494661ade004229bd5077452acd20735.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 Networking with TCP/IP and the Application Layers
Networking with TCP/IP and the Application Layers
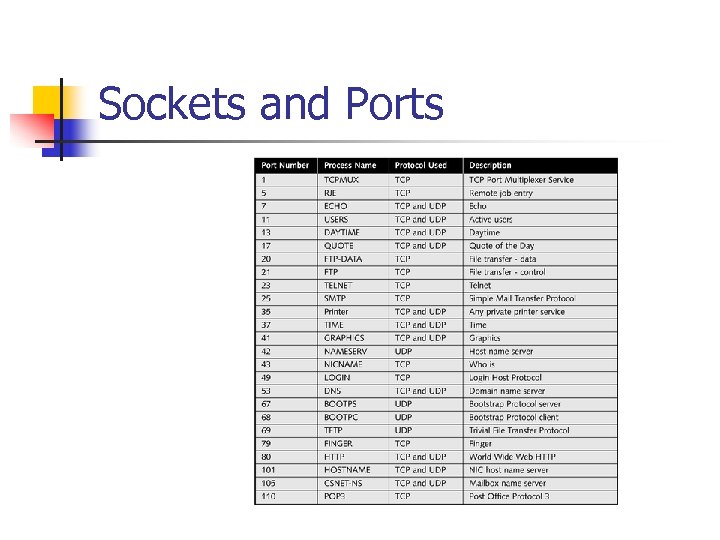
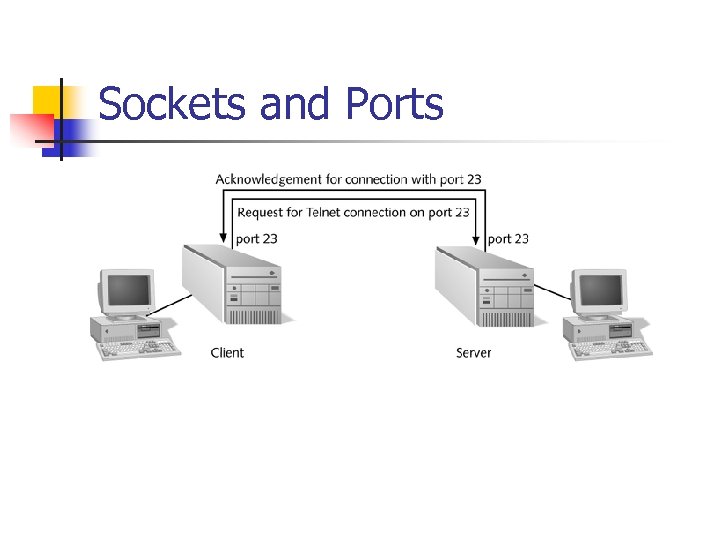
 Sockets and Ports n Socket n n n Logical address assigned to a specific process running on a host computer The socket’s address combines the host computer’s IP address with the port number associated with a process Port numbers in the range of 0 to 1023 are called well-known ports
Sockets and Ports n Socket n n n Logical address assigned to a specific process running on a host computer The socket’s address combines the host computer’s IP address with the port number associated with a process Port numbers in the range of 0 to 1023 are called well-known ports
 Sockets and Ports
Sockets and Ports
 Sockets and Ports
Sockets and Ports
 Host Names and Domain Name System (DNS) n Host name n n Symbolic name that describes a TCP/IP device Domain n Group of computers that belong to the same organization and have part of their IP addresses in common
Host Names and Domain Name System (DNS) n Host name n n Symbolic name that describes a TCP/IP device Domain n Group of computers that belong to the same organization and have part of their IP addresses in common
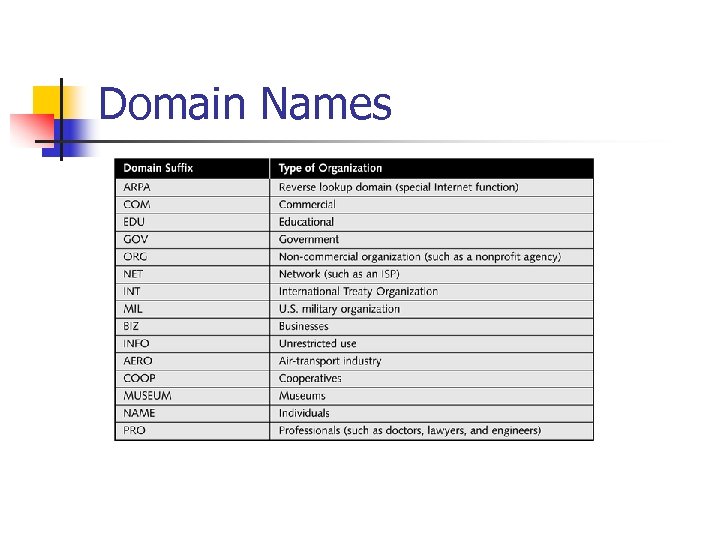
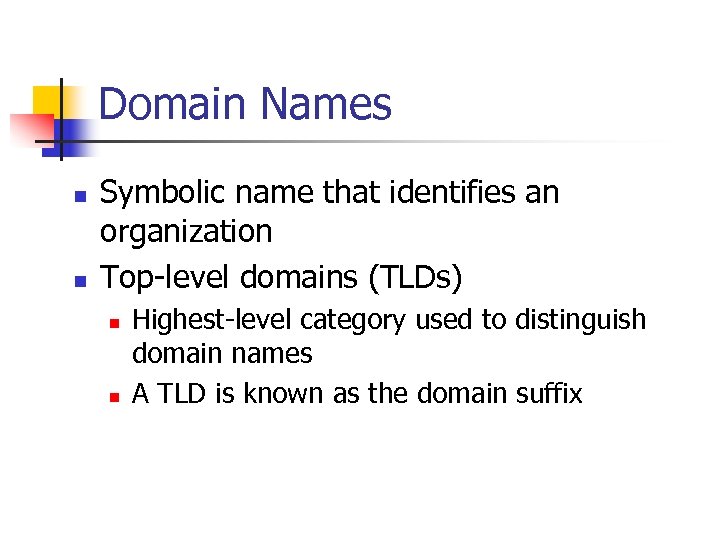 Domain Names n n Symbolic name that identifies an organization Top-level domains (TLDs) n n Highest-level category used to distinguish domain names A TLD is known as the domain suffix
Domain Names n n Symbolic name that identifies an organization Top-level domains (TLDs) n n Highest-level category used to distinguish domain names A TLD is known as the domain suffix
 Domain Names
Domain Names
 Host Files n n Text file that associates TCP/IP host names with IP addresses Alias n Nickname for a node’s host name
