19fa507589ab6dffeadca8efea59c52b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 NFPA 306 STANDARD FOR THE CONTROL OF GAS HAZARDS ON VESSELS 2013 REVISION CYCLE A SUMMARY OF THE CHANGES
NFPA 306 STANDARD FOR THE CONTROL OF GAS HAZARDS ON VESSELS 2013 REVISION CYCLE A SUMMARY OF THE CHANGES
 Changes to 306 There were about 110 suggested changes proposed to 306, the most in recent memory. The committee initially spent two full days reviewing each proposal in January and another full day in September reviewing 49 comments on the initial proposals. As we go through the major changes in this presentation you will begin to notice a shift in 306 to enable it to provide direction for spaces which are not cargo tanks and are not adjacent to cargo tanks. This presentation will not cover every change, only the major ones.
Changes to 306 There were about 110 suggested changes proposed to 306, the most in recent memory. The committee initially spent two full days reviewing each proposal in January and another full day in September reviewing 49 comments on the initial proposals. As we go through the major changes in this presentation you will begin to notice a shift in 306 to enable it to provide direction for spaces which are not cargo tanks and are not adjacent to cargo tanks. This presentation will not cover every change, only the major ones.
 SCOPE Modified scope to show 306 can be applied to other spaces within the shipyard (Log 69, pg 4) 1. 1. 5 This standard applies specifically to those spaces on vessels that are subject to concentrations of combustible gas, flammable and toxic liquids, vapors, gases, and chemicals as here-in after described. This standard is also applicable in those spaces on vessels that might not contain sufficient oxygen to permit safe entry. This standard shall also apply may also be applied other spaces aboard vessels to ensure, and promote safe working conditions. 1. 1. 5. 1 When requested the Marine Chemist shall apply this standard to other spaces to ensure and promote safe working conditions. (Log 104, 96, 99. pg 4, 14, 60) 1. 1. 6 This standard applies to land-side confined spaces, whether stationary or mobile, underground above ground storage tanks, or other hollow structures throughout a shipyard such as tank trucks, railroad tank cars, power plant fuel tanks, storage tanks, dip and laundry tanks, vaults, tunnels or other spaces that may contain dangerous atmospheres located within the boundaries of a shipyard or ship repair facility.
SCOPE Modified scope to show 306 can be applied to other spaces within the shipyard (Log 69, pg 4) 1. 1. 5 This standard applies specifically to those spaces on vessels that are subject to concentrations of combustible gas, flammable and toxic liquids, vapors, gases, and chemicals as here-in after described. This standard is also applicable in those spaces on vessels that might not contain sufficient oxygen to permit safe entry. This standard shall also apply may also be applied other spaces aboard vessels to ensure, and promote safe working conditions. 1. 1. 5. 1 When requested the Marine Chemist shall apply this standard to other spaces to ensure and promote safe working conditions. (Log 104, 96, 99. pg 4, 14, 60) 1. 1. 6 This standard applies to land-side confined spaces, whether stationary or mobile, underground above ground storage tanks, or other hollow structures throughout a shipyard such as tank trucks, railroad tank cars, power plant fuel tanks, storage tanks, dip and laundry tanks, vaults, tunnels or other spaces that may contain dangerous atmospheres located within the boundaries of a shipyard or ship repair facility.
 Governmental Regulations Removed wording stating that the standard cannot supersede governmental regulations. OSHA stated that a NFPA standard can exceed minimum governmental regulations if the committee feels it enhances worker safety (Log 72 Pg 5) 1. 4* Governmental Regulations. Nothing in this standard shall be construed as superseding existing requirements of any governmental or local authority. The intent of this standard is to assist those using it to meet minimum governmental safety objectives. Attention of owners, repairers, and Marine Chemists is directed to the rules and regulations for tank vessels in 46 CFR 35, "Operations, " and other rules and regulations for vessel inspection of the United States Coast Guard and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration Standards (OSHA) of the United States Department of Labor, in 29 CFR 1915, which prescribe an inspection prior to making repairs involving hot work and prior to entering spaces where oxygen deficiency can exist. Those standards provide, under the conditions stated therein, for inspection by a Marine Chemist certificated by the National Fire Protection Association or, alternatively, for inspection by certain other persons. A. 1. 4 All applicable regulations, requirements, and standards should be consulted. Some of the requirements in this standard might exceed differ from minimum governmental regulations to better protect personnel and property.
Governmental Regulations Removed wording stating that the standard cannot supersede governmental regulations. OSHA stated that a NFPA standard can exceed minimum governmental regulations if the committee feels it enhances worker safety (Log 72 Pg 5) 1. 4* Governmental Regulations. Nothing in this standard shall be construed as superseding existing requirements of any governmental or local authority. The intent of this standard is to assist those using it to meet minimum governmental safety objectives. Attention of owners, repairers, and Marine Chemists is directed to the rules and regulations for tank vessels in 46 CFR 35, "Operations, " and other rules and regulations for vessel inspection of the United States Coast Guard and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration Standards (OSHA) of the United States Department of Labor, in 29 CFR 1915, which prescribe an inspection prior to making repairs involving hot work and prior to entering spaces where oxygen deficiency can exist. Those standards provide, under the conditions stated therein, for inspection by a Marine Chemist certificated by the National Fire Protection Association or, alternatively, for inspection by certain other persons. A. 1. 4 All applicable regulations, requirements, and standards should be consulted. Some of the requirements in this standard might exceed differ from minimum governmental regulations to better protect personnel and property.
