63c052636c5c9c168075c6574032900b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
New Data Exchange Standards Briefing Tf. L RTIP User’s forum Windsor House 11 July 2006 nick_knowles@kizoom. com © Kizoom 2006
Topics • Introduction • Key Data Exchange Standards in Progress New – Fixed Objects (IFOPT ) – SIRI PT Situations/Incidents (& Datex 2) • What should Tf. L be doing? © Kizoom 2006

Motivation – Standards as A Tool for Managing Complexity • Value to Passenger Transport Executives and Authorities / Operators – – – • Value to Suppliers – – • Open, modular architectures Higher quality & function, lower technical risk Protection of investment, strategic availability. & supplier independence. Wide availability of interoperable data management tools Efficient tender specification criteria. European economies of scale & markets. Reduced complexity & deployment costs More reuse, Cheaper integration Simplified tendering, quality differentiator. Value to Both – – – Enables new types of services European / World economies of scale Lowers costs - creating new markets Modern, Modular, scaleable architectures Harnesses commodity open internet technologies for transport. © Kizoom 2006
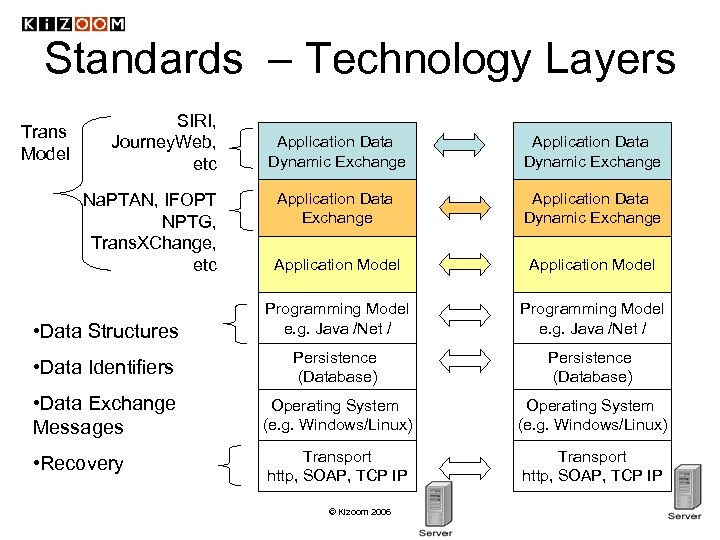
