9b4a4f9a2068fa4833dc3906d62fe37c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Next Generation Network - a PIONIER example Maciej Stroiński, Artur Binczewski, Michał Przybylski Poznań Supercomputing and Networking Center TNC, Zagreb 19 -22 May 2003 TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
Next Generation Network - a PIONIER example Maciej Stroiński, Artur Binczewski, Michał Przybylski Poznań Supercomputing and Networking Center TNC, Zagreb 19 -22 May 2003 TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
 Fascination of fiber • • • Used since 1990 in buildings, campus or metro Multi – technologies: Ethernet, ATM, POS, DWDM, . . . Cost efective solution Supports the advanced requirements of science Many implementations in academic community – regional networks: Cal. REN, NCNI, . . . – national networks: CA*net 4, SWITCH, CESNET, PIONIER, . . . GOAL: TOWARDS ALL OPTICAL NETWORKS TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
Fascination of fiber • • • Used since 1990 in buildings, campus or metro Multi – technologies: Ethernet, ATM, POS, DWDM, . . . Cost efective solution Supports the advanced requirements of science Many implementations in academic community – regional networks: Cal. REN, NCNI, . . . – national networks: CA*net 4, SWITCH, CESNET, PIONIER, . . . GOAL: TOWARDS ALL OPTICAL NETWORKS TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
 New, simple landscape for „All Optical Europe for Mobile Europeans” Broadband access for residential and mobile users Voice Data Video IPv 6 Ethernet GMPLS Wi-Fi WDM Free space FO TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
New, simple landscape for „All Optical Europe for Mobile Europeans” Broadband access for residential and mobile users Voice Data Video IPv 6 Ethernet GMPLS Wi-Fi WDM Free space FO TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
 PIONIER - an idea of „All Optical Network” - facts: • 4 Q 1999 – proposal of program submited to KBN • 2 Q 2000 – PIONIER testbed (DWDM, TNC 2001) • 3 Q 2000 – project accepted (tender for co-operation, negotiations with Telcos) • 4 Q 2001 – I Phase: ~10 mln Euro – contracts with Telbank and Szeptel (1434 km) • 4 Q 2002 – II Phase: ~18. 5 mln Euro – Contracts with Telbank, regional Power Grids Companies (1214 km) – Contract for equipment: 10 GE&DWDM and IP router • 2 Q 2003 – installation of 10 GE with DWDM rep. /amp. – 16 MANs connected and 2648 km of fibers installed • 2004 – 21 MANs connected with 5200 km of fiber TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
