a2fca4b40cc9c17bf01e20a516218dd4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33

New service development using gap-based quality function deployment A mobile telecommunication case Jing-hua Li Zhejiang Gongshang University P. R. China 02/06/2008

Research questions • Why study new service development ? • Why combine the Gaps and QFD ? • Why employ mobile telecom case ? 2

Contents • Combining two models ? • New model • Mobile phones in China • What this means ? 3
Combining two models? • House of quality • Gap model 4
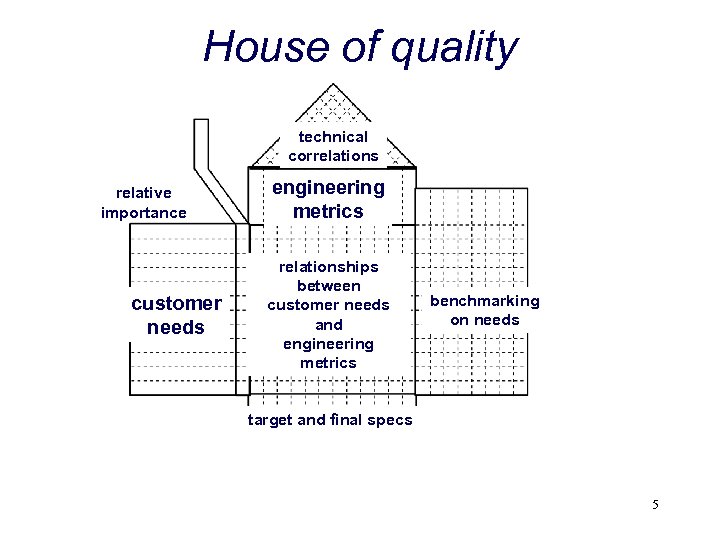
House of quality technical correlations relative importance customer needs engineering metrics relationships between customer needs and engineering metrics benchmarking on needs target and final specs 5
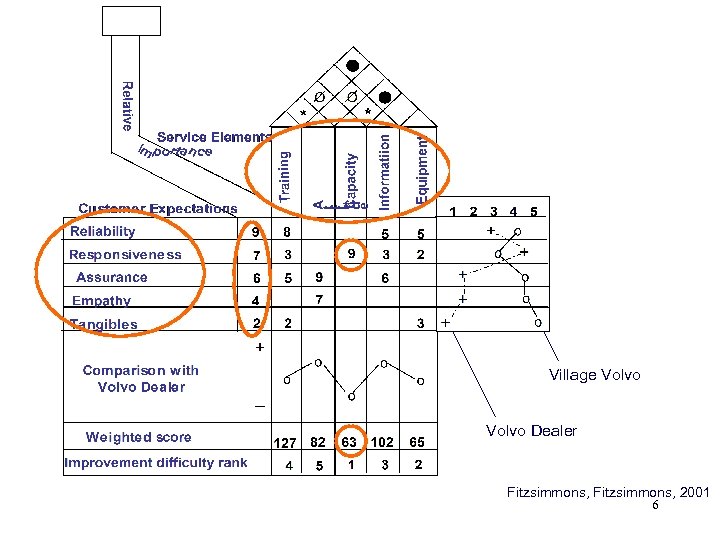
1 1 1 Village Volvo Dealer Fitzsimmons, 2001 6
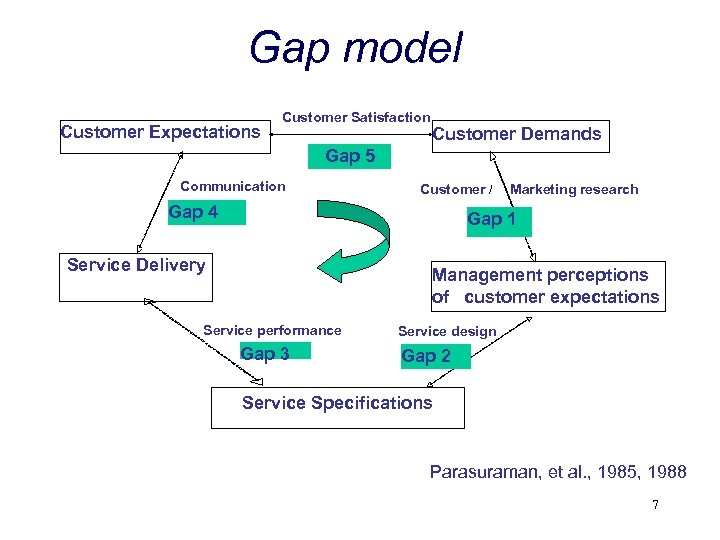
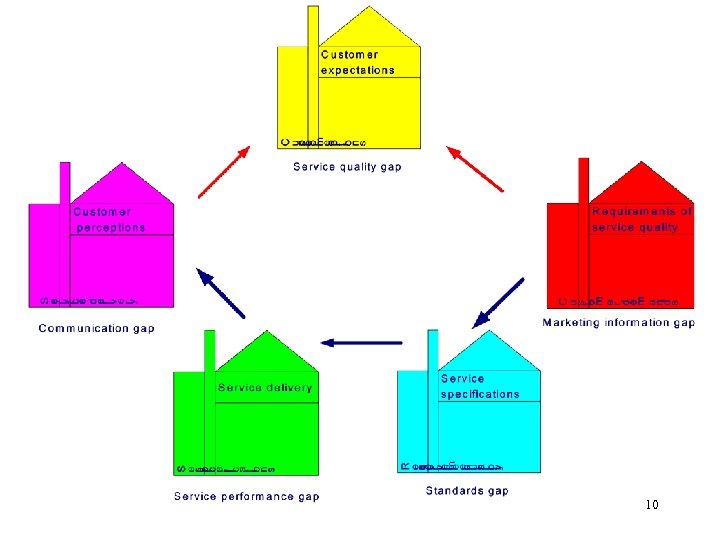
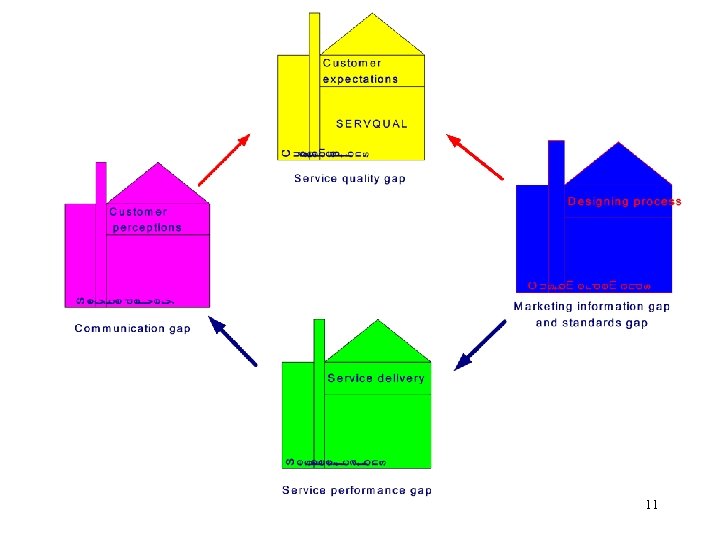
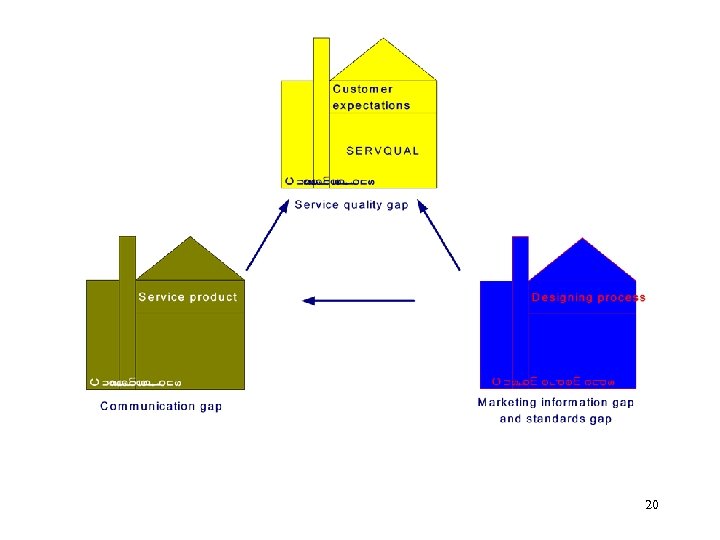
Gap model Customer Expectations Customer Satisfaction Customer Demands Gap 5 Communication Customer / Gap 4 Marketing research Gap 1 Service Delivery Management perceptions of customer expectations Service performance Gap 3 Service design Gap 2 Service Specifications Parasuraman, et al. , 1985, 1988 7