Host Files n n Text file that associates TCP/IP host names with IP addresses Alias n Nickname for a node’s host name
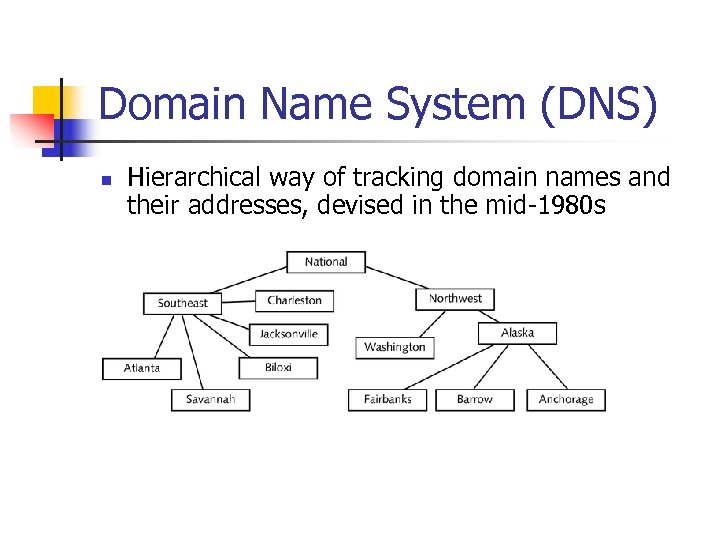 Domain Name System (DNS) n Hierarchical way of tracking domain names and their addresses, devised in the mid-1980 s
Domain Name System (DNS) n Hierarchical way of tracking domain names and their addresses, devised in the mid-1980 s
 Domain Name System (DNS) n Resolvers n n Hosts on the Internet that need to look up domain name information Name servers n n Servers that contain databases of names and their associated IP addresses Each name server manages a group of device, collectively known as a zone
Domain Name System (DNS) n Resolvers n n Hosts on the Internet that need to look up domain name information Name servers n n Servers that contain databases of names and their associated IP addresses Each name server manages a group of device, collectively known as a zone
 Configuring DNS
Configuring DNS
 DNS Name Space n Name space n n n Refers to the actual database of Internet IP addresses and their associated names Every name server holds a piece of the DNS name space At the highest level of the hierarchy sit the root servers Visit: http: //www. icann. org/ And: http: //www. newroot. com/rootservers. htm
DNS Name Space n Name space n n n Refers to the actual database of Internet IP addresses and their associated names Every name server holds a piece of the DNS name space At the highest level of the hierarchy sit the root servers Visit: http: //www. icann. org/ And: http: //www. newroot. com/rootservers. htm
 DNS Name Space n Resource record n n Element of a DNS database stored on a name server that contains information about TCP/IP host names and their addresses Address resource record n Type of resource record that maps the IP address of an Internet-connected device to its domain name
