66851662318f68d87ed40c2bb2d74c31.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 New Approaches In Medication Management and Care Transition e-Prescribing and Remote Dispensing in Long Term Care AHRQ Annual Conference September 27, 2007 Presenter – Michael Bordelon
New Approaches In Medication Management and Care Transition e-Prescribing and Remote Dispensing in Long Term Care AHRQ Annual Conference September 27, 2007 Presenter – Michael Bordelon
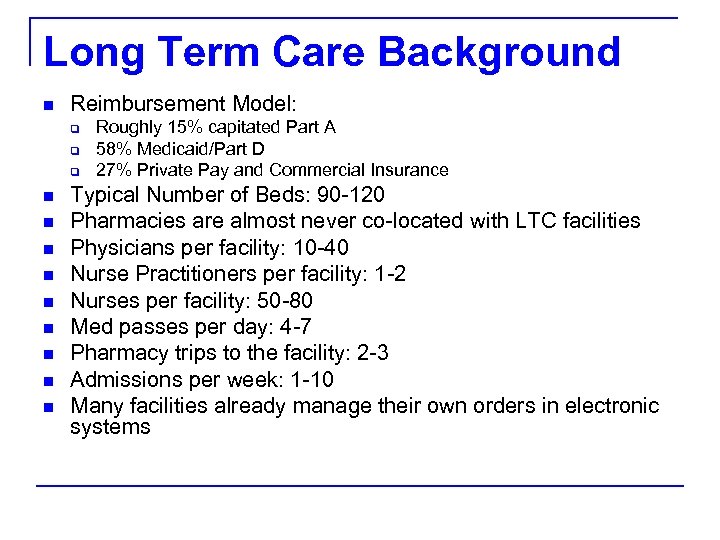 Long Term Care Background n Reimbursement Model: q q q n n n n n Roughly 15% capitated Part A 58% Medicaid/Part D 27% Private Pay and Commercial Insurance Typical Number of Beds: 90 -120 Pharmacies are almost never co-located with LTC facilities Physicians per facility: 10 -40 Nurse Practitioners per facility: 1 -2 Nurses per facility: 50 -80 Med passes per day: 4 -7 Pharmacy trips to the facility: 2 -3 Admissions per week: 1 -10 Many facilities already manage their own orders in electronic systems
Long Term Care Background n Reimbursement Model: q q q n n n n n Roughly 15% capitated Part A 58% Medicaid/Part D 27% Private Pay and Commercial Insurance Typical Number of Beds: 90 -120 Pharmacies are almost never co-located with LTC facilities Physicians per facility: 10 -40 Nurse Practitioners per facility: 1 -2 Nurses per facility: 50 -80 Med passes per day: 4 -7 Pharmacy trips to the facility: 2 -3 Admissions per week: 1 -10 Many facilities already manage their own orders in electronic systems
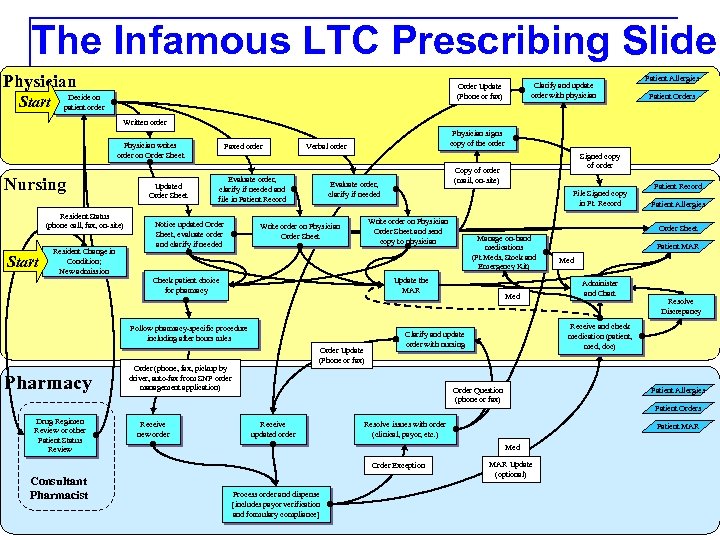 The Infamous LTC Prescribing Slide Physician Start Clarify and update order with physician Order Update (Phone or fax) Decide on patient order Patient Allergies Patient Orders Written order Physician writes order on Order Sheet Nursing Resident Status (phone call, fax, on-site) Start Resident Change in Condition; New admission Updated Order Sheet Faxed order Evaluate order, clarify if needed and file in Patient Record Notice updated Order Sheet, evaluate order and clarify if needed Physician signs copy of the order Verbal order Order Update (Phone or fax) Order (phone, fax, pickup by driver, auto-fax from SNF order management application) Receive new order Patient MAR Med Administer and Chart Resolve Discrepancy Patient Allergies Patient Orders Resolve issues with order (clinical, payor, etc. ) Patient MAR Med Process order and dispense [includes payor verification and formulary compliance] Patient Allergies Receive and check medication (patient, med, doc) Clarify and update order with nursing Order Exception Consultant Pharmacist Med Order Question (phone or fax) Receive updated order Patient Record Order Sheet Manage on-hand medications (Pt Meds, Stock and Emergency Kit) Update the MAR Follow pharmacy-specific procedure including after hours rules Drug Regimen Review or other Patient Status Review File Signed copy in Pt. Record Write order on Physician Order Sheet and send copy to physician Check patient choice for pharmacy Pharmacy Copy of order (mail, on-site) Evaluate order, clarify if needed Write order on Physician Order Sheet Signed copy of order MAR Update (optional)
The Infamous LTC Prescribing Slide Physician Start Clarify and update order with physician Order Update (Phone or fax) Decide on patient order Patient Allergies Patient Orders Written order Physician writes order on Order Sheet Nursing Resident Status (phone call, fax, on-site) Start Resident Change in Condition; New admission Updated Order Sheet Faxed order Evaluate order, clarify if needed and file in Patient Record Notice updated Order Sheet, evaluate order and clarify if needed Physician signs copy of the order Verbal order Order Update (Phone or fax) Order (phone, fax, pickup by driver, auto-fax from SNF order management application) Receive new order Patient MAR Med