 Networking in UE 4 Joe Graf @Epic. Cog
Networking in UE 4 Joe Graf @Epic. Cog
 Introduction • Network topology and NATs • C++ Replication • Blueprint Replication • Low Level Networking • Diagnostic Tools
Introduction • Network topology and NATs • C++ Replication • Blueprint Replication • Low Level Networking • Diagnostic Tools
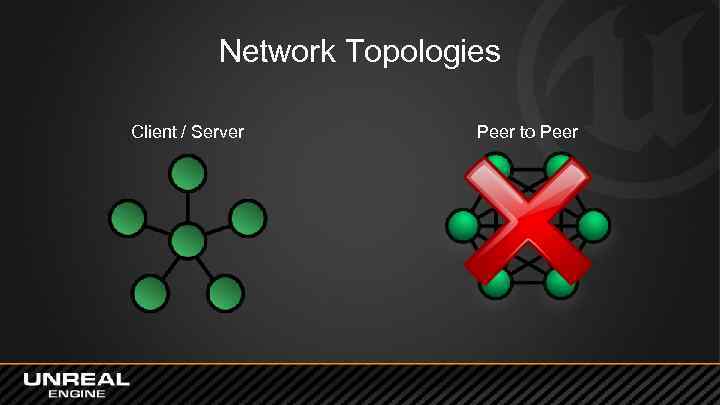 Network Topologies Client / Server Peer to Peer
Network Topologies Client / Server Peer to Peer
 Network Address Translation (NAT) • Three types to think about – Open • Can accept unsolicited connections – Moderate • Can sometimes accept unsolicited connections – Strict • Can only accept connections from known addresses
Network Address Translation (NAT) • Three types to think about – Open • Can accept unsolicited connections – Moderate • Can sometimes accept unsolicited connections – Strict • Can only accept connections from known addresses
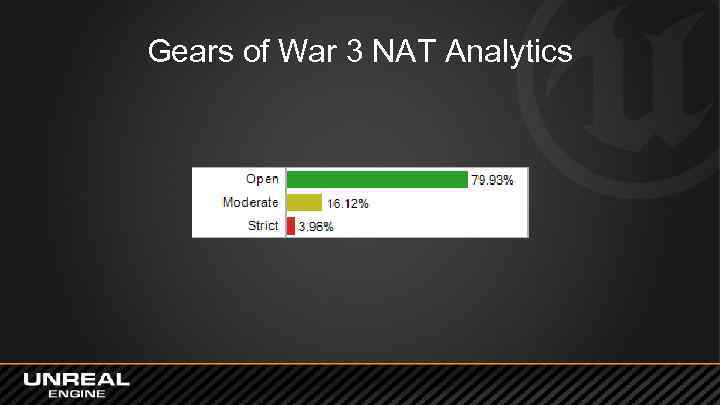 Gears of War 3 NAT Analytics
Gears of War 3 NAT Analytics
 NAT Implications • Client/Server – Server should have Open NAT – Client can be any NAT type • Peer to Peer – All clients need Open NATs – ~20% of players can’t play your game
NAT Implications • Client/Server – Server should have Open NAT – Client can be any NAT type • Peer to Peer – All clients need Open NATs – ~20% of players can’t play your game
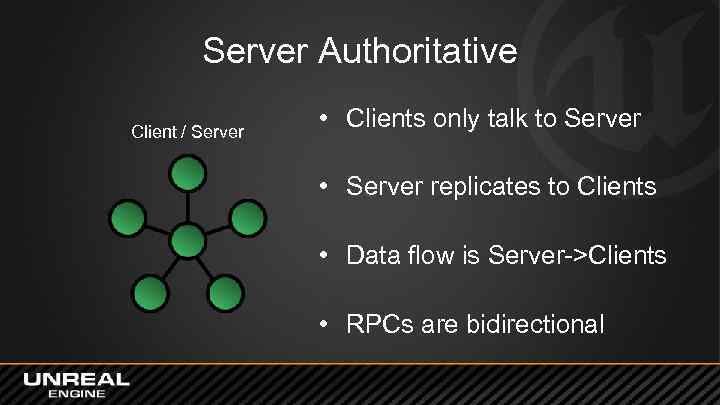 Server Authoritative Client / Server • Clients only talk to Server • Server replicates to Clients • Data flow is Server->Clients • RPCs are bidirectional
Server Authoritative Client / Server • Clients only talk to Server • Server replicates to Clients • Data flow is Server->Clients • RPCs are bidirectional
 C++ Replication
C++ Replication
 Basic Gameplay Classes Server • Game. Mode • Game. State • Player. Controller – One for each player • Player. State – One for each player Client • Game. State • Player. Controller – One for each local player • Player. State – One for each player
Basic Gameplay Classes Server • Game. Mode • Game. State • Player. Controller – One for each player • Player. State – One for each player Client • Game. State • Player. Controller – One for each local player • Player. State – One for each player
 Gameplay Classes • Game. Mode – Rules for your game • Game. State – Replicated information about your Game. Mode
Gameplay Classes • Game. Mode – Rules for your game • Game. State – Replicated information about your Game. Mode
 Gameplay Classes (cont) • Player. Controller – Primary interaction with your Game. Mode • Player. State – Replicated information about your player
Gameplay Classes (cont) • Player. Controller – Primary interaction with your Game. Mode • Player. State – Replicated information about your player
