045b23e6d35d509f47c5af7851e3fe90.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 NIDRR Site Visit / RERC IDEA Center | ORTC
NIDRR Site Visit / RERC IDEA Center | ORTC
 “Universal design is an approach to design that incorporates products as well as building feature which, to the greatest extent feasible, can be used by everyone” (Mace, 1985). Rehabilitation technology + Environmental design Reshape the physical world using human-centered design Importance of the Problem RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
“Universal design is an approach to design that incorporates products as well as building feature which, to the greatest extent feasible, can be used by everyone” (Mace, 1985). Rehabilitation technology + Environmental design Reshape the physical world using human-centered design Importance of the Problem RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
 Keys to Advancing Universal Design 1. Clarify universal design as an evolutionary concept 2. Encourage greater integration between research and practice 3. Fill critical gaps in knowledge base 4. Develop models of successful practice 5. Support key change agents and stakeholder groups Importance of the Problem RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
Keys to Advancing Universal Design 1. Clarify universal design as an evolutionary concept 2. Encourage greater integration between research and practice 3. Fill critical gaps in knowledge base 4. Develop models of successful practice 5. Support key change agents and stakeholder groups Importance of the Problem RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
 End Users of Universal Design • People with mobility, sensory and cognitive impairments (50 million people) • Aging population(40 million by 2010) • People of extreme stature, left-handed individuals, children, urban, low-income people, pregnant women, etc. Other Key Stakeholders • Designers, builders and manufacturers of environmental features and products • Building regulatory community, including representatives of professional design and consumer advocates • Educators who disseminate knowledge and train researchers Importance of the Problem RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
End Users of Universal Design • People with mobility, sensory and cognitive impairments (50 million people) • Aging population(40 million by 2010) • People of extreme stature, left-handed individuals, children, urban, low-income people, pregnant women, etc. Other Key Stakeholders • Designers, builders and manufacturers of environmental features and products • Building regulatory community, including representatives of professional design and consumer advocates • Educators who disseminate knowledge and train researchers Importance of the Problem RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
 Mission: The RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment will research and develop critical tools for advancing the field of universal design and apply those tools to develop exemplar products through industry partnerships. Education and dissemination activities will increase awareness of the RERC activities and universal design in general as well as improve capacity in research and practice. All these activities will be founded on and guided by a model of “evidence based practice. ” RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
Mission: The RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment will research and develop critical tools for advancing the field of universal design and apply those tools to develop exemplar products through industry partnerships. Education and dissemination activities will increase awareness of the RERC activities and universal design in general as well as improve capacity in research and practice. All these activities will be founded on and guided by a model of “evidence based practice. ” RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
