560d6636fa0ccdff62d04868831785d5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

Next Generation Logistics Transactions – Extensible Markup Language (XML) Kick-Off Meeting DLSS/DLMS X 12 & XML – Our Approach Dale Yeakel & Nat Obey Defense Logistics Management Standards Office http: //www. dla. mil/j-6/dlmso/

MODELS 1984 XML 2002 xx xx FIPS 161. 2 1996 Do. DD 8190. 1 2000 2

Business Rules and Standards Outline: • Purpose/mission • Key Do. D oversight policy • What we do • Who we do it for • How we do it • Not easy stuff • Current focus areas – Migrating Do. D unique information standards to common commercial standards – Supporting modernization (ERPs) – Exploring new technology solutions XML within the DLMS • Summary 3

Business Rules and Standards Purpose/Mission: • Facilitate enterprise integration and continuous process improvements to logistics management and operations by: – Developing business rules and implementation of Do. D policy – Developing and managing the Do. D logistics information exchange infrastructure – Publishing detailed procedures that identify who does what, when, and how along the Do. D supply chain: 4

Business Rules and Standard Key Do. D oversight policy: • Do. DD 8190. 1, Do. D Logistics Use of EDI Standards: – Do. D Executive Agent for logistics data interchange • Do. DD 4140. 1 Materiel Management Policy – Authorizes publication of Do. D business rules and standards • Do. D 4140. 1 -R Materiel Management Regulation – “Loaded” with policy, procedure, and guidance • Do. D 4000. 25 series of Manuals covering both the DLMS and DLSS/MILS (8 K pages) ―Prescribes logistics management policy, responsibilities, procedures, rules, and electronic data Business rule and standard operational development and communications standards implementation is well grounded in Do. D policy 5

Business Rules and Standards What we do: • DLMSO administers Do. D-wide: – Defense Logistics Standard Systems (DLSS) – Defense Logistics Management System (DLMS) – Do. D Physical Inventory Control Program – Do. D Logistics Functional Data Administration Program • DLMSO chairs: – DLMS Process Review Committees (PRCs) – Unique Item Tracking Committee – Customer Wait Time / Logistics Response Time Comm – Do. D Supply Discrepancy Reporting Sub-Committee – Joint Physical Inventory Working Group – Joint Small Arms Coordinating Group – Do. DAAD/MAPAD Committees 6
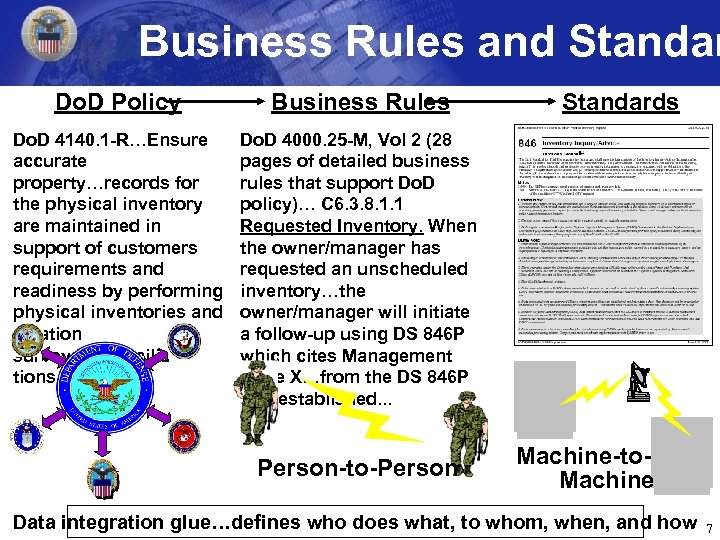
Business Rules and Standar Do. D Policy Business Rules Do. D 4140. 1 -R…Ensure accurate property…records for the physical inventory are maintained in support of customers requirements and readiness by performing physical inventories and location surveys/reconcilia - tions. Do. D 4000. 25 -M, Vol 2 (28 pages of detailed business rules that support Do. D policy)… C 6. 3. 8. 1. 1 Requested Inventory. When the owner/manager has requested an unscheduled inventory…the owner/manager will initiate a follow-up using DS 846 P which cites Management Code X…from the DS 846 P that established. . . Person-to-Person Standards Machine-to. Machine Data integration glue…defines who does what, to whom, when, and how 7