Standards – Technology Layers Trans Model SIRI, Journey. Web, etc Application Data Dynamic Exchange Application Data Dynamic Exchange Application Model • Data Structures Programming Model e. g. Java /Net / • Data Identifiers Persistence (Database) • Data Exchange Messages Operating System (e. g. Windows/Linux) • Recovery Transport http, SOAP, TCP IP Na. PTAN, IFOPT NPTG, Trans. XChange, etc © Kizoom 2006
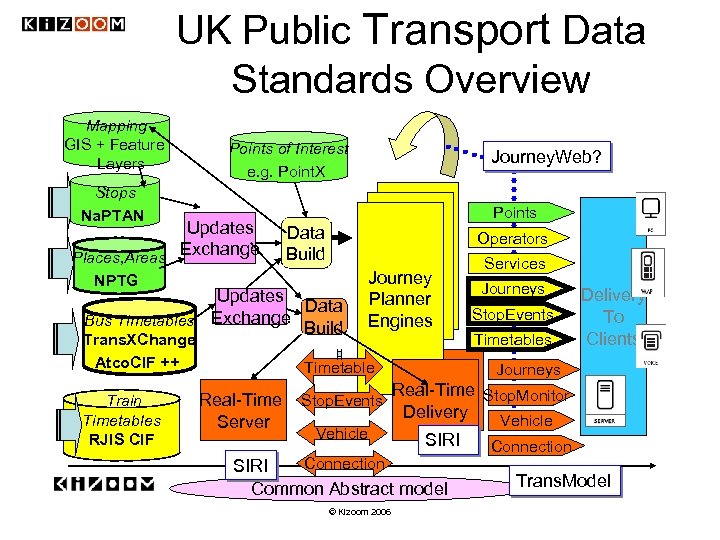
UK Public Transport Data Standards Overview Mapping GIS + Feature Layers Points of Interest e. g. Point. X Stops Na. PTAN Updates Places, Areas Exchange NPTG Points Data Build Operators Updates Data Bus Timetables Exchange Build Trans. XChange Atco. CIF ++ Train Timetables RJIS CIF Journey. Web? Journey Planner Engines Timetable Real-Time Server Stop. Events Vehicle Journeys Stop. Events Timetables Delivery To Clients Journeys Real-Time Stop. Monitor Delivery Vehicle SIRI Connection SIRI Common Abstract model © Kizoom 2006 Services Connection Trans. Model
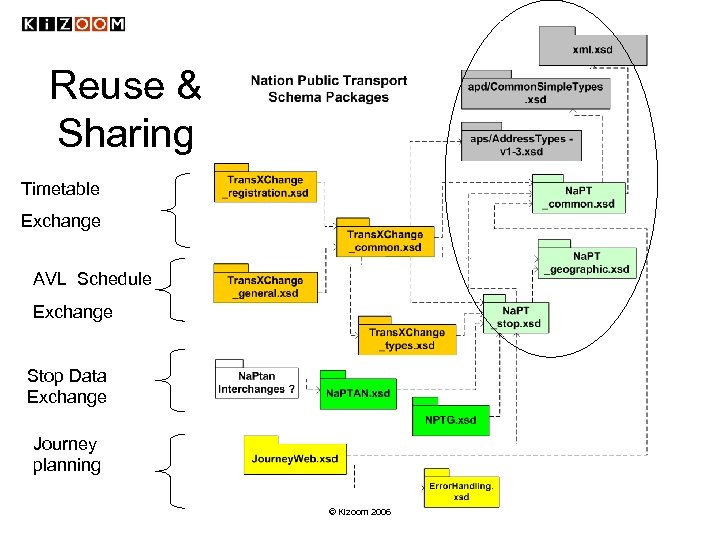
Reuse & Sharing Timetable Exchange AVL Schedule Exchange Stop Data Exchange Journey planning © Kizoom 2006
CEN SIRI Server Interface for Real-time Information Intro © Kizoom 2006
