0f6100d665f78630c8fa26af62fb3567.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 56
 NEW UNIT : THE PROGRESSIVES 1865 -1920 REFORMERS WHO WANT TO CHANGE GOVERNMENT, ECONOMY, SOCIETY TO EMPOWER MORE PEOPLE, IMPROVE LIVING CONDITIONS AND CREATE EQUALITY
NEW UNIT : THE PROGRESSIVES 1865 -1920 REFORMERS WHO WANT TO CHANGE GOVERNMENT, ECONOMY, SOCIETY TO EMPOWER MORE PEOPLE, IMPROVE LIVING CONDITIONS AND CREATE EQUALITY
 Why did city populations boom? • • Urban Overcrowding Industrial growth; must live near work Millions of Immigrants from ____ Great Migration many African Americans leave the _____ and ________ to find ______ and ______ in the North and Midwest • Jobs in ___________
Why did city populations boom? • • Urban Overcrowding Industrial growth; must live near work Millions of Immigrants from ____ Great Migration many African Americans leave the _____ and ________ to find ______ and ______ in the North and Midwest • Jobs in ___________
 How did people live in the city?
How did people live in the city?
 Wealthy Business Owners • Mansions • Luxury • Exclusive
Wealthy Business Owners • Mansions • Luxury • Exclusive
 Vanderbilt’s NYC Home
Vanderbilt’s NYC Home
 Carnegie’s NYC Home
Carnegie’s NYC Home
 Middle Class • More space in apartments than in poor neighborhoods • More parks • More plumbing, heating, cooling, light • Safer structures • Safer streets/neighborhoods
Middle Class • More space in apartments than in poor neighborhoods • More parks • More plumbing, heating, cooling, light • Safer structures • Safer streets/neighborhoods
 Middle Class NYC
Middle Class NYC
 How did most people live in the city? • Majority of people are poor ; live in _________ • Lack windows, plumbing, heating, cooling, electricity • Diseases spread easily • Fire Hazards • Crime