PIONIER - an idea of „All Optical Network” - facts: • 4 Q 1999 – proposal of program submited to KBN • 2 Q 2000 – PIONIER testbed (DWDM, TNC 2001) • 3 Q 2000 – project accepted (tender for co-operation, negotiations with Telcos) • 4 Q 2001 – I Phase: ~10 mln Euro – contracts with Telbank and Szeptel (1434 km) • 4 Q 2002 – II Phase: ~18. 5 mln Euro – Contracts with Telbank, regional Power Grids Companies (1214 km) – Contract for equipment: 10 GE&DWDM and IP router • 2 Q 2003 – installation of 10 GE with DWDM rep. /amp. – 16 MANs connected and 2648 km of fibers installed • 2004 – 21 MANs connected with 5200 km of fiber TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
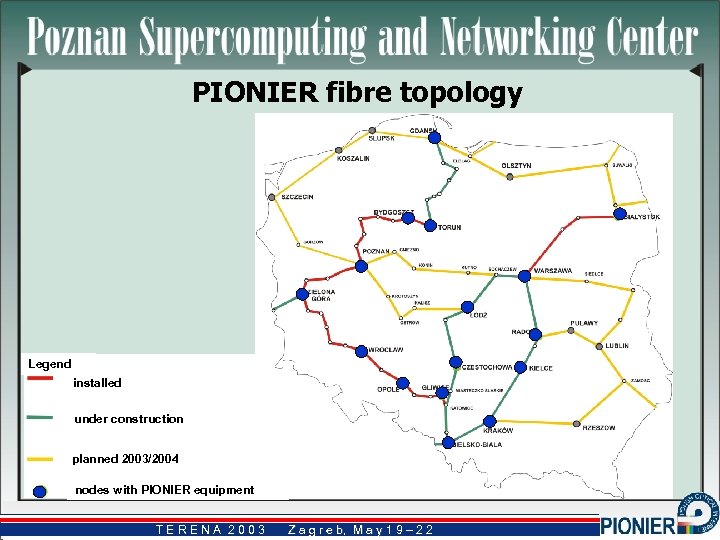 PIONIER fibre topology Legend installed under construction planned 2003/2004 nodes with PIONIER equipment TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
PIONIER fibre topology Legend installed under construction planned 2003/2004 nodes with PIONIER equipment TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
 How we build fibers • Co-investment with telco operators or self-investment (with right of way: power distribution, railways and public roads) • Average of 16 fibers available (4 x. G. 652 for national backbone, 8 x. G. 652 for regional use, 4 x. G. 655 for long haul transmission) • Average span length 60 km for national backbone (regeneration possible) • Local loop contruction is sometimes difficult (urban area - average 6 months waiting time for permissions) TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
How we build fibers • Co-investment with telco operators or self-investment (with right of way: power distribution, railways and public roads) • Average of 16 fibers available (4 x. G. 652 for national backbone, 8 x. G. 652 for regional use, 4 x. G. 655 for long haul transmission) • Average span length 60 km for national backbone (regeneration possible) • Local loop contruction is sometimes difficult (urban area - average 6 months waiting time for permissions) TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