Combining two models? 8
New Model • Theoretical model • Operational model • Weights
10
11
Questionnaire Interview Literature 12
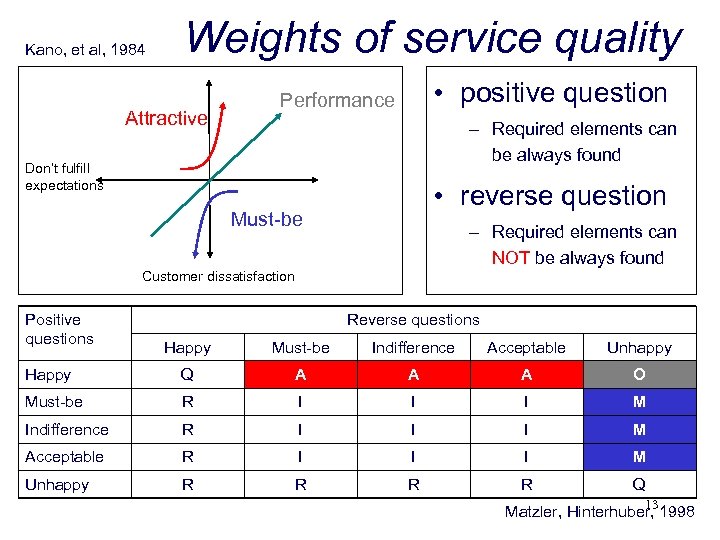
Kano, et al, 1984 Weights of service quality Attractive • positive question Performance – Required elements can be always found Don’t fulfill expectations • reverse question Must-be – Required elements can NOT be always found Customer dissatisfaction Positive questions Reverse questions Happy Must-be Indifference Acceptable Unhappy Happy Q A A A O Must-be R I I I M Indifference R I I I M Acceptable R I I I M Unhappy R R Q 13 Matzler, Hinterhuber, 1998

Mobile phones in China • • Background Model Questionnaire Interview 14
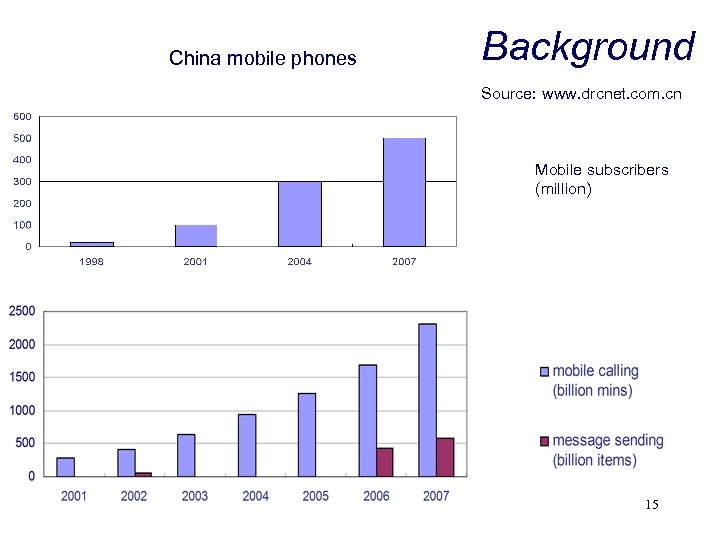
China mobile phones Background Source: www. drcnet. com. cn Mobile subscribers (million) 15
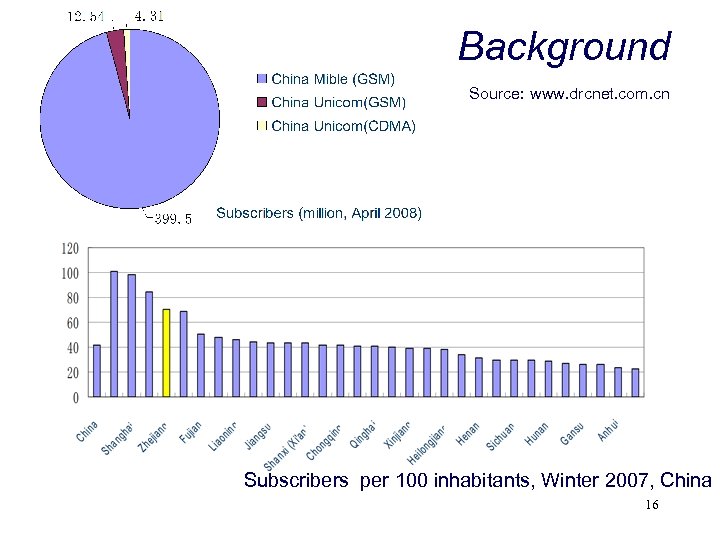
Background Source: www. drcnet. com. cn Subscribers per 100 inhabitants, Winter 2007, China 16
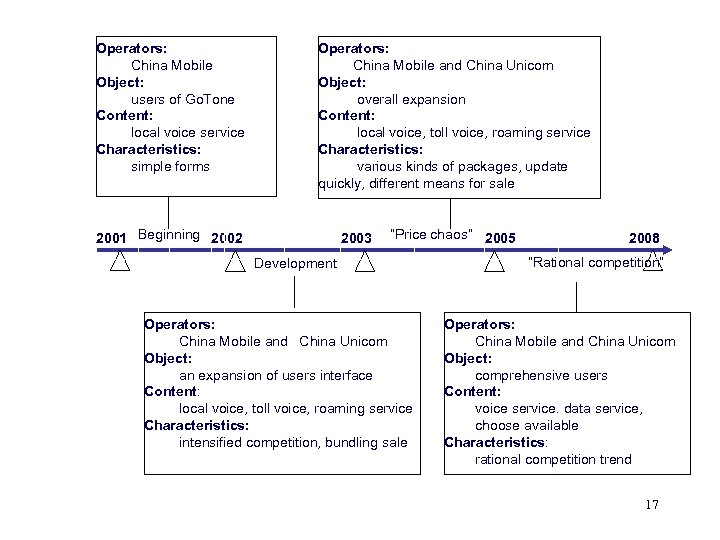
