efa769042821273800045d815e007530.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 95
 Nile Civilizations Section 1 “It’s not the years in your life that count, but the life in your years. ” - Abraham Lincoln A flamingo can swallow only if its head is facing downwards.
Nile Civilizations Section 1 “It’s not the years in your life that count, but the life in your years. ” - Abraham Lincoln A flamingo can swallow only if its head is facing downwards.
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
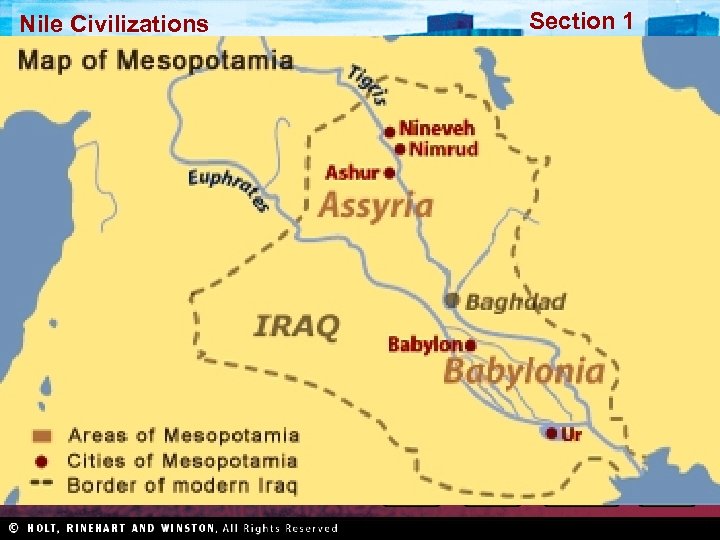
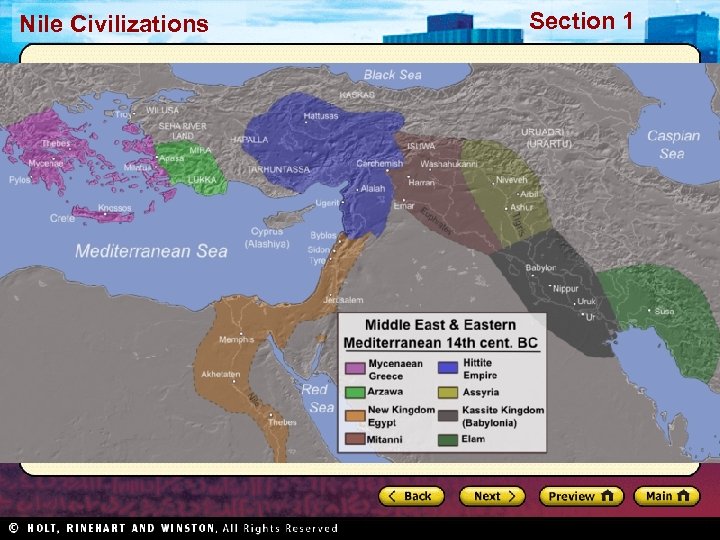
 Nile Civilizations Section 1 Mesopotamia and Sumer Main Idea The first known civilization arose in Mesopotamia, and its culture and innovations influenced later civilizations in the region for thousands of years.
Nile Civilizations Section 1 Mesopotamia and Sumer Main Idea The first known civilization arose in Mesopotamia, and its culture and innovations influenced later civilizations in the region for thousands of years.
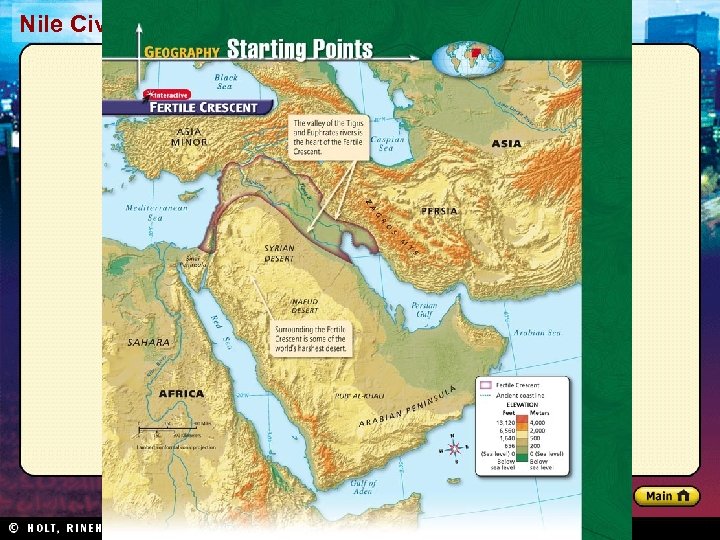
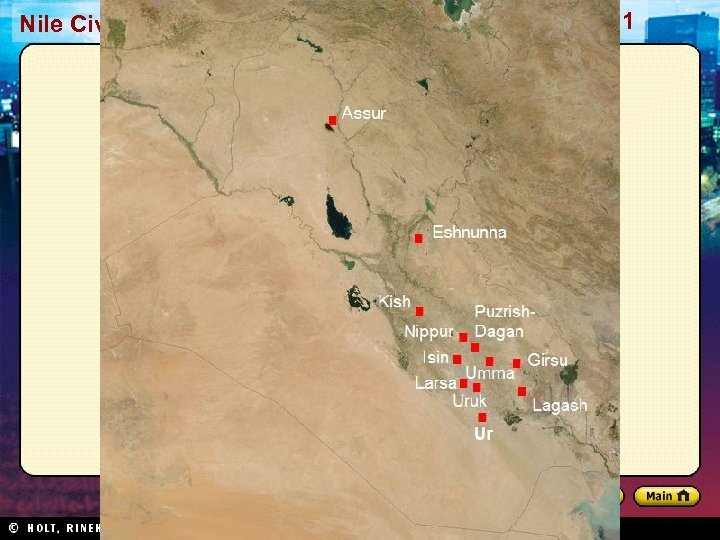
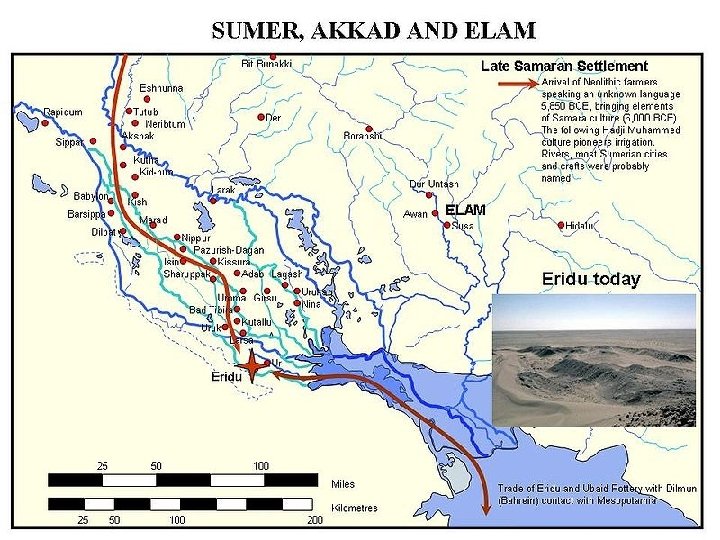
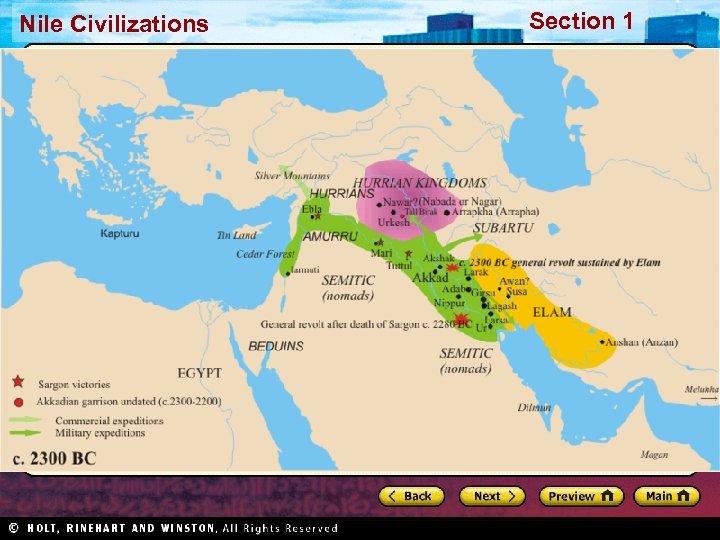
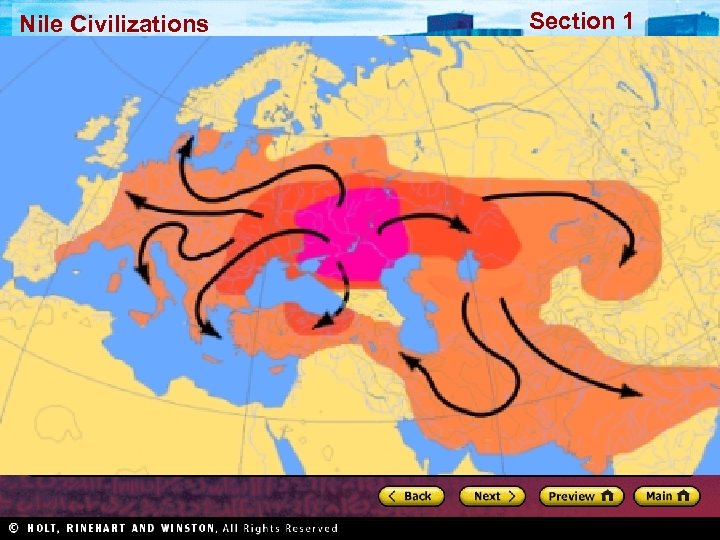
 Nile Civilizations Section 1 Geography Promotes Civilization • Fertile area between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers became site of world’s first civilization • Fertile Crescent well suited for agriculture • Farming in Mesopotamia posed challenges: – If water levels too high, crops washed away – If water levels too low, crops died • People developed methods to control water: – Basins, canals, and dikes – Organization: assigning jobs, allocating resources
Nile Civilizations Section 1 Geography Promotes Civilization • Fertile area between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers became site of world’s first civilization • Fertile Crescent well suited for agriculture • Farming in Mesopotamia posed challenges: – If water levels too high, crops washed away – If water levels too low, crops died • People developed methods to control water: – Basins, canals, and dikes – Organization: assigning jobs, allocating resources
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Section 1 Nile Civilizations Question: What factors influenced the rise of civilization in Mesopotamia? Answer(s): fertile land; plentiful food; need to organize people for jobs
Section 1 Nile Civilizations Question: What factors influenced the rise of civilization in Mesopotamia? Answer(s): fertile land; plentiful food; need to organize people for jobs
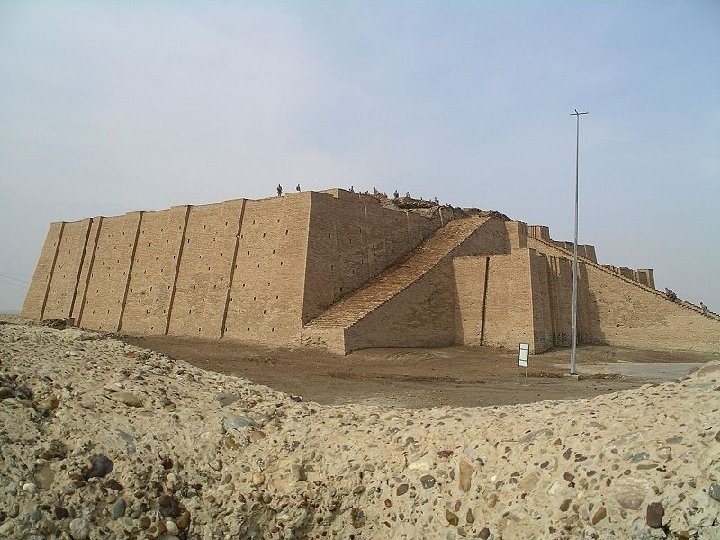
