepting reality of pregnancy • 2 nd Trimester – Resolving feelings about her own mother; defining herself as a mother • 3 rd Trimester – Active preparation for childbirth and baby
 The First Prenatal Visit: History • • • Past medical history Family medical history Gynecologic history Past OB history Exposures to infections, teratogens, genetic problems • Social history • Nutritional status
The First Prenatal Visit: History • • • Past medical history Family medical history Gynecologic history Past OB history Exposures to infections, teratogens, genetic problems • Social history • Nutritional status
 The First Prenatal Visit: Exam • • • HEENT Fundoscopic exam Teeth Thyroid Breasts Lungs Heart Abdomen Extremities • Skin • Lymph nodes
The First Prenatal Visit: Exam • • • HEENT Fundoscopic exam Teeth Thyroid Breasts Lungs Heart Abdomen Extremities • Skin • Lymph nodes
 The First Prenatal Visit: Pelvic Exam • • • Vulva Vagina Cervix Uterine size Adnexae Rectum • Labs: – Pap – GC & chlamydia • Clinical pelvimetry: – – – Diagonal conjugate Ischial spines Sacrum Subpubic arch Gynecoid pelvic type?
The First Prenatal Visit: Pelvic Exam • • • Vulva Vagina Cervix Uterine size Adnexae Rectum • Labs: – Pap – GC & chlamydia • Clinical pelvimetry: – – – Diagonal conjugate Ischial spines Sacrum Subpubic arch Gynecoid pelvic type?
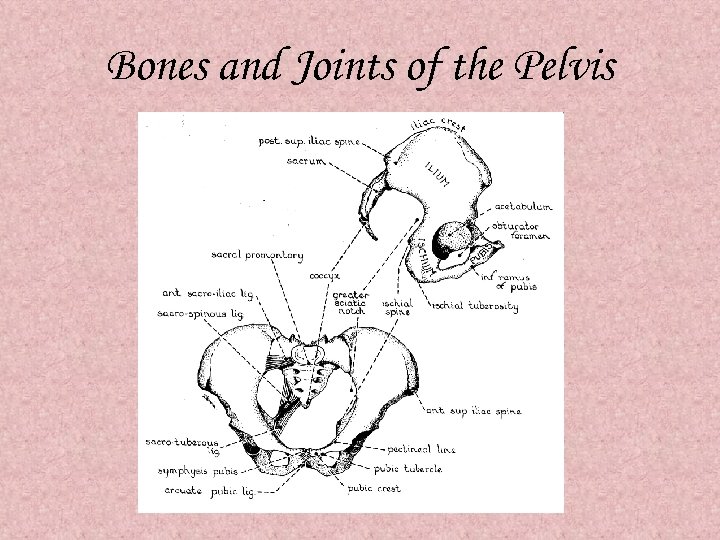 Bones and Joints of the Pelvis
Bones and Joints of the Pelvis
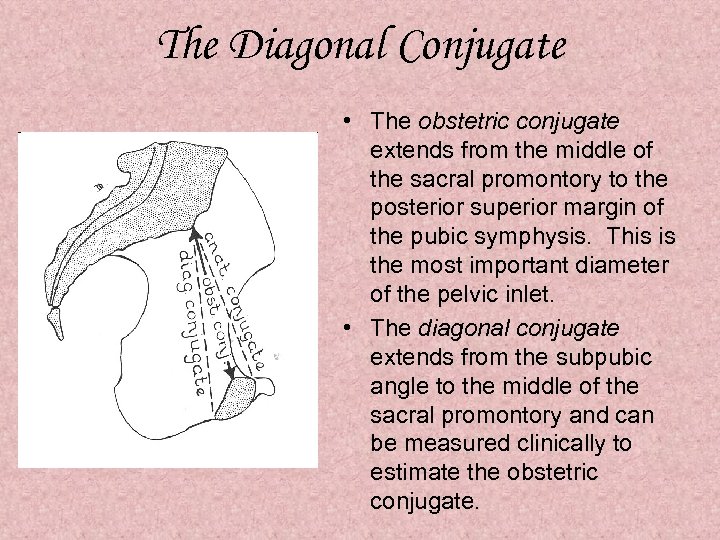 The Diagonal Conjugate • The obstetric conjugate extends from the middle of the sacral promontory to the posterior superior margin of the pubic symphysis. This is the most important diameter of the pelvic inlet. • The diagonal conjugate extends from the subpubic angle to the middle of the sacral promontory and can be measured clinically to estimate the obstetric conjugate.
