771c12fcb90c95f3cd92feca339bb75f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42

New Political Parties The Years Before the Civil War

Think about it • The differences between the North and the South were enough to cause political conflict, why did they lead to a Civil War? • Ralph Waldo Emerson, “The US will conquer Mexico, but it will be as the man who swallows the arsenic; Mexico will poison us. ”

The Free Soil Party Free Soil! Free Speech! Free Labor! Free Men! Anti –slave expansionists from the Whig and Democratic parties
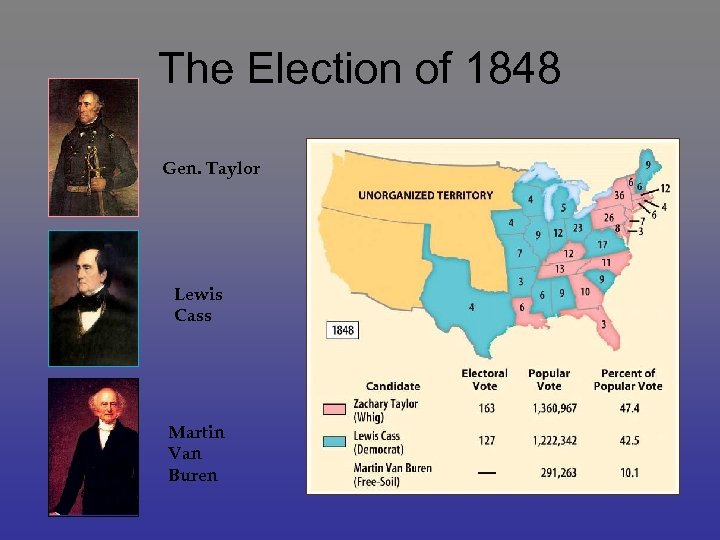
The Election of 1848 Gen. Taylor Lewis Cass Martin Van Buren
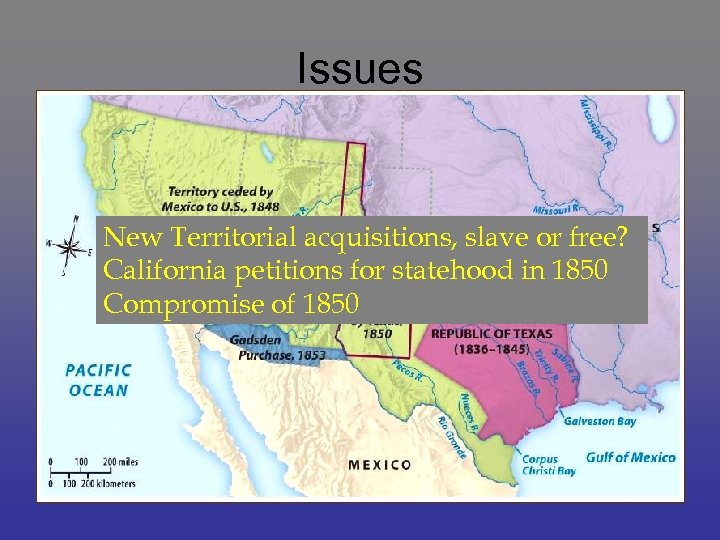
Issues New Territorial acquisitions, slave or free? California petitions for statehood in 1850 Compromise of 1850

Political Changes • - Decline of the Whigs due to: Slavery issue General good times Old and dying leaders Weak candidates Daniel Webster Henry Clay

The Know-Nothings or American Party • Attempt to wrap themselves in the flag Nativists –pro-American bor Anti-immigrant, Irish and German Anti-Catholic Want longer wait for citizenship Strong in the Northern cities