Business Rules and Standar Business Rule Hierarchy Governing Rules - Operating Rules - Automated Rules Physical Inventory Control Governing Rules Do. D Policy is contained in Do. D 4140. 1 -R, paragraph C 5. 7. 5. 1. 1 Physical inventory procedures are contained in Do. D 4000. 25 -M, Vol 2, Chapter 6 Operating Rules Example: Paragraph C 6. 2. 6. 1: Owners/managers and storage activities shall daily match all active record (stock number which had any transactions affecting record balances) on hand balances. Automated Rules The storage activity shall submit the daily closing balance to each affected owner/manager using DLMS supplements to Federal IC 846 R with Code List Qualifier Code FH citing code 1 (End of Day Processing) Computer Speak If DS 846 R LQ 02 QTY 02 Quantity. Qualifer. Code = SYSTEM. BALANCE then Generate DS 846 R LQ 01 Code. List. Qualifier. Code FH=1 (To show Balance is End of Day) and LQ 02 QTY 02 Code. List. Qualifier Quantity(End of Day Balance) If DS 846 R LQ 02 QTY 02 Quantity. Qualifier. Coder Not Equal SYSTEM. BALANCE then Generate DS 947 I W 1901 Quantity. or. Status. Adjustsment. Reason. Code=AB and W 1902 Credit. Debit. Quantity (End of Day Balance) 8
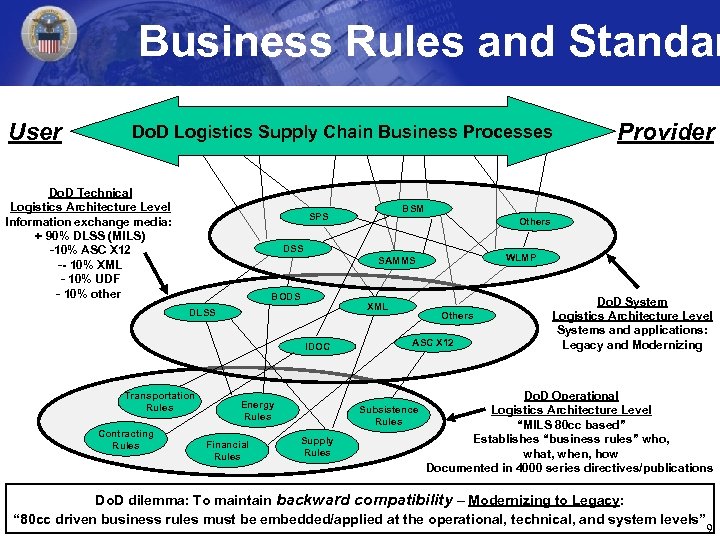
Business Rules and Standar User Do. D Logistics Supply Chain Business Processes Do. D Technical Logistics Architecture Level Information exchange media: + 90% DLSS (MILS) -10% ASC X 12 -- 10% XML - 10% UDF - 10% other Others DSS WLMP SAMMS XML DLSS IDOC Transportation Rules Contracting Rules BSM SPS BODS Energy Rules Financial Rules Others ASC X 12 Subsistence Rules Supply Rules Provider Do. D System Logistics Architecture Level Systems and applications: Legacy and Modernizing Do. D Operational Logistics Architecture Level “MILS 80 cc based” Establishes “business rules” who, what, when, how Documented in 4000 series directives/publications Do. D dilemma: To maintain backward compatibility – Modernizing to Legacy: “ 80 cc driven business rules must be embedded/applied at the operational, technical, and system levels” 9
