1f78575e3d302a2bab02d7157fe6ccee.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 69
 Network Security Attacks Technical Solutions
Network Security Attacks Technical Solutions
 Acknowledgments Material is sourced from: n CISA® Review Manual 2011, © 2010, ISACA. All rights reserved. Used by permission. n CISM® Review Manual 2012, © 2011, ISACA. All rights reserved. Used by permission. n Many other Network Security sources n http: //www. csrc. nist. gov/publications/drafts/800 -118/draft-sp 800 -118. pdf Author: Susan J Lincke, Ph. D Univ. of Wisconsin-Parkside Reviewers/Contributors: Todd Burri, Kahili Cheng Funded by National Science Foundation (NSF) Course, Curriculum and Laboratory Improvement (CCLI) grant 0837574: Information Security: Audit, Case Study, and Service Learning. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and/or source(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
Acknowledgments Material is sourced from: n CISA® Review Manual 2011, © 2010, ISACA. All rights reserved. Used by permission. n CISM® Review Manual 2012, © 2011, ISACA. All rights reserved. Used by permission. n Many other Network Security sources n http: //www. csrc. nist. gov/publications/drafts/800 -118/draft-sp 800 -118. pdf Author: Susan J Lincke, Ph. D Univ. of Wisconsin-Parkside Reviewers/Contributors: Todd Burri, Kahili Cheng Funded by National Science Foundation (NSF) Course, Curriculum and Laboratory Improvement (CCLI) grant 0837574: Information Security: Audit, Case Study, and Service Learning. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and/or source(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
 Objectives The student should be able to: n Define attacks: script kiddy, social engineering, logic bomb, Trojan horse, phishing, pharming, war driving, war dialing, man-in-the-middle attack, SQL injection, virus, worm, root kit, dictionary attack, brute force attack, DOS, DDOS, botnet, spoofing, packet reply. n Describe defenses: defense in depth, bastion host, content filter, packet filter, stateful inspection, circuit-level firewall, application-level firewall, demilitarized zone, multi-homed firewall, IDS, IPS, NIDS, HIDS, signature-based IDS, statistical-based IDS, neural network, VPN, network access server (RADIUS/TACACS), honeypot, honeynet, hash, secret key encryption, public key encryption, digital signature, PKI, vulnerability assessment n Identify techniques (what they do): SHA 1/SHA 2, MD 2/MD 4/MD 5, DES, AES, RSA, ECC. n Describe and define security goals: confidentiality, authenticity, integrity, nonrepudiation n Define service’s & server’s data in the correct sensitivity class and roles with access n Define services that can enter and leave a network n Draw network Diagram with proper zones and security equipment
Objectives The student should be able to: n Define attacks: script kiddy, social engineering, logic bomb, Trojan horse, phishing, pharming, war driving, war dialing, man-in-the-middle attack, SQL injection, virus, worm, root kit, dictionary attack, brute force attack, DOS, DDOS, botnet, spoofing, packet reply. n Describe defenses: defense in depth, bastion host, content filter, packet filter, stateful inspection, circuit-level firewall, application-level firewall, demilitarized zone, multi-homed firewall, IDS, IPS, NIDS, HIDS, signature-based IDS, statistical-based IDS, neural network, VPN, network access server (RADIUS/TACACS), honeypot, honeynet, hash, secret key encryption, public key encryption, digital signature, PKI, vulnerability assessment n Identify techniques (what they do): SHA 1/SHA 2, MD 2/MD 4/MD 5, DES, AES, RSA, ECC. n Describe and define security goals: confidentiality, authenticity, integrity, nonrepudiation n Define service’s & server’s data in the correct sensitivity class and roles with access n Define services that can enter and leave a network n Draw network Diagram with proper zones and security equipment
 The Problem of Network Security The Internet allows an attacker to attack from anywhere in the world from their home desk. They just need to find one vulnerability: a security analyst need to close every vulnerability. Solution: Layered defense
The Problem of Network Security The Internet allows an attacker to attack from anywhere in the world from their home desk. They just need to find one vulnerability: a security analyst need to close every vulnerability. Solution: Layered defense
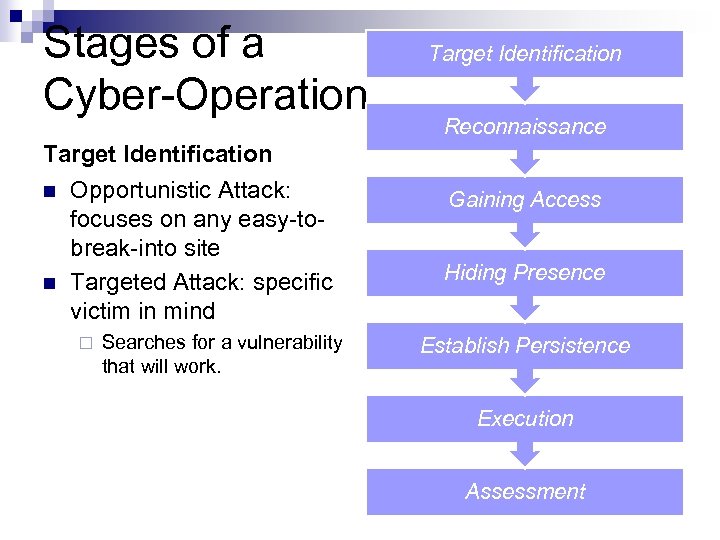 Stages of a Cyber-Operation Target Identification Reconnaissance Target Identification n n Opportunistic Attack: focuses on any easy-tobreak-into site Targeted Attack: specific victim in mind ¨ Searches for a vulnerability that will work. Gaining Access Hiding Presence Establish Persistence Execution Assessment
Stages of a Cyber-Operation Target Identification Reconnaissance Target Identification n n Opportunistic Attack: focuses on any easy-tobreak-into site Targeted Attack: specific victim in mind ¨ Searches for a vulnerability that will work. Gaining Access Hiding Presence Establish Persistence Execution Assessment
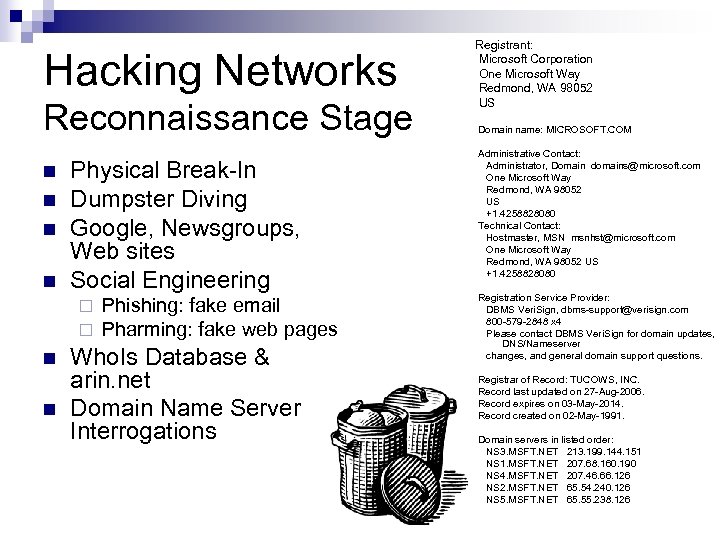 Hacking Networks Reconnaissance Stage n n Physical Break-In Dumpster Diving Google, Newsgroups, Web sites Social Engineering ¨ ¨ n n Phishing: fake email Pharming: fake web pages Who. Is Database & arin. net Domain Name Server Interrogations Registrant: Microsoft Corporation One Microsoft Way Redmond, WA 98052 US Domain name: MICROSOFT. COM Administrative Contact: Administrator, Domain domains@microsoft. com One Microsoft Way Redmond, WA 98052 US +1. 4258828080 Technical Contact: Hostmaster, MSN msnhst@microsoft. com One Microsoft Way Redmond, WA 98052 US +1. 4258828080 Registration Service Provider: DBMS Veri. Sign, dbms-support@verisign. com 800 -579 -2848 x 4 Please contact DBMS Veri. Sign for domain updates, DNS/Nameserver changes, and general domain support questions. Registrar of Record: TUCOWS, INC. Record last updated on 27 -Aug-2006. Record expires on 03 -May-2014. Record created on 02 -May-1991. Domain servers in listed order: NS 3. MSFT. NET 213. 199. 144. 151 NS 1. MSFT. NET 207. 68. 160. 190 NS 4. MSFT. NET 207. 46. 66. 126 NS 2. MSFT. NET 65. 54. 240. 126 NS 5. MSFT. NET 65. 55. 238. 126
Hacking Networks Reconnaissance Stage n n Physical Break-In Dumpster Diving Google, Newsgroups, Web sites Social Engineering ¨ ¨ n n Phishing: fake email Pharming: fake web pages Who. Is Database & arin. net Domain Name Server Interrogations Registrant: Microsoft Corporation One Microsoft Way Redmond, WA 98052 US Domain name: MICROSOFT. COM Administrative Contact: Administrator, Domain domains@microsoft. com One Microsoft Way Redmond, WA 98052 US +1. 4258828080 Technical Contact: Hostmaster, MSN msnhst@microsoft. com One Microsoft Way Redmond, WA 98052 US +1. 4258828080 Registration Service Provider: DBMS Veri. Sign, dbms-support@verisign. com 800 -579 -2848 x 4 Please contact DBMS Veri. Sign for domain updates, DNS/Nameserver changes, and general domain support questions. Registrar of Record: TUCOWS, INC. Record last updated on 27 -Aug-2006. Record expires on 03 -May-2014. Record created on 02 -May-1991. Domain servers in listed order: NS 3. MSFT. NET 213. 199. 144. 151 NS 1. MSFT. NET 207. 68. 160. 190 NS 4. MSFT. NET 207. 46. 66. 126 NS 2. MSFT. NET 65. 54. 240. 126 NS 5. MSFT. NET 65. 55. 238. 126
 Hacking Networks Reconnaissance Stage War Driving: Can I find a wireless network? War Dialing: Can I find a modem to connect to? Network Scanning: What IP addresses, open ports, applications exist? Protocol Sniffing: What is being sent over communications lines?
Hacking Networks Reconnaissance Stage War Driving: Can I find a wireless network? War Dialing: Can I find a modem to connect to? Network Scanning: What IP addresses, open ports, applications exist? Protocol Sniffing: What is being sent over communications lines?
