f2d70b52065d7f9774ff7ab8f085b676.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13

Nokia/Nokia Siemens Network Mobile learning for mathematics -project in South Africa • • • 1 Background Mobile Internet usage in South-Africa example Goal for “mobile learning for mathematics project” Approach Collaboration partners and their roles Learning context and process SMS based solution or/and browser based solution? Framework for learning components and technology Proposal for potential technology concept – browser based solution User scenario for browser based solution Project timeline Riitta Vänskä (Nokia) / Lucky Masilela (NSN) 21. 11. 2008

Background • There is a need to improve the consistent level of mathematical skills is South. Africa • The mobile phone penetration among pupils is very high and there is a need for proof of concept on how those devices could be applied for enhanced learning purposes in formal education • Importance of maths in any future career and its importance as a study discipline/subject • Most of the trials that have been done so far for harnessing mobile devices formal education have been short term pilots testing different technical possibilities without proof for sustainability and affordability issues for wider usage in formal education in South Africa • E-skills council and PIAC recommendations (Nokia NSN has been in PIAC 6 years) • Interaction with former Deputy President (Ms Mlambo-Ngcuka) 2 Riitta Vänskä (Nokia) / Lucky Masilela (NSN) 21. 11. 2008

Mobile Internet usage by low income South African Youth example • "Assessing Cell Phone Usage in a South African Township School" (Tino Kreutzer, UCT) looks at the mobile phone usage patterns of teenagers in Samora Machel, an informal settlement in Cape Town as opposed to a black township • 75% of learners had their own phone, 25% shared a phone • 86% could play games on their phones • 67% could take photos • 60% could play/record videos • 50% could access the internet (with own phone) • 96% used prepaid • 80% had used mobile instant messaging • 97% have used a mobile phone to access the internet (multiphone usage) • Larger study underway (600 – 700 respondents) by Tino Kreutzer in Dec 2008 and national study in 2009 • Other indicators: South Africa no. 6 user of Opera Mini browser for cell phones worldwide 3 Riitta Vänskä (Nokia) / Lucky Masilela (NSN) 21. 11. 2008

Goal for “Mobile learning for mathematics ” project To give a solution for following questions • What type of content will give added value for maths studies (for pupils and teachers) (what is the pedagogical approach for mobile learning) • What type of learning interventions are needed to enhance maths skills and maths understanding and abstract thinking in general • What is the delivery channel so that learners • Can use their own phones • Learning is free of charge for students • How easily solution can be cascaded to masses • Sustainability • Affordability AND develop a technical solution (combing existing technologies) and pilot that with the most appropriate content This mobile learning solution is not replacing computers at school but taking the learning to new level 4 Riitta Vänskä (Nokia) / Lucky Masilela (NSN) 21. 11. 2008

Approach • Focused on South African context • • Lack of sustainable provision of traditional IT in schools and in communities Lack of traditional access to technology (i. e. computers linked to the internet) Issues around digital literacy Cultural diversity • Philosophy • • Open access Open Source Open Content Inclusivity Accessibility Sustainability Affordability Scalability • Pedagogically-appropriate models • • 5 Group-centred learning Project-based learning Problem solving Inquiry learning Collaborative learning Experiential learning Active participation Riitta Vänskä (Nokia) / Lucky Masilela (NSN) 21. 11. 2008

Collaboration partners – local solutions through global partnership Local Partners: • • • Deputy President’s office Department of Education Department of Communication Department of Science and Technology GCIS Meraka SAFIPA project NBA (Neil Butcher & Associates) Midrand Graduate Institute Global Partners: • Nokia • NSN Finnish Partners: • Bitville Oy • Mobiletools International Ltd 6 Riitta Vänskä (Nokia) / Lucky Masilela (NSN) 21. 11. 2008