How did most people live in the city? • Majority of people are poor ; live in _________ • Lack windows, plumbing, heating, cooling, electricity • Diseases spread easily • Fire Hazards • Crime
 Tenement Life
Tenement Life
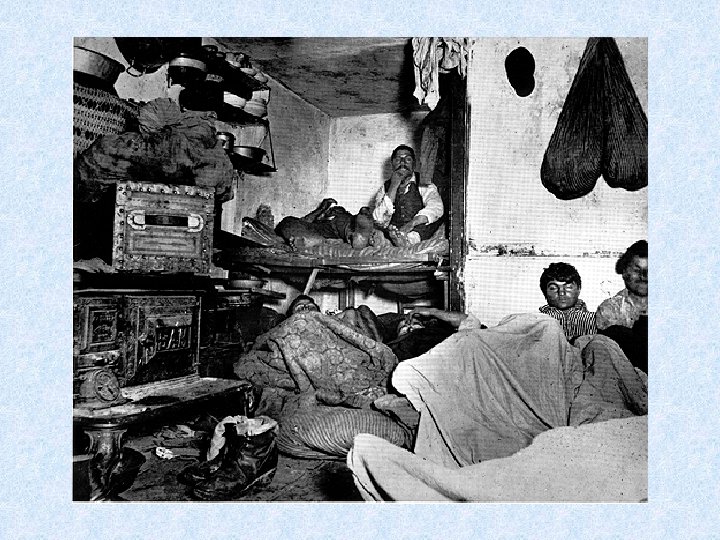
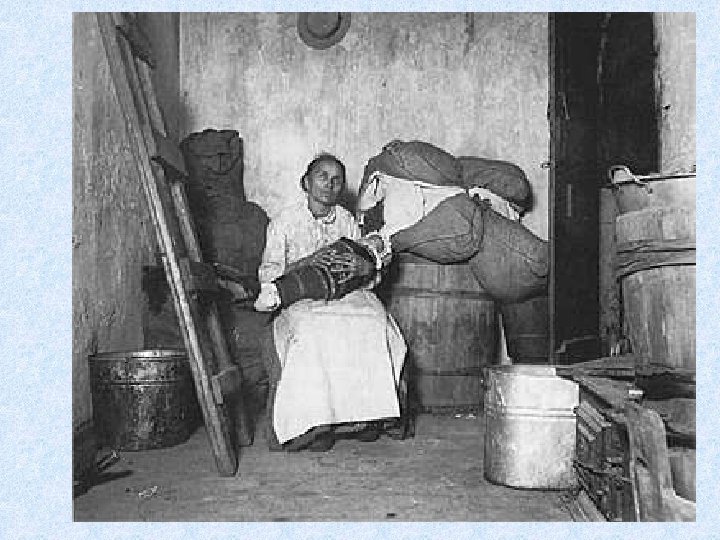


 Jacob Riis - NYC housing and children in poverty
Jacob Riis - NYC housing and children in poverty
 Progressive Strategies • Inform the public • Investigative reporting - muckraking • Books, newspaper and magazine articles (Mc. Clure’s) • Photographs - Jacob Riis, Lewis Hine • Political Cartoons – Thomas Nast • Support new laws and amendments
Progressive Strategies • Inform the public • Investigative reporting - muckraking • Books, newspaper and magazine articles (Mc. Clure’s) • Photographs - Jacob Riis, Lewis Hine • Political Cartoons – Thomas Nast • Support new laws and amendments
 PROBLEMS IN GOVERNMENT • CORRUPTION • SPOILS SYSTEM • PATRONAGE - GIVING JOBS TO FRIENDS AND POLITICAL SUPPORTERS; REGARDLESS OF SKILL>>>EMBEZZLE, TAKE BRIBES
PROBLEMS IN GOVERNMENT • CORRUPTION • SPOILS SYSTEM • PATRONAGE - GIVING JOBS TO FRIENDS AND POLITICAL SUPPORTERS; REGARDLESS OF SKILL>>>EMBEZZLE, TAKE BRIBES
 CIVIL SERVICE • 1883 - CONGRESS CREATES CIVIL SERVICE COMMISSION – • REQUIRES EXAMS FOR ALL CIVIL SERVICE JOBS >>working for the government; not military, not elected officials • Jobs go to people with ____
CIVIL SERVICE • 1883 - CONGRESS CREATES CIVIL SERVICE COMMISSION – • REQUIRES EXAMS FOR ALL CIVIL SERVICE JOBS >>working for the government; not military, not elected officials • Jobs go to people with ____
 PROBLEMS IN BUSINESS • UNFAIR TO SMALL BUSINESSES AND FARMERS • REBATES, POOLING • BRIBERY • NO REGULATIONS • ILLEGAL MONOPOLIES
