c79e3421f5d20139206f6c0dc6c26e85.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43
 New Parallel Queue Processor PQP Queue Machines as Next Generation Computer Systems For mobile, embedded and super computers Over Queue Prof. Masahiro SOWA University of Electro-Communications in Tokyo, JAPAN Over Queue
New Parallel Queue Processor PQP Queue Machines as Next Generation Computer Systems For mobile, embedded and super computers Over Queue Prof. Masahiro SOWA University of Electro-Communications in Tokyo, JAPAN Over Queue
 Contents ● Introduction of the University of Electro. Communications ● Introduction of Japan ● Queue computer
Contents ● Introduction of the University of Electro. Communications ● Introduction of Japan ● Queue computer
 Japan Bulgaria
Japan Bulgaria
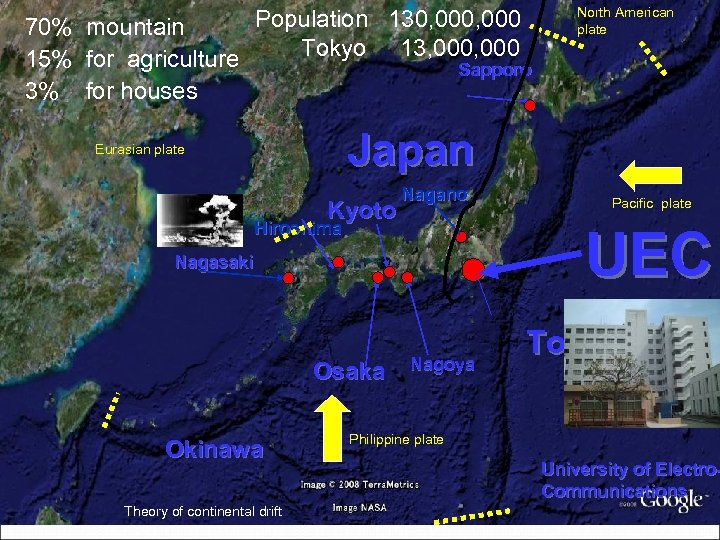 Population 130, 000 70% mountain Tokyo 13, 000 15% for agriculture Sapporo 3% for houses North American plate Japan Eurasian plate Kyoto Nagano Hiroshima UEC Nagasaki Osaka Okinawa Theory of continental drift Pacific plate Nagoya Tokyo Philippine plate University of Electro. Communications
Population 130, 000 70% mountain Tokyo 13, 000 15% for agriculture Sapporo 3% for houses North American plate Japan Eurasian plate Kyoto Nagano Hiroshima UEC Nagasaki Osaka Okinawa Theory of continental drift Pacific plate Nagoya Tokyo Philippine plate University of Electro. Communications
 National university corporation The University of Electro-Communications Tokyo MT. FUJI , Japan Since 1918. Number of Students Doctor’s Program Master’s Program Under Graduate Academic Staffs Administrative Staffs 5, 516 206 974 4, 336 359 175 University with Large Doctor’s and Master’s Programs
National university corporation The University of Electro-Communications Tokyo MT. FUJI , Japan Since 1918. Number of Students Doctor’s Program Master’s Program Under Graduate Academic Staffs Administrative Staffs 5, 516 206 974 4, 336 359 175 University with Large Doctor’s and Master’s Programs
 ブルガリア 32 kg オランダ 20. 8 kg フランス 17. 7 kg デンマーク 15. 1 kg ドイツ 12. 5 kg スペイン 9. 8 kg* 日本 5. 1 kg イギリス 4. 6 kg アメリカ 2. 1 kg* 1970年の大阪万博に「ブルガリア館」 1973年にブルガリアの国名使用許可 メチニコフ博士スモーリアン地方。
ブルガリア 32 kg オランダ 20. 8 kg フランス 17. 7 kg デンマーク 15. 1 kg ドイツ 12. 5 kg スペイン 9. 8 kg* 日本 5. 1 kg イギリス 4. 6 kg アメリカ 2. 1 kg* 1970年の大阪万博に「ブルガリア館」 1973年にブルガリアの国名使用許可 メチニコフ博士スモーリアン地方。
 Koto oushuu 琴 欧州
Koto oushuu 琴 欧州
 Many kind of natural disaster Earthquake
Many kind of natural disaster Earthquake
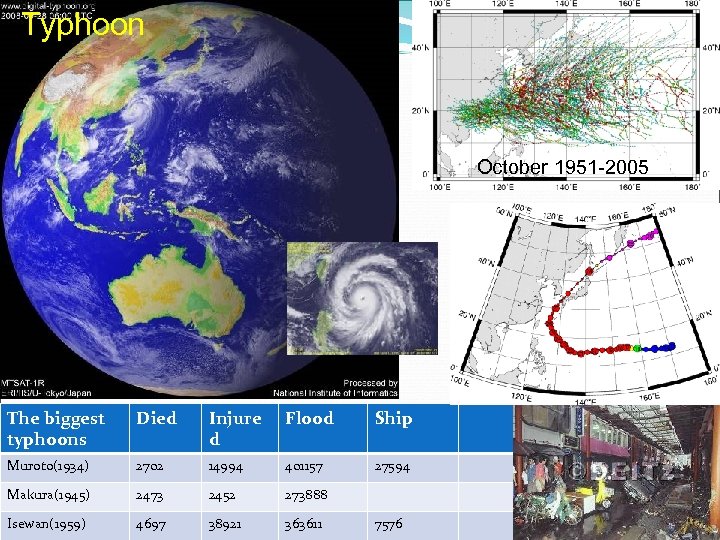 Typhoon October 1951 -2005 The biggest typhoons Died Injure d Flood Ship Muroto(1934) 2702 14994 401157 27594 Makura(1945) 2473 2452 273888 Isewan(1959) 4697 38921 363611 7576
Typhoon October 1951 -2005 The biggest typhoons Died Injure d Flood Ship Muroto(1934) 2702 14994 401157 27594 Makura(1945) 2473 2452 273888 Isewan(1959) 4697 38921 363611 7576
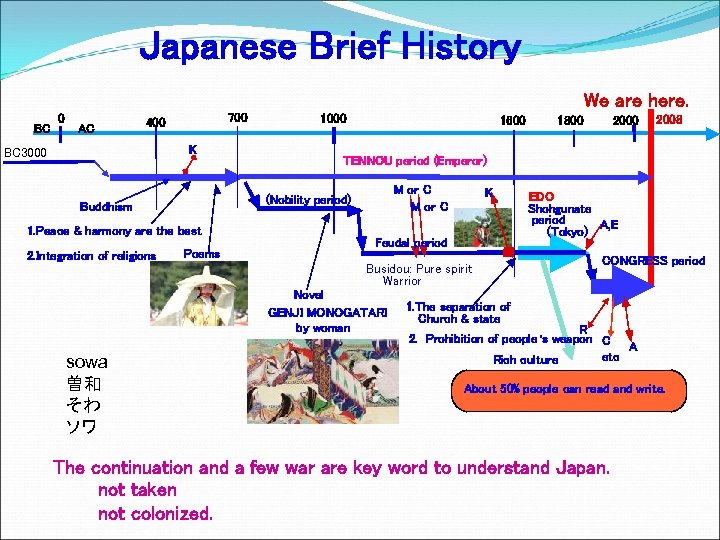 Japanese Brief History We are here. BC 0 AC 700 400 K BC 3000 1600 1. Peace & harmony are the best Poems M or C K Feudal period Busidou: Pure spirit Warrior Novel GENJI MONOGATARI by woman sowa 曽和 そわ ソワ 1800 2008 TENNOU period (Emperor) (Nobility period) Buddhism 2. Integration of religions 1000 EDO Shohgunate period (Tokyo) A, E CONGRESS period 1. The separation of Church & state R 2. Prohibition of people’s weapon C A etc Rich culture About 50% people can read and write. The continuation and a few war are key word to understand Japan. not taken not colonized.