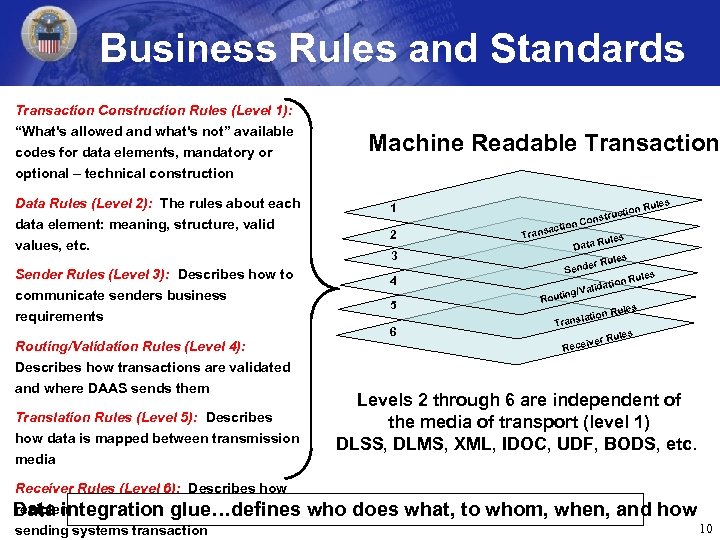
Business Rules and Standards Transaction Construction Rules (Level 1): “What's allowed and what's not” available codes for data elements, mandatory or optional – technical construction Data Rules (Level 2): The rules about each data element: meaning, structure, valid values, etc. Sender Rules (Level 3): Describes how to communicate senders business requirements Routing/Validation Rules (Level 4): Describes how transactions are validated and where DAAS sends them Translation Rules (Level 5): Describes how data is mapped between transmission media Machine Readable Transaction 2 Rules Data les er Ru Send 4 6 uctio onstr n C actio Trans 3 5 s e n Rul 1 R les on Ru ti alida ting/V ou es n Rul slatio Tran ules iver R Rece Levels 2 through 6 are independent of the media of transport (level 1) DLSS, DLMS, XML, IDOC, UDF, BODS, etc. Receiver Rules (Level 6): Describes how recipient system is to process/react to the Data integration glue…defines who does what, to whom, when, and how 10 sending systems transaction
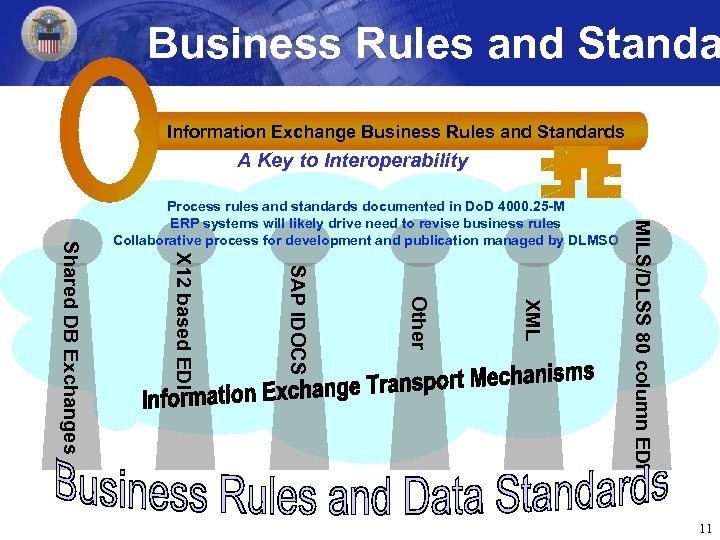
Business Rules and Standa Information Exchange Business Rules and Standards A Key to Interoperability MILS/DLSS 80 column EDI XML Other SAP IDOCS X 12 based EDI Shared DB Exchanges Process rules and standards documented in Do. D 4000. 25 -M ERP systems will likely drive need to revise business rules Collaborative process for development and publication managed by DLMSO 11
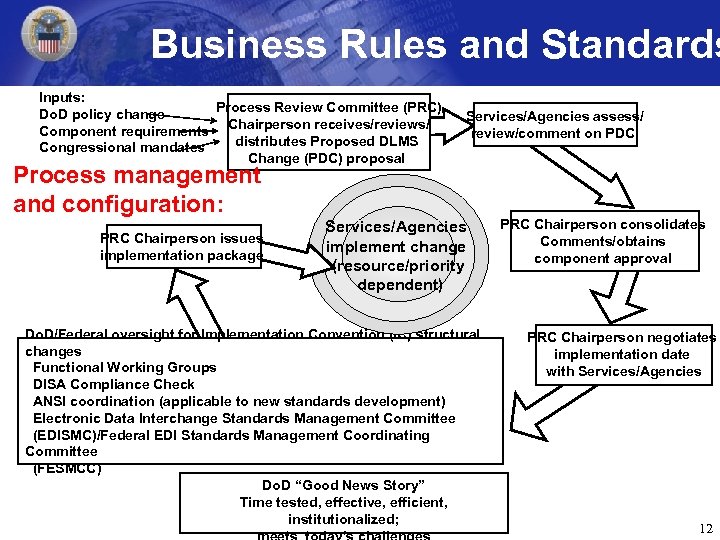
Business Rules and Standards Inputs: Process Review Committee (PRC) Do. D policy change Component requirements Chairperson receives/reviews/ distributes Proposed DLMS Congressional mandates Change (PDC) proposal Services/Agencies assess/ review/comment on PDC Process management and configuration: PRC Chairperson issues