Nativist imagery

The Unmixable violent Irish

Irish and Germans impact an election

Irish stereotypes

NINA
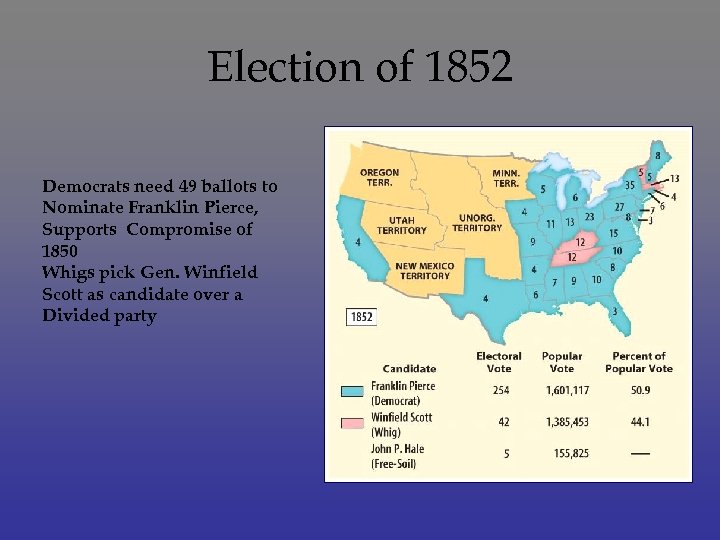
Election of 1852 Democrats need 49 ballots to Nominate Franklin Pierce, Supports Compromise of 1850 Whigs pick Gen. Winfield Scott as candidate over a Divided party

Pierce the President • Expansionist • Cabinet w/ Southerners • Jefferson Davis Sec. of War • Slavocrats – proslavery Dems. • Eyes on Cuba • Ostend Manifesto –embarrassing memo On Cuba

Ostend Manifesto Secretary of State James Buchanan being Robbed as a result of the Manifesto It declared that if Spain refused to sell Cuba, “then, by every law, human and divine, we shall be justified in wresting it from Spain if we possess the power. ” It was an explosive issue because Cuba, if it became a U. S. possession, would presumably be admitted to the Union as a slave state.

1856 Candidates James Buchanan John C. Fremont Millard Fillmore

Election of 1856 • Republican Platform – “Free Soil, Free Speech, Free Men, Fremont!” • Federal dollars for internal improvements, railroad to California and focus on slavery as a moral cause • Democratic Platform – popular sovereignty, Republicans were a sectional party, “Black Republicans” • American Party Platform - nativism

Candidates • James Buchanan – unsoiled by slavery controversy, supports Compromise of 1850, opposed federal interference in slavery, supports California railroad • John C. Fremont – goodness of the North, no extension of slavery, blame Democrats for Bleeding Kansas • Millard Fillmore – split the election, go to House, anti-immigrant & Catholic • Election turns on threat of Southern secession
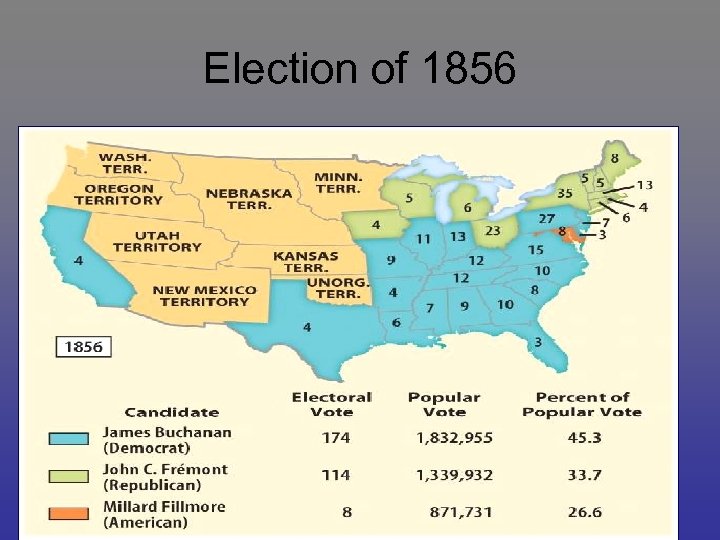
Election of 1856

Election Events • Mark by controversy of Kansas-Nebraska Act • Republican Party born from discontent - opposed to expansion of slavery - Want repeal of K & N Act • - made up of Democrats, Whigs & Free-Soilers • 2 contests in 1 election – Dems. v. American Party in South, Dems. v. Repubs. In the North

