bf88c8ac6acca789065ff9573abe4c88.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 51
 No. C General concepts Andreas Ehliar - Per Karlström
No. C General concepts Andreas Ehliar - Per Karlström
 Outline • Background • Some Implementations • Design Issues / Tools • Example Application • Conclusions
Outline • Background • Some Implementations • Design Issues / Tools • Example Application • Conclusions
 Current Situation Transistors Time
Current Situation Transistors Time
 Current Situation IP IP IP
Current Situation IP IP IP
 NOC implementations • So. CBUS • x. Pipes • Pleiades • Eclipse • (FPGA)
NOC implementations • So. CBUS • x. Pipes • Pleiades • Eclipse • (FPGA)
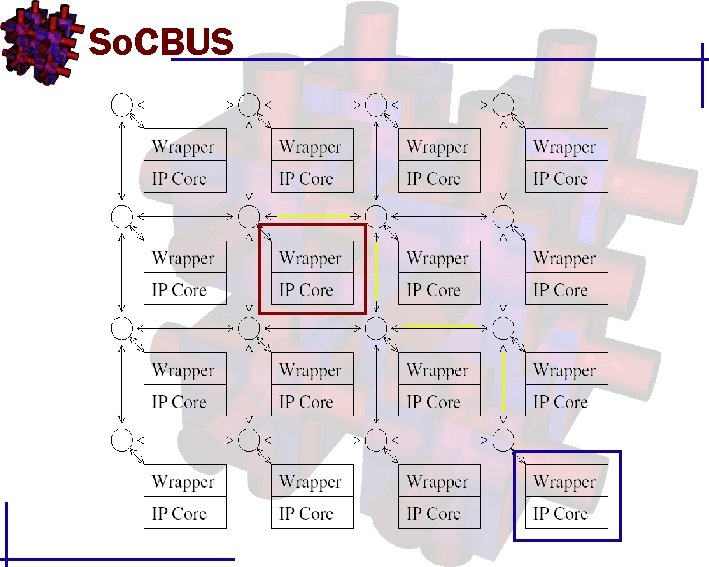 So. CBUS
So. CBUS
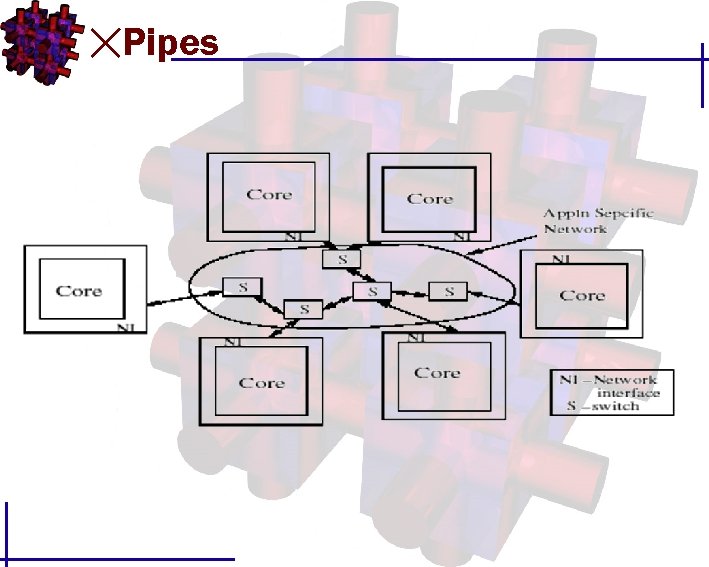 Pipes
Pipes
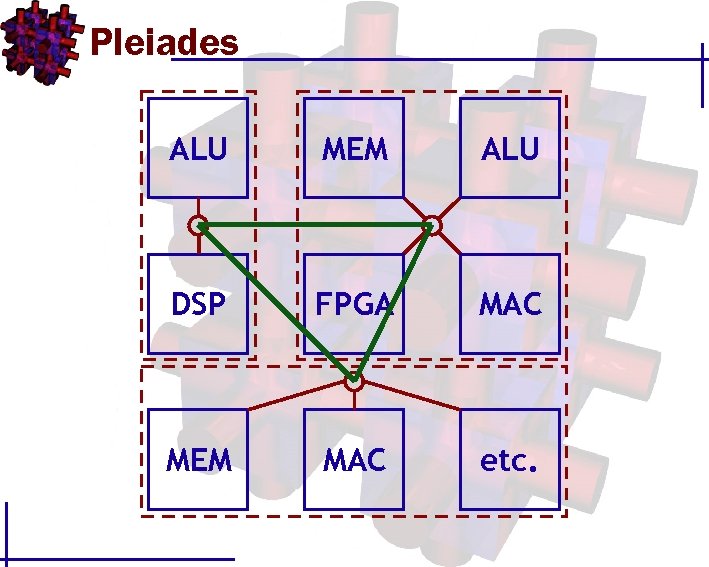 Pleiades ALU MEM ALU DSP FPGA MAC MEM MAC etc.
Pleiades ALU MEM ALU DSP FPGA MAC MEM MAC etc.