 Adjacent Spaces Changed Definition 3. 3. 1 Adjacent Spaces. Those spaces in all directions from subject space, including all points of contact, corners, diagonals, decks, tank tops, and bulkheads, and including areas affected by hot work, where slag, products of combustion, and sparks would be expected to fall or accumulate. (Current wording) 3. 3. 1 Adjacent Spaces. Those spaces in all directions from subject space, including all points of contact, corners, diagonals, decks, tank tops, and bulkheads. Pipelines are not adjacent spaces and are considered Not Safe for Hot Work unless noted on the Marine Chemist Certificate. (ROC 306 -3, pg. 2) (This definition reverts back to a point of contact definition, addressing areas affected by hot work has been moved to 4. 2. 2. )
Adjacent Spaces Changed Definition 3. 3. 1 Adjacent Spaces. Those spaces in all directions from subject space, including all points of contact, corners, diagonals, decks, tank tops, and bulkheads, and including areas affected by hot work, where slag, products of combustion, and sparks would be expected to fall or accumulate. (Current wording) 3. 3. 1 Adjacent Spaces. Those spaces in all directions from subject space, including all points of contact, corners, diagonals, decks, tank tops, and bulkheads. Pipelines are not adjacent spaces and are considered Not Safe for Hot Work unless noted on the Marine Chemist Certificate. (ROC 306 -3, pg. 2) (This definition reverts back to a point of contact definition, addressing areas affected by hot work has been moved to 4. 2. 2. )
 Revised Hot Work Definition 3. 4. 2* Hot Work. Any activity involving any of the following: (A) Riveting, welding, burning, the use of powder actuated tools or similar fire producing operations, or, (B) Any operation that raises the temperature of the work piece equal to or greater than 204°C (400°F). or higher. (C)*Grinding, drilling, abrasive blasting, the activation of non-intrinsically safe or non-explosion-proof equipment or similar operations, in the presence of or against accumulations of readily combustible materials, or flammable or combustible liquids gasses or their vapors when the atmosphere exceeds 10 percent of the LEL. (Log 102 pg 16)(Changed in ROC 306 -6 pg 5) A. 3. 4. 2. (C) Grinding, drilling, abrasive blasting, or similar spark-producing operations should always be considered hot work when conducted in the presence of accumulations of flammable gases, flammable or combustible liquids, their vapors or accumulations of other common combustible materials. (ROP 306 -106 pg 60)
Revised Hot Work Definition 3. 4. 2* Hot Work. Any activity involving any of the following: (A) Riveting, welding, burning, the use of powder actuated tools or similar fire producing operations, or, (B) Any operation that raises the temperature of the work piece equal to or greater than 204°C (400°F). or higher. (C)*Grinding, drilling, abrasive blasting, the activation of non-intrinsically safe or non-explosion-proof equipment or similar operations, in the presence of or against accumulations of readily combustible materials, or flammable or combustible liquids gasses or their vapors when the atmosphere exceeds 10 percent of the LEL. (Log 102 pg 16)(Changed in ROC 306 -6 pg 5) A. 3. 4. 2. (C) Grinding, drilling, abrasive blasting, or similar spark-producing operations should always be considered hot work when conducted in the presence of accumulations of flammable gases, flammable or combustible liquids, their vapors or accumulations of other common combustible materials. (ROP 306 -106 pg 60)
 Changes to Calibration Wording 4. 2. 1. 1* The accuracy and sampling integrity of all instruments used by the Marine Chemist shall be verified before each day's use. by using with a known concentration of test gases in a manner consistent with the manufacturer's recommendations. 4. 2. 1. 2 Calibration of sensors shall be verified using a known concentration of test gas. in a manner consistent with the manufacturer's recommendations. 4. 2. 1. 2 3 A record of verification of accuracy or calibration This record of calibration shall be maintained for at least 3 months. A. 4. 2. 1. 1 It is recognized that in limited circumstances the marine chemist may not be able to transport compressed calibration gas by air. In these limited cases the chemist shall should make every attempt to verify the accuracy of their instruments prior to use. (Logs 75 and 76 Pg. 18)
Changes to Calibration Wording 4. 2. 1. 1* The accuracy and sampling integrity of all instruments used by the Marine Chemist shall be verified before each day's use. by using with a known concentration of test gases in a manner consistent with the manufacturer's recommendations. 4. 2. 1. 2 Calibration of sensors shall be verified using a known concentration of test gas. in a manner consistent with the manufacturer's recommendations. 4. 2. 1. 2 3 A record of verification of accuracy or calibration This record of calibration shall be maintained for at least 3 months. A. 4. 2. 1. 1 It is recognized that in limited circumstances the marine chemist may not be able to transport compressed calibration gas by air. In these limited cases the chemist shall should make every attempt to verify the accuracy of their instruments prior to use. (Logs 75 and 76 Pg. 18)
 Marine Chemist Determinations 4. 2. 2 The Marine Chemist's determinations shall include a visual inspection and tests of the spaces to be certified, and for repair or alterations involving hot work, all adjacent cargo tanks, spaces adjacent to cargo tanks, and other adjacent spaces containing or having contained flammable or combustible cargo, fuels, or oils spaces and other spaces/areas that may be affected by the hot work are treated in accordance with 4. 3. 4(4) and 4. 3. 4(5). The inspection shall include spaces or areas where products of hot work such as sparks, slag or embers can act as ignition sources. The determinations also shall include the following: (1) The three previous cargo loadings (2) Nature and extent of the work (3) Starting time and duration of the work (4) Tests of cargo and vent lines at manifolds and accessible openings associated with the scope of work on or in the compartments concerned (5) Verification that pipelines that could release hazardous materials into spaces that will be certified for entry and/or hot work ATMOSPHERE SAFE FOR WORKERS or SAFE FOR HOT WORK are either disconnected, blanked off, or otherwise blocked by a positive method, or the valves are positioned and tagged in such a manner to prevent, or by written notice restrict, operation (6) Tests of cargo heating coils. (7) In spaces which are not cargo tanks or are not adjacent to cargo tanks the Marine Chemist shall carry out tests to determine the atmospheric or fire hazards that may exist within each affected compartment or space, and any adjacent spaces which may be affected by hot work, ensuring compliance with the minimum applicable requirements prior to issuing a Certificate. (ROP 306 -29 pg. 20. ROC Pg 8 Log 18)