implementation package Services/Agencies implement change (resource/priority dependent) Do. D/Federal oversight for Implementation Convention (IC) structural changes Functional Working Groups DISA Compliance Check ANSI coordination (applicable to new standards development) Electronic Data Interchange Standards Management Committee (EDISMC)/Federal EDI Standards Management Coordinating Committee (FESMCC) Do. D “Good News Story” Time tested, effective, efficient, institutionalized; PRC Chairperson consolidates Comments/obtains component approval PRC Chairperson negotiates implementation date with Services/Agencies 12
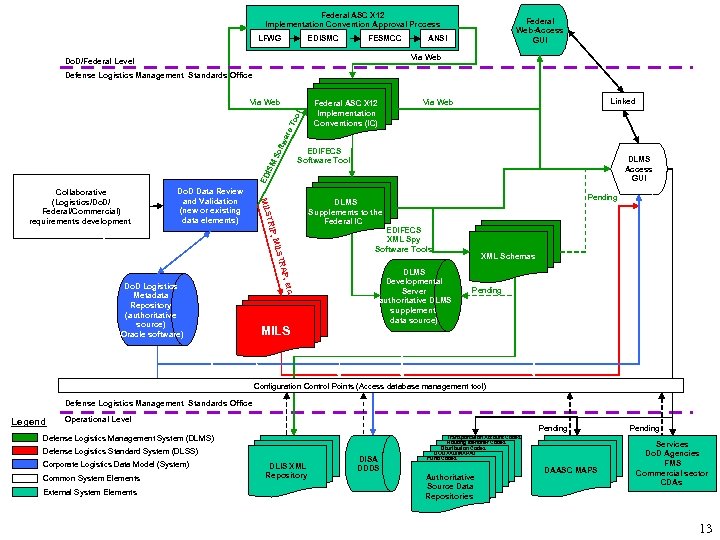
Federal ASC X 12 Implementation Convention Approval Process LFWG EDISMC FESMCC Federal Web-Access GUI ANSI Via Web Do. D/Federal Level Defense Logistics Management Standards Office Via Web Linked Via Web EDIFECS Software Tool DLMS Access GUI ED ISM So ftw are To ol Federal ASC X 12 Implementation Conventions (IC) etc. AP, STR , MIL Do. D Logistics Metadata Repository (authoritative source) (Oracle software) Pending DLMS Supplements to the Federal IC TRIP Do. D Data Review and Validation (new or existing data elements) MILS Collaborative (Logistics/Do. D/ Federal/Commercial) requirements development MILS EDIFECS XML Spy Software Tools DLMS Developmental Server (authoritative DLMS supplement data source) XML Schemas Pending Configuration Control Points (Access database management tool) Defense Logistics Management Standards Office Legend Operational Level Pending Defense Logistics Management System (DLMS) Defense Logistics Standard System (DLSS) Corporate Logistics Data Model (System) Common System Elements External System Elements DLIS XML Repository DISA DDDS Transportation Account Codes Routing Identifier Codes Distribution Codes DODAAD/MAPAD Fund Codes Authoritative Source Data Repositories DAASC MAPS Pending Services Do. D Agencies FMS Commercial sector CDAs 13

