f3c69d6eddae3db8ed9f0fe7a47b655b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 Network Programming OSI Model Client-server programming
Network Programming OSI Model Client-server programming
 ISO-OSI Model • ISO= International Standards Organization • OSI = Open Systems Interconnection
ISO-OSI Model • ISO= International Standards Organization • OSI = Open Systems Interconnection
 7 Layers • • Physical - bits Data Link – dlpdu (frames) no routing Network – IP (192. 168. 1. 1) - routing Transport – TCP/IP, UDP/IP-transmission control Session – login Presentation – http – iiop /corba, rmi, dbnet Application - browser
7 Layers • • Physical - bits Data Link – dlpdu (frames) no routing Network – IP (192. 168. 1. 1) - routing Transport – TCP/IP, UDP/IP-transmission control Session – login Presentation – http – iiop /corba, rmi, dbnet Application - browser
 What is a domain? • • id for network, tlds’. edu, . com, . gov, . net, biz, org, name, info DNS – maps domain names to IP addresses. lookups or reverse lookups.
What is a domain? • • id for network, tlds’. edu, . com, . gov, . net, biz, org, name, info DNS – maps domain names to IP addresses. lookups or reverse lookups.
 Using a windows hosts table • • • Windows 95/98/Me c: windowshosts Windows NT/2000/XP Pro c: winntsystem 32driversetchosts Windows XP Home c: windowssystem 32driversetchosts
Using a windows hosts table • • • Windows 95/98/Me c: windowshosts Windows NT/2000/XP Pro c: winntsystem 32driversetchosts Windows XP Home c: windowssystem 32driversetchosts
 Mac/Unix • /etc/hosts • 127. 0. 0. 1 localhost • 172. 16. 11. 202 linux 1
Mac/Unix • /etc/hosts • 127. 0. 0. 1 localhost • 172. 16. 11. 202 linux 1
 What is socket programming? • A means of using TCP/IP or UDP/IP along with a PORT to: – connect – transmit bytes in a stream – disconnect – Inter-process communication
What is socket programming? • A means of using TCP/IP or UDP/IP along with a PORT to: – connect – transmit bytes in a stream – disconnect – Inter-process communication
 Why do I need socket programming? • • • web/http IIOP, RMI distributed computing concurrent computing Network computing open a virtual connection
Why do I need socket programming? • • • web/http IIOP, RMI distributed computing concurrent computing Network computing open a virtual connection
 Why do I need ports? • 1 computer has many services • ports are sometimes standard. . – 80 – default web service port – 7 – ping – 13 – time – 25 – snmtp – /etc/services – to see the ports in UNIX
Why do I need ports? • 1 computer has many services • ports are sometimes standard. . – 80 – default web service port – 7 – ping – 13 – time – 25 – snmtp – /etc/services – to see the ports in UNIX
 A simple server (simplified code) import java. net. *; import java. io. *; public class ASimple. Server { public static void main(String args[]) { // Register service on port 1234 Server. Socket s = new Server. Socket(1234); Socket s 1=s. accept(); // Wait and accept a connection // Get a communication stream associated with the socket Output. Stream s 1 out = s 1. get. Output. Stream(); Data. Output. Stream dos = new Data. Output. Stream (s 1 out); // Send a string! dos. write. UTF(“Hi there”); // Close the connection, but not the server socket dos. close(); s 1 out. close(); s 1. close(); } 10 }
A simple server (simplified code) import java. net. *; import java. io. *; public class ASimple. Server { public static void main(String args[]) { // Register service on port 1234 Server. Socket s = new Server. Socket(1234); Socket s 1=s. accept(); // Wait and accept a connection // Get a communication stream associated with the socket Output. Stream s 1 out = s 1. get. Output. Stream(); Data. Output. Stream dos = new Data. Output. Stream (s 1 out); // Send a string! dos. write. UTF(“Hi there”); // Close the connection, but not the server socket dos. close(); s 1 out. close(); s 1. close(); } 10 }
 A simple client (simplified code) import java. net. *; import java. io. *; public class Simple. Client { public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException { // Open your connection to a server, at port 1234 Socket s 1 = new Socket("130. 63. 122. 1", 1234); // Get an input file handle from the socket and read the input Input. Stream s 1 In = s 1. get. Input. Stream(); Data. Input. Stream dis = new Data. Input. Stream(s 1 In); String st = new String (dis. read. UTF()); System. out. println(st); // When done, just close the connection and exit dis. close(); s 1 In. close(); s 1. close(); } 11 }