Marine Chemist Determinations 4. 2. 2 The Marine Chemist's determinations shall include a visual inspection and tests of the spaces to be certified, and for repair or alterations involving hot work, all adjacent cargo tanks, spaces adjacent to cargo tanks, and other adjacent spaces containing or having contained flammable or combustible cargo, fuels, or oils spaces and other spaces/areas that may be affected by the hot work are treated in accordance with 4. 3. 4(4) and 4. 3. 4(5). The inspection shall include spaces or areas where products of hot work such as sparks, slag or embers can act as ignition sources. The determinations also shall include the following: (1) The three previous cargo loadings (2) Nature and extent of the work (3) Starting time and duration of the work (4) Tests of cargo and vent lines at manifolds and accessible openings associated with the scope of work on or in the compartments concerned (5) Verification that pipelines that could release hazardous materials into spaces that will be certified for entry and/or hot work ATMOSPHERE SAFE FOR WORKERS or SAFE FOR HOT WORK are either disconnected, blanked off, or otherwise blocked by a positive method, or the valves are positioned and tagged in such a manner to prevent, or by written notice restrict, operation (6) Tests of cargo heating coils. (7) In spaces which are not cargo tanks or are not adjacent to cargo tanks the Marine Chemist shall carry out tests to determine the atmospheric or fire hazards that may exist within each affected compartment or space, and any adjacent spaces which may be affected by hot work, ensuring compliance with the minimum applicable requirements prior to issuing a Certificate. (ROP 306 -29 pg. 20. ROC Pg 8 Log 18)
 Toxicity Testing Change to the Body of 306 4. 3. 1(3)* Any toxic chemicals in the atmosphere associated with cargo, fuel, tank coatings, inerting mediums, adjacent spaces, or fumigants are within permissible concentrations at the time of inspection. NO CHANGE TO TOXICITY DIRECTION (ROC 306 -14 Log 30 pg. 13)
Toxicity Testing Change to the Body of 306 4. 3. 1(3)* Any toxic chemicals in the atmosphere associated with cargo, fuel, tank coatings, inerting mediums, adjacent spaces, or fumigants are within permissible concentrations at the time of inspection. NO CHANGE TO TOXICITY DIRECTION (ROC 306 -14 Log 30 pg. 13)
 TOXICITY TESTING QUESTIONS If a PEL and a TLV exist for a substance does 306 require the CMC to use the lower of the two? If there is no PEL listed does but there is a TLV, does 306 require the CMC to use the TLV? If there is no PEL does 306 require the CMC to make any measurement at all? What is the definition of "permissible concentrations"
TOXICITY TESTING QUESTIONS If a PEL and a TLV exist for a substance does 306 require the CMC to use the lower of the two? If there is no PEL listed does but there is a TLV, does 306 require the CMC to use the TLV? If there is no PEL does 306 require the CMC to make any measurement at all? What is the definition of "permissible concentrations"
 ASFW Change 4. 3. 1. (4) 4. 3. 1* ATMOSPHERE SAFE FOR WORKERS requires that in the compartment or space so designated the following criteria shall be met at the time the Certificate is issued: (1) *The oxygen content of the atmosphere is at least 19. 5 percent and not greater than 22 percent by volume. (2)*The concentration of flammable materials is below 10 percent of the lower explosive limit (LEL). (3) *Any toxic chemicals in the atmosphere associated with cargo, fuel, tank coatings, inerting mediums, adjacent spaces, or fumigants are within permissible concentrations at the time of the inspection. Exception: Further testing of toxic materials shall not be required if previous testing indicates that these materials have been eliminated M are not capable of regeneration to hazardous levels while maintained as directed on the Marine Chemist's Certificate. (4) *The residues or chemicals remaining in a certified space associated with the work authorized by the Certificate are not capable of producing unacceptable chemicals concentrations of toxic materials that exceed permissible concentrations under existing atmospheric conditions while maintained as directed on the certificate. (ROC Log 47, Pg. 16)
ASFW Change 4. 3. 1. (4) 4. 3. 1* ATMOSPHERE SAFE FOR WORKERS requires that in the compartment or space so designated the following criteria shall be met at the time the Certificate is issued: (1) *The oxygen content of the atmosphere is at least 19. 5 percent and not greater than 22 percent by volume. (2)*The concentration of flammable materials is below 10 percent of the lower explosive limit (LEL). (3) *Any toxic chemicals in the atmosphere associated with cargo, fuel, tank coatings, inerting mediums, adjacent spaces, or fumigants are within permissible concentrations at the time of the inspection. Exception: Further testing of toxic materials shall not be required if previous testing indicates that these materials have been eliminated M are not capable of regeneration to hazardous levels while maintained as directed on the Marine Chemist's Certificate. (4) *The residues or chemicals remaining in a certified space associated with the work authorized by the Certificate are not capable of producing unacceptable chemicals concentrations of toxic materials that exceed permissible concentrations under existing atmospheric conditions while maintained as directed on the certificate. (ROC Log 47, Pg. 16)
 Enter With Restrictions New Requirement 4. 3. 3(1) The Certificate shall include a statement describing the specific conditions of personal protection equipment, or clothing, or time, or any, or all of the aforementioned. These areas shall be listed on the Certificate under the heading "Restrictions. " (Log 39 Pg. 28)
Enter With Restrictions New Requirement 4. 3. 3(1) The Certificate shall include a statement describing the specific conditions of personal protection equipment, or clothing, or time, or any, or all of the aforementioned. These areas shall be listed on the Certificate under the heading "Restrictions. " (Log 39 Pg. 28)
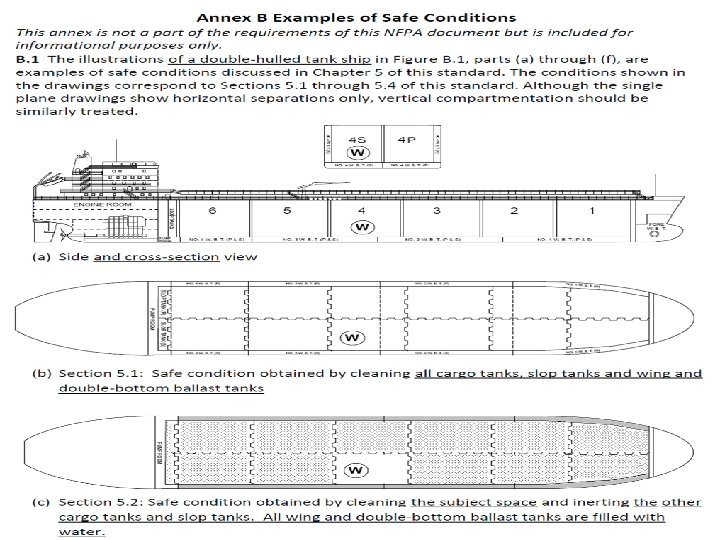
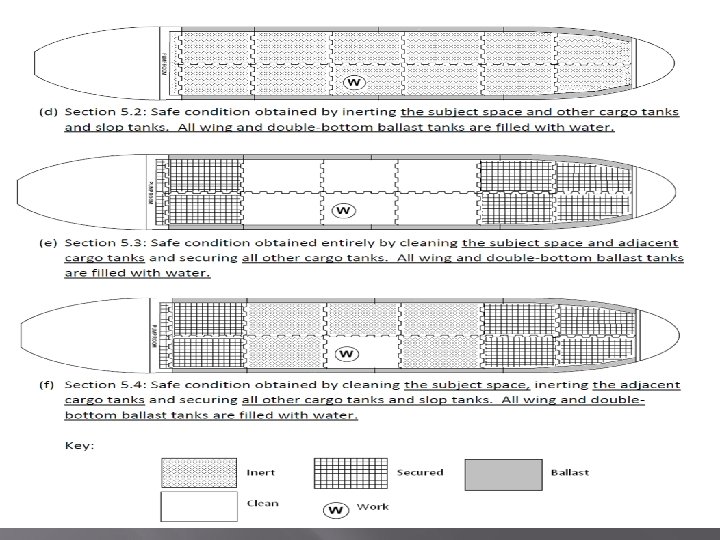
 Revised Safe for Hot Work Definition 4. 3. 4 SAFE FOR HOT WORK requires that in the compartment or space so designated, the following criteria shall be met at the time the Certificate is issued: (1) *The oxygen content of the atmosphere is not greater than 22 percent by volume. (2)*The concentration of flammable materials in the atmosphere is less than 10 percent of the LEL. (3) The residues, scale, or soft and greasy coatings in the entire space are cleaned sufficiently to prevent the spread of fire and are not capable of producing a higher concentration than permitted by 4. 3. 4(1) or (2) under existing atmospheric conditions in the presence of hot work and while maintained as directed on the Certificate. or, in the case of the engine room or fire room bilges, or other machinery spaces, or spaces that have not contained flammable or combustible cargo, fuels, or coils are treated in accordance with the Marine Chemist's requirements. ( from Log 5, pg 30. ROC 306 -21 pg 18) (4) All spaces adjacent to cargo tanks to be certified "Safe for Hot Work", as well as any cargo tank adjacent to a hot work site, have combustible gas readings less than 10 percent of the LEL, have been cleaned sufficiently of residues, scale or preservative coatings to prevent the spread of fire, or are have been inerted. (from Log 53, pg 32) (5) Non-cargo tank spaces adjacent to cargo spaces certified “SAFE FOR HOT WORK” must be treated in accordance with Marine Chemist requirements and acknowledged on the Certificate. (from Log 7 pg 34) (6) Spaces such as passage ways, living spaces or store rooms which are not adjacent to cargo tanks, and are undergoing hot work, must meet the requirements of section 4. 3. 4 (1) and (2). These spaces along with any adjacent spaces shall be treated in accordance with the Marine Chemists instructions and be free of material which could ignite under conditions of work or be protected with barriers to prevent the spread of fire. (from Log 8, pg 34) (7) The residues scale, or preservative coatings in the entire space are cleaned sufficiently to prevent the spread of fire and are not capable of producing a higher concentration than permitted by 4. 3. 4(1) or (2) under existing atmospheric conditions in the presence of hot work and while maintained as directed on the Certificate. or, in In the case of the Engine room or fire room bilges, or other machinery spaces, or spaces that have not contained flammable or combustible cargo, fuels, or oils they are treated in accordance with the Marine Chemist's requirements. (from Log 5, pg 30, ROC 306 -25)
