03f9642cc70709c585d2523f3d0d6171.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52
 Non–Ig. E-mediated Gl Food Allergy (FA) Dr. Raga Sirror, MBBS, FRCPC Thunder Bay Regional Health Sciences Centre Pediatrics, Allergy
Non–Ig. E-mediated Gl Food Allergy (FA) Dr. Raga Sirror, MBBS, FRCPC Thunder Bay Regional Health Sciences Centre Pediatrics, Allergy
 Conflict of Interest Declaration: Presenter: Dr. Raga Sirror Title of Presentation: Non Ig. E mediated Gastrointestinal Food Allergy I have no financial or personal relationship related to this presentation to disclose.
Conflict of Interest Declaration: Presenter: Dr. Raga Sirror Title of Presentation: Non Ig. E mediated Gastrointestinal Food Allergy I have no financial or personal relationship related to this presentation to disclose.
 Objectives: I. To identify different types of Non Ig. E mediated FA. II. To discuss the management of Non Ig. E mediated FA. III. To discuss the possible associations between common GI issues & FA.
Objectives: I. To identify different types of Non Ig. E mediated FA. II. To discuss the management of Non Ig. E mediated FA. III. To discuss the possible associations between common GI issues & FA.
 History of Food Allergy Hippocrates noted: cow’s milk (CM) caused GI symptoms, as well as urticaria, and that some infants fed CM had diarrhea, vomiting, and FTT that resolved only after removal of CM from their diets Wuthrich B. History of food allergy. Chem Immunol Allergy 2014
History of Food Allergy Hippocrates noted: cow’s milk (CM) caused GI symptoms, as well as urticaria, and that some infants fed CM had diarrhea, vomiting, and FTT that resolved only after removal of CM from their diets Wuthrich B. History of food allergy. Chem Immunol Allergy 2014
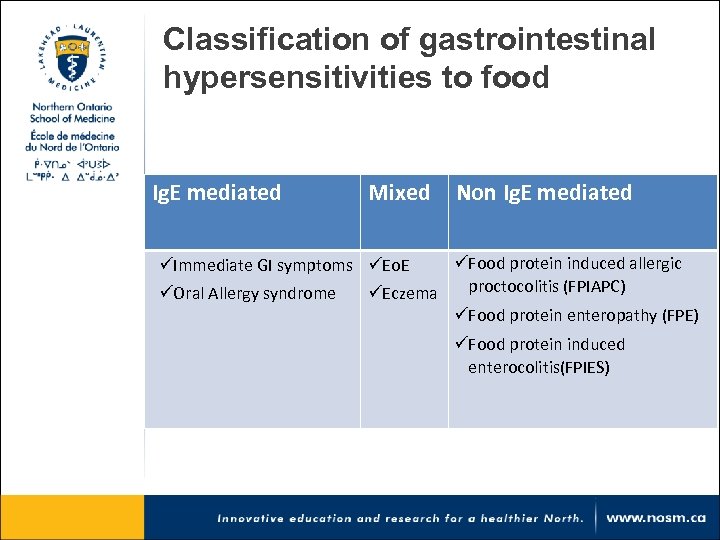 Classification of gastrointestinal hypersensitivities to food Ig. E mediated Mixed Non Ig. E mediated üFood protein induced allergic üImmediate GI symptoms üEo. E proctocolitis (FPIAPC) üOral Allergy syndrome üEczema üFood protein enteropathy (FPE) üFood protein induced enterocolitis(FPIES)
Classification of gastrointestinal hypersensitivities to food Ig. E mediated Mixed Non Ig. E mediated üFood protein induced allergic üImmediate GI symptoms üEo. E proctocolitis (FPIAPC) üOral Allergy syndrome üEczema üFood protein enteropathy (FPE) üFood protein induced enterocolitis(FPIES)
 Case No. 1 2 m old, Frank A. Peter, breastfed with bloody stool. Aside from the diaper, the baby is well. What’s Frank A. Peter diagnosis? (a)FPIAP (b)FPIES (c)FPE
Case No. 1 2 m old, Frank A. Peter, breastfed with bloody stool. Aside from the diaper, the baby is well. What’s Frank A. Peter diagnosis? (a)FPIAP (b)FPIES (c)FPE
 Case No. 1 2 m old, Frank A. Peter, breastfed with bloody stool. Aside from the diaper, the baby is well. What’s Frank A. Peter diagnosis? (a)FPIAP (b)FPIES (c)FPE
Case No. 1 2 m old, Frank A. Peter, breastfed with bloody stool. Aside from the diaper, the baby is well. What’s Frank A. Peter diagnosis? (a)FPIAP (b)FPIES (c)FPE
 Food Protein Induced Allergic Proctocolitis (FPIAP) Clinical presentation: üMucousy, bloody stools in otherwise healthy infant üNo vomiting üNo FTT üNo malabsorbtion üOccasional colic or diarrhea Elizur A. et al. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2012
Food Protein Induced Allergic Proctocolitis (FPIAP) Clinical presentation: üMucousy, bloody stools in otherwise healthy infant üNo vomiting üNo FTT üNo malabsorbtion üOccasional colic or diarrhea Elizur A. et al. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2012
 What is one physical exam you don’t want to miss in an infant with suspected FPIAP?