PROBLEMS IN BUSINESS • UNFAIR TO SMALL BUSINESSES AND FARMERS • REBATES, POOLING • BRIBERY • NO REGULATIONS • ILLEGAL MONOPOLIES
 INTERSTATE COMMERCE ACT • NEW LAW 1887 • OUTLAW REBATES AND POOLS • ESTABLISH INTERSTATE COMMERCE COMMISSION • TO REGULATE RAILROADS/TRADE • Weak at first, then stronger over time
INTERSTATE COMMERCE ACT • NEW LAW 1887 • OUTLAW REBATES AND POOLS • ESTABLISH INTERSTATE COMMERCE COMMISSION • TO REGULATE RAILROADS/TRADE • Weak at first, then stronger over time
 More RR Reforms • Elkins Act – 1903 outlaw rebates (really!!!) • Hepburn Act – 1906 make ICC stronger
More RR Reforms • Elkins Act – 1903 outlaw rebates (really!!!) • Hepburn Act – 1906 make ICC stronger
 SHERMAN ANTI-TRUST ACT • • PASSED in 1890 STOP ILLEGAL MONOPOLIES REGULATE LARGE TRUSTS LIKE THE INTERSTATE COMMERCE ACT, ____AT FIRST; STRONGER OVER TIME
SHERMAN ANTI-TRUST ACT • • PASSED in 1890 STOP ILLEGAL MONOPOLIES REGULATE LARGE TRUSTS LIKE THE INTERSTATE COMMERCE ACT, ____AT FIRST; STRONGER OVER TIME
 PROBLEMS IN CITY GOV’T. • BOSS SYSTEM - URBAN POLITICAL LEADERS WHO CONTROLLED JOBS, SERVICES AND VOTES • drawing • Example William “Boss” Tweed - ran NYC in 1860 s-1870 s
PROBLEMS IN CITY GOV’T. • BOSS SYSTEM - URBAN POLITICAL LEADERS WHO CONTROLLED JOBS, SERVICES AND VOTES • drawing • Example William “Boss” Tweed - ran NYC in 1860 s-1870 s
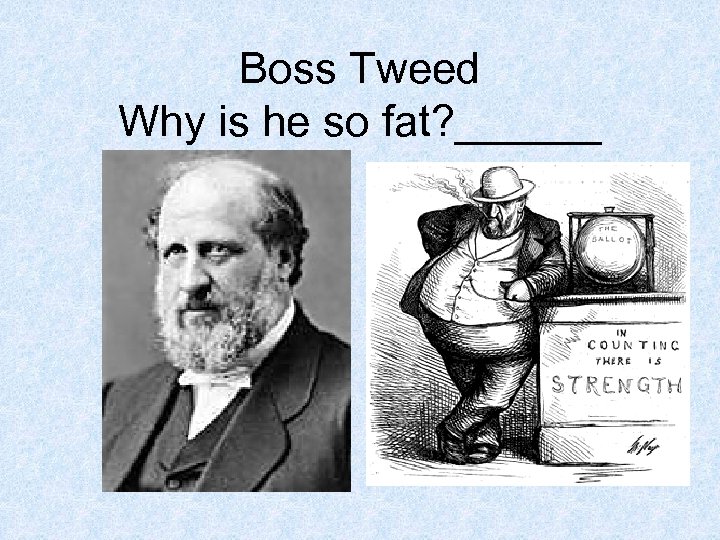 Boss Tweed Why is he so fat? ______
Boss Tweed Why is he so fat? ______

 What happened to Tweed? • Target of Progressive reporters, writers, and cartoonist Thomas Nast • Embezzled over $100 million from NYC • Tried to bribe Nast, then ran away to Europe • Recognized in Spain - because of cartoons >>>died in jail in NYC