 The RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment Research Activities R 1 The Effectiveness of Universal Design in Practice R 2 Targeted Human Factors Studies for Design Practice Development Activities DV 1 Evidence Based Guidelines for Universal Design DV 2 Evaluation Tools DV 3 Design with Industry Partnerships Training (T) Dissemination (D) Major Projects RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
The RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment Research Activities R 1 The Effectiveness of Universal Design in Practice R 2 Targeted Human Factors Studies for Design Practice Development Activities DV 1 Evidence Based Guidelines for Universal Design DV 2 Evaluation Tools DV 3 Design with Industry Partnerships Training (T) Dissemination (D) Major Projects RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
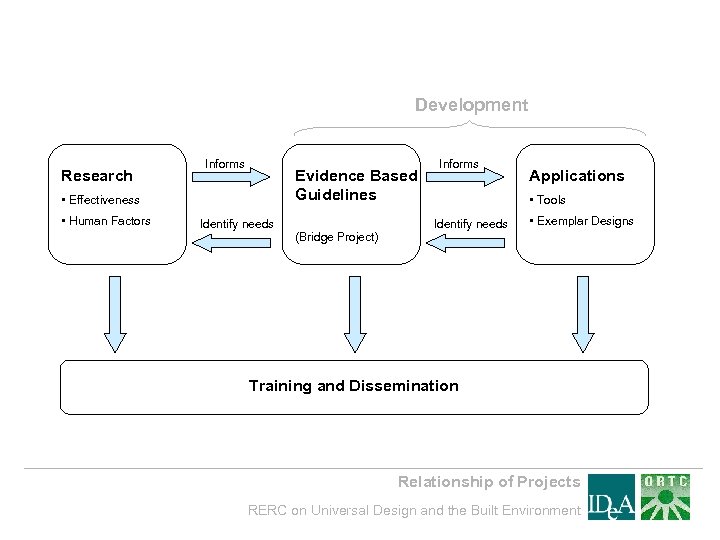 Development Research Informs Evidence Based Guidelines • Effectiveness • Human Factors Identify needs (Bridge Project) Informs Applications • Tools Identify needs • Exemplar Designs Training and Dissemination Relationship of Projects RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
Development Research Informs Evidence Based Guidelines • Effectiveness • Human Factors Identify needs (Bridge Project) Informs Applications • Tools Identify needs • Exemplar Designs Training and Dissemination Relationship of Projects RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
 R 1: The Effectiveness of Universal Design in Practice Objectives: • Identify needs and priorities for UD features • Assess the effectiveness of existing UD features • Create benchmarks for UD performance Research Hypotheses: H 1: Perceived needs for UD features will not vary significantly across different target populations H 2: Reliable and valid simulations of UD applications can be developed and used effectively by respondents with a wide range of functional limitations H 3: UD features are rated significantly higher in usability than conventional features by respondents Research Activities RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
R 1: The Effectiveness of Universal Design in Practice Objectives: • Identify needs and priorities for UD features • Assess the effectiveness of existing UD features • Create benchmarks for UD performance Research Hypotheses: H 1: Perceived needs for UD features will not vary significantly across different target populations H 2: Reliable and valid simulations of UD applications can be developed and used effectively by respondents with a wide range of functional limitations H 3: UD features are rated significantly higher in usability than conventional features by respondents Research Activities RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
 Research Methods: • Online Survey • Video simulations • Effectiveness Survey • Innovative Feature Survey Project Outputs: • Valid, reliable and affordable methods • Identify priority needs for UD • Data to inform DV 1 project • Papers submitted to peer-reviewed journals • Conference presentations Research Activities RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
Research Methods: • Online Survey • Video simulations • Effectiveness Survey • Innovative Feature Survey Project Outputs: • Valid, reliable and affordable methods • Identify priority needs for UD • Data to inform DV 1 project • Papers submitted to peer-reviewed journals • Conference presentations Research Activities RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
 R 2: Targeted Human Factors Studies for Design Practice R 2. 1 Usability and Universal Design of Products Objectives: • Apply and test UD guidelines in evaluations of 9 household products Research Hypotheses: H 1: The design guidelines will closely follow the principles of UD H 2: There will be differences in the product user and professional observer survey scores across products of the same type H 3: Wheelchair users and older adults will have greater difficulty than younger adults with products H 4: Scores on the product user and professional observer surveys will be correlated with measures of task difficulty Research Activities RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