What is one physical exam you don’t want to miss in an infant with suspected FPIAP?
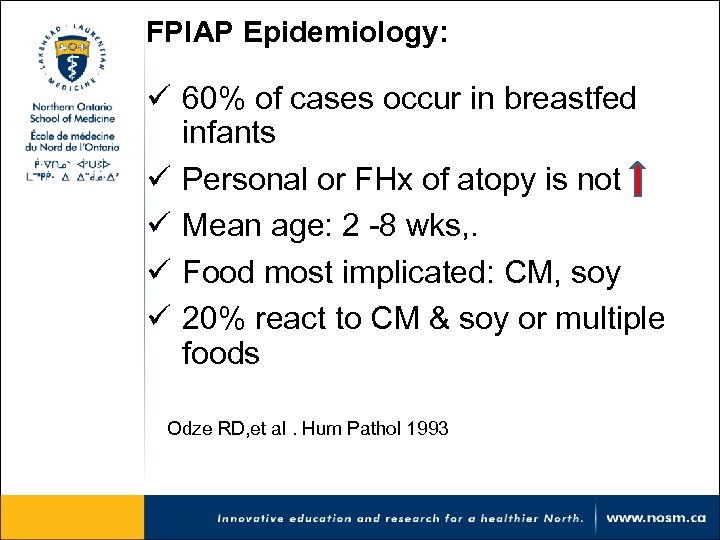 FPIAP Epidemiology: ü 60% of cases occur in breastfed infants ü Personal or FHx of atopy is not ü Mean age: 2 -8 wks, . ü Food most implicated: CM, soy ü 20% react to CM & soy or multiple foods Odze RD, et al. Hum Pathol 1993
FPIAP Epidemiology: ü 60% of cases occur in breastfed infants ü Personal or FHx of atopy is not ü Mean age: 2 -8 wks, . ü Food most implicated: CM, soy ü 20% react to CM & soy or multiple foods Odze RD, et al. Hum Pathol 1993
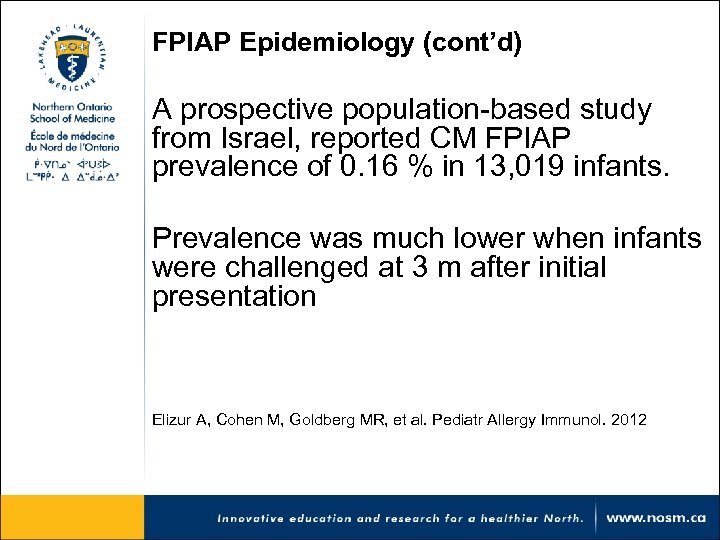 FPIAP Epidemiology (cont’d) A prospective population-based study from Israel, reported CM FPIAP prevalence of 0. 16 % in 13, 019 infants. Prevalence was much lower when infants were challenged at 3 m after initial presentation Elizur A, Cohen M, Goldberg MR, et al. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2012
FPIAP Epidemiology (cont’d) A prospective population-based study from Israel, reported CM FPIAP prevalence of 0. 16 % in 13, 019 infants. Prevalence was much lower when infants were challenged at 3 m after initial presentation Elizur A, Cohen M, Goldberg MR, et al. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2012
 FPIAP in Children üRavelli et al. reported 16 cases of rectal bleeding in children 2 -14 yr; resolved with elimination of CM üThe symptoms recurred in all cases with reintroduction of CM üEndoscopic and histologic findings were consistent with FPIAP Ravelli A et al. Am J Gastroenterol, 2008
FPIAP in Children üRavelli et al. reported 16 cases of rectal bleeding in children 2 -14 yr; resolved with elimination of CM üThe symptoms recurred in all cases with reintroduction of CM üEndoscopic and histologic findings were consistent with FPIAP Ravelli A et al. Am J Gastroenterol, 2008