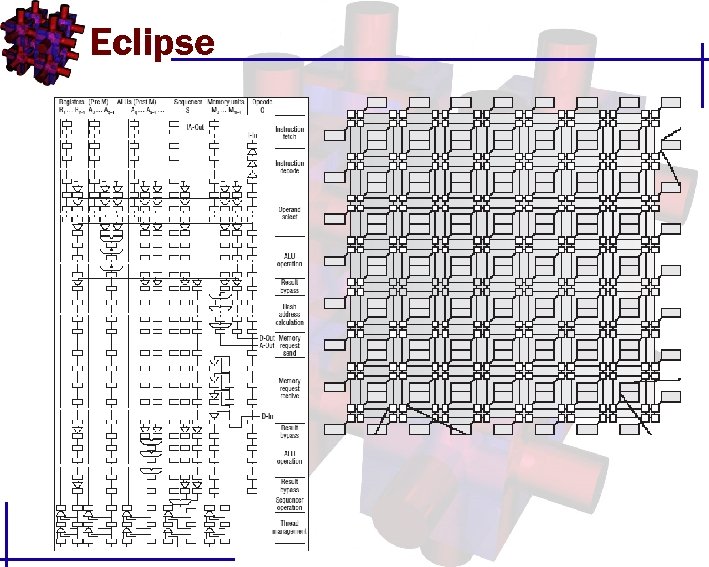 Eclipse
Eclipse
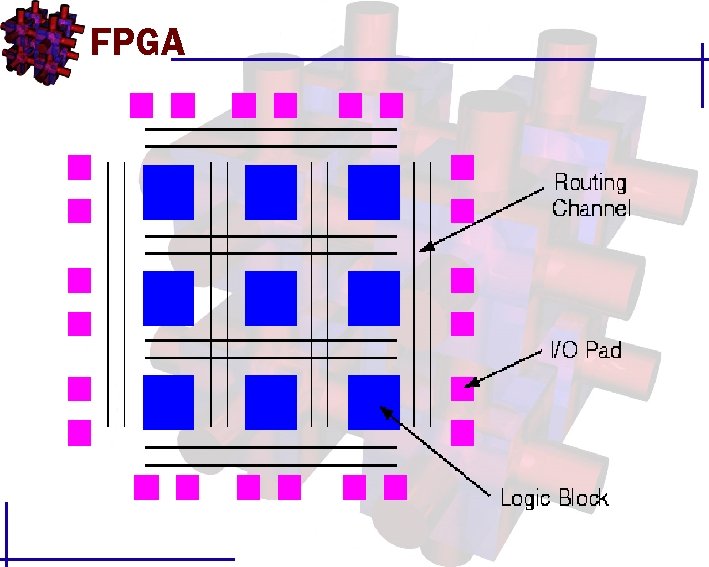 FPGA
FPGA
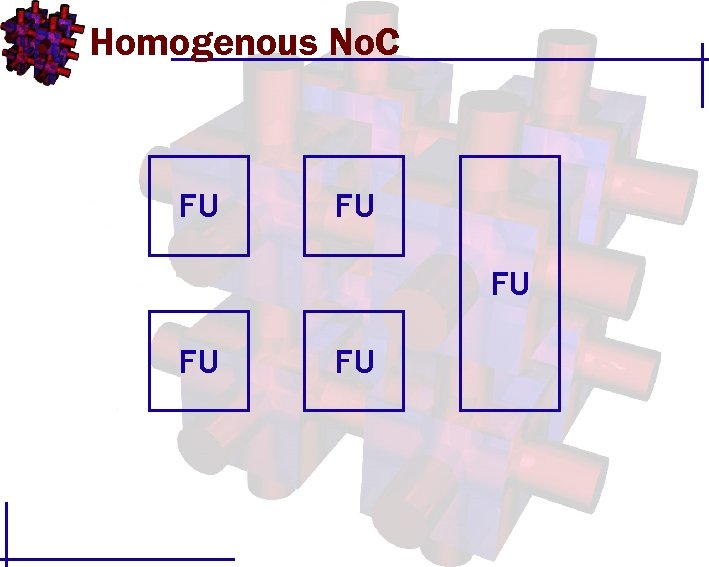 Homogenous No. C FU FU FU
Homogenous No. C FU FU FU
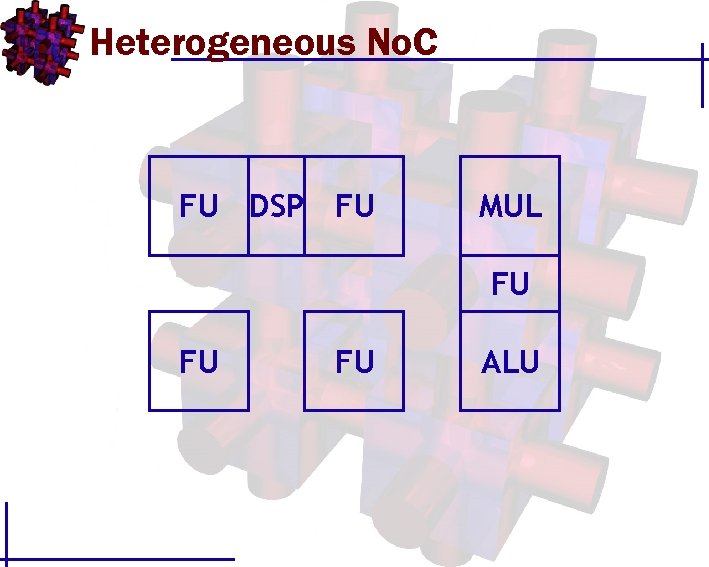 Heterogeneous No. C FU DSP FU MUL FU FU FU ALU
Heterogeneous No. C FU DSP FU MUL FU FU FU ALU
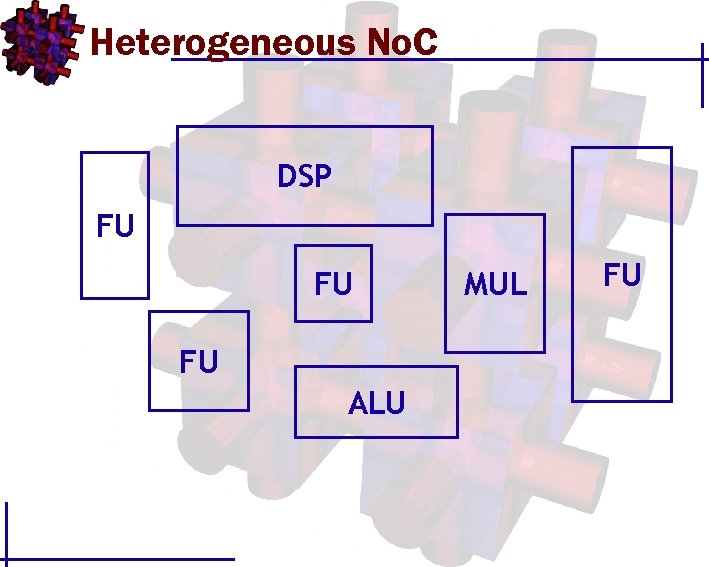 Heterogeneous No. C DSP FU FU FU ALU MUL FU
Heterogeneous No. C DSP FU FU FU ALU MUL FU
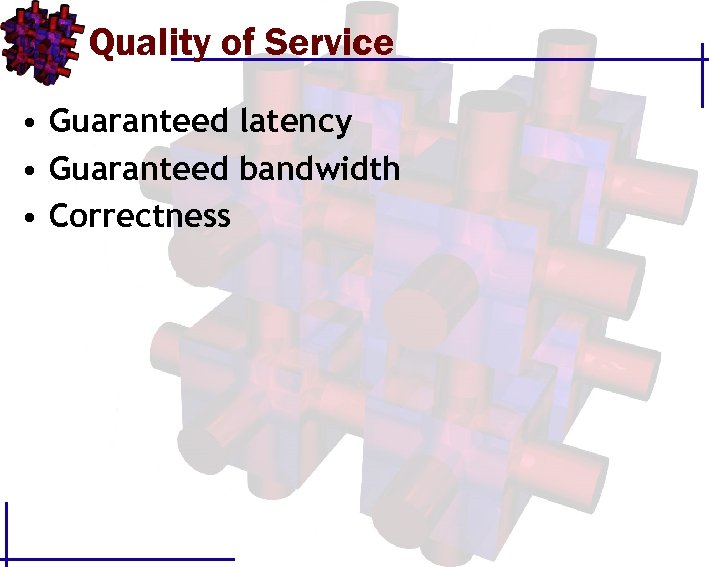 Quality of Service • Guaranteed latency • Guaranteed bandwidth • Correctness
Quality of Service • Guaranteed latency • Guaranteed bandwidth • Correctness
 Design Issues - Signaling V t
Design Issues - Signaling V t
 Design Issues - Clocking ALU MEM DSP FPGA
