cf46611753740412ac8a9fa60f70e9e5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 NOAA’s National Geodetic Survey Height Modernization Implementation Helena, Mt October 17, 2006 Renee Shields National Geodetic Survey National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
NOAA’s National Geodetic Survey Height Modernization Implementation Helena, Mt October 17, 2006 Renee Shields National Geodetic Survey National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
 Height Mod Implementation How has Height Mod been implemented in other states? How does the U. S. Federal Budget process work? How do NOAA Grants work?
Height Mod Implementation How has Height Mod been implemented in other states? How does the U. S. Federal Budget process work? How do NOAA Grants work?
 California • Leveling could not be used in NAVD 88 adjustment so couldn’t implement NAVD 88 • Some heights in CA in error by more than a meter • No way to keep up with continuously releveling • GPS could be immediately used to meet some of California’s requirements
California • Leveling could not be used in NAVD 88 adjustment so couldn’t implement NAVD 88 • Some heights in CA in error by more than a meter • No way to keep up with continuously releveling • GPS could be immediately used to meet some of California’s requirements
 California (Scripps Institution of Oceanography) • Establish California Spatial Reference Center • Projects – – • • • San Francisco Bay Demonstration Project Hamilton Field Restoration Post-earthquake surveys, e. g. Hector Mine, Yolo County Leveling support from Cal. Trans Densify CORS Network Establish NAVD 88 orthometric heights on CORS Develop RTK networks Educate users on Epochs Update HTDP, Geoid models
California (Scripps Institution of Oceanography) • Establish California Spatial Reference Center • Projects – – • • • San Francisco Bay Demonstration Project Hamilton Field Restoration Post-earthquake surveys, e. g. Hector Mine, Yolo County Leveling support from Cal. Trans Densify CORS Network Establish NAVD 88 orthometric heights on CORS Develop RTK networks Educate users on Epochs Update HTDP, Geoid models
 North Carolina • • • (North Carolina Department of Environmental and Natural Resources ) Become Cooperative Technical State Get additional grant funds from FEMA – update flood maps Contract GPS Height Mod projects by county NCGS perform leveling concurrent with GPS Distribute data, maps via web site Partner with NCA&T – develop training materials for workshops (non-traditional and traditional users) – Develop 4 -year Geospatial degree program – Perform studies to develop standards for new techniques – Develop software, tools, models
North Carolina • • • (North Carolina Department of Environmental and Natural Resources ) Become Cooperative Technical State Get additional grant funds from FEMA – update flood maps Contract GPS Height Mod projects by county NCGS perform leveling concurrent with GPS Distribute data, maps via web site Partner with NCA&T – develop training materials for workshops (non-traditional and traditional users) – Develop 4 -year Geospatial degree program – Perform studies to develop standards for new techniques – Develop software, tools, models
 Louisiana (Louisiana State University) • Establish LSRC • Re-establish outdated vertical network – update NAVD 88, tie to sea-level datums • Perform subsidence, coastal erosion studies – develop HTDP, storm surge models for vertical motion • Study new technologies for GPS surveys • Educate users, managers to subsidence issues
Louisiana (Louisiana State University) • Establish LSRC • Re-establish outdated vertical network – update NAVD 88, tie to sea-level datums • Perform subsidence, coastal erosion studies – develop HTDP, storm surge models for vertical motion • Study new technologies for GPS surveys • Educate users, managers to subsidence issues
