0bff7371f26e959f7ffaecd45c0169da.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Networks : What is a network? A Network is formed when 2 or more computers (devices) are linked together. Every computer or device on a network can send and receive data from any of the other computers or devices connected to the network. A computer which is not part of a network is called a stand-alone computer. Networks v 2 1
Networks : What is a network? A Network is formed when 2 or more computers (devices) are linked together. Every computer or device on a network can send and receive data from any of the other computers or devices connected to the network. A computer which is not part of a network is called a stand-alone computer. Networks v 2 1
 Network Advantages 1. Allows you to share data. 2. Allows access to files from any computer anywhere on the network. 3. Allows communication via email. 4. Software sharing (subject to the necessary licences being in place). 5. Video conferencing can save time, travel and environmental costs. Networks v 2 2
Network Advantages 1. Allows you to share data. 2. Allows access to files from any computer anywhere on the network. 3. Allows communication via email. 4. Software sharing (subject to the necessary licences being in place). 5. Video conferencing can save time, travel and environmental costs. Networks v 2 2
 Networks: Local Area Networks (LANs) A Local Area Network (LAN) covers a small geographical area such as a classroom or school building. Computers and devices are connected in a LAN by wired connections or by wireless connections. In a LAN you can also share expensive computer peripherals e. g. A colour laser printer. Networks v 2 3
Networks: Local Area Networks (LANs) A Local Area Network (LAN) covers a small geographical area such as a classroom or school building. Computers and devices are connected in a LAN by wired connections or by wireless connections. In a LAN you can also share expensive computer peripherals e. g. A colour laser printer. Networks v 2 3
 Networks: Wide Area Network (WAN) A Wide Area Network (WAN) covers a larger geographical area than a LAN – typically a country or a continent. Telecommunication links (BT, Virgin) are used to transmit and receive data in a WAN. These links include fibre optic, satellite links and microwave transmission. Fibre optic cables for WANs are frequently laid on the seabed. Networks v 2 4
Networks: Wide Area Network (WAN) A Wide Area Network (WAN) covers a larger geographical area than a LAN – typically a country or a continent. Telecommunication links (BT, Virgin) are used to transmit and receive data in a WAN. These links include fibre optic, satellite links and microwave transmission. Fibre optic cables for WANs are frequently laid on the seabed. Networks v 2 4
 Networks: Wide Area Network (WAN) A single satellite channel is capable of carrying large numbers of separate transmissions. A WAN often connect lots of smaller LANs. The Internet is a good example of a WAN which spans the globe – the name Internet coming from Interconnecting Networks v 2 5
Networks: Wide Area Network (WAN) A single satellite channel is capable of carrying large numbers of separate transmissions. A WAN often connect lots of smaller LANs. The Internet is a good example of a WAN which spans the globe – the name Internet coming from Interconnecting Networks v 2 5
 Networks: The Internet and the WWW The Internet is a global system of computer networks that enables computers and peripheral devices worldwide to connect with each other using a range of telecommunication systems. The WWW (World Wide Web) is made up of millions of web pages that are stored on computers across the world. Web pages display different data types : text, graphics, sounds, animations and video. The term web comes from the fact that web pages are linked together using hyperlinks. Link to video showing undersea cables Link to video showing cable laying ship Networks v 2 6
Networks: The Internet and the WWW The Internet is a global system of computer networks that enables computers and peripheral devices worldwide to connect with each other using a range of telecommunication systems. The WWW (World Wide Web) is made up of millions of web pages that are stored on computers across the world. Web pages display different data types : text, graphics, sounds, animations and video. The term web comes from the fact that web pages are linked together using hyperlinks. Link to video showing undersea cables Link to video showing cable laying ship Networks v 2 6
 Networks: Search Engines and Browsers A Search Engine is a software system that is designed to search for information on the WWW. They help users find their way around the web by searching web pages for keywords. A Web Browser is a program that allow internet users to view data on the WWW. Examples are Internet Explorer, Firefox, Google chrome. Networks v 2 7