Japanese Brief History We are here. BC 0 AC 700 400 K BC 3000 1600 1. Peace & harmony are the best Poems M or C K Feudal period Busidou: Pure spirit Warrior Novel GENJI MONOGATARI by woman sowa 曽和 そわ ソワ 1800 2008 TENNOU period (Emperor) (Nobility period) Buddhism 2. Integration of religions 1000 EDO Shohgunate period (Tokyo) A, E CONGRESS period 1. The separation of Church & state R 2. Prohibition of people’s weapon C A etc Rich culture About 50% people can read and write. The continuation and a few war are key word to understand Japan. not taken not colonized.
 They made a lot of small schools for pleasure. 20, 000 Literacy Rate(1860) Samurai 100% Men 50% Women 20% Edo(Tokyo) London 70% 30% The most clean country in the world. People's prevailing satisfaction Rich, safety and perfect orderly country Well plowed farmland People likes gardening The most big insult is to send money Furniture is needless By Heinrich Schliemann(1865) Now you can see many products for common people, produced by people.
They made a lot of small schools for pleasure. 20, 000 Literacy Rate(1860) Samurai 100% Men 50% Women 20% Edo(Tokyo) London 70% 30% The most clean country in the world. People's prevailing satisfaction Rich, safety and perfect orderly country Well plowed farmland People likes gardening The most big insult is to send money Furniture is needless By Heinrich Schliemann(1865) Now you can see many products for common people, produced by people.
 The common people, having a big economic power, leads big peaceful consumption and big peaceful production in EDO period regardless of feudal period. Ukiyoe ( Wood engraving printing) Poem (Haiku, Senryu. . ) Schools (20, 000) Sushi Tenpura Comic Book Dance Sports (Judou, Kendou. Sumou. ) Tea ceremony Flower arrangement Music Travel 1200
The common people, having a big economic power, leads big peaceful consumption and big peaceful production in EDO period regardless of feudal period. Ukiyoe ( Wood engraving printing) Poem (Haiku, Senryu. . ) Schools (20, 000) Sushi Tenpura Comic Book Dance Sports (Judou, Kendou. Sumou. ) Tea ceremony Flower arrangement Music Travel 1200




 Parallel queue computers Why do we recommend queue computers? Because the conventional computers use inefficient computing method.
Parallel queue computers Why do we recommend queue computers? Because the conventional computers use inefficient computing method.
 Inefficient computing principle of conventional computers When we buy milk, breads and apples ■Conventional computer Bring milk to the cashier Pay for the milk Bring back the milk Bring breads to the cashier Pay for the breads We never use this kind inefficient method Bring back the breads Bring apples to the cashier Pay for the apples Bring back the apples ■Parallel Queue Computer ・ Bring milk, breads and apples to the cashier, pay for all then bring back them.
Inefficient computing principle of conventional computers When we buy milk, breads and apples ■Conventional computer Bring milk to the cashier Pay for the milk Bring back the milk Bring breads to the cashier Pay for the breads We never use this kind inefficient method Bring back the breads Bring apples to the cashier Pay for the apples Bring back the apples ■Parallel Queue Computer ・ Bring milk, breads and apples to the cashier, pay for all then bring back them.
 Almost electric products are computers with Net work Processor is the most important.
Almost electric products are computers with Net work Processor is the most important.