 Wisconsin (Wisconsin Department of Transportation) • Provide accurate vertical data for highway design (vertical component of the geodetic network) • Improve ability to delineate basins • Improve data quality to provide more accurate DTMs Supplement control where marks have been destroyed • Create network that can fully utilize GPS technologies (cost effective) • Become role model and trainer for other states’ programs
Wisconsin (Wisconsin Department of Transportation) • Provide accurate vertical data for highway design (vertical component of the geodetic network) • Improve ability to delineate basins • Improve data quality to provide more accurate DTMs Supplement control where marks have been destroyed • Create network that can fully utilize GPS technologies (cost effective) • Become role model and trainer for other states’ programs
 Mississippi (USM) • Expand CORS network throughout the State • USM Gulf Coast Research Lab installed National Water Level Observation Network (NWLON) station co-located with CORS Alabama(ALDOR) • Height Modernization survey along Mississippi River (Cairo, IL to the Gulf) completed in cooperation • Alabama Department of Revenue manage program; Department of with USACE Transportation oversees surveying tasks • Densify CORS and HARN • Re-level where needed • Educate surveyors for contract work • Establish statewide SLIMS (Statewide Land Info Management Systems)
Mississippi (USM) • Expand CORS network throughout the State • USM Gulf Coast Research Lab installed National Water Level Observation Network (NWLON) station co-located with CORS Alabama(ALDOR) • Height Modernization survey along Mississippi River (Cairo, IL to the Gulf) completed in cooperation • Alabama Department of Revenue manage program; Department of with USACE Transportation oversees surveying tasks • Densify CORS and HARN • Re-level where needed • Educate surveyors for contract work • Establish statewide SLIMS (Statewide Land Info Management Systems)
 Other Funded States • Washington (DNR) • Ensure a high-accuracy geodetic reference network in WA (GPS, monuments, CORS, VRS networks, geodetic models) • Promote the development of specifications and guidelines for GPS surveys; Serve as an educational source for users • Texas (TAMUCC) • Establish TSRC • Improve Gulf Coast geoid model • NAVD 88 heights on all CORS; tie CORS to tidal datums • Measure/monitor subsidence in Harris Galveston area • Kentucky (Morehead State) • Arizona (ASLD)
Other Funded States • Washington (DNR) • Ensure a high-accuracy geodetic reference network in WA (GPS, monuments, CORS, VRS networks, geodetic models) • Promote the development of specifications and guidelines for GPS surveys; Serve as an educational source for users • Texas (TAMUCC) • Establish TSRC • Improve Gulf Coast geoid model • NAVD 88 heights on all CORS; tie CORS to tidal datums • Measure/monitor subsidence in Harris Galveston area • Kentucky (Morehead State) • Arizona (ASLD)
 Other Interested States • Invited to brief congressional staff and/or present at conferences, forums: AK, AR, FL, CO, HI, IL, MI, MO, MT, NH, NM, PA, PR, TN, VI • Height Mod projects done: FL, NE
Other Interested States • Invited to brief congressional staff and/or present at conferences, forums: AK, AR, FL, CO, HI, IL, MI, MO, MT, NH, NM, PA, PR, TN, VI • Height Mod projects done: FL, NE
 Evaluate your needs • How much vertical control do you have/need? – Passive control disappearing because of development or other activities? – Control network easily maintained or densified to suit community’s needs? • How valid is the control network? – Is there movement from crustal deformation, e. g. earthquakes (Yellowstone), glacial rebound? • What will it take to fix it?
Evaluate your needs • How much vertical control do you have/need? – Passive control disappearing because of development or other activities? – Control network easily maintained or densified to suit community’s needs? • How valid is the control network? – Is there movement from crustal deformation, e. g. earthquakes (Yellowstone), glacial rebound? • What will it take to fix it?