Administer and Chart Resolve Discrepancy Patient Allergies Patient Orders Resolve issues with order (clinical, payor, etc. ) Patient MAR Med Process order and dispense [includes payor verification and formulary compliance] Patient Allergies Receive and check medication (patient, med, doc) Clarify and update order with nursing Order Exception Consultant Pharmacist Med Order Question (phone or fax) Receive updated order Patient Record Order Sheet Manage on-hand medications (Pt Meds, Stock and Emergency Kit) Update the MAR Follow pharmacy-specific procedure including after hours rules Drug Regimen Review or other Patient Status Review File Signed copy in Pt. Record Write order on Physician Order Sheet and send copy to physician Check patient choice for pharmacy Pharmacy Copy of order (mail, on-site) Evaluate order, clarify if needed Write order on Physician Order Sheet Signed copy of order MAR Update (optional)
 LTC Prescribing Nuances n Three way communication between q Prescriber – Nurse – Pharmacy Most orders have no end date or quantity n Refill requests represent 80% of orders n No concept of Renewals n Need unique formulary and benefit information n q Part A, Part D and Medicaid
LTC Prescribing Nuances n Three way communication between q Prescriber – Nurse – Pharmacy Most orders have no end date or quantity n Refill requests represent 80% of orders n No concept of Renewals n Need unique formulary and benefit information n q Part A, Part D and Medicaid
 e-Prescribing in Long Term Care n e-Prescribing is new to LTC n 2006 CMS Pilot Study was first official standards based e-prescribing study in Long Term Care n There are less than 5 standards based e. Prescribing installations today
e-Prescribing in Long Term Care n e-Prescribing is new to LTC n 2006 CMS Pilot Study was first official standards based e-prescribing study in Long Term Care n There are less than 5 standards based e. Prescribing installations today
 LTC e-Rx Pilot Study Abstract n 2006 study focused on e-Rx standards most relevant to LTC q SCRIPT q Formulary Benefits q Electronic Prior Authorization n Other Capabilities Studied q Facility Managed Electronic Orders q Patient Safety Checks (DUR) q Electronic Signature q Automated Refill Requests n The study included two geographically diverse treatments facilities and two comparison facilities
LTC e-Rx Pilot Study Abstract n 2006 study focused on e-Rx standards most relevant to LTC q SCRIPT q Formulary Benefits q Electronic Prior Authorization n Other Capabilities Studied q Facility Managed Electronic Orders q Patient Safety Checks (DUR) q Electronic Signature q Automated Refill Requests n The study included two geographically diverse treatments facilities and two comparison facilities
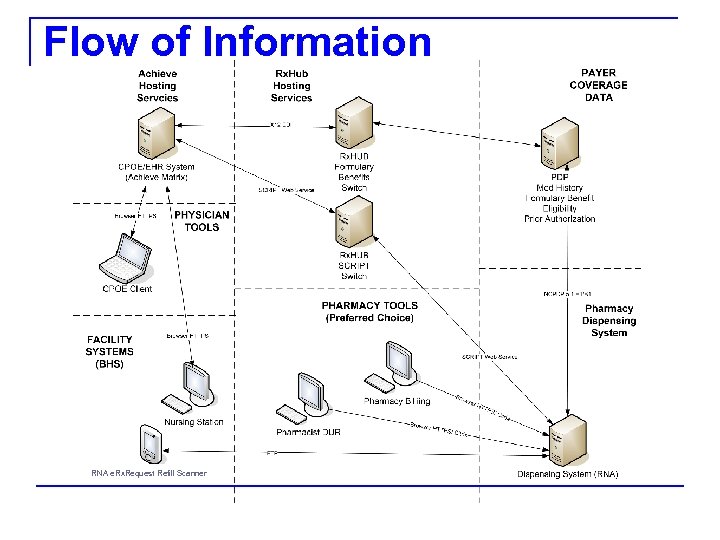 Flow of Information RNA e. Rx. Request Refill Scanner
Flow of Information RNA e. Rx. Request Refill Scanner
 e-Rx Findings - Facility Impacts n n Benefits q Facilities currently using electronic Physicians Orders will see modest change or disruption to current workflow q Ability to transmit orders directly to the pharmacy yielded benefits in reduced rework and callbacks q Management of Orders at the facility streamlines reconciliation processes New Challenges q Prescriber adoption is vital q Integration with clinical systems (EHR) is critical q Nurses do not effectively use patient safety (DUR) tools q Even with Formulary Benefits data, managing complex Part D health plans is an ongoing challenge q Nursing staff now has to enter and manage data that the pharmacy once managed q Data entry errors can still happen