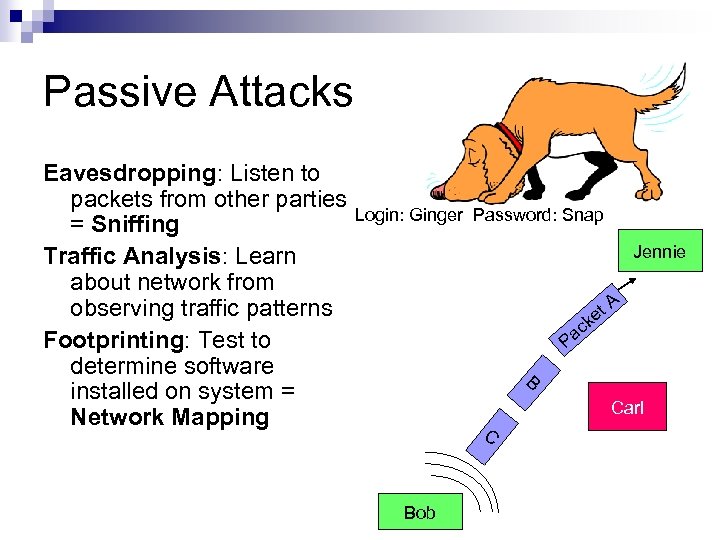 Passive Attacks Eavesdropping: Listen to packets from other parties Login: Ginger Password: Snap = Sniffing Jennie Traffic Analysis: Learn about network from A observing traffic patterns et k ac Footprinting: Test to P determine software B installed on system = Carl Network Mapping C Bob
Passive Attacks Eavesdropping: Listen to packets from other parties Login: Ginger Password: Snap = Sniffing Jennie Traffic Analysis: Learn about network from A observing traffic patterns et k ac Footprinting: Test to P determine software B installed on system = Carl Network Mapping C Bob
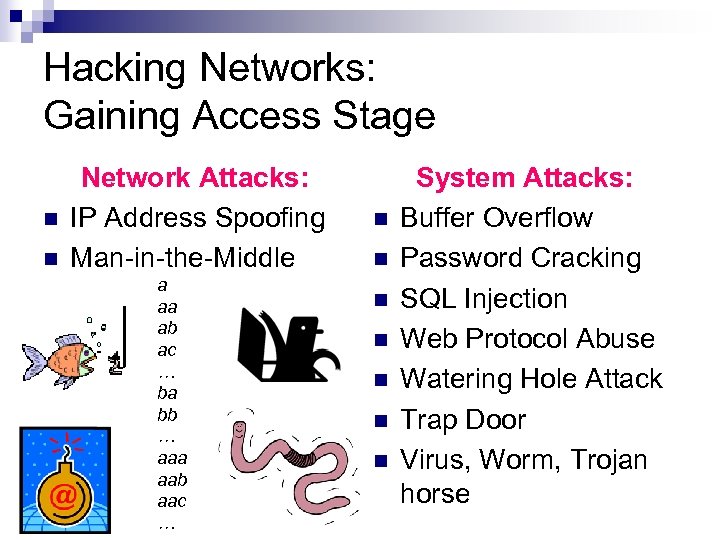 Hacking Networks: Gaining Access Stage n n Network Attacks: IP Address Spoofing Man-in-the-Middle a aa ab ac … ba bb … aaa aab aac … n n n n System Attacks: Buffer Overflow Password Cracking SQL Injection Web Protocol Abuse Watering Hole Attack Trap Door Virus, Worm, Trojan horse
Hacking Networks: Gaining Access Stage n n Network Attacks: IP Address Spoofing Man-in-the-Middle a aa ab ac … ba bb … aaa aab aac … n n n n System Attacks: Buffer Overflow Password Cracking SQL Injection Web Protocol Abuse Watering Hole Attack Trap Door Virus, Worm, Trojan horse
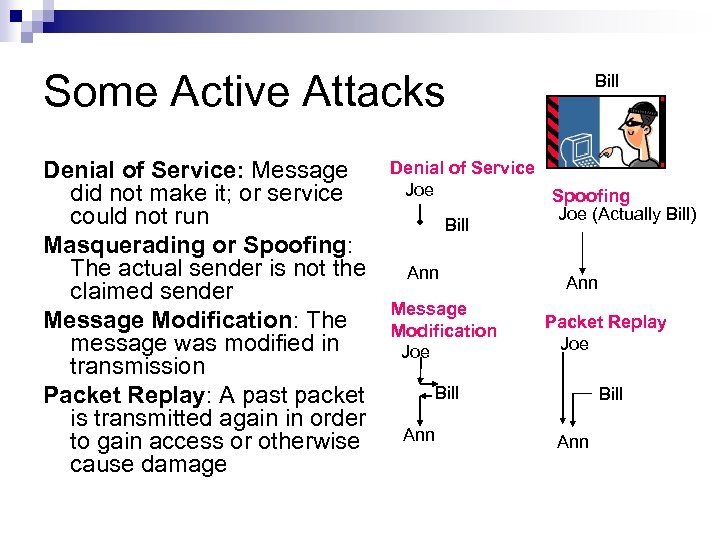 Some Active Attacks Denial of Service: Message did not make it; or service could not run Masquerading or Spoofing: The actual sender is not the claimed sender Message Modification: The message was modified in transmission Packet Replay: A past packet is transmitted again in order to gain access or otherwise cause damage Bill Denial of Service Joe Spoofing Joe (Actually Bill) Bill Ann Message Modification Joe Ann Packet Replay Joe Bill Ann
Some Active Attacks Denial of Service: Message did not make it; or service could not run Masquerading or Spoofing: The actual sender is not the claimed sender Message Modification: The message was modified in transmission Packet Replay: A past packet is transmitted again in order to gain access or otherwise cause damage Bill Denial of Service Joe Spoofing Joe (Actually Bill) Bill Ann Message Modification Joe Ann Packet Replay Joe Bill Ann
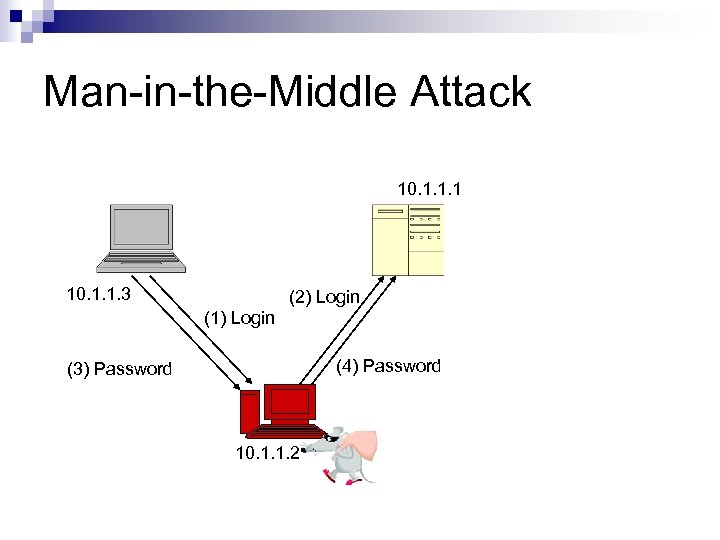 Man-in-the-Middle Attack 10. 1. 1. 1 10. 1. 1. 3 (2) Login (1) Login (4) Password (3) Password 10. 1. 1. 2
Man-in-the-Middle Attack 10. 1. 1. 1 10. 1. 1. 3 (2) Login (1) Login (4) Password (3) Password 10. 1. 1. 2
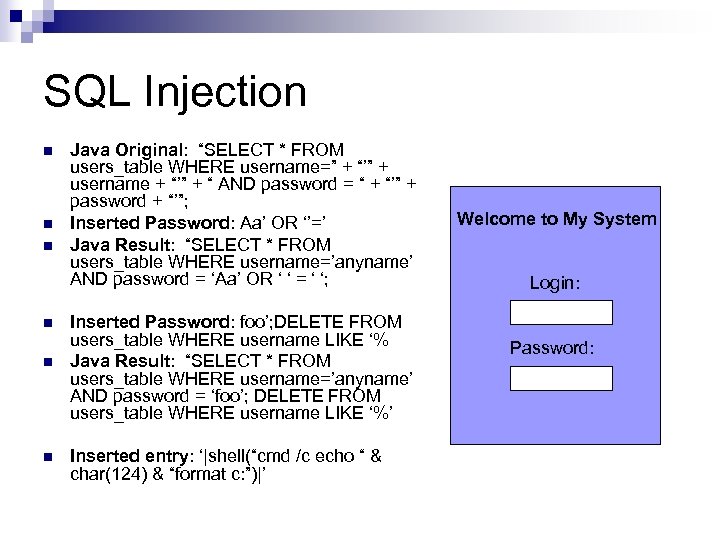 SQL Injection n n n Java Original: “SELECT * FROM users_table WHERE username=” + “’” + username + “’” + “ AND password = “ + “’” + password + “’”; Inserted Password: Aa’ OR ‘’=’ Java Result: “SELECT * FROM users_table WHERE username=’anyname’ AND password = ‘Aa’ OR ‘ ‘ = ‘ ‘; Inserted Password: foo’; DELETE FROM users_table WHERE username LIKE ‘% Java Result: “SELECT * FROM users_table WHERE username=’anyname’ AND password = ‘foo’; DELETE FROM users_table WHERE username LIKE ‘%’ Inserted entry: ‘|shell(“cmd /c echo “ & char(124) & “format c: ”)|’ Welcome to My System Login: Password:
SQL Injection n n n Java Original: “SELECT * FROM users_table WHERE username=” + “’” + username + “’” + “ AND password = “ + “’” + password + “’”; Inserted Password: Aa’ OR ‘’=’ Java Result: “SELECT * FROM users_table WHERE username=’anyname’ AND password = ‘Aa’ OR ‘ ‘ = ‘ ‘; Inserted Password: foo’; DELETE FROM users_table WHERE username LIKE ‘% Java Result: “SELECT * FROM users_table WHERE username=’anyname’ AND password = ‘foo’; DELETE FROM users_table WHERE username LIKE ‘%’ Inserted entry: ‘|shell(“cmd /c echo “ & char(124) & “format c: ”)|’ Welcome to My System Login: Password:
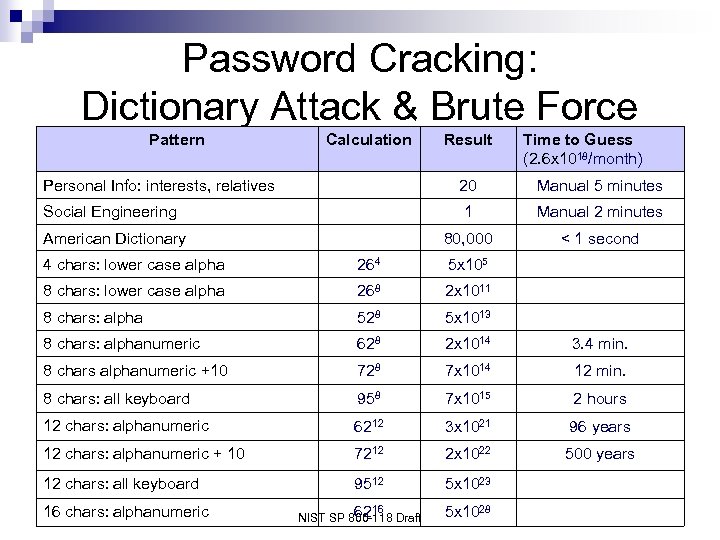 Password Cracking: Dictionary Attack & Brute Force Pattern Calculation Result Time to Guess (2. 6 x 1018/month) Personal Info: interests, relatives 20 Manual 5 minutes Social Engineering 1 Manual 2 minutes 80, 000 < 1 second American Dictionary 4 chars: lower case alpha 264 5 x 105 8 chars: lower case alpha 268 2 x 1011 8 chars: alpha 528 5 x 1013 8 chars: alphanumeric 628 2 x 1014 3. 4 min. 8 chars alphanumeric +10 728 7 x 1014 12 min. 8 chars: all keyboard 958 7 x 1015 2 hours 12 chars: alphanumeric 6212 3 x 1021 96 years 12 chars: alphanumeric + 10 7212 2 x 1022 500 years 12 chars: all keyboard 9512 5 x 1023 16 chars: alphanumeric 62 NIST SP 800 -118 Draft 16 5 x 1028
Password Cracking: Dictionary Attack & Brute Force Pattern Calculation Result Time to Guess (2. 6 x 1018/month) Personal Info: interests, relatives 20 Manual 5 minutes Social Engineering 1 Manual 2 minutes 80, 000 < 1 second American Dictionary 4 chars: lower case alpha 264 5 x 105 8 chars: lower case alpha 268 2 x 1011 8 chars: alpha 528 5 x 1013 8 chars: alphanumeric 628 2 x 1014 3. 4 min. 8 chars alphanumeric +10 728 7 x 1014 12 min. 8 chars: all keyboard 958 7 x 1015 2 hours 12 chars: alphanumeric 6212 3 x 1021 96 years 12 chars: alphanumeric + 10 7212 2 x 1022 500 years 12 chars: all keyboard 9512 5 x 1023 16 chars: alphanumeric 62 NIST SP 800 -118 Draft 16 5 x 1028
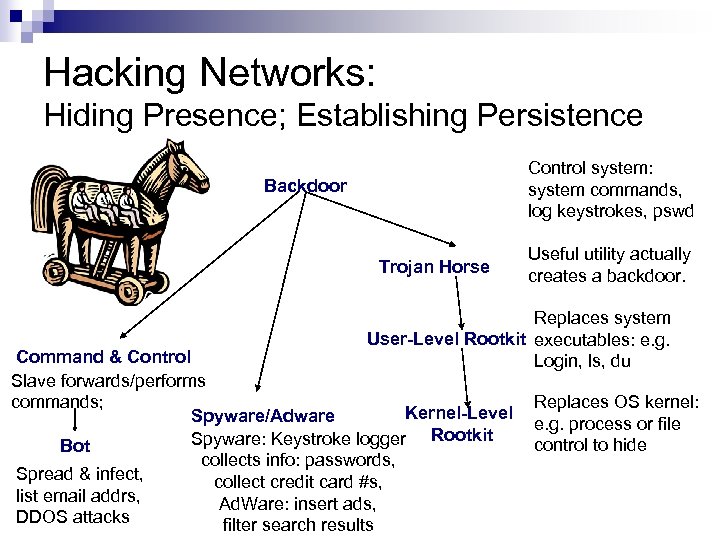 Hacking Networks: Hiding Presence; Establishing Persistence Control system: system commands, log keystrokes, pswd Backdoor Trojan Horse Useful utility actually creates a backdoor. Replaces system User-Level Rootkit executables: e. g. Login, ls, du Command & Control Slave forwards/performs Replaces OS kernel: commands; Kernel-Level Spyware/Adware e. g. process or file Rootkit Spyware: Keystroke logger control to hide Bot collects info: passwords, Spread & infect, collect credit card #s, list email addrs, Ad. Ware: insert ads, DDOS attacks filter search results
Hacking Networks: Hiding Presence; Establishing Persistence Control system: system commands, log keystrokes, pswd Backdoor Trojan Horse Useful utility actually creates a backdoor. Replaces system User-Level Rootkit executables: e. g. Login, ls, du Command & Control Slave forwards/performs Replaces OS kernel: commands; Kernel-Level Spyware/Adware e. g. process or file Rootkit Spyware: Keystroke logger control to hide Bot collects info: passwords, Spread & infect, collect credit card #s, list email addrs, Ad. Ware: insert ads, DDOS attacks filter search results
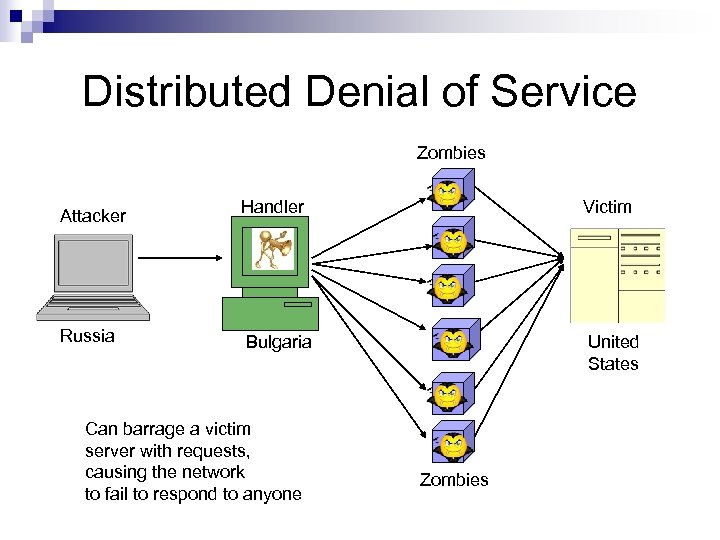 Distributed Denial of Service Zombies Attacker Handler Victim Russia Bulgaria United States Can barrage a victim server with requests, causing the network to fail to respond to anyone Zombies