 Community demands as a driving force • Academic Internet – interational connections (2. 5 Gb/s now, 10 Gb/s in October) – national connections between MANs (n x 622 Gb/s now, 10 Gb/s in June) – near future – n x 10 Gb/s • High Performance Computing Centers (FC, GE, 10 GE) – Project PROGRESS - SUN cluster (3 sites x 1 Gb/s) – Project SGI cluster (6 sites x 1 Gb/s) – Projects in preparation • National Data Storage system (5 sites x 1 Gb/s) • CLUSTERIX (12 sites x 1 Gb/s) – near future - n x 10, 40 Gb/s TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
Community demands as a driving force • Academic Internet – interational connections (2. 5 Gb/s now, 10 Gb/s in October) – national connections between MANs (n x 622 Gb/s now, 10 Gb/s in June) – near future – n x 10 Gb/s • High Performance Computing Centers (FC, GE, 10 GE) – Project PROGRESS - SUN cluster (3 sites x 1 Gb/s) – Project SGI cluster (6 sites x 1 Gb/s) – Projects in preparation • National Data Storage system (5 sites x 1 Gb/s) • CLUSTERIX (12 sites x 1 Gb/s) – near future - n x 10, 40 Gb/s TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
 Community demands as a driving force. . . Dedicated Capacity for European Projects – – – ATRIUM (622 Mb/s) 6 NET (155 -622 Mb/s) VLBI (2 x 1 Gb/s dedicated) CERN-ATLAS (>1 Gb/s dedicated per site, 2 sites) near future – 6 FP IST TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
Community demands as a driving force. . . Dedicated Capacity for European Projects – – – ATRIUM (622 Mb/s) 6 NET (155 -622 Mb/s) VLBI (2 x 1 Gb/s dedicated) CERN-ATLAS (>1 Gb/s dedicated per site, 2 sites) near future – 6 FP IST TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
 How PIONIER will adress them • • Start with 10 GE over fiber as an intermediate stage (June 2003) DWDM System with 40 Gb/s lambdas Optical switches with GMPLS Services: Optical VPN Ø Internet Ø HPC network Ø Goverment network Ø Dedicated networks for projects - ATLAS, VLBI, . . . Ø Access via optical MANs Ø near future: access via optical regional networks TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