e-Rx Findings - Facility Impacts n n Benefits q Facilities currently using electronic Physicians Orders will see modest change or disruption to current workflow q Ability to transmit orders directly to the pharmacy yielded benefits in reduced rework and callbacks q Management of Orders at the facility streamlines reconciliation processes New Challenges q Prescriber adoption is vital q Integration with clinical systems (EHR) is critical q Nurses do not effectively use patient safety (DUR) tools q Even with Formulary Benefits data, managing complex Part D health plans is an ongoing challenge q Nursing staff now has to enter and manage data that the pharmacy once managed q Data entry errors can still happen
 e-Rx Findings - Pharmacy Impacts n Benefits q q q n Demographics pre-populated on new admissions Straightforward new order processing Discontinued orders Readmissions streamlined Do not have to manage MARs and Order Sheets Refill requests streamlined New challenges q q Combination & Tapered Orders – Need codified SIG standard Transcription accuracy Timely transmission on admission orders Fax mode for controlled substances leads to process inconsistencies
e-Rx Findings - Pharmacy Impacts n Benefits q q q n Demographics pre-populated on new admissions Straightforward new order processing Discontinued orders Readmissions streamlined Do not have to manage MARs and Order Sheets Refill requests streamlined New challenges q q Combination & Tapered Orders – Need codified SIG standard Transcription accuracy Timely transmission on admission orders Fax mode for controlled substances leads to process inconsistencies
 Standards Findings q q q NCPDP SCRIPT Standard works with new changes in Version 10. 1 NCPDP Formulary Benefits V 1. 0 technically works, but is dependent on greater prescriber adoption Electronic Prior Authorization Technically works, but will require greater prescriber adoption A Refill messaging standard is needed in LTC An Admission, Discharge, Transfer (ADT) messaging standard is needed
Standards Findings q q q NCPDP SCRIPT Standard works with new changes in Version 10. 1 NCPDP Formulary Benefits V 1. 0 technically works, but is dependent on greater prescriber adoption Electronic Prior Authorization Technically works, but will require greater prescriber adoption A Refill messaging standard is needed in LTC An Admission, Discharge, Transfer (ADT) messaging standard is needed
 What is Remote Dispensing? Automated oral solid dispensing in healthcare settings, such as nursing homes and correctional facilities, that have no onsite pharmacist Remote dispensing can work hand in hand with e-Prescribing
What is Remote Dispensing? Automated oral solid dispensing in healthcare settings, such as nursing homes and correctional facilities, that have no onsite pharmacist Remote dispensing can work hand in hand with e-Prescribing
 Oral Solid Packaging Medication Canister Remote Dispensing Packager
Oral Solid Packaging Medication Canister Remote Dispensing Packager
 Process Overview
Process Overview
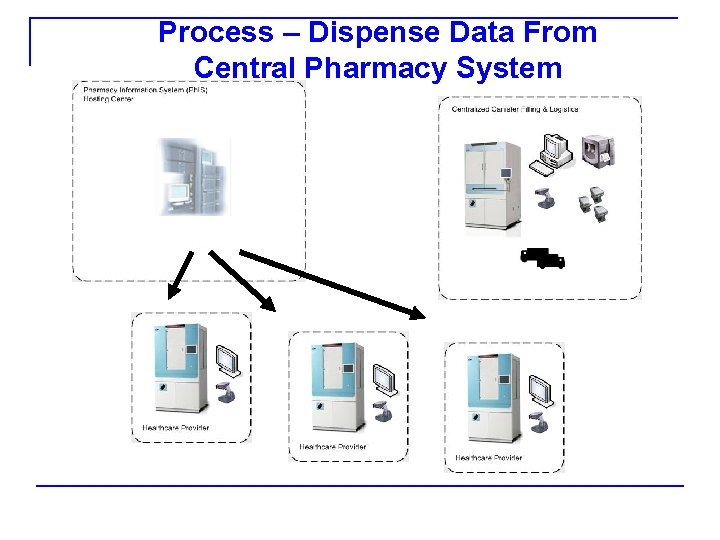 Process – Dispense Data From Central Pharmacy System
Process – Dispense Data From Central Pharmacy System
 On Site Strip Packaging
On Site Strip Packaging
 On Site Strip Packaging • Daily Dispense • Med Pass/Resident Sort • Multi Dose Packing • PRN, New, Re-dispense
On Site Strip Packaging • Daily Dispense • Med Pass/Resident Sort • Multi Dose Packing • PRN, New, Re-dispense
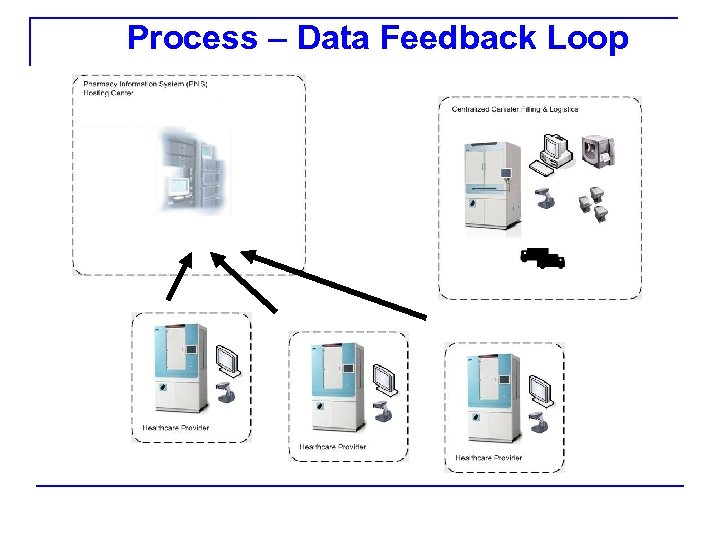 Process – Data Feedback Loop
Process – Data Feedback Loop
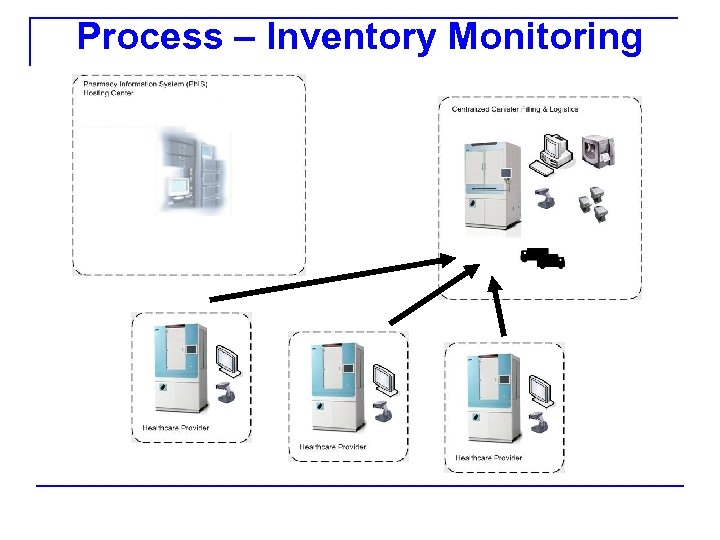 Process – Inventory Monitoring
Process – Inventory Monitoring
 Process – Canister Fill at Pharmacy
Process – Canister Fill at Pharmacy
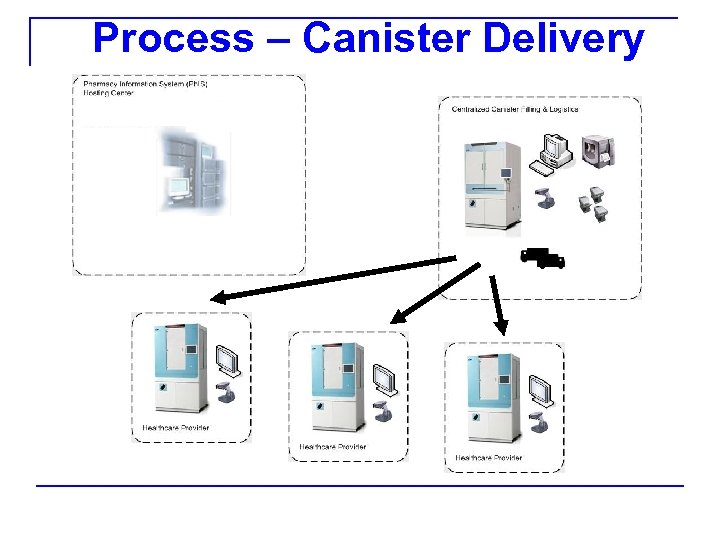 Process – Canister Delivery
Process – Canister Delivery
 Value Proposition n Virtually eliminates drug waste n Significantly reduces delivery costs n Eliminates delay of first dose n Decreases administration time n Reduces medication errors n Eliminates the need for a refill process