The Diagonal Conjugate • The obstetric conjugate extends from the middle of the sacral promontory to the posterior superior margin of the pubic symphysis. This is the most important diameter of the pelvic inlet. • The diagonal conjugate extends from the subpubic angle to the middle of the sacral promontory and can be measured clinically to estimate the obstetric conjugate.
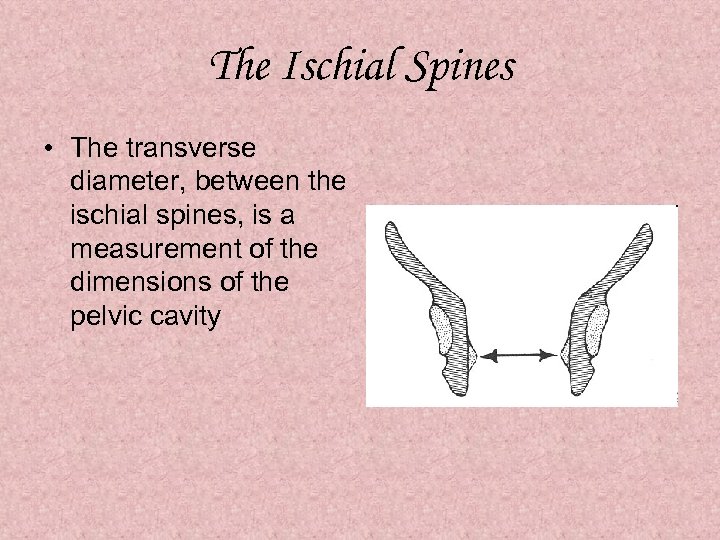 The Ischial Spines • The transverse diameter, between the ischial spines, is a measurement of the dimensions of the pelvic cavity
The Ischial Spines • The transverse diameter, between the ischial spines, is a measurement of the dimensions of the pelvic cavity
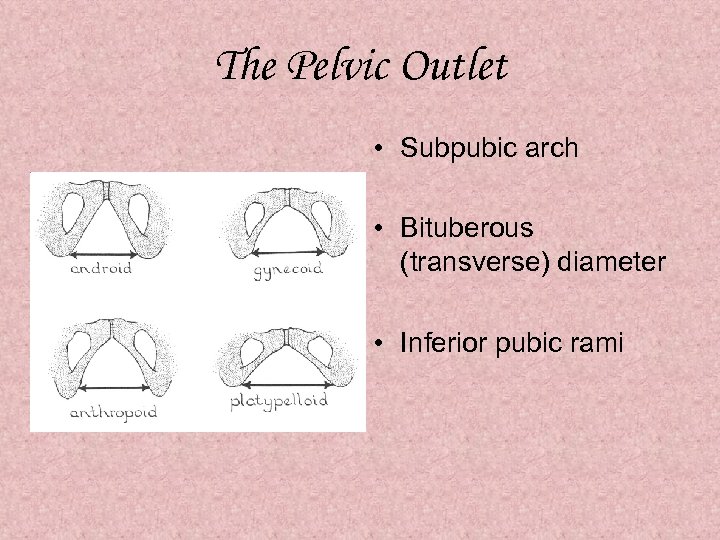 The Pelvic Outlet • Subpubic arch • Bituberous (transverse) diameter • Inferior pubic rami
The Pelvic Outlet • Subpubic arch • Bituberous (transverse) diameter • Inferior pubic rami
 The First Prenatal Visit: Labs • • • ABO blood type D (Rh) type Antibody screen CBC Rubella VDRL or RPR HBs. Ag HIV (optional) Hemoglobin electrophoresis (as appropriate)
The First Prenatal Visit: Labs • • • ABO blood type D (Rh) type Antibody screen CBC Rubella VDRL or RPR HBs. Ag HIV (optional) Hemoglobin electrophoresis (as appropriate)