How PIONIER will adress them • • Start with 10 GE over fiber as an intermediate stage (June 2003) DWDM System with 40 Gb/s lambdas Optical switches with GMPLS Services: Optical VPN Ø Internet Ø HPC network Ø Goverment network Ø Dedicated networks for projects - ATLAS, VLBI, . . . Ø Access via optical MANs Ø near future: access via optical regional networks TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
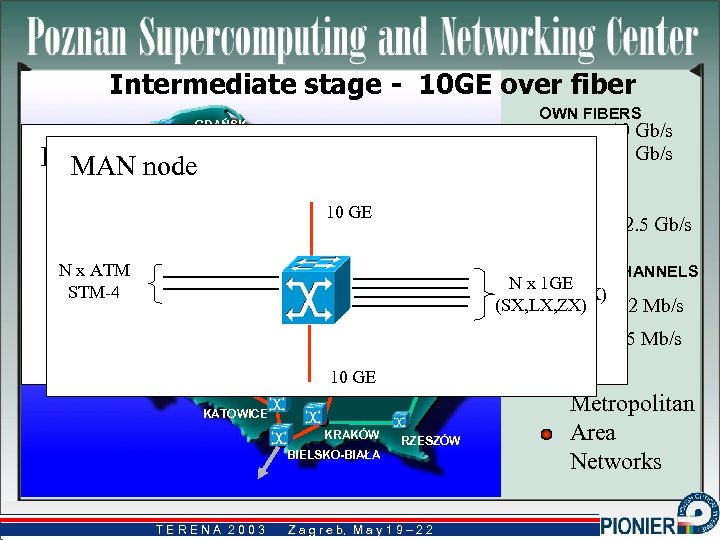 Intermediate stage - 10 GE over fiber OWN FIBERS GDAŃSK 10 Gb/s 1 Gb/s KOSZALIN POZNAN node MAN node SZCZECIN OLSZTYN BYDGOSZCZ TORUŃ GEANT M 160 GÉANT 10 BIAŁYSTOK GE 10 GE GÉANT 2. 5 Gb/s POZNAŃ 2. 5 G POS N ZIELONA x ATM GÓRA STM-4 WARSZAWA 10 G POS ŁÓDŹ WROCŁAW CZĘSTOCHOWA OPOLE 155 Mb/s RADOM KIELCE 10 10 GE PUŁAWY GE LUBLIN KATOWICE KRAKÓW RZESZÓW BIELSKO-BIAŁA TERENA 2003 NLEASED CHANNELS x 1 GE N x 1 GE (SX, LX, ZX) 622 Mb/s Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b, Metropolitan Area Networks
Intermediate stage - 10 GE over fiber OWN FIBERS GDAŃSK 10 Gb/s 1 Gb/s KOSZALIN POZNAN node MAN node SZCZECIN OLSZTYN BYDGOSZCZ TORUŃ GEANT M 160 GÉANT 10 BIAŁYSTOK GE 10 GE GÉANT 2. 5 Gb/s POZNAŃ 2. 5 G POS N ZIELONA x ATM GÓRA STM-4 WARSZAWA 10 G POS ŁÓDŹ WROCŁAW CZĘSTOCHOWA OPOLE 155 Mb/s RADOM KIELCE 10 10 GE PUŁAWY GE LUBLIN KATOWICE KRAKÓW RZESZÓW BIELSKO-BIAŁA TERENA 2003 NLEASED CHANNELS x 1 GE N x 1 GE (SX, LX, ZX) 622 Mb/s Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b, Metropolitan Area Networks
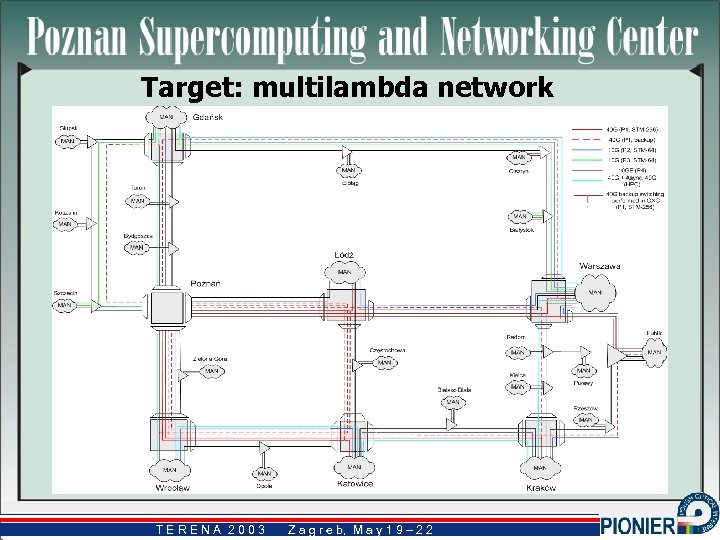 Target: multilambda network TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
Target: multilambda network TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
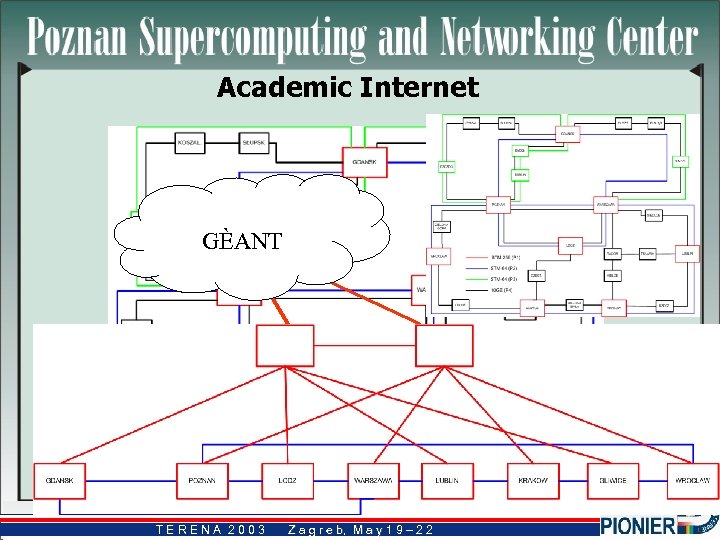 Academic Internet GÈANT TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
Academic Internet GÈANT TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
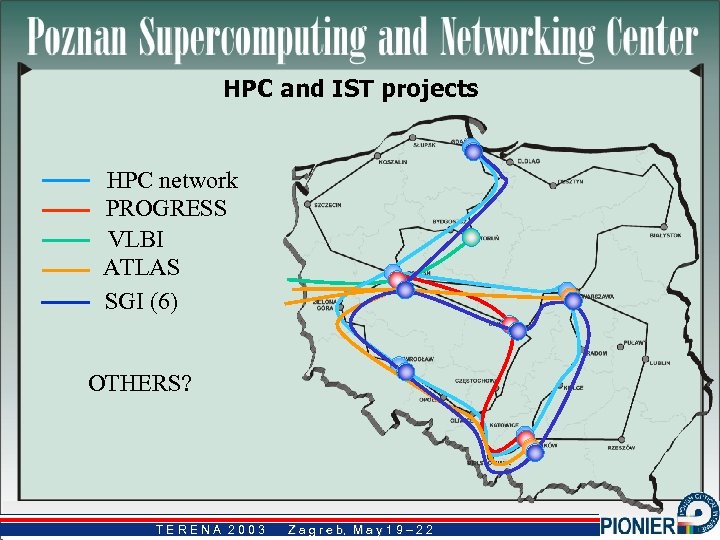 HPC and IST projects HPC network PROGRESS VLBI ATLAS SGI (6) OTHERS? TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
HPC and IST projects HPC network PROGRESS VLBI ATLAS SGI (6) OTHERS? TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
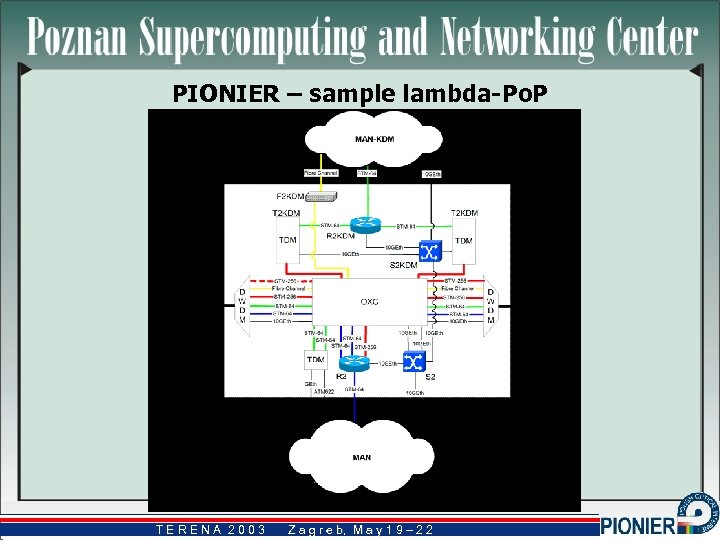 PIONIER – sample lambda-Po. P TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