R 2: Targeted Human Factors Studies for Design Practice R 2. 1 Usability and Universal Design of Products Objectives: • Apply and test UD guidelines in evaluations of 9 household products Research Hypotheses: H 1: The design guidelines will closely follow the principles of UD H 2: There will be differences in the product user and professional observer survey scores across products of the same type H 3: Wheelchair users and older adults will have greater difficulty than younger adults with products H 4: Scores on the product user and professional observer surveys will be correlated with measures of task difficulty Research Activities RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
 Research Methods: • Simulations of daily living tasks with products in the kitchen, bathroom or home office • Self-report usability measurement tools • Observer usability measurement tool • Analyses to identify themes, relationships of measures and differences Project Outputs: • Information on how usability can be measured • Determine how closely the Principles of UD identify the key attributes of usability • Identify differences across respondents and products Research Activities RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
Research Methods: • Simulations of daily living tasks with products in the kitchen, bathroom or home office • Self-report usability measurement tools • Observer usability measurement tool • Analyses to identify themes, relationships of measures and differences Project Outputs: • Information on how usability can be measured • Determine how closely the Principles of UD identify the key attributes of usability • Identify differences across respondents and products Research Activities RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
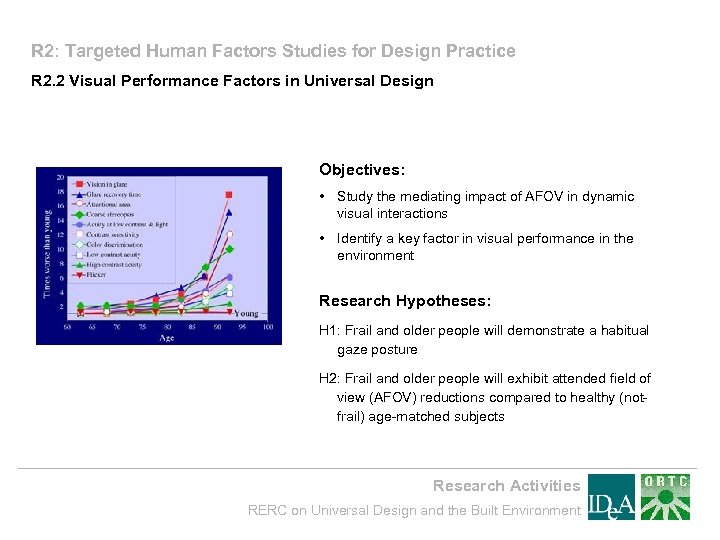 R 2: Targeted Human Factors Studies for Design Practice R 2. 2 Visual Performance Factors in Universal Design Objectives: • Study the mediating impact of AFOV in dynamic visual interactions • Identify a key factor in visual performance in the environment Research Hypotheses: H 1: Frail and older people will demonstrate a habitual gaze posture H 2: Frail and older people will exhibit attended field of view (AFOV) reductions compared to healthy (notfrail) age-matched subjects Research Activities RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
R 2: Targeted Human Factors Studies for Design Practice R 2. 2 Visual Performance Factors in Universal Design Objectives: • Study the mediating impact of AFOV in dynamic visual interactions • Identify a key factor in visual performance in the environment Research Hypotheses: H 1: Frail and older people will demonstrate a habitual gaze posture H 2: Frail and older people will exhibit attended field of view (AFOV) reductions compared to healthy (notfrail) age-matched subjects Research Activities RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
 Research Methods: • Experimental study using case-control design • Collect data on eye movements and head position and superimpose on view of visual scene • Compare the attended fields of view and habitual gaze of frail older adults to that of age-matched well elderly Project Outputs: • An understanding of the role that visual performance plays in micro-scale interactions with the environment Research Activities RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
Research Methods: • Experimental study using case-control design • Collect data on eye movements and head position and superimpose on view of visual scene • Compare the attended fields of view and habitual gaze of frail older adults to that of age-matched well elderly Project Outputs: • An understanding of the role that visual performance plays in micro-scale interactions with the environment Research Activities RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
