6270771980f2812a15444a9e2f79b9b0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30

NIS Linkages : A Policy Perspective Presentation by NIRAJ KUMAR National Project Head (IMTT) Centre for International Trade in Technology Indian Institute of Foreign Trade , New Delhi (Ministry of Commerce, GOVT OF INDIA)

NIS Overview NIS past trends NIS developments NIS models NIC Index-cross country Linkages sub index-cross country NIC index and sub index-INDIA Actors and Linkages in NIS

NIS-past trends Freeman(1987) Dosi et al (1988) Lundvall(1992) Nelson(1993) Ohmae(1995) Edquist(1997) Malerba(1997) Braczyk et al(1998) Porter and Stern(2002)

NIS-developments Ohmae(1995)-concept of regional innovation systems Malerba(1997)-sectoral innovation systems Porter(1998)-concept of industrial clusters

NIS-models Liu and White(2001)-conceptual framework built on 5 different activities of innovation process. Research, production, enduse, linkage and education. Chang and Shih(2003)-model made up of 6 elements. R&D expenditure, R&D performance, Technology policy, human capital development, technology transfer, entrepreneurial climate. Furman et al(2002)-concept of NIC Porter and Stern(2002)-development of NIC Index based on 4 sub indexes namely-innovation policy, cluster innovation, proportion of scientists and engineers & linkages.
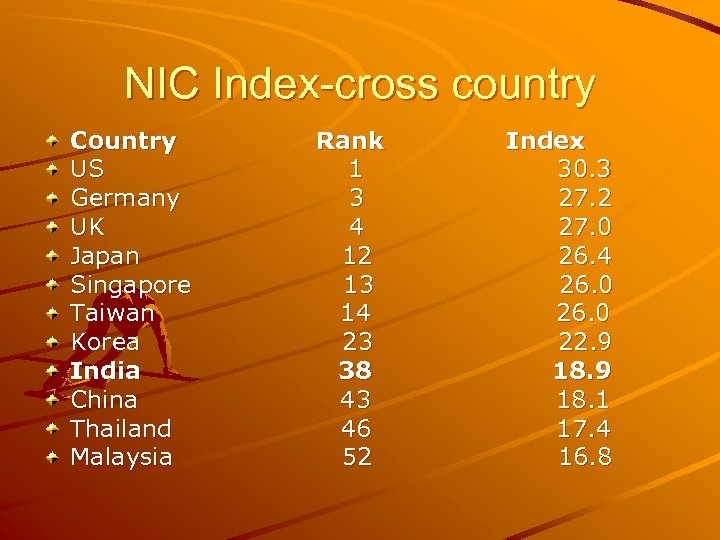
NIC Index-cross country Country US Germany UK Japan Singapore Taiwan Korea India China Thailand Malaysia Rank 1 3 4 12 13 14 23 38 43 46 52 Index 30. 3 27. 2 27. 0 26. 4 26. 0 22. 9 18. 1 17. 4 16. 8

Linkages sub Index-cross country Country US Germany UK Japan Singapore Taiwan Korea India China Thailand Malaysia Rank 1 10 9 21 15 17 24 23 41 49 46 sub Index 7. 1 6. 3 5. 4 5. 8 5. 6 5. 1 5. 2 4. 3 4. 1 4. 2

NIC Index and sub index-INDIA NIC Index 18. 9(rank-38) Innovation policy 4. 8(rank-39) Scientists/engineers 1. 2(rank-59) Cluster innovation 7. 8(rank-31) Linkages 5. 2(rank-23)

Actors in NIS Governments (local, regional, national, international)-setting policy directions Bridging institutions-intermediaries between governments and research performers. Private enterprises & research institutes they finance Universities and institutions-provide key knowledge and skills. Other public and private organizations (labs, TTOs, patent offices etc. )

NIS Linkages: Policy Formulation Objective 1 -foster scientific research in Universities and scientific institutions. Objective 2 -promote interaction between private and public institutions. Objective 3 -Leverage technologies such as IT, Biotechnology etc. Objective 4 -strengthen enabling mechanisms relating to technology development and absorption. Objective 5 -promote international S&T cooperation.

NIS linkages: Strategy 1(Policyobjective 1)-estb of research institute, Setting up world class R&D centers. Strategy 2(Policyobjective 2)-synergy between industry &scientific research, increased R&D investments by industry. Strategy 3(Policyobjective 3)-capacity buiding, global competitiveness. Strategy 4(Policyobjective 4)-Technology transfer and diffusion. Strategy 5(Policyobjective 5)-MOUs, collaboration, foreign R&D centers.

Policy impact: sectoral view (Biotechnology) R&D Institutions Public-private partnership Technology Transfer Applications S&T Cooperation Foreign R&D Centres
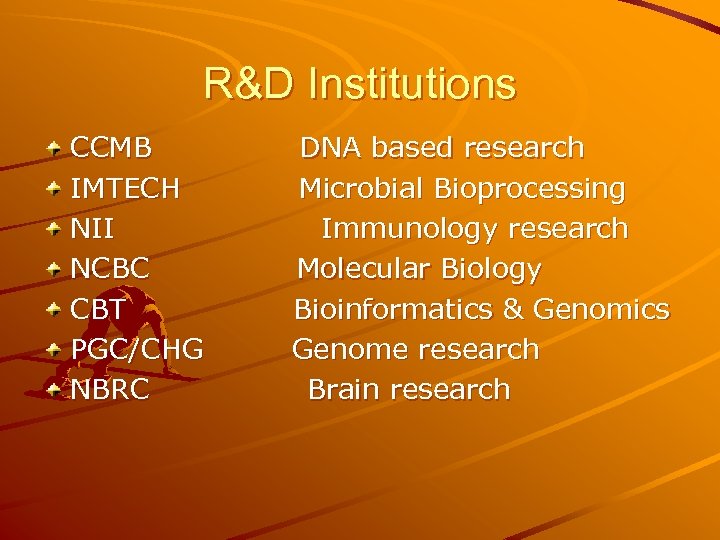
R&D Institutions CCMB IMTECH NII NCBC CBT PGC/CHG NBRC DNA based research Microbial Bioprocessing Immunology research Molecular Biology Bioinformatics & Genomics Genome research Brain research

