dc3684d8e225035d9e5510d187581f61.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 NFI Presentation - Part II Impact of Technology on the Built Environment & the Design Process
NFI Presentation - Part II Impact of Technology on the Built Environment & the Design Process
 Vocabulary • Same language? • IT Department • Architects and Facility Managers
Vocabulary • Same language? • IT Department • Architects and Facility Managers
 Vocabulary Information Technology Architects § Assessment § Programming/Schematic Design § Requirements definition § Design Development § Bid documents § Construction Documents § Bid evaluation § Acquisition Process § Contract signing § Contracting Process § Implementation § Construction Administration § VALUE ENGINEERING § FIELD ENGINEERING
Vocabulary Information Technology Architects § Assessment § Programming/Schematic Design § Requirements definition § Design Development § Bid documents § Construction Documents § Bid evaluation § Acquisition Process § Contract signing § Contracting Process § Implementation § Construction Administration § VALUE ENGINEERING § FIELD ENGINEERING
 Apply Construction Methodologies to Technology Implementations • Contract Documents (drawings & specifications) • Competitive bid process • Performance Bonds • Contracts should include – Schedule milestones – Payment milestones – Retainage and/or Liquidated Damages terms • Construction Administration – Contractor payment review and approval – Inspections (how many? )
Apply Construction Methodologies to Technology Implementations • Contract Documents (drawings & specifications) • Competitive bid process • Performance Bonds • Contracts should include – Schedule milestones – Payment milestones – Retainage and/or Liquidated Damages terms • Construction Administration – Contractor payment review and approval – Inspections (how many? )
 Handout – Responsibility Matrix
Handout – Responsibility Matrix
 Who’s Involved? • Owner (district) – Facilities (Buildings & Grounds) – Finance – School Leaders (Supt. , Principals) – YOU! • • • Architects CM (Construction Manager) MEP (Mechanical Electrical Planner) GC (General Contractor) Subcontractors (lots!)
Who’s Involved? • Owner (district) – Facilities (Buildings & Grounds) – Finance – School Leaders (Supt. , Principals) – YOU! • • • Architects CM (Construction Manager) MEP (Mechanical Electrical Planner) GC (General Contractor) Subcontractors (lots!)
 Technology Systems • Cabling Infrastructure • Data Center/equipment rooms • Network (LAN, WAN, wireless) • Voice and voicemail • Multimedia • Public address, bell and clock • Security systems
Technology Systems • Cabling Infrastructure • Data Center/equipment rooms • Network (LAN, WAN, wireless) • Voice and voicemail • Multimedia • Public address, bell and clock • Security systems
 Lessons Learned: Coordinate – EARLY • Ensure electrical power of the right types in the right places and right amounts – One phase vs. three phase power – 110/120 and 208 Volt – Receptacle types – Ceiling mounted systems – where to put outlets • Proper grounding is essential
Lessons Learned: Coordinate – EARLY • Ensure electrical power of the right types in the right places and right amounts – One phase vs. three phase power – 110/120 and 208 Volt – Receptacle types – Ceiling mounted systems – where to put outlets • Proper grounding is essential
 More Coordination Issues • • • Ambient noise/sound level in classrooms Glare from windows/natural lighting Light fixture locations and switching in classrooms Location & routing of conduits from outside Cable support systems Cable pathways from MER to TRs
More Coordination Issues • • • Ambient noise/sound level in classrooms Glare from windows/natural lighting Light fixture locations and switching in classrooms Location & routing of conduits from outside Cable support systems Cable pathways from MER to TRs
 Technology Infrastructure
Technology Infrastructure
 Data Centers • Terms – Data Center/ Server Room – NOC – MER – EIA/TIA 942 – HVAC – UPS
Data Centers • Terms – Data Center/ Server Room – NOC – MER – EIA/TIA 942 – HVAC – UPS
 What’s in a Data Center? • Servers • Legacy mini-computers • SAN and NAS equipment • Backup systems: tape and disk-to-disk • Network switches, routers, etc. • Phone system (switch and/or servers) • Video equipment/encoders • Audio/paging system • Security control system/servers
What’s in a Data Center? • Servers • Legacy mini-computers • SAN and NAS equipment • Backup systems: tape and disk-to-disk • Network switches, routers, etc. • Phone system (switch and/or servers) • Video equipment/encoders • Audio/paging system • Security control system/servers
 Data Center - Design Issues • Location • Size • Cooling • Electrical and UPS • Fire protection • Security • Disaster recovery
Data Center - Design Issues • Location • Size • Cooling • Electrical and UPS • Fire protection • Security • Disaster recovery
 Data Centers - Physical Setup • A minimum of 280 sq. ft. (~ 17’ x 17’) • Minimum ceiling height 8. 5 clear (below lights) • Measure physical sizes of all items - height in rack units (1 RU = 1. 75 inches) • Account for floor space for HVAC equipment, power distribution, and UPS systems • High voltage electrical panels and transformers must be at least 36” from racks & equipment • Raised flooring ?