Design Issues - Clocking ALU MEM DSP FPGA
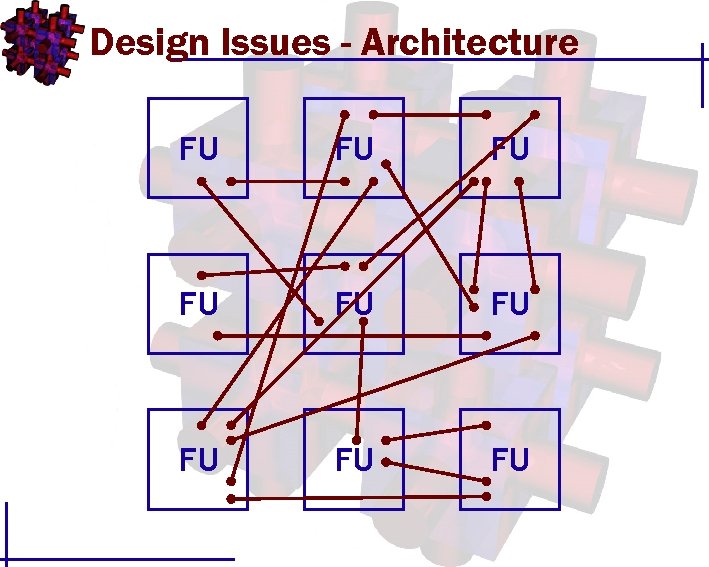 Design Issues - Architecture FU FU FU
Design Issues - Architecture FU FU FU
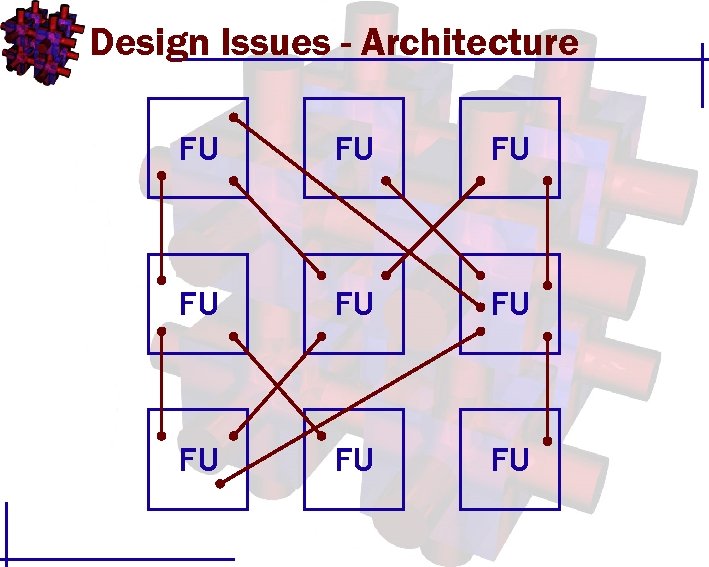 Design Issues - Architecture FU FU FU
Design Issues - Architecture FU FU FU
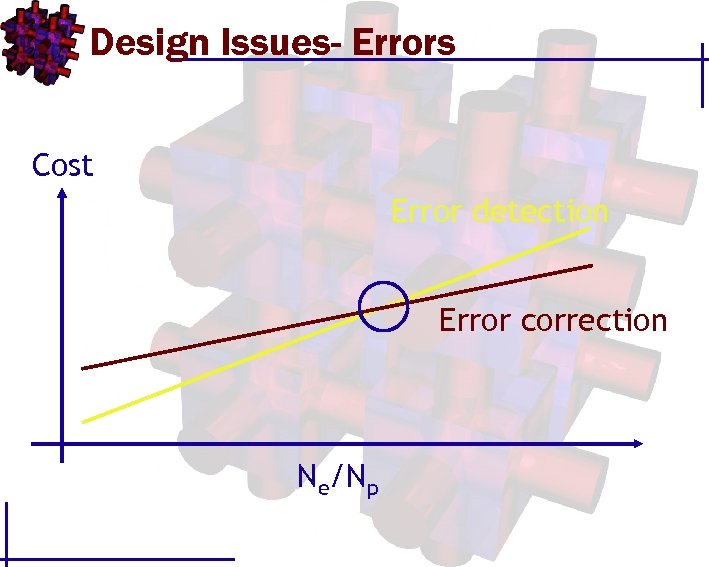 Design Issues- Errors Cost Error detection Error correction Ne/Np
Design Issues- Errors Cost Error detection Error correction Ne/Np
 Design Issues - Flow Control
Design Issues - Flow Control
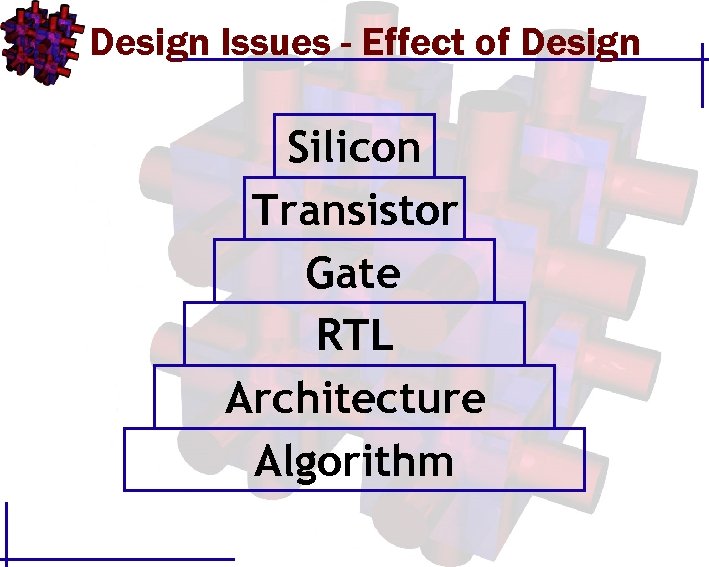 Design Issues - Effect of Design Silicon Transistor Gate RTL Architecture Algorithm
Design Issues - Effect of Design Silicon Transistor Gate RTL Architecture Algorithm
 Design Issues - Power Control