 Data Replication • b. Replicates – Set as part of the Actor’s construction • UPROPERTY Macro – Replicated. Using • Get. Lifetime. Replicated. Props Function – Determines the set of properties for replication
Data Replication • b. Replicates – Set as part of the Actor’s construction • UPROPERTY Macro – Replicated. Using • Get. Lifetime. Replicated. Props Function – Determines the set of properties for replication
 b. Replicates ACool. Actor: : ACool. Actor(…) : Super( PCIP ) { b. Replicates = true; }
b. Replicates ACool. Actor: : ACool. Actor(…) : Super( PCIP ) { b. Replicates = true; }
 Replicated Example /** number of kills */ UPROPERTY(Transient, Replicated) int 32 Num. Kills;
Replicated Example /** number of kills */ UPROPERTY(Transient, Replicated) int 32 Num. Kills;
 Replicated. Using Example /** team number */ UPROPERTY(Transient, Replicated. Using=On. Rep_Team. Color) int 32 Team. Number; void AShooter. Player. State: : On. Rep_Team. Color() { Update. Team. Colors(); }
Replicated. Using Example /** team number */ UPROPERTY(Transient, Replicated. Using=On. Rep_Team. Color) int 32 Team. Number; void AShooter. Player. State: : On. Rep_Team. Color() { Update. Team. Colors(); }
 Get. Lifetime. Replicated. Props Example void AShooter. Player. State: : Get. Lifetime. Replicated. Props( TArray
Get. Lifetime. Replicated. Props Example void AShooter. Player. State: : Get. Lifetime. Replicated. Props( TArray
 Conditional Replication • Property is only replicated when a condition is met • Can reduce bandwidth consumed • Done via a similar macro
Conditional Replication • Property is only replicated when a condition is met • Can reduce bandwidth consumed • Done via a similar macro
 Conditional Replication Example void AMy. Player. State: : Get. Lifetime. Replicated. Props( TArray
Conditional Replication Example void AMy. Player. State: : Get. Lifetime. Replicated. Props( TArray
 Common Replication Conditions • COND_Initial. Only – • COND_Owner. Only – • This property send to every connection EXCEPT the owner COND_Simulated. Only – • This property will only send to the actor's owner COND_Skip. Owner – • This property will only attempt to send on the initial replication This property will only send to simulated actors COND_Autonomous. Only – This property will only send to autonomous actors
Common Replication Conditions • COND_Initial. Only – • COND_Owner. Only – • This property send to every connection EXCEPT the owner COND_Simulated. Only – • This property will only send to the actor's owner COND_Skip. Owner – • This property will only attempt to send on the initial replication This property will only send to simulated actors COND_Autonomous. Only – This property will only send to autonomous actors