 Section 1 Nile Civilizations Sumer The Cities of Sumer • Large cities developed by 4000 BC • Structures made of mud bricks • Ziggurat: pyramid-shaped temple Religion and Government • Shaped life in city-states • Polytheism: worship of many gods • Priests had high status and were the first rulers • Massive wall encircled each city • War chiefs began to rule as kings • Each city and its land formed a city-state, with its own government • Dynasty: series of rulers from one family
Section 1 Nile Civilizations Sumer The Cities of Sumer • Large cities developed by 4000 BC • Structures made of mud bricks • Ziggurat: pyramid-shaped temple Religion and Government • Shaped life in city-states • Polytheism: worship of many gods • Priests had high status and were the first rulers • Massive wall encircled each city • War chiefs began to rule as kings • Each city and its land formed a city-state, with its own government • Dynasty: series of rulers from one family
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
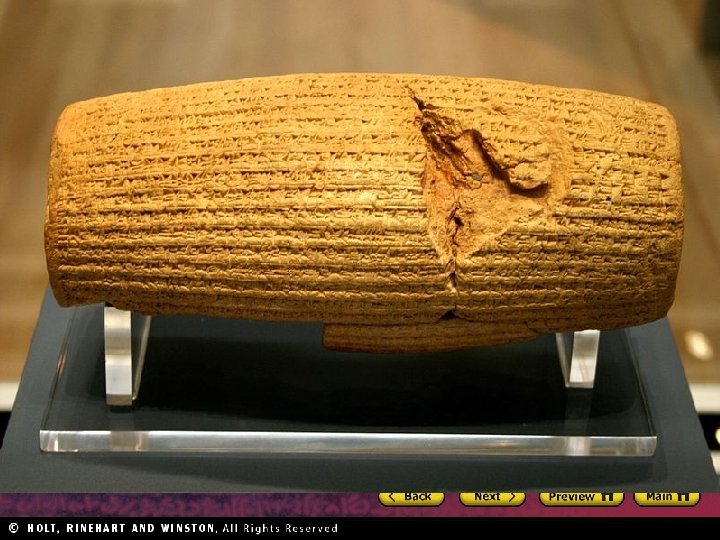
 Section 1 Nile Civilizations Sumerian Culture Writing • Cuneiform: Sumerian writing • Business accounts and records • Law, grammar, literature The Arts • Arches, ramps, columns • Sculpture • Cylinder seals Math and Sciences • System based on number 60 • Geometry • May have been the first to use the wheel • Invented the plow • Basic surgery Trade and Society • Traded for wood and metals • Social hierarchy • Distinct male/female roles
Section 1 Nile Civilizations Sumerian Culture Writing • Cuneiform: Sumerian writing • Business accounts and records • Law, grammar, literature The Arts • Arches, ramps, columns • Sculpture • Cylinder seals Math and Sciences • System based on number 60 • Geometry • May have been the first to use the wheel • Invented the plow • Basic surgery Trade and Society • Traded for wood and metals • Social hierarchy • Distinct male/female roles
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Anu Section 1 Enki
Nile Civilizations Anu Section 1 Enki
 Section 1 Nile Civilizations Enlil Inanna
Section 1 Nile Civilizations Enlil Inanna
 Section 1 Nile Civilizations Utu Gilgamesh
Section 1 Nile Civilizations Utu Gilgamesh
 Nile Civilizations The Epic of Gilgamesh Section 1
Nile Civilizations The Epic of Gilgamesh Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Section 1 Nile Civilizations Question: Why was the Sumerians’ development of cuneiform a major turning point in history? Answer(s): After the development of cuneiform, humankind moved from prehistory into the historical age.
Section 1 Nile Civilizations Question: Why was the Sumerians’ development of cuneiform a major turning point in history? Answer(s): After the development of cuneiform, humankind moved from prehistory into the historical age.