Data Centers - Physical Setup • A minimum of 280 sq. ft. (~ 17’ x 17’) • Minimum ceiling height 8. 5 clear (below lights) • Measure physical sizes of all items - height in rack units (1 RU = 1. 75 inches) • Account for floor space for HVAC equipment, power distribution, and UPS systems • High voltage electrical panels and transformers must be at least 36” from racks & equipment • Raised flooring ?
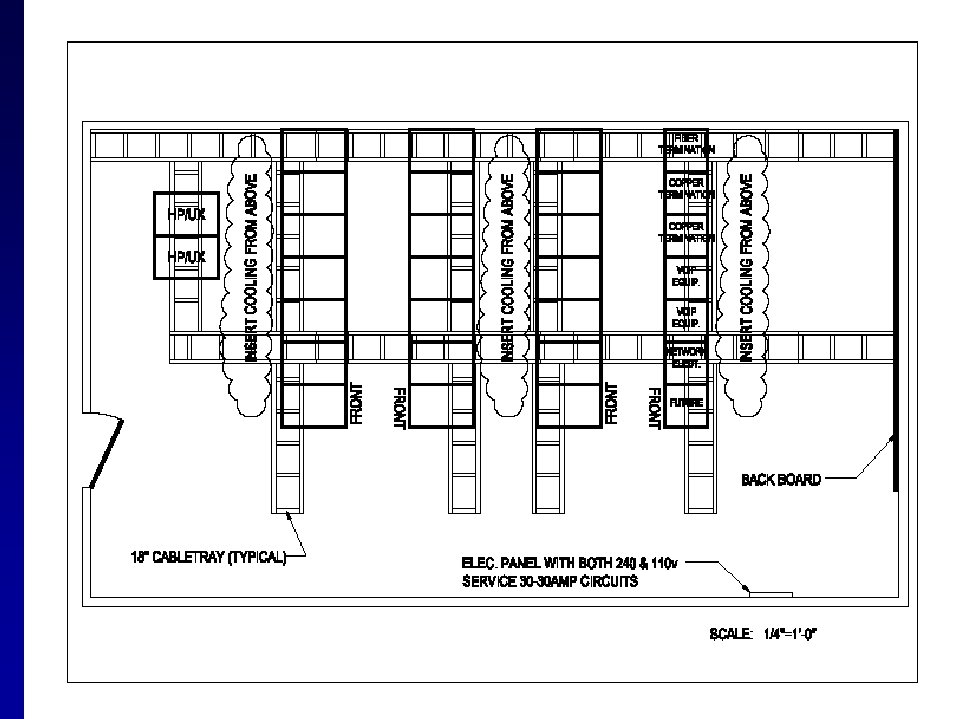
 Data Centers - Environmental • Non-water based fire suppression preferred; second choice: “pre-action” • Lots of options for cooling, just be sure there is enough • For a greener data center, place cooling close to the sources of heat – duct directly to racks or within cabinets
Data Centers - Environmental • Non-water based fire suppression preferred; second choice: “pre-action” • Lots of options for cooling, just be sure there is enough • For a greener data center, place cooling close to the sources of heat – duct directly to racks or within cabinets
 Business Continuity/Disaster Recovery • • Generator w/48 hours fuel at main Data Center UPS – test monthly; choose SNMP manageable Redundant cooling Alternate/backup data center site – Hot site – redundantly equipped and running – Warm site – equipped with mission critical systems (only) and ready to start up – Cold site – space and connections only, no equipment
Business Continuity/Disaster Recovery • • Generator w/48 hours fuel at main Data Center UPS – test monthly; choose SNMP manageable Redundant cooling Alternate/backup data center site – Hot site – redundantly equipped and running – Warm site – equipped with mission critical systems (only) and ready to start up – Cold site – space and connections only, no equipment