 Function Replication • UFUNCTION Macro – – – – Reliable Unreliable Client Server Net. Multicast With. Validation Blueprint. Authority. Only Blueprint. Cosmetic
Function Replication • UFUNCTION Macro – – – – Reliable Unreliable Client Server Net. Multicast With. Validation Blueprint. Authority. Only Blueprint. Cosmetic
 Reliable • Function is guaranteed to be called • Resent when an error is present • Delayed when bandwidth is saturated
Reliable • Function is guaranteed to be called • Resent when an error is present • Delayed when bandwidth is saturated
 Reliable Example /** notify player about started match */ UFUNCTION(Reliable, Client) void Client. Game. Started(); void AShooter. Player. Controller: : Client. Game. Started_Implementation() { b. Allow. Game. Actions = true; // Enable controls and disable cinematic mode now the game has started Set. Cinematic. Mode(false, true, true); AShooter. HUD* Shooter. HUD = Get. Shooter. HUD(); if (Shooter. HUD) { Shooter. HUD->Set. Match. State(EShooter. Match. State: : Playing); Shooter. HUD->Show. Scoreboard(false); } … }
Reliable Example /** notify player about started match */ UFUNCTION(Reliable, Client) void Client. Game. Started(); void AShooter. Player. Controller: : Client. Game. Started_Implementation() { b. Allow. Game. Actions = true; // Enable controls and disable cinematic mode now the game has started Set. Cinematic. Mode(false, true, true); AShooter. HUD* Shooter. HUD = Get. Shooter. HUD(); if (Shooter. HUD) { Shooter. HUD->Set. Match. State(EShooter. Match. State: : Playing); Shooter. HUD->Show. Scoreboard(false); } … }
 Unreliable • Function is attempted to be sent • Not sent again when an error is present • Skipped when bandwidth is saturated
Unreliable • Function is attempted to be sent • Not sent again when an error is present • Skipped when bandwidth is saturated
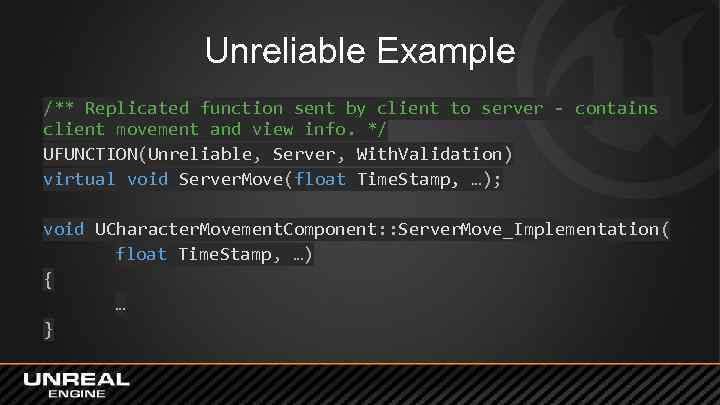 Unreliable Example /** Replicated function sent by client to server - contains client movement and view info. */ UFUNCTION(Unreliable, Server, With. Validation) virtual void Server. Move(float Time. Stamp, …); void UCharacter. Movement. Component: : Server. Move_Implementation( float Time. Stamp, …) { … }
Unreliable Example /** Replicated function sent by client to server - contains client movement and view info. */ UFUNCTION(Unreliable, Server, With. Validation) virtual void Server. Move(float Time. Stamp, …); void UCharacter. Movement. Component: : Server. Move_Implementation( float Time. Stamp, …) { … }
 Net. Multicast • Sends to all clients – Reliable or Unreliable applies here too
Net. Multicast • Sends to all clients – Reliable or Unreliable applies here too