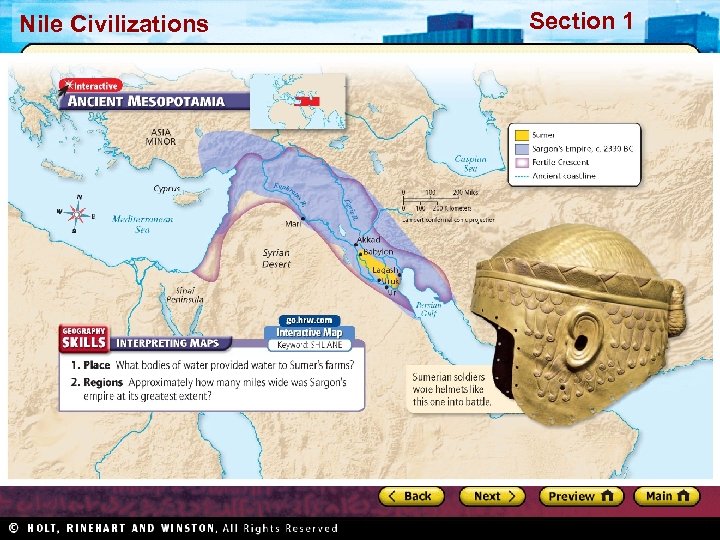
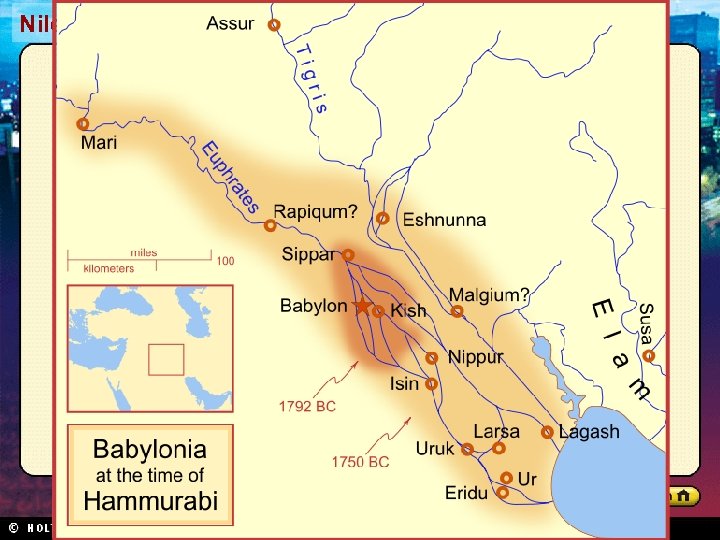
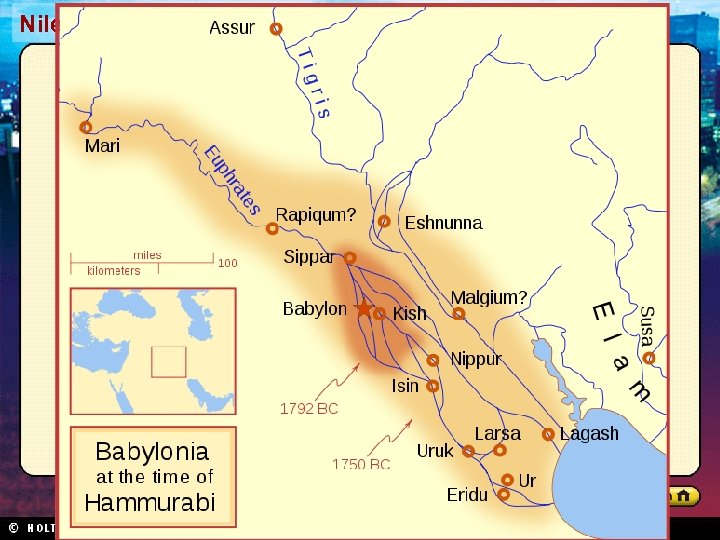
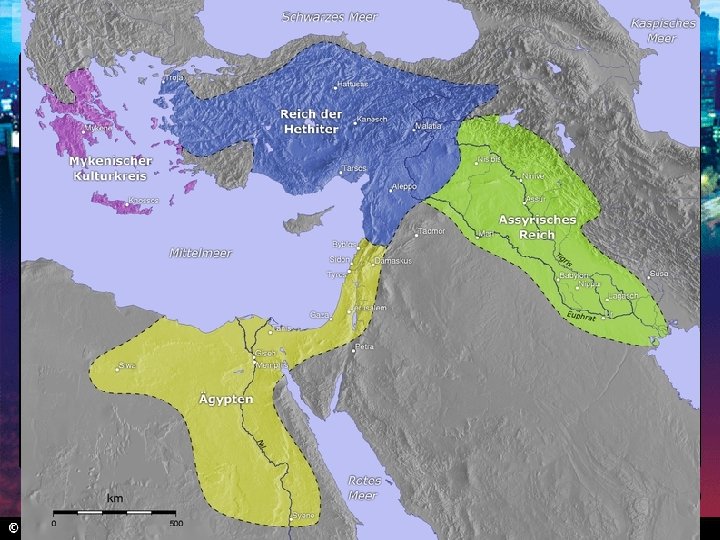
 Section 1 Nile Civilizations Empires in Mesopotamia • Each conquering invader adapted aspects of Sumerian culture. • Thus Sumerian civilization continued to influence life in Mesopotamia. Sargon’s Empire • Sargon I: – Around 2330 BC, created first permanent army – Conquered Sumer and northern Mesopotamia – Established world’s first empire (Akkadian), which lasted about 100 years • Sumerian culture spread far beyond Tigris and Euphrates valleys The Babylonian Empire • Hammurabi became king in 1792 BC • United all of Mesopotamia • Able ruler and administrator • Hammurabi’s Code: – 282 laws covering everything from trade to murder – Written for all to see – Babylon became Mesopotamia’s greatest city
Section 1 Nile Civilizations Empires in Mesopotamia • Each conquering invader adapted aspects of Sumerian culture. • Thus Sumerian civilization continued to influence life in Mesopotamia. Sargon’s Empire • Sargon I: – Around 2330 BC, created first permanent army – Conquered Sumer and northern Mesopotamia – Established world’s first empire (Akkadian), which lasted about 100 years • Sumerian culture spread far beyond Tigris and Euphrates valleys The Babylonian Empire • Hammurabi became king in 1792 BC • United all of Mesopotamia • Able ruler and administrator • Hammurabi’s Code: – 282 laws covering everything from trade to murder – Written for all to see – Babylon became Mesopotamia’s greatest city
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1 Fertile Crescent Empires Main Idea Indo-European invaders introduced new technologies to the Fertile Crescent while adapting earlier technologies developed by the civilizations they encountered there.
Nile Civilizations Section 1 Fertile Crescent Empires Main Idea Indo-European invaders introduced new technologies to the Fertile Crescent while adapting earlier technologies developed by the civilizations they encountered there.
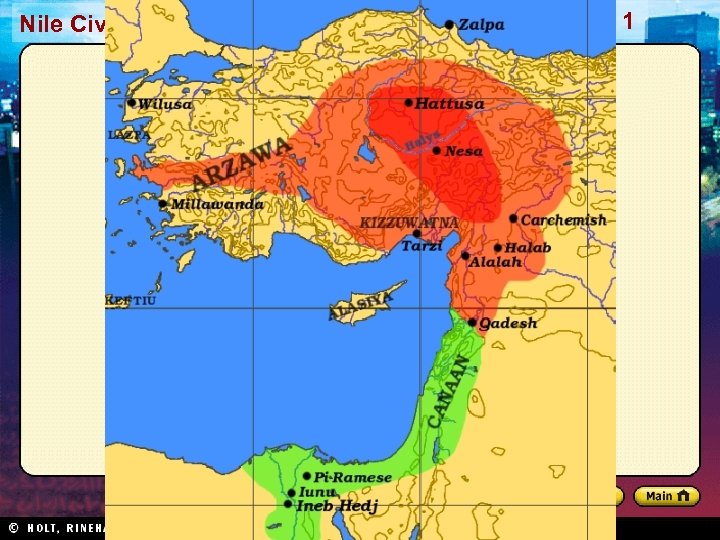
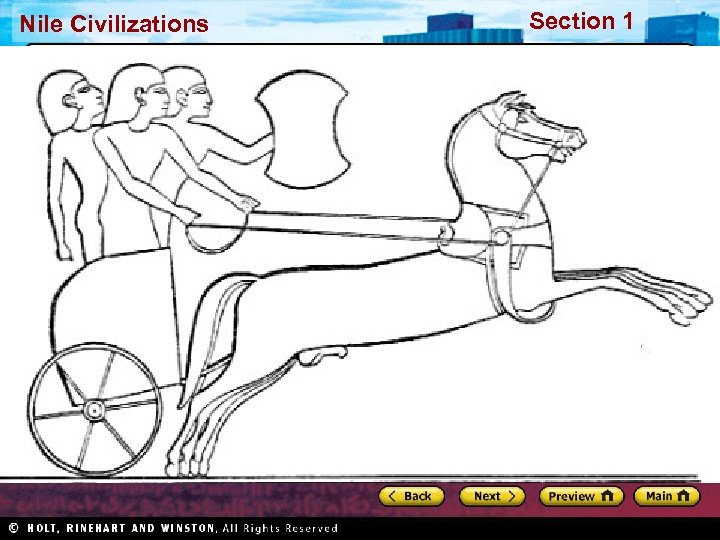
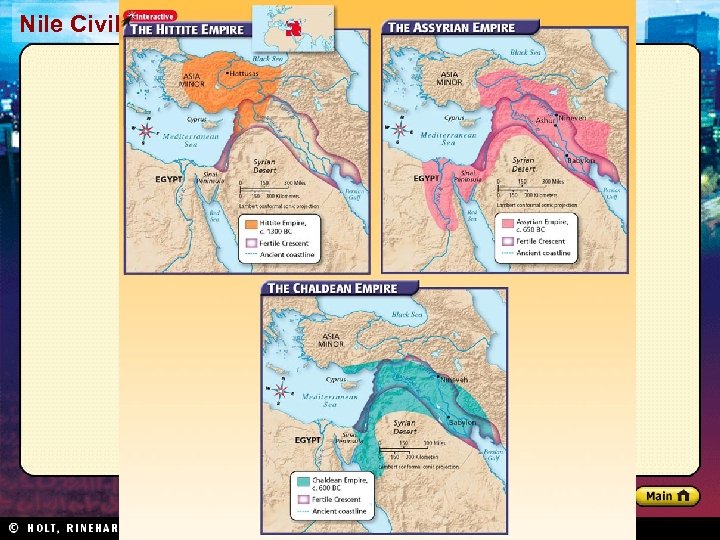
 Section 1 Nile Civilizations The Hittites Decline of Babylonian Empire • Nomadic tribes moved into the region, drawn by wealth • Included Indo-Europeans • Steppes: arid grasslands north of the Black Sea Hittite Military Might • Hittites: warlike Indo-European tribe • Built strong empire in Asia Minor (now Turkey) • Horse-drawn war chariot and new techniques Hittite Culture • Blended their culture with cultures around them • First to make objects out of iron • Rule reached peak in 1300 s BC
Section 1 Nile Civilizations The Hittites Decline of Babylonian Empire • Nomadic tribes moved into the region, drawn by wealth • Included Indo-Europeans • Steppes: arid grasslands north of the Black Sea Hittite Military Might • Hittites: warlike Indo-European tribe • Built strong empire in Asia Minor (now Turkey) • Horse-drawn war chariot and new techniques Hittite Culture • Blended their culture with cultures around them • First to make objects out of iron • Rule reached peak in 1300 s BC
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Section 1 Nile Civilizations Question: How were the Hittites able to build an empire in Asia Minor? Answer(s): With their military advantages, they were able to conquer people in surrounding areas.