Distributed Denial of Service Zombies Attacker Handler Victim Russia Bulgaria United States Can barrage a victim server with requests, causing the network to fail to respond to anyone Zombies
 Question An attack where multiple computers send connection packets to a server simultaneously to slow the firewall is known as: 1. Spoofing 2. DDOS 3. Worm 4. Rootkit
Question An attack where multiple computers send connection packets to a server simultaneously to slow the firewall is known as: 1. Spoofing 2. DDOS 3. Worm 4. Rootkit
 Question A man in the middle attack is implementing which additional type of attack: 1. Spoofing 2. Do. S 3. Phishing 4. Pharming
Question A man in the middle attack is implementing which additional type of attack: 1. Spoofing 2. Do. S 3. Phishing 4. Pharming
 Network Security Network Defense Encryption
Network Security Network Defense Encryption
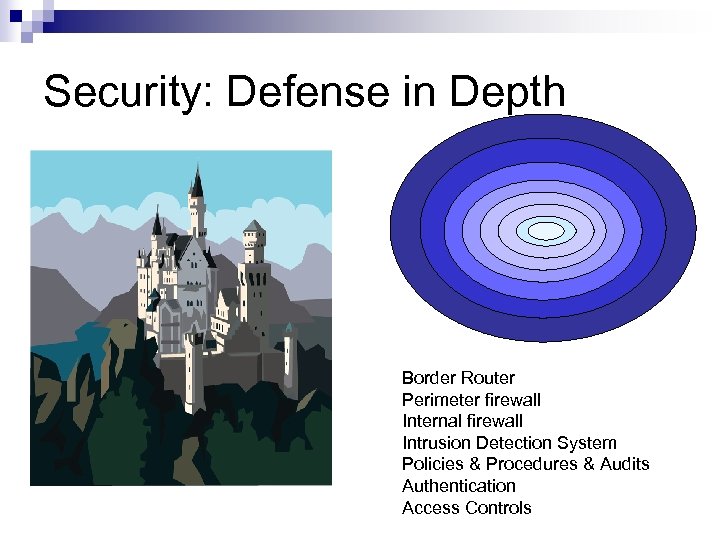 Security: Defense in Depth Border Router Perimeter firewall Internal firewall Intrusion Detection System Policies & Procedures & Audits Authentication Access Controls
Security: Defense in Depth Border Router Perimeter firewall Internal firewall Intrusion Detection System Policies & Procedures & Audits Authentication Access Controls
 Bastion Host Computer fortified against attackers n Applications turned off n Operating system patched n Security configuration tightened
Bastion Host Computer fortified against attackers n Applications turned off n Operating system patched n Security configuration tightened
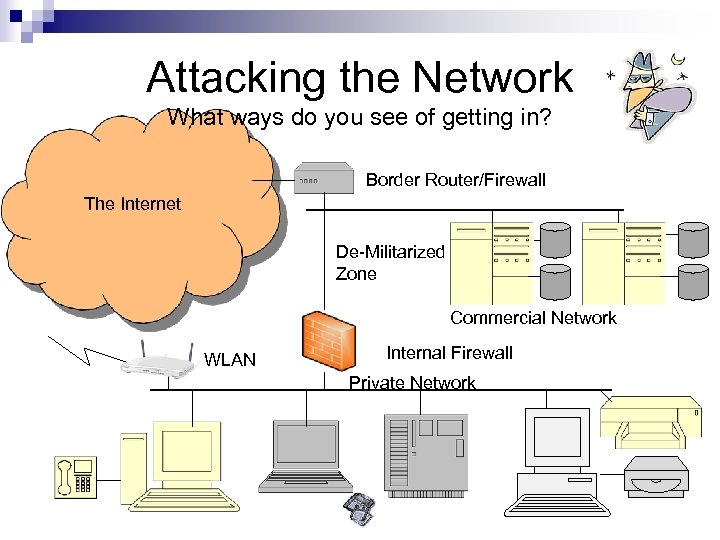 Attacking the Network What ways do you see of getting in? Border Router/Firewall The Internet De-Militarized Zone Commercial Network WLAN Internal Firewall Private Network
Attacking the Network What ways do you see of getting in? Border Router/Firewall The Internet De-Militarized Zone Commercial Network WLAN Internal Firewall Private Network
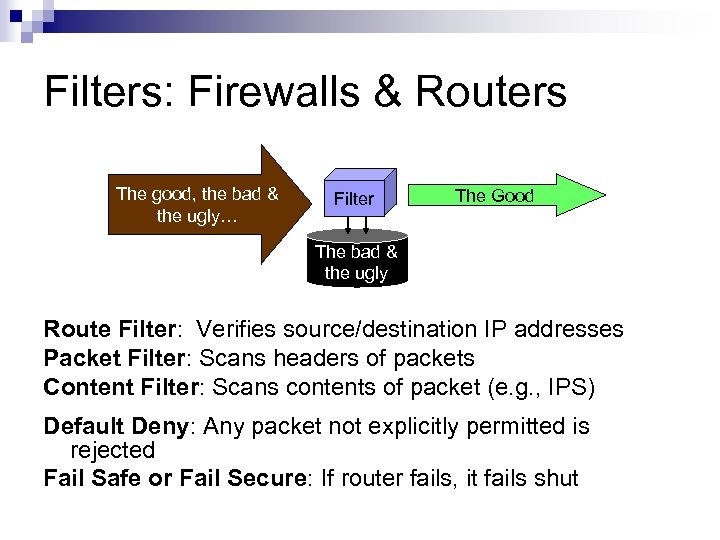 Filters: Firewalls & Routers The good, the bad & the ugly… Filter The Good The bad & the ugly Route Filter: Verifies source/destination IP addresses Packet Filter: Scans headers of packets Content Filter: Scans contents of packet (e. g. , IPS) Default Deny: Any packet not explicitly permitted is rejected Fail Safe or Fail Secure: If router fails, it fails shut
Filters: Firewalls & Routers The good, the bad & the ugly… Filter The Good The bad & the ugly Route Filter: Verifies source/destination IP addresses Packet Filter: Scans headers of packets Content Filter: Scans contents of packet (e. g. , IPS) Default Deny: Any packet not explicitly permitted is rejected Fail Safe or Fail Secure: If router fails, it fails shut
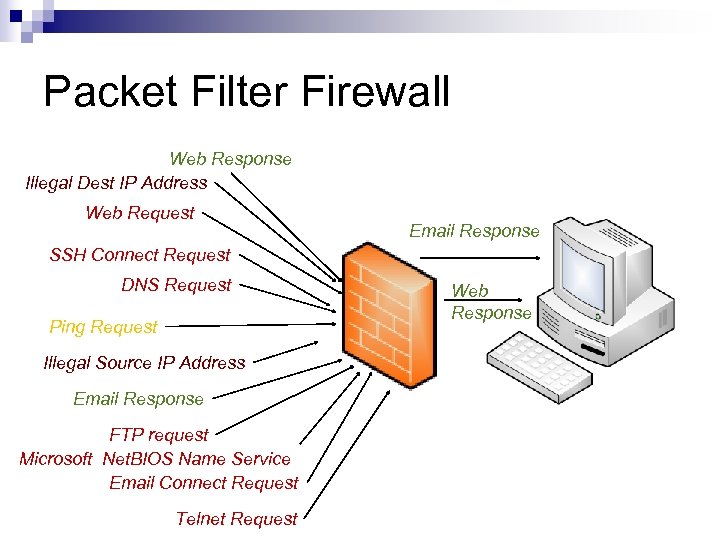 Packet Filter Firewall Web Response Illegal Dest IP Address Web Request Email Response SSH Connect Request DNS Request Ping Request Illegal Source IP Address Email Response FTP request Microsoft Net. BIOS Name Service Email Connect Request Telnet Request Web Response
Packet Filter Firewall Web Response Illegal Dest IP Address Web Request Email Response SSH Connect Request DNS Request Ping Request Illegal Source IP Address Email Response FTP request Microsoft Net. BIOS Name Service Email Connect Request Telnet Request Web Response
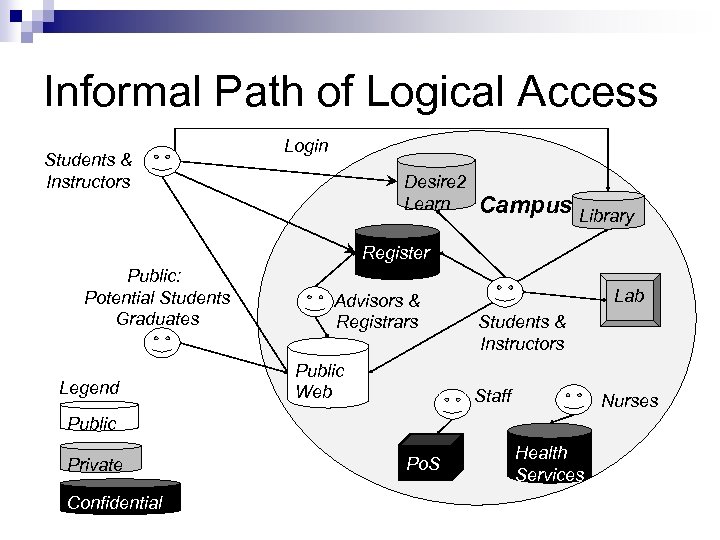 Informal Path of Logical Access Students & Instructors Login Desire 2 Learn Campus Library Register Public: Potential Students Graduates Legend Advisors & Registrars Public Web Lab Students & Instructors Staff Nurses Public Private Confidential Po. S Health Services
Informal Path of Logical Access Students & Instructors Login Desire 2 Learn Campus Library Register Public: Potential Students Graduates Legend Advisors & Registrars Public Web Lab Students & Instructors Staff Nurses Public Private Confidential Po. S Health Services
 Step 1: Determine Services: Who, What, Where? Workbook Service (e. g. , web, sales database) Source (e. g. , home, world, local computer) Destination (local server, home, world, etc. ) Registration, Desire 2 Learn Students and Instructors: Anywhere in the World Computer Service Servers Registration Registrars and Advisers: On campus students and staff. Off-campus requires login Computer Service Servers Health Services On campus: nurses office Computer Service Servers External (Internet) web services On campus: Campus labs, dorms, Anywhere in the world faculty offices Library databases Specific off-site library facilities
Step 1: Determine Services: Who, What, Where? Workbook Service (e. g. , web, sales database) Source (e. g. , home, world, local computer) Destination (local server, home, world, etc. ) Registration, Desire 2 Learn Students and Instructors: Anywhere in the World Computer Service Servers Registration Registrars and Advisers: On campus students and staff. Off-campus requires login Computer Service Servers Health Services On campus: nurses office Computer Service Servers External (Internet) web services On campus: Campus labs, dorms, Anywhere in the world faculty offices Library databases Specific off-site library facilities
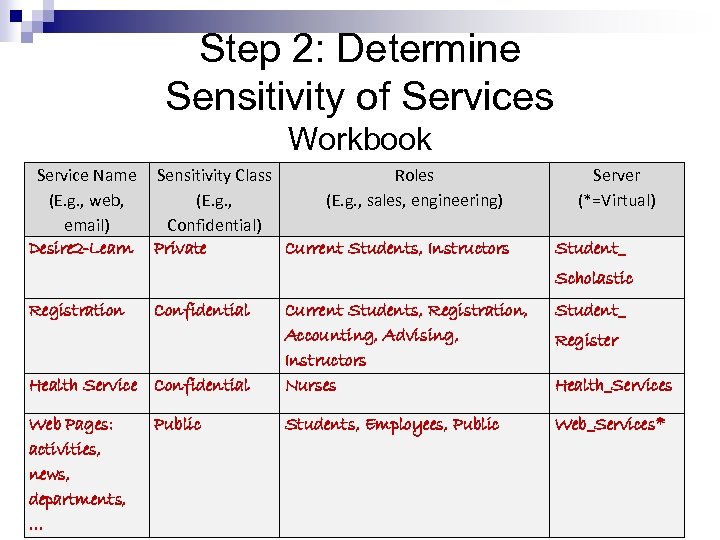 Step 2: Determine Sensitivity of Services Workbook Service Name (E. g. , web, email) Desire 2 -Learn Sensitivity Class Roles (E. g. , sales, engineering) Confidential) Private Current Students, Instructors Server (*=Virtual) Student_ Scholastic Registration Confidential Health Service Confidential Web Pages: activities, news, departments, … Public Current Students, Registration, Accounting, Advising, Instructors Nurses Student_ Students, Employees, Public Web_Services* Register Health_Services
Step 2: Determine Sensitivity of Services Workbook Service Name (E. g. , web, email) Desire 2 -Learn Sensitivity Class Roles (E. g. , sales, engineering) Confidential) Private Current Students, Instructors Server (*=Virtual) Student_ Scholastic Registration Confidential Health Service Confidential Web Pages: activities, news, departments, … Public Current Students, Registration, Accounting, Advising, Instructors Nurses Student_ Students, Employees, Public Web_Services* Register Health_Services
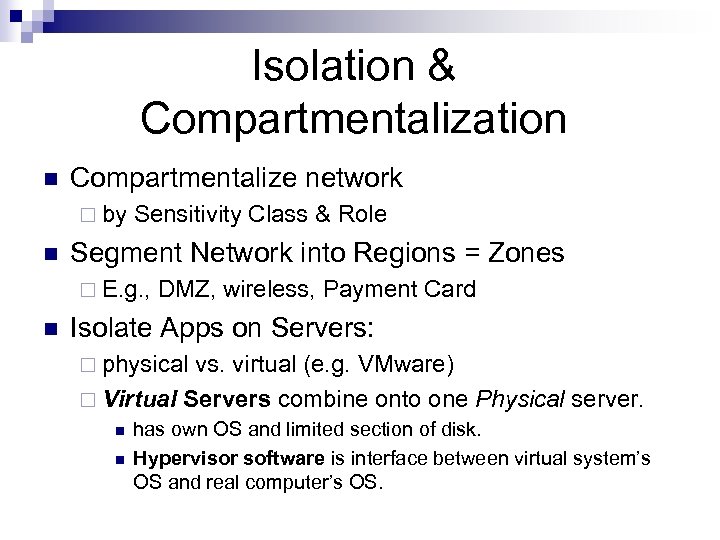 Isolation & Compartmentalization n Compartmentalize network ¨ by Sensitivity Class & Role n Segment Network into Regions = Zones ¨ E. g. , DMZ, wireless, Payment Card n Isolate Apps on Servers: ¨ physical vs. virtual (e. g. VMware) ¨ Virtual n n Servers combine onto one Physical server. has own OS and limited section of disk. Hypervisor software is interface between virtual system’s OS and real computer’s OS.