PIONIER – sample lambda-Po. P TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
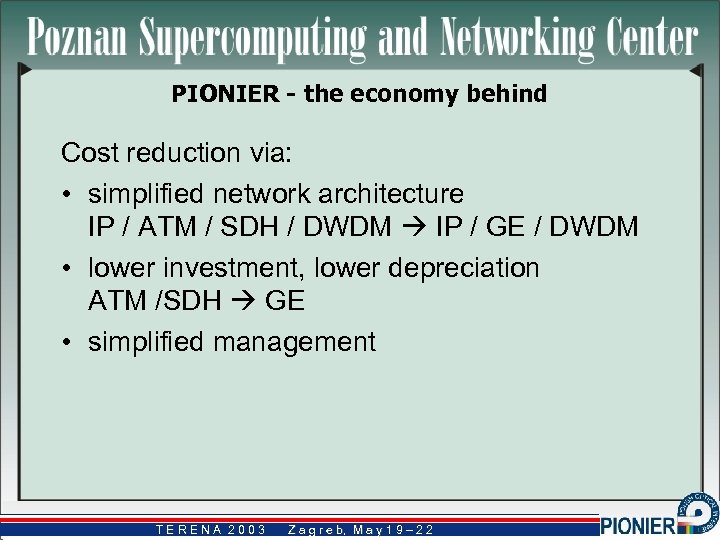 PIONIER - the economy behind Cost reduction via: • simplified network architecture IP / ATM / SDH / DWDM IP / GE / DWDM • lower investment, lower depreciation ATM /SDH GE • simplified management TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
PIONIER - the economy behind Cost reduction via: • simplified network architecture IP / ATM / SDH / DWDM IP / GE / DWDM • lower investment, lower depreciation ATM /SDH GE • simplified management TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
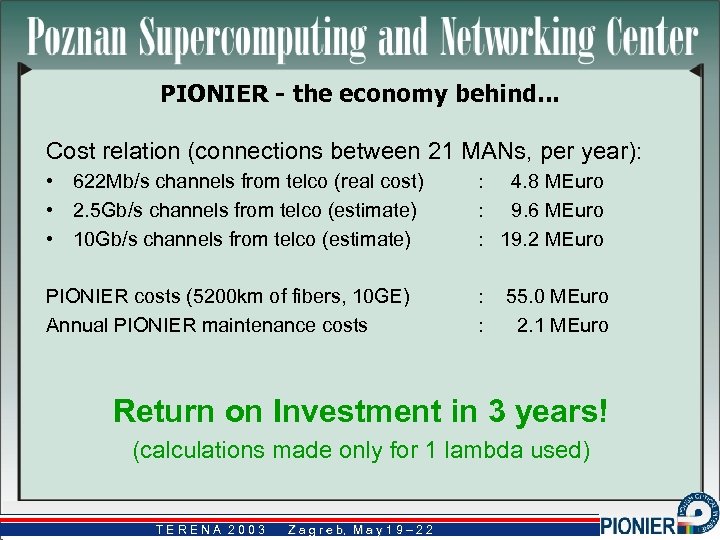 PIONIER - the economy behind. . . Cost relation (connections between 21 MANs, per year): • 622 Mb/s channels from telco (real cost) • 2. 5 Gb/s channels from telco (estimate) • 10 Gb/s channels from telco (estimate) : 4. 8 MEuro : 9. 6 MEuro : 19. 2 MEuro PIONIER costs (5200 km of fibers, 10 GE) Annual PIONIER maintenance costs : : 55. 0 MEuro 2. 1 MEuro Return on Investment in 3 years! (calculations made only for 1 lambda used) TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
PIONIER - the economy behind. . . Cost relation (connections between 21 MANs, per year): • 622 Mb/s channels from telco (real cost) • 2. 5 Gb/s channels from telco (estimate) • 10 Gb/s channels from telco (estimate) : 4. 8 MEuro : 9. 6 MEuro : 19. 2 MEuro PIONIER costs (5200 km of fibers, 10 GE) Annual PIONIER maintenance costs : : 55. 0 MEuro 2. 1 MEuro Return on Investment in 3 years! (calculations made only for 1 lambda used) TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
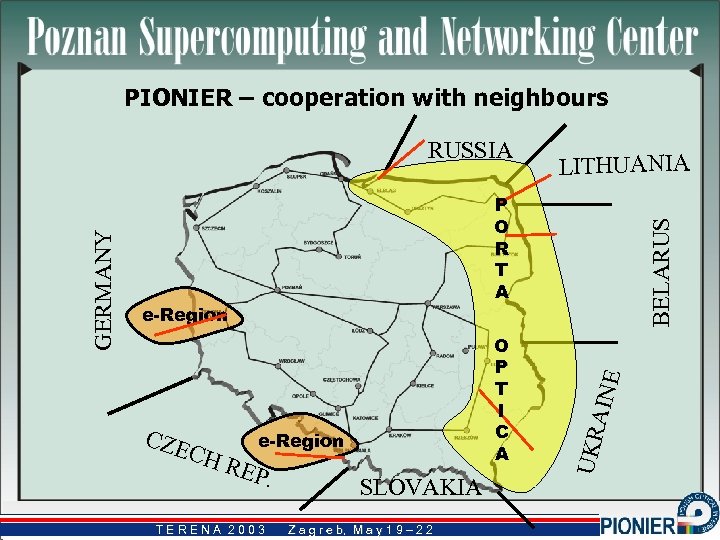 PIONIER – cooperation with neighbours e-Region CH REP. TERENA 2003 SLOVAKIA Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b, AINE O P T I C A BELARUS P O R T A e-Region CZE LITHUANIA UKR GERMANY RUSSIA
PIONIER – cooperation with neighbours e-Region CH REP. TERENA 2003 SLOVAKIA Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b, AINE O P T I C A BELARUS P O R T A e-Region CZE LITHUANIA UKR GERMANY RUSSIA
