f40172dc73fdb6a8a74b43c9889dcb60.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 10
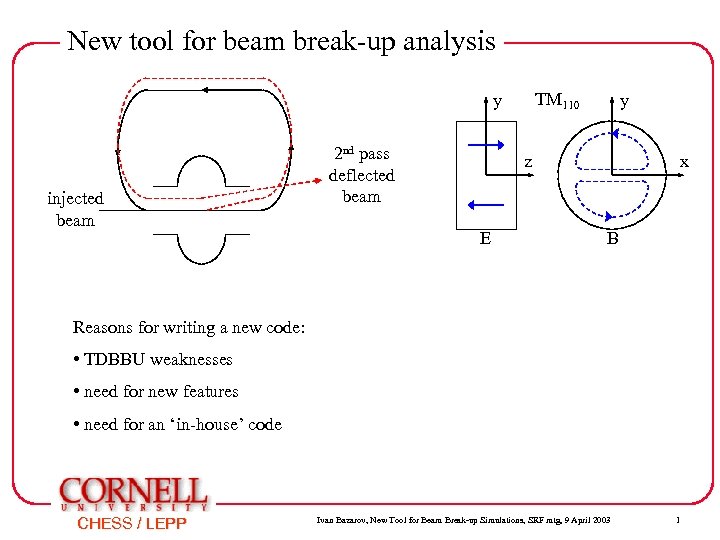
New tool for beam break-up analysis TM 110 y injected beam 2 nd pass deflected beam y z E x B Reasons for writing a new code: • TDBBU weaknesses • need for new features • need for an ‘in-house’ code CHESS / LEPP Ivan Bazarov, New Tool for Beam Break-up Simulations, SRF mtg, 9 April 2003 1
bi - ‘beam instability’ code Features: • allows any ERL topology • cleaner algorithm than TDBBU (very likely a personal bias) • written in C++ (compiles with GNU GCC, i. e. all major OS) • faster than TDBBU (a single 5 Ge. V ERL run takes less than a minute; execution time is estimated to be 7 -9 times faster than TDBBU when no coupling is present; with coupling it is estimated to be at least 4 times faster) • easier to use CHESS / LEPP Ivan Bazarov, New Tool for Beam Break-up Simulations, SRF mtg, 9 April 2003 2
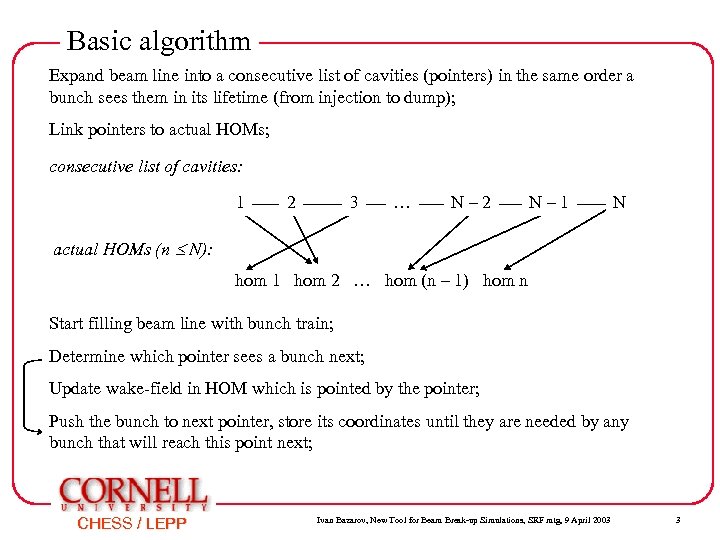
Basic algorithm Expand beam line into a consecutive list of cavities (pointers) in the same order a bunch sees them in its lifetime (from injection to dump); Link pointers to actual HOMs; consecutive list of cavities: 1 2 3 … N– 2 N– 1 N actual HOMs (n N): hom 1 hom 2 … hom (n – 1) hom n Start filling beam line with bunch train; Determine which