 R 2: Targeted Human Factors Studies for Design Practice R 2. 3 The Impact of Familiarity on the Usability of Innovative Products Objectives: • Develop method to study impact of cognitive limitations on environmental interaction • Assess the impact of familiarity in the design of new, everyday products for older adults with cognitive impairments Research Questions: Q 1: How does familiarity affect the ability of an older adult with a cognitive impairment to learn to use a new product? Q 2: What aspects of familiarity are important in facilitating the learning? Q 3: Can automated data collection tools be used to study the effects of familiarity on ability? Research Activities RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
R 2: Targeted Human Factors Studies for Design Practice R 2. 3 The Impact of Familiarity on the Usability of Innovative Products Objectives: • Develop method to study impact of cognitive limitations on environmental interaction • Assess the impact of familiarity in the design of new, everyday products for older adults with cognitive impairments Research Questions: Q 1: How does familiarity affect the ability of an older adult with a cognitive impairment to learn to use a new product? Q 2: What aspects of familiarity are important in facilitating the learning? Q 3: Can automated data collection tools be used to study the effects of familiarity on ability? Research Activities RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
 Research Methods: • Subjective assessments • Direct observation of subject actions • Videotaped trials • Verbal protocol analysis • Quantitative scales that measure workload and agitation Project Outputs: • Data on how familiarity in product features influences usability for people with cognitive impairments Research Activities RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
Research Methods: • Subjective assessments • Direct observation of subject actions • Videotaped trials • Verbal protocol analysis • Quantitative scales that measure workload and agitation Project Outputs: • Data on how familiarity in product features influences usability for people with cognitive impairments Research Activities RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
 R 2: Targeted Human Factors Studies for Design Practice R 2. 4 Cold Weather Climate Study Objectives: • Gather descriptive data on: • conditions of streetscape elements in all weathers • the exposure to extreme weather Research Questions: Q 1: In what ways does winter weather alter the properties of curb ramps and bus shelters? Q 2: How do these changes affect the ability of people with mobility limitations to use the curb ramps and bus shelters easily and safely? Q 3: Is cold weather enough to create an increased risk of exposure and/or falls for older adults? Research Activities RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
R 2: Targeted Human Factors Studies for Design Practice R 2. 4 Cold Weather Climate Study Objectives: • Gather descriptive data on: • conditions of streetscape elements in all weathers • the exposure to extreme weather Research Questions: Q 1: In what ways does winter weather alter the properties of curb ramps and bus shelters? Q 2: How do these changes affect the ability of people with mobility limitations to use the curb ramps and bus shelters easily and safely? Q 3: Is cold weather enough to create an increased risk of exposure and/or falls for older adults? Research Activities RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
 Research Methods: • Gather descriptive data on: • conditions of streetscape elements in all weathers • the exposure to extreme weather Outputs: • Detailed understanding of the impact of cold weather on design of streetscapes and outdoor clothing Research Activities RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
Research Methods: • Gather descriptive data on: • conditions of streetscape elements in all weathers • the exposure to extreme weather Outputs: • Detailed understanding of the impact of cold weather on design of streetscapes and outdoor clothing Research Activities RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