 FPIAP Pathogenesis ü Largely unknown ü Dietary Ag complexed to breast milk Ig. A → eosinophil activation
FPIAP Pathogenesis ü Largely unknown ü Dietary Ag complexed to breast milk Ig. A → eosinophil activation
 FPIAP Diagnosis: Typical presentation and resolution of symptoms with elimination Rechallenge in 4 -8 wks is recommended Endoscopy – generally not needed ü Patchy erythema, loss of vascularity in rectum, sometimes extending to colon ü ↑ eosinophils (5 -20/hpf) Lozinsky AC, et al. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2014
FPIAP Diagnosis: Typical presentation and resolution of symptoms with elimination Rechallenge in 4 -8 wks is recommended Endoscopy – generally not needed ü Patchy erythema, loss of vascularity in rectum, sometimes extending to colon ü ↑ eosinophils (5 -20/hpf) Lozinsky AC, et al. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2014
 Is FPIAP over diagnosed?
Is FPIAP over diagnosed?
 The etiology of small and fresh rectal bleeding(RB) in not-sick neonates: should we initially suspect FPIAP? Eur J Pediatr. 2012. Jang HJ 1, et al. ü 16 , not sick neonates with fresh RB ü 10, satisfied endoscopic findings of FPIAP ü ECT in cases with over 4 d of persistent RB ü Only two confirmed as FPIAP by food ECT. ü In 14 , RB disappeared at 4 (1 -8) d idiopathic neonatal transient colitis (INTC).
The etiology of small and fresh rectal bleeding(RB) in not-sick neonates: should we initially suspect FPIAP? Eur J Pediatr. 2012. Jang HJ 1, et al. ü 16 , not sick neonates with fresh RB ü 10, satisfied endoscopic findings of FPIAP ü ECT in cases with over 4 d of persistent RB ü Only two confirmed as FPIAP by food ECT. ü In 14 , RB disappeared at 4 (1 -8) d idiopathic neonatal transient colitis (INTC).