Design Issues - Power Control
 Design Issues - Long Wires • Solving the global interconnect mess – – Delay Bit errors Repeaters Clock domains • Create one optimized solution that can be reused
Design Issues - Long Wires • Solving the global interconnect mess – – Delay Bit errors Repeaters Clock domains • Create one optimized solution that can be reused
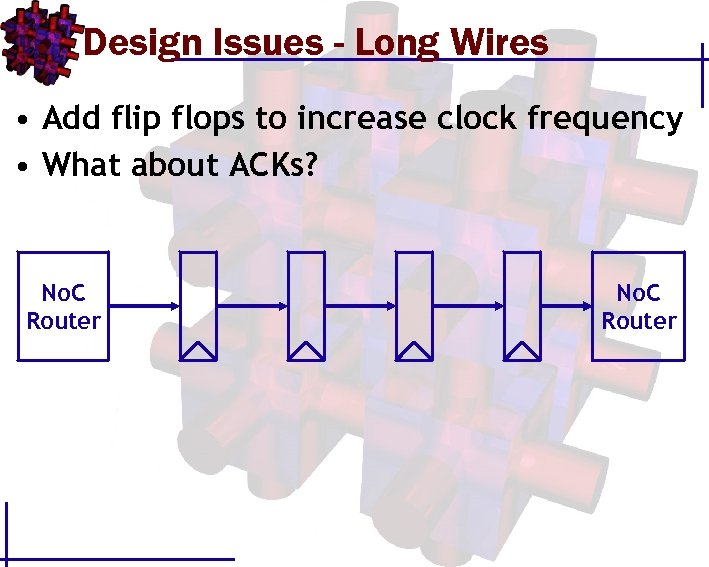 Design Issues - Long Wires • Add flip flops to increase clock frequency • What about ACKs? No. C Router
Design Issues - Long Wires • Add flip flops to increase clock frequency • What about ACKs? No. C Router
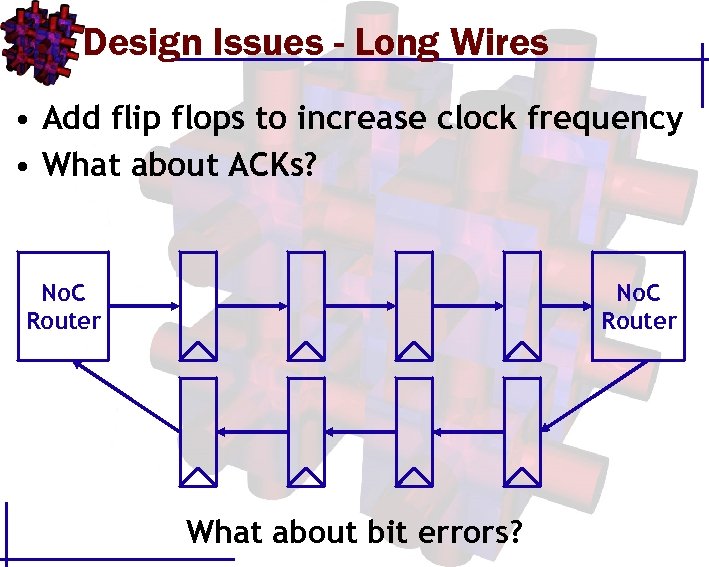 Design Issues - Long Wires • Add flip flops to increase clock frequency • What about ACKs? No. C Router What about bit errors?
