2a94cf5f5d79b6a4c6fffcee5fbb8380.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 New Government Software Models: An Introduction to Saa. S and Application Outsourcing Presented to State of Oregon Oct. 15 th, 2009 Rishi Sood Vice President, Government Gartner rishi. sood@gartner. com
New Government Software Models: An Introduction to Saa. S and Application Outsourcing Presented to State of Oregon Oct. 15 th, 2009 Rishi Sood Vice President, Government Gartner rishi. sood@gartner. com
 Presentation Outline State & Local Environment • Market Segmentation and Solutions Map • Major Cost Optimization Strategies • Budget Battles: Traditional vs. Innovative Saa. S and AO: An Introduction • Alternative Delivery Models & The Cloud: A Primer • Saa. S and AO: Working Definitions • Saa. S and AO: A Comparative Look • Saa. S Areas of Development • Saa. S and AO: State & Local Government Users Practical Steps to Saa. S • Centralized IT and the Agencies: Building Collaborative Spirit • Cloud Myths and Saa. S Benefits © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. • Saa. S Differentiation 2
Presentation Outline State & Local Environment • Market Segmentation and Solutions Map • Major Cost Optimization Strategies • Budget Battles: Traditional vs. Innovative Saa. S and AO: An Introduction • Alternative Delivery Models & The Cloud: A Primer • Saa. S and AO: Working Definitions • Saa. S and AO: A Comparative Look • Saa. S Areas of Development • Saa. S and AO: State & Local Government Users Practical Steps to Saa. S • Centralized IT and the Agencies: Building Collaborative Spirit • Cloud Myths and Saa. S Benefits © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. • Saa. S Differentiation 2
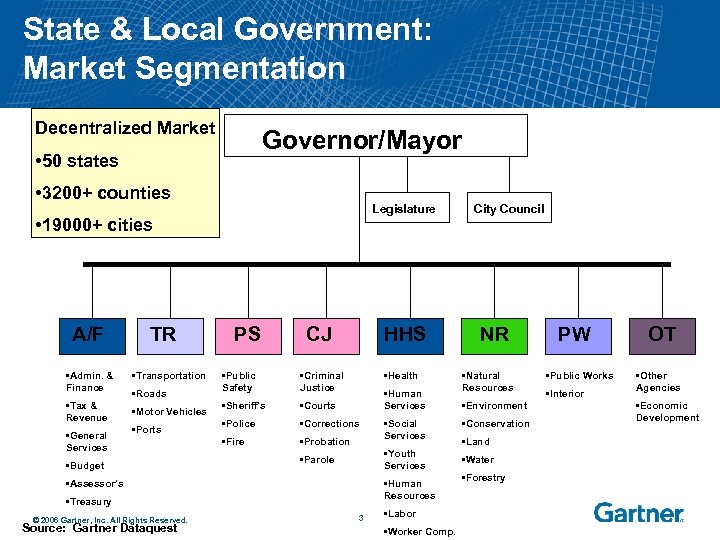 State & Local Government: Market Segmentation Decentralized Market Governor/Mayor • 50 states • 3200+ counties Legislature • 19000+ cities A/F • Admin. & Finance • Tax & Revenue • General Services TR • Transportation • Roads • Motor Vehicles • Ports • Budget PS CJ HHS • Public Safety • Criminal Justice • Health • Sheriff’s • Courts • Police • Corrections • Fire • Probation • Human Services • Youth Services • Parole • Assessor’s • Human Resources • Treasury © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Source: Gartner Dataquest • Social Services 3 • Labor • Worker Comp. City Council NR • Natural Resources • Environment • Conservation • Land • Water • Forestry PW • Public Works • Interior OT • Other Agencies • Economic Development
State & Local Government: Market Segmentation Decentralized Market Governor/Mayor • 50 states • 3200+ counties Legislature • 19000+ cities A/F • Admin. & Finance • Tax & Revenue • General Services TR • Transportation • Roads • Motor Vehicles • Ports • Budget PS CJ HHS • Public Safety • Criminal Justice • Health • Sheriff’s • Courts • Police • Corrections • Fire • Probation • Human Services • Youth Services • Parole • Assessor’s • Human Resources • Treasury © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Source: Gartner Dataquest • Social Services 3 • Labor • Worker Comp. City Council NR • Natural Resources • Environment • Conservation • Land • Water • Forestry PW • Public Works • Interior OT • Other Agencies • Economic Development
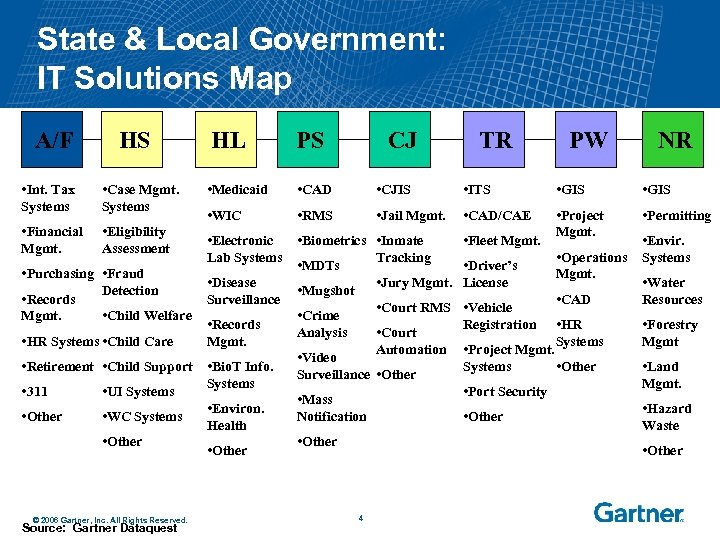 State & Local Government: IT Solutions Map A/F HS • Int. Tax Systems • Case Mgmt. Systems • Financial Mgmt. HL PS CJ • Medicaid • CAD • CJIS • ITS • GIS • WIC • RMS • Jail Mgmt. • CAD/CAE • Permitting • Inmate Tracking • Fleet Mgmt. • Project Mgmt. • Eligibility Assessment • Electronic • Biometrics Lab Systems • MDTs • Purchasing • Fraud • Disease Detection • Mugshot Surveillance • Records • Child Welfare • Crime Mgmt. • Records Analysis Mgmt. • HR Systems • Child Care • Video • Retirement • Child Support • Bio. T Info. Surveillance Systems • UI Systems • 311 • Mass • Environ. • WC Systems • Other Notification Health • Other © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Source: Gartner Dataquest 4 TR • Driver’s • Jury Mgmt. License PW • Envir. • Operations Systems Mgmt. • Water Resources • CAD • Court RMS • Vehicle Registration • HR • Court Systems Automation • Project Mgmt. Systems • Other • Port Security • Other NR • Forestry Mgmt • Land Mgmt. • Hazard Waste • Other