A simple client (simplified code) import java. net. *; import java. io. *; public class Simple. Client { public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException { // Open your connection to a server, at port 1234 Socket s 1 = new Socket("130. 63. 122. 1", 1234); // Get an input file handle from the socket and read the input Input. Stream s 1 In = s 1. get. Input. Stream(); Data. Input. Stream dis = new Data. Input. Stream(s 1 In); String st = new String (dis. read. UTF()); System. out. println(st); // When done, just close the connection and exit dis. close(); s 1 In. close(); s 1. close(); } 11 }
 Sockets – TCP/IP • • reliable means of data transmission Routing is automatic on the Internet. UNICAST – one-to-one If you want one to MANY then you use – MULTICAST – Requires a MULTICAST enabled router! – TTL = number of router hops before the packet is blocked.
Sockets – TCP/IP • • reliable means of data transmission Routing is automatic on the Internet. UNICAST – one-to-one If you want one to MANY then you use – MULTICAST – Requires a MULTICAST enabled router! – TTL = number of router hops before the packet is blocked.
![Class Inet. Address public boolean equals(Object obj); public public byte[] static String static get. Class Inet. Address public boolean equals(Object obj); public public byte[] static String static get.](https://present5.com/presentation/f3c69d6eddae3db8ed9f0fe7a47b655b/image-13.jpg) Class Inet. Address public boolean equals(Object obj); public public byte[] static String static get. Address(); Inet. Address[] get. All. By. Name(String host); Inet. Address get. By. Name(String host); get. Host. Name(); Inet. Address get. Local. Host(); public int hash. Code(); public String to. String(); This class represents an Internet Protocol (IP) address. Applications should use the methods get. Local. Host(), get. By. Name(), or get. All. By. Name() to create a new Inet. Address instance.
Class Inet. Address public boolean equals(Object obj); public public byte[] static String static get. Address(); Inet. Address[] get. All. By. Name(String host); Inet. Address get. By. Name(String host); get. Host. Name(); Inet. Address get. Local. Host(); public int hash. Code(); public String to. String(); This class represents an Internet Protocol (IP) address. Applications should use the methods get. Local. Host(), get. By. Name(), or get. All. By. Name() to create a new Inet. Address instance.
 Host. Info. java import java. net. *; public class Host. Info { public static void main( String args[] ) { Inet. Address ip. Addr; try { ip. Addr = Inet. Address. get. Local. Host(); System. out. println( "This is " + ip. Addr ); } catch ( Unknown. Host. Exception ex ) { System. out. println( "Unknown host" ); } }
Host. Info. java import java. net. *; public class Host. Info { public static void main( String args[] ) { Inet. Address ip. Addr; try { ip. Addr = Inet. Address. get. Local. Host(); System. out. println( "This is " + ip. Addr ); } catch ( Unknown. Host. Exception ex ) { System. out. println( "Unknown host" ); } }
 Resolver. java import java. net. *; public class Resolver { public static void main( String args[] ) { Inet. Address ip. Addr; try { ip. Addr = Inet. Address. get. By. Name( args[0] ); System. out. print( "IP address = " + ip. Addr + "n " ); } catch ( Unknown. Host. Exception ex ){ System. out. println( "Unknown host " ); } } }
Resolver. java import java. net. *; public class Resolver { public static void main( String args[] ) { Inet. Address ip. Addr; try { ip. Addr = Inet. Address. get. By. Name( args[0] ); System. out. print( "IP address = " + ip. Addr + "n " ); } catch ( Unknown. Host. Exception ex ){ System. out. println( "Unknown host " ); } } }
 Daytime Service Most UNIX servers run the daytime service on TCP port 13. cobalt> telnet kiev. cs. rit. edu 13 Trying 129. 21. 38. 145. . . Connected to kiev. Escape character is '^]'. Fri Feb 6 08: 33: 44 1998 Connection closed by foreign host. It is easy to write a Java daytime client. All the program needs to do is to establish a TCP connection on port 13 of a remote host. A TCP style connection is made using the Socket class.