Isolation & Compartmentalization n Compartmentalize network ¨ by Sensitivity Class & Role n Segment Network into Regions = Zones ¨ E. g. , DMZ, wireless, Payment Card n Isolate Apps on Servers: ¨ physical vs. virtual (e. g. VMware) ¨ Virtual n n Servers combine onto one Physical server. has own OS and limited section of disk. Hypervisor software is interface between virtual system’s OS and real computer’s OS.
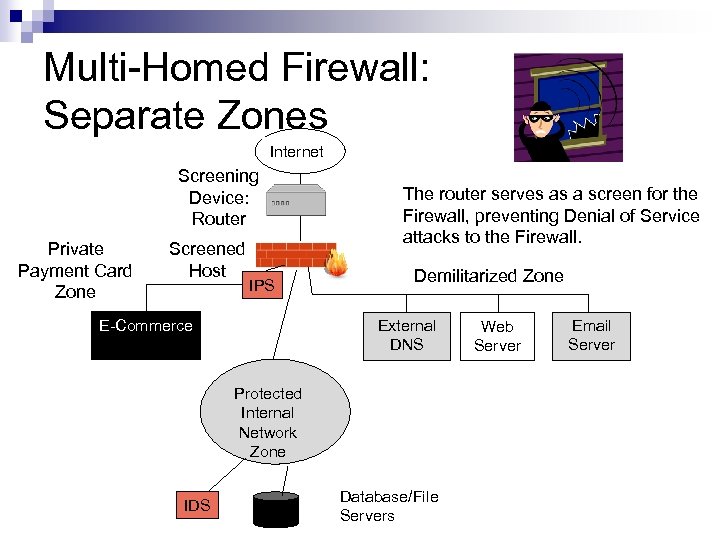 Multi-Homed Firewall: Separate Zones Internet Screening Device: Router Private Payment Card Zone Screened Host IPS E-Commerce The router serves as a screen for the Firewall, preventing Denial of Service attacks to the Firewall. Demilitarized Zone External DNS Protected Internal Network Zone IDS Database/File Servers Web Server Email Server
Multi-Homed Firewall: Separate Zones Internet Screening Device: Router Private Payment Card Zone Screened Host IPS E-Commerce The router serves as a screen for the Firewall, preventing Denial of Service attacks to the Firewall. Demilitarized Zone External DNS Protected Internal Network Zone IDS Database/File Servers Web Server Email Server
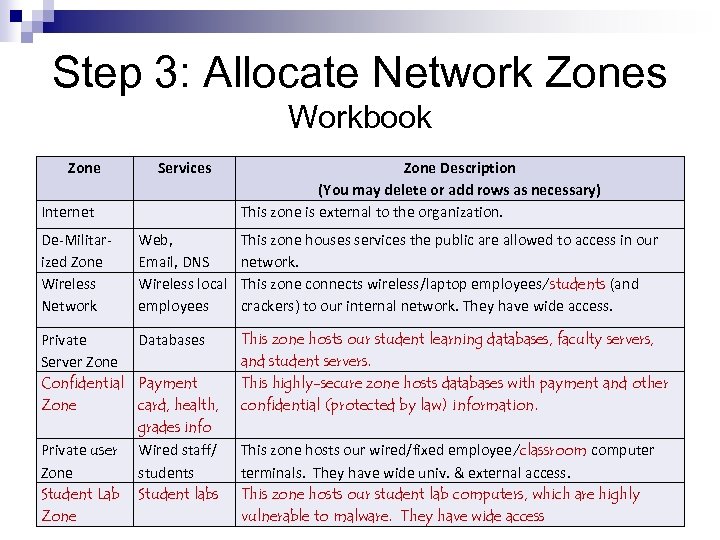 Step 3: Allocate Network Zones Workbook Zone Services Internet Zone Description (You may delete or add rows as necessary) This zone is external to the organization. De-Militarized Zone Wireless Network Web, Email, DNS Wireless local employees This zone houses services the public are allowed to access in our network. This zone connects wireless/laptop employees/students (and crackers) to our internal network. They have wide access. Private Databases Server Zone Confidential Payment Zone card, health, grades info Private user Wired staff/ Zone students Student Lab Student labs Zone This zone hosts our student learning databases, faculty servers, and student servers. This highly-secure zone hosts databases with payment and other confidential (protected by law) information. This zone hosts our wired/fixed employee/classroom computer terminals. They have wide univ. & external access. This zone hosts our student lab computers, which are highly vulnerable to malware. They have wide access
Step 3: Allocate Network Zones Workbook Zone Services Internet Zone Description (You may delete or add rows as necessary) This zone is external to the organization. De-Militarized Zone Wireless Network Web, Email, DNS Wireless local employees This zone houses services the public are allowed to access in our network. This zone connects wireless/laptop employees/students (and crackers) to our internal network. They have wide access. Private Databases Server Zone Confidential Payment Zone card, health, grades info Private user Wired staff/ Zone students Student Lab Student labs Zone This zone hosts our student learning databases, faculty servers, and student servers. This highly-secure zone hosts databases with payment and other confidential (protected by law) information. This zone hosts our wired/fixed employee/classroom computer terminals. They have wide univ. & external access. This zone hosts our student lab computers, which are highly vulnerable to malware. They have wide access
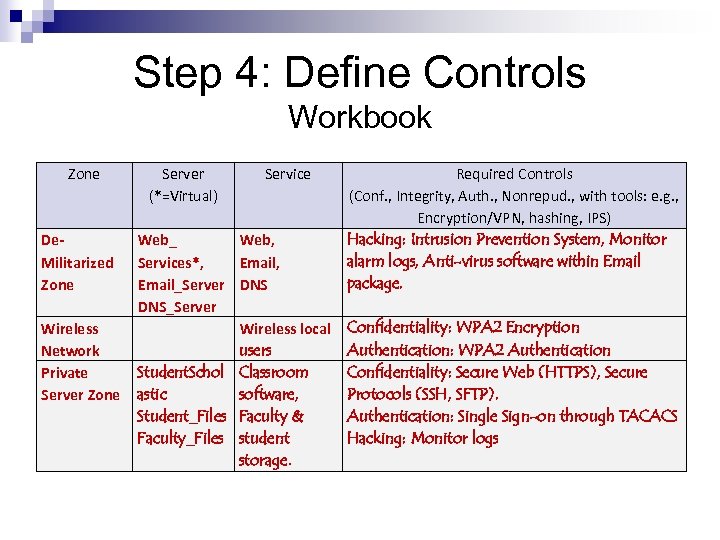 Step 4: Define Controls Workbook Zone De. Militarized Zone Wireless Network Private Server Zone Server (*=Virtual) Web_ Services*, Email_Server DNS_Server Service Web, Email, DNS Wireless local users Student. Schol Classroom astic software, Student_Files Faculty & Faculty_Files student storage. Required Controls (Conf. , Integrity, Auth. , Nonrepud. , with tools: e. g. , Encryption/VPN, hashing, IPS) Hacking: Intrusion Prevention System, Monitor alarm logs, Anti-virus software within Email package. Confidentiality: WPA 2 Encryption Authentication: WPA 2 Authentication Confidentiality: Secure Web (HTTPS), Secure Protocols (SSH, SFTP). Authentication: Single Sign-on through TACACS Hacking: Monitor logs
Step 4: Define Controls Workbook Zone De. Militarized Zone Wireless Network Private Server Zone Server (*=Virtual) Web_ Services*, Email_Server DNS_Server Service Web, Email, DNS Wireless local users Student. Schol Classroom astic software, Student_Files Faculty & Faculty_Files student storage. Required Controls (Conf. , Integrity, Auth. , Nonrepud. , with tools: e. g. , Encryption/VPN, hashing, IPS) Hacking: Intrusion Prevention System, Monitor alarm logs, Anti-virus software within Email package. Confidentiality: WPA 2 Encryption Authentication: WPA 2 Authentication Confidentiality: Secure Web (HTTPS), Secure Protocols (SSH, SFTP). Authentication: Single Sign-on through TACACS Hacking: Monitor logs
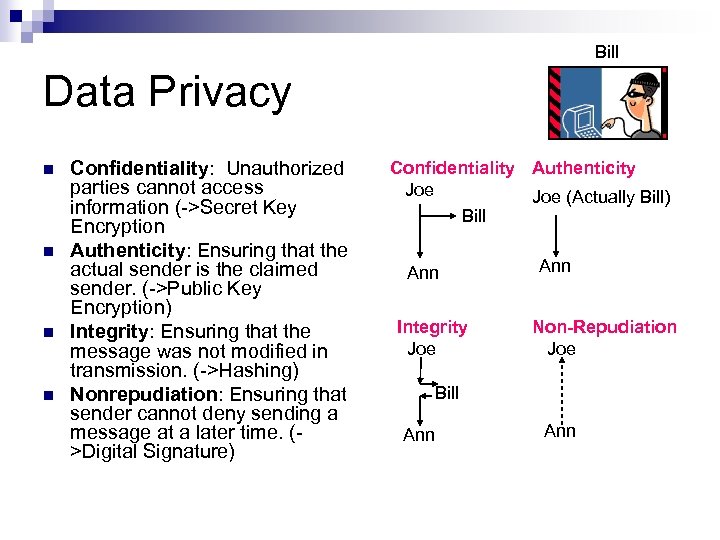 Bill Data Privacy n n Confidentiality: Unauthorized parties cannot access information (->Secret Key Encryption Authenticity: Ensuring that the actual sender is the claimed sender. (->Public Key Encryption) Integrity: Ensuring that the message was not modified in transmission. (->Hashing) Nonrepudiation: Ensuring that sender cannot deny sending a message at a later time. (>Digital Signature) Confidentiality Authenticity Joe (Actually Bill) Bill Ann Integrity Joe Ann Non-Repudiation Joe Bill Ann
Bill Data Privacy n n Confidentiality: Unauthorized parties cannot access information (->Secret Key Encryption Authenticity: Ensuring that the actual sender is the claimed sender. (->Public Key Encryption) Integrity: Ensuring that the message was not modified in transmission. (->Hashing) Nonrepudiation: Ensuring that sender cannot deny sending a message at a later time. (>Digital Signature) Confidentiality Authenticity Joe (Actually Bill) Bill Ann Integrity Joe Ann Non-Repudiation Joe Bill Ann
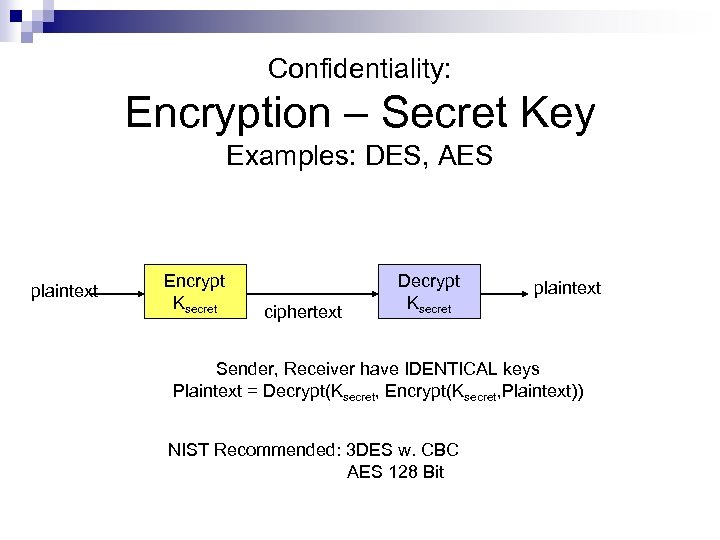 Confidentiality: Encryption – Secret Key Examples: DES, AES plaintext Encrypt Ksecret ciphertext Decrypt Ksecret plaintext Sender, Receiver have IDENTICAL keys Plaintext = Decrypt(Ksecret, Encrypt(Ksecret, Plaintext)) NIST Recommended: 3 DES w. CBC AES 128 Bit
Confidentiality: Encryption – Secret Key Examples: DES, AES plaintext Encrypt Ksecret ciphertext Decrypt Ksecret plaintext Sender, Receiver have IDENTICAL keys Plaintext = Decrypt(Ksecret, Encrypt(Ksecret, Plaintext)) NIST Recommended: 3 DES w. CBC AES 128 Bit