 What is required to a Computer ●To process big video and big photo data such as HDTV in high speed ● To process many kind of programs ● To be high performance (Approaching the limit) ● Small energy consumption (Approaching the limit) Break through is needed!! ● To decrease surface temperature of the LSI (Approaching the limit) ● Small is better (Approaching the limit)
What is required to a Computer ●To process big video and big photo data such as HDTV in high speed ● To process many kind of programs ● To be high performance (Approaching the limit) ● Small energy consumption (Approaching the limit) Break through is needed!! ● To decrease surface temperature of the LSI (Approaching the limit) ● Small is better (Approaching the limit)
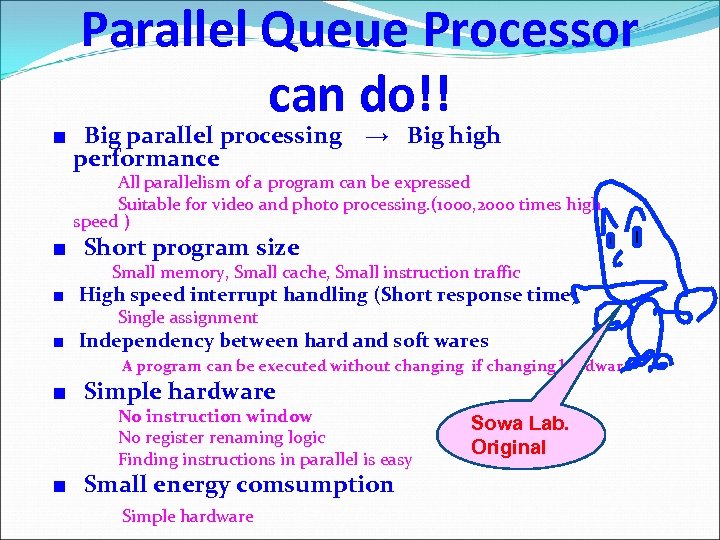 Parallel Queue Processor can do!! ■ Big parallel processing Big high → performance All parallelism of a program can be expressed Suitable for video and photo processing. (1000, 2000 times high speed) ■ Short program size Small memory, Small cache, Small instruction traffic ■ High speed interrupt handling (Short response time) Single assignment ■ Independency between hard and soft wares program can be executed without changing if changing hardware A ■ Simple hardware instruction window No No register renaming logic Finding instructions in parallel is easy ■ Small energy comsumption Simple hardware Sowa Lab. Original
Parallel Queue Processor can do!! ■ Big parallel processing Big high → performance All parallelism of a program can be expressed Suitable for video and photo processing. (1000, 2000 times high speed) ■ Short program size Small memory, Small cache, Small instruction traffic ■ High speed interrupt handling (Short response time) Single assignment ■ Independency between hard and soft wares program can be executed without changing if changing hardware A ■ Simple hardware instruction window No No register renaming logic Finding instructions in parallel is easy ■ Small energy comsumption Simple hardware Sowa Lab. Original
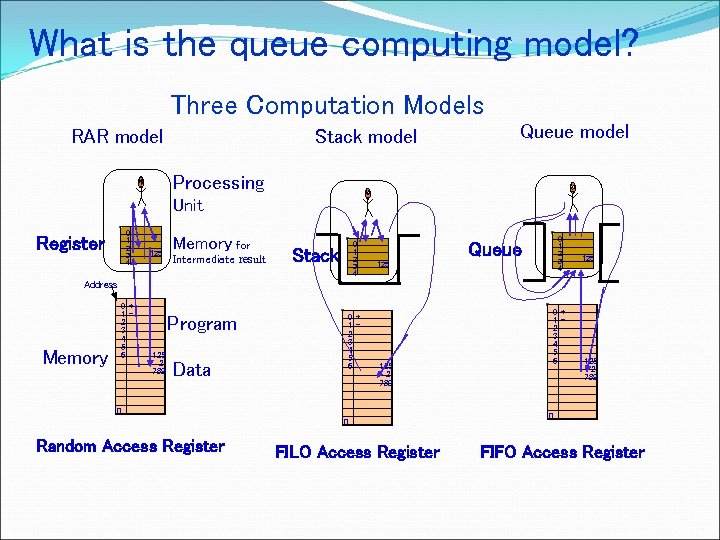 What is the queue computing model? Three Computation Models RAR model Stack model Queue model Processing Unit 0 1 2 3 4 Register 125 Memory for Intermediate result 0 1 2 3 4 Stack 0 1 2 3 4 Queue 125 Address Memory 0+ 12 3 4 5 6 Program 125 2 789 Data n Random Access Register 0+ 12 3 4 5 6 125 2 789 n FILO Access Register 0+ 12 3 4 5 6 125 2 789 n FIFO Access Register