What happened to Tweed? • Target of Progressive reporters, writers, and cartoonist Thomas Nast • Embezzled over $100 million from NYC • Tried to bribe Nast, then ran away to Europe • Recognized in Spain - because of cartoons >>>died in jail in NYC
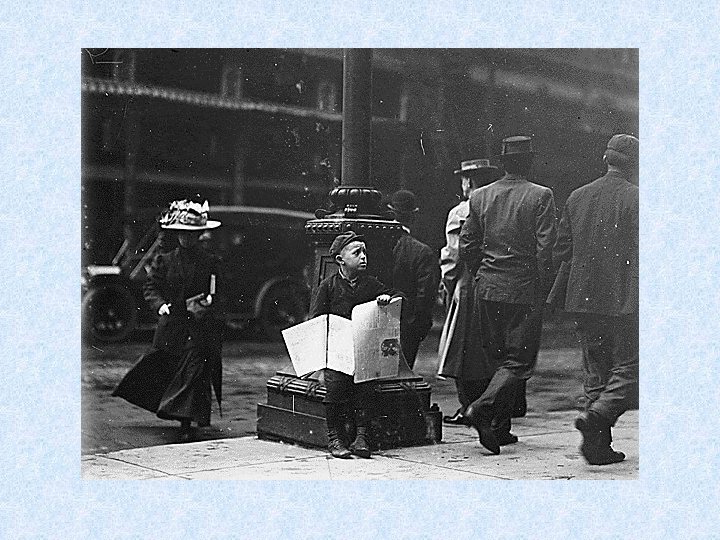
 Child Labor • • • Low wages Long hours Cheaper than hiring adults No unions Missing school >> not learning new skills>>>cycle of poverty
Child Labor • • • Low wages Long hours Cheaper than hiring adults No unions Missing school >> not learning new skills>>>cycle of poverty
 Jacob Riis - Homeless Children, NYC
Jacob Riis - Homeless Children, NYC
 Lewis Hine - NC factory girl
Lewis Hine - NC factory girl
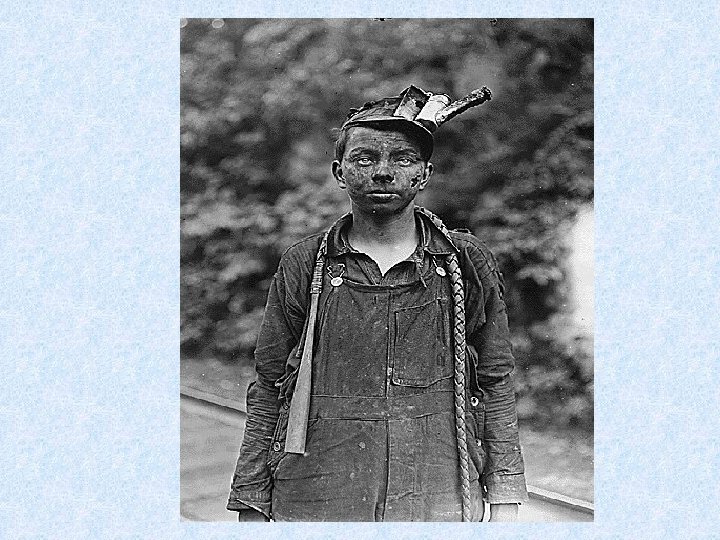
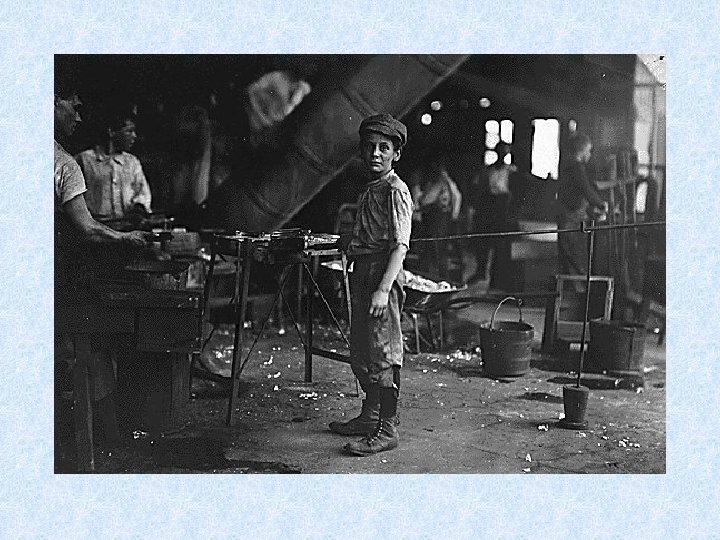
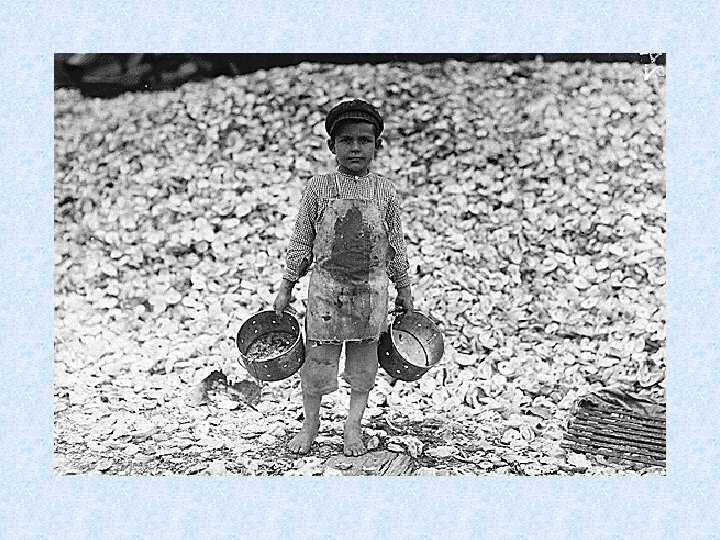
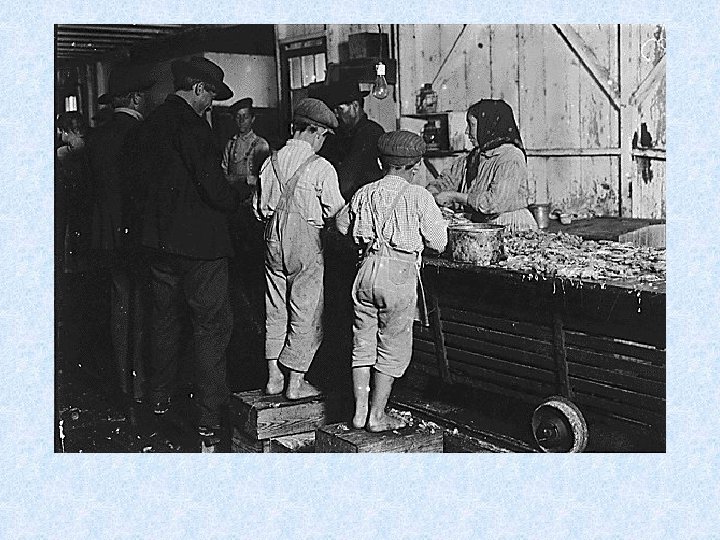
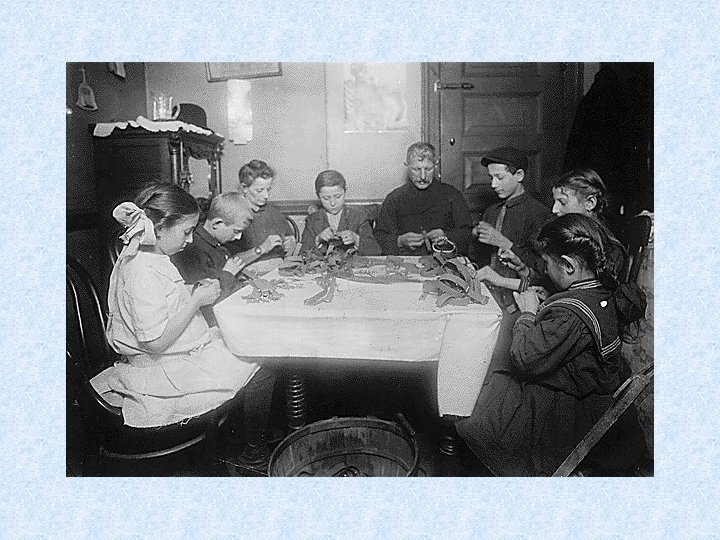






 Muckrakers Issues • Lincoln Steffens • City govt. ; reporter • Ida Tarbell • Standard Oil; author • Jacob Riis • Lewis Hine • Upton Sinclair • Poverty; photographer and author : How the Other Half Lives • Child Labor; Photographer • Writer - The Jungle ; meatpacking, working conditions
Muckrakers Issues • Lincoln Steffens • City govt. ; reporter • Ida Tarbell • Standard Oil; author • Jacob Riis • Lewis Hine • Upton Sinclair • Poverty; photographer and author : How the Other Half Lives • Child Labor; Photographer • Writer - The Jungle ; meatpacking, working conditions
 The Jungle
The Jungle
 Progressive Political Strategies • Laws - sunshine and regulatory • Elect honest official (goo-goos - good government leagues) • Increase legal voter registration and turnout • Amend United States Constitution
Progressive Political Strategies • Laws - sunshine and regulatory • Elect honest official (goo-goos - good government leagues) • Increase legal voter registration and turnout • Amend United States Constitution