 Montana’s needs? Management of forest fires - evacuation planning, effective firefighting by knowing accurate positioning and slope Forests in western 1/3 of MT Mudslides, rockslides – may have contributed to decimation of passive control; accurate control network assists with cost effective rebuilding efforts Agriculture – effective use of irrigation, pesticides, fertilizer, saves money and environment Conversion from NGVD 29 to NAVD 88 for water management, GIS applications Wheat in eastern 2/3 of MT
Montana’s needs? Management of forest fires - evacuation planning, effective firefighting by knowing accurate positioning and slope Forests in western 1/3 of MT Mudslides, rockslides – may have contributed to decimation of passive control; accurate control network assists with cost effective rebuilding efforts Agriculture – effective use of irrigation, pesticides, fertilizer, saves money and environment Conversion from NGVD 29 to NAVD 88 for water management, GIS applications Wheat in eastern 2/3 of MT
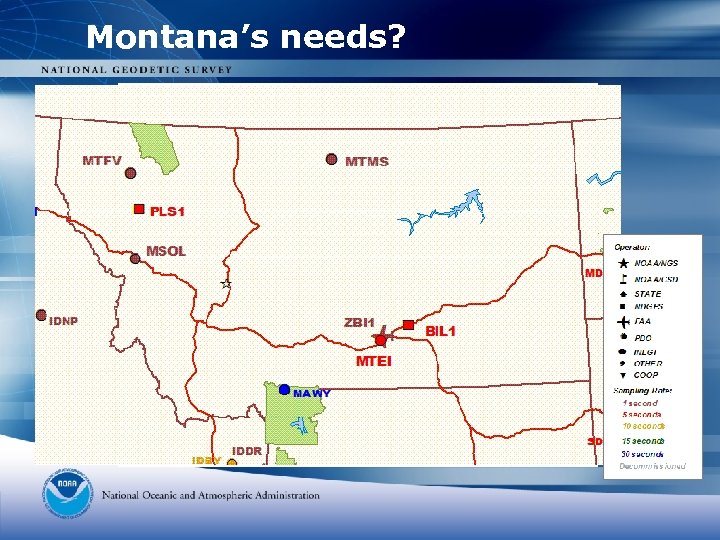 Montana’s needs?
Montana’s needs?
 U. S. Federal Budget Process • Federal Fiscal Year: October 1 – September 30 • Budget Process – Presidential budget – Congress adopts budget resolution – response to the Presidents budget – Consideration of appropriations – House and Senate conferences – Negotiate differences – Budget Bill goes to President to veto or sign – Bill signed into law
U. S. Federal Budget Process • Federal Fiscal Year: October 1 – September 30 • Budget Process – Presidential budget – Congress adopts budget resolution – response to the Presidents budget – Consideration of appropriations – House and Senate conferences – Negotiate differences – Budget Bill goes to President to veto or sign – Bill signed into law
 President’s Budget • Initiates Budget Process • Submitted to Congress February 2 for upcoming FY • Recommended spending levels for programs and agencies • Represents “Budget Authority” • Budget submitted to Congress with justification materials from agencies
President’s Budget • Initiates Budget Process • Submitted to Congress February 2 for upcoming FY • Recommended spending levels for programs and agencies • Represents “Budget Authority” • Budget submitted to Congress with justification materials from agencies
 Budget Resolution • Congress’ response to President’s budget • A Guide for considering various budget bills – Not law, i. e. doesn’t go to President – Does set ceilings for each bill • Covers at least 5 years, upcoming plus 4 more • Required by Congressional Budget Act of 1974 – No penalty for not adopting a resolution – 1999 and 2001 are only 2 years Congress has failed to adopt a resolution
Budget Resolution • Congress’ response to President’s budget • A Guide for considering various budget bills – Not law, i. e. doesn’t go to President – Does set ceilings for each bill • Covers at least 5 years, upcoming plus 4 more • Required by Congressional Budget Act of 1974 – No penalty for not adopting a resolution – 1999 and 2001 are only 2 years Congress has failed to adopt a resolution