What is the queue computing model? Three Computation Models RAR model Stack model Queue model Processing Unit 0 1 2 3 4 Register 125 Memory for Intermediate result 0 1 2 3 4 Stack 0 1 2 3 4 Queue 125 Address Memory 0+ 12 3 4 5 6 Program 125 2 789 Data n Random Access Register 0+ 12 3 4 5 6 125 2 789 n FILO Access Register 0+ 12 3 4 5 6 125 2 789 n FIFO Access Register
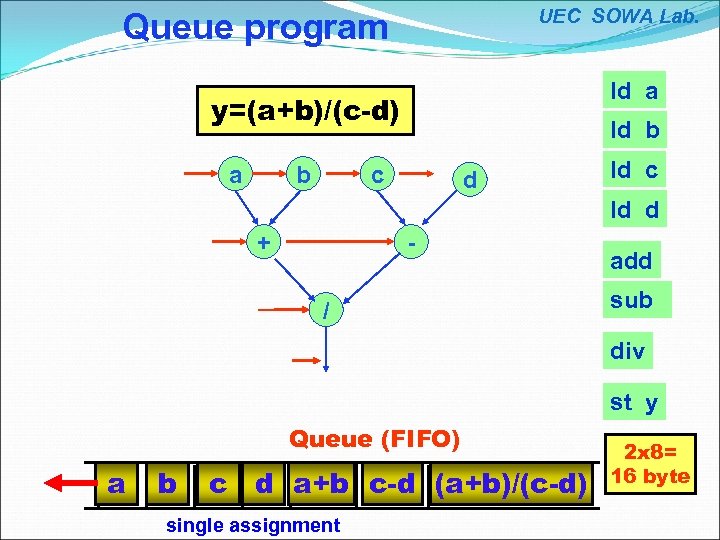 UEC SOWA Lab. Queue program ld a y=(a+b)/(c-d) a b ld b c d ld c ld d + / add sub div st y Queue (FIFO) a b c d a+b c-d (a+b)/(c-d) single assignment 2 x 8= 16 byte
UEC SOWA Lab. Queue program ld a y=(a+b)/(c-d) a b ld b c d ld c ld d + / add sub div st y Queue (FIFO) a b c d a+b c-d (a+b)/(c-d) single assignment 2 x 8= 16 byte
 Original queue computing had a lot of drawbacks It can’t do parallel computing Program becomes longer Hardware is complex Data disappears by its access One procedure is separated
Original queue computing had a lot of drawbacks It can’t do parallel computing Program becomes longer Hardware is complex Data disappears by its access One procedure is separated
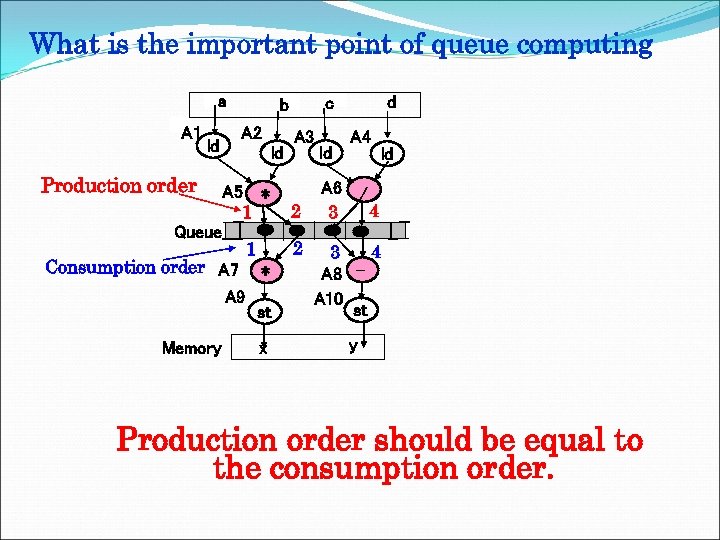 What is the important point of queue computing a A 1 ld A 2 ld A 3 Production order A 5 * 1 Queue 1 Consumption order A 7 * A 9 st Memory x d c b 2 2 ld A 4 ld A 6 / 4 3 A 8 A 10 st y Production order should be equal to the consumption order.
What is the important point of queue computing a A 1 ld A 2 ld A 3 Production order A 5 * 1 Queue 1 Consumption order A 7 * A 9 st Memory x d c b 2 2 ld A 4 ld A 6 / 4 3 A 8 A 10 st y Production order should be equal to the consumption order.
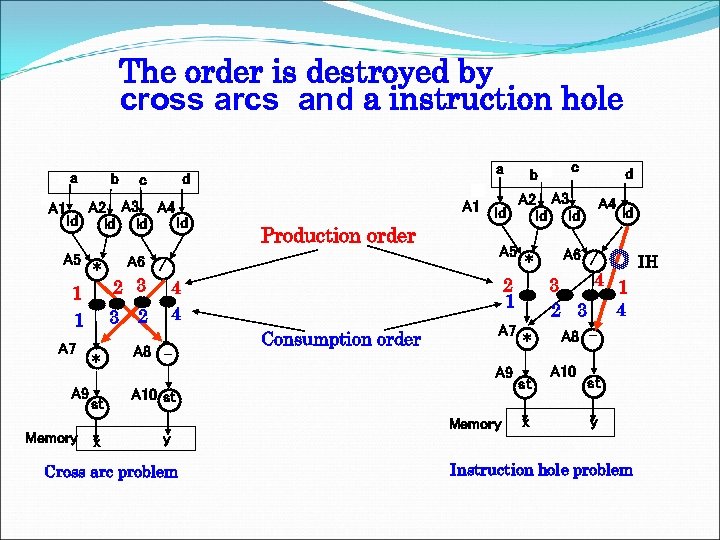 The order is destroyed by cross arcs and a instruction hole a A 1 b A 2 A 3 A 4 ld ld A 5 * 1 1 A 7 A 9 st Memory x Production order A 6 / 2 3 3 * a d c 2 Consumption order A 5 * A 10 st Cross arc problem d Memory A 4 ld A 6 / 4 1 3 4 2 3 A 7 * A 9 y c A 3 A 1 ld A 2 ld ld 2 1 4 4 A 8 - b st x A 8 A 10 st y Instruction hole problem IH
The order is destroyed by cross arcs and a instruction hole a A 1 b A 2 A 3 A 4 ld ld A 5 * 1 1 A 7 A 9 st Memory x Production order A 6 / 2 3 3 * a d c 2 Consumption order A 5 * A 10 st Cross arc problem d Memory A 4 ld A 6 / 4 1 3 4 2 3 A 7 * A 9 y c A 3 A 1 ld A 2 ld ld 2 1 4 4 A 8 - b st x A 8 A 10 st y Instruction hole problem IH