DNS Name Space n Resource record n n Element of a DNS database stored on a name server that contains information about TCP/IP host names and their addresses Address resource record n Type of resource record that maps the IP address of an Internet-connected device to its domain name
 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) n n Automated means of assigning a unique IP address to every device on a network Reasons for implementing DHCP n n Reduce the time and planning spent on IP address management Reduce the potential for errors in assigning IP addresses Enable users to move their workstations and printers without having to change their TCP/IP configuration Make IP addressing transparent for mobile users
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) n n Automated means of assigning a unique IP address to every device on a network Reasons for implementing DHCP n n Reduce the time and planning spent on IP address management Reduce the potential for errors in assigning IP addresses Enable users to move their workstations and printers without having to change their TCP/IP configuration Make IP addressing transparent for mobile users
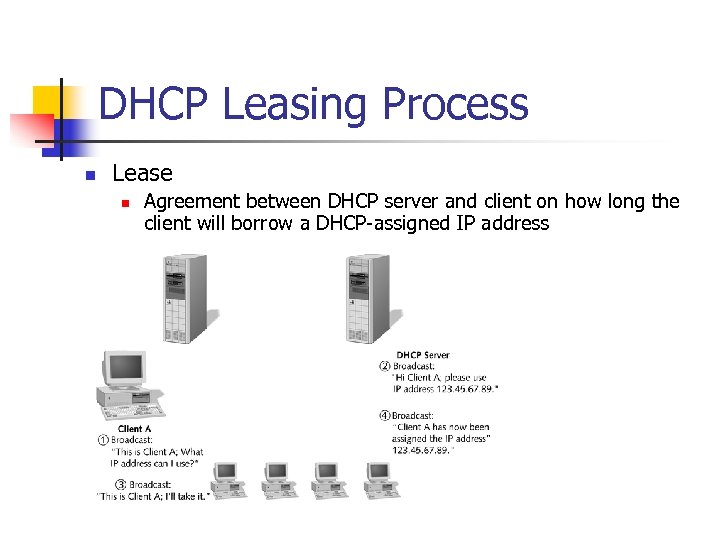 DHCP Leasing Process n Lease n Agreement between DHCP server and client on how long the client will borrow a DHCP-assigned IP address
DHCP Leasing Process n Lease n Agreement between DHCP server and client on how long the client will borrow a DHCP-assigned IP address
 Terminating a DHCP Lease n n A DHCP lease may expire based on the period established for it in the server configuration A DHCP lease may be manually terminated at any time from either the client’s TCP/IP configuration or the server’s DHCP configuration In some instances, a user must terminate a lease Release n The act of terminating a DHCP lease