Networks: Search Engines and Browsers A Search Engine is a software system that is designed to search for information on the WWW. They help users find their way around the web by searching web pages for keywords. A Web Browser is a program that allow internet users to view data on the WWW. Examples are Internet Explorer, Firefox, Google chrome. Networks v 2 7
 Networks: Network Interface Cards (NICs) All computers on a network must have a either a Network Interface Card (NIC) or a Wireless Network Interface Card. This device allows the computer to connect to the network and to send and receive data to and from other devices. These cards are fitted inside the computer. Networks v 2 8
Networks: Network Interface Cards (NICs) All computers on a network must have a either a Network Interface Card (NIC) or a Wireless Network Interface Card. This device allows the computer to connect to the network and to send and receive data to and from other devices. These cards are fitted inside the computer. Networks v 2 8
 Networks Now Read pages 1 to 8 and do: • Revision 1 - Networks (Page 35) in your jotter. • Task 1 – (Page 8) at the computer. Networks v 2 9
Networks Now Read pages 1 to 8 and do: • Revision 1 - Networks (Page 35) in your jotter. • Task 1 – (Page 8) at the computer. Networks v 2 9
 Networks: Wired v Wireless A wired connection uses a physical wire to send data. In a school or office, these are normally hidden away with many access points built into walls. Wired connections can make use of different types of wires, fibre optic or copper, each having different data transfer speeds. A wireless connection can connect devices without any wires needed between the devices. Networks v 2 10
Networks: Wired v Wireless A wired connection uses a physical wire to send data. In a school or office, these are normally hidden away with many access points built into walls. Wired connections can make use of different types of wires, fibre optic or copper, each having different data transfer speeds. A wireless connection can connect devices without any wires needed between the devices. Networks v 2 10
 Networks: Wired v Wireless Wired connection advantages: 1. It is normally very secure. (Hard to hack into) 2. Connection speed is usually faster than wireless. Wired connection disadvantages: 1. It can leave many wires trailing around an office. 2. A very large amount of cabling and network hubs may be needed in large premises. 3. You cannot move around easily. Networks v 2 11
Networks: Wired v Wireless Wired connection advantages: 1. It is normally very secure. (Hard to hack into) 2. Connection speed is usually faster than wireless. Wired connection disadvantages: 1. It can leave many wires trailing around an office. 2. A very large amount of cabling and network hubs may be needed in large premises. 3. You cannot move around easily. Networks v 2 11
 Networks: Wired v Wireless connection advantages: 1. There are no wires that could be accidentally stood on or tripped over. 2. A connection can be made anywhere (within the range of the device). Wireless connection disadvantages: 1. If the connection is unsecured then unauthorised users could access it. 2. There could be interference with the wireless signal from other devices. Networks v 2 12
Networks: Wired v Wireless connection advantages: 1. There are no wires that could be accidentally stood on or tripped over. 2. A connection can be made anywhere (within the range of the device). Wireless connection disadvantages: 1. If the connection is unsecured then unauthorised users could access it. 2. There could be interference with the wireless signal from other devices. Networks v 2 12
 Networks: Optical Cables Fibre optic: fibre optic cable is made up of fine strands of glass that carry pulses of light. These pulses of light represent the 1 s and 0 s that are being transferred. Advantages of Optical Cables 1. It is more secure than copper cabling as any break in the cable can be detected. 2. Fibre optic cable does not suffer from electromagnetic interference. 3. It can transmit data at much higher speeds than any other wired or wireless methods. Networks v 2 13
Networks: Optical Cables Fibre optic: fibre optic cable is made up of fine strands of glass that carry pulses of light. These pulses of light represent the 1 s and 0 s that are being transferred. Advantages of Optical Cables 1. It is more secure than copper cabling as any break in the cable can be detected. 2. Fibre optic cable does not suffer from electromagnetic interference. 3. It can transmit data at much higher speeds than any other wired or wireless methods. Networks v 2 13
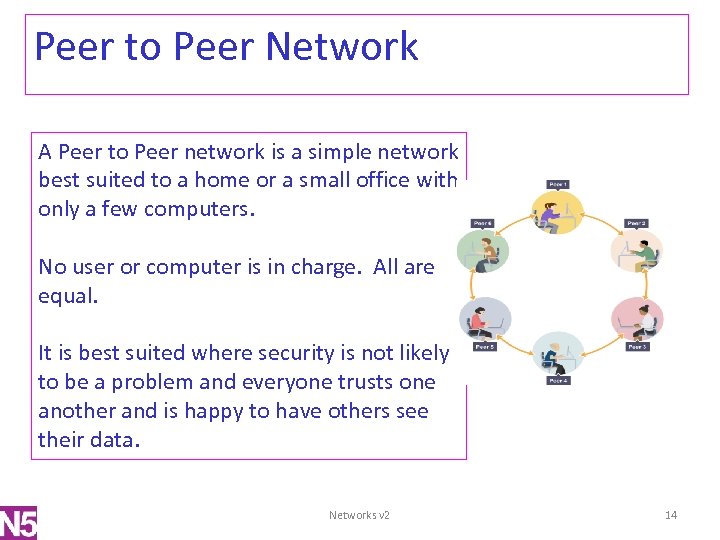 Peer to Peer Network A Peer to Peer network is a simple network best suited to a home or a small office with only a few computers. No user or computer is in charge. All are equal. It is best suited where security is not likely to be a problem and everyone trusts one another and is happy to have others see their data. Networks v 2 14