Section 1 Nile Civilizations Question: How were the Hittites able to build an empire in Asia Minor? Answer(s): With their military advantages, they were able to conquer people in surrounding areas.
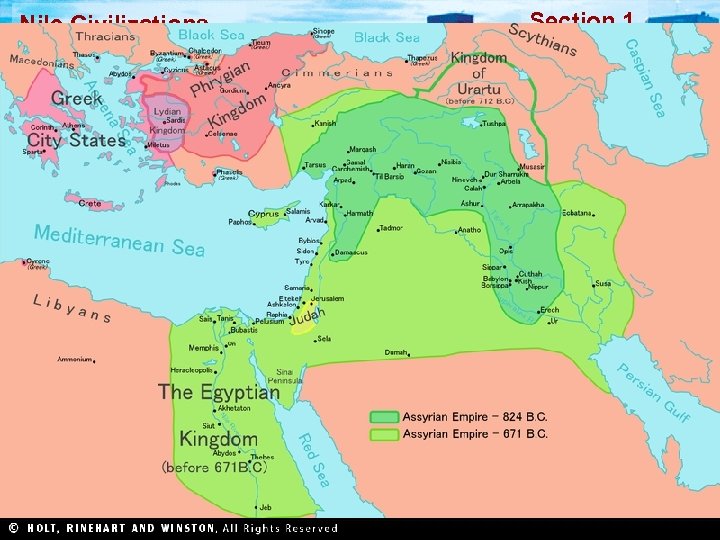
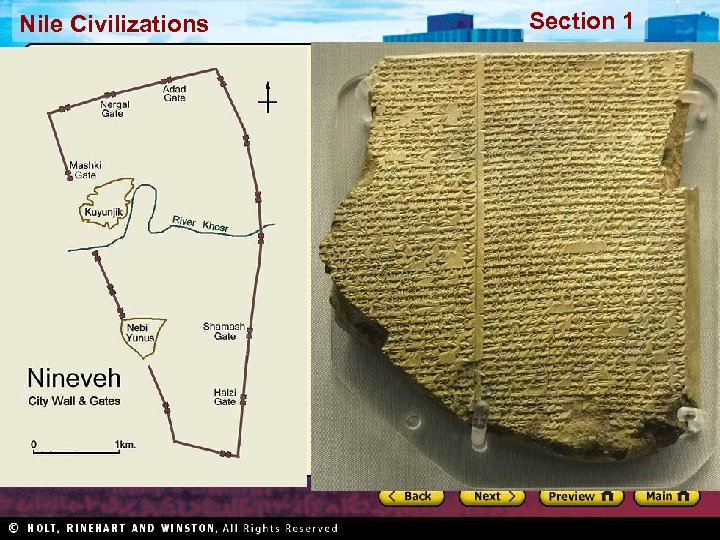
 Section 1 Nile Civilizations The Assyrians and the Chaldeans After the Hittite empire fell, other peoples fought for dominance in western Asia. In time, the Assyrians became the supreme power in the region; later the Chaldeans formed their own empire. The Assyrians • (Neo) From Northern Mesopotamia War Machine Assyrian Rule • Fierce warrior society • Efficient system • Local leaders • Barley, cattle • War chariots, foot soldiers, cavalry • Adopted Sumerian culture • Masters of siege warfare; terror • Brutal with opposition • New empire in 900 BC • Bible called it “the Land Bathed in Blood” • Cultural achievements, library – Nineveh – 22, 000 cuneiform tablets • Mesopotamia, Asia Minor, Egypt • Nineveh - capital • System of roads
Section 1 Nile Civilizations The Assyrians and the Chaldeans After the Hittite empire fell, other peoples fought for dominance in western Asia. In time, the Assyrians became the supreme power in the region; later the Chaldeans formed their own empire. The Assyrians • (Neo) From Northern Mesopotamia War Machine Assyrian Rule • Fierce warrior society • Efficient system • Local leaders • Barley, cattle • War chariots, foot soldiers, cavalry • Adopted Sumerian culture • Masters of siege warfare; terror • Brutal with opposition • New empire in 900 BC • Bible called it “the Land Bathed in Blood” • Cultural achievements, library – Nineveh – 22, 000 cuneiform tablets • Mesopotamia, Asia Minor, Egypt • Nineveh - capital • System of roads
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1 Notable Assyrian Kings • Sargon II – 721 -705 • Assurbanipal – 668 BC -627 BC • Sennacharib – 704 - • Had the library of 681 BC Nineveh built (Epic of G) • Both involved in the • Last of the Neoconquest of Israel Assyrian kings • The Ten Lost Tribes • Gave way to the Neo-Babylonians
Nile Civilizations Section 1 Notable Assyrian Kings • Sargon II – 721 -705 • Assurbanipal – 668 BC -627 BC • Sennacharib – 704 - • Had the library of 681 BC Nineveh built (Epic of G) • Both involved in the • Last of the Neoconquest of Israel Assyrian kings • The Ten Lost Tribes • Gave way to the Neo-Babylonians
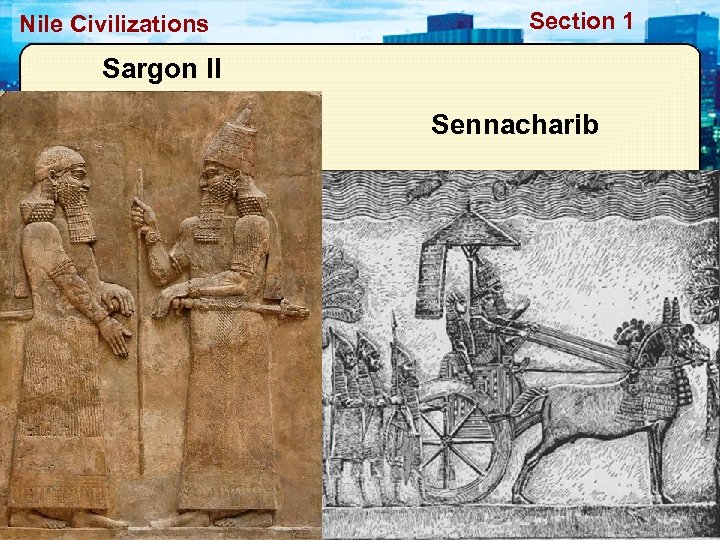 Nile Civilizations Section 1 Sargon II Sennacharib
Nile Civilizations Section 1 Sargon II Sennacharib
 Section 1 Nile Civilizations Assurbanipal
Section 1 Nile Civilizations Assurbanipal
 Nile Civilizations Section 1 The Chaldeans (Neo-Babylonians) As Assyria began to decline, the Chaldeans swooped in. • Babylon, capital of their new empire • Nebuchadnezzar II – Warrior and builder – Hanging Gardens of Babylon • Chaldean culture – Admired ancient Sumerian culture – Developed calendar; advances in astronomy
Nile Civilizations Section 1 The Chaldeans (Neo-Babylonians) As Assyria began to decline, the Chaldeans swooped in. • Babylon, capital of their new empire • Nebuchadnezzar II – Warrior and builder – Hanging Gardens of Babylon • Chaldean culture – Admired ancient Sumerian culture – Developed calendar; advances in astronomy
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1 • Biblical references: • Daniel Ch. 3 – story of the three Hebrew children who were thrown into the fiery furnace for not worshipping the Babylonian idol at Dura. • Daniel Ch. 4 • Had a bout of insanity for 7 years – boanthropy or porphyria?