Design Issues - Long Wires • Add flip flops to increase clock frequency • What about ACKs? No. C Router What about bit errors?
 Design Issues - Long Wires • Bit errors on long wires will not be avoidable in the future • Use error correcting codes – Disadvantage: More wires • Use parity bits to discover errors – Resend damaged packets – No longer possible to guarantee real-time performance
Design Issues - Long Wires • Bit errors on long wires will not be avoidable in the future • Use error correcting codes – Disadvantage: More wires • Use parity bits to discover errors – Resend damaged packets – No longer possible to guarantee real-time performance
 Design Issues - Long Wires • Possibility to create heavily optimized solution – Low voltage signaling – Advanced symbol encoding/decoding – Wave pipelining
Design Issues - Long Wires • Possibility to create heavily optimized solution – Low voltage signaling – Advanced symbol encoding/decoding – Wave pipelining
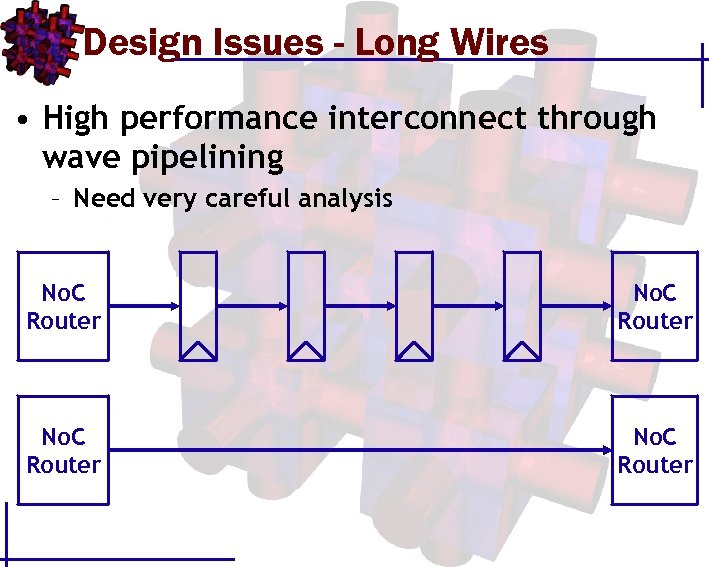 Design Issues - Long Wires • High performance interconnect through wave pipelining – Need very careful analysis No. C Router
Design Issues - Long Wires • High performance interconnect through wave pipelining – Need very careful analysis No. C Router
 Design Issues - Long Wires • Wave pipelining performance – 3. 45 Ghz signaling on one bit line in 0. 25 um – More energy efficient than regular pipeline – Faster than regular pipeline • Disadvantage – Much harder to test/verify
Design Issues - Long Wires • Wave pipelining performance – 3. 45 Ghz signaling on one bit line in 0. 25 um – More energy efficient than regular pipeline – Faster than regular pipeline • Disadvantage – Much harder to test/verify
 System design • Typical tools – Simulator – Network generator
System design • Typical tools – Simulator – Network generator
 System design • What I would want – – – Graphical frontend to design No. C C and RTL models of the finished No. C C API to create C level models of the No. C Mix C and RTL models in RTL simulator And of course. . .
System design • What I would want – – – Graphical frontend to design No. C C and RTL models of the finished No. C C API to create C level models of the No. C Mix C and RTL models in RTL simulator And of course. . .
 System design IP cores
System design IP cores
 Example: Core Router • So. CBUS Simulation • Study of 16 port core router on a chip • 16 x 10 Gigabit Ethernet Ports • Prove feasibility of using So. CBUS