 DV 1: Evidence Based Guidelines for Universal Design Objectives: • Translate research findings into practical design directives Project Outputs: • A compendium of evidence based guidelines for the domains of community infrastructure, public buildings, housing, and products used in them • An interactive public website that provides accessible information • Evaluation tools based on the guidelines for targeted applications Development Activities RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
DV 1: Evidence Based Guidelines for Universal Design Objectives: • Translate research findings into practical design directives Project Outputs: • A compendium of evidence based guidelines for the domains of community infrastructure, public buildings, housing, and products used in them • An interactive public website that provides accessible information • Evaluation tools based on the guidelines for targeted applications Development Activities RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
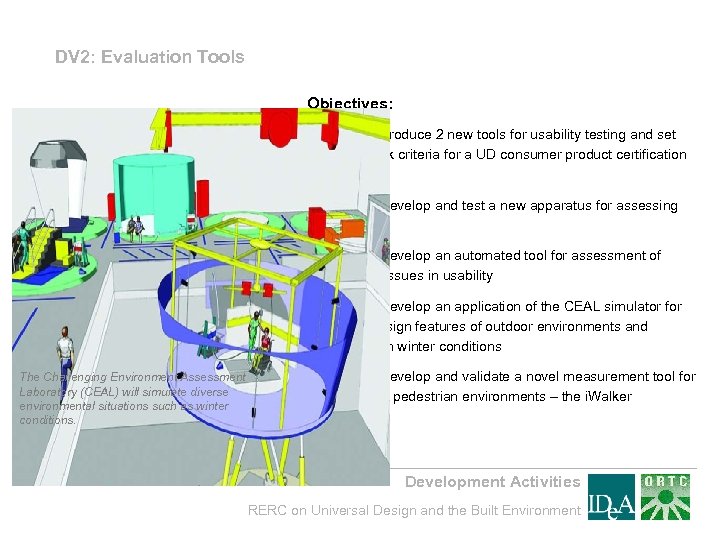 DV 2: Evaluation Tools Objectives: • DV 2. 1 – Produce 2 new tools for usability testing and set benchmark criteria for a UD consumer product certification process • DV 2. 2 – Develop and test a new apparatus for assessing AFOV • DV 2. 3 – Develop an automated tool for assessment of cognitive issues in usability • DV 2. 4 – Develop an application of the CEAL simulator for testing design features of outdoor environments and products in winter conditions The Challenging Environment Assessment Laboratory (CEAL) will simulate diverse environmental situations such as winter conditions. • DV 2. 5 – Develop and validate a novel measurement tool for evaluating pedestrian environments – the i. Walker Development Activities RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
DV 2: Evaluation Tools Objectives: • DV 2. 1 – Produce 2 new tools for usability testing and set benchmark criteria for a UD consumer product certification process • DV 2. 2 – Develop and test a new apparatus for assessing AFOV • DV 2. 3 – Develop an automated tool for assessment of cognitive issues in usability • DV 2. 4 – Develop an application of the CEAL simulator for testing design features of outdoor environments and products in winter conditions The Challenging Environment Assessment Laboratory (CEAL) will simulate diverse environmental situations such as winter conditions. • DV 2. 5 – Develop and validate a novel measurement tool for evaluating pedestrian environments – the i. Walker Development Activities RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
 DV 3: Design with Industry Partnerships Objectives: • Bring at least 3 ideas to commercialization and at least 3 more to the prototype stage Project Outputs: • DV 3. 1 – Intelligent Priority Parking Systems (IP 3) • DV 3. 2 –Touch-Smart Graphic Navigation System • DV 3. 3 – Universal Lift • DV 3. 4 – Integrated Grab Bar System • DV 3. 5 – Winter Climate Interventions • Model streetscape elements • Model bus shelters • Extreme climate mitigation systems • Winter coats Development Activities RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
DV 3: Design with Industry Partnerships Objectives: • Bring at least 3 ideas to commercialization and at least 3 more to the prototype stage Project Outputs: • DV 3. 1 – Intelligent Priority Parking Systems (IP 3) • DV 3. 2 –Touch-Smart Graphic Navigation System • DV 3. 3 – Universal Lift • DV 3. 4 – Integrated Grab Bar System • DV 3. 5 – Winter Climate Interventions • Model streetscape elements • Model bus shelters • Extreme climate mitigation systems • Winter coats Development Activities RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
 Training Objectives: • Increase understanding and build capacity for practicing universal design for designers, builders, manufacturers, standards developers, educators and students • Develop and support sustainable efforts by mentoring young faculty, producing online resources and providing advanced research opportunities Training Activities: • T 1 – Continuing Education • T 2 -- The University Education Consortium • T 3 – Universal Design Online • T 4 – Advanced Graduate Education Training RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