 FPIAP Management: Exclusively breastfed: ü CM should be eliminated from maternal diet first, followed by soy, then egg ü Clinical bleeding typically clears within 3 d after complete elimination, but may take up to 2 wk
FPIAP Management: Exclusively breastfed: ü CM should be eliminated from maternal diet first, followed by soy, then egg ü Clinical bleeding typically clears within 3 d after complete elimination, but may take up to 2 wk
 Formula fed: ü Protein hydrolysate formula ü Soy formula not generally recommended ü 5 -10% of infants need to be switched to amino acid based formula
Formula fed: ü Protein hydrolysate formula ü Soy formula not generally recommended ü 5 -10% of infants need to be switched to amino acid based formula
 FPIAP Natural HX ü Majority resolve by age 12 m ü Reintroduction, over 3 -5 d ü Some experts- reintroduce at 4 -6 m ü Reintroduction can be done at home ü If symptoms recur, try in 5 -6 m Elizur A, et al. JACI, 2012
FPIAP Natural HX ü Majority resolve by age 12 m ü Reintroduction, over 3 -5 d ü Some experts- reintroduce at 4 -6 m ü Reintroduction can be done at home ü If symptoms recur, try in 5 -6 m Elizur A, et al. JACI, 2012

 Case No. 2 ü 5 m old, Fred Pies, previously well, exclusively BF. At 4 m, introduced to CM formula ü 2 wks after, fed CM formula for 2 nd time. 2 h later, he developed repetitive vomiting, looked lethargic, hypotensive ü Leucocytosis, Methemoglobimemia
Case No. 2 ü 5 m old, Fred Pies, previously well, exclusively BF. At 4 m, introduced to CM formula ü 2 wks after, fed CM formula for 2 nd time. 2 h later, he developed repetitive vomiting, looked lethargic, hypotensive ü Leucocytosis, Methemoglobimemia
 What is Fred Pies diagnosis? a) FPIAP b) FPIES c) FPE
What is Fred Pies diagnosis? a) FPIAP b) FPIES c) FPE
 What’s Fred Pies diagnosis? a) FPIAP b) FPIES c) FPE
What’s Fred Pies diagnosis? a) FPIAP b) FPIES c) FPE
 Acute FPIES: ü Intermittent exposure or re-exposure after a period of food avoidance ü Severe, projectile emesis in 1 to 3 h, +/- diarrhea ü Pallor, lethargy ü Hypotension in 15% of reactions ü Cyanosis ü Hypothermia
Acute FPIES: ü Intermittent exposure or re-exposure after a period of food avoidance ü Severe, projectile emesis in 1 to 3 h, +/- diarrhea ü Pallor, lethargy ü Hypotension in 15% of reactions ü Cyanosis ü Hypothermia
 ER doc call Peds. re: an infant with possible septic shock: Hmm, This could be FPIES Allergist, on call for Peds
ER doc call Peds. re: an infant with possible septic shock: Hmm, This could be FPIES Allergist, on call for Peds
 Chronic FPIES ü Infants with regular intake of the food, e. g. formula ü Intermittent, progressive emesis, bloody diarrhea ü FTT ü Dehydration
Chronic FPIES ü Infants with regular intake of the food, e. g. formula ü Intermittent, progressive emesis, bloody diarrhea ü FTT ü Dehydration
 FPIES Supporting lab findings ü ü ü ü Leukocytosis, ↑neutro Thrombocytosis Metabolic acidosis Methemoglobinemia Hypoalbuminemia Anemia Food skin prick test, +ve in 4 to 30%
FPIES Supporting lab findings ü ü ü ü Leukocytosis, ↑neutro Thrombocytosis Metabolic acidosis Methemoglobinemia Hypoalbuminemia Anemia Food skin prick test, +ve in 4 to 30%
 FPIES Implicated foods ü CM & soy (present 3 to 6 m) ü Rice, Oat ü Chicken, green bean, sweet potato ü Fish and shellfish FPIES observed in older children and adults Mehr S, et al. Pediatrics 2009
FPIES Implicated foods ü CM & soy (present 3 to 6 m) ü Rice, Oat ü Chicken, green bean, sweet potato ü Fish and shellfish FPIES observed in older children and adults Mehr S, et al. Pediatrics 2009