pointer sees a bunch next; Update wake-field in HOM which is pointed by the pointer; Push the bunch to next pointer, store its coordinates until they are needed by any bunch that will reach this point next; CHESS / LEPP Ivan Bazarov, New Tool for Beam Break-up Simulations, SRF mtg, 9 April 2003 3
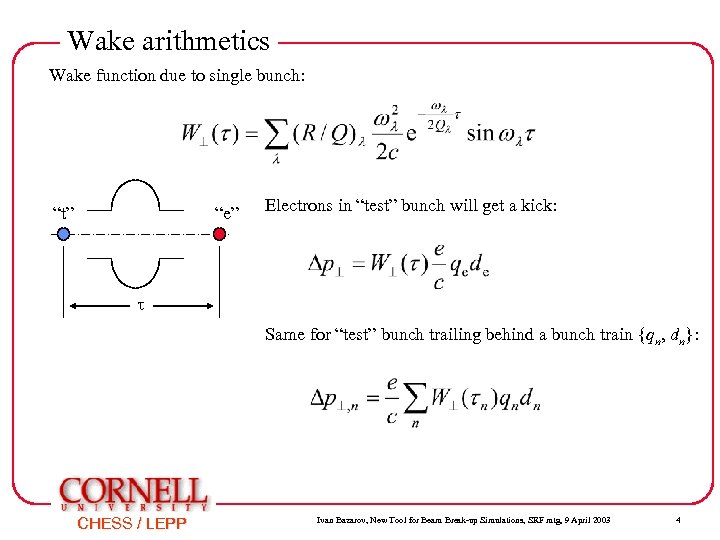
Wake arithmetics Wake function due to single bunch: “t” “e” Electrons in “test” bunch will get a kick: t Same for “test” bunch trailing behind a bunch train {qn, dn}: CHESS / LEPP Ivan Bazarov, New Tool for Beam Break-up Simulations, SRF mtg, 9 April 2003 4
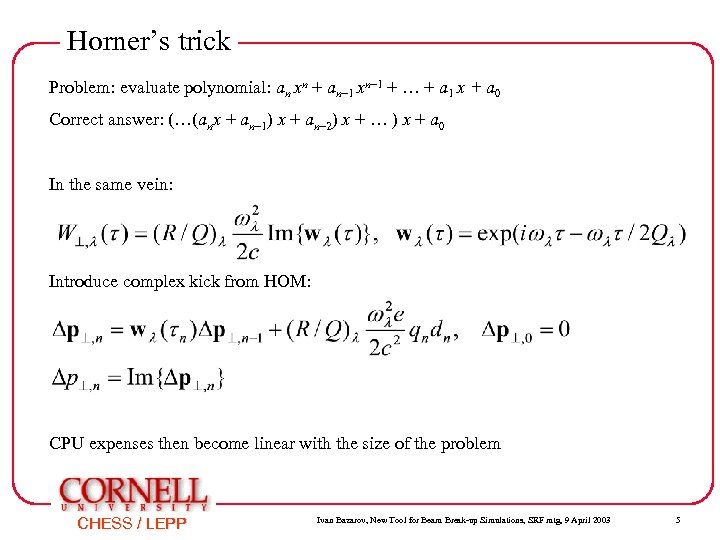
Horner’s trick Problem: evaluate polynomial: an xn + an– 1 xn– 1 + … + a 1 x + a 0 Correct answer: (…(anx + an– 1) x + an– 2) x + … ) x + a 0 In the same vein: Introduce complex kick from HOM: CPU expenses then become linear with the size of the problem CHESS / LEPP Ivan Bazarov, New Tool for Beam Break-up Simulations, SRF mtg, 9 April 2003 5
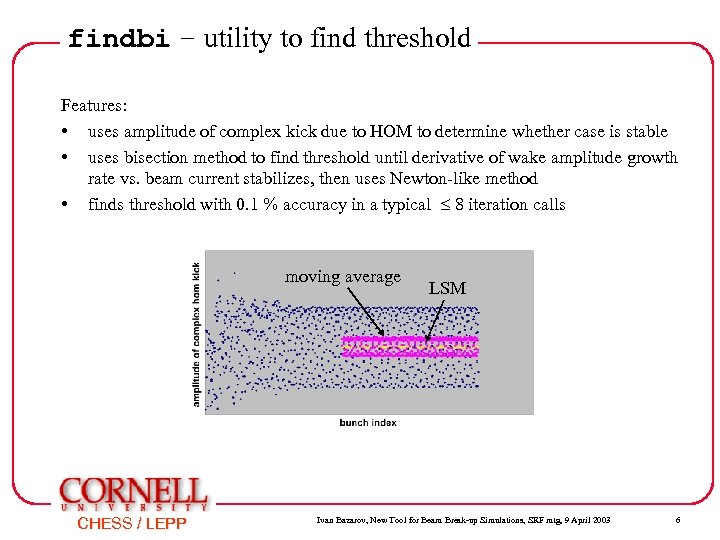
findbi – utility to find threshold Features: • uses amplitude of complex kick due to HOM to determine whether case is stable • uses bisection method to find threshold until derivative of wake amplitude growth rate vs. beam current stabilizes, then uses Newton-like method • finds threshold with 0. 1 % accuracy in a typical 8 iteration calls moving average CHESS / LEPP LSM Ivan Bazarov, New Tool for Beam Break-up Simulations, SRF mtg, 9 April 2003 6