Inside the Election • Northern voters were not all anti-slave 1. Eastern city and rural voters were often anti-black and antiabolition • Democratic portrayal of Republicans as being “Black Republicans” 1. Favored racial equality 2. Favored economic equality 3. Southern treat of secession

The Results • Buchanan wins: inherits Kansas issue, Le. Compton Constitution, statehood • Failures of Buchanan – Kansas not admitted as a free state or slave state • Oregon, Nebraska, Minnesota, Washington, Utah and New Mexico will all be free • Territorial/slavery issue not resolved

Buchanan’s Presidency • Dred Scott case • Financial Crisis – due to California Gold, land Railroad speculation • Homestead Act proposal • Lowest Tariff since 1812 • Northern dissatisfaction • Secession of the South begins • John Brown’s Raid

Dred Scott Case (1857) • Dred Scott was slave of army surgeon • Master went to territory where slavery had been outlawed by Missouri Compromise – Stayed for 4 years before back to slave state • When returned to Missouri and following his owners death , Scott sued for his freedom • Case weaves it’s way through state to federal and finally the Supreme Court

Dred Scott v. Sandford • Polarized country about slavery – South happy; North angry – Supreme Court had a Southern majority • Roger B. Taney (Chief Justice) – Slaves were not citizens of U. S. so could not sue for freedom – Congress could not forbid importation of slaves into any region of U. S. • Discriminate against citizens of state because not allowing them to bring personal property

Dissenting Viewpoint • Blacks were legal citizens • Congress had power to make “all needful rules and regulations” thus the power to prevent territorial slavery • Republican viewpoint – Republican president could reconstitute the court (OBAMA), “the remedy is the ballot box. ”

The Lincoln Douglas debates • A portrait in contrasts, • Lincoln 6’ 4”, Douglas the “Little Giant” a foot shorter • Lincoln – rising star of the Republican Party, Douglas – leading Democrat in the Senate

Political Beginnings one time member of House of Representatives from Illinois Loses Senate race to Stephen Douglas in 1858 Has a series of 7 debates Gains national recognition from debates due to telegraph & railroads

“House Divided” • Lincoln – “ A house divided against itself cannot stand” “It will become all of one thing, or all the other. ” Lincoln believes there is a wide gap between free soil and popular sovereignty, he hints at a Democratic plot to overthrown the Constitution and prevent any action restricting slavery

“House Divided” • Douglas – House divided is an invitation to secession, expansion of white settlement was the issue, not slavery, popular sovereignty was the solution, no plot to overthrow Constitution, Lincoln is an abolitionist advocate of racial equality

Freeport Doctrine • Lincoln asks Douglas how do you reconcile Dred Scott with popular sovereignty? • Douglas, “If slavery not popularly supported it won’t exist”
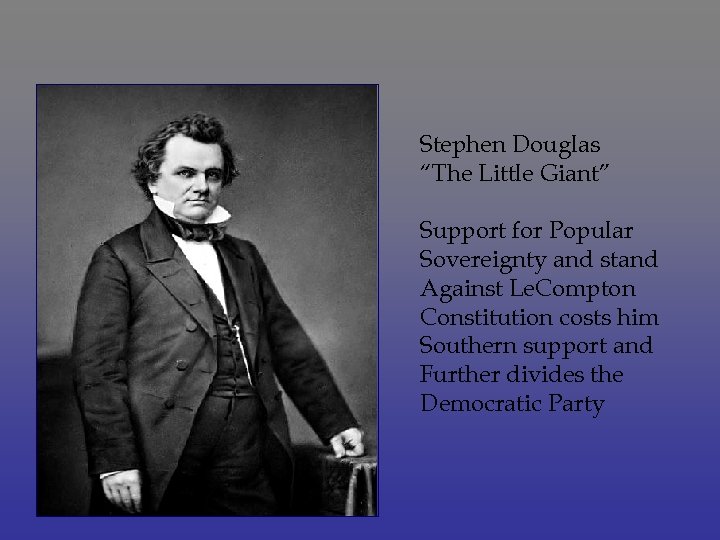
Stephen Douglas “The Little Giant” Support for Popular Sovereignty and stand Against Le. Compton Constitution costs him Southern support and Further divides the Democratic Party