 FPIES Implicated foods (cont’d) Multiple food FPIES ü Up to 50% of pts react to both CM & soy in US studies ü 65% with CM or soy FPIES develop solid food FPIES ü 50% infants reacted to >1 grain Nowak-Wegrzyn A, Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 2008; 9: 371 -7
FPIES Implicated foods (cont’d) Multiple food FPIES ü Up to 50% of pts react to both CM & soy in US studies ü 65% with CM or soy FPIES develop solid food FPIES ü 50% infants reacted to >1 grain Nowak-Wegrzyn A, Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 2008; 9: 371 -7
 FPIES - Epidemiology Israeli population based cohort: ü CM FPIES in 0. 34% of 13, 019 infants (0. 5% Ig. E mediated CMA) in 1 st yr of life ü Slight male predominance ü 40 -80% have FHx of atopy ü Personal Hx of atopy up to 30% Elizur A, et al. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2012
FPIES - Epidemiology Israeli population based cohort: ü CM FPIES in 0. 34% of 13, 019 infants (0. 5% Ig. E mediated CMA) in 1 st yr of life ü Slight male predominance ü 40 -80% have FHx of atopy ü Personal Hx of atopy up to 30% Elizur A, et al. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2012
 FPIES - Pathophysiology ü Mostly formula fed infants ü Immunologic mechanism unclear ü ? T cell mediated ü Food allergens may cause local inflammation, subsequent increased intestinal permeability and fluid shift
FPIES - Pathophysiology ü Mostly formula fed infants ü Immunologic mechanism unclear ü ? T cell mediated ü Food allergens may cause local inflammation, subsequent increased intestinal permeability and fluid shift
 FPIES Diagnosis NIAID-sponsored panel in 2010 advise: ü Diagnosis for FPIES based on typical presenting features, resolution with removal of the offending protein, and reoccurrence of symptoms with OFC ü OFC is not necessary when Hx is convincing or the reaction was severe
FPIES Diagnosis NIAID-sponsored panel in 2010 advise: ü Diagnosis for FPIES based on typical presenting features, resolution with removal of the offending protein, and reoccurrence of symptoms with OFC ü OFC is not necessary when Hx is convincing or the reaction was severe
 Management: Acute FPIES (symptoms resolve in hrs) ü Rehydration ü IV Methylprednisolone ü Ondansetron ü Methylene blue when necessary ü Food avoidance ü Epinephrine is not of help Holbrook et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2013
Management: Acute FPIES (symptoms resolve in hrs) ü Rehydration ü IV Methylprednisolone ü Ondansetron ü Methylene blue when necessary ü Food avoidance ü Epinephrine is not of help Holbrook et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2013
 Management( cont’d) Chronic FPIES ü Food elimination ü Sx resolved in 3 -10 days ü 80% respond to hydrolysate formula ü Soy formula can be introduced under supervision ü Rechallenge in 1 -2 yr in hospital setting
Management( cont’d) Chronic FPIES ü Food elimination ü Sx resolved in 3 -10 days ü 80% respond to hydrolysate formula ü Soy formula can be introduced under supervision ü Rechallenge in 1 -2 yr in hospital setting

 Case No. 3: ü 9 m old, Fae P. Edward, presented with recurrent vomiting, diarrhea, FTT, malabsorption and anemia. ü Negative celiac screen ü Endoscopy findings: villous atrophy
Case No. 3: ü 9 m old, Fae P. Edward, presented with recurrent vomiting, diarrhea, FTT, malabsorption and anemia. ü Negative celiac screen ü Endoscopy findings: villous atrophy
 What’s Fae P. Edward diagnosis? a) FPIAP b) FPIES c) FPE
What’s Fae P. Edward diagnosis? a) FPIAP b) FPIES c) FPE
 What’s Fae P. Edward diagnosis? a) FPIAP b) FPIES c) FPE
What’s Fae P. Edward diagnosis? a) FPIAP b) FPIES c) FPE
 What dietary intervention is a risk factor for FPE?
What dietary intervention is a risk factor for FPE?