Collaboration partners and their roles Local Partners: • Deputy President’s office – driving the project, chair of Steering Group, driving the negotiations with operators for delivery costs, secretary for sg • Department of Education – quality insurance, pedagogical consultancy, Steering Group member • Department of Communication – Steering Group member • Department of Science and Technology – Steering Group member • GCIS – Steering Group member • Meraka – Pedagogical and technical consultation, Steering Group member • SAFIPA project – project sponsor, Steering Group member • NBA (Neil Butcher & Associates) – evaluation responsibility and technical consultation • Midrand Graduate Institute – technical and pedagogical consultation, Steering Group member Global Partners: • Nokia, project sponsor, project leader, full time pedagogical and technical resource • NSN, project sponsor, project consultation Finnish Partners: • Bitville Oy, technical and pedagogical consultation • Mobiletools International Ltd, technical and pedagogical consultation 7 Riitta Vänskä (Nokia) / Lucky Masilela (NSN) 21. 11. 2008

Learning context and process • Digital citizenship as part of the “Life Skills” curriculum at the schools • Safety issues • Do's and don'ts (“mobiquette”) • Opportunities and responsibilities • Training for teachers • Exposure to the possibilities of using cellphones in a school environment • Role as facilitator – pedagogical process • Technical skills (using the cell phone in the classroom – bluetooth, instant messaging, SMS) • Parents info and involvement • Curriculum development to include the m-learning support 8 Riitta Vänskä (Nokia) / Lucky Masilela (NSN) 21. 11. 2008

SMS based solution or/and browser based solution? • SMS based solution • Possible in all rural area • Possible in all phones • Gives equality by offering possibility to mobile learning to all mobile phone owners • Possible for primary school mathematics (symbols at keyboard not sufficient for high school maths) • Browser based solution • Widens the possibilities for different learning components • Future-oriented solution • Resource-rich 9 Riitta Vänskä (Nokia) / Lucky Masilela (NSN) 21. 11. 2008
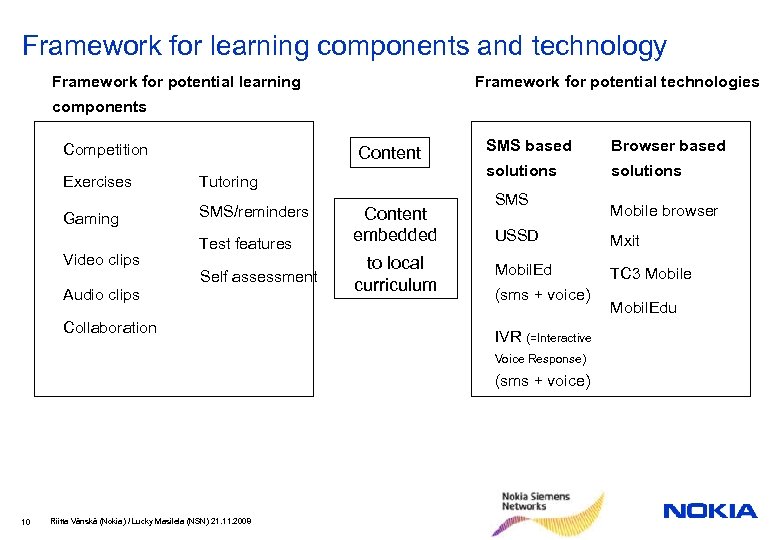
Framework for learning components and technology Framework for potential learning Framework for potential technologies components Competition Content Exercises Tutoring Gaming SMS/reminders Video clips Test features Self assessment Audio clips Collaboration Content embedded to local curriculum SMS based Browser based solutions SMS USSD Mxit Mobil. Ed TC 3 Mobile (sms + voice) IVR (=Interactive Voice Response) (sms + voice) 10 Riitta Vänskä (Nokia) / Lucky Masilela (NSN) 21. 11. 2008 Mobile browser Mobil. Edu
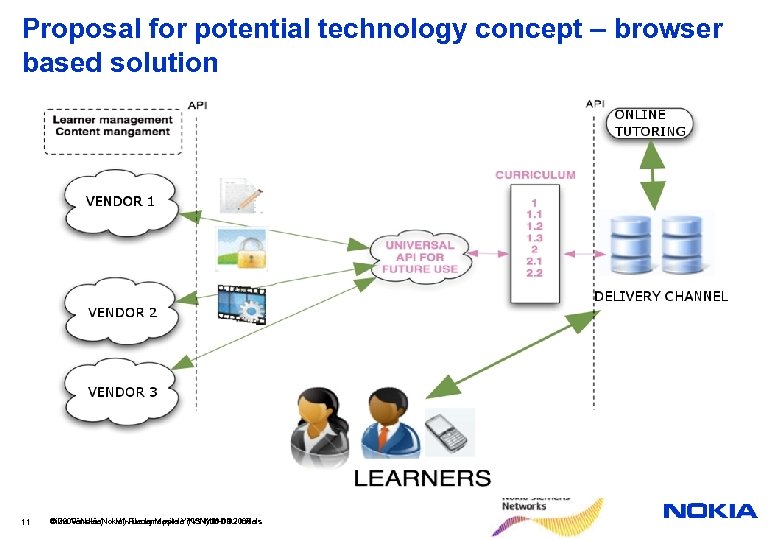
Proposal for potential technology concept – browser based solution 11 © 2008 Nokia Riitta Vänskä (Nokia) / Lucky Masilela (NSN) 21. 11. 2008 V 1 -Filename. ppt / YYYY-MM-DD / Initials 10. 09. 2008