Public-Private partnership Monsanto Research (R&D Center) @ IISc Bangalore (plant genomics) GENOMED(JV between CBT & Nicholas Piramal) [pharmaco -genomics] Institute of Bioinformatics and Applied Biotechnology (Govt of Karnataka & ICICI) Biotech Consortium India Ltd. TATA-CSIR Initiative for Bio Suite.

Technology Transfer Immunodiagnostics Crop Biotechnology Animal Biotechnology Biomass Biofertilizers Industrial Biotech

Applications (consumption of biotech products) Human/Animal healthcare products Agricultural products Industrial products Other Biotech products

S&T Cooperation MOUs(Germany, Switzerland, USA, UK, Sweden). Coordinating G 15 Nations in establishment of Gene Banks. (medicinal and aromatic plants) More than 15 foreign R&D Centers.

Foreign R&D Centers Astrazeneca, b’lore -dev of prescription medicines (cancer, neuroscience, cardiovascular, respiratory &inflammation) Gangagen Biotechnologies , b’lore-prevention & treatment of bacterial functions Novartis, Mumbai (Human vaccines) Novo Nordisk, b’lore (Diabetes care) R&D Millipore, b’lore (protein/DNA research) Intervet India, pune (animal health products) ……………. . and many more.

Policy Impact: sectoral view (Nanotechnology) R&D Institutions Public-private partnership Industry R&D Applications S&T Cooperation
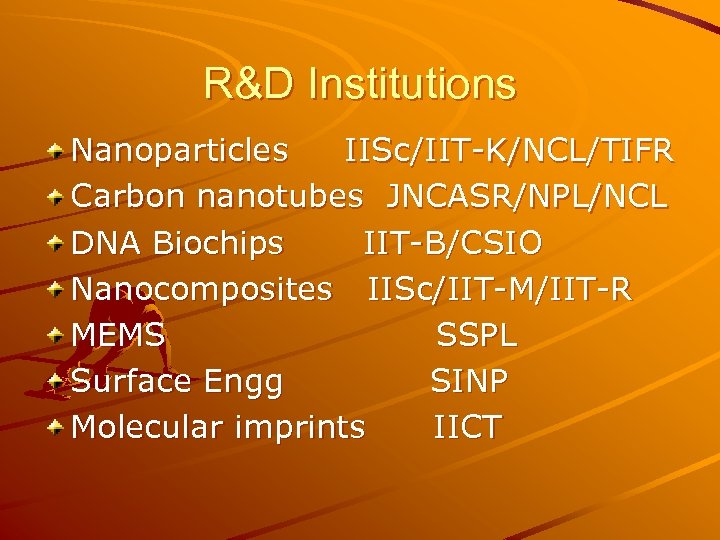
R&D Institutions Nanoparticles IISc/IIT-K/NCL/TIFR Carbon nanotubes JNCASR/NPL/NCL DNA Biochips IIT-B/CSIO Nanocomposites IISc/IIT-M/IIT-R MEMS SSPL Surface Engg SINP Molecular imprints IICT

Public-Private Partnership MEMS RESEARCH LAB Collaboration between Cranes software International Limited & IISc Bangalore

Industry R&D Biomix Network Limited, Mumbai (Developing biotechnology tools) Velbionanotech, Mumbai (Bionanotechnology products) Nano Tex LLc -dev centre in India.

Applications Dabur and Shantha Biotech (Using drug delivery applications on commercial scale). Raymonds and Grasim (Using nano –chemicals). Samsung and LG (using nano-coating).

S&T Cooperation US based Nano- tex planning an R&D center in India. Ranbaxy has already signed a deal with Bayer.

Innovation tomorrow: Policy Implications 3 rd generation innovation policy Technological capability development route Technological learning processes Capacity Building in IMTT: An IIFT initiative

3 rd generation policy Core emphasis on innovation across. Placing innovation at the heart of policy areas shaping innovation performance. Developing interfaces that allow for pooling of knowledge. Developing interfaces that allow for Experience learning. Coordination of policy initiatives.

Technological capability development routes Reverse Value Chain Reverse PLC Process Specialist Product pioneering Application pioneering

Technological learning processes Reverse value chain-learning by doing, learning by transacting, R&D. Reverse PLC-learning by doing, reverse engineering, imitative R&D. Process specialist-learning by doing, learning by transacting, R&D. Product pioneering- R&D, market research. Application pioneering-Technology scanning, Integration with Domain Knowledge.

Capacity Building in IMTT An IIFT initiative Developing masters program in innovation management and technology transfer. 4 partners-UCE, UK; DMU, China; IEH, Poland; IIFT, India. Knowledge dissemination through workshops, training sessions, forums. Beneficiaries shall include knowledge workers from academia, R&D, SMEs, industry, policymakers.

THANK YOU
6270771980f2812a15444a9e2f79b9b0.ppt