 Power to the People • Primary - people vote for the party candidate before the general election • Initiative - voters put a bill on the state legislative agenda; it must be debated • Referendum - voters can make a ballot proposal become state law • Recall - voters can remove elected officials
Power to the People • Primary - people vote for the party candidate before the general election • Initiative - voters put a bill on the state legislative agenda; it must be debated • Referendum - voters can make a ballot proposal become state law • Recall - voters can remove elected officials
 TR Takes Over • Teddy Roosevelt - (R) from NY; • served on Civil Service Commission; head of NYPD; in U. S. army during Spanish-American War; governor of NY • Mc. Kinley’s vice-pres; becomes pres in 1901, when Mc. Kinley is shot; elected in 1904 • strong reformer
TR Takes Over • Teddy Roosevelt - (R) from NY; • served on Civil Service Commission; head of NYPD; in U. S. army during Spanish-American War; governor of NY • Mc. Kinley’s vice-pres; becomes pres in 1901, when Mc. Kinley is shot; elected in 1904 • strong reformer
 Teddy Roosevelt as Pres. • Trustbuster - TR used the __________ • Labor - threatened to use federal troops unless coal mine owners sat down with strikers. • _____- owners/workers/farmers and consumers
Teddy Roosevelt as Pres. • Trustbuster - TR used the __________ • Labor - threatened to use federal troops unless coal mine owners sat down with strikers. • _____- owners/workers/farmers and consumers
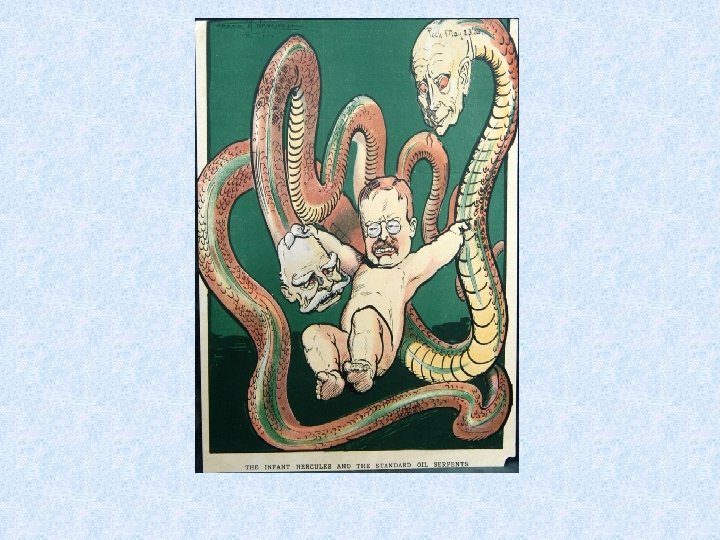
 New Laws supported by TR • Elkins Act (1903) - NO rebates • Hepburn Act (1906) - control RR (support for a weak IC bill) • Meat Inspection Act (1906) • Pure Food and Drug Act (1906) • Used executive orders to create national parks; land conservation