Example: Core Router • So. CBUS Simulation • Study of 16 port core router on a chip • 16 x 10 Gigabit Ethernet Ports • Prove feasibility of using So. CBUS
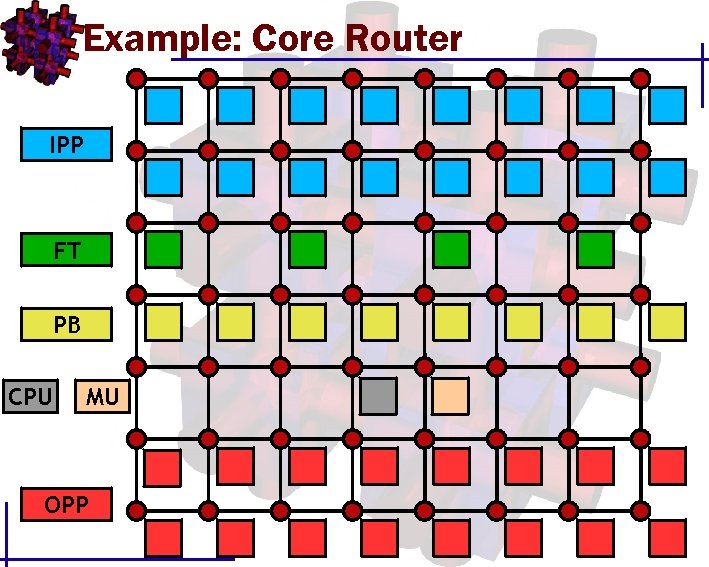 Example: Core Router IPP FT PB CPU MU OPP
Example: Core Router IPP FT PB CPU MU OPP
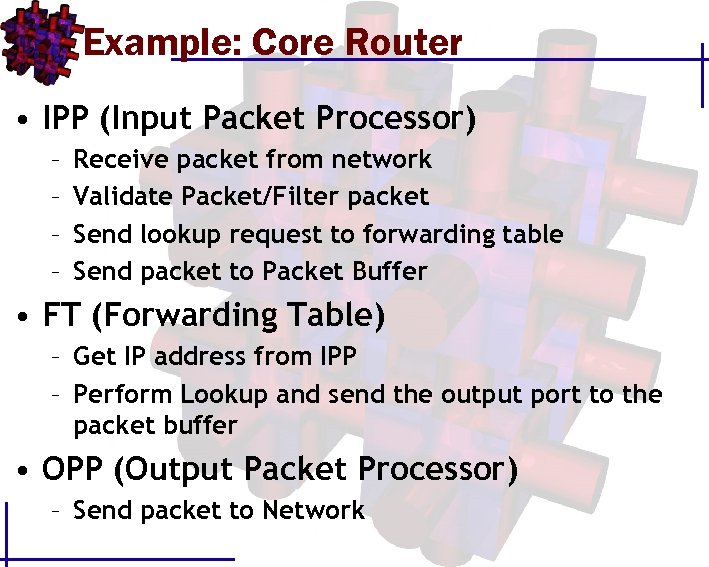 Example: Core Router • IPP (Input Packet Processor) – – Receive packet from network Validate Packet/Filter packet Send lookup request to forwarding table Send packet to Packet Buffer • FT (Forwarding Table) – Get IP address from IPP – Perform Lookup and send the output port to the packet buffer • OPP (Output Packet Processor) – Send packet to Network
Example: Core Router • IPP (Input Packet Processor) – – Receive packet from network Validate Packet/Filter packet Send lookup request to forwarding table Send packet to Packet Buffer • FT (Forwarding Table) – Get IP address from IPP – Perform Lookup and send the output port to the packet buffer • OPP (Output Packet Processor) – Send packet to Network
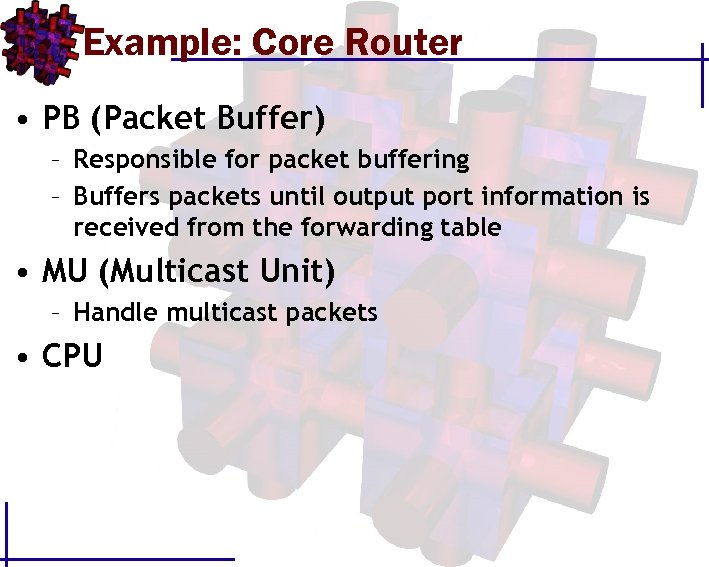 Example: Core Router • PB (Packet Buffer) – Responsible for packet buffering – Buffers packets until output port information is received from the forwarding table • MU (Multicast Unit) – Handle multicast packets • CPU
Example: Core Router • PB (Packet Buffer) – Responsible for packet buffering – Buffers packets until output port information is received from the forwarding table • MU (Multicast Unit) – Handle multicast packets • CPU
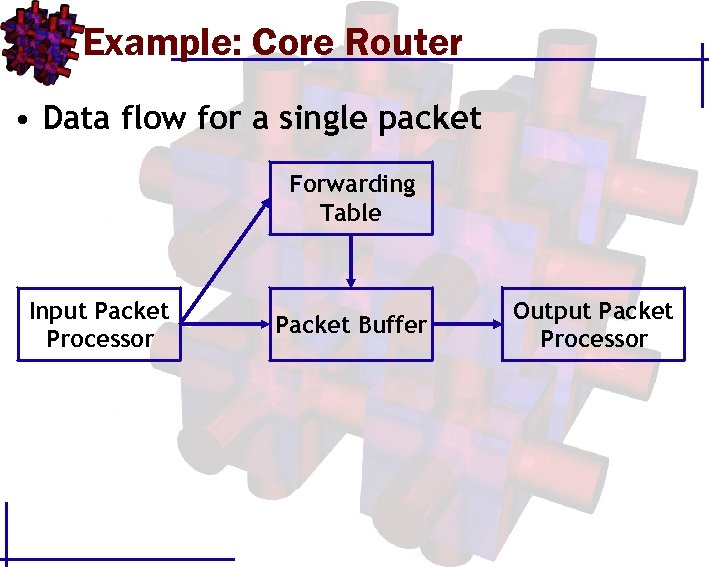 Example: Core Router • Data flow for a single packet Forwarding Table Input Packet Processor Packet Buffer Output Packet Processor
Example: Core Router • Data flow for a single packet Forwarding Table Input Packet Processor Packet Buffer Output Packet Processor
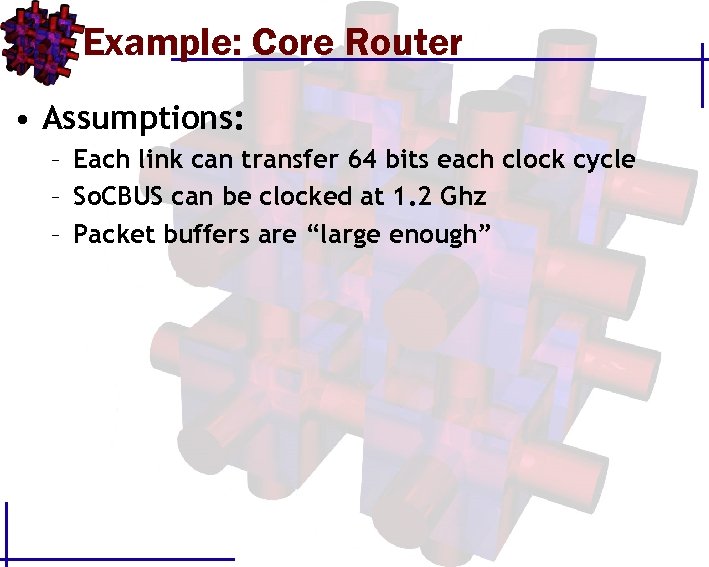 Example: Core Router • Assumptions: – Each link can transfer 64 bits each clock cycle – So. CBUS can be clocked at 1. 2 Ghz – Packet buffers are “large enough”
Example: Core Router • Assumptions: – Each link can transfer 64 bits each clock cycle – So. CBUS can be clocked at 1. 2 Ghz – Packet buffers are “large enough”
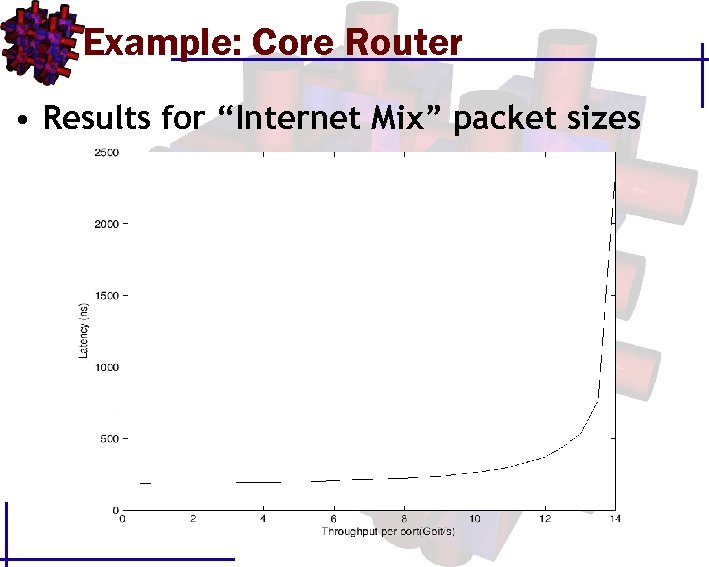 Example: Core Router • Results for “Internet Mix” packet sizes
Example: Core Router • Results for “Internet Mix” packet sizes
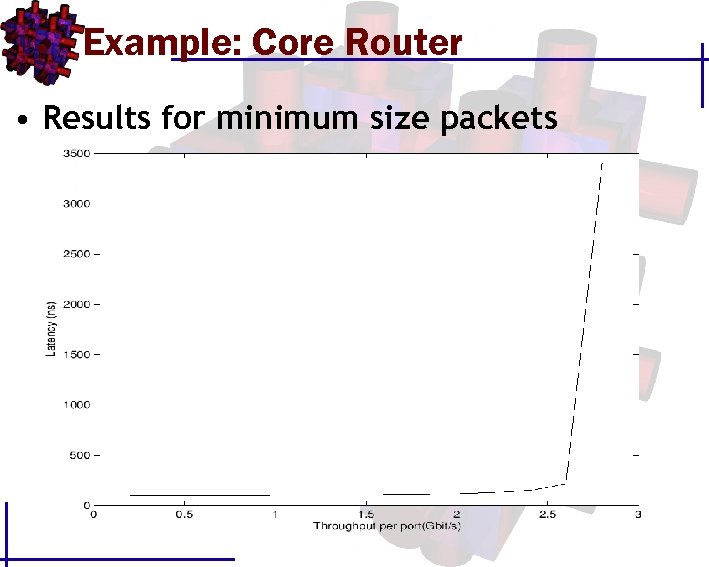 Example: Core Router • Results for minimum size packets
Example: Core Router • Results for minimum size packets
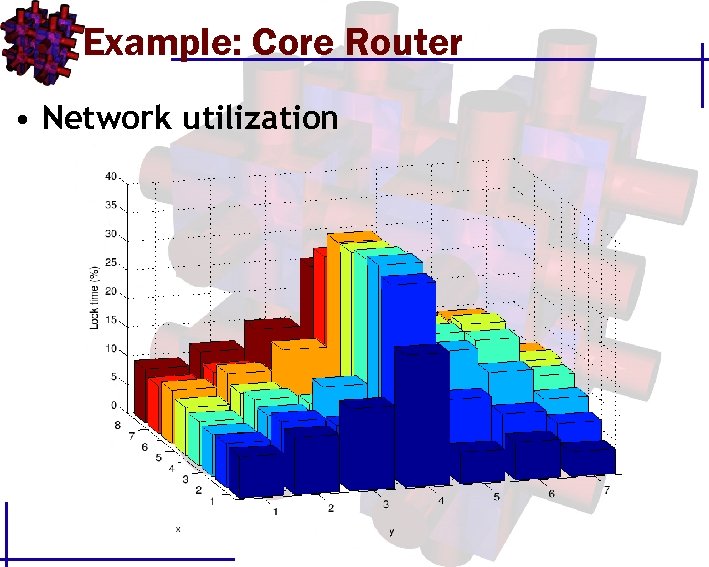 Example: Core Router • Network utilization