State & Local Government: IT Solutions Map A/F HS • Int. Tax Systems • Case Mgmt. Systems • Financial Mgmt. HL PS CJ • Medicaid • CAD • CJIS • ITS • GIS • WIC • RMS • Jail Mgmt. • CAD/CAE • Permitting • Inmate Tracking • Fleet Mgmt. • Project Mgmt. • Eligibility Assessment • Electronic • Biometrics Lab Systems • MDTs • Purchasing • Fraud • Disease Detection • Mugshot Surveillance • Records • Child Welfare • Crime Mgmt. • Records Analysis Mgmt. • HR Systems • Child Care • Video • Retirement • Child Support • Bio. T Info. Surveillance Systems • UI Systems • 311 • Mass • Environ. • WC Systems • Other Notification Health • Other © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Source: Gartner Dataquest 4 TR • Driver’s • Jury Mgmt. License PW • Envir. • Operations Systems Mgmt. • Water Resources • CAD • Court RMS • Vehicle Registration • HR • Court Systems Automation • Project Mgmt. Systems • Other • Port Security • Other NR • Forestry Mgmt • Land Mgmt. • Hazard Waste • Other
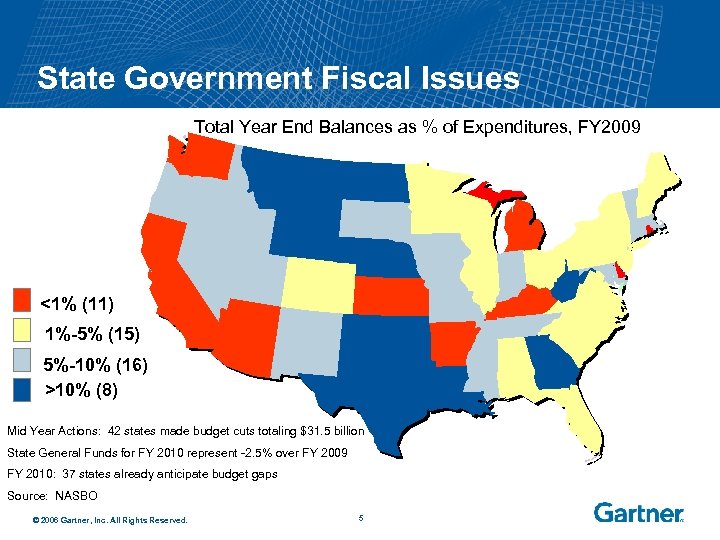 State Government Fiscal Issues Total Year End Balances as % of Expenditures, FY 2009 <1% (11) 1%-5% (15) 5%-10% (16) >10% (8) Mid Year Actions: 42 states made budget cuts totaling $31. 5 billion State General Funds for FY 2010 represent -2. 5% over FY 2009 FY 2010: 37 states already anticipate budget gaps Source: NASBO © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 5
State Government Fiscal Issues Total Year End Balances as % of Expenditures, FY 2009 <1% (11) 1%-5% (15) 5%-10% (16) >10% (8) Mid Year Actions: 42 states made budget cuts totaling $31. 5 billion State General Funds for FY 2010 represent -2. 5% over FY 2009 FY 2010: 37 states already anticipate budget gaps Source: NASBO © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 5
 Mapping all Cost Cutting Items Manage Demand Cost containment Reduce Resource Costs Shift to Variable Cost Enable shared risk / reward contracts Reduce Labor Cost Link costs to demand Canceling non-viable projects Offshore application development Project prioritization Pay for IT investments with bonds Offshore application maintenance Standardize administrative applications Reduce Technology Cost Desktop printer consolidation Implementing Vo. IP Change Operating Practices Adopting open-source server software Renegotiate network rates Create shared disaster recovery centers Create a shared services environment for IT infrastructure Renegotiate shelfware maintenance Discard unused equipment Convert networks to VPN High-volume print rationalization / consolidation Call center consolidation across government Using tools to reduce travel (e. g. video conferencing) Centralize portal management and development Create a project management office Consolidate mainframes Reuse software components Remove games from PCs and PDAs Cell phone usage Centralize application development Improve IS Business Practices Server cons. (physical, rational, capacity) Enterprise call center consolidation within government Teleworking Utilizing fewer contractors and consultants Implementing energy saving measures Standardize e-mail Restructure email storage Create a project management office Consider Saa. S for certain applications Automate software distribution Adopting open-source desktop software Discontinue buying proprietary hardware Change Operating Model Break-up large projects and defer pieces Negotiate enterprise email agreement Consolidate and renegotiate vendor contracts Benchmarking Centralize desktop application management Telecommunications audit Confiscate underused equipment 6 © 2006 Gartner, Inc. Source: Cost All Rights Reserved. to Cope with Economic Slowdown, Gartner Cutting in IT Consolidate IT procurement Helpdesk consolidation Defer purchases of desktop products