Operators: China Mobile Object: users of Go. Tone Content: local voice service Characteristics: simple forms Operators: China Mobile and China Unicom Object: overall expansion Content: local voice, toll voice, roaming service Characteristics: various kinds of packages, update quickly, different means for sale 2001 Beginning 2002 2003 “Price chaos” 2005 Development Operators: China Mobile and China Unicom Object: an expansion of users interface Content: local voice, toll voice, roaming service Characteristics: intensified competition, bundling sale 2008 “Rational competition” Operators: China Mobile and China Unicom Object: comprehensive users Content: voice service. data service, choose available Characteristics: rational competition trend 17

Tariff brands in China Mobile • Go. Tone businessman and other high earners • M-zone students • Easyown remaining sections of society 18
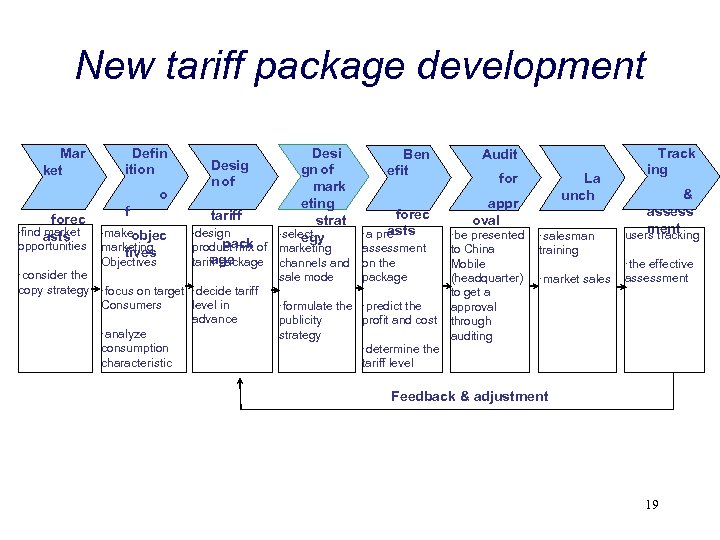
New tariff package development Mar ket Defin ition o forec ·find market asts f ·make objec Desig n of tariff ·design Desi gn of mark eting strat ·select egy pack product mix of marketing age tariff package channels and ·consider the sale mode copy strategy ·focus on target ·decide tariff Consumers level in ·formulate the advance publicity ·analyze strategy consumption characteristic opportunities