Value Proposition n Virtually eliminates drug waste n Significantly reduces delivery costs n Eliminates delay of first dose n Decreases administration time n Reduces medication errors n Eliminates the need for a refill process
 Experience in early commercial pilots n n n High Adoption Rate with nursing staff On demand PRNs and quick access to meds for new admissions are big wins Will save a typical nursing facility more than $25 K per year in Part A drug waste May save $150 K per year per facility for Part D drug waste savings Robust canister logistics is the key to success
Experience in early commercial pilots n n n High Adoption Rate with nursing staff On demand PRNs and quick access to meds for new admissions are big wins Will save a typical nursing facility more than $25 K per year in Part A drug waste May save $150 K per year per facility for Part D drug waste savings Robust canister logistics is the key to success
 Medication Reconciliation in Long Term Care AHRQ Annual Conference September 27, 2007 Presenter – Michael Bordelon
Medication Reconciliation in Long Term Care AHRQ Annual Conference September 27, 2007 Presenter – Michael Bordelon
 Long Term Care Background n Reimbursement Model: q q q n n n n n Roughly 15% capitated Part A 58% Medicaid/Part D 27% Private Pay and Commercial Insurance Typical Number of Beds: 90 -120 Pharmacies are almost never co-located with LTC facilities Physicians per facility: 10 -40 Nurse Practitioners per facility: 1 -2 Nurses per facility: 50 -80 Med passes per day: 4 -7 Pharmacy trips to the facility: 2 -3 Admissions per week: 1 -10 Many facilities already manage their own orders in electronic systems
Long Term Care Background n Reimbursement Model: q q q n n n n n Roughly 15% capitated Part A 58% Medicaid/Part D 27% Private Pay and Commercial Insurance Typical Number of Beds: 90 -120 Pharmacies are almost never co-located with LTC facilities Physicians per facility: 10 -40 Nurse Practitioners per facility: 1 -2 Nurses per facility: 50 -80 Med passes per day: 4 -7 Pharmacy trips to the facility: 2 -3 Admissions per week: 1 -10 Many facilities already manage their own orders in electronic systems
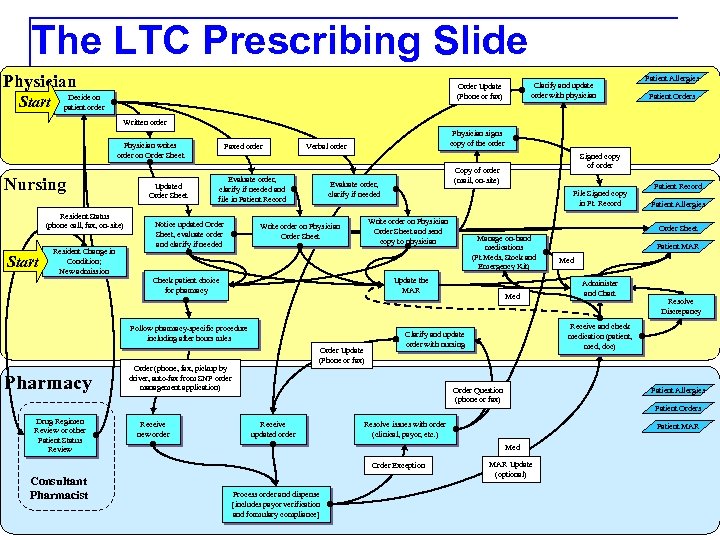 The LTC Prescribing Slide Physician Start Clarify and update order with physician Order Update (Phone or fax) Decide on patient order Patient Allergies Patient Orders Written order Physician writes order on Order Sheet Nursing Resident Status (phone call, fax, on-site) Start Resident Change in Condition; New admission Updated Order Sheet Faxed order Evaluate order, clarify if needed and file in Patient Record Notice updated Order Sheet, evaluate order and clarify if needed Physician signs copy of the order Verbal order Order Update (Phone or fax) Order (phone, fax, pickup by driver, auto-fax from SNF order management application) Receive new order Patient MAR Med Administer and Chart Resolve Discrepancy Patient Allergies Patient Orders Resolve issues with order (clinical, payor, etc. ) Patient MAR Med Process order and dispense [includes payor verification and formulary compliance] Patient Allergies Receive and check medication (patient, med, doc) Clarify and update order with nursing Order Exception Consultant Pharmacist Med Order Question (phone or fax) Receive updated order Patient Record Order Sheet Manage on-hand medications (Pt Meds, Stock and Emergency Kit) Update the MAR Follow pharmacy-specific procedure including after hours rules Drug Regimen Review or other Patient Status Review File Signed copy in Pt. Record Write order on Physician Order Sheet and send copy to physician Check patient choice for pharmacy Pharmacy Copy of order (mail, on-site) Evaluate order, clarify if needed Write order on Physician Order Sheet Signed copy of order MAR Update (optional)