Nile Civilizations Section 1 • Biblical references: • Daniel Ch. 3 – story of the three Hebrew children who were thrown into the fiery furnace for not worshipping the Babylonian idol at Dura. • Daniel Ch. 4 • Had a bout of insanity for 7 years – boanthropy or porphyria?
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
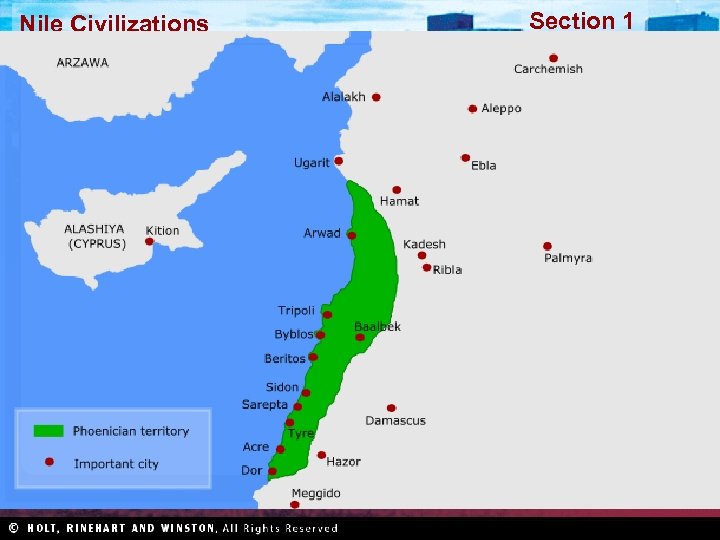
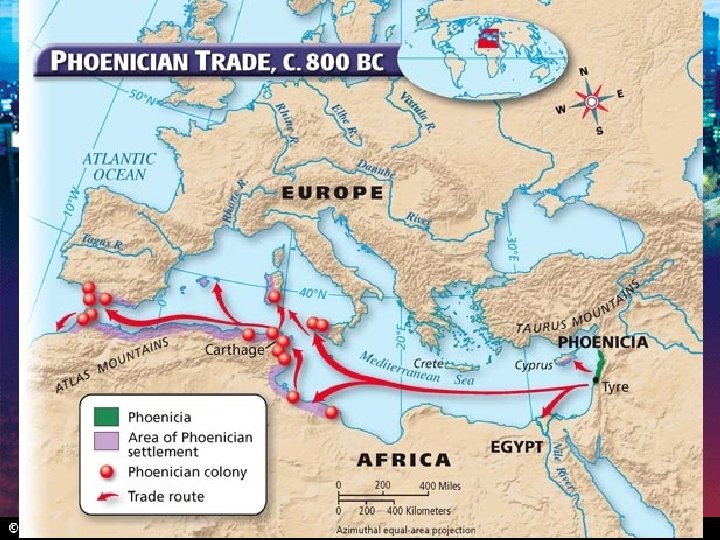
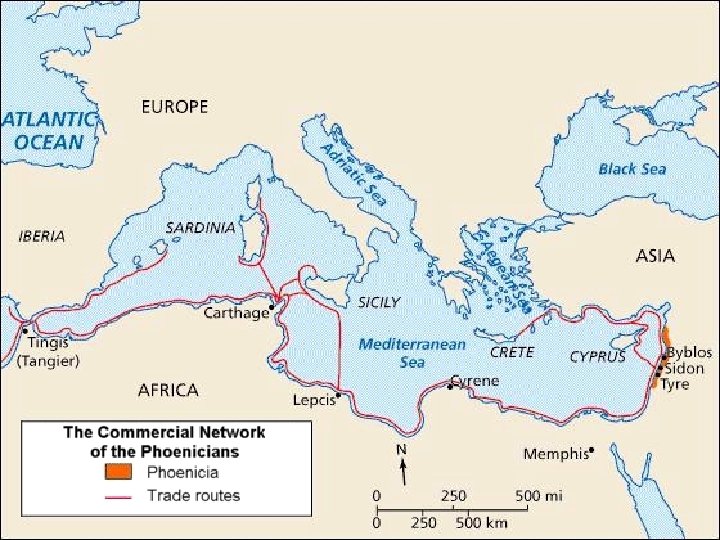
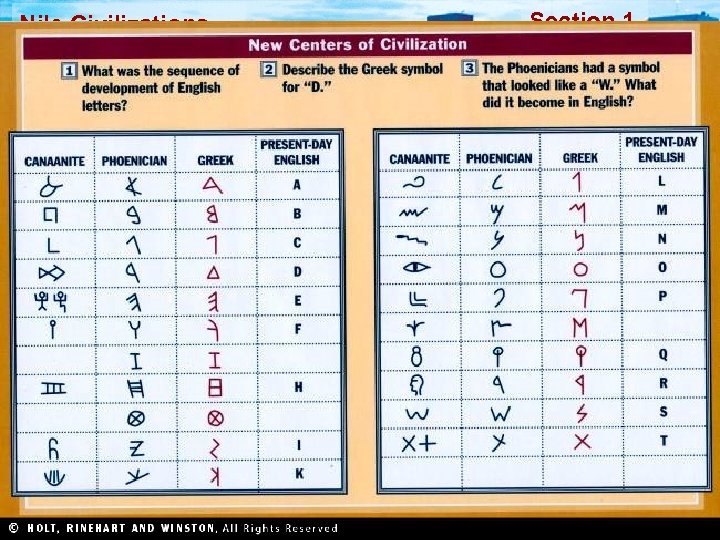
 Section 1 Nile Civilizations The Phoenicians In an area of western Asia called Phoenicia, city-states emerged as trading centers, and Phoenicians built a wealthy trading society. Trading Society • Western end of Fertile Crescent • Farming difficult • Trade and sea for livelihood • Expert sailors • Founded colonies on routes • Trade brought great wealth • Invented glassblowing • Exports: ivory, silver, slaves Alphabet • Greatest achievement • Invented by traders to record activities • Adopted by many, including the Greeks • Ancestor of the English language alphabet
Section 1 Nile Civilizations The Phoenicians In an area of western Asia called Phoenicia, city-states emerged as trading centers, and Phoenicians built a wealthy trading society. Trading Society • Western end of Fertile Crescent • Farming difficult • Trade and sea for livelihood • Expert sailors • Founded colonies on routes • Trade brought great wealth • Invented glassblowing • Exports: ivory, silver, slaves Alphabet • Greatest achievement • Invented by traders to record activities • Adopted by many, including the Greeks • Ancestor of the English language alphabet
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1 The Hebrews and Judaism Main Idea The ancient Hebrews and their religion, Judaism, have been a major influence on Western civilization.
Nile Civilizations Section 1 The Hebrews and Judaism Main Idea The ancient Hebrews and their religion, Judaism, have been a major influence on Western civilization.