Example: Core Router • Network utilization
 Example: Core Router • Bottleneck in forwarding table access – Current version of So. CBUS creates a virtual circuit for each request • Proposal: Extend So. CBUS – Reliable delivery of small (64 bit or less) packets without setting up a virtual circuit
Example: Core Router • Bottleneck in forwarding table access – Current version of So. CBUS creates a virtual circuit for each request • Proposal: Extend So. CBUS – Reliable delivery of small (64 bit or less) packets without setting up a virtual circuit
 Example: Core Router • Conclusion on this application example – Initial concept seems to work in simulation • Current work: – Master thesis to test concept in an FPGA
Example: Core Router • Conclusion on this application example – Initial concept seems to work in simulation • Current work: – Master thesis to test concept in an FPGA
 Our Reflections • Many papers use routers for each connection core – Not every IP core has to have a No. C Uplink – Probably better to use local shared buses with a common No. C Uplink – On the Internet, terminals are not connected directly to routers • Hard to design a network if the traffic is unknown
Our Reflections • Many papers use routers for each connection core – Not every IP core has to have a No. C Uplink – Probably better to use local shared buses with a common No. C Uplink – On the Internet, terminals are not connected directly to routers • Hard to design a network if the traffic is unknown
 Our Reflections • Research on how to improve No. Cs can often be used to improve non-No. C based designs – Communication over long distances – Improved crossbars • It will be hard to guarantee real-time performance on No. Cs
Our Reflections • Research on how to improve No. Cs can often be used to improve non-No. C based designs – Communication over long distances – Improved crossbars • It will be hard to guarantee real-time performance on No. Cs
 Conclusions • No. C seems to be a reasonable tradeoff – Similar to how standard cells make it easier to design chips • No industry usage (yet? ) • As yet, no killer application has been demonstrated • Next level of abstraction – IP centric design
Conclusions • No. C seems to be a reasonable tradeoff – Similar to how standard cells make it easier to design chips • No industry usage (yet? ) • As yet, no killer application has been demonstrated • Next level of abstraction – IP centric design
 Questions/Discussion • Will future chips have communication patterns favoring No. Cs?