Terminating a DHCP Lease n n A DHCP lease may expire based on the period established for it in the server configuration A DHCP lease may be manually terminated at any time from either the client’s TCP/IP configuration or the server’s DHCP configuration In some instances, a user must terminate a lease Release n The act of terminating a DHCP lease
 Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS) n n Provides a means of resolving Net. BIOS names with IP addresses WINS offers several advantages n n n Guarantees a unique Net. BIOS name is used for each computer on a network Support for DHCP Better network performance
Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS) n n Provides a means of resolving Net. BIOS names with IP addresses WINS offers several advantages n n n Guarantees a unique Net. BIOS name is used for each computer on a network Support for DHCP Better network performance
 Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS)
Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS)
 Review of TCP/IP Subprotocols n n n n Internet Protocol (IP) Transport Control Protocol (TCP) User Datagram Protocol (UDP) Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Telnet File Transfer Protocol (FTP) Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
Review of TCP/IP Subprotocols n n n n Internet Protocol (IP) Transport Control Protocol (TCP) User Datagram Protocol (UDP) Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Telnet File Transfer Protocol (FTP) Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
 Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) n SMTP n Responsible for moving messages from one e-mail server to another
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) n SMTP n Responsible for moving messages from one e-mail server to another
 Internet Mail Access Protocol (IMAP) n Mail storage and manipulation protocol that depends on SMTP’s transport system