 FPE (Food Protein Enteropathy) ü Most likely to occur in infants fed intact CM prior to 9 m ü Described following gastroenteritis ü The prevalence of FPE is obscure ü Decline in the prevalence is noted Kleinman RE, J Pediatr, 19991
FPE (Food Protein Enteropathy) ü Most likely to occur in infants fed intact CM prior to 9 m ü Described following gastroenteritis ü The prevalence of FPE is obscure ü Decline in the prevalence is noted Kleinman RE, J Pediatr, 19991
 FPE Clinical Presentation: ü Usually induced by CM ü Diarrhea, emesis, abdominal distension, FTT Distinguishing features from FPIES: ü Malabsorption with steatorrhea in 80% ü Lack of acute symptoms
FPE Clinical Presentation: ü Usually induced by CM ü Diarrhea, emesis, abdominal distension, FTT Distinguishing features from FPIES: ü Malabsorption with steatorrhea in 80% ü Lack of acute symptoms
 FPE Diagnosis ü Overlap with other enteropathies, e. g. celiac ü Endoscopy with biopsy to confirm villus injury with a cellular infiltrate ü Generally resolves spontaneously after age 2
FPE Diagnosis ü Overlap with other enteropathies, e. g. celiac ü Endoscopy with biopsy to confirm villus injury with a cellular infiltrate ü Generally resolves spontaneously after age 2
 FPE Management: ü Food elimination ü Symptoms clear in 1 -3 wk ü Rechallenge in 1 -2 yr
FPE Management: ü Food elimination ü Symptoms clear in 1 -3 wk ü Rechallenge in 1 -2 yr
 Common GI Problems & Food Allergy
Common GI Problems & Food Allergy
 GERD ü A subset of infants with GERD can have CM allergy ü More likely in pts with severe and persistent regurgitation, FTT, and eczema.
GERD ü A subset of infants with GERD can have CM allergy ü More likely in pts with severe and persistent regurgitation, FTT, and eczema.
 GERD (cont’d) ü 204 infants diagnosed with GERD based on 24 h p. H monitoring and histology ü CM free diet and two successive blind challenges confirmed CM allergy in 41. 8% pts with GERD Giuseppe lacono, et al, Journal of Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996
GERD (cont’d) ü 204 infants diagnosed with GERD based on 24 h p. H monitoring and histology ü CM free diet and two successive blind challenges confirmed CM allergy in 41. 8% pts with GERD Giuseppe lacono, et al, Journal of Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996
 GERD (cont’d) ü Empiric trial of CM elimination for infants with problematic GERD can be considered ü Especially, those with gross or occult blood in stool, eczema, or a strong FHx of atopy
GERD (cont’d) ü Empiric trial of CM elimination for infants with problematic GERD can be considered ü Especially, those with gross or occult blood in stool, eczema, or a strong FHx of atopy
 Colic ü A subgroup of infants with colic can have intolerance to CM ü Specially, those with bloody stool, vomiting, and eczema ü The transient nature of colic make the investigations of effect of diet restrictions difficult David J. Pediatrics 2005
Colic ü A subgroup of infants with colic can have intolerance to CM ü Specially, those with bloody stool, vomiting, and eczema ü The transient nature of colic make the investigations of effect of diet restrictions difficult David J. Pediatrics 2005
 Constipation ü 10 prospective clinical trials reported a CM protein free diet success rate 28 -78% ü More likely in pts with coexistent atopy ü More likely to have anal fissures, perianal erythema and/or eczema Caubet et al. Pediatric Allergy and Immunology, 2016
Constipation ü 10 prospective clinical trials reported a CM protein free diet success rate 28 -78% ü More likely in pts with coexistent atopy ü More likely to have anal fissures, perianal erythema and/or eczema Caubet et al. Pediatric Allergy and Immunology, 2016
 Constipation and cow’s milk allergy: a review of the literature Miceli Sopo S, et al. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2014 “We believe that a CM-free diet for 2 -4 wk should be proposed for children with chronic functional constipation, even if it is not severe or resistant to laxatives”
Constipation and cow’s milk allergy: a review of the literature Miceli Sopo S, et al. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2014 “We believe that a CM-free diet for 2 -4 wk should be proposed for children with chronic functional constipation, even if it is not severe or resistant to laxatives”

 thank you Comments, Questions?
thank you Comments, Questions?