 The First Prenatal Visit: Counseling • What to expect during the course of prenatal care • Risk factors encountered • Nutrition • Exercise • Work • Sexual activity • Travel, seat belts • Smoking cessation • Avoidance of drugs and alcohol • Warning signs • Where to go or call in case of problems • Prenatal vitamins
The First Prenatal Visit: Counseling • What to expect during the course of prenatal care • Risk factors encountered • Nutrition • Exercise • Work • Sexual activity • Travel, seat belts • Smoking cessation • Avoidance of drugs and alcohol • Warning signs • Where to go or call in case of problems • Prenatal vitamins
 The Return Prenatal Visit • REVIEW THE CHART! – Calculate the EGA – Check the labs – Review weight gain – Review blood pressure – Review results of UA
The Return Prenatal Visit • REVIEW THE CHART! – Calculate the EGA – Check the labs – Review weight gain – Review blood pressure – Review results of UA
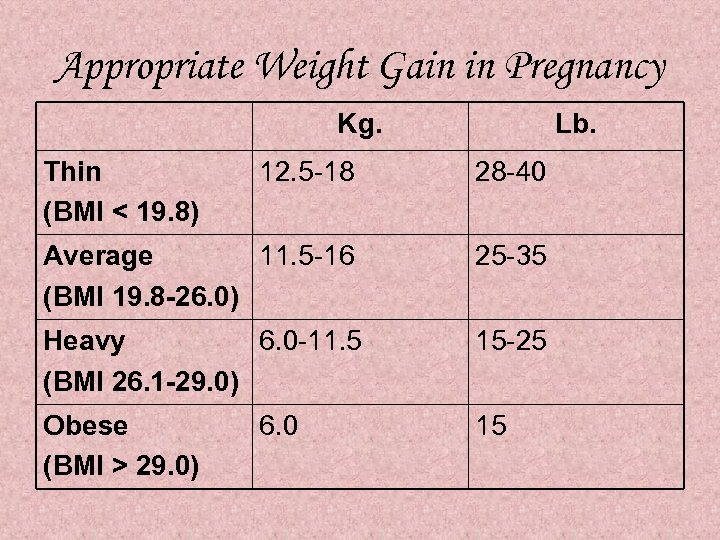 Appropriate Weight Gain in Pregnancy Kg. Thin (BMI < 19. 8) Lb. 12. 5 -18 28 -40 Average 11. 5 -16 (BMI 19. 8 -26. 0) 25 -35 Heavy 6. 0 -11. 5 (BMI 26. 1 -29. 0) 15 -25 Obese (BMI > 29. 0) 15 6. 0
Appropriate Weight Gain in Pregnancy Kg. Thin (BMI < 19. 8) Lb. 12. 5 -18 28 -40 Average 11. 5 -16 (BMI 19. 8 -26. 0) 25 -35 Heavy 6. 0 -11. 5 (BMI 26. 1 -29. 0) 15 -25 Obese (BMI > 29. 0) 15 6. 0
 The Three “B’s” --- Baby, Belly, Bottom
The Three “B’s” --- Baby, Belly, Bottom
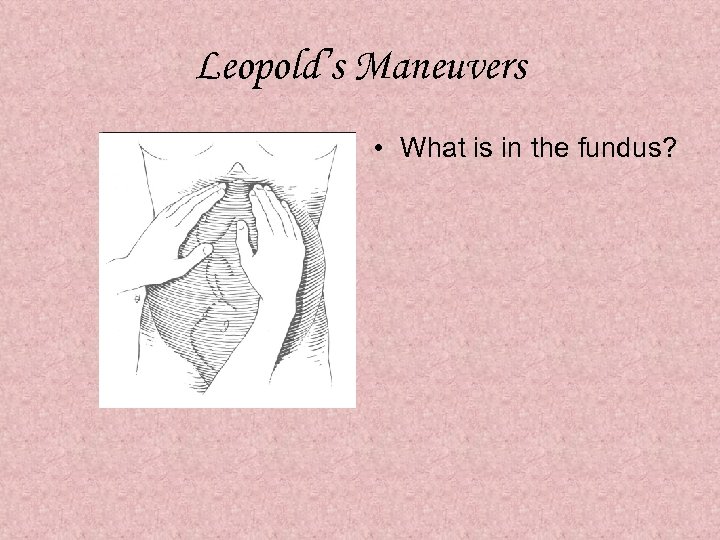 Leopold’s Maneuvers • What is in the fundus?