Revised Safe for Hot Work Definition 4. 3. 4 SAFE FOR HOT WORK requires that in the compartment or space so designated, the following criteria shall be met at the time the Certificate is issued: (1) *The oxygen content of the atmosphere is not greater than 22 percent by volume. (2)*The concentration of flammable materials in the atmosphere is less than 10 percent of the LEL. (3) The residues, scale, or soft and greasy coatings in the entire space are cleaned sufficiently to prevent the spread of fire and are not capable of producing a higher concentration than permitted by 4. 3. 4(1) or (2) under existing atmospheric conditions in the presence of hot work and while maintained as directed on the Certificate. or, in the case of the engine room or fire room bilges, or other machinery spaces, or spaces that have not contained flammable or combustible cargo, fuels, or coils are treated in accordance with the Marine Chemist's requirements. ( from Log 5, pg 30. ROC 306 -21 pg 18) (4) All spaces adjacent to cargo tanks to be certified "Safe for Hot Work", as well as any cargo tank adjacent to a hot work site, have combustible gas readings less than 10 percent of the LEL, have been cleaned sufficiently of residues, scale or preservative coatings to prevent the spread of fire, or are have been inerted. (from Log 53, pg 32) (5) Non-cargo tank spaces adjacent to cargo spaces certified “SAFE FOR HOT WORK” must be treated in accordance with Marine Chemist requirements and acknowledged on the Certificate. (from Log 7 pg 34) (6) Spaces such as passage ways, living spaces or store rooms which are not adjacent to cargo tanks, and are undergoing hot work, must meet the requirements of section 4. 3. 4 (1) and (2). These spaces along with any adjacent spaces shall be treated in accordance with the Marine Chemists instructions and be free of material which could ignite under conditions of work or be protected with barriers to prevent the spread of fire. (from Log 8, pg 34) (7) The residues scale, or preservative coatings in the entire space are cleaned sufficiently to prevent the spread of fire and are not capable of producing a higher concentration than permitted by 4. 3. 4(1) or (2) under existing atmospheric conditions in the presence of hot work and while maintained as directed on the Certificate. or, in In the case of the Engine room or fire room bilges, or other machinery spaces, or spaces that have not contained flammable or combustible cargo, fuels, or oils they are treated in accordance with the Marine Chemist's requirements. (from Log 5, pg 30, ROC 306 -25)
 SFLHW Changes 4. 3. 6 SAFE FOR LIMITED HOT WORK indicates that all of the following criteria shall be met at the time the Certificate is issued: (1) Any compartment or space so designated meets the requirements of 4. 3. 4(1) and 4. 3. 4(2) (unless inerted in accordance with 4. 3. 8). (2) The Certificate shall include a statement describing the specific location and type of the hot work. The Marine Chemist shall also be permitted to list any areas to be excluded from hot work. These areas shall be listed on the Certificate under the heading "limitations. " (3) The space meets one of the following conditions: (a) The space or compartment is inerted in accordance with 4. 3. 8, adjacent spaces shall be treated in accordance with 4. 3. 4( 4), and the hot work shall be limited to the specific location or locations described in the "limitations" in 4. 3. 6(2). The marine chemist shall ensure At the time of the inspection the Marine Chemist shall verify that the atmospheres of adjacent space(s) meet the requirements of sections below in accordance with 4. 3. 4 (4) or (5), or are inerted. (ROP 306 -56) (b) The space or compartment meets the requirements of 4. 3. 4 (1), (2), (3) and (4); and adjacent spaces meet 4. 3. 4 (4) or (5) and the hot work shall not be allowed on adjacent spaces or pipelines. or both as applicable; and The hot work limitations restrictions shall be described in the listed under "limitations" in accordance with 4. 3. 6(2). The marine chemist shall ensure that the atmospheres of adjacent space(s) are maintained below 10%, of the lower explosive level concentration of flammable materials in the atmosphere is less than 10 percent of the LEL or are inerted. (ROP 306 -56) (c) Portions of the space or compartment meet the requirements of 4. 3. 4(3) and (4), and (5) as well as applicable portions of 5. 1. 3 and the hot work shall be limited to the location or locations described listed under "limitations" in accordance with 4. 3. 6(2). (d) In compartments/spaces on vessels, that are not considered cargo or fuel spaces and have not contained and are not subject to concentrations of combustible, flammable or toxic liquids, vapors, or gases, the Marine Chemist shall survey the spaces and adjacent spaces in accordance with Section 4. 2. 2. The Certificate shall include a statement under the heading "Limitations" describing the locations and type of Hot Work along with any directions for the Competent Person to maintain safe work conditions. (ROP 306 -55) maintain replaced ensure in ROC) (Log 81, Pg 37 and Log 66 Pg 36)
SFLHW Changes 4. 3. 6 SAFE FOR LIMITED HOT WORK indicates that all of the following criteria shall be met at the time the Certificate is issued: (1) Any compartment or space so designated meets the requirements of 4. 3. 4(1) and 4. 3. 4(2) (unless inerted in accordance with 4. 3. 8). (2) The Certificate shall include a statement describing the specific location and type of the hot work. The Marine Chemist shall also be permitted to list any areas to be excluded from hot work. These areas shall be listed on the Certificate under the heading "limitations. " (3) The space meets one of the following conditions: (a) The space or compartment is inerted in accordance with 4. 3. 8, adjacent spaces shall be treated in accordance with 4. 3. 4( 4), and the hot work shall be limited to the specific location or locations described in the "limitations" in 4. 3. 6(2). The marine chemist shall ensure At the time of the inspection the Marine Chemist shall verify that the atmospheres of adjacent space(s) meet the requirements of sections below in accordance with 4. 3. 4 (4) or (5), or are inerted. (ROP 306 -56) (b) The space or compartment meets the requirements of 4. 3. 4 (1), (2), (3) and (4); and adjacent spaces meet 4. 3. 4 (4) or (5) and the hot work shall not be allowed on adjacent spaces or pipelines. or both as applicable; and The hot work limitations restrictions shall be described in the listed under "limitations" in accordance with 4. 3. 6(2). The marine chemist shall ensure that the atmospheres of adjacent space(s) are maintained below 10%, of the lower explosive level concentration of flammable materials in the atmosphere is less than 10 percent of the LEL or are inerted. (ROP 306 -56) (c) Portions of the space or compartment meet the requirements of 4. 3. 4(3) and (4), and (5) as well as applicable portions of 5. 1. 3 and the hot work shall be limited to the location or locations described listed under "limitations" in accordance with 4. 3. 6(2). (d) In compartments/spaces on vessels, that are not considered cargo or fuel spaces and have not contained and are not subject to concentrations of combustible, flammable or toxic liquids, vapors, or gases, the Marine Chemist shall survey the spaces and adjacent spaces in accordance with Section 4. 2. 2. The Certificate shall include a statement under the heading "Limitations" describing the locations and type of Hot Work along with any directions for the Competent Person to maintain safe work conditions. (ROP 306 -55) maintain replaced ensure in ROC) (Log 81, Pg 37 and Log 66 Pg 36)