 Net. Multicast Example /** broadcast death to local clients */ UFUNCTION(Reliable, Net. Multicast) void Broadcast. Death(…); void AShooter. Player. State: : Broadcast. Death_Implementation(…) { for (auto It = Get. World()->Get. Player. Controller. Iterator(); It; ++It) { // all local players get death messages so they can update their huds. AShooter. Player. Controller* Test. PC = Cast
Net. Multicast Example /** broadcast death to local clients */ UFUNCTION(Reliable, Net. Multicast) void Broadcast. Death(…); void AShooter. Player. State: : Broadcast. Death_Implementation(…) { for (auto It = Get. World()->Get. Player. Controller. Iterator(); It; ++It) { // all local players get death messages so they can update their huds. AShooter. Player. Controller* Test. PC = Cast
 With. Validation • Called before the target function • Used to validate parameters of a function – Meant to detect cheating/hacking • Return value affects whether function is called – false skips the call and kills the connection
With. Validation • Called before the target function • Used to validate parameters of a function – Meant to detect cheating/hacking • Return value affects whether function is called – false skips the call and kills the connection
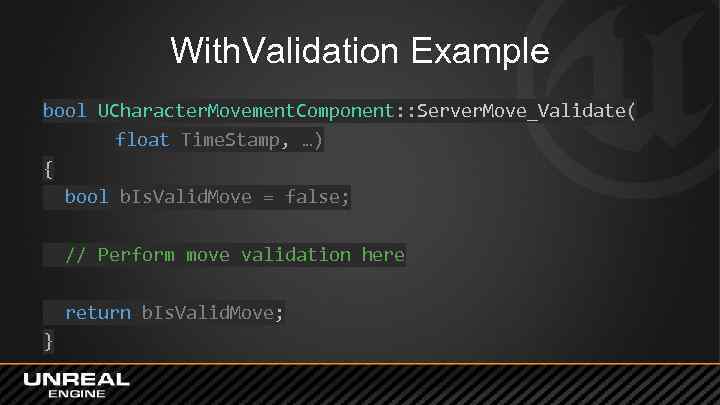 With. Validation Example bool UCharacter. Movement. Component: : Server. Move_Validate( float Time. Stamp, …) { bool b. Is. Valid. Move = false; // Perform move validation here return b. Is. Valid. Move; }
With. Validation Example bool UCharacter. Movement. Component: : Server. Move_Validate( float Time. Stamp, …) { bool b. Is. Valid. Move = false; // Perform move validation here return b. Is. Valid. Move; }
 Blueprint. Authority. Only • UE 4 all are functions are Simulated – This is the opposite of UE 3 • Opt out via Blueprint. Authority. Only
Blueprint. Authority. Only • UE 4 all are functions are Simulated – This is the opposite of UE 3 • Opt out via Blueprint. Authority. Only
 Blueprint. Authority. Only Example UFUNCTION(Blueprint. Implementable. Event, Blueprint. Authority. Only, meta=(Friendly. Name = "Any. Damage"), Category="Damage") virtual void Receive. Any. Damage(float Damage, const UDamage. Type* Damage. Type, AController* Instigated. By, AActor* Damage. Causer);
Blueprint. Authority. Only Example UFUNCTION(Blueprint. Implementable. Event, Blueprint. Authority. Only, meta=(Friendly. Name = "Any. Damage"), Category="Damage") virtual void Receive. Any. Damage(float Damage, const UDamage. Type* Damage. Type, AController* Instigated. By, AActor* Damage. Causer);
 Blueprint. Cosmetic • Opposite of Blueprint. Authority. Only – Runs on the client not server • An optimization to skip execution of slow cosmetic code on the server
Blueprint. Cosmetic • Opposite of Blueprint. Authority. Only – Runs on the client not server • An optimization to skip execution of slow cosmetic code on the server