Mapping all Cost Cutting Items Manage Demand Cost containment Reduce Resource Costs Shift to Variable Cost Enable shared risk / reward contracts Reduce Labor Cost Link costs to demand Canceling non-viable projects Offshore application development Project prioritization Pay for IT investments with bonds Offshore application maintenance Standardize administrative applications Reduce Technology Cost Desktop printer consolidation Implementing Vo. IP Change Operating Practices Adopting open-source server software Renegotiate network rates Create shared disaster recovery centers Create a shared services environment for IT infrastructure Renegotiate shelfware maintenance Discard unused equipment Convert networks to VPN High-volume print rationalization / consolidation Call center consolidation across government Using tools to reduce travel (e. g. video conferencing) Centralize portal management and development Create a project management office Consolidate mainframes Reuse software components Remove games from PCs and PDAs Cell phone usage Centralize application development Improve IS Business Practices Server cons. (physical, rational, capacity) Enterprise call center consolidation within government Teleworking Utilizing fewer contractors and consultants Implementing energy saving measures Standardize e-mail Restructure email storage Create a project management office Consider Saa. S for certain applications Automate software distribution Adopting open-source desktop software Discontinue buying proprietary hardware Change Operating Model Break-up large projects and defer pieces Negotiate enterprise email agreement Consolidate and renegotiate vendor contracts Benchmarking Centralize desktop application management Telecommunications audit Confiscate underused equipment 6 © 2006 Gartner, Inc. Source: Cost All Rights Reserved. to Cope with Economic Slowdown, Gartner Cutting in IT Consolidate IT procurement Helpdesk consolidation Defer purchases of desktop products
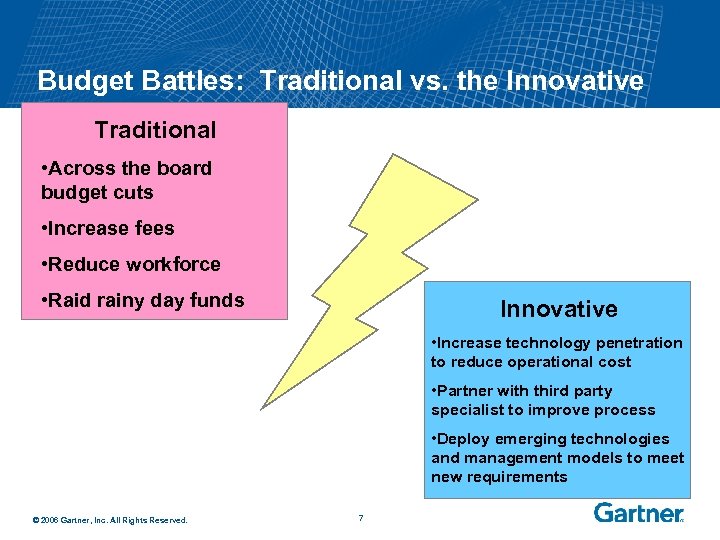 Budget Battles: Traditional vs. the Innovative Traditional • Across the board budget cuts • Increase fees • Reduce workforce • Raid rainy day funds Innovative • Increase technology penetration to reduce operational cost • Partner with third party specialist to improve process • Deploy emerging technologies and management models to meet new requirements © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 7
Budget Battles: Traditional vs. the Innovative Traditional • Across the board budget cuts • Increase fees • Reduce workforce • Raid rainy day funds Innovative • Increase technology penetration to reduce operational cost • Partner with third party specialist to improve process • Deploy emerging technologies and management models to meet new requirements © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 7
 II. Changing Government Software: An Introduction to Cloud, Saa. S, and AO © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 8
II. Changing Government Software: An Introduction to Cloud, Saa. S, and AO © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 8
 Cloud Computing: Definition and Perspective "All that matters is results; I don't care how it's done. " "I don't want to own assets — I want to pay for elastic use, like a utility. " "I want accessibility from anywhere, from any device. " "It's about economies of scale, with effective and dynamic sharing. " Acquisition Model Service Business Model Pay for use Access Model Internet Technical Model Scalable, elastic, shareable Global-class industrialization of computing resources and services EC 2 and S 3 © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 9 Cloud Computing: A style of computing where massively scalable and elastic IT-enabled capabilities are provided "as a service" to external customers using Internet technologies* *It would be easy to add this refining statement: "Where the consumers of the services need only care about what the service does for them, not how it is implemented. "