 Appropriations Committees • House and Senate Appropriations Committees hold hearings for consideration of 13 separate bills via 13 sub-committees • Adopted Budget Resolution provides ceilings for sub-committees to use as guidelines • Sub-committees begin to mark up bills under their jurisdiction
Appropriations Committees • House and Senate Appropriations Committees hold hearings for consideration of 13 separate bills via 13 sub-committees • Adopted Budget Resolution provides ceilings for sub-committees to use as guidelines • Sub-committees begin to mark up bills under their jurisdiction
 Appropriations Committees • House – 65 members: 35(R), 29(D), 1(I) – Current Chair: Jerry Lewis, CA (R) • Senate – 28 members: 15(R), 13(D) – Current Chair: Thad Cochran, MS(R) • 13 Subcommittees – – – Agriculture, Rural Development, and Related Agencies Commerce, Justice, and Science Defense District of Columbia Energy and Water Homeland Security Interior and Related Agencies Labor, Health and Human Services, Education and Related Agencies Legislative Branch Military Construction and Veterans Affairs State, Foreign Operations, and Related Programs Transportation, Treasury, the Judiciary, Housing and Urban Development, and Related Agencies
Appropriations Committees • House – 65 members: 35(R), 29(D), 1(I) – Current Chair: Jerry Lewis, CA (R) • Senate – 28 members: 15(R), 13(D) – Current Chair: Thad Cochran, MS(R) • 13 Subcommittees – – – Agriculture, Rural Development, and Related Agencies Commerce, Justice, and Science Defense District of Columbia Energy and Water Homeland Security Interior and Related Agencies Labor, Health and Human Services, Education and Related Agencies Legislative Branch Military Construction and Veterans Affairs State, Foreign Operations, and Related Programs Transportation, Treasury, the Judiciary, Housing and Urban Development, and Related Agencies
 Appropriations Committees Senate Appropriations Committee SA Sub 1 SA Sub 3 SA Sub 13 House Appropriations Committee HA Sub 1 HA Sub 2 HA Sub 3 HA Sub 13
Appropriations Committees Senate Appropriations Committee SA Sub 1 SA Sub 3 SA Sub 13 House Appropriations Committee HA Sub 1 HA Sub 2 HA Sub 3 HA Sub 13
 Appropriations Committees • Sub-committees submit bills to full House/Senate for vote • Bills are considered and passed in each chamber in August and September • There are still big differences between the House version and Senate version • Little time left before start of FY to resolve differences Hence - CONTINUING RESOLUTION
Appropriations Committees • Sub-committees submit bills to full House/Senate for vote • Bills are considered and passed in each chamber in August and September • There are still big differences between the House version and Senate version • Little time left before start of FY to resolve differences Hence - CONTINUING RESOLUTION