 INERTING CHANGE 4. 3. 8 INERTED requires that one of the following procedures shall have been completed in the compartment or space so designated: (1) *Carbon dioxide or other nonflammable gas acceptable to the Marine Chemist shall have been introduced into the space in sufficient volume to maintain the oxygen content of the atmosphere of the enclosed space at or below 6 percent or 50 percent of the amount required to support combustion, whichever is less. (See Annex E. ) The Marine Chemist shall note on the Certificate the kind of inert gas, the methods for maintaining safe conditions, and the measures for safe disposal of the inert gas upon completion of repairs in accordance with 5. 2. 1. Closing and securing of hatches and other openings, except vents, shall be permitted to be used as "safe disposal" methods by the Marine Chemist. 4. 3. 8(2) The space Spaces other than cargo tanks, (or) fuel tanks have has been filled to overflow with water and the water level shall be maintained throughout the intended work. Valves shall be tagged or by written notice positioned to restrict operation to maintain the water level. If any headspace remains in the tank, it shall meet the requirements of 4. 3. 4(2). Any such procedure shall be approved by the Marine Chemist. 4. 3. 8(3)The space has been filled with water so that the water level is a minimum of 0. 9 m (3 feet) above the intended exterior hot work and the atmosphere of the headspace meets the requirements of 4. 3. 4(2). The water level shall be maintained throughout the intended work by tagging valves in a position to maintain the water level. Any procedure shall be approved by the Marine Chemist. 4. 3. 8(4)* All valves, vent lines and other openings to the inerted spaces shall be positioned in such a manner and tagged and positioned in such a manner as to prevent or, by written notice, restrict operation. A. 4. 3. 8(4) Valves may be opened, closed or blanked as necessary to maintain the inert condition of the space. (Log 50, 9, 10, 11 pg. 37, 38, 39)
INERTING CHANGE 4. 3. 8 INERTED requires that one of the following procedures shall have been completed in the compartment or space so designated: (1) *Carbon dioxide or other nonflammable gas acceptable to the Marine Chemist shall have been introduced into the space in sufficient volume to maintain the oxygen content of the atmosphere of the enclosed space at or below 6 percent or 50 percent of the amount required to support combustion, whichever is less. (See Annex E. ) The Marine Chemist shall note on the Certificate the kind of inert gas, the methods for maintaining safe conditions, and the measures for safe disposal of the inert gas upon completion of repairs in accordance with 5. 2. 1. Closing and securing of hatches and other openings, except vents, shall be permitted to be used as "safe disposal" methods by the Marine Chemist. 4. 3. 8(2) The space Spaces other than cargo tanks, (or) fuel tanks have has been filled to overflow with water and the water level shall be maintained throughout the intended work. Valves shall be tagged or by written notice positioned to restrict operation to maintain the water level. If any headspace remains in the tank, it shall meet the requirements of 4. 3. 4(2). Any such procedure shall be approved by the Marine Chemist. 4. 3. 8(3)The space has been filled with water so that the water level is a minimum of 0. 9 m (3 feet) above the intended exterior hot work and the atmosphere of the headspace meets the requirements of 4. 3. 4(2). The water level shall be maintained throughout the intended work by tagging valves in a position to maintain the water level. Any procedure shall be approved by the Marine Chemist. 4. 3. 8(4)* All valves, vent lines and other openings to the inerted spaces shall be positioned in such a manner and tagged and positioned in such a manner as to prevent or, by written notice, restrict operation. A. 4. 3. 8(4) Valves may be opened, closed or blanked as necessary to maintain the inert condition of the space. (Log 50, 9, 10, 11 pg. 37, 38, 39)
 Preparation of Certificates 4. 4 Preparation of Certificates. When the Marine Chemist is satisfied that the related requirements necessary for the safe conduct of the work have or have not been met, a Certificate shall be prepared in form and manner prescribed by this standard. prepared in accordance with this standard and in the format of the most recent Certificate of Style published by the Marine Chemist Qualification Board in conjunction with the Marine Chemist Association. The Certificate shall be written legibly. If ink stamps are used, all copies of the Certificate shall be stamped and legible. (Log 33, pg 40)(This was changed back to its initial wording during the ROC review. )
Preparation of Certificates 4. 4 Preparation of Certificates. When the Marine Chemist is satisfied that the related requirements necessary for the safe conduct of the work have or have not been met, a Certificate shall be prepared in form and manner prescribed by this standard. prepared in accordance with this standard and in the format of the most recent Certificate of Style published by the Marine Chemist Qualification Board in conjunction with the Marine Chemist Association. The Certificate shall be written legibly. If ink stamps are used, all copies of the Certificate shall be stamped and legible. (Log 33, pg 40)(This was changed back to its initial wording during the ROC review. )
 Preparation of Certificates 4. 4. 3* Such qualifications and requirements shall include precautions, including protective equipment and devices, necessary to eliminate or minimize hazards that could be present from protective coatings or residues from cargoes. These qualifications also shall include limitations or restrictions, if any, on the areas where work is to be done. (Current wording) 4. 4. 3 Such qualifications and requirements shall include precautions, including protective equipment and devices, necessary to eliminate or minimize hazards that could be present from combustibles, protective coatings or residues from cargoes. These qualifications shall include limitations or restrictions, if any, on the areas where work is to be done and shall be listed on the certificate. A. 4. 4. 3 If there is no additional statement regarding the scope of the work on the Certificate, any hot work or cold work can proceed as indicated by the standard safety designation. If all types of work cannot be conducted safely under a standard safety designation, then the authorized work or prohibited work should be listed on the Certificate. (Log 82, pg. 41) (Deleted Annex Section)
Preparation of Certificates 4. 4. 3* Such qualifications and requirements shall include precautions, including protective equipment and devices, necessary to eliminate or minimize hazards that could be present from protective coatings or residues from cargoes. These qualifications also shall include limitations or restrictions, if any, on the areas where work is to be done. (Current wording) 4. 4. 3 Such qualifications and requirements shall include precautions, including protective equipment and devices, necessary to eliminate or minimize hazards that could be present from combustibles, protective coatings or residues from cargoes. These qualifications shall include limitations or restrictions, if any, on the areas where work is to be done and shall be listed on the certificate. A. 4. 4. 3 If there is no additional statement regarding the scope of the work on the Certificate, any hot work or cold work can proceed as indicated by the standard safety designation. If all types of work cannot be conducted safely under a standard safety designation, then the authorized work or prohibited work should be listed on the Certificate. (Log 82, pg. 41) (Deleted Annex Section)