SIRI – Introduction • Real-time Server-to-Server Services for Public Transport • Defines a Service Interface for exchanging real-time information for public transport networks. • Complements an underlying static information model for network and timetable description • Provides information on any change on the timetabled information, from original publication to the actual & predicted transport running times. © Kizoom 2006
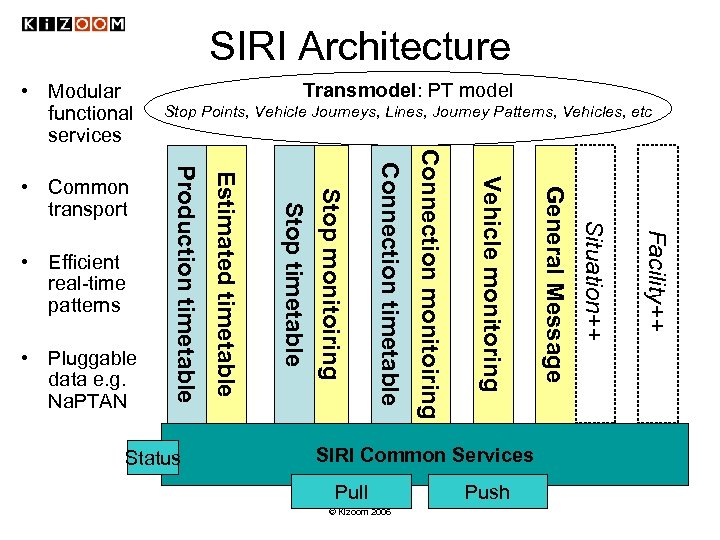
SIRI Architecture • Modular functional services © Kizoom 2006 Push Facility++ Pull Situation++ SIRI Common Services General Message Vehicle monitoring Connection monitoiring Connection timetable Stop monitoiring Status Stop timetable • Pluggable data e. g. Na. PTAN Estimated timetable • Efficient real-time patterns Stop Points, Vehicle Journeys, Lines, Journey Patterns, Vehicles, etc Production timetable • Common transport Transmodel: PT model
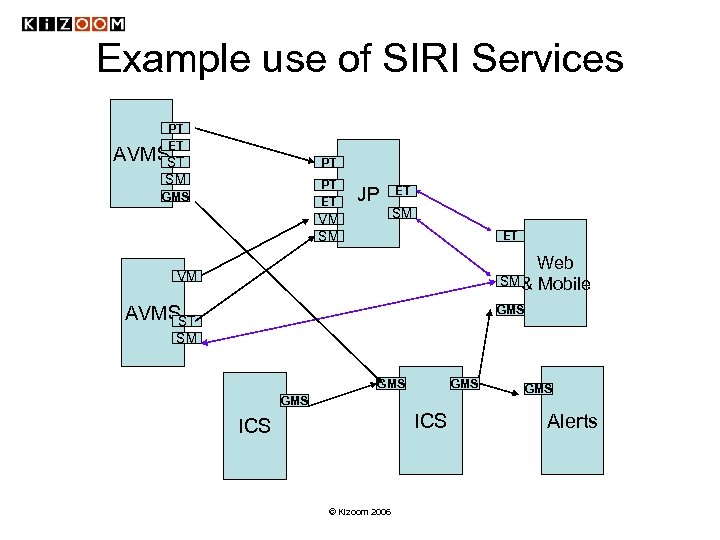
Example use of SIRI Services PT ET AVMSST PT SM PT ET GMS JP ET SM VM SM ET Web SM& Mobile VM AVMSST GMS SM GMS GMS ICS © Kizoom 2006 GMS Alerts
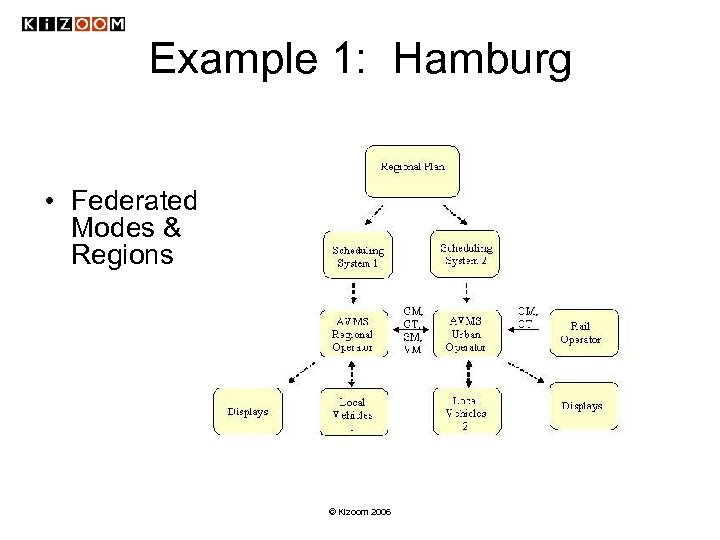
Example 1: Hamburg • Federated Modes & Regions © Kizoom 2006