marketing tives Objectives Ben efit forec asts ·a preassessment on the package ·predict the profit and cost Audit for La unch appr oval ·be presented to China Mobile (headquarter) to get a approval through auditing ·salesman training ·market sales Track ing & assess ment users tracking ·the effective assessment ·determine the tariff level Feedback & adjustment 19
20

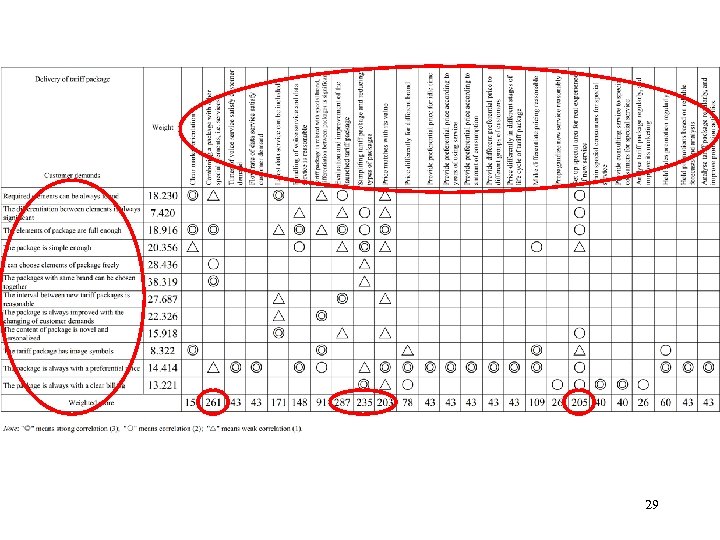
Questionnaire Elements of package • G 1 Required elements can be always found • G 2 The differentiation between elements is always significant • G 3 The elements of package are full enough • G 4 The package is simple enough Range of free choice • G 5 I can choose elements of package freely • G 6 The packages with same brand can be chosen together Personalization of package • G 7 The interval between new tariff packages is reasonable • G 8 The package is always improved with the changing of customer demands • G 9 The content of package is novel and personalized • G 10 The tariff package has image symbols Price • G 11 The package is always with a preferential price • G 12 The package is always with a clear billing 21
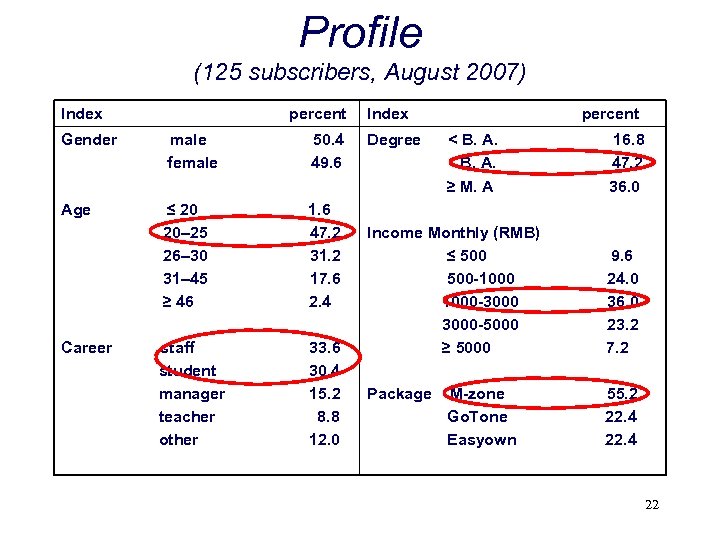