User scenario for browser based solution • User will contact maths channel and gets the list of curriculum items and user will choose what she/he wants to study. The maths channel will deliver the user information to content vendor(s) • The content vendor(s) will chose appropriate content according to user’s choice and deliver that content via maths channel to user • While doing exercises the user has a possibility via multitasking to ask questions from online tutor • Teacher can via mobile connection to internet • send sms’es to pupils as reminders • follow up how pupils have solved exercises • Create easily mobile tests for pupils 12 Riitta Vänskä (Nokia) / Lucky Masilela (NSN) 21. 11. 2008 10. 09. 2008
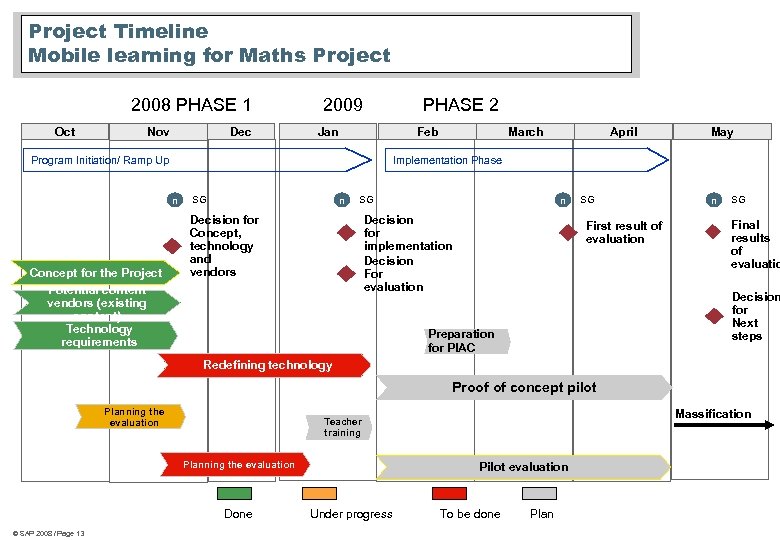
Project Timeline Mobile learning for Maths Project 2008 PHASE 1 Oct Dec Nov 2009 PHASE 2 Jan Feb Program Initiation/ Ramp Up April May Implementation Phase n Concept for the Project Potential content vendors (existing content) Technology requirements March SG n Decision for implementation Decision For evaluation Decision for Concept, technology and vendors SG First result of evaluation n SG Final results of evaluatio Decision for Next steps Preparation for PIAC Redefining technology Proof of concept pilot Planning the evaluation Done © SAP 2008 / Page 13 Massification Teacher training Pilot evaluation Under progress To be done Plan
f2d70b52065d7f9774ff7ab8f085b676.ppt