Cloud Computing: Definition and Perspective "All that matters is results; I don't care how it's done. " "I don't want to own assets — I want to pay for elastic use, like a utility. " "I want accessibility from anywhere, from any device. " "It's about economies of scale, with effective and dynamic sharing. " Acquisition Model Service Business Model Pay for use Access Model Internet Technical Model Scalable, elastic, shareable Global-class industrialization of computing resources and services EC 2 and S 3 © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 9 Cloud Computing: A style of computing where massively scalable and elastic IT-enabled capabilities are provided "as a service" to external customers using Internet technologies* *It would be easy to add this refining statement: "Where the consumers of the services need only care about what the service does for them, not how it is implemented. "
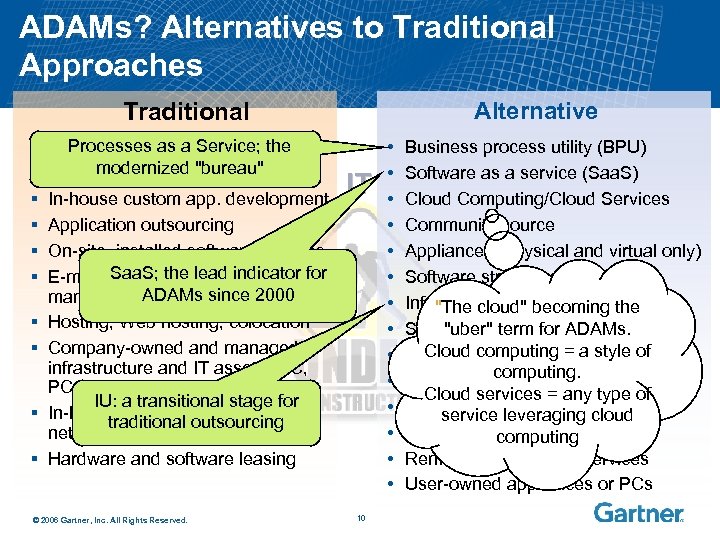 ADAMs? Alternatives to Traditional Approaches Alternative Traditional § § § Processes as a Service; the Systems Integration modernized "bureau" Business process outsourcing In-house custom app. development Application outsourcing On-site, installed software licenses Saa. S; the lead indicator E-mail outsourcing, document for ADAMs since 2000 management/print outsourcing IT § Hosting, Web hosting, colocation § Company-owned and managed infrastructure and IT assets (DC, PCs, network, software) IU: a transitional stage for § In-house managed networks, traditional outsourcing network outsourcing § Hardware and software leasing © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 10 • • • • Business process utility (BPU) Software as a service (Saa. S) Cloud Computing/Cloud Services Community source Appliances (physical and virtual only) Software streaming Infrastructure utility (IU) the "The cloud" becoming Storage as a service "uber" term for ADAMs. Cloud computing = a style of Grid computing. Utility computing Cloud services = any type of Capacity on leveraging cloud service demand Communication as a service computing Remote management services User-owned appliances or PCs
ADAMs? Alternatives to Traditional Approaches Alternative Traditional § § § Processes as a Service; the Systems Integration modernized "bureau" Business process outsourcing In-house custom app. development Application outsourcing On-site, installed software licenses Saa. S; the lead indicator E-mail outsourcing, document for ADAMs since 2000 management/print outsourcing IT § Hosting, Web hosting, colocation § Company-owned and managed infrastructure and IT assets (DC, PCs, network, software) IU: a transitional stage for § In-house managed networks, traditional outsourcing network outsourcing § Hardware and software leasing © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 10 • • • • Business process utility (BPU) Software as a service (Saa. S) Cloud Computing/Cloud Services Community source Appliances (physical and virtual only) Software streaming Infrastructure utility (IU) the "The cloud" becoming Storage as a service "uber" term for ADAMs. Cloud computing = a style of Grid computing. Utility computing Cloud services = any type of Capacity on leveraging cloud service demand Communication as a service computing Remote management services User-owned appliances or PCs
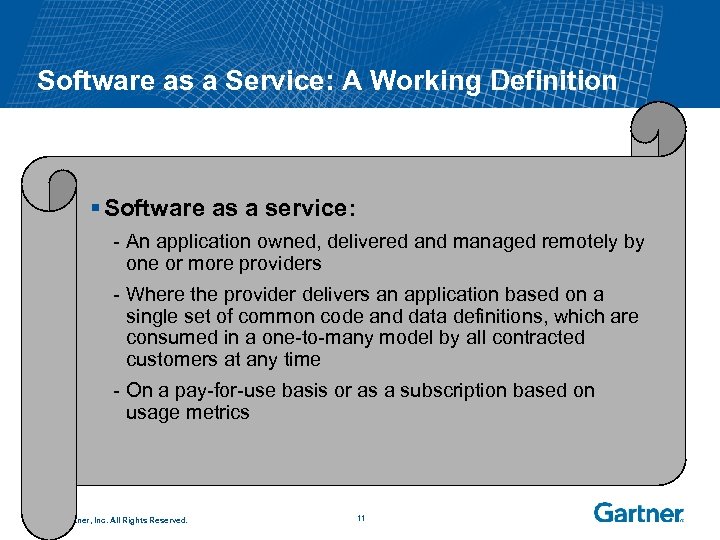 Software as a Service: A Working Definition § Software as a service: - An application owned, delivered and managed remotely by one or more providers - Where the provider delivers an application based on a single set of common code and data definitions, which are consumed in a one-to-many model by all contracted customers at any time - On a pay-for-use basis or as a subscription based on usage metrics © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 11
Software as a Service: A Working Definition § Software as a service: - An application owned, delivered and managed remotely by one or more providers - Where the provider delivers an application based on a single set of common code and data definitions, which are consumed in a one-to-many model by all contracted customers at any time - On a pay-for-use basis or as a subscription based on usage metrics © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 11