 Actor Relevancy • Trades CPU time for network bandwidth • Distance based – Are these actors close enough – Default implementation right now • Line of sight – Can these actors see each other – UE 3 default implementation • Always relevant is an option – Trades bandwidth for CPU time
Actor Relevancy • Trades CPU time for network bandwidth • Distance based – Are these actors close enough – Default implementation right now • Line of sight – Can these actors see each other – UE 3 default implementation • Always relevant is an option – Trades bandwidth for CPU time
 Blueprint Replication
Blueprint Replication
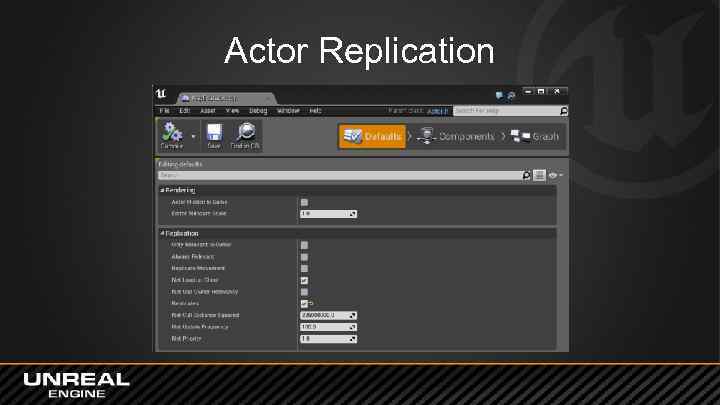 Actor Replication
Actor Replication
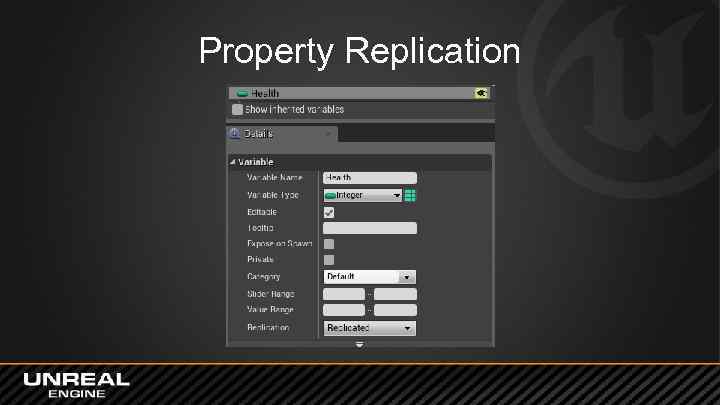 Property Replication
Property Replication
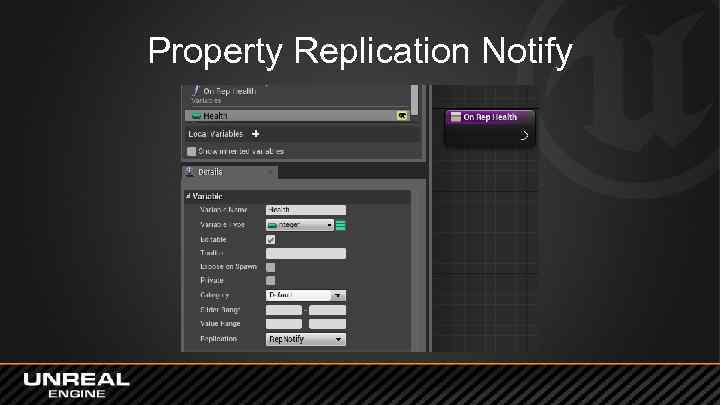 Property Replication Notify
Property Replication Notify
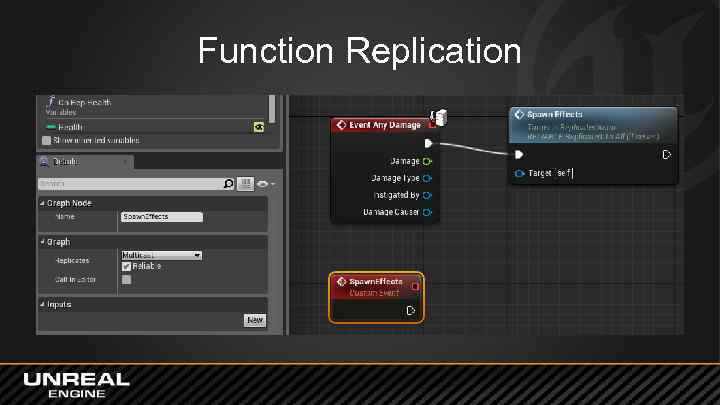 Function Replication
Function Replication
 Low Level Details
Low Level Details
 Low Level Implementation • UNet. Driver • UNet. Connection • UChannel – UControl. Channel – UVoice. Channel – UActor. Channel
Low Level Implementation • UNet. Driver • UNet. Connection • UChannel – UControl. Channel – UVoice. Channel – UActor. Channel
 UNet. Driver • Contains a list of connections to Tick • On client, one connection • On Server, N connections
UNet. Driver • Contains a list of connections to Tick • On client, one connection • On Server, N connections
 UNet. Connection • Contains a list of channels to replicate • UChild. Connection – Used as an optimization for split-screen games
UNet. Connection • Contains a list of channels to replicate • UChild. Connection – Used as an optimization for split-screen games
 UChannel Objects • Logical construct – Routes data to the proper object • Accessed by Channel. ID – Some channels have predefined IDs
UChannel Objects • Logical construct – Routes data to the proper object • Accessed by Channel. ID – Some channels have predefined IDs
 UControl. Channel • Handles connection handshaking • Processes object loading requests • Deals with misc. non-gameplay communication
UControl. Channel • Handles connection handshaking • Processes object loading requests • Deals with misc. non-gameplay communication
 UVoice. Channel • Sends and receives voice data – Voice channel routes data to platform handler • Voice data is platform dependent • Voice data is sent as speaker ID and payload
UVoice. Channel • Sends and receives voice data – Voice channel routes data to platform handler • Voice data is platform dependent • Voice data is sent as speaker ID and payload