Profile (125 subscribers, August 2007) Index percent Gender male female 50. 4 49. 6 Age ≤ 20 20– 25 26– 30 31– 45 ≥ 46 1. 6 47. 2 31. 2 17. 6 2. 4 staff student manager teacher other 33. 6 30. 4 15. 2 8. 8 12. 0 Career Index Degree percent < B. A. ≥ M. A Income Monthly (RMB) ≤ 500 -1000 -3000 -5000 ≥ 5000 Package M-zone Go. Tone Easyown 16. 8 47. 2 36. 0 9. 6 24. 0 36. 0 23. 2 7. 2 55. 2 22. 4 22
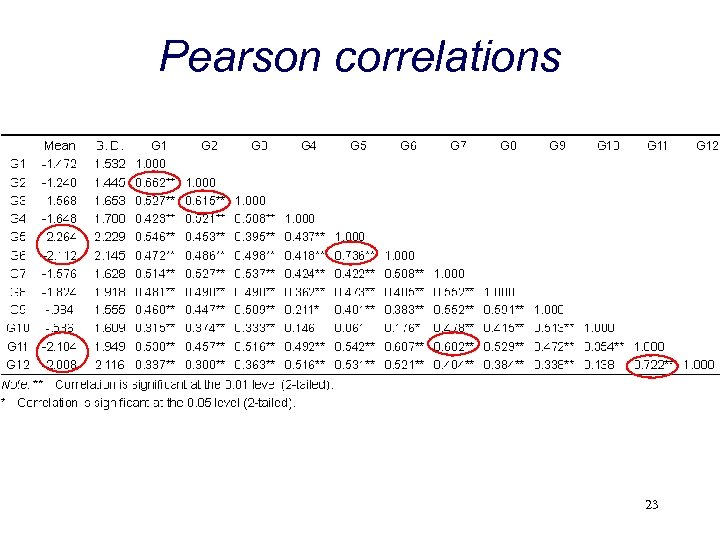
Pearson correlations 23
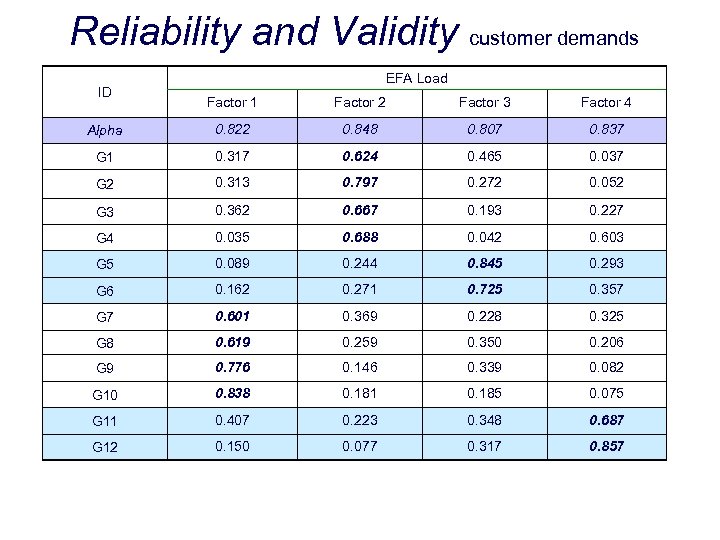
Reliability and Validity customer demands ID EFA Load Factor 1 Factor 2 Factor 3 Factor 4 Alpha 0. 822 0. 848 0. 807 0. 837 G 1 0. 317 0. 624 0. 465 0. 037 G 2 0. 313 0. 797 0. 272 0. 052 G 3 0. 362 0. 667 0. 193 0. 227 G 4 0. 035 0. 688 0. 042 0. 603 G 5 0. 089 0. 244 0. 845 0. 293 G 6 0. 162 0. 271 0. 725 0. 357 G 7 0. 601 0. 369 0. 228 0. 325 G 8 0. 619 0. 259 0. 350 0. 206 G 9 0. 776 0. 146 0. 339 0. 082 G 10 0. 838 0. 181 0. 185 0. 075 G 11 0. 407 0. 223 0. 348 0. 687 G 12 0. 150 0. 077 0. 317 0. 857
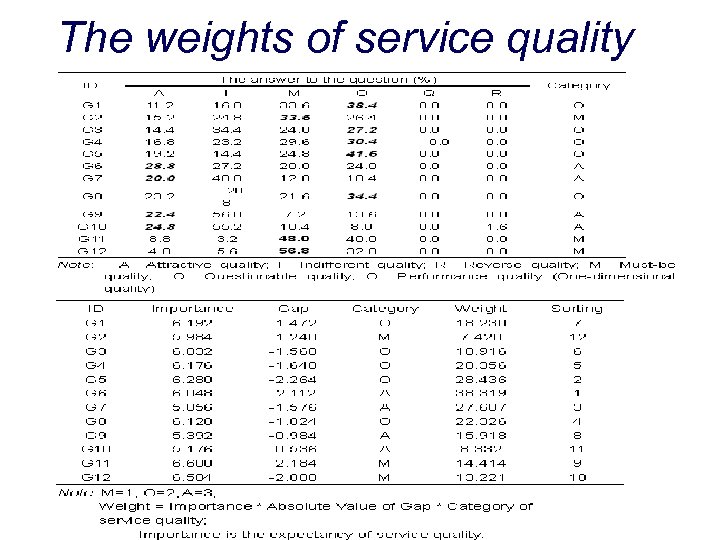
The weights of service quality

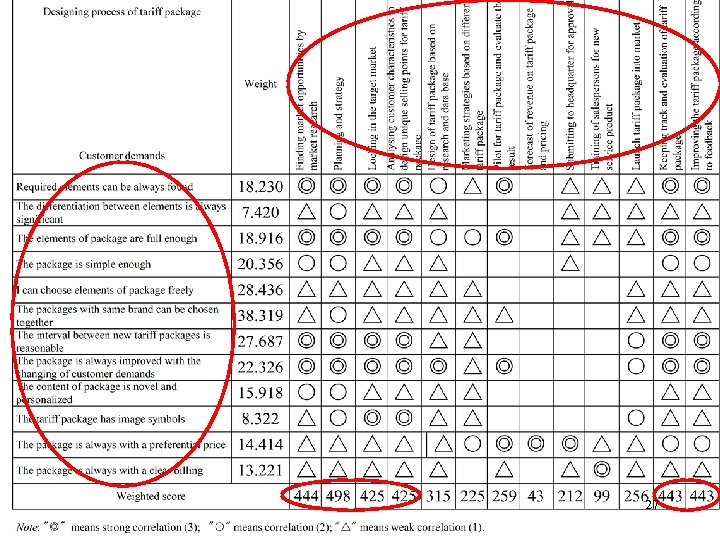