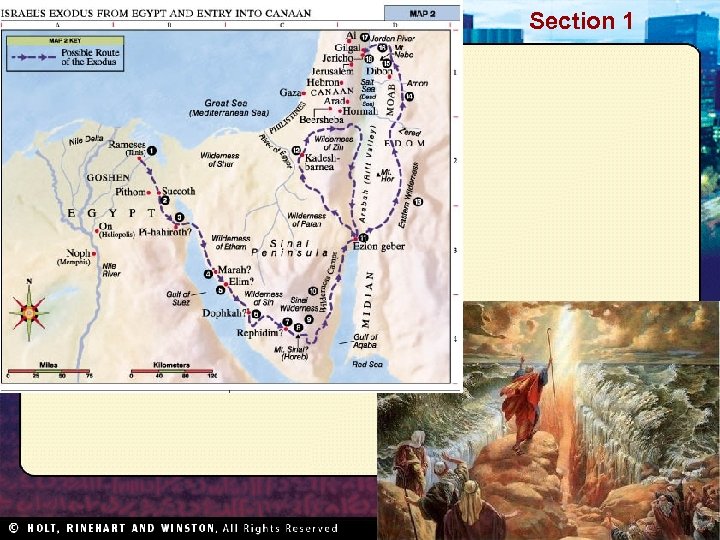
 Section 1 Nile Civilizations The Early Hebrews The Hebrews were the ancestors of the Jews, and most of what we know, including the laws and requirements of their religion, Judaism, comes from their later writings. Hebrew Fathers Moses and Exodus Promised Land • The Torah • Slaves in Egypt • Israelites in desert • Abraham, father of the Hebrews • Moses • Canaan • Pharaoh, plagues • God’s covenant • Exodus • Land of “milk and honey” • 12 Tribes of Israel • Abraham, Isaac, and Jacob were patriarchs • Israelites in Egypt – Israelites out of Egypt • Israelites battled for land – Passover • Canaan = Israel • The Ten Commandments
Section 1 Nile Civilizations The Early Hebrews The Hebrews were the ancestors of the Jews, and most of what we know, including the laws and requirements of their religion, Judaism, comes from their later writings. Hebrew Fathers Moses and Exodus Promised Land • The Torah • Slaves in Egypt • Israelites in desert • Abraham, father of the Hebrews • Moses • Canaan • Pharaoh, plagues • God’s covenant • Exodus • Land of “milk and honey” • 12 Tribes of Israel • Abraham, Isaac, and Jacob were patriarchs • Israelites in Egypt – Israelites out of Egypt • Israelites battled for land – Passover • Canaan = Israel • The Ten Commandments
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
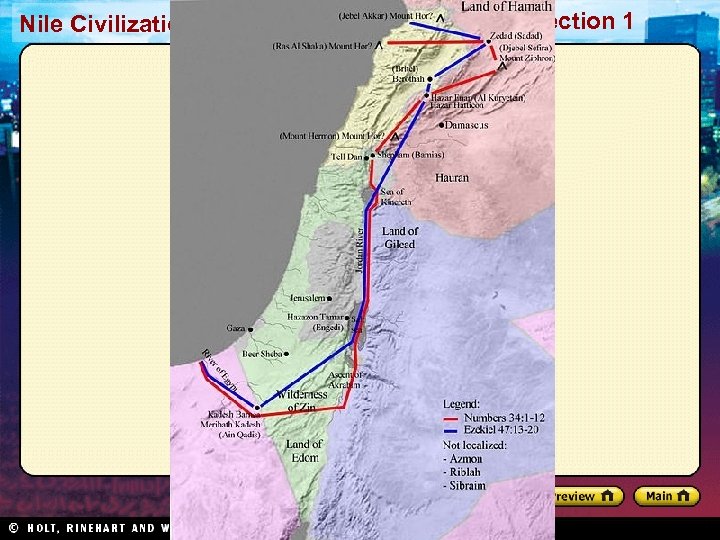
 Section 1 Nile Civilizations The Kingdom of Israel The Period of the Judges • • Scattered communities No central government Judges enforce laws Prophets keep Israelites focused on faith Saul, David, Solomon • • Israelites united against Philistines Saul, first Israelite king Never won full support David, second king Strong king, gifted poet Solomon, David’s son Israel reached height of wealth Division and Conquest • • Conflict after Solomon’s death Two kingdoms, Israel and Judah 722 BC, Israel fell to Assyrians 586 BC, Judah fell to Chaldeans enslaved Jews Diaspora = scattering of Jews Persians conquered Chaldeans
Section 1 Nile Civilizations The Kingdom of Israel The Period of the Judges • • Scattered communities No central government Judges enforce laws Prophets keep Israelites focused on faith Saul, David, Solomon • • Israelites united against Philistines Saul, first Israelite king Never won full support David, second king Strong king, gifted poet Solomon, David’s son Israel reached height of wealth Division and Conquest • • Conflict after Solomon’s death Two kingdoms, Israel and Judah 722 BC, Israel fell to Assyrians 586 BC, Judah fell to Chaldeans enslaved Jews Diaspora = scattering of Jews Persians conquered Chaldeans
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
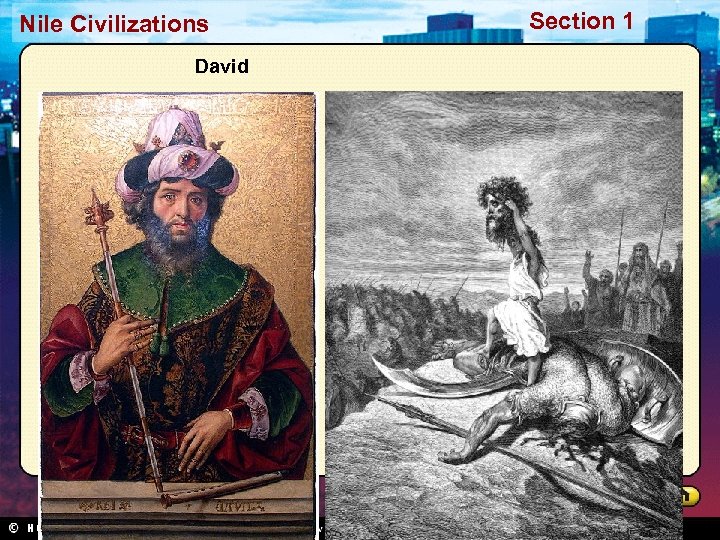 Nile Civilizations David Section 1
Nile Civilizations David Section 1
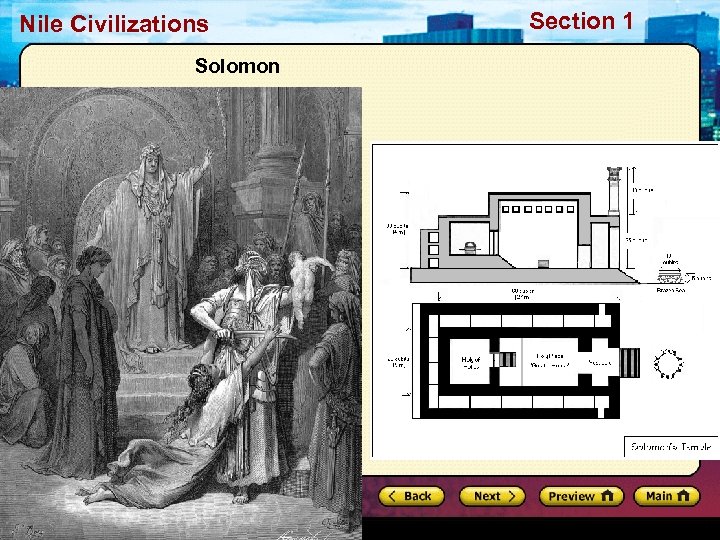 Nile Civilizations Solomon Section 1
Nile Civilizations Solomon Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1 The Teachings of Judaism Religion the foundation of Hebrew and Jewish societies • Belief in One God – Monotheism • Justice and Righteousness – Kindness, fairness, code of ethics • Obedience to the Law – Ten Commandments, Mosaic Law • Jewish Sacred Texts – Torah, Talmud, Tanakh
Nile Civilizations Section 1 The Teachings of Judaism Religion the foundation of Hebrew and Jewish societies • Belief in One God – Monotheism • Justice and Righteousness – Kindness, fairness, code of ethics • Obedience to the Law – Ten Commandments, Mosaic Law • Jewish Sacred Texts – Torah, Talmud, Tanakh
 Nile Civilizations Section 1 • Semite – descendent of Shem, son of Noah • Rabbi – teacher • Synagogue • Mitzvot – observance of the 613 commandments • Messiah – from the family of David • Covenant – between God and Abraham • Kosher • Jewish calendar – lunisolar, for holiday purposes • Revolt of the Maccabees – Seleucid Empire, statue of Zeus • Hanukkah (Chanukah) – 165 BC, 8 days, Festival of Ligths, menorah, shamash light, dreidel • Rosh Hashanah – Jewish New Year – 10 Days of Repentance • Yom Kippur – Day of Atonement, prayer and fasting • Passover – 7 days, spring, celebrates Exodus, matza • 3 branches – Orthodox, Conservative, Reform
Nile Civilizations Section 1 • Semite – descendent of Shem, son of Noah • Rabbi – teacher • Synagogue • Mitzvot – observance of the 613 commandments • Messiah – from the family of David • Covenant – between God and Abraham • Kosher • Jewish calendar – lunisolar, for holiday purposes • Revolt of the Maccabees – Seleucid Empire, statue of Zeus • Hanukkah (Chanukah) – 165 BC, 8 days, Festival of Ligths, menorah, shamash light, dreidel • Rosh Hashanah – Jewish New Year – 10 Days of Repentance • Yom Kippur – Day of Atonement, prayer and fasting • Passover – 7 days, spring, celebrates Exodus, matza • 3 branches – Orthodox, Conservative, Reform
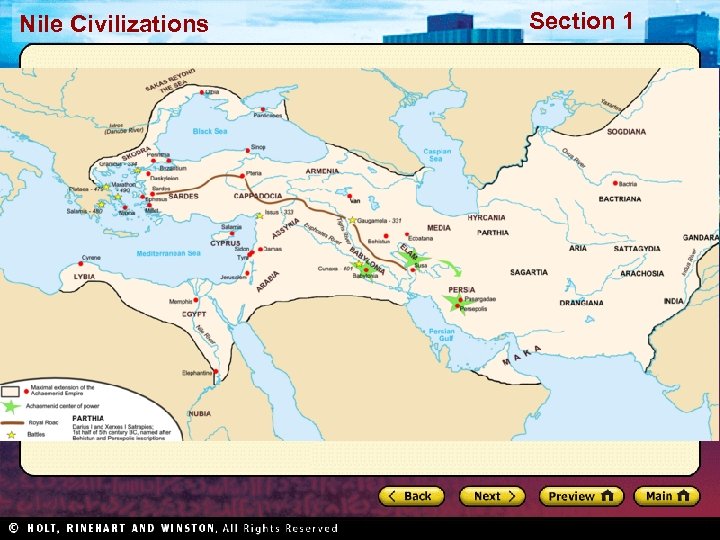
 Section 1 Nile Civilizations The Persian Empire Main Idea The Persians formed one of the largest and best governed empires in the ancient world and made great cultural achievements.