Internet Mail Access Protocol (IMAP) n Mail storage and manipulation protocol that depends on SMTP’s transport system
 Hypertext Transport Protocol (HTTP) n n n Language that Web clients and servers use to communicate Forms the backbone of the Web Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) n Language that defines formatting standards for Web documents
Hypertext Transport Protocol (HTTP) n n n Language that Web clients and servers use to communicate Forms the backbone of the Web Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) n Language that defines formatting standards for Web documents
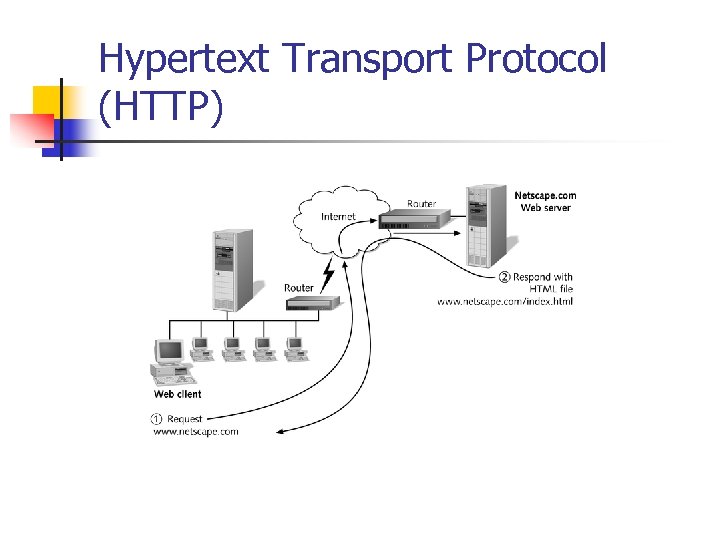 Hypertext Transport Protocol (HTTP)
Hypertext Transport Protocol (HTTP)
 Network Time Protocol (NTP) n n Used to synchronize the clocks of a computers on a network Very simple protocol Belongs to Application Layer of TCP/IP Model Depends on UDP
Network Time Protocol (NTP) n n Used to synchronize the clocks of a computers on a network Very simple protocol Belongs to Application Layer of TCP/IP Model Depends on UDP
 TCP/IP Troubleshooting n n n Of all network protocols, TCP/IP is most likely to cause problems because it requires the most planning and post-installation configuration Be aware of the troubleshooting tools and their switches These troubleshooting utilities can be accessed from the command prompt on a server or client running TCP/IP
TCP/IP Troubleshooting n n n Of all network protocols, TCP/IP is most likely to cause problems because it requires the most planning and post-installation configuration Be aware of the troubleshooting tools and their switches These troubleshooting utilities can be accessed from the command prompt on a server or client running TCP/IP