 PIONIER – e-Region Two e-Regions already defined: • • Cottbus – Zielona Gora (D-PL) Ostrava – Bielsko Biala (CZ-PL) e-Region objectives: 1. Creation of a rational base and possibility of integrated work between institutions across the border, as defined by e-Europe. (. . . ) education, medicine, natural disasters, information bases, protection of environment. 2. Enchancing the abilities of co-operation by developing new generation of services and applications. 3. Promoting the region in the Europe (as a micro scale of e-Europe concept) TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
PIONIER – e-Region Two e-Regions already defined: • • Cottbus – Zielona Gora (D-PL) Ostrava – Bielsko Biala (CZ-PL) e-Region objectives: 1. Creation of a rational base and possibility of integrated work between institutions across the border, as defined by e-Europe. (. . . ) education, medicine, natural disasters, information bases, protection of environment. 2. Enchancing the abilities of co-operation by developing new generation of services and applications. 3. Promoting the region in the Europe (as a micro scale of e-Europe concept) TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
 PIONIER – „Porta Optica” • „PORTA OPTICA” - a distributed optical gateway to eastern neigbours of Poland (project proposal) • A chance for close cooperation in scientific projects, by the means of providing multichannel/multilambda Internet connections to the neighbouring countries. • An easy way to extend GEANT to Eastern European countries TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
PIONIER – „Porta Optica” • „PORTA OPTICA” - a distributed optical gateway to eastern neigbours of Poland (project proposal) • A chance for close cooperation in scientific projects, by the means of providing multichannel/multilambda Internet connections to the neighbouring countries. • An easy way to extend GEANT to Eastern European countries TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
 European network for advanced services - New generation of global value added services (GRIDs) - resources all over the world - large bandwidth requirements (>1 Gb/s) - dedicated core capacity - access via Internet or dedicated channel/lambda - Examples: - Tera. GRID computing and storage (TFlops & PB/s) - TV distribution GRID - x. Content GRID - Global Internet - dynamically created, n x between Po. Ps - broadband mobile access (EFM, Wi-Fi) Problem: how to build networks supporting such services? TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