Section 1 Nile Civilizations The Persian Empire Main Idea The Persians formed one of the largest and best governed empires in the ancient world and made great cultural achievements.
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
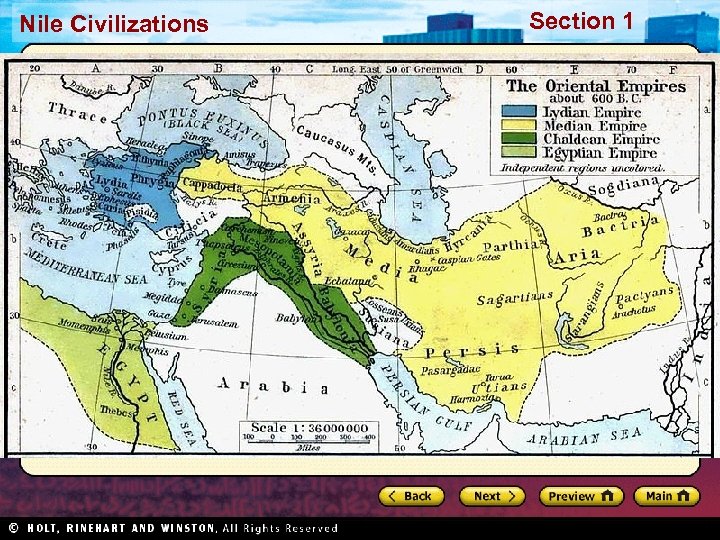
 Section 1 Nile Civilizations Persian Beginnings Persia under the Medes • Both the Medes and Persians were Indo-European tribes • Both are pre-Islamic Iranians • Medes helped Babylonians overthrow Assyria and had conquered the Persians • Persians allowed to keep their own leaders as long as they did not rebel • 559 BC – Persian King Cyrus leads a rebellion against the Medes
Section 1 Nile Civilizations Persian Beginnings Persia under the Medes • Both the Medes and Persians were Indo-European tribes • Both are pre-Islamic Iranians • Medes helped Babylonians overthrow Assyria and had conquered the Persians • Persians allowed to keep their own leaders as long as they did not rebel • 559 BC – Persian King Cyrus leads a rebellion against the Medes
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
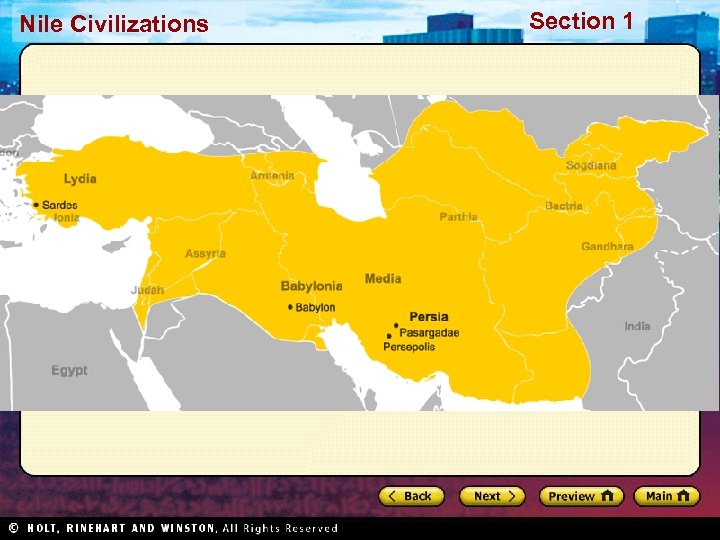
 Nile Civilizations Cyrus the Great • Defeated Medes in 559 BC • Founded and expanded the Achaemenid Persian Empire, largest in the ancient world • Freed Jews in Babylon – allowed them to rebuild their temple in Jerusalem • Respected by those he conquered • 539 BC – Defeats and ends the Neo-Babylonian Empire Section 1
Nile Civilizations Cyrus the Great • Defeated Medes in 559 BC • Founded and expanded the Achaemenid Persian Empire, largest in the ancient world • Freed Jews in Babylon – allowed them to rebuild their temple in Jerusalem • Respected by those he conquered • 539 BC – Defeats and ends the Neo-Babylonian Empire Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
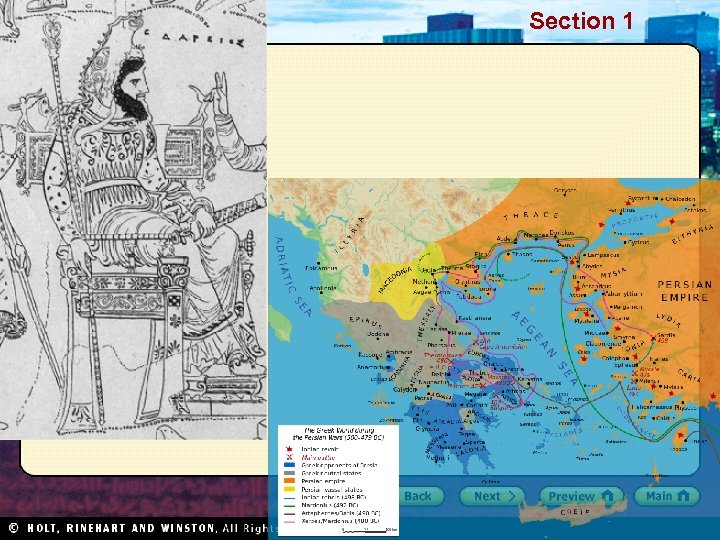
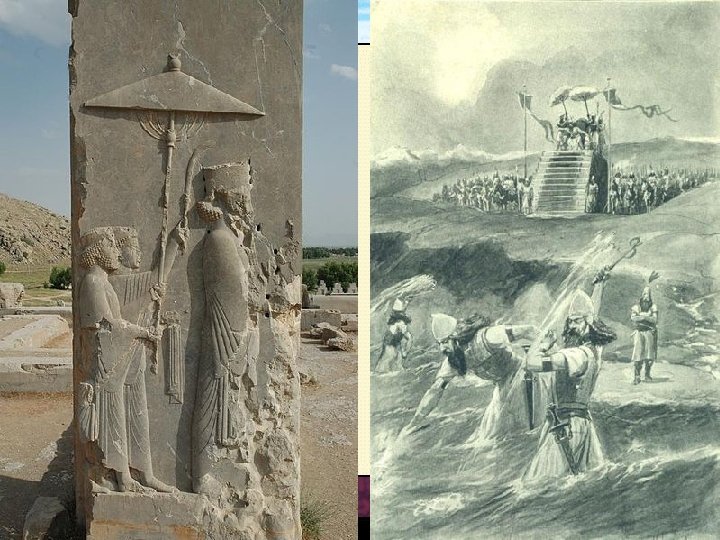
 Section 1 Nile Civilizations Darius I • Crushed rebellion after death of Cyrus’s son, rose to power in 522 BC • Created standing army, built roads, strengthened army, empire • Strong follower of Zoroastrianism • Created satraps to help govern the 20 newly provinces of the empire • 499 BC – Miletus rebellion leads to Persian Wars • 490 BC – failed invasion of Greece at Marathon • High point of Persian culture • Famous in the Bible as the king who threw Daniel into the den of lions for praying to God
Section 1 Nile Civilizations Darius I • Crushed rebellion after death of Cyrus’s son, rose to power in 522 BC • Created standing army, built roads, strengthened army, empire • Strong follower of Zoroastrianism • Created satraps to help govern the 20 newly provinces of the empire • 499 BC – Miletus rebellion leads to Persian Wars • 490 BC – failed invasion of Greece at Marathon • High point of Persian culture • Famous in the Bible as the king who threw Daniel into the den of lions for praying to God