 Packet Internet Groper (PING) n n Troubleshooting utility that can verify TCP/IP is installed, bound to the NIC, configured correctly, and communicating with the network An echo request is a signal sent out to another computer An echo reply is the other computer’s response signal Process of sending this signal back and forth is known as pinging
Packet Internet Groper (PING) n n Troubleshooting utility that can verify TCP/IP is installed, bound to the NIC, configured correctly, and communicating with the network An echo request is a signal sent out to another computer An echo reply is the other computer’s response signal Process of sending this signal back and forth is known as pinging
 Netstat n Netstat utility display TCP/IP statistics and details about TCP/IP components and connections on a host
Netstat n Netstat utility display TCP/IP statistics and details about TCP/IP components and connections on a host
 Nbstat n The nbstat utility can provide information about Net. BIOS statistics and resolve Net. BIOS names to their IP addresses n n In other words, if you know the Net. BIOS name of a workstation, you can use nbstat to determine its IP address Nbstat is useful on networks that run Windows-based operating systems and Net. BIOS
Nbstat n The nbstat utility can provide information about Net. BIOS statistics and resolve Net. BIOS names to their IP addresses n n In other words, if you know the Net. BIOS name of a workstation, you can use nbstat to determine its IP address Nbstat is useful on networks that run Windows-based operating systems and Net. BIOS
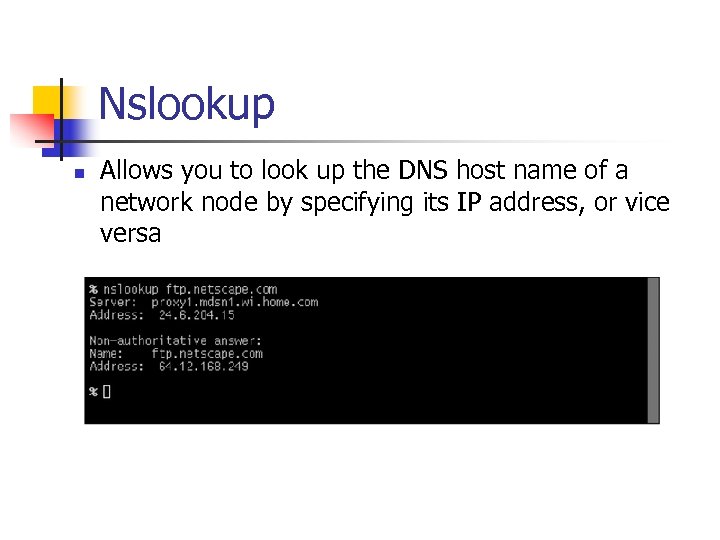 Nslookup n Allows you to look up the DNS host name of a network node by specifying its IP address, or vice versa
Nslookup n Allows you to look up the DNS host name of a network node by specifying its IP address, or vice versa
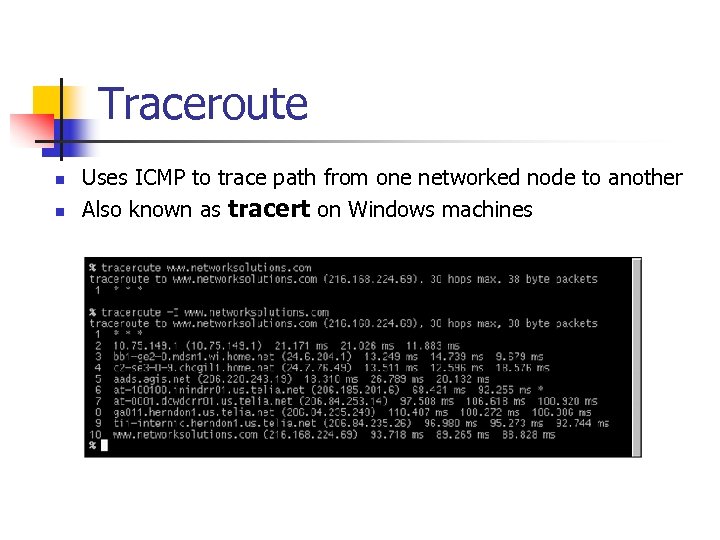 Traceroute n n Uses ICMP to trace path from one networked node to another Also known as tracert on Windows machines