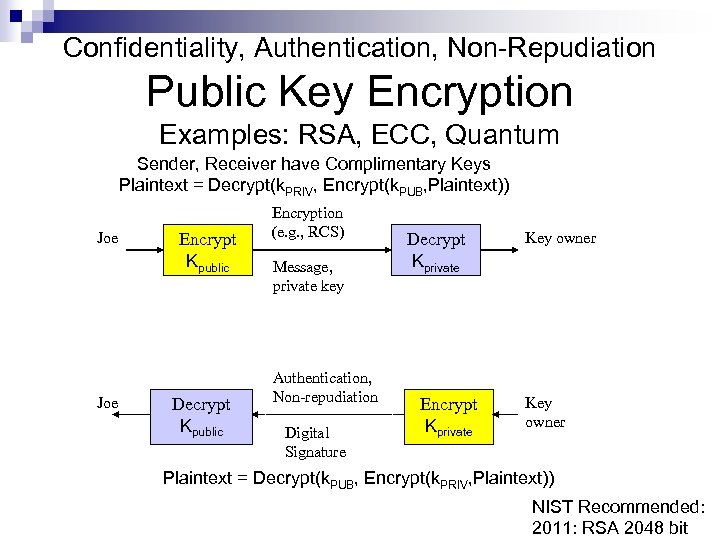 Confidentiality, Authentication, Non-Repudiation Public Key Encryption Examples: RSA, ECC, Quantum Sender, Receiver have Complimentary Keys Plaintext = Decrypt(k. PRIV, Encrypt(k. PUB, Plaintext)) Joe Encrypt Kpublic Decrypt Kpublic Encryption (e. g. , RCS) Message, private key Authentication, Non-repudiation Digital Signature Decrypt Kprivate Encrypt Kprivate Key owner Plaintext = Decrypt(k. PUB, Encrypt(k. PRIV, Plaintext)) NIST Recommended: 2011: RSA 2048 bit
Confidentiality, Authentication, Non-Repudiation Public Key Encryption Examples: RSA, ECC, Quantum Sender, Receiver have Complimentary Keys Plaintext = Decrypt(k. PRIV, Encrypt(k. PUB, Plaintext)) Joe Encrypt Kpublic Decrypt Kpublic Encryption (e. g. , RCS) Message, private key Authentication, Non-repudiation Digital Signature Decrypt Kprivate Encrypt Kprivate Key owner Plaintext = Decrypt(k. PUB, Encrypt(k. PRIV, Plaintext)) NIST Recommended: 2011: RSA 2048 bit
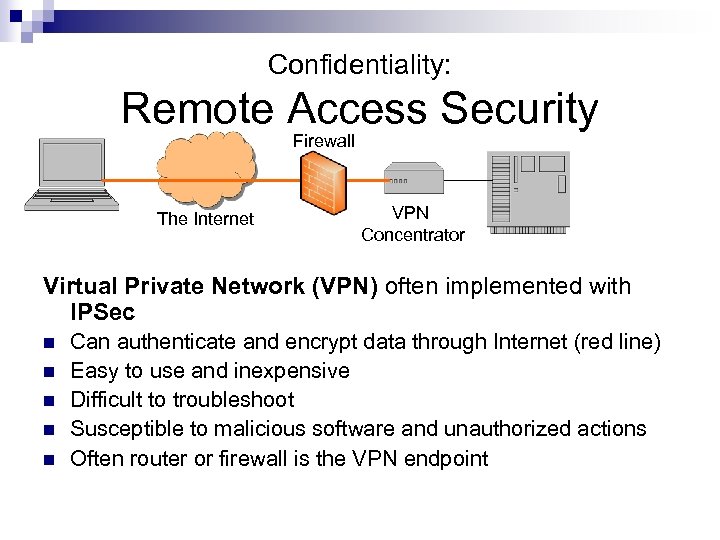 Confidentiality: Remote Access Security Firewall The Internet VPN Concentrator Virtual Private Network (VPN) often implemented with IPSec n n n Can authenticate and encrypt data through Internet (red line) Easy to use and inexpensive Difficult to troubleshoot Susceptible to malicious software and unauthorized actions Often router or firewall is the VPN endpoint
Confidentiality: Remote Access Security Firewall The Internet VPN Concentrator Virtual Private Network (VPN) often implemented with IPSec n n n Can authenticate and encrypt data through Internet (red line) Easy to use and inexpensive Difficult to troubleshoot Susceptible to malicious software and unauthorized actions Often router or firewall is the VPN endpoint
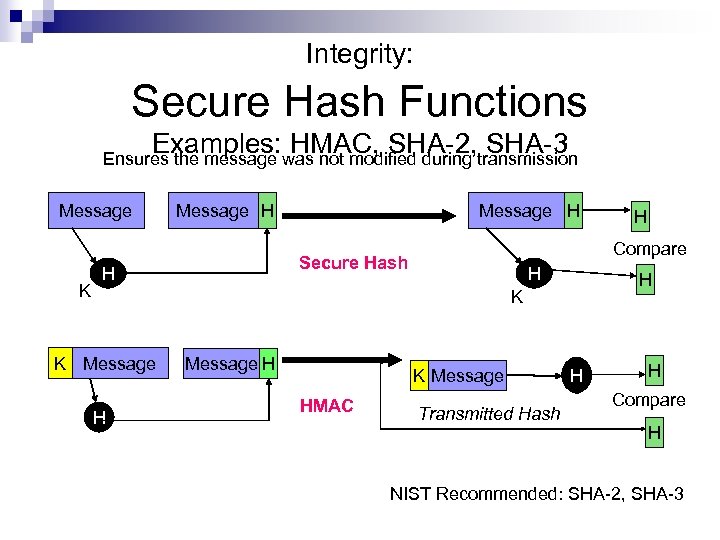 Integrity: Secure Hash Functions Examples: HMAC, SHA-2, SHA-3 Ensures the message was not modified during transmission Message K Message H Compare Secure Hash H H H K K Message HMAC H Transmitted Hash H H Compare H NIST Recommended: SHA-2, SHA-3
Integrity: Secure Hash Functions Examples: HMAC, SHA-2, SHA-3 Ensures the message was not modified during transmission Message K Message H Compare Secure Hash H H H K K Message HMAC H Transmitted Hash H H Compare H NIST Recommended: SHA-2, SHA-3
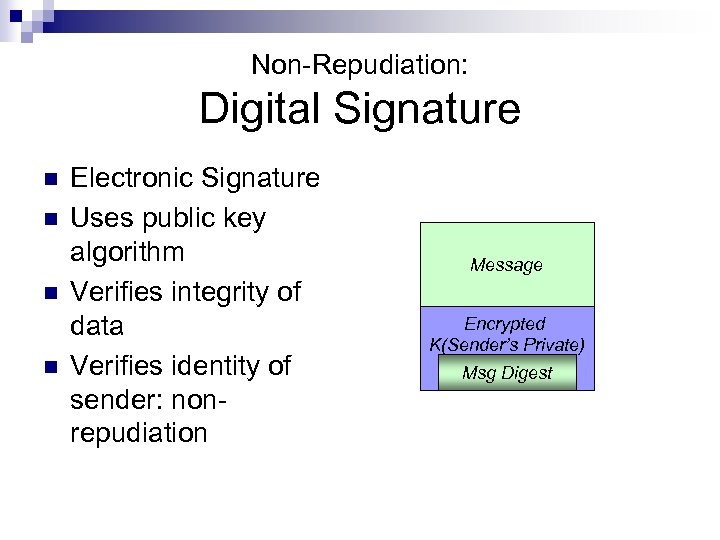 Non-Repudiation: Digital Signature n n Electronic Signature Uses public key algorithm Verifies integrity of data Verifies identity of sender: nonrepudiation Message Encrypted K(Sender’s Private) Msg Digest
Non-Repudiation: Digital Signature n n Electronic Signature Uses public key algorithm Verifies integrity of data Verifies identity of sender: nonrepudiation Message Encrypted K(Sender’s Private) Msg Digest
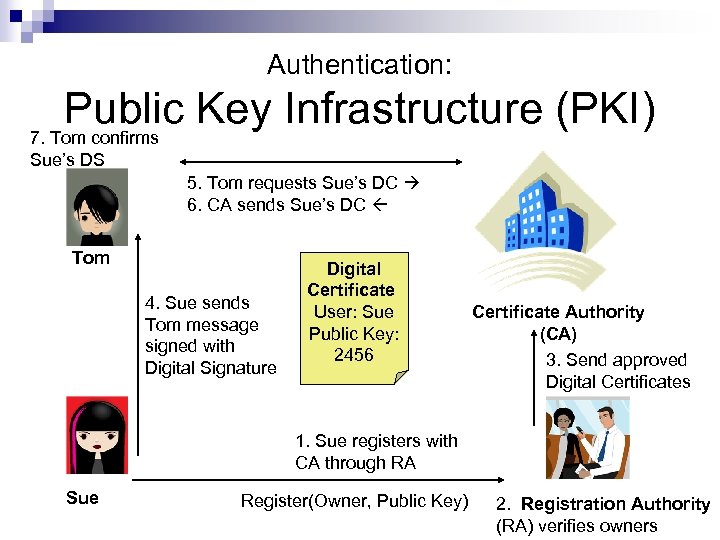 Authentication: Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) 7. Tom confirms Sue’s DS 5. Tom requests Sue’s DC 6. CA sends Sue’s DC Tom 4. Sue sends Tom message signed with Digital Signature Digital Certificate User: Sue Public Key: 2456 Certificate Authority (CA) 3. Send approved Digital Certificates 1. Sue registers with CA through RA Sue Register(Owner, Public Key) 2. Registration Authority (RA) verifies owners
Authentication: Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) 7. Tom confirms Sue’s DS 5. Tom requests Sue’s DC 6. CA sends Sue’s DC Tom 4. Sue sends Tom message signed with Digital Signature Digital Certificate User: Sue Public Key: 2456 Certificate Authority (CA) 3. Send approved Digital Certificates 1. Sue registers with CA through RA Sue Register(Owner, Public Key) 2. Registration Authority (RA) verifies owners
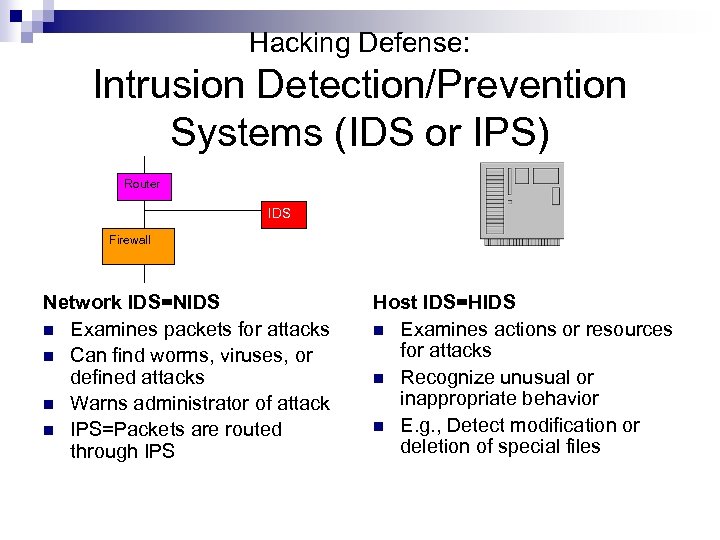 Hacking Defense: Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS or IPS) Router IDS Firewall Network IDS=NIDS n Examines packets for attacks n Can find worms, viruses, or defined attacks n Warns administrator of attack n IPS=Packets are routed through IPS Host IDS=HIDS n Examines actions or resources for attacks n Recognize unusual or inappropriate behavior n E. g. , Detect modification or deletion of special files
Hacking Defense: Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS or IPS) Router IDS Firewall Network IDS=NIDS n Examines packets for attacks n Can find worms, viruses, or defined attacks n Warns administrator of attack n IPS=Packets are routed through IPS Host IDS=HIDS n Examines actions or resources for attacks n Recognize unusual or inappropriate behavior n E. g. , Detect modification or deletion of special files
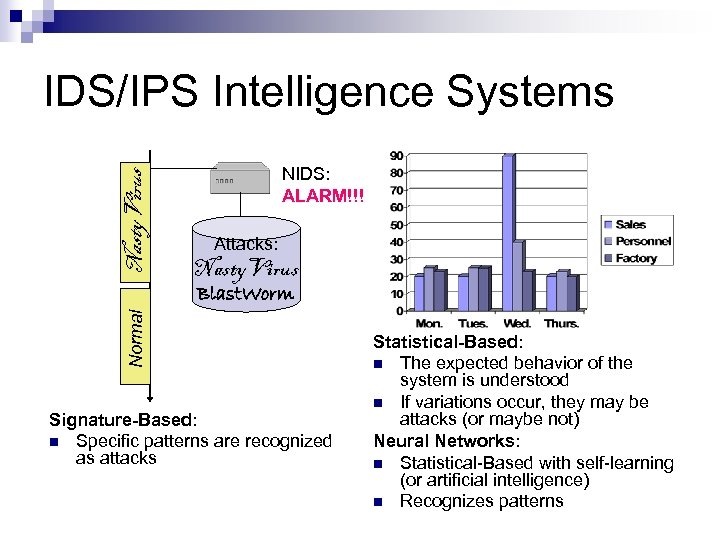 Nasty. Virus IDS/IPS Intelligence Systems NIDS: ALARM!!! Attacks: Nasty. Virus Normal Blast. Worm Signature-Based: n Specific patterns are recognized as attacks Statistical-Based: n The expected behavior of the system is understood n If variations occur, they may be attacks (or maybe not) Neural Networks: n Statistical-Based with self-learning (or artificial intelligence) n Recognizes patterns
Nasty. Virus IDS/IPS Intelligence Systems NIDS: ALARM!!! Attacks: Nasty. Virus Normal Blast. Worm Signature-Based: n Specific patterns are recognized as attacks Statistical-Based: n The expected behavior of the system is understood n If variations occur, they may be attacks (or maybe not) Neural Networks: n Statistical-Based with self-learning (or artificial intelligence) n Recognizes patterns
 Hacking Defense: Evaluating Applications n Unified Threat Management = Super. Firewall = firewall + IPS + anti-virus + VPN capabilities ¨ Concerns are redundancy and bandwidth. Blacklist= restrict access to particular web sites, e. g. , social and email sites n Whitelist= permit access to only a limited set of web sites. n
Hacking Defense: Evaluating Applications n Unified Threat Management = Super. Firewall = firewall + IPS + anti-virus + VPN capabilities ¨ Concerns are redundancy and bandwidth. Blacklist= restrict access to particular web sites, e. g. , social and email sites n Whitelist= permit access to only a limited set of web sites. n
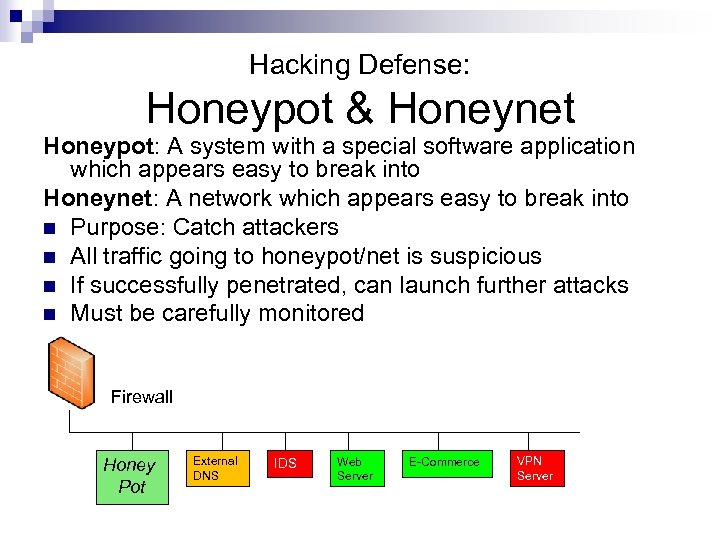 Hacking Defense: Honeypot & Honeynet Honeypot: A system with a special software application which appears easy to break into Honeynet: A network which appears easy to break into n Purpose: Catch attackers n All traffic going to honeypot/net is suspicious n If successfully penetrated, can launch further attacks n Must be carefully monitored Firewall Honey Pot External DNS IDS Web Server E-Commerce VPN Server