Leopold’s Maneuvers • What is in the fundus?
 Leopold’s Maneuvers • Where is the back and where are the small parts?
Leopold’s Maneuvers • Where is the back and where are the small parts?
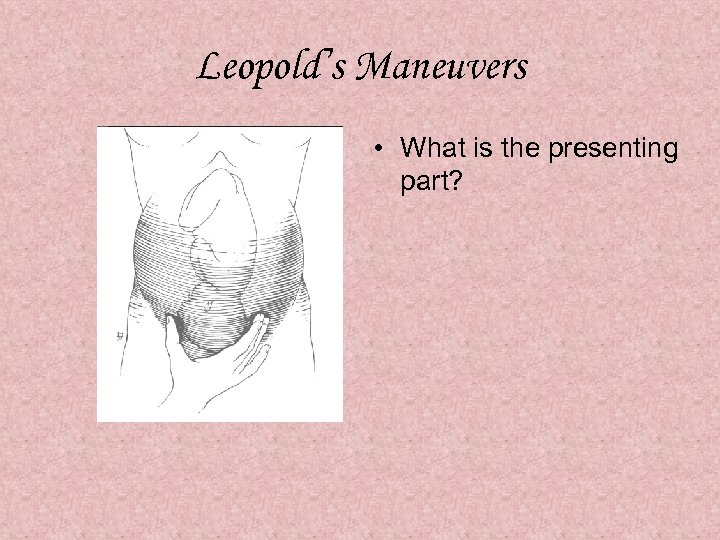 Leopold’s Maneuvers • What is the presenting part?
Leopold’s Maneuvers • What is the presenting part?
 Measuring Fundal Height
Measuring Fundal Height
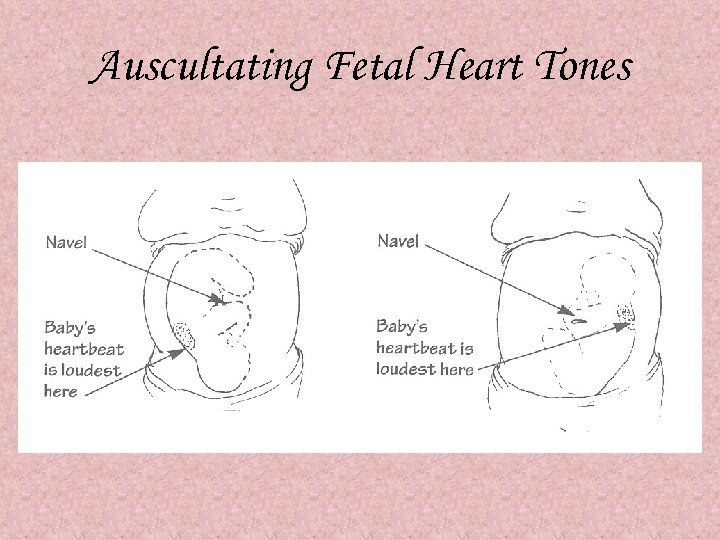 Auscultating Fetal Heart Tones
Auscultating Fetal Heart Tones
 The Routine OB Visit Schedule • Every 4 weeks until 28 weeks • Every 2 weeks from 28 until 36 weeks • Every week from 36 weeks until delivery • Six weeks postpartum
The Routine OB Visit Schedule • Every 4 weeks until 28 weeks • Every 2 weeks from 28 until 36 weeks • Every week from 36 weeks until delivery • Six weeks postpartum
 Other Routine OB Labs • 15 -20 weeks • Quad Screen • 24 -28 weeks • Diabetes Screen • H&H • Rhogam workup & injection • 35 -37 weeks • Group B strep culture
Other Routine OB Labs • 15 -20 weeks • Quad Screen • 24 -28 weeks • Diabetes Screen • H&H • Rhogam workup & injection • 35 -37 weeks • Group B strep culture
 Pregnancy is a normal physiologic process, not a disease. . . • however, pregnancy tends to be UNCOMFORTABLE. Your challenge is to differentiate common discomforts of pregnancy from pathology!