 Obtaining the Certificate 4. 61 (D) Only one requestor will be listed on the certificate. The requester is responsible for providing a complete statement of the scope of the work at the time of the Marine Chemist’s inspection… (ROC Log 36, pg. 30)
Obtaining the Certificate 4. 61 (D) Only one requestor will be listed on the certificate. The requester is responsible for providing a complete statement of the scope of the work at the time of the Marine Chemist’s inspection… (ROC Log 36, pg. 30)
 Maintaining the Certificate 4. 6. 2(3)*Unless otherwise stated on the Certificate, all spaces including adjacent spaces documented on the. Marine Chemist Certificate shall be reinspected daily, or more often as necessary, by the shipyard competent person in support of work prior to entry or recommencement of work. 4. 6. 2(3)* Unless otherwise stated on the Certificate, certified spaces including spaces adjacent to hot work, where work is being done shall be re-inspected daily, or more often as necessary, by the shipyard competent person, prior to entry or external hot work. (5) (4) It is the responsibility of the Certificate requester, vessel owner, or their representative to ensure that the prescribed work is carried out at the original location within the facility for which the Certificate was issued, unless movement is authorized within that facility by the Marine Chemist on the Certificate. If movement is authorized within the facility, a reinspection shall be performed by a competent person. The Marine Chemist shall include on the Certificate the nature of any tests to be performed after the move is complete and prior to beginning work. (6) (5) The calibration of all instruments used by a competent person to maintain a Marine Chemist’s Certificate shall be verified by either the competent person, another qualified individual, or metrology laboratory, before each day’s use by using a known concentration of test gas in a manner consistent with the manufacturer’s recommendations. A record shall be maintained for at least 3 months. (4) (6) Certificates not maintained according to the requirements in 4. 6. 2(1) through (5) shall be void. Log 30 pg. 45 Log 83 pg 44
Maintaining the Certificate 4. 6. 2(3)*Unless otherwise stated on the Certificate, all spaces including adjacent spaces documented on the. Marine Chemist Certificate shall be reinspected daily, or more often as necessary, by the shipyard competent person in support of work prior to entry or recommencement of work. 4. 6. 2(3)* Unless otherwise stated on the Certificate, certified spaces including spaces adjacent to hot work, where work is being done shall be re-inspected daily, or more often as necessary, by the shipyard competent person, prior to entry or external hot work. (5) (4) It is the responsibility of the Certificate requester, vessel owner, or their representative to ensure that the prescribed work is carried out at the original location within the facility for which the Certificate was issued, unless movement is authorized within that facility by the Marine Chemist on the Certificate. If movement is authorized within the facility, a reinspection shall be performed by a competent person. The Marine Chemist shall include on the Certificate the nature of any tests to be performed after the move is complete and prior to beginning work. (6) (5) The calibration of all instruments used by a competent person to maintain a Marine Chemist’s Certificate shall be verified by either the competent person, another qualified individual, or metrology laboratory, before each day’s use by using a known concentration of test gas in a manner consistent with the manufacturer’s recommendations. A record shall be maintained for at least 3 months. (4) (6) Certificates not maintained according to the requirements in 4. 6. 2(1) through (5) shall be void. Log 30 pg. 45 Log 83 pg 44
 Annex to 4. 6. 2(3) A. 4. 6. 2(3) The Marine Chemist can recognize a facility's procedures and infrastructure used to minimize risk and hazards to people and equipment through engineering controls supplemented by administrative controls. As an example, mechanical exhaust ventilation for the space has been installed and will operate continuously. OSHA, in 29 CFR 1915. 13, notes that the frequency of retesting the atmospheric conditions of a space should be a function of several factors, including temperature, work in the tank, period of time elapsed, unattended tanks, work breaks, or ballasting. This section allows the rotation of work away from spaces that have been certified and worked in or on, but where work has been suspended due to schedule requirements. It requires the shipyard competent person (if not the Marine Chemist) to reinspect and establish that safe conditions remain in certified spaces and applicable adjacent spaces before work resumes in or on such spaces. Vessel or shipyard management must always be aware however. that any suspension of work in or on a confined or enclosed space constitutes a time for significant potential accumulation of hazards. and careful and documented reinspection before reentry and resumption of work is a strict necessity and requirement. The intent of this wording is to clarify that spaces listed on the Marine Chemist Certificate do not need to be tested by the competent person unless work is being done on or in a space. For example, spaces on a certificate do not need to be tested and inspected on a weekend if no work or entry is taking place. However, nothing shall prevent a competent person from testing more frequently than the minimum. Log 83 pg 45, Log 30 pg 46, Log 98 pg 65
Annex to 4. 6. 2(3) A. 4. 6. 2(3) The Marine Chemist can recognize a facility's procedures and infrastructure used to minimize risk and hazards to people and equipment through engineering controls supplemented by administrative controls. As an example, mechanical exhaust ventilation for the space has been installed and will operate continuously. OSHA, in 29 CFR 1915. 13, notes that the frequency of retesting the atmospheric conditions of a space should be a function of several factors, including temperature, work in the tank, period of time elapsed, unattended tanks, work breaks, or ballasting. This section allows the rotation of work away from spaces that have been certified and worked in or on, but where work has been suspended due to schedule requirements. It requires the shipyard competent person (if not the Marine Chemist) to reinspect and establish that safe conditions remain in certified spaces and applicable adjacent spaces before work resumes in or on such spaces. Vessel or shipyard management must always be aware however. that any suspension of work in or on a confined or enclosed space constitutes a time for significant potential accumulation of hazards. and careful and documented reinspection before reentry and resumption of work is a strict necessity and requirement. The intent of this wording is to clarify that spaces listed on the Marine Chemist Certificate do not need to be tested by the competent person unless work is being done on or in a space. For example, spaces on a certificate do not need to be tested and inspected on a weekend if no work or entry is taking place. However, nothing shall prevent a competent person from testing more frequently than the minimum. Log 83 pg 45, Log 30 pg 46, Log 98 pg 65