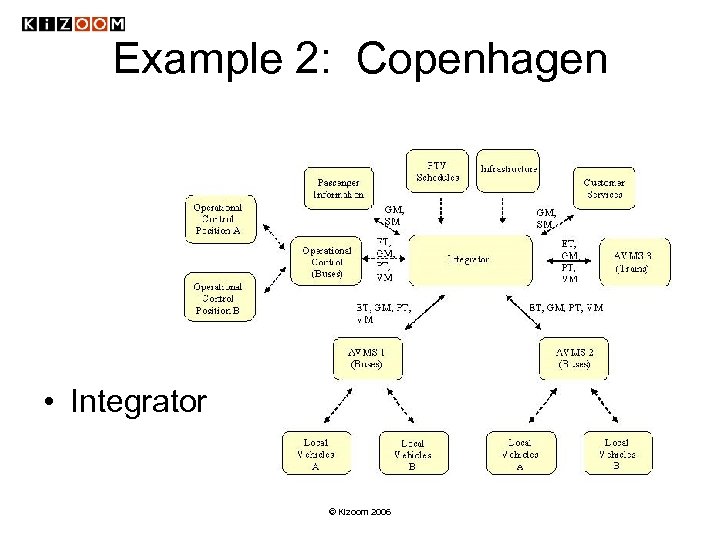
Example 2: Copenhagen • Integrator © Kizoom 2006
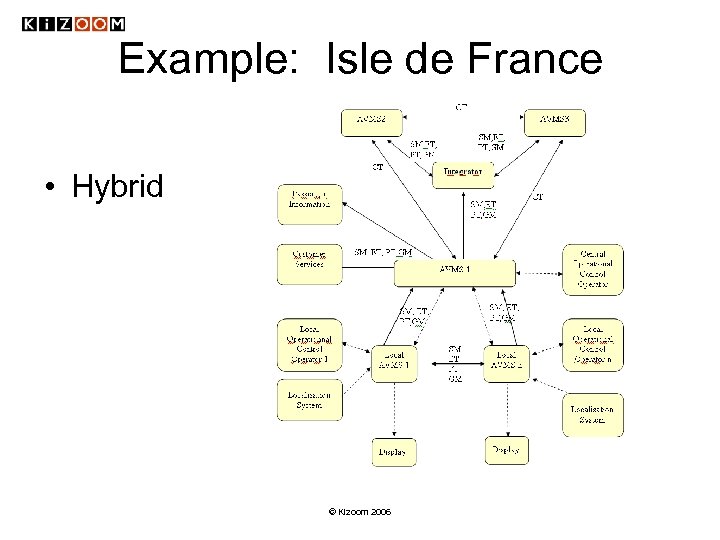
Example: Isle de France • Hybrid © Kizoom 2006
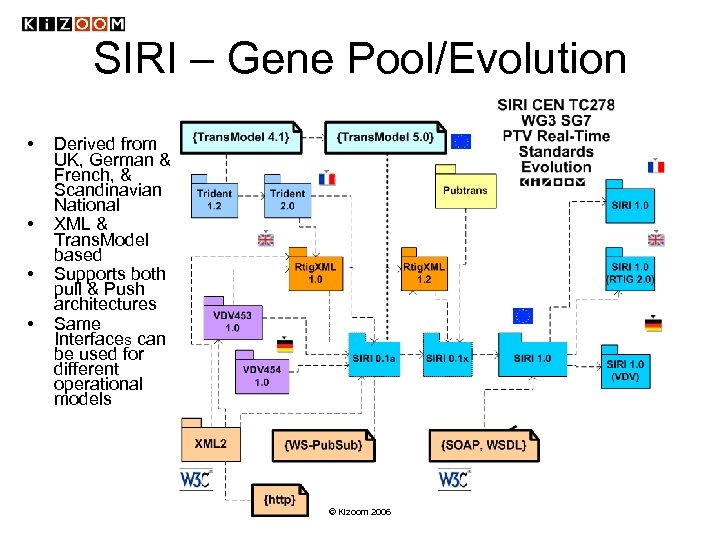
SIRI – Gene Pool/Evolution • • Derived from UK, German & French, & Scandinavian National XML & Trans. Model based Supports both pull & Push architectures Same Interfaces can be used for different operational models © Kizoom 2006

Proposed New work Item SIRI Situation Model New • Add a Full Incident Service to – Includes addition information for internal management & user of incidents – Full XML integrated with SIRI models. • Requirements – – Support advanced ITS operations – eg RTJP, alerts, angels Multi-modal, Road Interoperable with TPEG – Export Interoperable with Datex • To do – Review Incident categories and properties – Review operational requirements – Review Datex 2 & Road requirements © Kizoom 2006
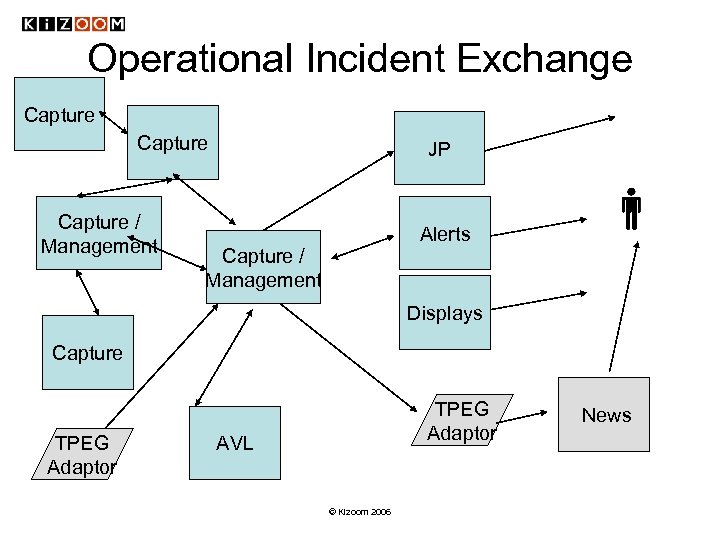
Operational Incident Exchange Capture / Management JP Alerts Capture / Management Displays Capture TPEG Adaptor AVL © Kizoom 2006 News

CEN Identification of Fixed Objects In Public Transport (IFOPT) © Kizoom 2006