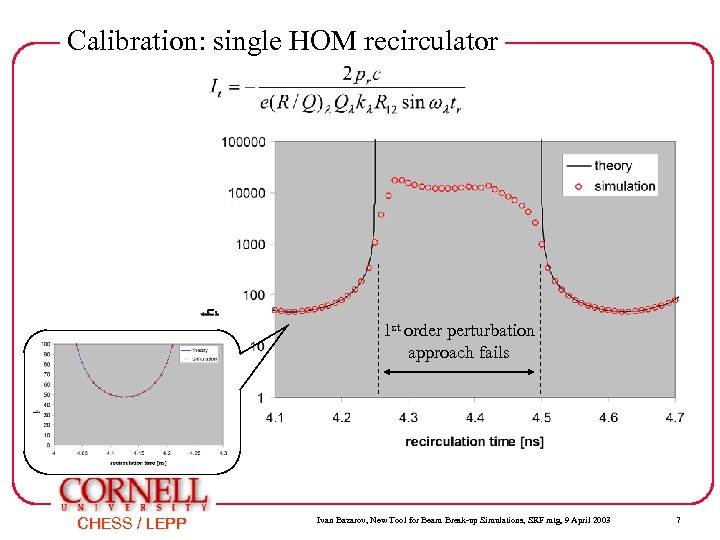
Calibration: single HOM recirculator 1 st order perturbation approach fails CHESS / LEPP Ivan Bazarov, New Tool for Beam Break-up Simulations, SRF mtg, 9 April 2003 7
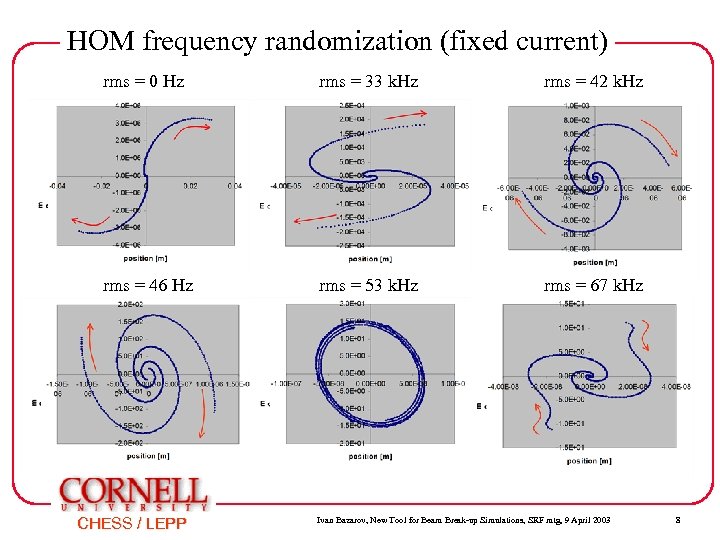
HOM frequency randomization (fixed current) rms = 0 Hz rms = 33 k. Hz rms = 42 k. Hz rms = 46 Hz rms = 53 k. Hz rms = 67 k. Hz CHESS / LEPP Ivan Bazarov, New Tool for Beam Break-up Simulations, SRF mtg, 9 April 2003 8
Simulation example: ‘ERL in CESR tunnel’ single “worst” HOM: R/Q = 51. 5 , Q = 50000, f = 2575 MHz frequency spread applied (rms): 3 MHz smallest threshold found so far: 163 m. A (linac lattice DCS, 04/01/03, max beta 80 m) CHESS / LEPP Ivan Bazarov, New Tool for Beam Break-up Simulations, SRF mtg, 9 April 2003 9
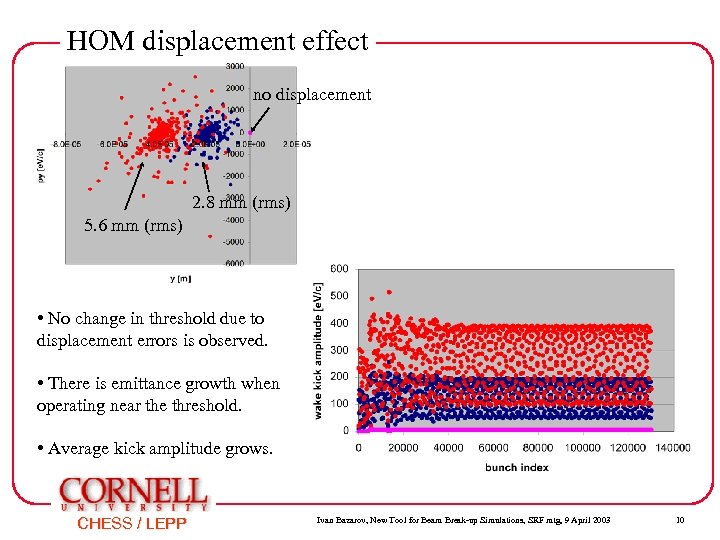
HOM displacement effect no displacement 2. 8 mm (rms) 5. 6 mm (rms) • No change in threshold due to displacement errors is observed. • There is emittance growth when operating near the threshold. • Average kick amplitude grows. CHESS / LEPP Ivan Bazarov, New Tool for Beam Break-up Simulations, SRF mtg, 9 April 2003 10
f40172dc73fdb6a8a74b43c9889dcb60.ppt