 UActor. Channel • Handles actor replication – Includes any replicated components • One actor channel for each replicated actor • Actors are replicated by channel ID – Dynamically assigned based upon array position
UActor. Channel • Handles actor replication – Includes any replicated components • One actor channel for each replicated actor • Actors are replicated by channel ID – Dynamically assigned based upon array position
 Voice Considerations • Game can choose to support or not • Platform can mute other players – Player muted another outside of the game • Players can mute other players • Gameplay can mute players – Team based, distance based, push to talk
Voice Considerations • Game can choose to support or not • Platform can mute other players – Player muted another outside of the game • Players can mute other players • Gameplay can mute players – Team based, distance based, push to talk
 Voice Functions UFUNCTION(Server, Reliable, With. Validation) virtual void Server. Mute. Player(FUnique. Net. Id. Repl Player. Id); UFUNCTION(Server, Reliable, With. Validation ) virtual void Server. Unmute. Player(FUnique. Net. Id. Repl Player. Id); UFUNCTION(Reliable, Client) virtual void Client. Mute. Player(FUnique. Net. Id. Repl Player. Id); UFUNCTION(Reliable, Client) virtual void Client. Unmute. Player(FUnique. Net. Id. Repl Player. Id); /** * Mutes a remote player on the server and then tells the client to mute * * @param Player. Net. Id the remote player to mute */ void Gameplay. Mute. Player(const FUnique. Net. Id. Repl& Player. Net. Id); /** * Unmutes a remote player on the server and then tells the client to unmute * * @param Player. Net. Id the remote player to unmute */ void Gameplay. Unmute. Player(const FUnique. Net. Id. Repl& Player. Net. Id);
Voice Functions UFUNCTION(Server, Reliable, With. Validation) virtual void Server. Mute. Player(FUnique. Net. Id. Repl Player. Id); UFUNCTION(Server, Reliable, With. Validation ) virtual void Server. Unmute. Player(FUnique. Net. Id. Repl Player. Id); UFUNCTION(Reliable, Client) virtual void Client. Mute. Player(FUnique. Net. Id. Repl Player. Id); UFUNCTION(Reliable, Client) virtual void Client. Unmute. Player(FUnique. Net. Id. Repl Player. Id); /** * Mutes a remote player on the server and then tells the client to mute * * @param Player. Net. Id the remote player to mute */ void Gameplay. Mute. Player(const FUnique. Net. Id. Repl& Player. Net. Id); /** * Unmutes a remote player on the server and then tells the client to unmute * * @param Player. Net. Id the remote player to unmute */ void Gameplay. Unmute. Player(const FUnique. Net. Id. Repl& Player. Net. Id);
 Diagnostic Tools
Diagnostic Tools
 Network Logging • Log. Net – Verbose information about the state of channels and connections • Log. Net. Player. Movement – Detailed information about movement from clients and corrections from server • Log. Net. Traffic – Verbose information about data sent on a connection