 Preparing Vessels 5. 1. 1 All cargo pumps, cargo lines, inert gas lines, crude oil wash lines, piped cargo fireextinguishing lines, vapor control and recovery lines and vent lines to the spaces involved in the scope of work shall have been flushed with water, blown with air or inerted. ROP 306 -75. pg. 46
Preparing Vessels 5. 1. 1 All cargo pumps, cargo lines, inert gas lines, crude oil wash lines, piped cargo fireextinguishing lines, vapor control and recovery lines and vent lines to the spaces involved in the scope of work shall have been flushed with water, blown with air or inerted. ROP 306 -75. pg. 46
 25 Foot Rule 5. 8* Vessel Fuel Oil Tanks. No hot work shall be permitted immediately adjacent to any vessel's fuel oil tanks unless the work has been authorized by the Marine Chemist. A. 5. 8 Vessel or other Fuel Oil Tanks. On dry cargo vessels, miscellaneous vessels, passenger vessels, and shipyard employment land-side operations no hot work shall be permitted adjacent to any vessel's or other fuel oil tanks unless the work has been authorized by the Marine Chemist. When the adjacent space contains flammable or combustible liquids with a flash point at or below 150 degrees-Fahrenheit, or flammable gasses and the distance between such spaces and the hot work is greater than 25 feet, then a competent person can visually inspect and test the space (if the hot work is 25 feet or closer to the adjacent space containing such flammables, then a Marine Chemist must certify the hot work. ) (Log 88 Pg 52)
25 Foot Rule 5. 8* Vessel Fuel Oil Tanks. No hot work shall be permitted immediately adjacent to any vessel's fuel oil tanks unless the work has been authorized by the Marine Chemist. A. 5. 8 Vessel or other Fuel Oil Tanks. On dry cargo vessels, miscellaneous vessels, passenger vessels, and shipyard employment land-side operations no hot work shall be permitted adjacent to any vessel's or other fuel oil tanks unless the work has been authorized by the Marine Chemist. When the adjacent space contains flammable or combustible liquids with a flash point at or below 150 degrees-Fahrenheit, or flammable gasses and the distance between such spaces and the hot work is greater than 25 feet, then a competent person can visually inspect and test the space (if the hot work is 25 feet or closer to the adjacent space containing such flammables, then a Marine Chemist must certify the hot work. ) (Log 88 Pg 52)
 Military Unique Vessels 6. 3. 4 All tanks, confined spaces, and machinery compartments in which internal repairs or alterations are to be undertaken shall be cleaned to comply with the requirements of either 4. 3. 1 or 4. 3. 3. For repair or alteration involving hot work, these spaces shall meet the requirements of 4. 3. 4 or 4. 3. 6 or 5. 1. 3 and adjacent compartments shall be cleaned to meet the requirements of 4. 3. 4 or 4. 3. 6 or 5. 1. 3 or shall be permitted to be inerted to meet the requirements of 4. 3. 8. The adjacent spaces shall be permitted to be secured in accordance with the Marine Chemist’s requirements and acknowledged on the Certificate. Exception: Spaces covered by 5. 1. 3, Section 5. 8, and 6. 3. 3. (Log 23 pg 54)
Military Unique Vessels 6. 3. 4 All tanks, confined spaces, and machinery compartments in which internal repairs or alterations are to be undertaken shall be cleaned to comply with the requirements of either 4. 3. 1 or 4. 3. 3. For repair or alteration involving hot work, these spaces shall meet the requirements of 4. 3. 4 or 4. 3. 6 or 5. 1. 3 and adjacent compartments shall be cleaned to meet the requirements of 4. 3. 4 or 4. 3. 6 or 5. 1. 3 or shall be permitted to be inerted to meet the requirements of 4. 3. 8. The adjacent spaces shall be permitted to be secured in accordance with the Marine Chemist’s requirements and acknowledged on the Certificate. Exception: Spaces covered by 5. 1. 3, Section 5. 8, and 6. 3. 3. (Log 23 pg 54)
 Chapter 7 Bulk Chemical Cargo Tankers Chapter 7. Additional Requirements for Bulk Chemical Cargo Tanks With the exception of the following words which have moved to the inerting section this section has been deleted. Chapter 5. 5. 2. 4 Care shall be exercised in the selection of methods and materials used for cleaning or inerting to avoid non-compatibility with previous cargoes. (Log CP 7 pg 56)
Chapter 7 Bulk Chemical Cargo Tankers Chapter 7. Additional Requirements for Bulk Chemical Cargo Tanks With the exception of the following words which have moved to the inerting section this section has been deleted. Chapter 5. 5. 2. 4 Care shall be exercised in the selection of methods and materials used for cleaning or inerting to avoid non-compatibility with previous cargoes. (Log CP 7 pg 56)
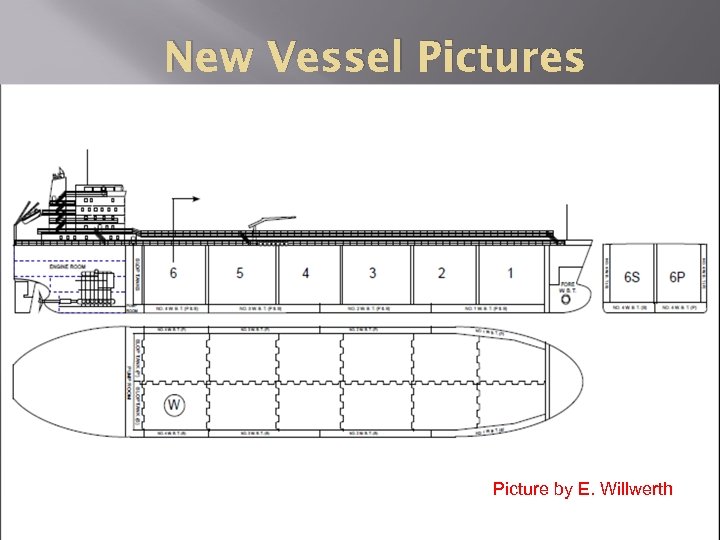 New Vessel Pictures Picture by E. Willwerth
New Vessel Pictures Picture by E. Willwerth
 1. Administration NFPA 306 CURRENT SECTIONS a. b. c. d. Scope Purpose Emergency Exception Governmental Regulations 2. Referenced Publications 3. Definitions 4. Minimum Requirements for Issuance of Marine Chemist Certificate and Maintenance of Conditions a. Determining Conditions – Enter a space and test. b. Procedures Prior to Issuance of a Certificate c. Calibration of instrumentation d. Determinations e. f. g. h. i. ii. iv. v. vi. Last three Cargoes Extent of work Starting time and duration of work Tests of cargo and vent lines Verification of pipelines Test heating coils 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Standard Safety Designations and Conditions Required i. iii. iv v. viii. ix. x Atmosphere Safe for Workers Not Safe for Workers Enter with Restrictions Safe for Hot Work Not Safe for Hot Work Safe for Limited Hot Work Safe for Shipbreaking Inerted for Flammable Compressed Gas Safe for Layup Preparation of Certificates Issuance of Certificates Responsibility for Obtaining the Certificate Maintaining the Certificate 5. Preparing Vessels for Issuance of a Marine Chemist’s Certificate Involving Hot Work a. Where a Safe Condition is to be Obtained Entirely by Cleaning b. Partial Cleaning for Limited Hot Work c. Where a Safe Condition is to be obtained by both cleaning and Inerting or Entirely by Inerting. 6. PROPOSED MODIFICATION TO 306 CHAPTERS Administration (No Change) a. Scope b. Purpose c. Emergency Exception d. Governmental Regulations Referenced Publications (No Change) Definitions (No Change) Vessels Required to Have a Marine Chemist’s Certificate a. Tank Vessels (6. 1) b. Vessels Other than Tank Vessels (6. 2) c. Military Unique Vessels (6. 4) d. Vessels in Layup (6. 4) e. Vessels Carrying Flammable Compressed Gas (6. 5) Preparing Vessels for Issuance of a Marine Chemist’s Certificate Involving Hot Work a. Responsibility for Obtaining the Certificate (4. 6. 1(A)) (modified to obtain cert only) b. Where a Safe Condition is to be Obtained Entirely by Cleaning (5. 1) c. Partial Cleaning for Limited Hot Work (5. 1. 3) d. Where a Safe Condition is to be obtained by both cleaning and Inerting or Entirely by Inerting. (5. 2) e. Where a Safe Condition is to be Obtained by Cleaning Certain Compartments and by Securing the Other Compartments. (5. 3) f. Where a Safe Condition is to be obtained by Cleaning Some Compartments and by Inerting Some Compartments and by Securing Some Compartments. (5. 4) g. Cargo Heating Coils (5. 5) h. Electric Welding Operations (5. 6) i. Requirements for use of a designated berthing area for Cleaning, Gas Freeing or Inerting. (5. 7) j. Vessel Fuel Oil Tanks (5. 8) Procedures for the Marine Chemist Prior to Issuing a Certificate a. Calibration of instrumentation (4. 2. 1) b. Determinations (4. 2. 2) i. iii. iv. v. 3 Cargoes Extent of work Starting time and duration of work Tests of cargo and vent lines Verification of pipelines vi. Test heating coils vii. Determination of conditions (4. 1 or combine with 4. 2. 2))