Business Rules and Standards Who we do it for --- customers/users: • TOP LEVEL MANAGEMENT: OSD PSAs, Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS), UCCs, Component Headquarters, Major Commands, Civil Agency Headquarters, etc. • Do. D & Non Do. D OPERATIONAL TRADING PARTNERS: Cradle-to-grave process management activities, enterprise-wide service providers, private sector product & service providers, and civil agencies, and foreign governments. • AUTOMATED INFORMATION SYSTEM (AIS) DEVELOPERS & INTEGRATORS: (technical community) 14

Business Rules and Standards Not Easy Stuff: • How does a customer identify when he wants delivery? – Priority designator --- maybe unless there’s an RDD – Required delivery date --- maybe unless RDD contains: § A special code or… § Transaction has special management indicator or… § There is pre-agreed to arrangement with supplier • The business rules governing this simple question are: – Managed by DLMSO – Published in the DLSS & DLMS manuals 15

Business Rules and Standards Current focus areas: • Migrating Do. D unique information standards to common commercial practices (Federally mandated standards) • Supporting modernization (Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)) • Exploring new technology solutions • Process management and configuration • Do. DAAD reengineering 16
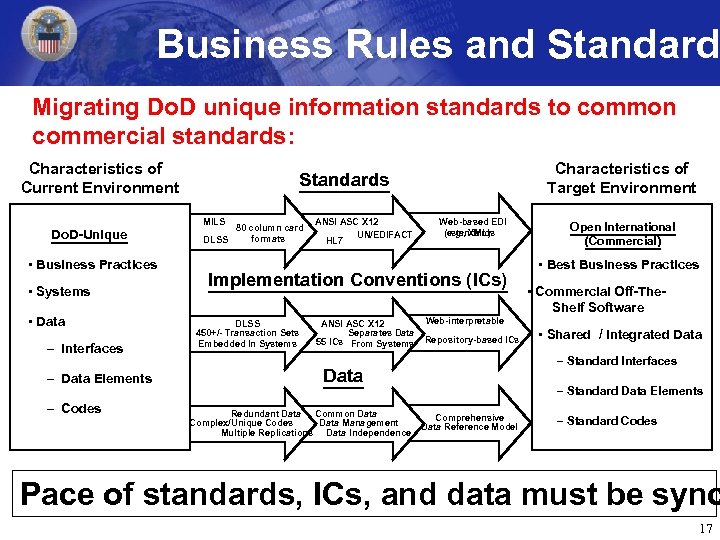
Business Rules and Standards Migrating Do. D unique information standards to common commercial standards: Characteristics of Current Environment Do. D-Unique • Business Practices • Systems • Data – Interfaces – Data Elements – Codes Characteristics of Target Environment Standards MILS 80 column card formats DLSS ANSI ASC X 12 UN/EDIFACT HL 7 Web-based EDI (e. g. , XML) standards Implementation Conventions (ICs) DLSS 450+/- Transaction Sets Embedded In Systems Web-interpretable ANSI ASC X 12 Separates Data 55 ICs From Systems Repository-based ICs • Best Business Practices • Commercial Off-The Shelf Software • Shared / Integrated Data – Standard Interfaces Data Redundant Data Common Data Complex/Unique Codes Data Management Multiple Replications Data Independence Open International (Commercial) – Standard Data Elements Comprehensive Data Reference Model – Standard Codes Pace of standards, ICs, and data must be sync 17

Business Rules and Standard Supporting modernization (ERPs): • IAW Do. D direction and in coordination with Components: – Identified common enterprise-wide requirements – Mapped requirements against current capabilities – revealed gaps – Identified policies/framework needed to ensure economic and effective implementation – Wrote plan of action with implementation milestones 18

Business Rules and Standards Exploring new technology solutions: Do. DD 8190. 1… “A broad base of business rules to include uniform policies, procedures, time standards, transactions, and data management designed to meet Do. D’s requirements for total logistics support. The DLMS is founded upon the sound application of ANSI ASC X 12 EDI and will be expanded to employ other emerging EB/EC technologies such as: data sharing, automated identification technology, object-oriented user interfaces, electronic malls, web-based technology, and electronic funds transfer, as appropriate. ” Opens the door to new and emerging technologies 19