John Brown, Murderer or Martyr Brown's last kiss Brown’s Raid on Harper’s Ferry

"I John Brown am now quite certain that the crimes of this guilty land will never be purged away, but with Blood. I had. . . vainly flattered myself that without very much bloodshed, it might be done. " -- John Brown. Wants to start a slave rebellion Capture Harper’s Ferry arsenal Caught, tried for treason Executed by hanging

Republican Lincoln Douglas Northern Democrat 1860 Presidential Election John Bell Constitutional Union John C. Breckinridge Southern Democrat

Republican Party Platform in 1860 • Non-extension of slavery [for the Free-Soilers. • Protective tariff [for the No. Industrialists]. • No abridgment of rights for immigrants [a disappointment for the “Know-Nothings”]. • Government aid to build a Pacific RR [for the Northwest]. • Internal improvements [for the West] at federal expense. • Free homesteads for the public domain [for farmers].

1860 Election: 3 “Outs” & 1 ”Run!”
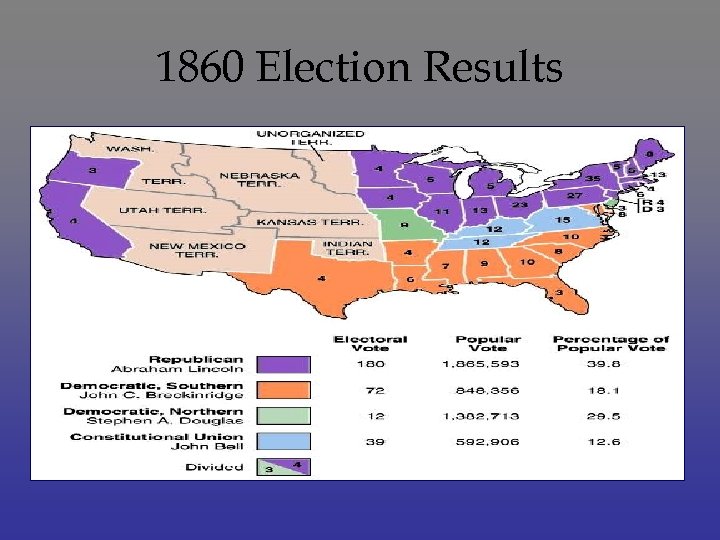
1860 Election Results

A Nation Torn Asunder

Immediate Impact • Before Lincoln’s inauguration seven Southern states secede • Despite controlling Supreme Court and no Republican majority in the House or Senate • Crittenden Compromise – resurrect the Missouri Compromise • Rejected by Lincoln, “no expansion of slavery”
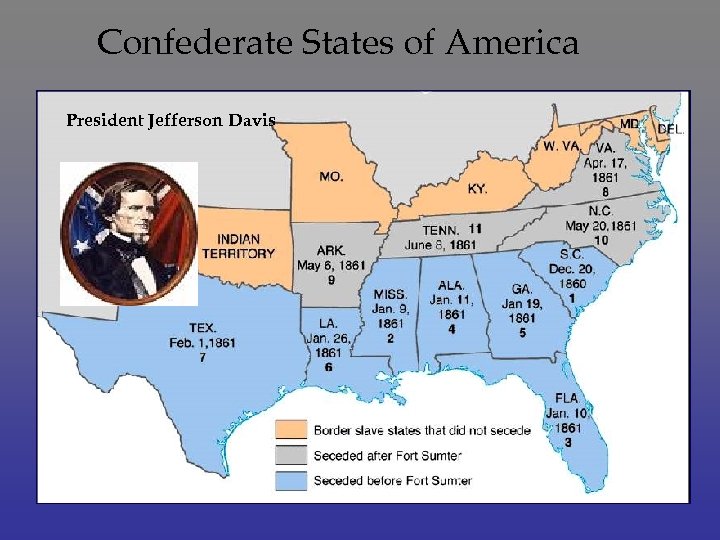
Confederate States of America President Jefferson Davis

Why did they leave? Slavery and it’s expansion States rights/self determination Nationalism overconfidence
771c12fcb90c95f3cd92feca339bb75f.ppt