Pregnancy is a normal physiologic process, not a disease. . . • however, pregnancy tends to be UNCOMFORTABLE. Your challenge is to differentiate common discomforts of pregnancy from pathology!
 Nausea with or without Vomiting • Starts at 4 -6 weeks, peaks at 8 -12 weeks, resolves by 14 -16 weeks • Causes: unknown; may be rapidly increasing and high levels of estrogen, h. CG, thyroxine; may have a psychological component • Rule out: hyperemesis gravidarum
Nausea with or without Vomiting • Starts at 4 -6 weeks, peaks at 8 -12 weeks, resolves by 14 -16 weeks • Causes: unknown; may be rapidly increasing and high levels of estrogen, h. CG, thyroxine; may have a psychological component • Rule out: hyperemesis gravidarum
 Ptyalism • Excessive salivation accompanied by nausea and inability to swallow saliva • Cause: unknown; may be related to increased acidity in the mouth
Ptyalism • Excessive salivation accompanied by nausea and inability to swallow saliva • Cause: unknown; may be related to increased acidity in the mouth
 Fatigue • Causes: unknown; may be related to gradual increase in BMR • Rule out: anemia, thyroid disease
Fatigue • Causes: unknown; may be related to gradual increase in BMR • Rule out: anemia, thyroid disease
 Upper Backache • Cause: increase in size and weight of the breasts • Relief: well-fitting, supportive bra
Upper Backache • Cause: increase in size and weight of the breasts • Relief: well-fitting, supportive bra
 Low Backache • Cause: weight of the enlarging uterus causing exaggerated lumbar lordosis • Rule out: pyelonephritis (CVAT)
Low Backache • Cause: weight of the enlarging uterus causing exaggerated lumbar lordosis • Rule out: pyelonephritis (CVAT)
 Leukorrhea • Definition: a profuse, thin or thick white vaginal discharge consisting of white blood cells, vaginal epithelial cells, and bacilli; acidic due to conversion of an increased amount of glycogen in vaginal epithelial cells into lactic acid by Doderlein’s bacilli • Rule out: vaginitis, STI, ruptured membranes
Leukorrhea • Definition: a profuse, thin or thick white vaginal discharge consisting of white blood cells, vaginal epithelial cells, and bacilli; acidic due to conversion of an increased amount of glycogen in vaginal epithelial cells into lactic acid by Doderlein’s bacilli • Rule out: vaginitis, STI, ruptured membranes