 Application Outsourcing: A Working Definition § Application Outsourcing: - An application owned by the customer, managed on premise or remotely by the provider(s) - Where the provider delivers an application based on a standardized set of common code and data definitions, which are consumed in a one-to-one model by the customer - Paid for generally as a percentage of the annual license fee © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 12
Application Outsourcing: A Working Definition § Application Outsourcing: - An application owned by the customer, managed on premise or remotely by the provider(s) - Where the provider delivers an application based on a standardized set of common code and data definitions, which are consumed in a one-to-one model by the customer - Paid for generally as a percentage of the annual license fee © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 12
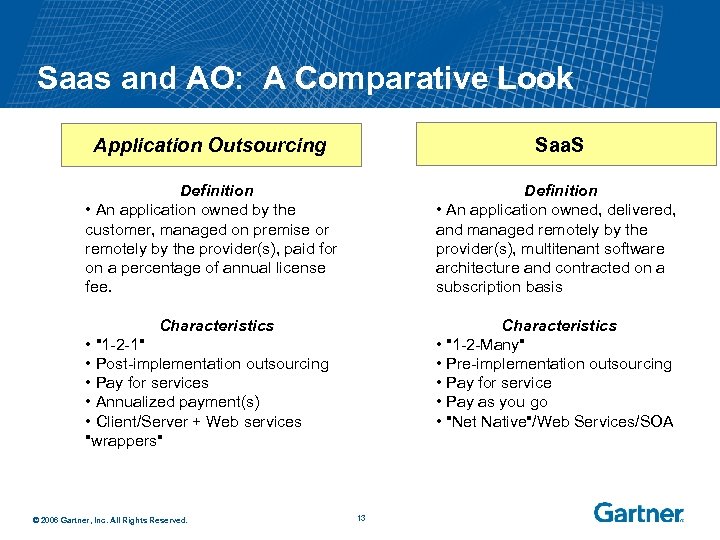 Saas and AO: A Comparative Look Application Outsourcing Saa. S Definition • An application owned by the customer, managed on premise or remotely by the provider(s), paid for on a percentage of annual license fee. Definition • An application owned, delivered, and managed remotely by the provider(s), multitenant software architecture and contracted on a subscription basis Characteristics • "1 -2 -Many" • Pre-implementation outsourcing • Pay for service • Pay as you go • "Net Native"/Web Services/SOA • "1 -2 -1" • Post-implementation outsourcing • Pay for services • Annualized payment(s) • Client/Server + Web services "wrappers" © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 13
Saas and AO: A Comparative Look Application Outsourcing Saa. S Definition • An application owned by the customer, managed on premise or remotely by the provider(s), paid for on a percentage of annual license fee. Definition • An application owned, delivered, and managed remotely by the provider(s), multitenant software architecture and contracted on a subscription basis Characteristics • "1 -2 -Many" • Pre-implementation outsourcing • Pay for service • Pay as you go • "Net Native"/Web Services/SOA • "1 -2 -1" • Post-implementation outsourcing • Pay for services • Annualized payment(s) • Client/Server + Web services "wrappers" © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 13
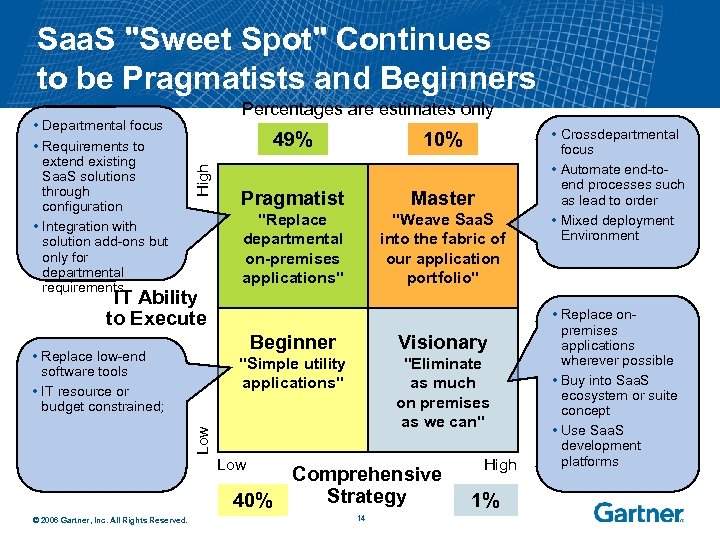 Saa. S "Sweet Spot" Continues to be Pragmatists and Beginners 49% High • Departmental focus • Requirements to extend existing Saa. S solutions through configuration • Integration with solution add-ons but only for departmental requirements Percentages are estimates only IT Ability to Execute 10% Pragmatist Master "Replace departmental on-premises applications" "Weave Saa. S into the fabric of our application portfolio" Beginner "Eliminate as much on premises as we can" Low Visionary "Simple utility applications" • Replace low-end software tools • IT resource or budget constrained; Low Comprehensive Strategy 40% © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 14 High 1% • Crossdepartmental focus • Automate end-toend processes such as lead to order • Mixed deployment Environment • Replace onpremises applications wherever possible • Buy into Saa. S ecosystem or suite concept • Use Saa. S development platforms
Saa. S "Sweet Spot" Continues to be Pragmatists and Beginners 49% High • Departmental focus • Requirements to extend existing Saa. S solutions through configuration • Integration with solution add-ons but only for departmental requirements Percentages are estimates only IT Ability to Execute 10% Pragmatist Master "Replace departmental on-premises applications" "Weave Saa. S into the fabric of our application portfolio" Beginner "Eliminate as much on premises as we can" Low Visionary "Simple utility applications" • Replace low-end software tools • IT resource or budget constrained; Low Comprehensive Strategy 40% © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 14 High 1% • Crossdepartmental focus • Automate end-toend processes such as lead to order • Mixed deployment Environment • Replace onpremises applications wherever possible • Buy into Saa. S ecosystem or suite concept • Use Saa. S development platforms