Hacking Defense: Honeypot & Honeynet Honeypot: A system with a special software application which appears easy to break into Honeynet: A network which appears easy to break into n Purpose: Catch attackers n All traffic going to honeypot/net is suspicious n If successfully penetrated, can launch further attacks n Must be carefully monitored Firewall Honey Pot External DNS IDS Web Server E-Commerce VPN Server
 Hacking Defense: Vulnerability Assessment n Scan servers, work stations, and control devices for vulnerabilities ¨ Open services, patching, configuration weaknesses n Testing controls for effectiveness ¨ Adherence to policy & standards n Penetration testing
Hacking Defense: Vulnerability Assessment n Scan servers, work stations, and control devices for vulnerabilities ¨ Open services, patching, configuration weaknesses n Testing controls for effectiveness ¨ Adherence to policy & standards n Penetration testing
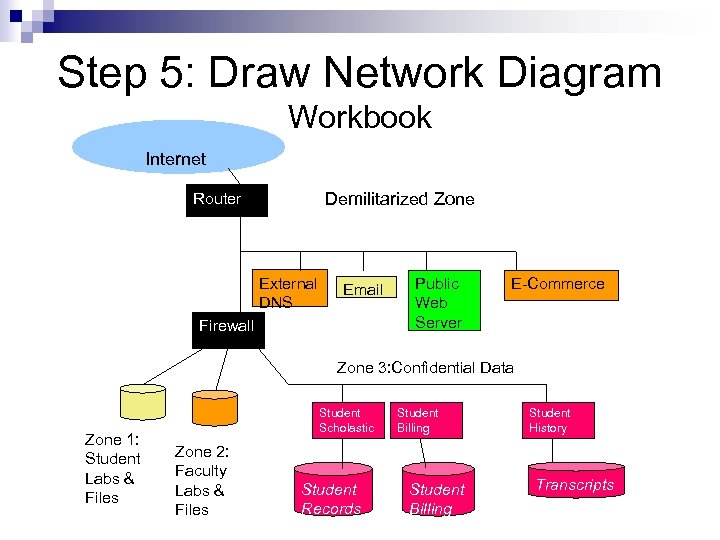 Step 5: Draw Network Diagram Workbook Internet Router Demilitarized Zone External DNS Email Firewall Public Web Server E-Commerce Zone 3: Confidential Data Zone 1: Student Labs & Files Student Scholastic Zone 2: Faculty Labs & Files Student Records Student Billing Student History Transcripts
Step 5: Draw Network Diagram Workbook Internet Router Demilitarized Zone External DNS Email Firewall Public Web Server E-Commerce Zone 3: Confidential Data Zone 1: Student Labs & Files Student Scholastic Zone 2: Faculty Labs & Files Student Records Student Billing Student History Transcripts
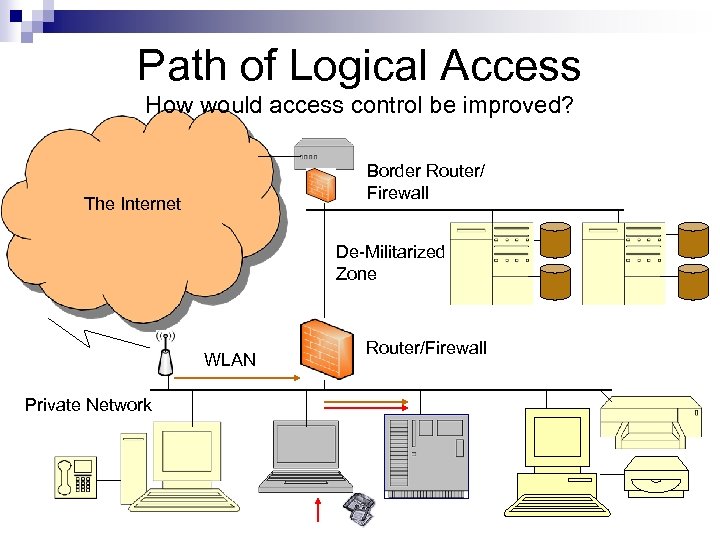 Path of Logical Access How would access control be improved? Border Router/ Firewall The Internet De-Militarized Zone WLAN Private Network Router/Firewall
Path of Logical Access How would access control be improved? Border Router/ Firewall The Internet De-Militarized Zone WLAN Private Network Router/Firewall
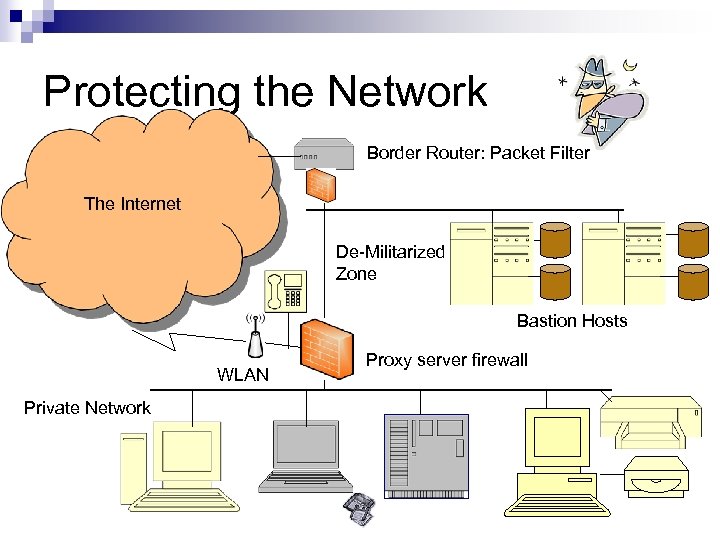 Protecting the Network Border Router: Packet Filter The Internet De-Militarized Zone Bastion Hosts WLAN Private Network Proxy server firewall
Protecting the Network Border Router: Packet Filter The Internet De-Militarized Zone Bastion Hosts WLAN Private Network Proxy server firewall
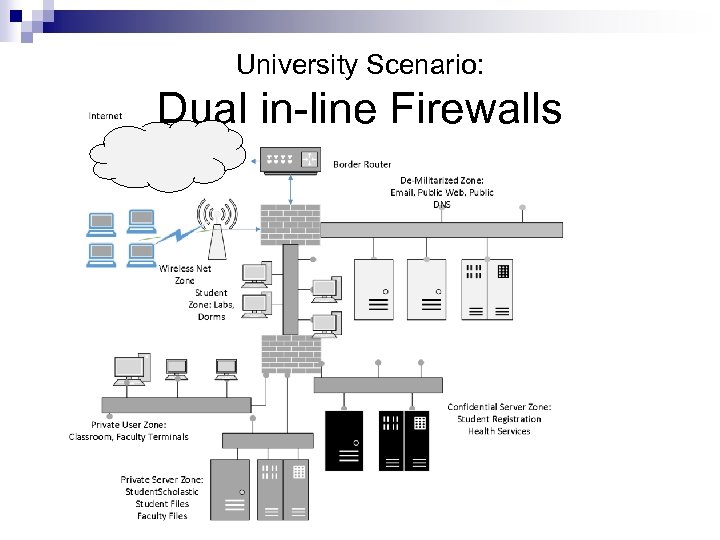 University Scenario: Dual in-line Firewalls
University Scenario: Dual in-line Firewalls
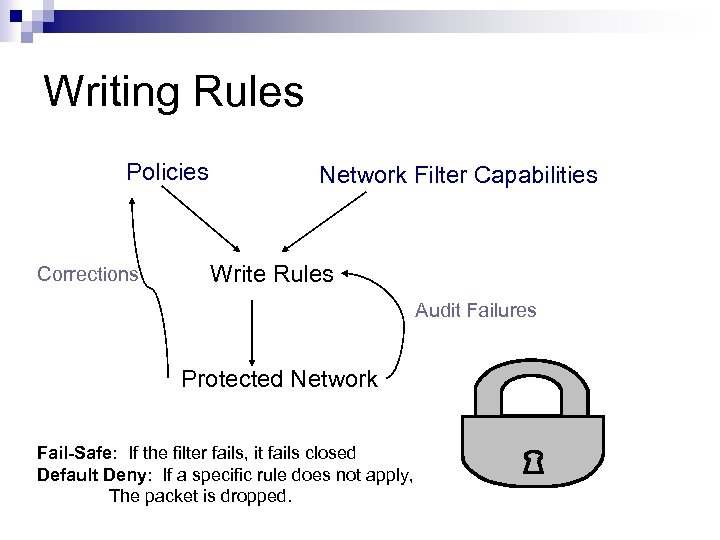 Writing Rules Policies Corrections Network Filter Capabilities Write Rules Audit Failures Protected Network Fail-Safe: If the filter fails, it fails closed Default Deny: If a specific rule does not apply, The packet is dropped.
Writing Rules Policies Corrections Network Filter Capabilities Write Rules Audit Failures Protected Network Fail-Safe: If the filter fails, it fails closed Default Deny: If a specific rule does not apply, The packet is dropped.
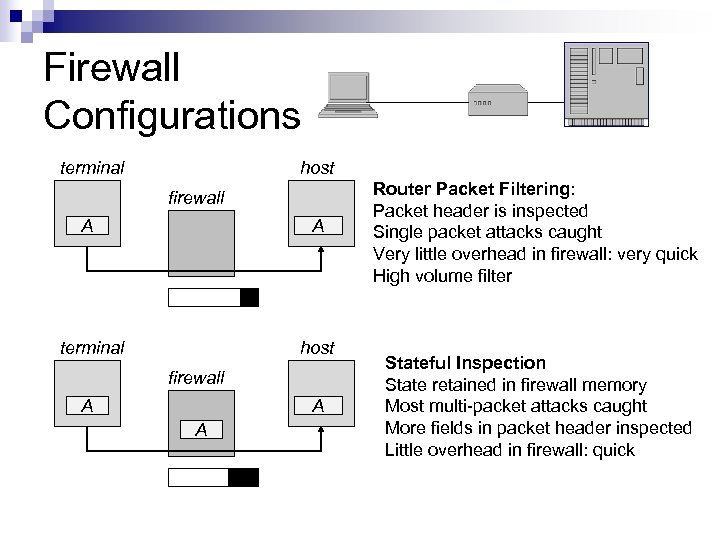 Firewall Configurations terminal host firewall A A A Router Packet Filtering: Packet header is inspected Single packet attacks caught Very little overhead in firewall: very quick High volume filter Stateful Inspection State retained in firewall memory Most multi-packet attacks caught More fields in packet header inspected Little overhead in firewall: quick
Firewall Configurations terminal host firewall A A A Router Packet Filtering: Packet header is inspected Single packet attacks caught Very little overhead in firewall: very quick High volume filter Stateful Inspection State retained in firewall memory Most multi-packet attacks caught More fields in packet header inspected Little overhead in firewall: quick
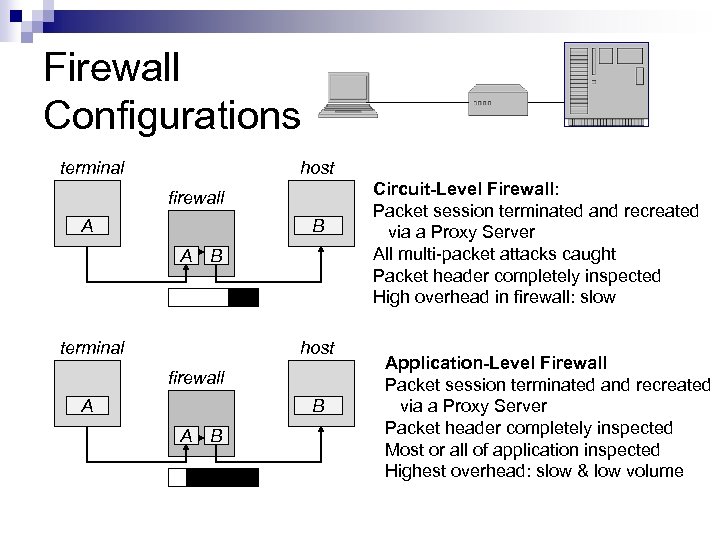 Firewall Configurations terminal host firewall A B A B Circuit-Level Firewall: Packet session terminated and recreated via a Proxy Server All multi-packet attacks caught Packet header completely inspected High overhead in firewall: slow Application-Level Firewall Packet session terminated and recreated via a Proxy Server Packet header completely inspected Most or all of application inspected Highest overhead: slow & low volume
Firewall Configurations terminal host firewall A B A B Circuit-Level Firewall: Packet session terminated and recreated via a Proxy Server All multi-packet attacks caught Packet header completely inspected High overhead in firewall: slow Application-Level Firewall Packet session terminated and recreated via a Proxy Server Packet header completely inspected Most or all of application inspected Highest overhead: slow & low volume
 Web Page Security SQL Filtering: Filtering of web input for SQL Injection Encryption/Authentication: Ensuring Confidentiality, Integrity, Authenticity, Nonrepudiation Web Protocol Protection: Protection of State
Web Page Security SQL Filtering: Filtering of web input for SQL Injection Encryption/Authentication: Ensuring Confidentiality, Integrity, Authenticity, Nonrepudiation Web Protocol Protection: Protection of State
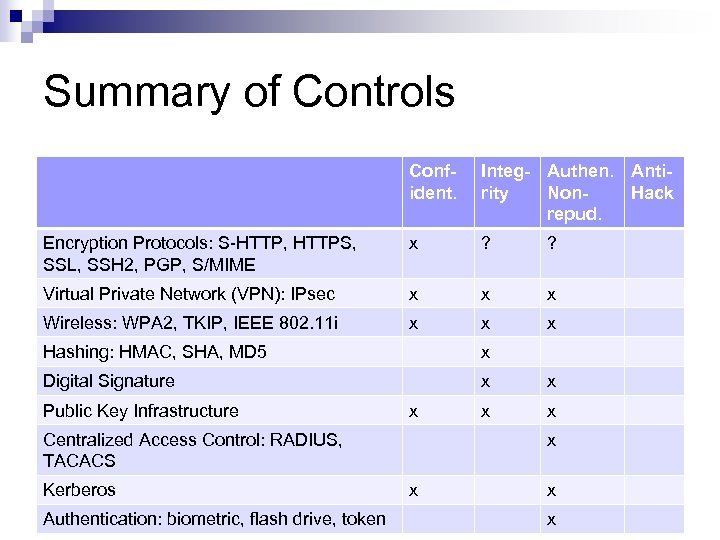 Summary of Controls Confident. Integ- Authen. Antirity Non. Hack repud. Encryption Protocols: S-HTTP, HTTPS, SSL, SSH 2, PGP, S/MIME x ? ? Virtual Private Network (VPN): IPsec x x x Wireless: WPA 2, TKIP, IEEE 802. 11 i x x x Hashing: HMAC, SHA, MD 5 x Digital Signature x x Public Key Infrastructure x Centralized Access Control: RADIUS, TACACS Kerberos Authentication: biometric, flash drive, token x x
Summary of Controls Confident. Integ- Authen. Antirity Non. Hack repud. Encryption Protocols: S-HTTP, HTTPS, SSL, SSH 2, PGP, S/MIME x ? ? Virtual Private Network (VPN): IPsec x x x Wireless: WPA 2, TKIP, IEEE 802. 11 i x x x Hashing: HMAC, SHA, MD 5 x Digital Signature x x Public Key Infrastructure x Centralized Access Control: RADIUS, TACACS Kerberos Authentication: biometric, flash drive, token x x
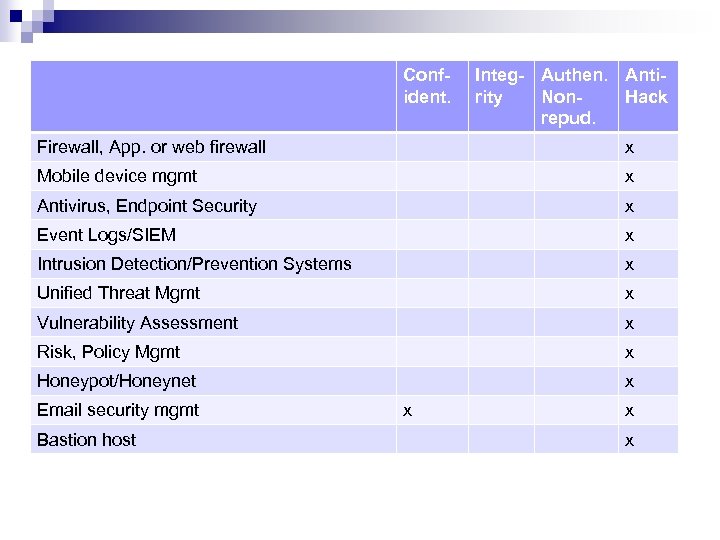 Confident. Integ- Authen. Antirity Non. Hack repud. Firewall, App. or web firewall x Mobile device mgmt x Antivirus, Endpoint Security x Event Logs/SIEM x Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems x Unified Threat Mgmt x Vulnerability Assessment x Risk, Policy Mgmt x Honeypot/Honeynet x Email security mgmt Bastion host x x x