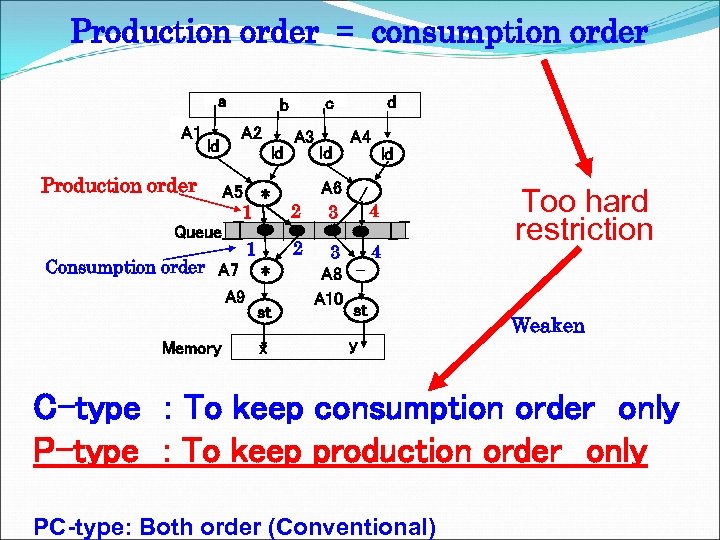 Production order = consumption order a A 1 ld A 2 ld A 3 Production order A 5 * 1 Queue 1 Consumption order A 7 * A 9 st Memory x d c b 2 2 ld A 4 ld A 6 / 4 3 A 8 A 10 st y Too hard restriction Weaken C-type : To keep consumption order only P-type : To keep production order only PC-type: Both order (Conventional)
Production order = consumption order a A 1 ld A 2 ld A 3 Production order A 5 * 1 Queue 1 Consumption order A 7 * A 9 st Memory x d c b 2 2 ld A 4 ld A 6 / 4 3 A 8 A 10 st y Too hard restriction Weaken C-type : To keep consumption order only P-type : To keep production order only PC-type: Both order (Conventional)
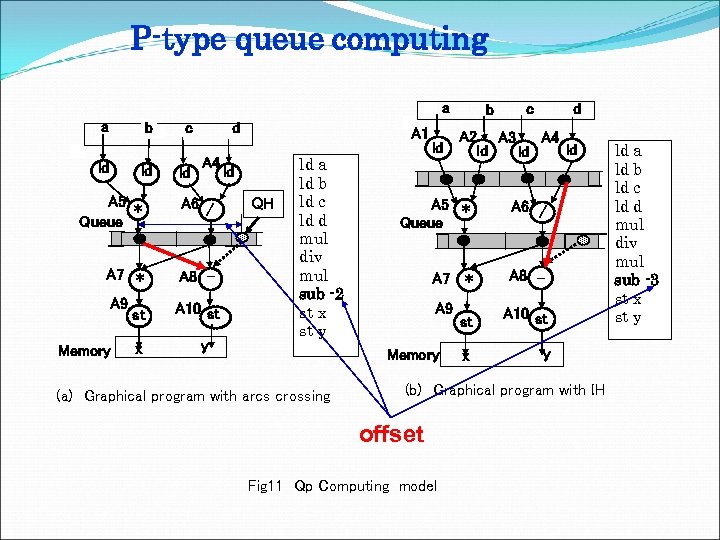 P-type queue computing a a b ld ld c ld d A 4 A 5 * Queue A 6 / A 7 * A 8 - A 9 A 10 st Memory st x y A 1 ld QH ld a ld b ld c ld d mul div mul sub -2 st x st y ld c d A 2 A 3 A 4 ld ld ld A 5 * Queue A 6 / A 7 * A 8 - A 9 Memory (a) Graphical program with arcs crossing b st A 10 st x y (b) Graphical program with IH offset Fig 11 Qp Computing model ld a ld b ld c ld d mul div mul sub -3 st x st y
P-type queue computing a a b ld ld c ld d A 4 A 5 * Queue A 6 / A 7 * A 8 - A 9 A 10 st Memory st x y A 1 ld QH ld a ld b ld c ld d mul div mul sub -2 st x st y ld c d A 2 A 3 A 4 ld ld ld A 5 * Queue A 6 / A 7 * A 8 - A 9 Memory (a) Graphical program with arcs crossing b st A 10 st x y (b) Graphical program with IH offset Fig 11 Qp Computing model ld a ld b ld c ld d mul div mul sub -3 st x st y
 This idea makes all drawbacks to good points. It can’t do parallel computing → It allows parallel computing → It can express all parallelism in group Big adaptability of parallel computing One procedure are separated Program becomes longer → By wreaking the order dependencies Shorter program size (1/3 -1/2) Complex hardware Simple hardware, nowadays Data disappears by its using Reference access All problems have been solved!!
This idea makes all drawbacks to good points. It can’t do parallel computing → It allows parallel computing → It can express all parallelism in group Big adaptability of parallel computing One procedure are separated Program becomes longer → By wreaking the order dependencies Shorter program size (1/3 -1/2) Complex hardware Simple hardware, nowadays Data disappears by its using Reference access All problems have been solved!!