Training Objectives: • Increase understanding and build capacity for practicing universal design for designers, builders, manufacturers, standards developers, educators and students • Develop and support sustainable efforts by mentoring young faculty, producing online resources and providing advanced research opportunities Training Activities: • T 1 – Continuing Education • T 2 -- The University Education Consortium • T 3 – Universal Design Online • T 4 – Advanced Graduate Education Training RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
 Dissemination Outputs: • Key reference material on RERC activities • Information products based on the research, development and training programs • An information delivery system for timely and economical access to RERC information products • Outreach activities through existing networks to reach and support change agents Dissemination Activities: • D 1 – Online Information Clearinghouse • D 2 – Print Media • D 3 – Special Interest Groups • D 4 – Model Homes • D 5 – State of the Science Conference • D 6 – Guidelines for Smart Products Core Activities Dissemination RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment Spin. Offs
Dissemination Outputs: • Key reference material on RERC activities • Information products based on the research, development and training programs • An information delivery system for timely and economical access to RERC information products • Outreach activities through existing networks to reach and support change agents Dissemination Activities: • D 1 – Online Information Clearinghouse • D 2 – Print Media • D 3 – Special Interest Groups • D 4 – Model Homes • D 5 – State of the Science Conference • D 6 – Guidelines for Smart Products Core Activities Dissemination RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment Spin. Offs
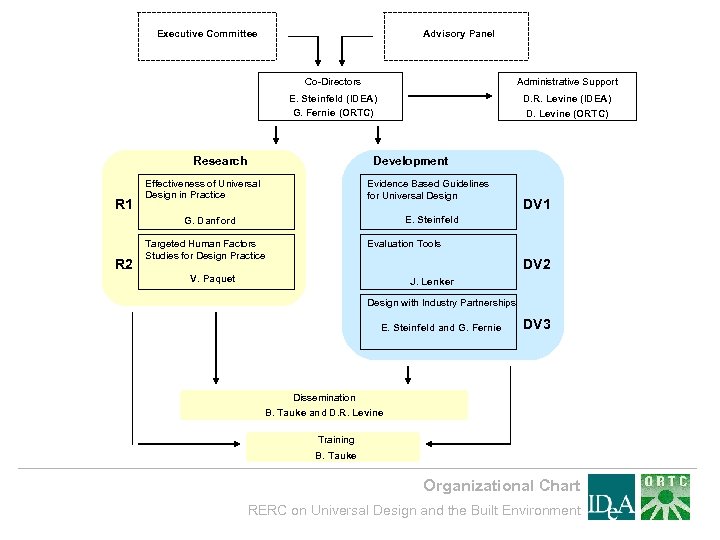 Executive Committee Advisory Panel Co-Directors Administrative Support E. Steinfeld (IDEA) G. Fernie (ORTC) D. R. Levine (IDEA) D. Levine (ORTC) Research R 1 Development Effectiveness of Universal Design in Practice Evidence Based Guidelines for Universal Design G. Danford R 2 DV 1 E. Steinfeld Targeted Human Factors Studies for Design Practice Evaluation Tools DV 2 V. Paquet J. Lenker Design with Industry Partnerships E. Steinfeld and G. Fernie DV 3 Dissemination B. Tauke and D. R. Levine Training B. Tauke Organizational Chart RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
Executive Committee Advisory Panel Co-Directors Administrative Support E. Steinfeld (IDEA) G. Fernie (ORTC) D. R. Levine (IDEA) D. Levine (ORTC) Research R 1 Development Effectiveness of Universal Design in Practice Evidence Based Guidelines for Universal Design G. Danford R 2 DV 1 E. Steinfeld Targeted Human Factors Studies for Design Practice Evaluation Tools DV 2 V. Paquet J. Lenker Design with Industry Partnerships E. Steinfeld and G. Fernie DV 3 Dissemination B. Tauke and D. R. Levine Training B. Tauke Organizational Chart RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
 Resources IDEA Center: • 5, 000 square feet—office work areas, experimental laboratory space, a library, conference room. • Accessible parking and restrooms • Equipment— Faro Arm, 3 -D motion measurement, full-scale simulation system, high end CAD and modeling; user testing lab (U. to fund) Ontario Rehabilitation Technology Consortium (ORTC): Hayes Hall University Centre • Over US$30 million in research funding; transferred 12 products to market • Toronto Rehab Institute (headquarters of ORTC) is Canada’s largest rehabilitation hospital • Equipment—simulator, latest computer-aided design stations and software, prototyping workshops, stereolithography, 3 D printing, electronic circuit design and testing equipment; 3 D motion measurement systems Resources RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