New Laws supported by TR • Elkins Act (1903) - NO rebates • Hepburn Act (1906) - control RR (support for a weak IC bill) • Meat Inspection Act (1906) • Pure Food and Drug Act (1906) • Used executive orders to create national parks; land conservation
 Race Relations in Progressive Era • Booker T. Washington • African- American man • Believed in success through hard work, vocational training • Up From Slavery • Equality eventually • Slavery>segregation >integration>equal • Accepted by more white leaders • W. E. B. Du. Bois • African- American man • Harvard Ph. D. • Cofounder of the NAACP • Believed in equality and integration now • Activist; fight for rights • Strong Progressive • Ideas used by MLK, jr.
Race Relations in Progressive Era • Booker T. Washington • African- American man • Believed in success through hard work, vocational training • Up From Slavery • Equality eventually • Slavery>segregation >integration>equal • Accepted by more white leaders • W. E. B. Du. Bois • African- American man • Harvard Ph. D. • Cofounder of the NAACP • Believed in equality and integration now • Activist; fight for rights • Strong Progressive • Ideas used by MLK, jr.
 Taft as President • William Howard Taft - supported by TR when he ran in 1908; different styles • Strong trustbuster • Support international investment (dollar diplomacy) • 1912 - TR opposes Taft for president • Taft >>Republican party, TR >> new Bull Moose Party …and the winner is…. .
Taft as President • William Howard Taft - supported by TR when he ran in 1908; different styles • Strong trustbuster • Support international investment (dollar diplomacy) • 1912 - TR opposes Taft for president • Taft >>Republican party, TR >> new Bull Moose Party …and the winner is…. .