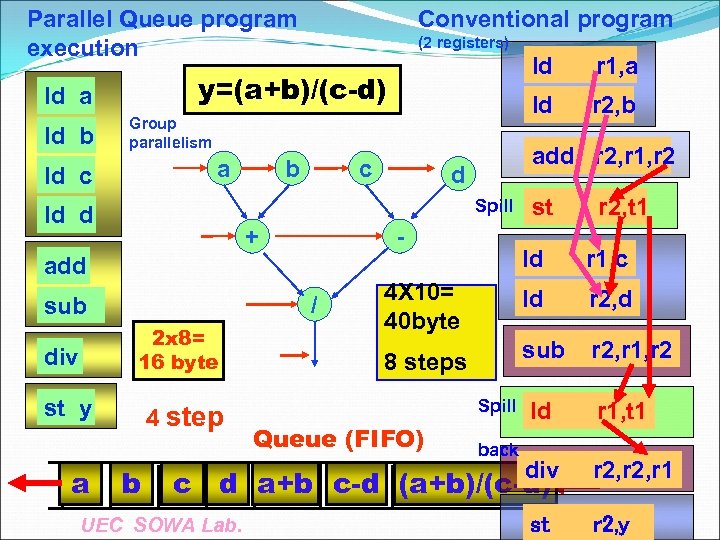 Parallel Queue program execution (2 registers) a b c add r 2, r 1, r 2 d Spill ld d + - add 2 x 8= 16 byte st y 4 step b st r 2, t 1 ld r 1, c 4 X 10= 40 byte ld r 2, d 8 steps / sub a ld r 2, b Group parallelism ld c div ld r 1, a y=(a+b)/(c-d) ld a ld b Conventional program sub r 2, r 1, r 2 Queue (FIFO) Spill back ld r 1, t 1 div r 2, r 1 c d a+b c-d (a+b)/(c-d) UEC SOWA Lab. st r 2, y
Parallel Queue program execution (2 registers) a b c add r 2, r 1, r 2 d Spill ld d + - add 2 x 8= 16 byte st y 4 step b st r 2, t 1 ld r 1, c 4 X 10= 40 byte ld r 2, d 8 steps / sub a ld r 2, b Group parallelism ld c div ld r 1, a y=(a+b)/(c-d) ld a ld b Conventional program sub r 2, r 1, r 2 Queue (FIFO) Spill back ld r 1, t 1 div r 2, r 1 c d a+b c-d (a+b)/(c-d) UEC SOWA Lab. st r 2, y
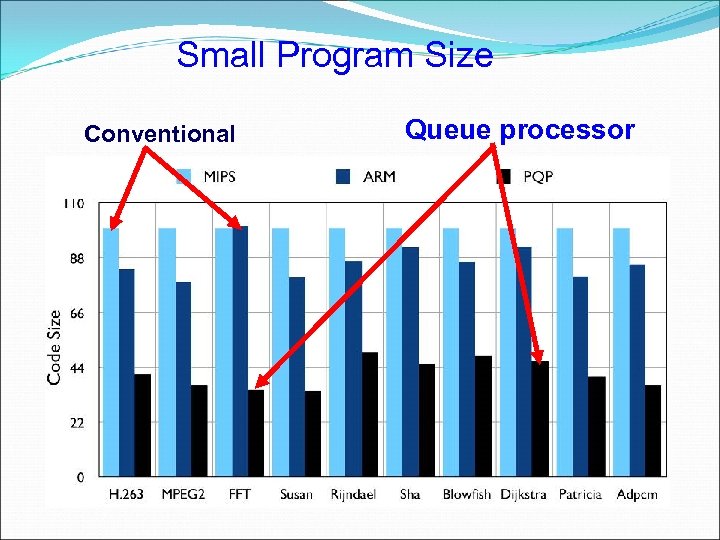 Small Program Size Conventional Queue processor
Small Program Size Conventional Queue processor
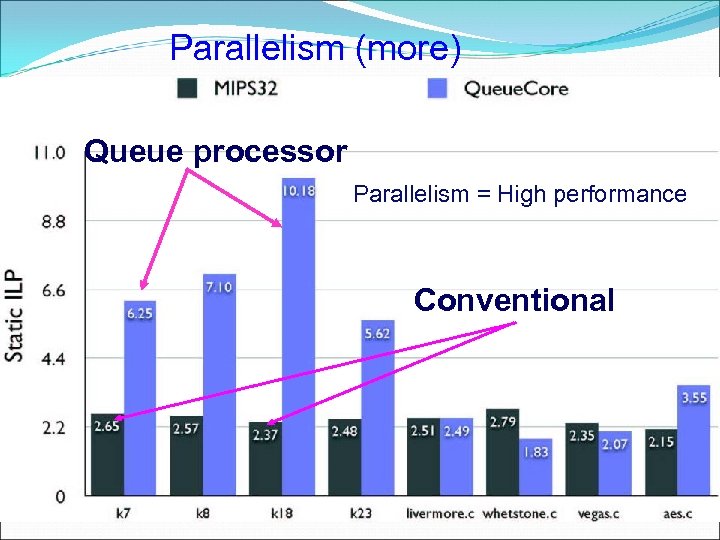 Parallelism (more) Queue processor Parallelism = High performance Conventional
Parallelism (more) Queue processor Parallelism = High performance Conventional
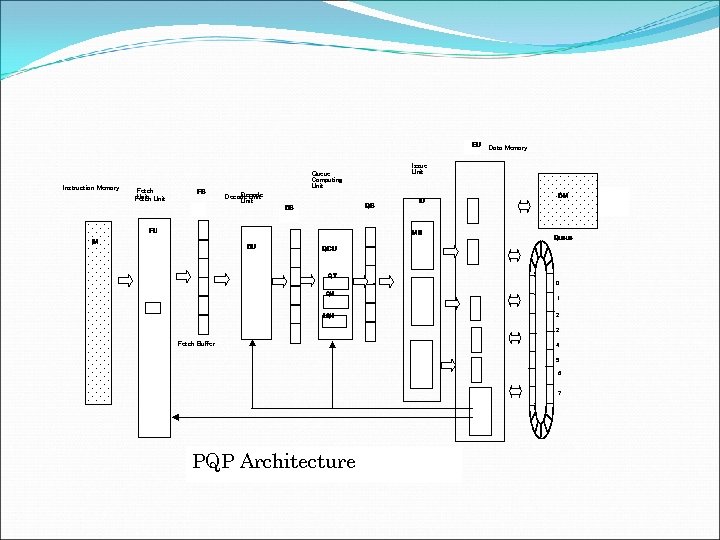 EU Instruction Memory Fetch Unit FB Issue Unit Queue Computing Unit Decode Unit QB DB FU IU MS IM DU Data Memory DM Queue QCU QT 0 QH 1 LQH 2 3 Fetch Buffer 4 5 6 7 PQP Architecture
EU Instruction Memory Fetch Unit FB Issue Unit Queue Computing Unit Decode Unit QB DB FU IU MS IM DU Data Memory DM Queue QCU QT 0 QH 1 LQH 2 3 Fetch Buffer 4 5 6 7 PQP Architecture
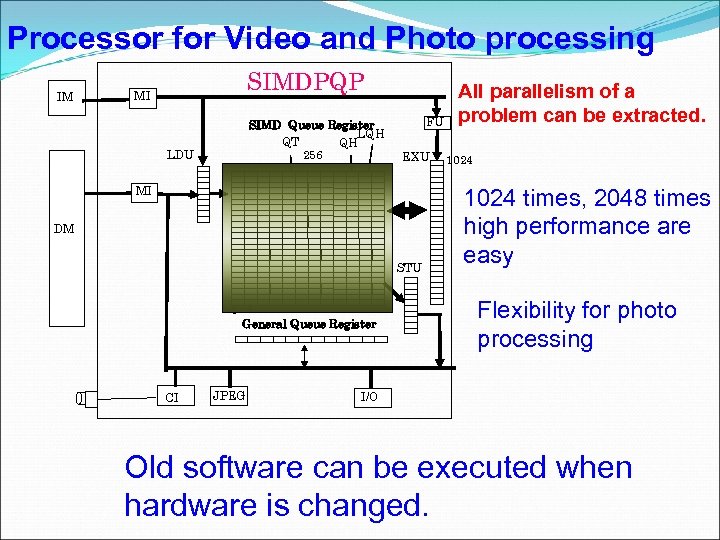 Processor for Video and Photo processing IM SIMDPQP MI SIMD Queue Register LQH QT QH 256 LDU FU EXU MI DM STU 4 4 General Queue Register CI JPEG All parallelism of a problem can be extracted. 1024 times, 2048 times high performance are easy Flexibility for photo processing I/O Old software can be executed when hardware is changed.