Resources IDEA Center: • 5, 000 square feet—office work areas, experimental laboratory space, a library, conference room. • Accessible parking and restrooms • Equipment— Faro Arm, 3 -D motion measurement, full-scale simulation system, high end CAD and modeling; user testing lab (U. to fund) Ontario Rehabilitation Technology Consortium (ORTC): Hayes Hall University Centre • Over US$30 million in research funding; transferred 12 products to market • Toronto Rehab Institute (headquarters of ORTC) is Canada’s largest rehabilitation hospital • Equipment—simulator, latest computer-aided design stations and software, prototyping workshops, stereolithography, 3 D printing, electronic circuit design and testing equipment; 3 D motion measurement systems Resources RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
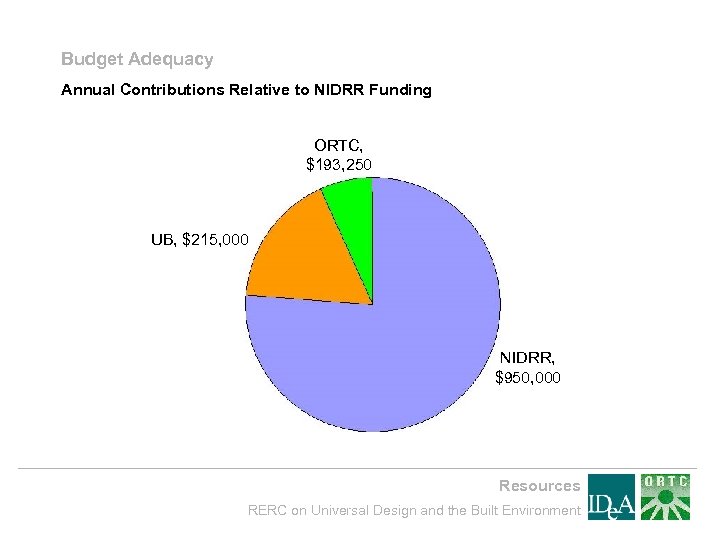 Budget Adequacy Annual Contributions Relative to NIDRR Funding ORTC, $193, 250 UB, $215, 000 NIDRR, $950, 000 Resources RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
Budget Adequacy Annual Contributions Relative to NIDRR Funding ORTC, $193, 250 UB, $215, 000 NIDRR, $950, 000 Resources RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
 Some RERC on UD at Buffalo Accomplishments… • Developed the only 3 D database on the anthropometry of wheeled mobility users • Developed evaluation methodologies for demonstrating the benefits of UD • Demonstrated value of universal design • Established a product design program to introduce innovative ideas into the market • Developed model homes toured by over 50, 000 people • Key role in expanding the visitability network and Visitability initiatives • Developed graduate concentrations in universal design in three fields at UB • Constructed key web resources on universal design • Developed and implemented a successful series of continuing education programs • Collaborated on the development of 4 exhibits that feature best practices in UD • Published extensively, including 26 peer reviewed articles, 33 book chapters, 3 books, a DVD series, a computer-based tutorial and 53 conference papers • Organized 4 symposia and workshops that identified unmet priorities and needs NIDRR Site Visit RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
Some RERC on UD at Buffalo Accomplishments… • Developed the only 3 D database on the anthropometry of wheeled mobility users • Developed evaluation methodologies for demonstrating the benefits of UD • Demonstrated value of universal design • Established a product design program to introduce innovative ideas into the market • Developed model homes toured by over 50, 000 people • Key role in expanding the visitability network and Visitability initiatives • Developed graduate concentrations in universal design in three fields at UB • Constructed key web resources on universal design • Developed and implemented a successful series of continuing education programs • Collaborated on the development of 4 exhibits that feature best practices in UD • Published extensively, including 26 peer reviewed articles, 33 book chapters, 3 books, a DVD series, a computer-based tutorial and 53 conference papers • Organized 4 symposia and workshops that identified unmet priorities and needs NIDRR Site Visit RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
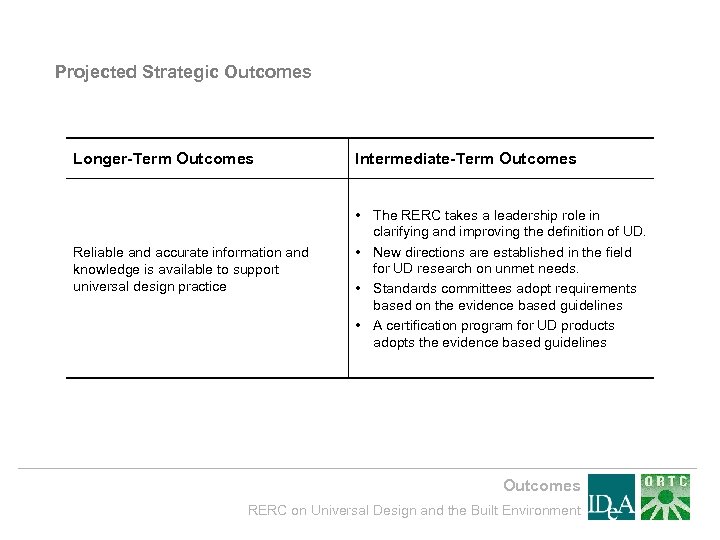 Projected Strategic Outcomes Longer-Term Outcomes Reliable and accurate information and knowledge is available to support universal design practice Intermediate-Term Outcomes • The RERC takes a leadership role in clarifying and improving the definition of UD. • New directions are established in the field for UD research on unmet needs. • Standards committees adopt requirements based on the evidence based guidelines • A certification program for UD products adopts the evidence based guidelines Outcomes RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
Projected Strategic Outcomes Longer-Term Outcomes Reliable and accurate information and knowledge is available to support universal design practice Intermediate-Term Outcomes • The RERC takes a leadership role in clarifying and improving the definition of UD. • New directions are established in the field for UD research on unmet needs. • Standards committees adopt requirements based on the evidence based guidelines • A certification program for UD products adopts the evidence based guidelines Outcomes RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