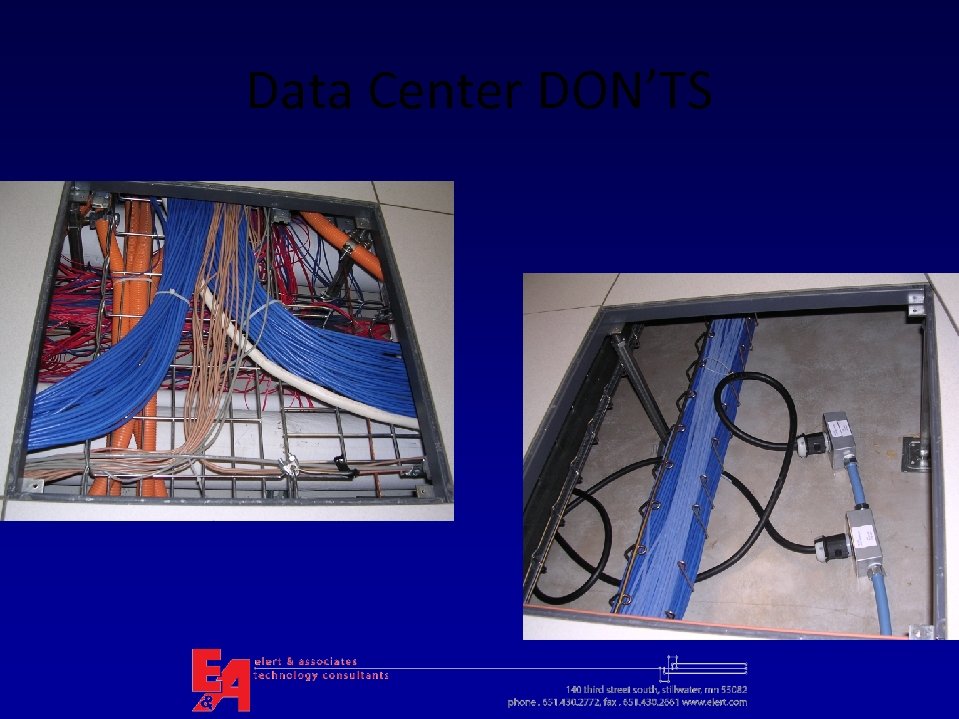 Data Center DON’TS
Data Center DON’TS
 Cabling • Standards continue to change – you must decide when/if to move to next versions – Category 6 (copper) – Multimode fiber – 50 micron • Plenum rated? • Fiber backbone – quantity of strands? • Exterior fiber – WDM capable
Cabling • Standards continue to change – you must decide when/if to move to next versions – Category 6 (copper) – Multimode fiber – 50 micron • Plenum rated? • Fiber backbone – quantity of strands? • Exterior fiber – WDM capable
 Distributed Antenna System (DAS) • Enhances wireless coverage to ensure Fire & Police handheld radios work well • Some cities require in new public buildings • Can combine with Wi-Fi system – but must design in from the beginning • Can design for “spot” coverage – Stairwells – Lower levels – Inside rooms
Distributed Antenna System (DAS) • Enhances wireless coverage to ensure Fire & Police handheld radios work well • Some cities require in new public buildings • Can combine with Wi-Fi system – but must design in from the beginning • Can design for “spot” coverage – Stairwells – Lower levels – Inside rooms
 Networking
Networking
 LAN and MAN Developments • 10 Gigabit Ethernet use increasing • 100 Gigabit Ethernet is in development - IEEE 802. 3 ba Task Force Pre-Standard • Disk-to-disk backup gaining over tape • Storage costs continue to fall – Terabyte storage now commonplace • SAN vs. NAS – what do you use?
LAN and MAN Developments • 10 Gigabit Ethernet use increasing • 100 Gigabit Ethernet is in development - IEEE 802. 3 ba Task Force Pre-Standard • Disk-to-disk backup gaining over tape • Storage costs continue to fall – Terabyte storage now commonplace • SAN vs. NAS – what do you use?