Interview I • “left wall”-- customer demands elements of package; range of free choice; personalization of package; price • “ceiling” -- design process of tariff package market forecasts; target orientation; design tariff package; planning marketing strategy; revenue forecasts; approval; launching into market; keeping track and evaluation; improving according to the feedback 26
27

Interview II • “left wall” -- customer perception elements of package range of free choice personalization of tariff package price • “ceiling”-- tariff package product price place promotion 28
29

What this means ? • New service development vs. service innovation • Engineering vs. marketing • Thought vs. methodology • Theory vs. practice 30

Acknowledgements Natural Science Fund of China (Grant No. 70402016) Natural Science Fund of Zhejiang Province (Grant No. Y 605404) Two co-authors’ contribution: Ms. Lei Xu, Ms. Xiu-lan Wu Two anonymous reviewers of International Journal of Services Technology and Management Mr. Jonathan Alyen’s kindly help on presentation and slide design 31

References in slides • James A. Fitzsimmons, Mona J. Fitzsimmons, Service Management: Operation, Strategy, and Information Technology, Third Edition, Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. 2001, p 58 • A. Parasuraman, L. L. Berry, V. A. Zeithaml, A conceptual model of service quality and its implications for future research, Journal of Marketing, Vol. 49, pp. 41– 50, 1985. • A. Parasuraman, L. L. Berry, V. A. Zeithaml, SERVQUAL: A multi-item scale for measuring consumer perceptions of service quality, Journal of Retailing, Vol. 64, No. 1, pp. 12– 40, 1988. • N. Kano, et al. Attractive quality and must-be quality, Hinshitsu (Quality, the Journal of Japanese Society for Quality Control), Vol. 14, pp. 39– 48, 1984. • K. C. Tan, T. A. Pawitra, Integrating SERVQUAL and Kano's model into QFD for service excellence development, Managing Service Quality, vol. 11, no. 6, pp. 418 -430, 2001. • K. Matzler, H. H. Hinterhuber, How to make product development projects more successful by integrating Kano’s model of customer satisfaction into quality function deployment? Technovation, Vol. 18, No. 1, pp. 25 -38, 1998. 32

Welcome comments and questions ! Academic Visitor Manchester Institute of Innovation Research Manchester Business School The University of Manchester 5. 10 Harold Hankins Building Tel: +44 161 275 0928(O) Mobile (UK): +44 779 982 1004 Mobile (China): +86 139 581 600 47 Email: jinghua. li@mbs. ac. uk Email: jhli@zju. edu. cn 33
a2fca4b40cc9c17bf01e20a516218dd4.ppt