1. Administration NFPA 306 CURRENT SECTIONS a. b. c. d. Scope Purpose Emergency Exception Governmental Regulations 2. Referenced Publications 3. Definitions 4. Minimum Requirements for Issuance of Marine Chemist Certificate and Maintenance of Conditions a. Determining Conditions – Enter a space and test. b. Procedures Prior to Issuance of a Certificate c. Calibration of instrumentation d. Determinations e. f. g. h. i. ii. iv. v. vi. Last three Cargoes Extent of work Starting time and duration of work Tests of cargo and vent lines Verification of pipelines Test heating coils 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Standard Safety Designations and Conditions Required i. iii. iv v. viii. ix. x Atmosphere Safe for Workers Not Safe for Workers Enter with Restrictions Safe for Hot Work Not Safe for Hot Work Safe for Limited Hot Work Safe for Shipbreaking Inerted for Flammable Compressed Gas Safe for Layup Preparation of Certificates Issuance of Certificates Responsibility for Obtaining the Certificate Maintaining the Certificate 5. Preparing Vessels for Issuance of a Marine Chemist’s Certificate Involving Hot Work a. Where a Safe Condition is to be Obtained Entirely by Cleaning b. Partial Cleaning for Limited Hot Work c. Where a Safe Condition is to be obtained by both cleaning and Inerting or Entirely by Inerting. 6. PROPOSED MODIFICATION TO 306 CHAPTERS Administration (No Change) a. Scope b. Purpose c. Emergency Exception d. Governmental Regulations Referenced Publications (No Change) Definitions (No Change) Vessels Required to Have a Marine Chemist’s Certificate a. Tank Vessels (6. 1) b. Vessels Other than Tank Vessels (6. 2) c. Military Unique Vessels (6. 4) d. Vessels in Layup (6. 4) e. Vessels Carrying Flammable Compressed Gas (6. 5) Preparing Vessels for Issuance of a Marine Chemist’s Certificate Involving Hot Work a. Responsibility for Obtaining the Certificate (4. 6. 1(A)) (modified to obtain cert only) b. Where a Safe Condition is to be Obtained Entirely by Cleaning (5. 1) c. Partial Cleaning for Limited Hot Work (5. 1. 3) d. Where a Safe Condition is to be obtained by both cleaning and Inerting or Entirely by Inerting. (5. 2) e. Where a Safe Condition is to be Obtained by Cleaning Certain Compartments and by Securing the Other Compartments. (5. 3) f. Where a Safe Condition is to be obtained by Cleaning Some Compartments and by Inerting Some Compartments and by Securing Some Compartments. (5. 4) g. Cargo Heating Coils (5. 5) h. Electric Welding Operations (5. 6) i. Requirements for use of a designated berthing area for Cleaning, Gas Freeing or Inerting. (5. 7) j. Vessel Fuel Oil Tanks (5. 8) Procedures for the Marine Chemist Prior to Issuing a Certificate a. Calibration of instrumentation (4. 2. 1) b. Determinations (4. 2. 2) i. iii. iv. v. 3 Cargoes Extent of work Starting time and duration of work Tests of cargo and vent lines Verification of pipelines vi. Test heating coils vii. Determination of conditions (4. 1 or combine with 4. 2. 2))
 NFPA 306 CURRENT SECTIONS d. Where a Safe Condition is to be obtained by Cleaning Certain Compartments and by Securing the Other Compartments. e. Where a Safe Condition is to be obtained by Cleaning Some Compartments and by, by Inerting Some Compartments and Securing Some Compartments. f. Cargo Heating Coils g. Electric Welding Operations h. Requirements for use of a designated berthing area for Cleaning, Gas Freeing or Inerting. i. Vessel Fuel Oil Tanks 6. Vessels Required to Have a Marine Chemist’s Certificate a. Tank Vessels b. Vessels Other than Tank Vessels c. Military Unique Vessels d. Vessels in Layup e. Vessels Carrying Flammable Compressed Gas 7. Additional Requirement for Bulk Chemical Cargo Tanks a. Scope b. Minimum Requirements c. Minimum Conditions 8. Additional Requirements for Flammable Cryogenic Liquid Carriers a. Scope b. Definitions c. Minimum Requirements d. Minimum Conditions PROPOSED MODIFICATION TO 306 CHAPTERS Standard Safety Designations and Conditions Required a. Atmosphere Safe for Workers (4. 3. 1) b. Not Safe for Workers (4. 3. 2) c. Enter with Restrictions (4. 3. 3) d. Safe for Hot Work (4. 3. 4) e. Not Safe for Hot Work (4. 3. 5) f. Safe for Limited Hot Work (4. 3. 6) g. Safe for Shipbreaking (4. 3. 7) h. Inerted (4. 3. 8) i. Inerted for Flammable Compressed Gas (4. 3. 9) j. Safe for Layup (4. 3. 10) 8. Marine Chemist Certificates a. Preparation of Certificates (4. 6. 1 (A))( modified to omit obtaining the cert) b. Issuance of Certificates (4. 6. 1(B)) c. Maintaining the Certificate (4. 6. 2) 9. Additional Requirements for Flammable Cryogenic Liquid Carriers a. Scope (8. 1) b. Definitions (8. 2) c. Minimum Requirements (8. 3) d. Minimum Conditions (8. 4) 10. Delete Prior Section 7 - Additional Requirements for Bulk Chemical Cargo Tanks – This section contains no unique requirements for these vessels and refers the reader back to other sections. It should be deleted. 7.
NFPA 306 CURRENT SECTIONS d. Where a Safe Condition is to be obtained by Cleaning Certain Compartments and by Securing the Other Compartments. e. Where a Safe Condition is to be obtained by Cleaning Some Compartments and by, by Inerting Some Compartments and Securing Some Compartments. f. Cargo Heating Coils g. Electric Welding Operations h. Requirements for use of a designated berthing area for Cleaning, Gas Freeing or Inerting. i. Vessel Fuel Oil Tanks 6. Vessels Required to Have a Marine Chemist’s Certificate a. Tank Vessels b. Vessels Other than Tank Vessels c. Military Unique Vessels d. Vessels in Layup e. Vessels Carrying Flammable Compressed Gas 7. Additional Requirement for Bulk Chemical Cargo Tanks a. Scope b. Minimum Requirements c. Minimum Conditions 8. Additional Requirements for Flammable Cryogenic Liquid Carriers a. Scope b. Definitions c. Minimum Requirements d. Minimum Conditions PROPOSED MODIFICATION TO 306 CHAPTERS Standard Safety Designations and Conditions Required a. Atmosphere Safe for Workers (4. 3. 1) b. Not Safe for Workers (4. 3. 2) c. Enter with Restrictions (4. 3. 3) d. Safe for Hot Work (4. 3. 4) e. Not Safe for Hot Work (4. 3. 5) f. Safe for Limited Hot Work (4. 3. 6) g. Safe for Shipbreaking (4. 3. 7) h. Inerted (4. 3. 8) i. Inerted for Flammable Compressed Gas (4. 3. 9) j. Safe for Layup (4. 3. 10) 8. Marine Chemist Certificates a. Preparation of Certificates (4. 6. 1 (A))( modified to omit obtaining the cert) b. Issuance of Certificates (4. 6. 1(B)) c. Maintaining the Certificate (4. 6. 2) 9. Additional Requirements for Flammable Cryogenic Liquid Carriers a. Scope (8. 1) b. Definitions (8. 2) c. Minimum Requirements (8. 3) d. Minimum Conditions (8. 4) 10. Delete Prior Section 7 - Additional Requirements for Bulk Chemical Cargo Tanks – This section contains no unique requirements for these vessels and refers the reader back to other sections. It should be deleted. 7.
 NFPA 306 Timeline • • ROP Published/Posted: 6/22/12 Comment Closing Date: 8/31/12 ROC Meeting: 9/25/12 ROC Published: 2/22/13 NITMAM Closing Date: 4/5/13 NITMAM/CAM Posting: Date: 5/13/13 NFPA Annual Meeting: 6/9 -6/13/13 Standards Council Issuance: 5/28/13 or 8/1/13 with 2014 edition date.
NFPA 306 Timeline • • ROP Published/Posted: 6/22/12 Comment Closing Date: 8/31/12 ROC Meeting: 9/25/12 ROC Published: 2/22/13 NITMAM Closing Date: 4/5/13 NITMAM/CAM Posting: Date: 5/13/13 NFPA Annual Meeting: 6/9 -6/13/13 Standards Council Issuance: 5/28/13 or 8/1/13 with 2014 edition date.
 QUESTIONS?
QUESTIONS?