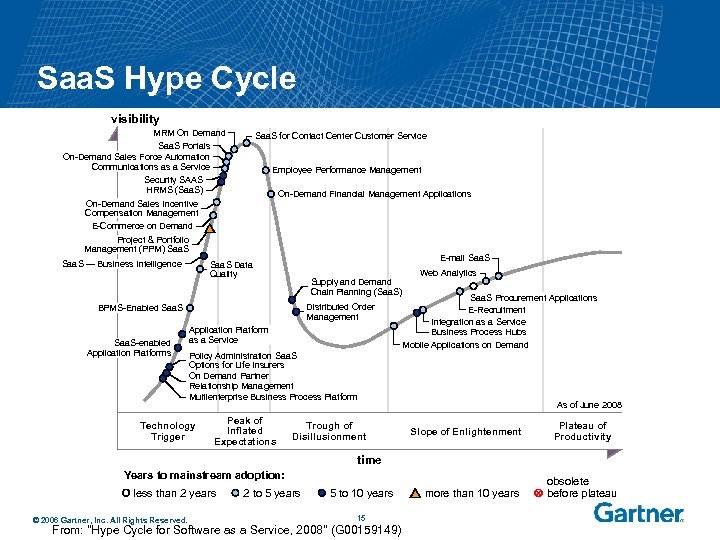 Saa. S Hype Cycle visibility MRM On Demand Saa. S Portals On-Demand Sales Force Automation Communications as a Service Security SAAS HRMS (Saa. S) On-Demand Sales Incentive Compensation Management E-Commerce on Demand Project & Portfolio Management (PPM) Saa. S — Business Intelligence Saa. S for Contact Center Customer Service Employee Performance Management On-Demand Financial Management Applications E-mail Saa. S Data Quality Supply and Demand Chain Planning (Saa. S) Distributed Order Management BPMS-Enabled Saa. S-enabled Application Platforms Application Platform as a Service Web Analytics Saa. S Procurement Applications E-Recruitment Integration as a Service Business Process Hubs Mobile Applications on Demand Policy Administration Saa. S Options for Life Insurers On Demand Partner Relationship Management Multienterprise Business Process Platform Technology Trigger Peak of Inflated Expectations Trough of Disillusionment As of June 2008 Slope of Enlightenment Plateau of Productivity time Years to mainstream adoption: less than 2 years © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 2 to 5 years 5 to 10 years 15 From: "Hype Cycle for Software as a Service, 2008" (G 00159149) more than 10 years obsolete before plateau
Saa. S Hype Cycle visibility MRM On Demand Saa. S Portals On-Demand Sales Force Automation Communications as a Service Security SAAS HRMS (Saa. S) On-Demand Sales Incentive Compensation Management E-Commerce on Demand Project & Portfolio Management (PPM) Saa. S — Business Intelligence Saa. S for Contact Center Customer Service Employee Performance Management On-Demand Financial Management Applications E-mail Saa. S Data Quality Supply and Demand Chain Planning (Saa. S) Distributed Order Management BPMS-Enabled Saa. S-enabled Application Platforms Application Platform as a Service Web Analytics Saa. S Procurement Applications E-Recruitment Integration as a Service Business Process Hubs Mobile Applications on Demand Policy Administration Saa. S Options for Life Insurers On Demand Partner Relationship Management Multienterprise Business Process Platform Technology Trigger Peak of Inflated Expectations Trough of Disillusionment As of June 2008 Slope of Enlightenment Plateau of Productivity time Years to mainstream adoption: less than 2 years © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 2 to 5 years 5 to 10 years 15 From: "Hype Cycle for Software as a Service, 2008" (G 00159149) more than 10 years obsolete before plateau
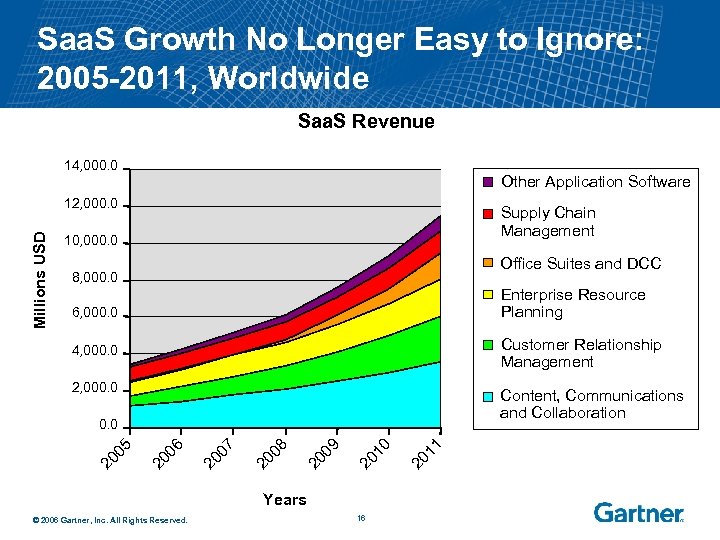 Saa. S Growth No Longer Easy to Ignore: 2005 -2011, Worldwide Saa. S Revenue 14, 000. 0 Other Application Software Millions USD 12, 000. 0 Supply Chain Management 10, 000. 0 Office Suites and DCC 8, 000. 0 Enterprise Resource Planning 6, 000. 0 4, 000. 0 Customer Relationship Management 2, 000. 0 Content, Communications and Collaboration Years © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 16 1 20 1 0 20 1 9 20 0 8 20 0 7 20 0 6 20 0 5 0. 0
Saa. S Growth No Longer Easy to Ignore: 2005 -2011, Worldwide Saa. S Revenue 14, 000. 0 Other Application Software Millions USD 12, 000. 0 Supply Chain Management 10, 000. 0 Office Suites and DCC 8, 000. 0 Enterprise Resource Planning 6, 000. 0 4, 000. 0 Customer Relationship Management 2, 000. 0 Content, Communications and Collaboration Years © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 16 1 20 1 0 20 1 9 20 0 8 20 0 7 20 0 6 20 0 5 0. 0
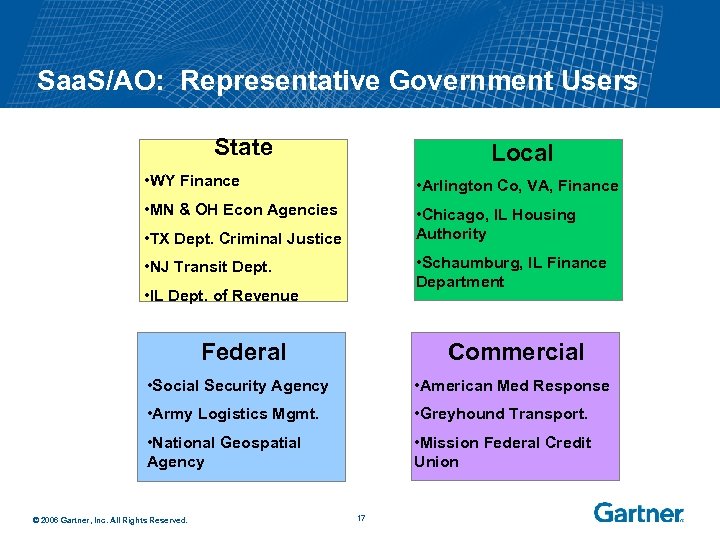 Saa. S/AO: Representative Government Users State Local • WY Finance • Arlington Co, VA, Finance • MN & OH Econ Agencies • Chicago, IL Housing Authority • TX Dept. Criminal Justice • Schaumburg, IL Finance Department • NJ Transit Dept. • IL Dept. of Revenue Federal Commercial • Social Security Agency • American Med Response • Army Logistics Mgmt. • Greyhound Transport. • National Geospatial Agency • Mission Federal Credit Union © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 17