What Is It? • Proposed European Technical Standard for data model & data exchange of – All PT Stops, (“Euro Na. PTAN”) Stations & Interchanges New • • Stop & Interchange structure & Navigation Stop Identification, Labelling Relationship to Topography, Access links Data Administration – Places that people travel to • Cities, Towns, suburbs, areas – Points of Interest • Relationship to Topography, Access links • Data Administration – Designed to allow incremental adoption • Works with partial data, doesn’t repeat GIS data • Efficient for journey planners • What Is it Useful for? – Journey Planning, Guidance, Navigators – Stop Finding, Interchange paths, Walk legs to POI – AVL / Real-time Info • Stop Finding, Direction Headings, Platform assignment – Scheduling, operations, AVL, statistics, etc © Kizoom 2006
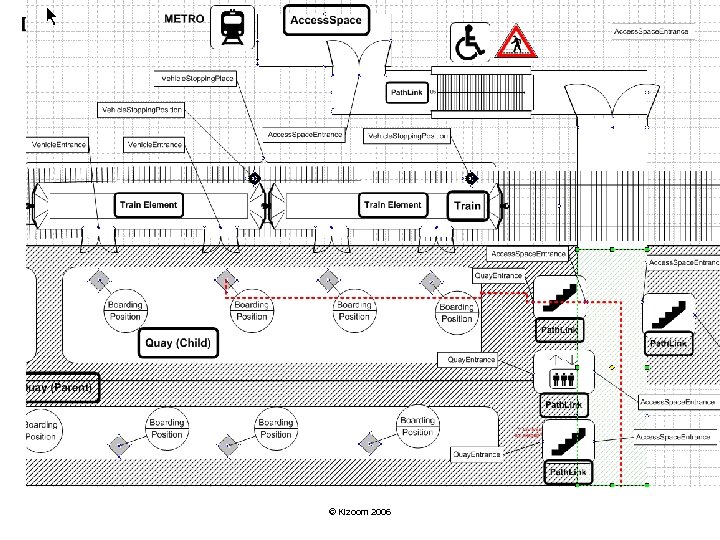
Physical Model © Kizoom 2006
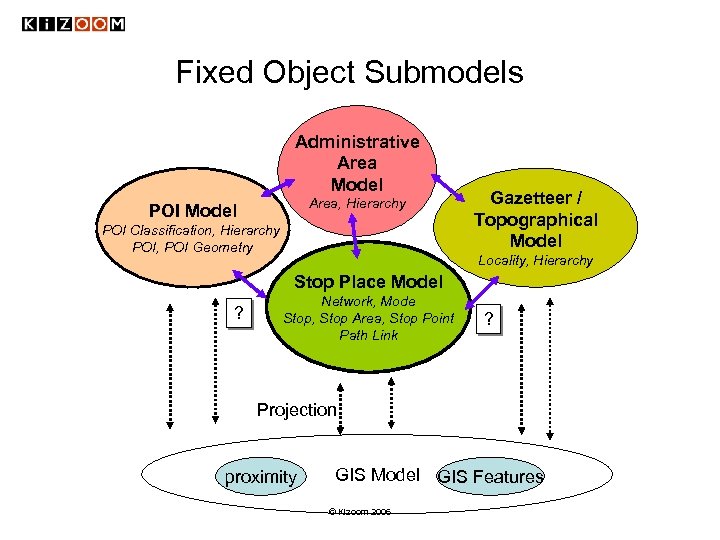
Fixed Object Submodels Administrative Area Model Area, Hierarchy POI Model POI Classification, Hierarchy POI, POI Geometry Gazetteer / Topographical Model Locality, Hierarchy Stop Place Model ? Network, Mode Stop, Stop Area, Stop Point Path Link ? Projection proximity GIS Model GIS Features © Kizoom 2006