Processor for Video and Photo processing IM SIMDPQP MI SIMD Queue Register LQH QT QH 256 LDU FU EXU MI DM STU 4 4 General Queue Register CI JPEG All parallelism of a problem can be extracted. 1024 times, 2048 times high performance are easy Flexibility for photo processing I/O Old software can be executed when hardware is changed.
 Characteristic of Queue Computer From bread first traverse and no register name in an instruction All parallelism can be expressed: Suitable for large parallel processing → → No register renaming logic → High performance Group parallelism → Easy to find parallel instructions → No instruction windows → Simple hardware → Small energy consumption and high speed From no register name No need of register renaming logic → Simple hardware → Small energy consumption and high speed Short instruction length → Small memory, small cache, small instruction traffic → Simple hardware → Small energy consumption and high speed Short instruction length → Small cache miss → Simple hardware → Small energy consumption and high speed Suitable for SMT( Simultaneously Multi Threading) Big independency between software and hardware From single assignment High interrupt response
Characteristic of Queue Computer From bread first traverse and no register name in an instruction All parallelism can be expressed: Suitable for large parallel processing → → No register renaming logic → High performance Group parallelism → Easy to find parallel instructions → No instruction windows → Simple hardware → Small energy consumption and high speed From no register name No need of register renaming logic → Simple hardware → Small energy consumption and high speed Short instruction length → Small memory, small cache, small instruction traffic → Simple hardware → Small energy consumption and high speed Short instruction length → Small cache miss → Simple hardware → Small energy consumption and high speed Suitable for SMT( Simultaneously Multi Threading) Big independency between software and hardware From single assignment High interrupt response
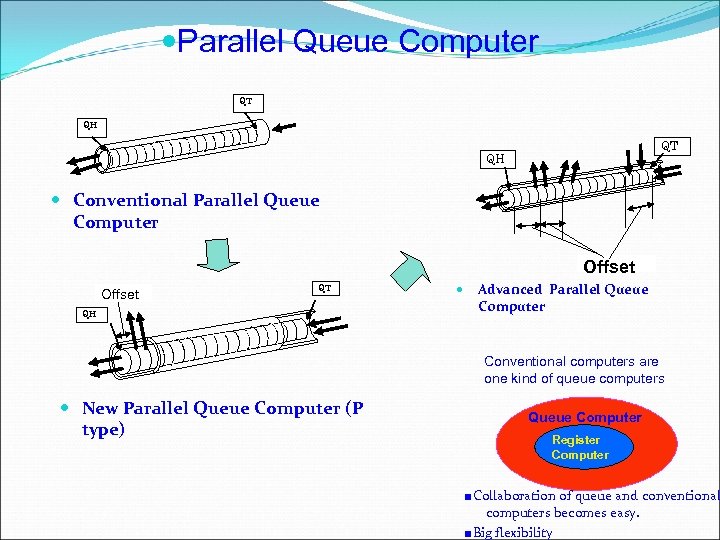 Parallel Queue Computer QT QH Conventional Parallel Queue Computer Offset QT QH Advanced Parallel Queue Computer Conventional computers are one kind of queue computers New Parallel Queue Computer (P type) Queue Computer Register Computer ■Collaboration of queue and conventional computers becomes easy. ■Big flexibility
Parallel Queue Computer QT QH Conventional Parallel Queue Computer Offset QT QH Advanced Parallel Queue Computer Conventional computers are one kind of queue computers New Parallel Queue Computer (P type) Queue Computer Register Computer ■Collaboration of queue and conventional computers becomes easy. ■Big flexibility
 2007 Arquimedes Canedo, Ben Abderazek, Masahiro Sowa ”, A New Code Generation Algorithm for 2 -offset Producer Order Queue Computation Model”, Journal of Computer Languages and Compiler Techniques, (2007) 2007 Arquimedes Canedo, Ben Abderazek, Masahiro Sowa ”, Queue Register File Optimization Algorithm for Queue. Core Processor”, 19 th International Symposium on Computer Architecture and High Performance Computing: SBAC-PAD 2007, OCt. 24 -27 (2007) Ben A. Abderazek, Tsutomu Yoshinga, and Masahiro Sowa, ” Mathematical Model for Multiobjective Synthesis of No. C Architectures”, IEEE Computer Society Proc. of the 35 th International Conference on Parallel Processing ICPP Workshop (2007) Md. Musfiquzzaman Akanda, Ben Abderazek, Masahiro Sowa , "Dual-Execution Mode Processor Architecture", Journal of Supercomputing, Teruhisa Yuuki, Arquimedes Canedo, Ben Abderazek, Masahiro Sowa , ”Novel Addressing Method for Aggregate Types in Queue Processors, 2007 International Conference on Convergence Information Technology (ICCIT¨ 07) (2007) Arquimedes Canedo, Ben Abderazek, Masahiro Sowa , ”Compiler Framework for an Embedded 32 -bit Queue Processor , 2007 International Conference on Convergence Information Technology (ICCIT¨ 07) (2007) Yuuki Nakanisi, Arquimedes