Saa. S/AO: Representative Government Users State Local • WY Finance • Arlington Co, VA, Finance • MN & OH Econ Agencies • Chicago, IL Housing Authority • TX Dept. Criminal Justice • Schaumburg, IL Finance Department • NJ Transit Dept. • IL Dept. of Revenue Federal Commercial • Social Security Agency • American Med Response • Army Logistics Mgmt. • Greyhound Transport. • National Geospatial Agency • Mission Federal Credit Union © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 17
 III. What Should You Do Next… © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 18
III. What Should You Do Next… © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 18
 Enterprise IT and the Agencies: Key Attributes to Working Together Positive Strategies and Tactics Negative Strategies and Tactics § Enterprise Wide Framework § Denial – “This is a fad” § Unified Governance Strategy § Avoidance – “NIMBY” § Future Investment analysis § Assuming that tomorrow’s CSFs are the same as yesterday’s § Collaborative Planning § Joint Prioritization § Adding hosting/specialization § Integration (OP & hosted) § Consulting about Saa. S/AO § Saa. S/AO Enablement § Clinging onto the hope that old norms will re-assert themselves § Ignoring the opportunity Saa. S/AO presents for re-invention, adaptation, innovation § Placing all or nothing bets § Hosted custom extensions © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 19
Enterprise IT and the Agencies: Key Attributes to Working Together Positive Strategies and Tactics Negative Strategies and Tactics § Enterprise Wide Framework § Denial – “This is a fad” § Unified Governance Strategy § Avoidance – “NIMBY” § Future Investment analysis § Assuming that tomorrow’s CSFs are the same as yesterday’s § Collaborative Planning § Joint Prioritization § Adding hosting/specialization § Integration (OP & hosted) § Consulting about Saa. S/AO § Saa. S/AO Enablement § Clinging onto the hope that old norms will re-assert themselves § Ignoring the opportunity Saa. S/AO presents for re-invention, adaptation, innovation § Placing all or nothing bets § Hosted custom extensions © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 19
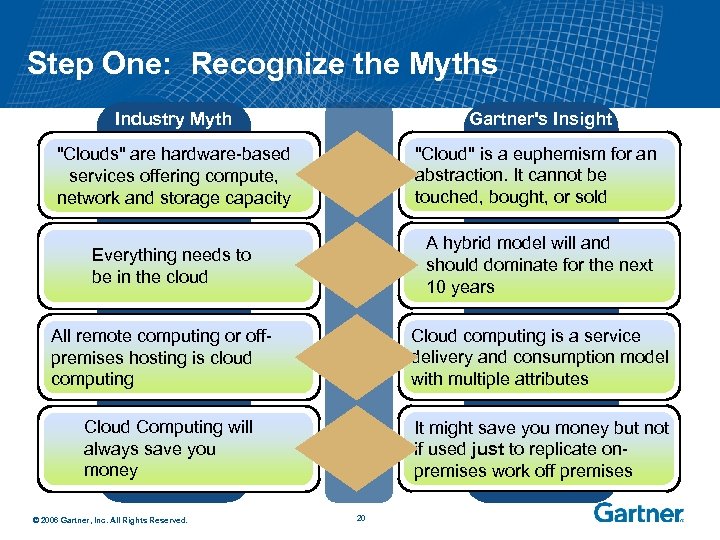 Step One: Recognize the Myths Industry Myth Gartner's Insight "Clouds" are hardware-based services offering compute, network and storage capacity "Cloud" is a euphemism for an abstraction. It cannot be touched, bought, or sold Everything needs to be in the cloud A hybrid model will and should dominate for the next 10 years Cloud computing is a service delivery and consumption model with multiple attributes All remote computing or offpremises hosting is cloud computing Cloud Computing will always save you money © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. It might save you money but not if used just to replicate onpremises work off premises 20
Step One: Recognize the Myths Industry Myth Gartner's Insight "Clouds" are hardware-based services offering compute, network and storage capacity "Cloud" is a euphemism for an abstraction. It cannot be touched, bought, or sold Everything needs to be in the cloud A hybrid model will and should dominate for the next 10 years Cloud computing is a service delivery and consumption model with multiple attributes All remote computing or offpremises hosting is cloud computing Cloud Computing will always save you money © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. It might save you money but not if used just to replicate onpremises work off premises 20
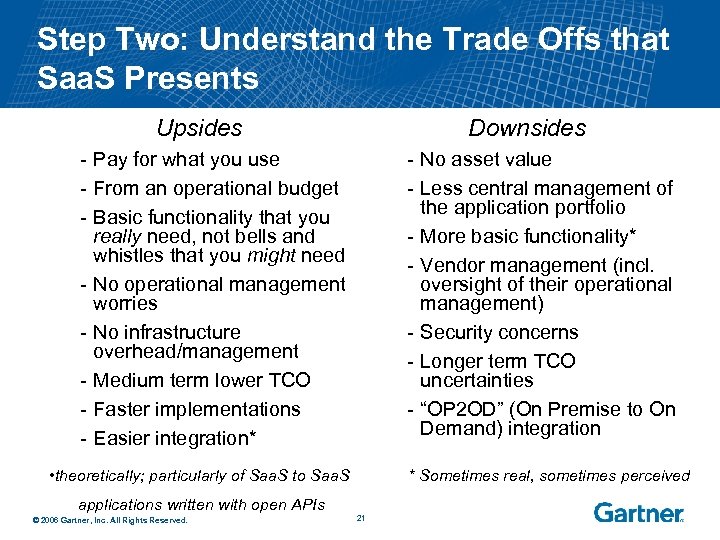 Step Two: Understand the Trade Offs that Saa. S Presents Upsides Downsides - Pay for what you use - From an operational budget - Basic functionality that you really need, not bells and whistles that you might need - No operational management worries - No infrastructure overhead/management - Medium term lower TCO - Faster implementations - Easier integration* - No asset value - Less central management of the application portfolio - More basic functionality* - Vendor management (incl. oversight of their operational management) - Security concerns - Longer term TCO uncertainties - “OP 2 OD” (On Premise to On Demand) integration • theoretically; particularly of Saa. S to Saa. S * Sometimes real, sometimes perceived applications written with open APIs © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 21