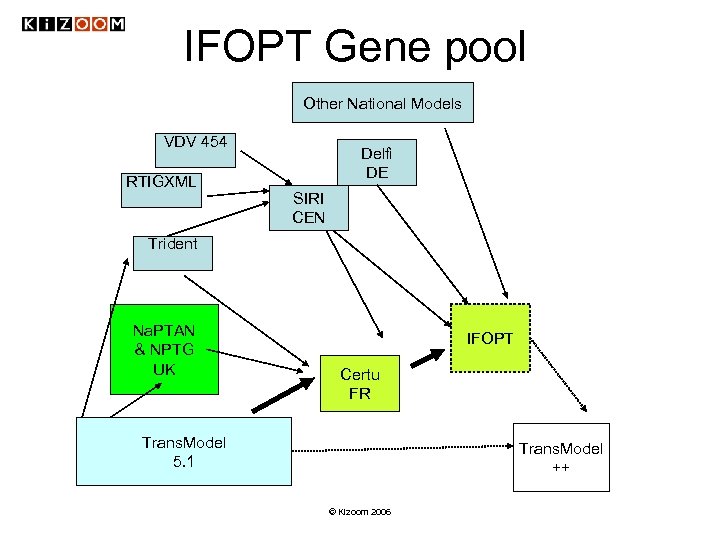
IFOPT Gene pool Other National Models VDV 454 RTIGXML Delfi DE SIRI CEN Trident Na. PTAN & NPTG UK IFOPT Certu FR Trans. Model 5. 1 Trans. Model ++ © Kizoom 2006
UK Perspective /Benefits • Na. PTAN is currently only simple PT nodes – Bus Stops, Platforms, entrances • Adds Interchange Model – Navigation: Improved Journey Planning – Uniform impaired access data (DDA) – Advanced Navigation & Real-time applications (Detailed digitalisation) • Adds POI model – Access link model • Enables data capture & incremental use © Kizoom 2006

What Should Tf. L be doing? © Kizoom 2006
In General • Use standards to achieve interoperability between modes – 1 to n rather than n-n – Needed for joined-up Journey planning – Needed for joined-up real-time – Use standards to achieve interoperability between external systems • Use standards to simplify ( & lower costs ) – Data maintenance – System procurement © Kizoom 2006

Specifically for new work items • Influence standard development to meet Tf. L’s needs – Detailed Transport Interchange (IFOPT) – Enhanced journey planning (IFOPT) – Alerts and Angels (SIRI SS) • Mandate relevant Standards in new projects © Kizoom 2006
63c052636c5c9c168075c6574032900b.ppt