Canedo, Ben Abderazek, Masahiro Sowa , ” Optimizing Reaching Definitions Overhead in Queue Processors , 2007 International Conference on Convergence Information Technology (ICCIT¨ 07) (2007) Arquimedes Canedo, Ben Abderazek, Masahiro Sowa , ”New Code Generation Algorithm for Queue Core - An Embedded Processor with High ILP, The International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Computing PDCAT 07(2007) Arquimedes Canedo, Ben Abderazek, Masahiro Sowa , ” An Efficient Code Generation Algorithm for Code Size Reduction using 1 -offset P-Code Queue Computation Model, EUC 2007 , Taiwan Taipei (2007)
2007 Arquimedes Canedo, Ben Abderazek, Masahiro Sowa ”, A New Code Generation Algorithm for 2 -offset Producer Order Queue Computation Model”, Journal of Computer Languages and Compiler Techniques, (2007) 2007 Arquimedes Canedo, Ben Abderazek, Masahiro Sowa ”, Queue Register File Optimization Algorithm for Queue. Core Processor”, 19 th International Symposium on Computer Architecture and High Performance Computing: SBAC-PAD 2007, OCt. 24 -27 (2007) Ben A. Abderazek, Tsutomu Yoshinga, and Masahiro Sowa, ” Mathematical Model for Multiobjective Synthesis of No. C Architectures”, IEEE Computer Society Proc. of the 35 th International Conference on Parallel Processing ICPP Workshop (2007) Md. Musfiquzzaman Akanda, Ben Abderazek, Masahiro Sowa , "Dual-Execution Mode Processor Architecture", Journal of Supercomputing, Teruhisa Yuuki, Arquimedes Canedo, Ben Abderazek, Masahiro Sowa , ”Novel Addressing Method for Aggregate Types in Queue Processors, 2007 International Conference on Convergence Information Technology (ICCIT¨ 07) (2007) Arquimedes Canedo, Ben Abderazek, Masahiro Sowa , ”Compiler Framework for an Embedded 32 -bit Queue Processor , 2007 International Conference on Convergence Information Technology (ICCIT¨ 07) (2007) Yuuki Nakanisi, Arquimedes Canedo, Ben Abderazek, Masahiro Sowa , ” Optimizing Reaching Definitions Overhead in Queue Processors , 2007 International Conference on Convergence Information Technology (ICCIT¨ 07) (2007) Arquimedes Canedo, Ben Abderazek, Masahiro Sowa , ”New Code Generation Algorithm for Queue Core - An Embedded Processor with High ILP, The International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Computing PDCAT 07(2007) Arquimedes Canedo, Ben Abderazek, Masahiro Sowa , ” An Efficient Code Generation Algorithm for Code Size Reduction using 1 -offset P-Code Queue Computation Model, EUC 2007 , Taiwan Taipei (2007)
 Research Results ■ Completion of the PQP in verilog HDL ■ Completion of 2 D PQP in verilog HDL ■ Completion of Parallelized C Compiler Near actual compiler est B Paper Award ■ Completion of Hybrid PQP in verilog HDL Queue and Stack computing ■QJAVA Parallel JAVA ■ SIMD Queue computer
Research Results ■ Completion of the PQP in verilog HDL ■ Completion of 2 D PQP in verilog HDL ■ Completion of Parallelized C Compiler Near actual compiler est B Paper Award ■ Completion of Hybrid PQP in verilog HDL Queue and Stack computing ■QJAVA Parallel JAVA ■ SIMD Queue computer
 Thank you for your attention! We are expecting you to attend our research group QCI (Queue Computer Initiative). Please mail me. University of Electro-Communications Tokyo, Japan sowa@is. uec. ac. jp http: //www. sowa. is. uec. ac. jp
Thank you for your attention! We are expecting you to attend our research group QCI (Queue Computer Initiative). Please mail me. University of Electro-Communications Tokyo, Japan sowa@is. uec. ac. jp http: //www. sowa. is. uec. ac. jp
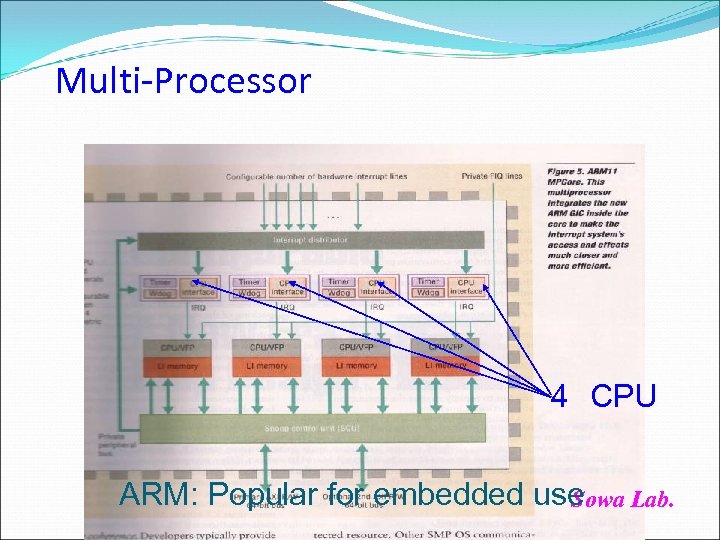 Multi-Processor 4 CPU ARM: Popular for embedded use Lab. Sowa
Multi-Processor 4 CPU ARM: Popular for embedded use Lab. Sowa
 Multi-Processor System To increase hardware To increase power consumption To increase difficulty for programming Break through is needed!! Large program
Multi-Processor System To increase hardware To increase power consumption To increase difficulty for programming Break through is needed!! Large program