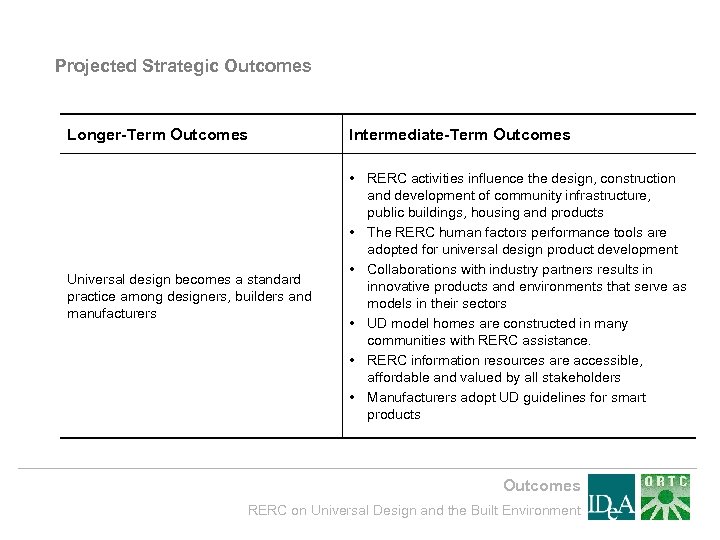 Projected Strategic Outcomes Longer-Term Outcomes Intermediate-Term Outcomes Universal design becomes a standard practice among designers, builders and manufacturers • RERC activities influence the design, construction and development of community infrastructure, public buildings, housing and products • The RERC human factors performance tools are adopted for universal design product development • Collaborations with industry partners results in innovative products and environments that serve as models in their sectors • UD model homes are constructed in many communities with RERC assistance. • RERC information resources are accessible, affordable and valued by all stakeholders • Manufacturers adopt UD guidelines for smart products Outcomes RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
Projected Strategic Outcomes Longer-Term Outcomes Intermediate-Term Outcomes Universal design becomes a standard practice among designers, builders and manufacturers • RERC activities influence the design, construction and development of community infrastructure, public buildings, housing and products • The RERC human factors performance tools are adopted for universal design product development • Collaborations with industry partners results in innovative products and environments that serve as models in their sectors • UD model homes are constructed in many communities with RERC assistance. • RERC information resources are accessible, affordable and valued by all stakeholders • Manufacturers adopt UD guidelines for smart products Outcomes RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
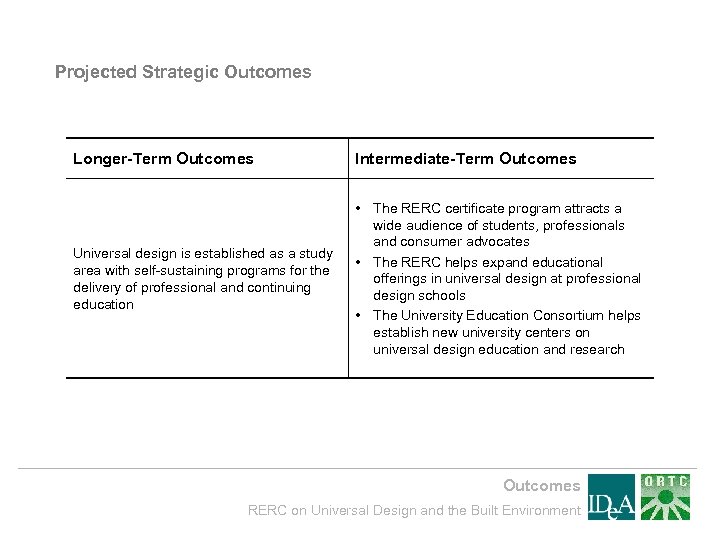 Projected Strategic Outcomes Longer-Term Outcomes Intermediate-Term Outcomes Universal design is established as a study area with self-sustaining programs for the delivery of professional and continuing education • The RERC certificate program attracts a wide audience of students, professionals and consumer advocates • The RERC helps expand educational offerings in universal design at professional design schools • The University Education Consortium helps establish new university centers on universal design education and research Outcomes RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
Projected Strategic Outcomes Longer-Term Outcomes Intermediate-Term Outcomes Universal design is established as a study area with self-sustaining programs for the delivery of professional and continuing education • The RERC certificate program attracts a wide audience of students, professionals and consumer advocates • The RERC helps expand educational offerings in universal design at professional design schools • The University Education Consortium helps establish new university centers on universal design education and research Outcomes RERC on Universal Design and the Built Environment
 IDEA Center Edward Steinfeld, Arch. D. Director; Professor of Architecture University at Buffalo 378 Hayes Hall Buffalo, NY 14214 -3087 Ontario Rehabilitation Technology Consortium (ORTC) Geoff Fernie, Ph. D. Professor, University of Toronto Vice President, Research Toronto Rehabilitation Institute Tel: 716 -829 -3485 ext. 329 TTY: 716 -829 -3758 Fax: 716 -829 -3861 Email: arced@ap. buffalo. edu Website: http: //www. ap. buffalo. edu/idea Tel: 416 -597 -3422 x 3738 Email: fernie. geoff@torontorehab. on. ca Website: http: //www. torontorehab. on. ca Contact Information IDEA Center | ORTC
IDEA Center Edward Steinfeld, Arch. D. Director; Professor of Architecture University at Buffalo 378 Hayes Hall Buffalo, NY 14214 -3087 Ontario Rehabilitation Technology Consortium (ORTC) Geoff Fernie, Ph. D. Professor, University of Toronto Vice President, Research Toronto Rehabilitation Institute Tel: 716 -829 -3485 ext. 329 TTY: 716 -829 -3758 Fax: 716 -829 -3861 Email: arced@ap. buffalo. edu Website: http: //www. ap. buffalo. edu/idea Tel: 416 -597 -3422 x 3738 Email: fernie. geoff@torontorehab. on. ca Website: http: //www. torontorehab. on. ca Contact Information IDEA Center | ORTC