The LTC Prescribing Slide Physician Start Clarify and update order with physician Order Update (Phone or fax) Decide on patient order Patient Allergies Patient Orders Written order Physician writes order on Order Sheet Nursing Resident Status (phone call, fax, on-site) Start Resident Change in Condition; New admission Updated Order Sheet Faxed order Evaluate order, clarify if needed and file in Patient Record Notice updated Order Sheet, evaluate order and clarify if needed Physician signs copy of the order Verbal order Order Update (Phone or fax) Order (phone, fax, pickup by driver, auto-fax from SNF order management application) Receive new order Patient MAR Med Administer and Chart Resolve Discrepancy Patient Allergies Patient Orders Resolve issues with order (clinical, payor, etc. ) Patient MAR Med Process order and dispense [includes payor verification and formulary compliance] Patient Allergies Receive and check medication (patient, med, doc) Clarify and update order with nursing Order Exception Consultant Pharmacist Med Order Question (phone or fax) Receive updated order Patient Record Order Sheet Manage on-hand medications (Pt Meds, Stock and Emergency Kit) Update the MAR Follow pharmacy-specific procedure including after hours rules Drug Regimen Review or other Patient Status Review File Signed copy in Pt. Record Write order on Physician Order Sheet and send copy to physician Check patient choice for pharmacy Pharmacy Copy of order (mail, on-site) Evaluate order, clarify if needed Write order on Physician Order Sheet Signed copy of order MAR Update (optional)
 Typical Admission in LTC n Most admissions in LTC are from a hospital setting n Most “residents” begin stay under Medicare Part A n Generally, discharge orders from the hospital are admission orders at the facility
Typical Admission in LTC n Most admissions in LTC are from a hospital setting n Most “residents” begin stay under Medicare Part A n Generally, discharge orders from the hospital are admission orders at the facility
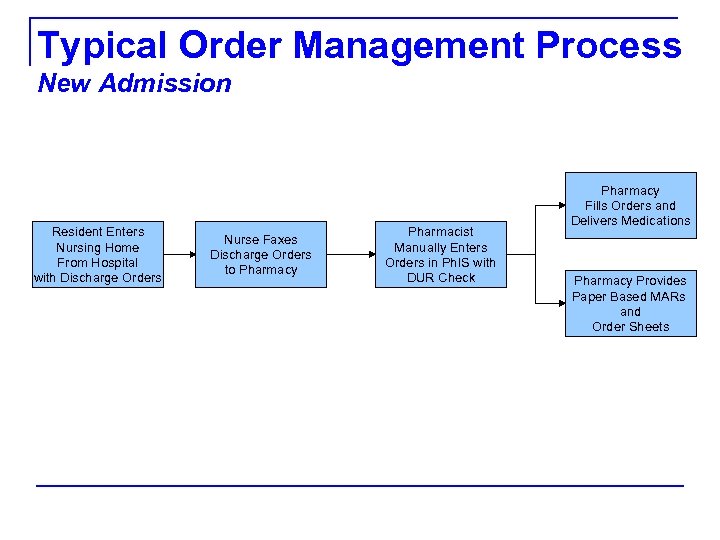 Typical Order Management Process New Admission Resident Enters Nursing Home From Hospital with Discharge Orders Nurse Faxes Discharge Orders to Pharmacy Pharmacist Manually Enters Orders in Ph. IS with DUR Check Pharmacy Fills Orders and Delivers Medications Pharmacy Provides Paper Based MARs and Order Sheets
Typical Order Management Process New Admission Resident Enters Nursing Home From Hospital with Discharge Orders Nurse Faxes Discharge Orders to Pharmacy Pharmacist Manually Enters Orders in Ph. IS with DUR Check Pharmacy Fills Orders and Delivers Medications Pharmacy Provides Paper Based MARs and Order Sheets
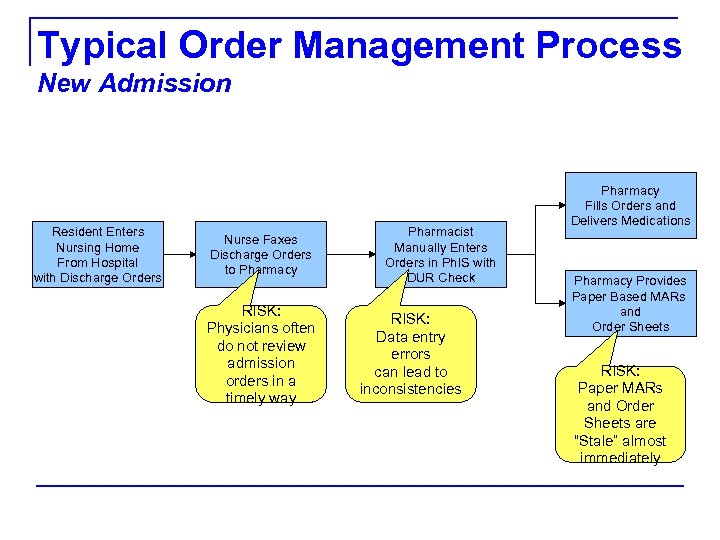 Typical Order Management Process New Admission Resident Enters Nursing Home From Hospital with Discharge Orders Nurse Faxes Discharge Orders to Pharmacy RISK: Physicians often do not review admission orders in a timely way Pharmacist Manually Enters Orders in Ph. IS with DUR Check RISK: Data entry errors can lead to inconsistencies Pharmacy Fills Orders and Delivers Medications Pharmacy Provides Paper Based MARs and Order Sheets RISK: Paper MARs and Order Sheets are “Stale” almost immediately
Typical Order Management Process New Admission Resident Enters Nursing Home From Hospital with Discharge Orders Nurse Faxes Discharge Orders to Pharmacy RISK: Physicians often do not review admission orders in a timely way Pharmacist Manually Enters Orders in Ph. IS with DUR Check RISK: Data entry errors can lead to inconsistencies Pharmacy Fills Orders and Delivers Medications Pharmacy Provides Paper Based MARs and Order Sheets RISK: Paper MARs and Order Sheets are “Stale” almost immediately