 Appropriations Committees • House and Senate Appropriations Committees negotiate their differences – Negotiate differences – Reach an agreement within range of differences – Budget Bill goes to President who has 10 days to veto or sign
Appropriations Committees • House and Senate Appropriations Committees negotiate their differences – Negotiate differences – Reach an agreement within range of differences – Budget Bill goes to President who has 10 days to veto or sign
 President Acts on Bill • Does nothing within 10 days – If Congress is in session, Bill becomes law – If Congress is adjourned, Bill is vetoed • Vetoes Bill – Bill goes back to Congress – If House and Senate pass bill with a 2/3 vote, Bill becomes law – If not, Bill dies and they start over • Signs Bill into law
President Acts on Bill • Does nothing within 10 days – If Congress is in session, Bill becomes law – If Congress is adjourned, Bill is vetoed • Vetoes Bill – Bill goes back to Congress – If House and Senate pass bill with a 2/3 vote, Bill becomes law – If not, Bill dies and they start over • Signs Bill into law
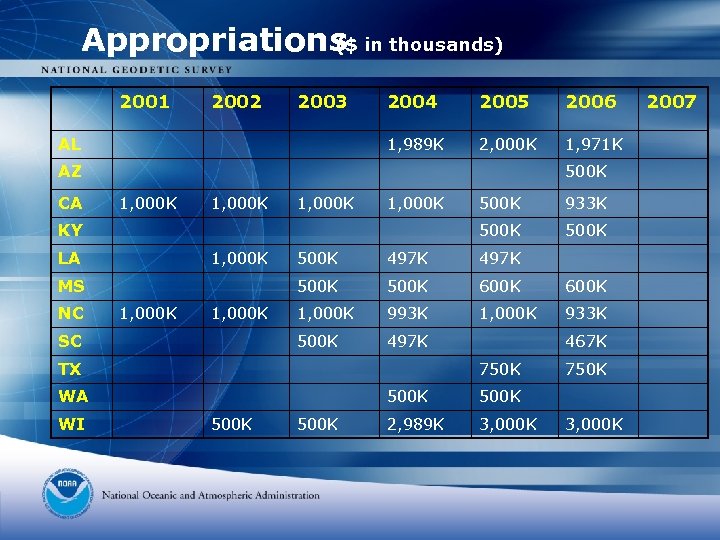 Appropriations in thousands) ($ 2001 2002 2003 2005 2006 1, 989 K AL 2004 2, 000 K 1, 971 K AZ CA 500 K 1, 000 K LA 1, 000 K 500 K 497 K 500 K 600 K 1, 000 K 993 K 1, 000 K 933 K 500 K 1, 000 K SC 497 K TX 467 K 750 K WA WI 500 K MS NC 933 K 500 K KY 500 K 500 K 2, 989 K 3, 000 K 750 K 3, 000 K 2007
Appropriations in thousands) ($ 2001 2002 2003 2005 2006 1, 989 K AL 2004 2, 000 K 1, 971 K AZ CA 500 K 1, 000 K LA 1, 000 K 500 K 497 K 500 K 600 K 1, 000 K 993 K 1, 000 K 933 K 500 K 1, 000 K SC 497 K TX 467 K 750 K WA WI 500 K MS NC 933 K 500 K KY 500 K 500 K 2, 989 K 3, 000 K 750 K 3, 000 K 2007
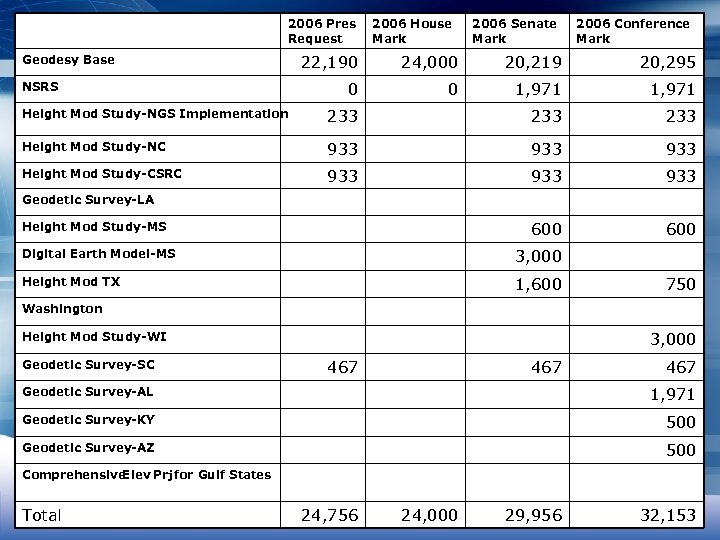 2007 Marks 2006 Pres Request Geodesy Base NSRS 2006 House Mark 2006 Senate Mark 2006 Conference Mark 22, 190 24, 000 20, 219 20, 295 0 0 1, 971 Height Mod Study-NGS Implementation 233 233 Height Mod Study-NC 933 933 Height Mod Study-CSRC 933 933 600 Geodetic Survey-LA Height Mod Study-MS Digital Earth Model-MS 3, 000 Height Mod TX 1, 600 750 Washington 3, 000 Height Mod Study-WI Geodetic Survey-SC 467 467 Geodetic Survey-AL 1, 971 Geodetic Survey-KY 500 Geodetic Survey-AZ 500 Comprehensive Elev Prj for Gulf States Total 24, 756 24, 000 29, 956 32, 153
2007 Marks 2006 Pres Request Geodesy Base NSRS 2006 House Mark 2006 Senate Mark 2006 Conference Mark 22, 190 24, 000 20, 219 20, 295 0 0 1, 971 Height Mod Study-NGS Implementation 233 233 Height Mod Study-NC 933 933 Height Mod Study-CSRC 933 933 600 Geodetic Survey-LA Height Mod Study-MS Digital Earth Model-MS 3, 000 Height Mod TX 1, 600 750 Washington 3, 000 Height Mod Study-WI Geodetic Survey-SC 467 467 Geodetic Survey-AL 1, 971 Geodetic Survey-KY 500 Geodetic Survey-AZ 500 Comprehensive Elev Prj for Gulf States Total 24, 756 24, 000 29, 956 32, 153