 Urinary Frequency • 1 st trimester: increased weight, softening of the isthmus, anteflexion of the uterus • 3 rd trimester: pressure of the presenting part • Rule out: UTI
Urinary Frequency • 1 st trimester: increased weight, softening of the isthmus, anteflexion of the uterus • 3 rd trimester: pressure of the presenting part • Rule out: UTI
 Heartburn • Relaxation of the cardiac sphincter due to progesterone • Decreased GI motility due to smooth muscle relaxation (progesterone) • Lack of functional room for the stomach because of its displacement and compression by the enlarging uterus • Rule out: GI disease
Heartburn • Relaxation of the cardiac sphincter due to progesterone • Decreased GI motility due to smooth muscle relaxation (progesterone) • Lack of functional room for the stomach because of its displacement and compression by the enlarging uterus • Rule out: GI disease
 Constipation • Decreased peristalsis due to relaxation of the smooth muscle of the large bowel under the influence of progesterone • Displacement of the bowel by the enlarging uterus • Administration of iron supplements
Constipation • Decreased peristalsis due to relaxation of the smooth muscle of the large bowel under the influence of progesterone • Displacement of the bowel by the enlarging uterus • Administration of iron supplements
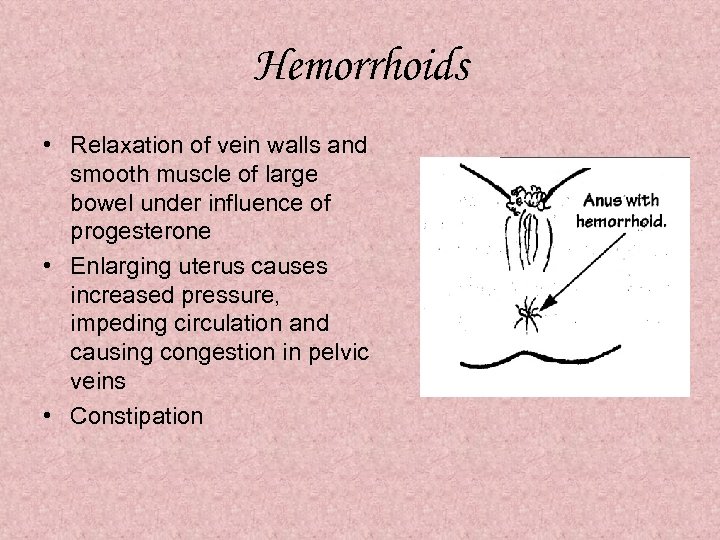 Hemorrhoids • Relaxation of vein walls and smooth muscle of large bowel under influence of progesterone • Enlarging uterus causes increased pressure, impeding circulation and causing congestion in pelvic veins • Constipation
Hemorrhoids • Relaxation of vein walls and smooth muscle of large bowel under influence of progesterone • Enlarging uterus causes increased pressure, impeding circulation and causing congestion in pelvic veins • Constipation
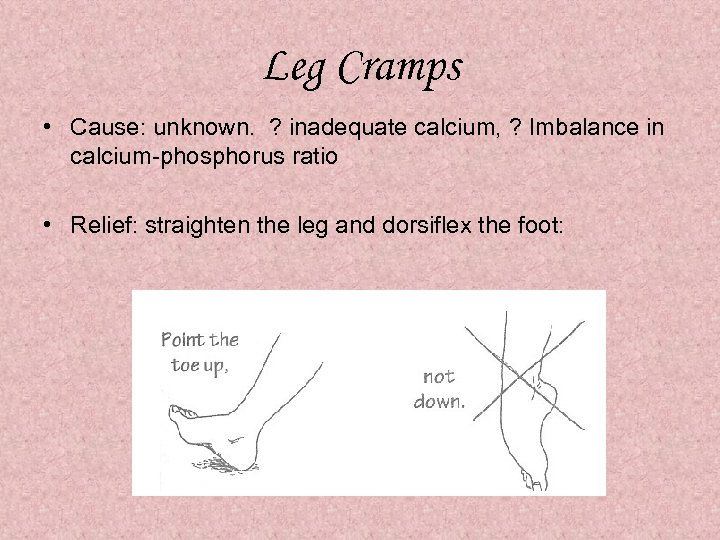 Leg Cramps • Cause: unknown. ? inadequate calcium, ? Imbalance in calcium-phosphorus ratio • Relief: straighten the leg and dorsiflex the foot:
Leg Cramps • Cause: unknown. ? inadequate calcium, ? Imbalance in calcium-phosphorus ratio • Relief: straighten the leg and dorsiflex the foot:
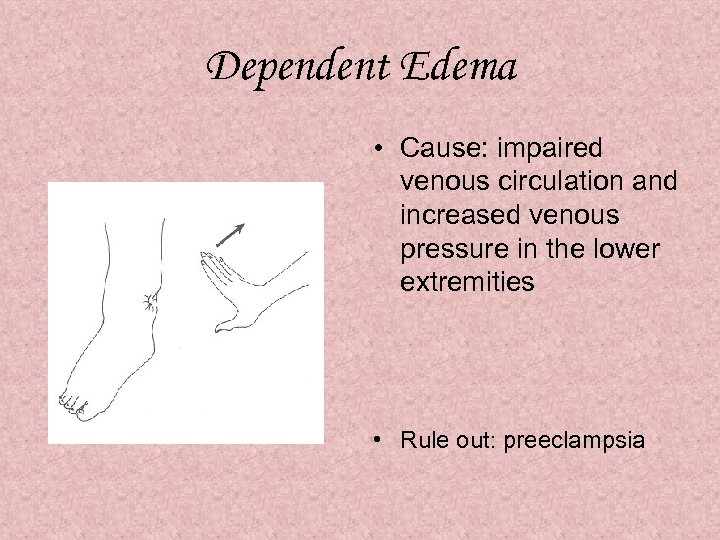 Dependent Edema • Cause: impaired venous circulation and increased venous pressure in the lower extremities • Rule out: preeclampsia
Dependent Edema • Cause: impaired venous circulation and increased venous pressure in the lower extremities • Rule out: preeclampsia
 Varicosities • Impaired venous circulation and increased venous pressure in lower extremities • Relaxation of vein walls and surrounding smooth muscle under the influence of progesterone • Increased blood volume • Familial predisposition
Varicosities • Impaired venous circulation and increased venous pressure in lower extremities • Relaxation of vein walls and surrounding smooth muscle under the influence of progesterone • Increased blood volume • Familial predisposition
 Insomnia • • Discomfort of the enlarged uterus Any of the common discomforts of pregnancy Fetal activity Psychological causes
Insomnia • • Discomfort of the enlarged uterus Any of the common discomforts of pregnancy Fetal activity Psychological causes
 Round Ligament Pain • Round ligaments attach on either side of the uterus just below and in front of insertion of fallopian tubes, cross the broad ligament in a fold of peritoneum, pass through the inguinal canal, insert in the anterior portion of the labia majora • When stretched, they hurt!
Round Ligament Pain • Round ligaments attach on either side of the uterus just below and in front of insertion of fallopian tubes, cross the broad ligament in a fold of peritoneum, pass through the inguinal canal, insert in the anterior portion of the labia majora • When stretched, they hurt!
 Hyperventilation and Shortness of Breath • Causes: – Increase in the BMR – Pressure of the uterus on the diaphragm – Changes in the oxygencarbon dioxide balance – Exertion of carrying extra weight • Rule out: asthma, pneumonia, TB, anxiety
Hyperventilation and Shortness of Breath • Causes: – Increase in the BMR – Pressure of the uterus on the diaphragm – Changes in the oxygencarbon dioxide balance – Exertion of carrying extra weight • Rule out: asthma, pneumonia, TB, anxiety
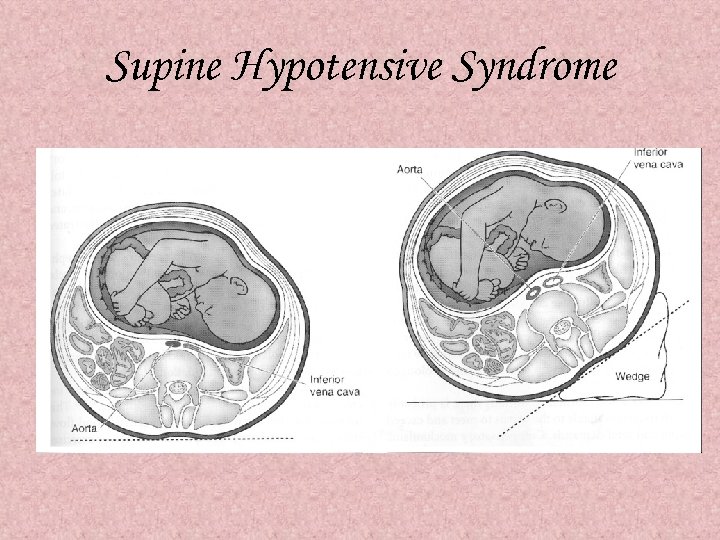 Supine Hypotensive Syndrome
Supine Hypotensive Syndrome
 Remember: Pregnancy is normal!
Remember: Pregnancy is normal!