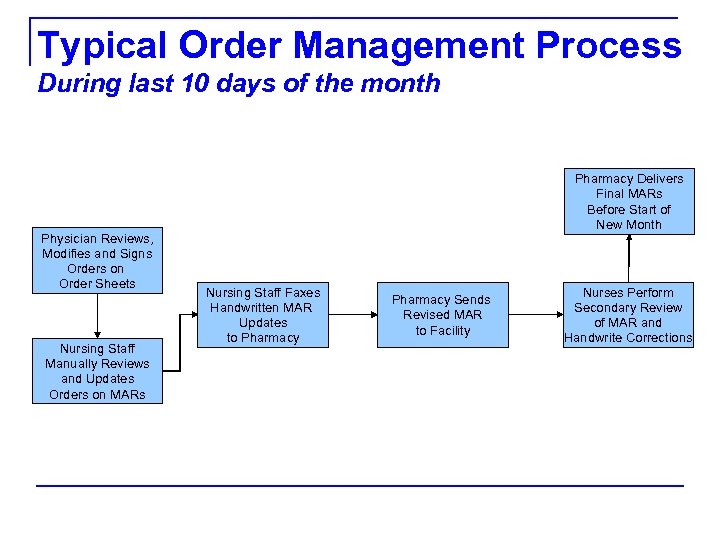 Typical Order Management Process During last 10 days of the month Physician Reviews, Modifies and Signs Orders on Order Sheets Nursing Staff Manually Reviews and Updates Orders on MARs Pharmacy Delivers Final MARs Before Start of New Month Nursing Staff Faxes Handwritten MAR Updates to Pharmacy Sends Revised MAR to Facility Nurses Perform Secondary Review of MAR and Handwrite Corrections
Typical Order Management Process During last 10 days of the month Physician Reviews, Modifies and Signs Orders on Order Sheets Nursing Staff Manually Reviews and Updates Orders on MARs Pharmacy Delivers Final MARs Before Start of New Month Nursing Staff Faxes Handwritten MAR Updates to Pharmacy Sends Revised MAR to Facility Nurses Perform Secondary Review of MAR and Handwrite Corrections
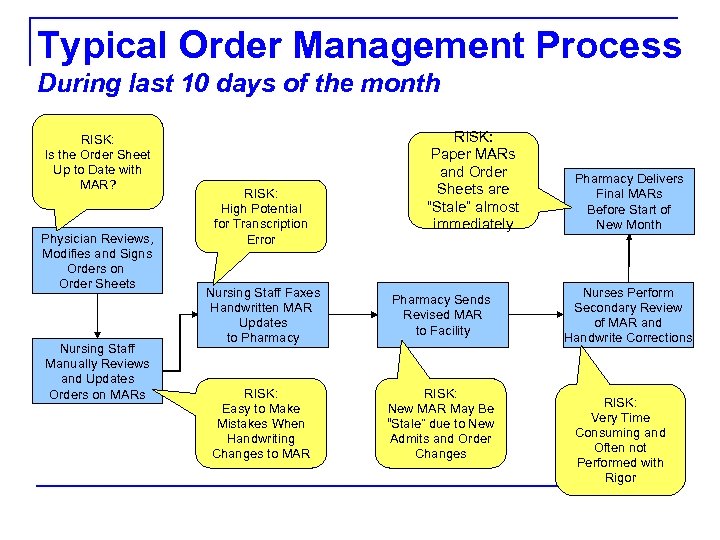 Typical Order Management Process During last 10 days of the month RISK: Is the Order Sheet Up to Date with MAR? Physician Reviews, Modifies and Signs Orders on Order Sheets Nursing Staff Manually Reviews and Updates Orders on MARs RISK: High Potential for Transcription Error RISK: Paper MARs and Order Sheets are “Stale” almost immediately Nursing Staff Faxes Handwritten MAR Updates to Pharmacy Sends Revised MAR to Facility RISK: Easy to Make Mistakes When Handwriting Changes to MAR RISK: New MAR May Be “Stale” due to New Admits and Order Changes Pharmacy Delivers Final MARs Before Start of New Month Nurses Perform Secondary Review of MAR and Handwrite Corrections RISK: Very Time Consuming and Often not Performed with Rigor
Typical Order Management Process During last 10 days of the month RISK: Is the Order Sheet Up to Date with MAR? Physician Reviews, Modifies and Signs Orders on Order Sheets Nursing Staff Manually Reviews and Updates Orders on MARs RISK: High Potential for Transcription Error RISK: Paper MARs and Order Sheets are “Stale” almost immediately Nursing Staff Faxes Handwritten MAR Updates to Pharmacy Sends Revised MAR to Facility RISK: Easy to Make Mistakes When Handwriting Changes to MAR RISK: New MAR May Be “Stale” due to New Admits and Order Changes Pharmacy Delivers Final MARs Before Start of New Month Nurses Perform Secondary Review of MAR and Handwrite Corrections RISK: Very Time Consuming and Often not Performed with Rigor
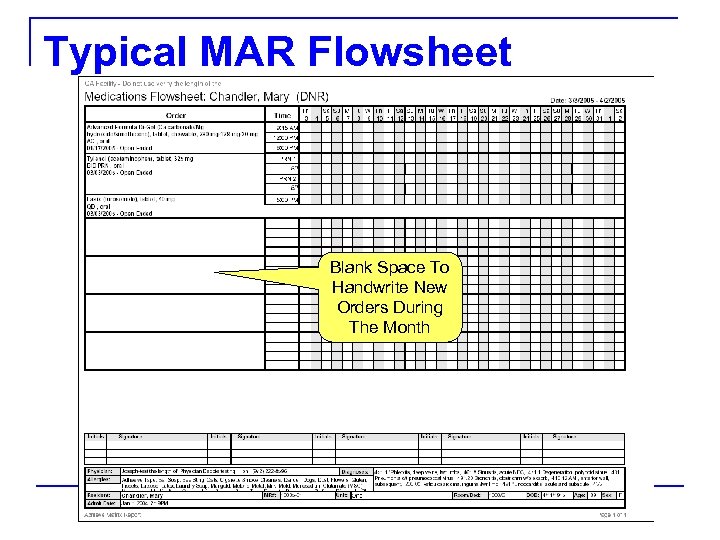 Typical MAR Flowsheet Blank Space To Handwrite New Orders During The Month
Typical MAR Flowsheet Blank Space To Handwrite New Orders During The Month
 Medication Reconciliation with e-Prescribing n n n Facility “owns” all orders Orders are managed in facility CPOE system MARs are printed from the CPOE system New orders are transmitted electronically to pharmacy Discontinued and changed orders are Transmitted electronically to pharmacy Note: CPOE = Computerized Physician Order Entry
Medication Reconciliation with e-Prescribing n n n Facility “owns” all orders Orders are managed in facility CPOE system MARs are printed from the CPOE system New orders are transmitted electronically to pharmacy Discontinued and changed orders are Transmitted electronically to pharmacy Note: CPOE = Computerized Physician Order Entry
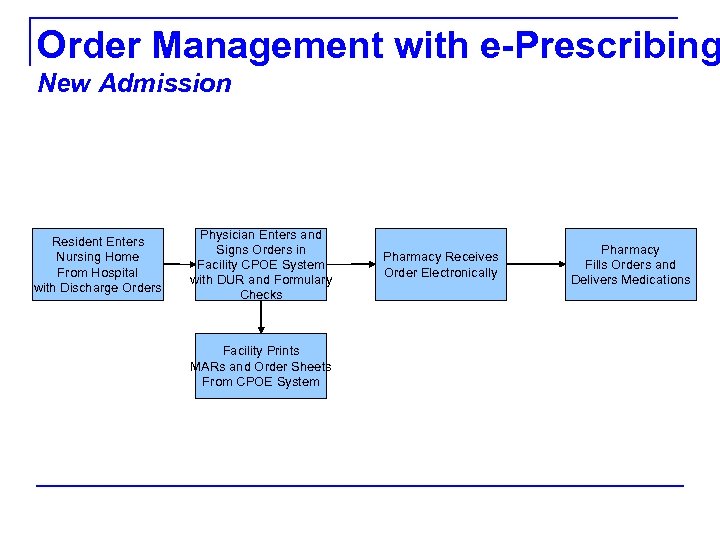 Order Management with e-Prescribing New Admission Resident Enters Nursing Home From Hospital with Discharge Orders Physician Enters and Signs Orders in Facility CPOE System with DUR and Formulary Checks Facility Prints MARs and Order Sheets From CPOE System Pharmacy Receives Order Electronically Pharmacy Fills Orders and Delivers Medications
Order Management with e-Prescribing New Admission Resident Enters Nursing Home From Hospital with Discharge Orders Physician Enters and Signs Orders in Facility CPOE System with DUR and Formulary Checks Facility Prints MARs and Order Sheets From CPOE System Pharmacy Receives Order Electronically Pharmacy Fills Orders and Delivers Medications