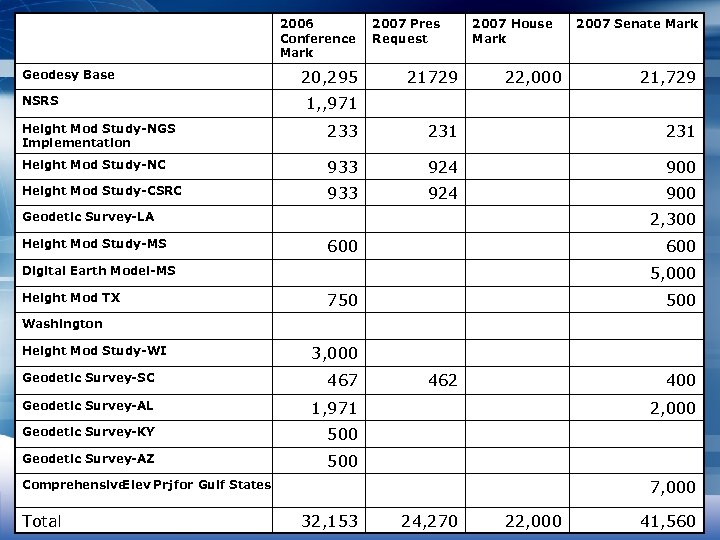 2006 Conference Mark 2007 Marks Geodesy Base NSRS 20, 295 2007 Pres Request 21729 2007 House Mark 22, 000 2007 Senate Mark 21, 729 1, , 971 Height Mod Study-NGS Implementation 233 231 Height Mod Study-NC 933 924 900 Height Mod Study-CSRC 933 924 900 2, 300 Geodetic Survey-LA Height Mod Study-MS 600 5, 000 Digital Earth Model-MS Height Mod TX 750 500 Washington Height Mod Study-WI 3, 000 Geodetic Survey-SC 467 Geodetic Survey-AL 1, 971 Geodetic Survey-KY 500 Geodetic Survey-AZ 462 400 500 2, 000 7, 000 Comprehensive Elev Prj for Gulf States Total 32, 153 24, 270 22, 000 41, 560
2006 Conference Mark 2007 Marks Geodesy Base NSRS 20, 295 2007 Pres Request 21729 2007 House Mark 22, 000 2007 Senate Mark 21, 729 1, , 971 Height Mod Study-NGS Implementation 233 231 Height Mod Study-NC 933 924 900 Height Mod Study-CSRC 933 924 900 2, 300 Geodetic Survey-LA Height Mod Study-MS 600 5, 000 Digital Earth Model-MS Height Mod TX 750 500 Washington Height Mod Study-WI 3, 000 Geodetic Survey-SC 467 Geodetic Survey-AL 1, 971 Geodetic Survey-KY 500 Geodetic Survey-AZ 462 400 500 2, 000 7, 000 Comprehensive Elev Prj for Gulf States Total 32, 153 24, 270 22, 000 41, 560
 Height Modernization Appropriations (FY 01 -FY 06) BACKGROUND Fiscal Year Appropriations States FY 2001 2. 25 M FY 2002 3. 75 M FY 2003 3. 75 M CA, NC, LA, WI, MS 9. 0 M CA, NC, LA, WI, MS, AL, WA, SC FY 2005 9. 6 M CA, NC, LA, WI, MS, AL, WA, TX, KY FY 2006 9. 9 M CA, NC, WI, MS, AL, SC, TX, KY, AZ FY 2004 CA, NC, LA, WI
Height Modernization Appropriations (FY 01 -FY 06) BACKGROUND Fiscal Year Appropriations States FY 2001 2. 25 M FY 2002 3. 75 M FY 2003 3. 75 M CA, NC, LA, WI, MS 9. 0 M CA, NC, LA, WI, MS, AL, WA, SC FY 2005 9. 6 M CA, NC, LA, WI, MS, AL, WA, TX, KY FY 2006 9. 9 M CA, NC, WI, MS, AL, SC, TX, KY, AZ FY 2004 CA, NC, LA, WI
 NGS’ Role - NOAA Grants • Appropriations puts funds in NGS budget – Amount and recipient designated by Congress • NGS publishes Request for Applications – Non-competitive – Available for particular applicants only – Can be up to 5 years
NGS’ Role - NOAA Grants • Appropriations puts funds in NGS budget – Amount and recipient designated by Congress • NGS publishes Request for Applications – Non-competitive – Available for particular applicants only – Can be up to 5 years
 NGS’ Role - NOAA Grants • Designated organization applies – Writes proposal, budget plan – Includes application forms, supporting documentation • Review by NGS and outside reviewers • Award managed and monitored by NGS
NGS’ Role - NOAA Grants • Designated organization applies – Writes proposal, budget plan – Includes application forms, supporting documentation • Review by NGS and outside reviewers • Award managed and monitored by NGS
 NGS’ Role and Responsibilities • Program Management -Congressional briefings, budget, grants management, coordination, outreach • Outreach/Technology Transfer advisors, -forums, workshops, conferences, publications, training, outsourcing • Project Leadership project planning, -specifications, guidelines, CORS management • Quality Control -training, assess techniques, survey control, load projects into NGS database • Research and Development software -development, remote sensing, modeling, investigate GPS techniques, antenna calibrations