Why Extensible Markup Language (XML)? Business Rules and Standards • XML - subset of SGML (Standardized General Markup Language) and HTML • Provides more flexible EDI form designed to support WEB based applications • DLA/DLMSO strongly supporting development of XML schemas and implementation of XML standard for Do. D • DLMSO has developed W 3 C compliant XML schemas, using EDIFECS Spec. Builder tool. The XML schemas equate to the DLMS ANSI ASC X 12 ICs/supplements. • DLMSO participating/supporting various industry groups (ASC X 12 XML Workgroup, Federal CIO XML Workgroup, and DISA Namespace Manager & Repositories) • DAASC has capability to translate - MILS/DLSS><DLMS X 12><DLMS XML • Using the DLMS XML capitalizes on existing data standards and maintains interoperability 20 with legacy system EDI capability
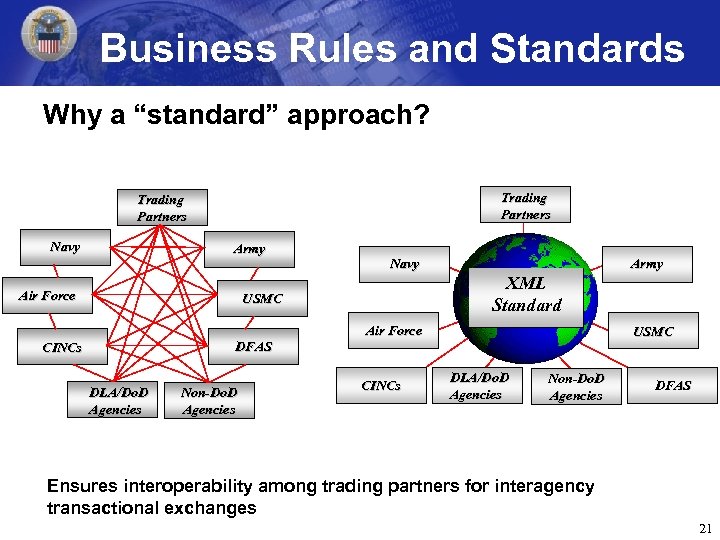
Business Rules and Standards Why a “standard” approach? Trading Partners Navy Army Air Force Navy XML Standard USMC DFAS CINCs DLA/Do. D Agencies Non-Do. D Agencies Army Air Force CINCs USMC DLA/Do. D Agencies Non-Do. D Agencies DFAS Ensures interoperability among trading partners for interagency transactional exchanges 21

Business Rules and Standards XML Schema 22

Business Rules and Standards Where We Are Current status: • DLMSO has acquired COTS tools: EDIFECS & XML Spy • Schema generation (version 2) is complete • DAASC has acquired Mercator v 6. 5 Schema Import To • DLIS & DISA repositories in place • Schemas posted to DLMSO’s XML web page Next steps: • DLMSO continue to post schemas to DISA/DLIS reposi • Continue to monitor progress of ANSI’s Context Inspir Component Architecture (CICA) for XML – target imple • DAASC develop maps • DLMSO/DAASC/DLIS develop operational systems test 23 • DLMSO prepare and have OSD issue policy memorand

Business Rules and Standards http: //diides. ncr. disa. mil/xmlreg/user/index. cfm DISA Repository 24