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1 Persia in Decline • Xerxes, son of Darius, took the throne in 485 BC and failed to conquer Greece during the Persian Wars • Famous battles – Thermopylae and Salamis • Last strong ruler of Persia - praised for being just • May be King Ahaseurus in the Bible, destroyer of Babylon’s golden idol • Succeeded by son, Artaxerxes I – one of which is thought to be the husband of Ester
Nile Civilizations Section 1 Persia in Decline • Xerxes, son of Darius, took the throne in 485 BC and failed to conquer Greece during the Persian Wars • Famous battles – Thermopylae and Salamis • Last strong ruler of Persia - praised for being just • May be King Ahaseurus in the Bible, destroyer of Babylon’s golden idol • Succeeded by son, Artaxerxes I – one of which is thought to be the husband of Ester
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Section 1 Nile Civilizations Zoroastrianism During the reigns of Cyrus and Darius, a new religion called Zoroastrianism took hold, based on the teachings of Zoroaster. Teachings Spread • Ahura Mazda, source of good • Much of Persian Empire • Ahriman, evil spirit • Darius worshipped Ahura Mazda • Dualism = good and evil • Free will • The Avesta, holy text • A savior will bring triumph • New spiritual bodies, one language, evil destroyed • Other religions discouraged • The Greeks converted the Persians but never completely disappeared – often persecuted • Still exists in India and Iran • Parsees (Parsis)
Section 1 Nile Civilizations Zoroastrianism During the reigns of Cyrus and Darius, a new religion called Zoroastrianism took hold, based on the teachings of Zoroaster. Teachings Spread • Ahura Mazda, source of good • Much of Persian Empire • Ahriman, evil spirit • Darius worshipped Ahura Mazda • Dualism = good and evil • Free will • The Avesta, holy text • A savior will bring triumph • New spiritual bodies, one language, evil destroyed • Other religions discouraged • The Greeks converted the Persians but never completely disappeared – often persecuted • Still exists in India and Iran • Parsees (Parsis)
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
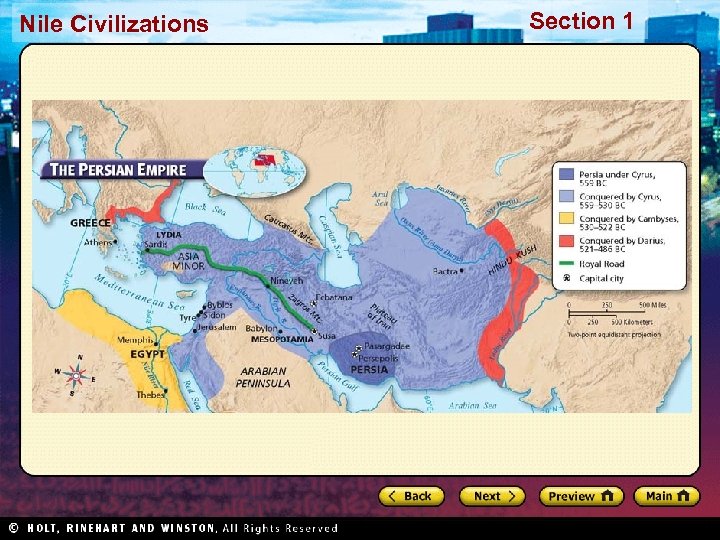
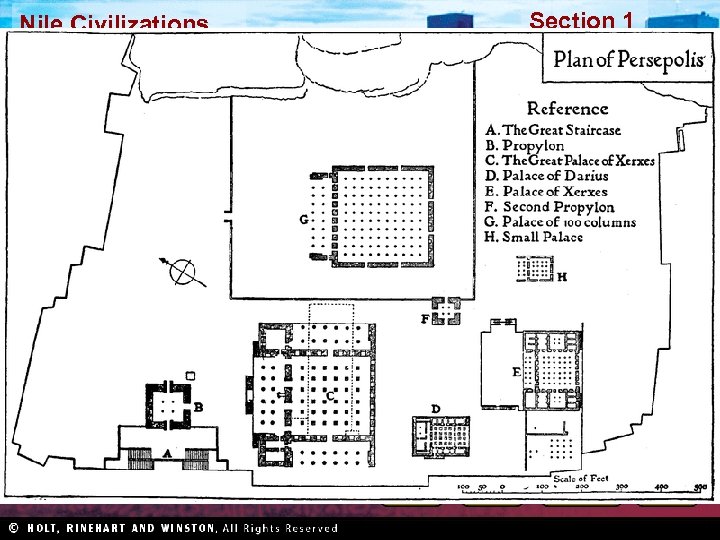
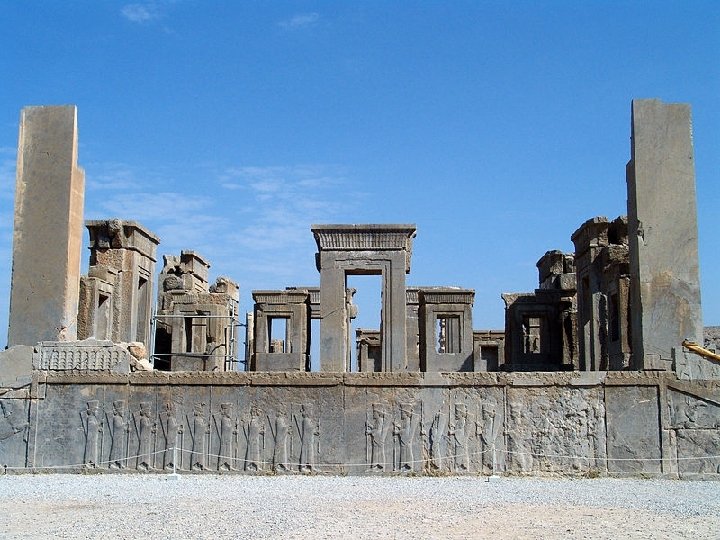
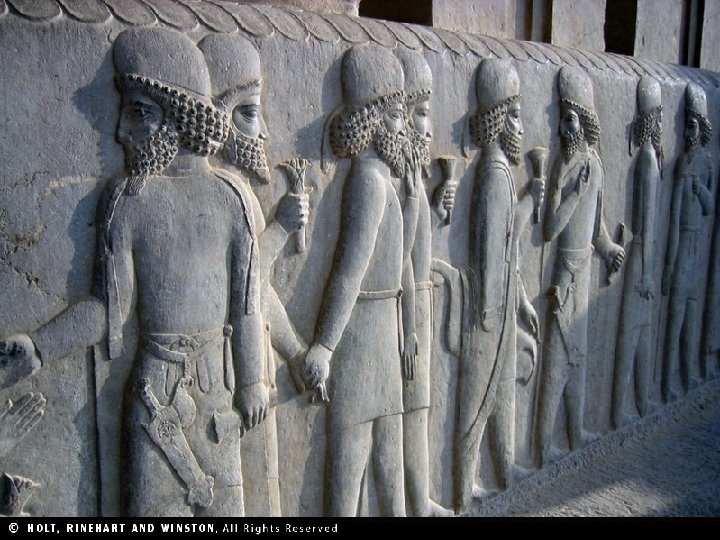
 Section 1 Nile Civilizations Persian Achievements Blended Culture • Cyrus and Darius encouraged cultural unity • Shared culture led to peace • People worked together to improve empire Communication • Network of high quality roads • Royal Road = world’s first long highway • Horseback messengers in shifts Art and Architecture • Animals a common subject • Persepolis, monument to Persia’s glory • Greatest example of Persian architecture
Section 1 Nile Civilizations Persian Achievements Blended Culture • Cyrus and Darius encouraged cultural unity • Shared culture led to peace • People worked together to improve empire Communication • Network of high quality roads • Royal Road = world’s first long highway • Horseback messengers in shifts Art and Architecture • Animals a common subject • Persepolis, monument to Persia’s glory • Greatest example of Persian architecture
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1
 Nile Civilizations Section 1
Nile Civilizations Section 1