NGS’ Role and Responsibilities • Program Management -Congressional briefings, budget, grants management, coordination, outreach • Outreach/Technology Transfer advisors, -forums, workshops, conferences, publications, training, outsourcing • Project Leadership project planning, -specifications, guidelines, CORS management • Quality Control -training, assess techniques, survey control, load projects into NGS database • Research and Development software -development, remote sensing, modeling, investigate GPS techniques, antenna calibrations
 Other Approaches – National • Funding included in NGS budget – consistent, not threatened by whims of Congress • Program recognized by NOAA – added support to continue • NGS coordinates activities around the country, prioritizing based on need • NGS can redirect funds as needed, not restricted to spending within one state
Other Approaches – National • Funding included in NGS budget – consistent, not threatened by whims of Congress • Program recognized by NOAA – added support to continue • NGS coordinates activities around the country, prioritizing based on need • NGS can redirect funds as needed, not restricted to spending within one state
 Other Approaches – Regional • Alternative if can’t get support for National program • Needs don’t stop at state boundaries • States within a region work in concert to support common issues/goals • More efficient use of funds • Encourages partnerships • Congress more likely to continue funding if affects a larger group – shows importance, commitment to program on part of users
Other Approaches – Regional • Alternative if can’t get support for National program • Needs don’t stop at state boundaries • States within a region work in concert to support common issues/goals • More efficient use of funds • Encourages partnerships • Congress more likely to continue funding if affects a larger group – shows importance, commitment to program on part of users
 Other Approaches – Regional
Other Approaches – Regional
 The Future • Continue efforts to maintain and grow the program • Research new technology to enhance HMP efforts • Continue to investigate opportunities to modify procedures and processes to improve efficiencies • Provide outreach, training, and support to states interested in Height Modernization
The Future • Continue efforts to maintain and grow the program • Research new technology to enhance HMP efforts • Continue to investigate opportunities to modify procedures and processes to improve efficiencies • Provide outreach, training, and support to states interested in Height Modernization
 Questions? Contact information Renee Shields Grants Manager N/NGS 1, SSMC 3, Room 9357 1315 East-West Highway Silver Spring, MD 20910 301 -713 -3231, x 116 Renee. Shields@noaa. gov
Questions? Contact information Renee Shields Grants Manager N/NGS 1, SSMC 3, Room 9357 1315 East-West Highway Silver Spring, MD 20910 301 -713 -3231, x 116 Renee. Shields@noaa. gov