Network Logging • Log. Net – Verbose information about the state of channels and connections • Log. Net. Player. Movement – Detailed information about movement from clients and corrections from server • Log. Net. Traffic – Verbose information about data sent on a connection
 Network Statistics • Stat Net – Lists ping, channel count, in/out bytes, etc. • Stat Game – List of network processing information
Network Statistics • Stat Net – Lists ping, channel count, in/out bytes, etc. • Stat Game – List of network processing information
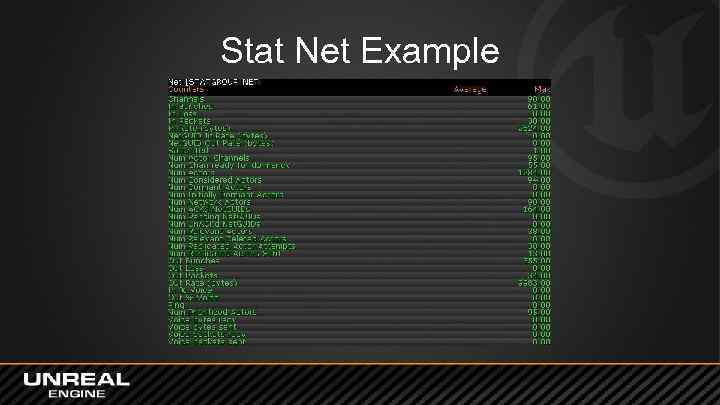 Stat Net Example
Stat Net Example
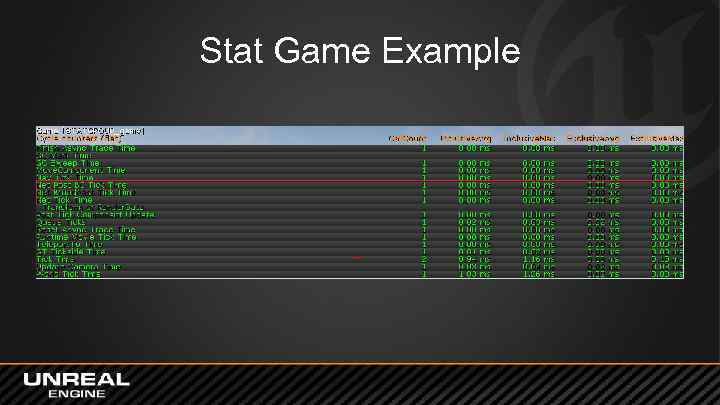 Stat Game Example
Stat Game Example
 Network Simulation Options • Pkt. Lag – Delays the sending of a packet by a N ms • Pkt. Lag. Variance – Provides some randomness to the Pkt. Lag option • Pkt. Loss – A percentage chance of not sending a packet
Network Simulation Options • Pkt. Lag – Delays the sending of a packet by a N ms • Pkt. Lag. Variance – Provides some randomness to the Pkt. Lag option • Pkt. Loss – A percentage chance of not sending a packet
 Network Simulation Options (cont) • Pkt. Dup – A percentage chance of sending duplicate packets • Pkt. Order – Sends packets out of order when enabled
Network Simulation Options (cont) • Pkt. Dup – A percentage chance of sending duplicate packets • Pkt. Order – Sends packets out of order when enabled
 Setting the Simulation Options • Console Net Pkt. Lag=100 • INI File [Packet. Simulation. Settings] Pkt. Lag=50 Pkt. Lag. Variance=10 Pkt. Loss=3 Pkt. Order=0 Pkt. Dup=10
Setting the Simulation Options • Console Net Pkt. Lag=100 • INI File [Packet. Simulation. Settings] Pkt. Lag=50 Pkt. Lag. Variance=10 Pkt. Loss=3 Pkt. Order=0 Pkt. Dup=10
 Questions? Documentation, Tutorials, and Help at: http: //answers. unrealengine. com • Answer. Hub: • Engine Documentation: http: //docs. unrealengine. com • Official Forums: http: //forums. unrealengine. com • Community Wiki: http: //wiki. unrealengine. com • You. Tube Videos: http: //www. youtube. com/user/Unreal. Development. Kit • Community IRC: #unrealengine on Free. Node Unreal Engine 4 Roadmap • lmgtfy. com/? q=Unreal+engine+Trello+
Questions? Documentation, Tutorials, and Help at: http: //answers. unrealengine. com • Answer. Hub: • Engine Documentation: http: //docs. unrealengine. com • Official Forums: http: //forums. unrealengine. com • Community Wiki: http: //wiki. unrealengine. com • You. Tube Videos: http: //www. youtube. com/user/Unreal. Development. Kit • Community IRC: #unrealengine on Free. Node Unreal Engine 4 Roadmap • lmgtfy. com/? q=Unreal+engine+Trello+