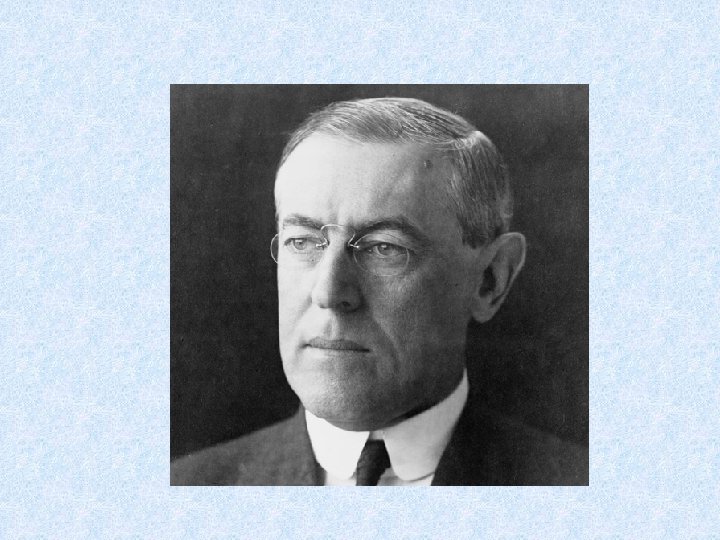

 Woodrow Wilson (D) • Elected in 1912 • Economic opportunities - supports income tax; lower tariffs, Federal Reserve • After YEARS of protests, supports suffrage for women • Needs to focus on international issues as World War I begins in Europe
Woodrow Wilson (D) • Elected in 1912 • Economic opportunities - supports income tax; lower tariffs, Federal Reserve • After YEARS of protests, supports suffrage for women • Needs to focus on international issues as World War I begins in Europe
 New Progressive Amendments 16 th amendment - ratified in 1913; established a graduated income tax 17 th amendment - ratified in 1913; Allowed voters to directly elect U. S. senators
New Progressive Amendments 16 th amendment - ratified in 1913; established a graduated income tax 17 th amendment - ratified in 1913; Allowed voters to directly elect U. S. senators
 Prohibition • • To stop the use and sale of alcohol Supported by temperance leaders Strategies Frances Willard - national group WCTU; prayer, sometimes at bars • Carry Nation - smash bars, kegs, bottles with a hatchet
Prohibition • • To stop the use and sale of alcohol Supported by temperance leaders Strategies Frances Willard - national group WCTU; prayer, sometimes at bars • Carry Nation - smash bars, kegs, bottles with a hatchet
 Women’s Christian Temperance Union
Women’s Christian Temperance Union
 Carry A. Nation
Carry A. Nation
 Result • 18 th amendment - bans or prohibits sale and use of alcohol in US • Ratified in 1917 • Organized crime increases (Al Capone) • Enforced, but illegal clubs, known as speakeasies, were everywhere • Bootlegging • Bathtub Gin, Moonshine
Result • 18 th amendment - bans or prohibits sale and use of alcohol in US • Ratified in 1917 • Organized crime increases (Al Capone) • Enforced, but illegal clubs, known as speakeasies, were everywhere • Bootlegging • Bathtub Gin, Moonshine
 Women’s Right to Vote suffrage • Susan B. Anthony • Elizabeth Cady Stanton • Why?
Women’s Right to Vote suffrage • Susan B. Anthony • Elizabeth Cady Stanton • Why?

 Women’s Right to Vote suffrage • How – • National Woman Suffrage Association • Carrie Chapman Catt - change over time, state by state, new laws • Alice Paul - marches on White House; chains, arrests, hunger strikes • Sufffrage Now, national amendment
Women’s Right to Vote suffrage • How – • National Woman Suffrage Association • Carrie Chapman Catt - change over time, state by state, new laws • Alice Paul - marches on White House; chains, arrests, hunger strikes • Sufffrage Now, national amendment

 The Result • 1920 - the 19 th amendment is passed and women have the right to vote
The Result • 1920 - the 19 th amendment is passed and women have the right to vote
 Progressive Goals • Make laws and support programs for public interest on state, local and national level
Progressive Goals • Make laws and support programs for public interest on state, local and national level