Confident. Integ- Authen. Antirity Non. Hack repud. Firewall, App. or web firewall x Mobile device mgmt x Antivirus, Endpoint Security x Event Logs/SIEM x Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems x Unified Threat Mgmt x Vulnerability Assessment x Risk, Policy Mgmt x Honeypot/Honeynet x Email security mgmt Bastion host x x x
 Question A map of the network that shows where service requests enter and are processed 1. Is called the Path of Physical Access 2. Is primarily used in developing security policies 3. Can be used to determine whether sufficient Defense in Depth is implemented 4. Helps to determine where antivirus software should be installed
Question A map of the network that shows where service requests enter and are processed 1. Is called the Path of Physical Access 2. Is primarily used in developing security policies 3. Can be used to determine whether sufficient Defense in Depth is implemented 4. Helps to determine where antivirus software should be installed
 Question The filter with the most extensive filtering capability is the 1. Packet filter 2. Application-level firewall 3. Circuit-level firewall 4. State Inspection
Question The filter with the most extensive filtering capability is the 1. Packet filter 2. Application-level firewall 3. Circuit-level firewall 4. State Inspection
 Question The technique which implements nonrepudiation is: 1. Hash 2. Secret Key Encryption 3. Digital Signature 4. IDS
Question The technique which implements nonrepudiation is: 1. Hash 2. Secret Key Encryption 3. Digital Signature 4. IDS
 Question Anti-virus software typically implements which type of defensive software: 1. Neural Network 2. Statistical-based 3. Signature-based 4. Packet filter
Question Anti-virus software typically implements which type of defensive software: 1. Neural Network 2. Statistical-based 3. Signature-based 4. Packet filter
 Question MD 5 is an example of what type of software: 1. Public Key Encryption 2. Secret Key Encryption 3. Message Authentication 4. PKI
Question MD 5 is an example of what type of software: 1. Public Key Encryption 2. Secret Key Encryption 3. Message Authentication 4. PKI
 Question A personal firewall implemented as part of the OS or antivirus software qualifies as a: 1. Dual-homed firewall 2. Packet filter 3. Screened host 4. Bastion host
Question A personal firewall implemented as part of the OS or antivirus software qualifies as a: 1. Dual-homed firewall 2. Packet filter 3. Screened host 4. Bastion host
 Jamie Ramon MD Doctor Chris Ramon RD Dietician Terry Pat Licensed Software Consultant Practicing Nurse HEALTH FIRST CASE STUDY Designing Network Security
Jamie Ramon MD Doctor Chris Ramon RD Dietician Terry Pat Licensed Software Consultant Practicing Nurse HEALTH FIRST CASE STUDY Designing Network Security
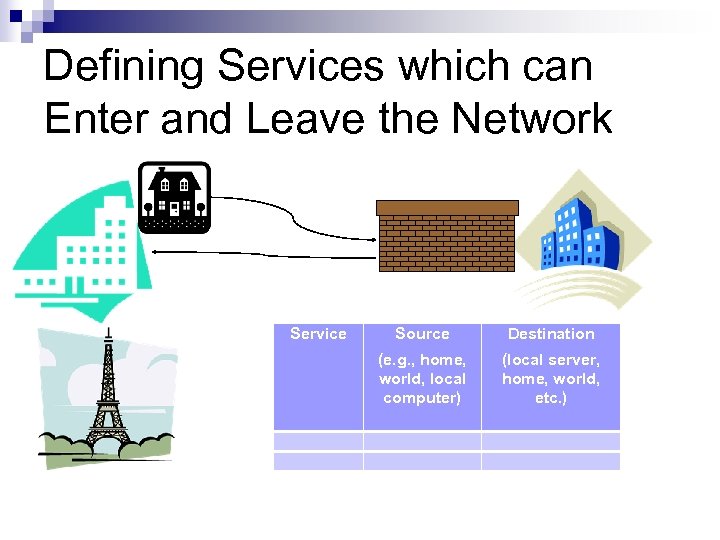 Defining Services which can Enter and Leave the Network Service Destination (e. g. , home, world, local computer) Source (local server, home, world, etc. )
Defining Services which can Enter and Leave the Network Service Destination (e. g. , home, world, local computer) Source (local server, home, world, etc. )
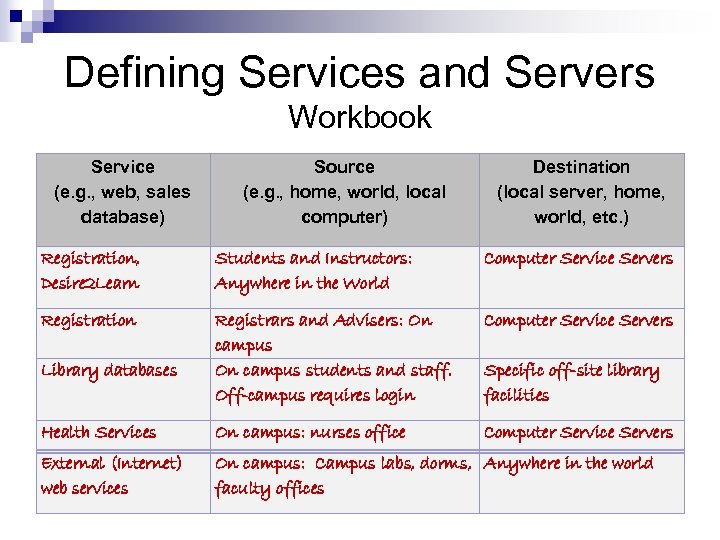 Defining Services and Servers Workbook Service (e. g. , web, sales database) Source (e. g. , home, world, local computer) Destination (local server, home, world, etc. ) Registration, Desire 2 Learn Students and Instructors: Anywhere in the World Computer Service Servers Registration Registrars and Advisers: On campus students and staff. Off-campus requires login Computer Service Servers Health Services On campus: nurses office Computer Service Servers External (Internet) web services On campus: Campus labs, dorms, Anywhere in the world faculty offices Library databases Specific off-site library facilities
Defining Services and Servers Workbook Service (e. g. , web, sales database) Source (e. g. , home, world, local computer) Destination (local server, home, world, etc. ) Registration, Desire 2 Learn Students and Instructors: Anywhere in the World Computer Service Servers Registration Registrars and Advisers: On campus students and staff. Off-campus requires login Computer Service Servers Health Services On campus: nurses office Computer Service Servers External (Internet) web services On campus: Campus labs, dorms, Anywhere in the world faculty offices Library databases Specific off-site library facilities
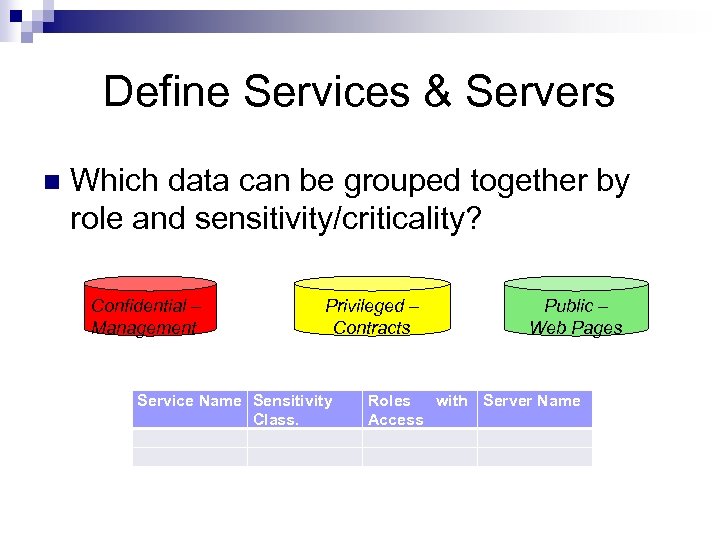 Define Services & Servers n Which data can be grouped together by role and sensitivity/criticality? Confidential – Management Privileged – Contracts Service Name Sensitivity Class. Public – Web Pages Roles with Server Name Access
Define Services & Servers n Which data can be grouped together by role and sensitivity/criticality? Confidential – Management Privileged – Contracts Service Name Sensitivity Class. Public – Web Pages Roles with Server Name Access
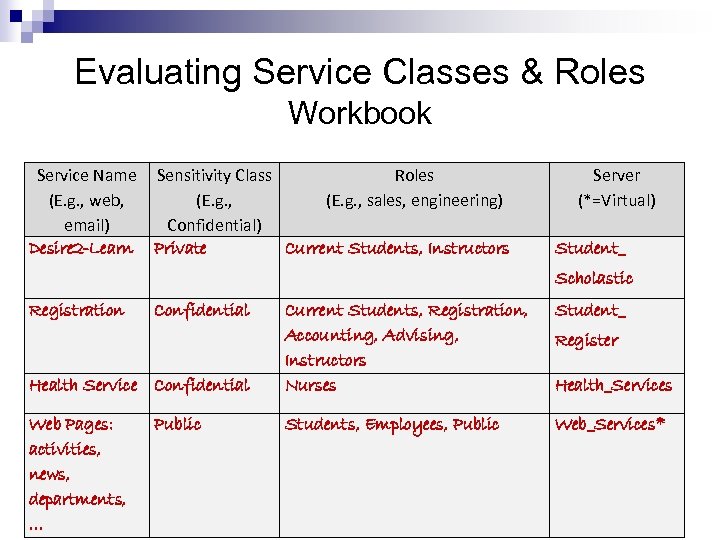 Evaluating Service Classes & Roles Workbook Service Name (E. g. , web, email) Desire 2 -Learn Sensitivity Class Roles (E. g. , sales, engineering) Confidential) Private Current Students, Instructors Server (*=Virtual) Student_ Scholastic Registration Confidential Health Service Confidential Web Pages: activities, news, departments, … Public Current Students, Registration, Accounting, Advising, Instructors Nurses Student_ Students, Employees, Public Web_Services* Register Health_Services
Evaluating Service Classes & Roles Workbook Service Name (E. g. , web, email) Desire 2 -Learn Sensitivity Class Roles (E. g. , sales, engineering) Confidential) Private Current Students, Instructors Server (*=Virtual) Student_ Scholastic Registration Confidential Health Service Confidential Web Pages: activities, news, departments, … Public Current Students, Registration, Accounting, Advising, Instructors Nurses Student_ Students, Employees, Public Web_Services* Register Health_Services
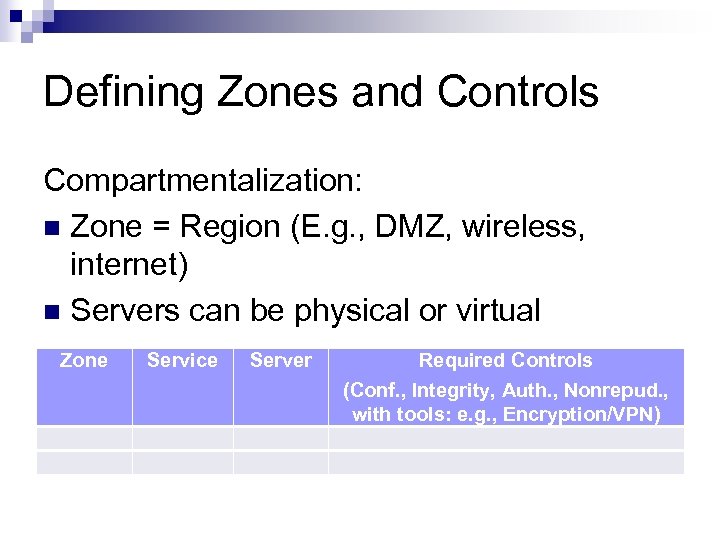 Defining Zones and Controls Compartmentalization: n Zone = Region (E. g. , DMZ, wireless, internet) n Servers can be physical or virtual Zone Service Server Required Controls (Conf. , Integrity, Auth. , Nonrepud. , with tools: e. g. , Encryption/VPN)