Peer to Peer Network A Peer to Peer network is a simple network best suited to a home or a small office with only a few computers. No user or computer is in charge. All are equal. It is best suited where security is not likely to be a problem and everyone trusts one another and is happy to have others see their data. Networks v 2 14
 Peer to Peer Network Users can choose to share resources and files located on their computers with other users and computers. Each machine is managed separately from the others. This means different software and programs can be installed on each. Each machine can have several accounts for different users and the user account remains on that computer system. Networks v 2 15
Peer to Peer Network Users can choose to share resources and files located on their computers with other users and computers. Each machine is managed separately from the others. This means different software and programs can be installed on each. Each machine can have several accounts for different users and the user account remains on that computer system. Networks v 2 15
 Advantages( ) and Disadvantages ( ) of a Peer to Peer Network Cheap to set up as there is no need for dedicated servers. Easy to set up as most modern operating systems can be set up for peer to peer networking. Data is stored separately on each device so it is not easy to make backups of data to prevent data loss. User names and passwords can be different on each computer so it is difficult to maintain security. Some computers may not even have passwords. Networks v 2 16
Advantages( ) and Disadvantages ( ) of a Peer to Peer Network Cheap to set up as there is no need for dedicated servers. Easy to set up as most modern operating systems can be set up for peer to peer networking. Data is stored separately on each device so it is not easy to make backups of data to prevent data loss. User names and passwords can be different on each computer so it is difficult to maintain security. Some computers may not even have passwords. Networks v 2 16
 A Client/Server Network In a Client Server network some computers are Clients. People use these to access the network. You use a Client computer in school to access the school network. Other computers are Servers. A Server is a computer which controls a resource that is made available to clients on the network. Resources might include applications, data files, printers, email or internet access. Networks v 2 17
A Client/Server Network In a Client Server network some computers are Clients. People use these to access the network. You use a Client computer in school to access the school network. Other computers are Servers. A Server is a computer which controls a resource that is made available to clients on the network. Resources might include applications, data files, printers, email or internet access. Networks v 2 17
 Advantages( ) and Disadvantages( ) A Client/Server Network Security is easy as all user names and passwords are stored in the one place. Easy to backup all network files at regular intervals as they are all stored in the one place. Can use any client to access your files. Expensive to setup as at least one computer has to become the server and so cannot be used normally. Administrator(person) required to maintain the server. Networks v 2 18
Advantages( ) and Disadvantages( ) A Client/Server Network Security is easy as all user names and passwords are stored in the one place. Easy to backup all network files at regular intervals as they are all stored in the one place. Can use any client to access your files. Expensive to setup as at least one computer has to become the server and so cannot be used normally. Administrator(person) required to maintain the server. Networks v 2 18
 Server types – File Server A file server is used on a client/server network to provide centralised storage. All the data is stored in one place. Every user will have their own allocated storage space. The file server controls file access so that each user only has access to the files they should be allowed to see. Networks v 2 19
Server types – File Server A file server is used on a client/server network to provide centralised storage. All the data is stored in one place. Every user will have their own allocated storage space. The file server controls file access so that each user only has access to the files they should be allowed to see. Networks v 2 19
 Server types – Print Server A Print Server is used to allow all the clients (workstations) access to printers on the network. The Print Server also provides a facility for queuing up printing requests so that they are printed out in order. Networks v 2 20
Server types – Print Server A Print Server is used to allow all the clients (workstations) access to printers on the network. The Print Server also provides a facility for queuing up printing requests so that they are printed out in order. Networks v 2 20