European network for advanced services - New generation of global value added services (GRIDs) - resources all over the world - large bandwidth requirements (>1 Gb/s) - dedicated core capacity - access via Internet or dedicated channel/lambda - Examples: - Tera. GRID computing and storage (TFlops & PB/s) - TV distribution GRID - x. Content GRID - Global Internet - dynamically created, n x between Po. Ps - broadband mobile access (EFM, Wi-Fi) Problem: how to build networks supporting such services? TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
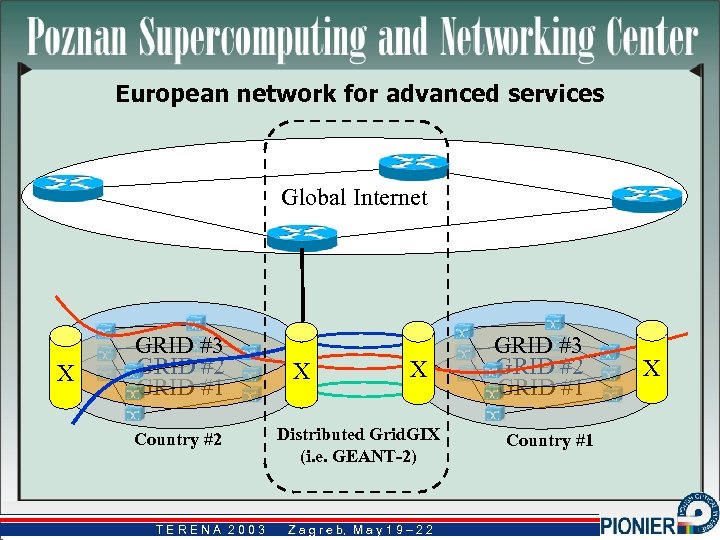 European network for advanced services Global Internet X GRID #3 GRID #2 GRID #1 Country #2 TERENA 2003 X X Distributed Grid. GIX (i. e. GEANT-2) Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b, GRID #3 GRID #2 GRID #1 Country #1 X
European network for advanced services Global Internet X GRID #3 GRID #2 GRID #1 Country #2 TERENA 2003 X X Distributed Grid. GIX (i. e. GEANT-2) Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b, GRID #3 GRID #2 GRID #1 Country #1 X
 What we believe in? 1. GEANT and NRENS should migrate to multilambda due to following facts: – Emergence of Global Value Added Services (in form of specialized GRIDs) – Ethernet and Wi-Fi technologies will revolutionize global broadband access 2. NRENs will embrace optical Regional and Metropolitan Area Networks – a move towards All Optical Network 3. Ethernet will be broadly used from first/last mile to WAN 4. IPv 6 will be common platform for integrated multiservice (voice, data, video) network TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,
What we believe in? 1. GEANT and NRENS should migrate to multilambda due to following facts: – Emergence of Global Value Added Services (in form of specialized GRIDs) – Ethernet and Wi-Fi technologies will revolutionize global broadband access 2. NRENs will embrace optical Regional and Metropolitan Area Networks – a move towards All Optical Network 3. Ethernet will be broadly used from first/last mile to WAN 4. IPv 6 will be common platform for integrated multiservice (voice, data, video) network TERENA 2003 Z a g r e b, M a y 1 9 – 2 2 b,