Traceroute n n Uses ICMP to trace path from one networked node to another Also known as tracert on Windows machines
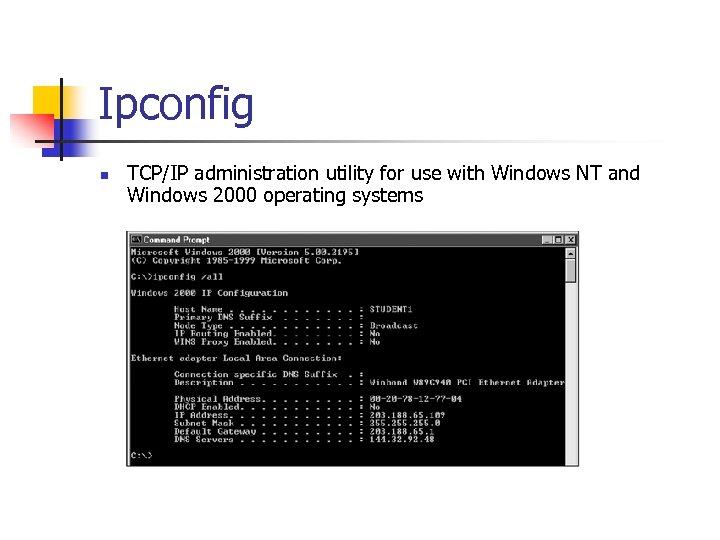 Ipconfig n TCP/IP administration utility for use with Windows NT and Windows 2000 operating systems
Ipconfig n TCP/IP administration utility for use with Windows NT and Windows 2000 operating systems
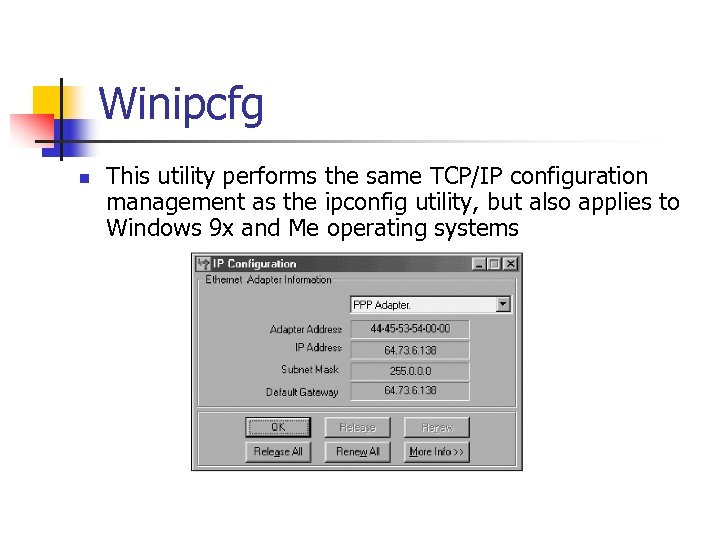 Winipcfg n This utility performs the same TCP/IP configuration management as the ipconfig utility, but also applies to Windows 9 x and Me operating systems
Winipcfg n This utility performs the same TCP/IP configuration management as the ipconfig utility, but also applies to Windows 9 x and Me operating systems
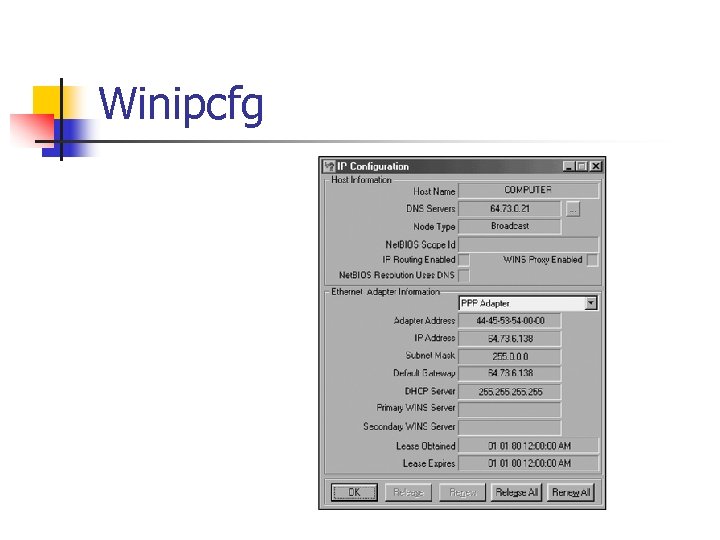 Winipcfg
Winipcfg
 Internet Services n World Wide Web (WWW, or Web) n n Collection of internetworked servers that share resources and exchange information according to specific protocols and formats Browser n Software that provides clients with a simple, graphical interface to the Web
Internet Services n World Wide Web (WWW, or Web) n n Collection of internetworked servers that share resources and exchange information according to specific protocols and formats Browser n Software that provides clients with a simple, graphical interface to the Web
 World Wide Web n Uniform Resource Locator (URL) n Standard means of identifying every Web page
World Wide Web n Uniform Resource Locator (URL) n Standard means of identifying every Web page
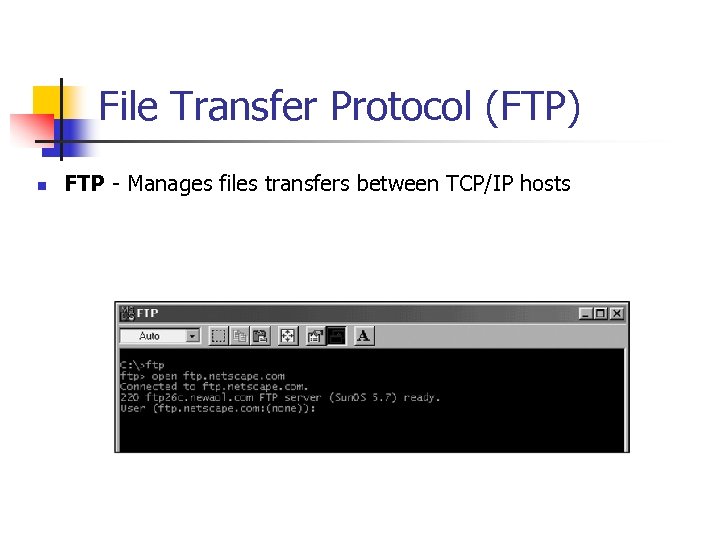 File Transfer Protocol (FTP) n FTP - Manages files transfers between TCP/IP hosts
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) n FTP - Manages files transfers between TCP/IP hosts
 E-commerce n Means of conducting business over the Web
E-commerce n Means of conducting business over the Web