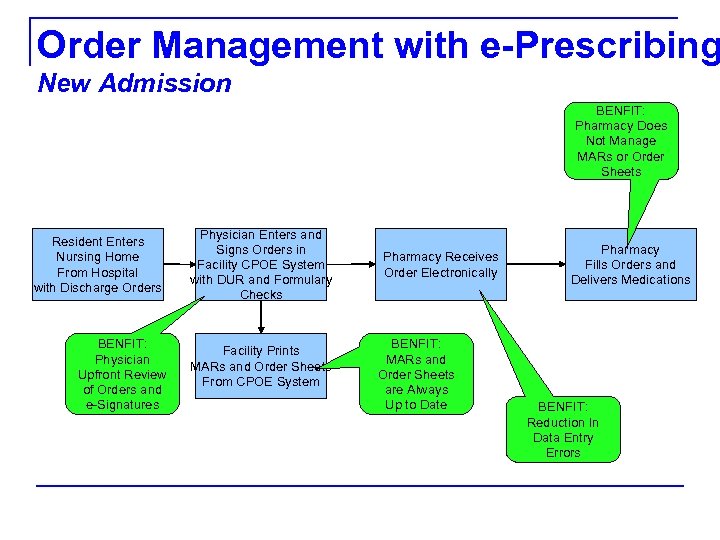 Order Management with e-Prescribing New Admission BENFIT: Pharmacy Does Not Manage MARs or Order Sheets Resident Enters Nursing Home From Hospital with Discharge Orders BENFIT: Physician Upfront Review of Orders and e-Signatures Physician Enters and Signs Orders in Facility CPOE System with DUR and Formulary Checks Facility Prints MARs and Order Sheets From CPOE System Pharmacy Receives Order Electronically BENFIT: MARs and Order Sheets are Always Up to Date Pharmacy Fills Orders and Delivers Medications BENFIT: Reduction In Data Entry Errors
Order Management with e-Prescribing New Admission BENFIT: Pharmacy Does Not Manage MARs or Order Sheets Resident Enters Nursing Home From Hospital with Discharge Orders BENFIT: Physician Upfront Review of Orders and e-Signatures Physician Enters and Signs Orders in Facility CPOE System with DUR and Formulary Checks Facility Prints MARs and Order Sheets From CPOE System Pharmacy Receives Order Electronically BENFIT: MARs and Order Sheets are Always Up to Date Pharmacy Fills Orders and Delivers Medications BENFIT: Reduction In Data Entry Errors
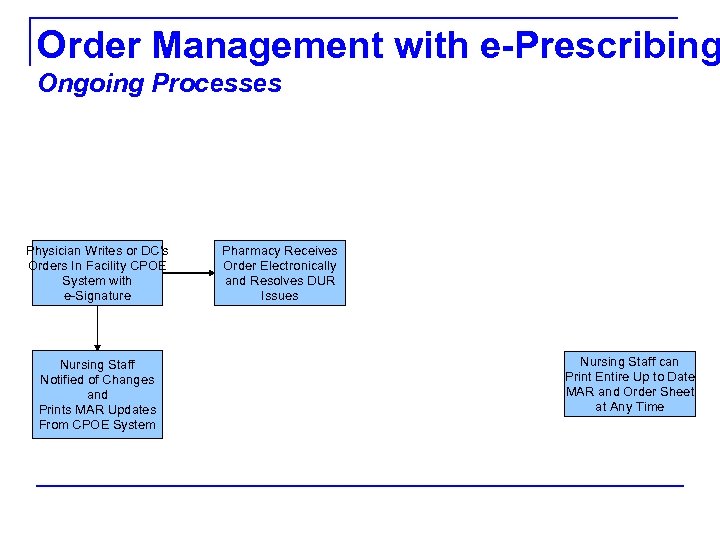 Order Management with e-Prescribing Ongoing Processes Physician Writes or DC's Orders In Facility CPOE System with e-Signature Nursing Staff Notified of Changes and Prints MAR Updates From CPOE System Pharmacy Receives Order Electronically and Resolves DUR Issues Nursing Staff can Print Entire Up to Date MAR and Order Sheet at Any Time
Order Management with e-Prescribing Ongoing Processes Physician Writes or DC's Orders In Facility CPOE System with e-Signature Nursing Staff Notified of Changes and Prints MAR Updates From CPOE System Pharmacy Receives Order Electronically and Resolves DUR Issues Nursing Staff can Print Entire Up to Date MAR and Order Sheet at Any Time
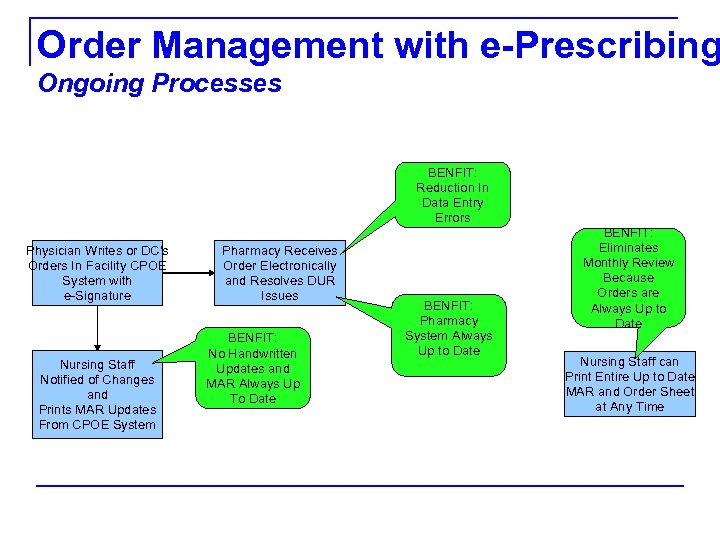 Order Management with e-Prescribing Ongoing Processes BENFIT: Reduction In Data Entry Errors Physician Writes or DC's Orders In Facility CPOE System with e-Signature Nursing Staff Notified of Changes and Prints MAR Updates From CPOE System Pharmacy Receives Order Electronically and Resolves DUR Issues BENFIT: No Handwritten Updates and MAR Always Up To Date BENFIT: Pharmacy System Always Up to Date BENFIT: Eliminates Monthly Review Because Orders are Always Up to Date Nursing Staff can Print Entire Up to Date MAR and Order Sheet at Any Time
Order Management with e-Prescribing Ongoing Processes BENFIT: Reduction In Data Entry Errors Physician Writes or DC's Orders In Facility CPOE System with e-Signature Nursing Staff Notified of Changes and Prints MAR Updates From CPOE System Pharmacy Receives Order Electronically and Resolves DUR Issues BENFIT: No Handwritten Updates and MAR Always Up To Date BENFIT: Pharmacy System Always Up to Date BENFIT: Eliminates Monthly Review Because Orders are Always Up to Date Nursing Staff can Print Entire Up to Date MAR and Order Sheet at Any Time
 e-Prescribing in Long Term Care n e-Prescribing is new to LTC n 2006 CMS Pilot Study was first official standards based e-prescribing study in Long Term Care n There are less than 5 standards based e. Prescribing installations today
e-Prescribing in Long Term Care n e-Prescribing is new to LTC n 2006 CMS Pilot Study was first official standards based e-prescribing study in Long Term Care n There are less than 5 standards based e. Prescribing installations today
 LTC e-Rx Pilot Study Abstract n 2006 study focused on e-Rx standards most relevant to LTC q SCRIPT q Formulary Benefits q Electronic Prior Authorization n Other Capabilities Studied q Facility Managed Electronic Orders q Patient Safety Checks (DUR) q Electronic Signature q Automated Refill Requests n The study included two geographically diverse treatments facilities and two comparison facilities