Step Two: Understand the Trade Offs that Saa. S Presents Upsides Downsides - Pay for what you use - From an operational budget - Basic functionality that you really need, not bells and whistles that you might need - No operational management worries - No infrastructure overhead/management - Medium term lower TCO - Faster implementations - Easier integration* - No asset value - Less central management of the application portfolio - More basic functionality* - Vendor management (incl. oversight of their operational management) - Security concerns - Longer term TCO uncertainties - “OP 2 OD” (On Premise to On Demand) integration • theoretically; particularly of Saa. S to Saa. S * Sometimes real, sometimes perceived applications written with open APIs © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 21
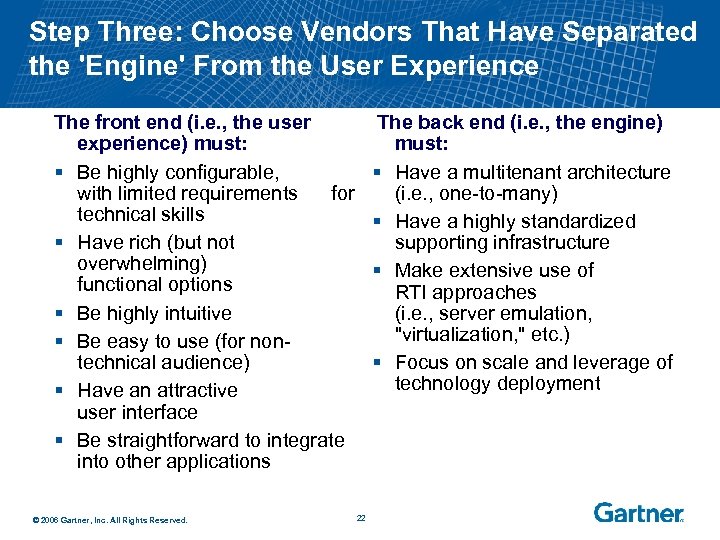 Step Three: Choose Vendors That Have Separated the 'Engine' From the User Experience The front end (i. e. , the user experience) must: § Be highly configurable, with limited requirements for technical skills § Have rich (but not overwhelming) functional options § Be highly intuitive § Be easy to use (for nontechnical audience) § Have an attractive user interface § Be straightforward to integrate into other applications © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. The back end (i. e. , the engine) must: § Have a multitenant architecture (i. e. , one-to-many) § Have a highly standardized supporting infrastructure § Make extensive use of RTI approaches (i. e. , server emulation, "virtualization, " etc. ) § Focus on scale and leverage of technology deployment 22
Step Three: Choose Vendors That Have Separated the 'Engine' From the User Experience The front end (i. e. , the user experience) must: § Be highly configurable, with limited requirements for technical skills § Have rich (but not overwhelming) functional options § Be highly intuitive § Be easy to use (for nontechnical audience) § Have an attractive user interface § Be straightforward to integrate into other applications © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. The back end (i. e. , the engine) must: § Have a multitenant architecture (i. e. , one-to-many) § Have a highly standardized supporting infrastructure § Make extensive use of RTI approaches (i. e. , server emulation, "virtualization, " etc. ) § Focus on scale and leverage of technology deployment 22
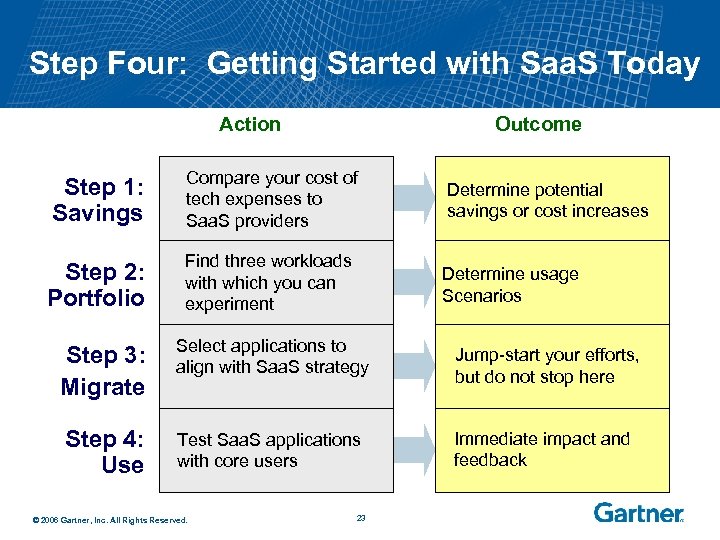 Step Four: Getting Started with Saa. S Today Action Outcome Step 1: Savings Compare your cost of tech expenses to Saa. S providers Determine potential savings or cost increases Step 2: Portfolio Find three workloads with which you can experiment Determine usage Scenarios Step 3: Migrate Select applications to align with Saa. S strategy Step 4: Use Test Saa. S applications with core users © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 23 Jump-start your efforts, but do not stop here Immediate impact and feedback
Step Four: Getting Started with Saa. S Today Action Outcome Step 1: Savings Compare your cost of tech expenses to Saa. S providers Determine potential savings or cost increases Step 2: Portfolio Find three workloads with which you can experiment Determine usage Scenarios Step 3: Migrate Select applications to align with Saa. S strategy Step 4: Use Test Saa. S applications with core users © 2006 Gartner, Inc. All Rights Reserved. 23 Jump-start your efforts, but do not stop here Immediate impact and feedback
 New Government Software Models: An Introduction to Saa. S and Application Outsourcing Presented to State of Oregon Oct. 15 th, 2009 Rishi Sood Vice President, Government Gartner rishi. sood@gartner. com
New Government Software Models: An Introduction to Saa. S and Application Outsourcing Presented to State of Oregon Oct. 15 th, 2009 Rishi Sood Vice President, Government Gartner rishi. sood@gartner. com