 Server types – Mail Server A Mail Server allows users to send and receive emails and have them stored on the server hard drives. Networks v 2 21
Server types – Mail Server A Mail Server allows users to send and receive emails and have them stored on the server hard drives. Networks v 2 21
 Server types – Web Server The Web Server deals with all requests for internet access including Web pages, email and file sharing. It includes a firewall which is software that prevents unauthorised access to the LAN from people on the Internet. Networks v 2 22
Server types – Web Server The Web Server deals with all requests for internet access including Web pages, email and file sharing. It includes a firewall which is software that prevents unauthorised access to the LAN from people on the Internet. Networks v 2 22
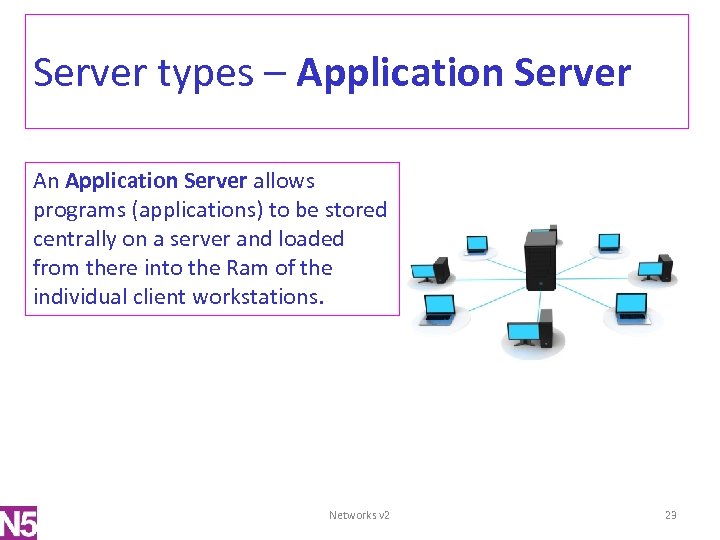 Server types – Application Server An Application Server allows programs (applications) to be stored centrally on a server and loaded from there into the Ram of the individual client workstations. Networks v 2 23
Server types – Application Server An Application Server allows programs (applications) to be stored centrally on a server and loaded from there into the Ram of the individual client workstations. Networks v 2 23
 Networks Now Read pages 9 to 12 and do: • Revision 2 – More on Networks (Page 35) in your jotter. • Task 2 – (Page 13) at the computer. Networks v 2 24
Networks Now Read pages 9 to 12 and do: • Revision 2 – More on Networks (Page 35) in your jotter. • Task 2 – (Page 13) at the computer. Networks v 2 24
 Cloud Storage Cloud storage computing simply means storing your files on huge Hard disk drives owned by Companies which give you space to store your information. You access your data using the Internet so can access your files from anywhere in the world with any device capable of connecting to the Internet. Cloud Computing video clip link Companies often give you some space for free and hope that you will need more and be willing to pay for it. Networks v 2 25
Cloud Storage Cloud storage computing simply means storing your files on huge Hard disk drives owned by Companies which give you space to store your information. You access your data using the Internet so can access your files from anywhere in the world with any device capable of connecting to the Internet. Cloud Computing video clip link Companies often give you some space for free and hope that you will need more and be willing to pay for it. Networks v 2 25
 Cloud Storage Cloud storage will be regularly backed up, meaning you don't have to save it yourself. Access anywhere with an internet connection. Easy to get more storage space although you may have to pay for it. Cannot be accessed if you have no connection; if the cloud storage website is down for maintenance or suffers a DOS attack. Speed of loading files will depend on internet connection speed but generally slower than Local storage. Concerns about the Cloud Storage Companies being hacked into. Is your data safe? Networks v 2 26
Cloud Storage Cloud storage will be regularly backed up, meaning you don't have to save it yourself. Access anywhere with an internet connection. Easy to get more storage space although you may have to pay for it. Cannot be accessed if you have no connection; if the cloud storage website is down for maintenance or suffers a DOS attack. Speed of loading files will depend on internet connection speed but generally slower than Local storage. Concerns about the Cloud Storage Companies being hacked into. Is your data safe? Networks v 2 26
 Local Storage This is when you store your files and data on your own Hard disks, solid state storage devices like memory sticks. Speed of loading files will be much faster and is NOT limited by the speed of the user’s internet connection. Can only be accessed on the computer or network where the storage is. You are responsible for keeping your data protected from viruses, Trojans and other malware. You need to remember to make backups regularly to make sure that you don’t lose your data. Networks v 2 27
Local Storage This is when you store your files and data on your own Hard disks, solid state storage devices like memory sticks. Speed of loading files will be much faster and is NOT limited by the speed of the user’s internet connection. Can only be accessed on the computer or network where the storage is. You are responsible for keeping your data protected from viruses, Trojans and other malware. You need to remember to make backups regularly to make sure that you don’t lose your data. Networks v 2 27
 Networks Now Read pages 14 and 15 and do: • Revision 3 – Cloud Computing(Page 35) in your jotter. • Task 3 – (Page 14) at the computer. Networks v 2 28
Networks Now Read pages 14 and 15 and do: • Revision 3 – Cloud Computing(Page 35) in your jotter. • Task 3 – (Page 14) at the computer. Networks v 2 28