LTC e-Rx Pilot Study Abstract n 2006 study focused on e-Rx standards most relevant to LTC q SCRIPT q Formulary Benefits q Electronic Prior Authorization n Other Capabilities Studied q Facility Managed Electronic Orders q Patient Safety Checks (DUR) q Electronic Signature q Automated Refill Requests n The study included two geographically diverse treatments facilities and two comparison facilities
 e-Rx Findings - Facility Impacts n n Benefits q Facilities currently using electronic Physicians Orders will see modest change or disruption to current workflow q Ability to transmit orders directly to the pharmacy yielded benefits in reduced rework and callbacks q Management of Orders at the facility streamlines reconciliation processes New Challenges q Prescriber adoption is vital q Integration with clinical systems (EHR) is critical q Nurses do not effectively use patient safety (DUR) tools q Even with Formulary Benefits data, managing complex Part D health plans is an ongoing challenge q Nursing staff now has to enter and manage data that the pharmacy once managed q Data entry errors can still happen
e-Rx Findings - Facility Impacts n n Benefits q Facilities currently using electronic Physicians Orders will see modest change or disruption to current workflow q Ability to transmit orders directly to the pharmacy yielded benefits in reduced rework and callbacks q Management of Orders at the facility streamlines reconciliation processes New Challenges q Prescriber adoption is vital q Integration with clinical systems (EHR) is critical q Nurses do not effectively use patient safety (DUR) tools q Even with Formulary Benefits data, managing complex Part D health plans is an ongoing challenge q Nursing staff now has to enter and manage data that the pharmacy once managed q Data entry errors can still happen
 e-Rx Findings - Pharmacy Impacts n Benefits q q q n Demographics pre-populated on new admissions Straightforward new order processing Discontinued orders Readmissions streamlined Do not have to manage MARs and Order Sheets Refill requests streamlined New challenges q q Combination & Tapered Orders – Need codified SIG standard Transcription accuracy Timely transmission on admission orders Fax mode for controlled substances leads to process inconsistencies
e-Rx Findings - Pharmacy Impacts n Benefits q q q n Demographics pre-populated on new admissions Straightforward new order processing Discontinued orders Readmissions streamlined Do not have to manage MARs and Order Sheets Refill requests streamlined New challenges q q Combination & Tapered Orders – Need codified SIG standard Transcription accuracy Timely transmission on admission orders Fax mode for controlled substances leads to process inconsistencies
 Med Reconciliation Conclusions n n n e-Prescribing forces facilities to take ownership of their orders Once a facility manages their own orders, they typically have up to date data for MARs and Order Sheets e-Prescribing can significantly streamline processes and reduce reconciliation errors during new admissions from hospitals e-Prescribing can reduce reconciliation errors between the nursing facility and the pharmacy It is difficult to keep a facility managed CPOE system in sync with a pharmacy system without e. Prescribing
Med Reconciliation Conclusions n n n e-Prescribing forces facilities to take ownership of their orders Once a facility manages their own orders, they typically have up to date data for MARs and Order Sheets e-Prescribing can significantly streamline processes and reduce reconciliation errors during new admissions from hospitals e-Prescribing can reduce reconciliation errors between the nursing facility and the pharmacy It is difficult to keep a facility managed CPOE system in sync with a pharmacy system without e. Prescribing