Defining Zones and Controls Compartmentalization: n Zone = Region (E. g. , DMZ, wireless, internet) n Servers can be physical or virtual Zone Service Server Required Controls (Conf. , Integrity, Auth. , Nonrepud. , with tools: e. g. , Encryption/VPN)
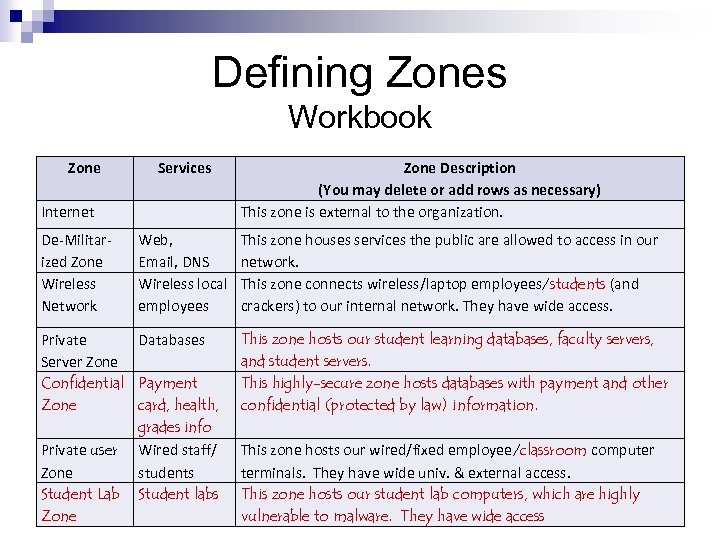 Defining Zones Workbook Zone Services Internet Zone Description (You may delete or add rows as necessary) This zone is external to the organization. De-Militarized Zone Wireless Network Web, Email, DNS Wireless local employees This zone houses services the public are allowed to access in our network. This zone connects wireless/laptop employees/students (and crackers) to our internal network. They have wide access. Private Databases Server Zone Confidential Payment Zone card, health, grades info Private user Wired staff/ Zone students Student Lab Student labs Zone This zone hosts our student learning databases, faculty servers, and student servers. This highly-secure zone hosts databases with payment and other confidential (protected by law) information. This zone hosts our wired/fixed employee/classroom computer terminals. They have wide univ. & external access. This zone hosts our student lab computers, which are highly vulnerable to malware. They have wide access
Defining Zones Workbook Zone Services Internet Zone Description (You may delete or add rows as necessary) This zone is external to the organization. De-Militarized Zone Wireless Network Web, Email, DNS Wireless local employees This zone houses services the public are allowed to access in our network. This zone connects wireless/laptop employees/students (and crackers) to our internal network. They have wide access. Private Databases Server Zone Confidential Payment Zone card, health, grades info Private user Wired staff/ Zone students Student Lab Student labs Zone This zone hosts our student learning databases, faculty servers, and student servers. This highly-secure zone hosts databases with payment and other confidential (protected by law) information. This zone hosts our wired/fixed employee/classroom computer terminals. They have wide univ. & external access. This zone hosts our student lab computers, which are highly vulnerable to malware. They have wide access
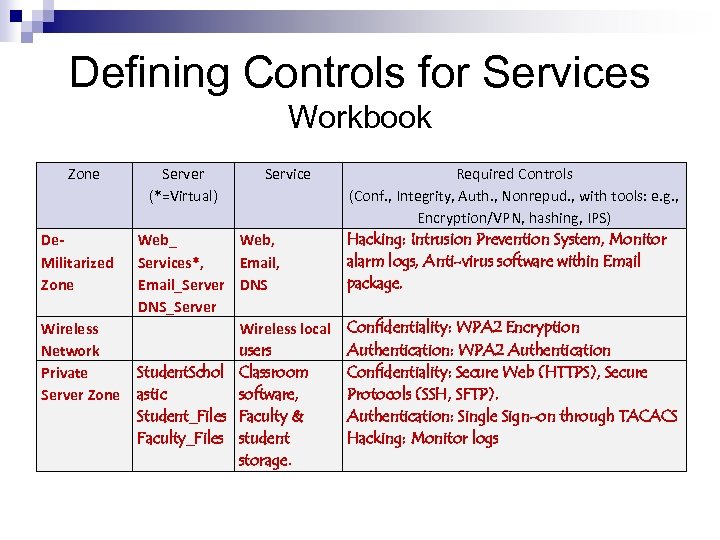 Defining Controls for Services Workbook Zone De. Militarized Zone Wireless Network Private Server Zone Server (*=Virtual) Web_ Services*, Email_Server DNS_Server Service Web, Email, DNS Wireless local users Student. Schol Classroom astic software, Student_Files Faculty & Faculty_Files student storage. Required Controls (Conf. , Integrity, Auth. , Nonrepud. , with tools: e. g. , Encryption/VPN, hashing, IPS) Hacking: Intrusion Prevention System, Monitor alarm logs, Anti-virus software within Email package. Confidentiality: WPA 2 Encryption Authentication: WPA 2 Authentication Confidentiality: Secure Web (HTTPS), Secure Protocols (SSH, SFTP). Authentication: Single Sign-on through TACACS Hacking: Monitor logs
Defining Controls for Services Workbook Zone De. Militarized Zone Wireless Network Private Server Zone Server (*=Virtual) Web_ Services*, Email_Server DNS_Server Service Web, Email, DNS Wireless local users Student. Schol Classroom astic software, Student_Files Faculty & Faculty_Files student storage. Required Controls (Conf. , Integrity, Auth. , Nonrepud. , with tools: e. g. , Encryption/VPN, hashing, IPS) Hacking: Intrusion Prevention System, Monitor alarm logs, Anti-virus software within Email package. Confidentiality: WPA 2 Encryption Authentication: WPA 2 Authentication Confidentiality: Secure Web (HTTPS), Secure Protocols (SSH, SFTP). Authentication: Single Sign-on through TACACS Hacking: Monitor logs
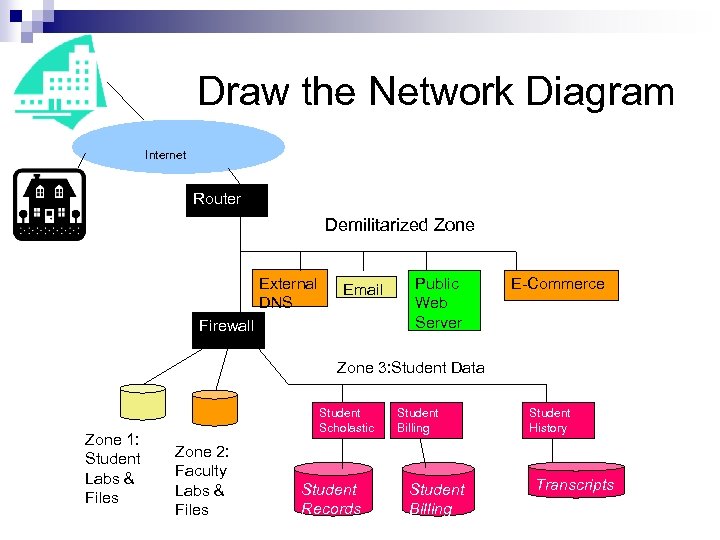 Draw the Network Diagram Internet Router Demilitarized Zone External DNS Email Firewall Public Web Server E-Commerce Zone 3: Student Data Zone 1: Student Labs & Files Student Scholastic Zone 2: Faculty Labs & Files Student Records Student Billing Student History Transcripts
Draw the Network Diagram Internet Router Demilitarized Zone External DNS Email Firewall Public Web Server E-Commerce Zone 3: Student Data Zone 1: Student Labs & Files Student Scholastic Zone 2: Faculty Labs & Files Student Records Student Billing Student History Transcripts
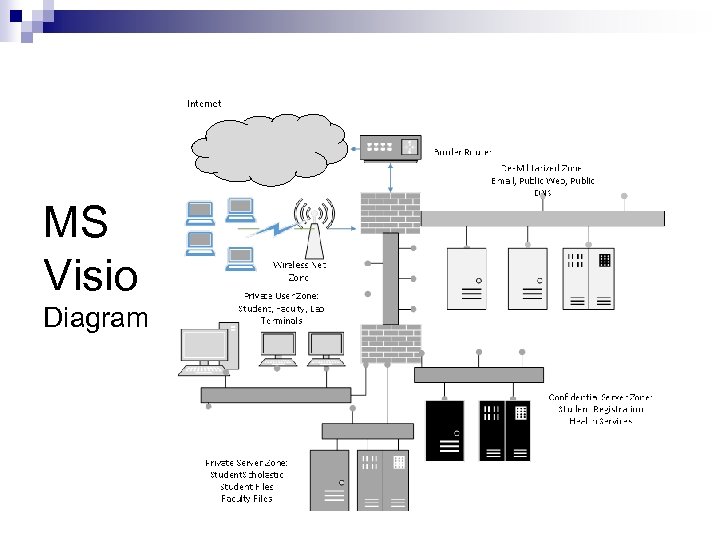 MS Visio Diagram
MS Visio Diagram
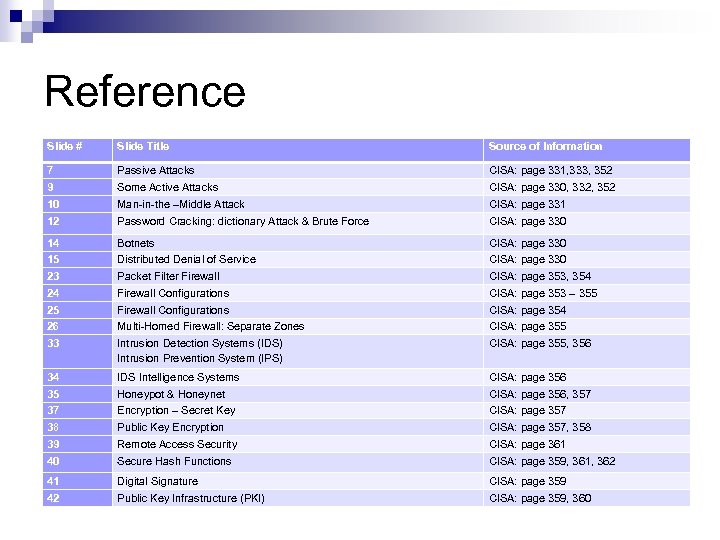 Reference Slide # Slide Title Source of Information 7 Passive Attacks CISA: page 331, 333, 352 9 Some Active Attacks CISA: page 330, 332, 352 10 Man-in-the –Middle Attack CISA: page 331 12 Password Cracking: dictionary Attack & Brute Force CISA: page 330 14 Botnets CISA: page 330 15 Distributed Denial of Service CISA: page 330 23 Packet Filter Firewall CISA: page 353, 354 24 Firewall Configurations CISA: page 353 – 355 25 Firewall Configurations CISA: page 354 26 Multi-Homed Firewall: Separate Zones CISA: page 355 33 Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) CISA: page 355, 356 34 IDS Intelligence Systems CISA: page 356 35 Honeypot & Honeynet CISA: page 356, 357 37 Encryption – Secret Key CISA: page 357 38 Public Key Encryption CISA: page 357, 358 39 Remote Access Security CISA: page 361 40 Secure Hash Functions CISA: page 359, 361, 362 41 Digital Signature CISA: page 359 42 Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) CISA: page 359, 360
Reference Slide # Slide Title Source of Information 7 Passive Attacks CISA: page 331, 333, 352 9 Some Active Attacks CISA: page 330, 332, 352 10 Man-in-the –Middle Attack CISA: page 331 12 Password Cracking: dictionary Attack & Brute Force CISA: page 330 14 Botnets CISA: page 330 15 Distributed Denial of Service CISA: page 330 23 Packet Filter Firewall CISA: page 353, 354 24 Firewall Configurations CISA: page 353 – 355 25 Firewall Configurations CISA: page 354 26 Multi-Homed Firewall: Separate Zones CISA: page 355 33 Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) CISA: page 355, 356 34 IDS Intelligence Systems CISA: page 356 35 Honeypot & Honeynet CISA: page 356, 357 37 Encryption – Secret Key CISA: page 357 38 Public Key Encryption CISA: page 357, 358 39 Remote Access Security CISA: page 361 40 Secure Hash Functions CISA: page 359, 361, 362 41 Digital Signature CISA: page 359 42 Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) CISA: page 359, 360