Questions/Discussion • Will future chips have communication patterns favoring No. Cs?
 References • Networks on chips: a new So. C paradigm Benini, L. ; De Micheli, G. ; Computer , Volume: 35 , Issue: 1 , Jan. 2002 Pages: 70 - 78 • Powering networks on chips Benini, L. ; De Micheli, G. ; System Synthesis, 2001. Proceedings. The 14 th International Symposium on, 30 Sept. -3 Oct. 2001 Pages: 33 – 38 • Addressing the system-on-a-chip interconnect woes through communication-based design Sgroi, M. ; Sheets, M. ; Mihal, A. ; Keutzer, K. ; Malik, S. ; Rabaey, J. ; Sangiovanni-Vincentelli, A. ; Design Automation Conference, 2001. Proceedings , 18 -22 June 2001 Pages: 667 - 672 • On-chip networks: a scalable, communication-centric embedded system design paradigm Henkel, J. ; Wolf, W. ; Chakradhar, S. ; VLSI Design, 2004. Proceedings. 17 th International Conference on , 2004 Pages: 845 - 851 • Design of a Core Router using the So. CBUS On-chip Network; Jimmy Svensson; Li. TH-ISY-EX-04/3562 -SE; Li. TH
References • Networks on chips: a new So. C paradigm Benini, L. ; De Micheli, G. ; Computer , Volume: 35 , Issue: 1 , Jan. 2002 Pages: 70 - 78 • Powering networks on chips Benini, L. ; De Micheli, G. ; System Synthesis, 2001. Proceedings. The 14 th International Symposium on, 30 Sept. -3 Oct. 2001 Pages: 33 – 38 • Addressing the system-on-a-chip interconnect woes through communication-based design Sgroi, M. ; Sheets, M. ; Mihal, A. ; Keutzer, K. ; Malik, S. ; Rabaey, J. ; Sangiovanni-Vincentelli, A. ; Design Automation Conference, 2001. Proceedings , 18 -22 June 2001 Pages: 667 - 672 • On-chip networks: a scalable, communication-centric embedded system design paradigm Henkel, J. ; Wolf, W. ; Chakradhar, S. ; VLSI Design, 2004. Proceedings. 17 th International Conference on , 2004 Pages: 845 - 851 • Design of a Core Router using the So. CBUS On-chip Network; Jimmy Svensson; Li. TH-ISY-EX-04/3562 -SE; Li. TH
 References • A scalable high-performance computing solution for networks on chips Forsell, M. ; Micro, IEEE , Volume: 22 , Issue: 5 , Sept. -Oct. 2002 Pages: 46 - 55 • Xpipes: a network-on-chip architecture for gigascale systems-on-chip Bertozzi, D. ; Benini, L. ; Circuits and Systems Magazine, IEEE , Volume: 4 , Issue: 2 , 2004 Pages: 18 - 31 • xpipes. Compiler: a tool for instantiating application specific networks on chip Jalabert, A. ; Murali, S. ; Benini, L. ; De Micheli, G. ; Design, Automation and Test in Europe Conference and Exhibition, 2004. Proceedings , Volume: 2 , 16 -20 Feb. 2004 Pages: 884 - 889 Vol. 2 • A wave-pipelined on-chip interconnect structure for networks-onchips Jiang Xu; Wayne, W. High Performance Interconnects, 2003. Proceedings. 11 th Symposium on, Vol. , Iss. , 20 -22 Aug. 2003 Pages: 10 - 14 • An on-chip network architecture for hard real time system; Daniel Wiklund; Li. U-TEK-LIC-2002: 69 LIU
References • A scalable high-performance computing solution for networks on chips Forsell, M. ; Micro, IEEE , Volume: 22 , Issue: 5 , Sept. -Oct. 2002 Pages: 46 - 55 • Xpipes: a network-on-chip architecture for gigascale systems-on-chip Bertozzi, D. ; Benini, L. ; Circuits and Systems Magazine, IEEE , Volume: 4 , Issue: 2 , 2004 Pages: 18 - 31 • xpipes. Compiler: a tool for instantiating application specific networks on chip Jalabert, A. ; Murali, S. ; Benini, L. ; De Micheli, G. ; Design, Automation and Test in Europe Conference and Exhibition, 2004. Proceedings , Volume: 2 , 16 -20 Feb. 2004 Pages: 884 - 889 Vol. 2 • A wave-pipelined on-chip interconnect structure for networks-onchips Jiang Xu; Wayne, W. High Performance Interconnects, 2003. Proceedings. 11 th Symposium on, Vol. , Iss. , 20 -22 Aug. 2003 Pages: 10 - 14 • An on-chip network architecture for hard real time system; Daniel Wiklund; Li. U-TEK-LIC-2002: 69 LIU