Business Rules and Standards h DLIS Repositoryttp: //www. dlis. dla. mil/XRL 25
Business Rules and Standards http: //www. dla. mil/j-6/dlmso/e. Library/Trans. Formats DLMSO XML Web Page 26
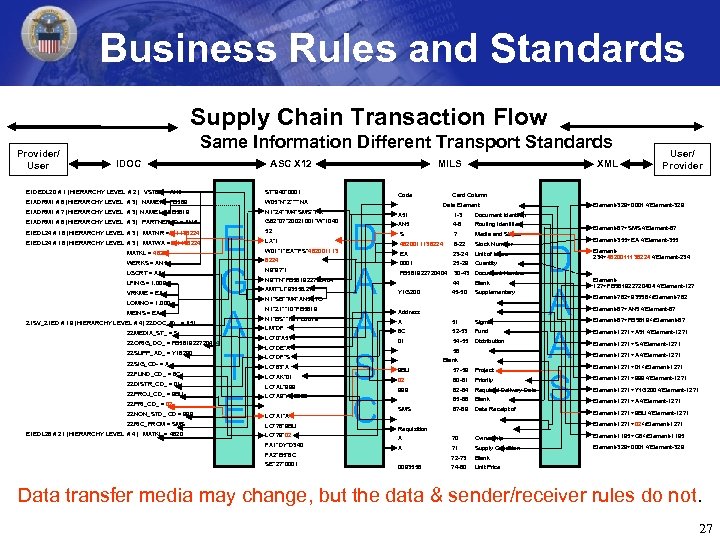
Business Rules and Standards Supply Chain Transaction Flow Provider/ User Same Information Different Transport Standards IDOC ASC X 12 E 1 DEDL 20 # 1 (HIERARCHY LEVEL # 2) VSTEL = AN 5 ST*940*0001 E 1 ADRM 1 # 6 (HIERARCHY LEVEL # 3) NAME 1 = FB 589 W 05*N*Z****NA E 1 ADRM 1 # 7 (HIERARCHY LEVEL # 3) NAME 1 = FB 5819 N 1*Z 4**M 4*SMS**FR E 1 ADRM 1 # 8 (HIERARCHY LEVEL # 3) PARTNER ID = AN 5 G 62*07*20021001*W*1040 MILS E 1 EDL 24 # 18 (HIERARCHY LEVEL # 3) MATNR =011138224 E 1 EDL 24 # 18 (HIERARCHY LEVEL # 3) MATWA =011138224 MATKL = 4820 WERKS = AN 5 LGORT = AA LFING = 1. 000 VRKME = EA LOMNO = 1. 000 MEINS = EA Z 1 SV_Z 1 ED # 19 (HIERARCHY LEVEL # 4) ZZDOC_ID_ = A 51 ZZMEDIA_ST_ = S ZZORIG_DO_ = FB 581922720404 ZZSUPP_AD_ = Y 16200 ZZSIG_CD- = A ZZFUND_CD_ = 6 C ZZDISTR_CD_ = 01 ZZPROJ_CD_ = 9 BU ZZPRI_CD_ = 02 ZZNON_STD_ CD = 999 ZZRIC_FROM = SMS E 1 EDL 26 # 21 (HIERARCHY LEVEL # 4) MATKL = 4820 E G A T E 52 LX*1 W 01*1*EA**FS*482001113 8224 N 9*97*1 N 9*TN*FB 581922720404 AMT*LI*93558. 27 N 1*SB**M 4*AN 5**TO N 1*Z 1**10*FB 5819 N 1*BS**10*FB 5819 LM*DF LQ*0*A 51 LQ*DE*A LQ*DF*S LQ*83*A LQ*AK*01 LQ*AL*999 LQ*A 9*Y 1 G 200 LQ*A 1*A LQ*78*9 BU Code XML Card Column Data Element D A A S C User/ Provider A 51 1 -3 AN 5 4 -6 Routing Identifier S 7 Media and Status 4820011138224 8 -22 Stock Number EA 23 -24 Unit of Issue 0001 25 -29 Quantity FB 581922720404 30 -43 Document Number Element-329>0001</Element-329 Document Identifier 44 Blank 45 -50 Supplementary A 51 Signal 6 C 52 -53 Fund 01 54 -55 Distribution Y 1 G 200 Address 56 Blank 9 BU 57 -59 Project 02 60 -61 Priority 999 62 -64 Required Delivery Date 65 -66 Blank 67 -69 Date Receipt of SMS Element-67>SMS</Element-67 D A A S Element-355>EA</Element-355 Element 234>4820011138224</Element-234 Element 127>FB 581922720404</Element-127 Element-782>93558</Element-782 Element-67>AN 5</Element-67>FB 5819</Element-67 Element-1271>A 51</Element-1271>S</Element-1271>A</Element-1271>01</Element-1271>999</Element-1271>Y 1 G 200</Element-1271>A</Element-1271>9 BU</Element-1271>02</Element-1271 Requisition LQ*79*02 A 70 Ownership Element-1195>C 6</Element-1195 FA 1*DY*D 340 A 71 Supply Condition Element-329>0001</Element-329 72 -73 Blank 74 -80 Unit Price FA 2*B 5*6 C SE*27*0001 0093558 Data transfer media may change, but the data & sender/receiver rules do not. 27

Business Rules and Standard Summary: • We are expanding our overarching logistics role to meet today’s enterprise integration challenge and support the future logistics enterprise by: – Migrating Do. D away from proprietary EDI standards – Actively supporting Component modernization – Exploring & implementing new technology solutions • End-state: – Support the adoption of the best business practices – Ensure that business transactions are successfully exchanged among Do. D AISs, regardless of the data transmission media (standards) used by the AISs involved. • The DLMS are now XML capable and ready for your use http: //www. dla. mil/j-6/dlmso/ 28

MODELS 1984 XML 2002 xx xx FIPS 161. 2 1996 Do. DD 8190. 1 2000 29
560d6636fa0ccdff62d04868831785d5.ppt