 Wireless LAN – 802. 11 n • Final standard expected 2009 • Many manufacturers have Draft 2 devices on the market • Multiple radios in most APs • Throughputs of ~250 Mbps per access point (download)
Wireless LAN – 802. 11 n • Final standard expected 2009 • Many manufacturers have Draft 2 devices on the market • Multiple radios in most APs • Throughputs of ~250 Mbps per access point (download)
 802. 11 n Power Issues • Some 802. 11 n APs need more power than 802. 3 af (Power over Ethernet) standard can provide (standard is 12. 95 watts over full 100 meters). Workarounds for now: – Local power – Use separate power injector instead of 802. 3 af – Use 2 cables from each AP to switch – Reduced range (Trapeze) – Turn off one radio or run 802. 11 g on second radio
802. 11 n Power Issues • Some 802. 11 n APs need more power than 802. 3 af (Power over Ethernet) standard can provide (standard is 12. 95 watts over full 100 meters). Workarounds for now: – Local power – Use separate power injector instead of 802. 3 af – Use 2 cables from each AP to switch – Reduced range (Trapeze) – Turn off one radio or run 802. 11 g on second radio
 Power over Ethernet New: Po. E Plus • IEEE is working on a higher power Po. E standard – 802. 3 at, due 2009 (draft 2 done) • 30 -56 watts • Backwards compatible with 803. af • Pre-standard power injectors available now • Needed to power Wi. MAX transmitters, pan-tilt-zoom cameras, videophones
Power over Ethernet New: Po. E Plus • IEEE is working on a higher power Po. E standard – 802. 3 at, due 2009 (draft 2 done) • 30 -56 watts • Backwards compatible with 803. af • Pre-standard power injectors available now • Needed to power Wi. MAX transmitters, pan-tilt-zoom cameras, videophones
 Wireless LAN Security • Most new wireless APs include WPA 2 – Check! • WPA 2 client built into MS XP service pack 2 and up • WPA 2 maintains authentication when roaming • Two versions of WPA 2: Personal and Enterprise – Personal protects unauthorized network access by utilizing a set-up password – Enterprise verifies network users through a server
Wireless LAN Security • Most new wireless APs include WPA 2 – Check! • WPA 2 client built into MS XP service pack 2 and up • WPA 2 maintains authentication when roaming • Two versions of WPA 2: Personal and Enterprise – Personal protects unauthorized network access by utilizing a set-up password – Enterprise verifies network users through a server
 WLAN Support for Voice • 802. 11 e – be sure you choose Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) certified APs • Cell phone makers supporting both cell and Wi-Fi in handsets (e. g. , i. Phone)
WLAN Support for Voice • 802. 11 e – be sure you choose Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) certified APs • Cell phone makers supporting both cell and Wi-Fi in handsets (e. g. , i. Phone)
 Physical Security Systems • Moving to all IP and network based – Door access and ID cards – Cameras – Motion detection • Who owns this now? District Facilities or IT? – Initial cost – Ongoing maintenance and upgrades – Ongoing costs
Physical Security Systems • Moving to all IP and network based – Door access and ID cards – Cameras – Motion detection • Who owns this now? District Facilities or IT? – Initial cost – Ongoing maintenance and upgrades – Ongoing costs
 Physical Security • ID cards can be “smart”– multipurpose – Door access – Use for lunches and other payments – Integrate to Directory Services • Visitor screening – automated systems can do checks based on photo IDs • Allow Police to view camera feeds • Via web • From vehicles on school property
Physical Security • ID cards can be “smart”– multipurpose – Door access – Use for lunches and other payments – Integrate to Directory Services • Visitor screening – automated systems can do checks based on photo IDs • Allow Police to view camera feeds • Via web • From vehicles on school property
 Security Cameras • IP cameras – be choosy! – Backlight – Night vision – Pan-tilt-zoom (PTZ) with or tied to motion detection – Po. E • Coordination very important – Locations – esp. exterior such as parking lots – Conduit for cabling and power – Backboxes - esp. on brick/stone
Security Cameras • IP cameras – be choosy! – Backlight – Night vision – Pan-tilt-zoom (PTZ) with or tied to motion detection – Po. E • Coordination very important – Locations – esp. exterior such as parking lots – Conduit for cabling and power – Backboxes - esp. on brick/stone
 Video Distribution & Broadcast • What are your requirements for video? – Carry cable TV channels? If yes, which and how many? – Create own video broadcasts? If yes: who, when, from where, and to where? – Production studio(s)? • “Headends” are now also IP-based – Centralized or at each building? – Digital CATV is more work to integrate • No coaxial cabling needed
Video Distribution & Broadcast • What are your requirements for video? – Carry cable TV channels? If yes, which and how many? – Create own video broadcasts? If yes: who, when, from where, and to where? – Production studio(s)? • “Headends” are now also IP-based – Centralized or at each building? – Digital CATV is more work to integrate • No coaxial cabling needed
 Public Address, Bells & Clocks • • • Talk back (from classroom) – hands-free or handset? Interconnection to phone system Zones Speaker types/features Clocks digital or analog (elementary schools different? )
Public Address, Bells & Clocks • • • Talk back (from classroom) – hands-free or handset? Interconnection to phone system Zones Speaker types/features Clocks digital or analog (elementary schools different? )
 Questions and Discussion
Questions and Discussion
 Thank You!
Thank You!