Daytime Service Most UNIX servers run the daytime service on TCP port 13. cobalt> telnet kiev. cs. rit. edu 13 Trying 129. 21. 38. 145. . . Connected to kiev. Escape character is '^]'. Fri Feb 6 08: 33: 44 1998 Connection closed by foreign host. It is easy to write a Java daytime client. All the program needs to do is to establish a TCP connection on port 13 of a remote host. A TCP style connection is made using the Socket class.
 A Java Daytime Server • It is easy to create a daytime server in Java (the only real problem is that your Java server will not be able to use port 13). • The server version of the program will use a Server. Socket to communicate with a client. • A Server. Socket will open a TCP port and wait for a connection. • Once a request is detected, a new port will be created, and the connection will be established between the client's source port and this new port. • Most servers listen for requests on a particular port, and then service that request on a different port. • This makes it easy for the server to accept and service requests at the same time.
A Java Daytime Server • It is easy to create a daytime server in Java (the only real problem is that your Java server will not be able to use port 13). • The server version of the program will use a Server. Socket to communicate with a client. • A Server. Socket will open a TCP port and wait for a connection. • Once a request is detected, a new port will be created, and the connection will be established between the client's source port and this new port. • Most servers listen for requests on a particular port, and then service that request on a different port. • This makes it easy for the server to accept and service requests at the same time.
 Day. Time. Client. java import java. net. *; import java. io. *; import java. util. *; public class Day. Time. Client { static int day. Time. Port = 13; public static void main(String args[]) { try { Socket sock = new Socket(args[0], day. Time. Port); Buffered. Reader din = new Buffered. Reader( new Input. Stream. Reader(sock. get. Input. Stream())); String r. Time = din. read. Line(); System. out. println(r. Time); sock. close(); } catch (exception e) {} } }
Day. Time. Client. java import java. net. *; import java. io. *; import java. util. *; public class Day. Time. Client { static int day. Time. Port = 13; public static void main(String args[]) { try { Socket sock = new Socket(args[0], day. Time. Port); Buffered. Reader din = new Buffered. Reader( new Input. Stream. Reader(sock. get. Input. Stream())); String r. Time = din. read. Line(); System. out. println(r. Time); sock. close(); } catch (exception e) {} } }
 Class Socket // Constructors (partial list) public Socket(Inet. Address address, int port); public Socket(String host, int port); // Methods (partial list) public void close(); public Inet. Address get. Inet. Address(); public int get. Local. Port(); public Input. Stream get. Input. Stream(); public Output. Stream get. Output. Stream(); public int get. Port(); public String to. String();
Class Socket // Constructors (partial list) public Socket(Inet. Address address, int port); public Socket(String host, int port); // Methods (partial list) public void close(); public Inet. Address get. Inet. Address(); public int get. Local. Port(); public Input. Stream get. Input. Stream(); public Output. Stream get. Output. Stream(); public int get. Port(); public String to. String();
 Class Socket • This class implements client sockets (also called just sockets). A socket is a end point for communication between two machines. • The actual work of the socket is performed by an instance of the Socket. Impl class. • It is possible to modify some TCP parameters: – SO_LINGER – SO_TIMEOUT – TCP_NODELAY – Enable/disable TCP_NODELAY (disable/enable Nagle's algorithm).
Class Socket • This class implements client sockets (also called just sockets). A socket is a end point for communication between two machines. • The actual work of the socket is performed by an instance of the Socket. Impl class. • It is possible to modify some TCP parameters: – SO_LINGER – SO_TIMEOUT – TCP_NODELAY – Enable/disable TCP_NODELAY (disable/enable Nagle's algorithm).
 Class Server. Socket // Constructors (partial list) public Server. Socket(int port); public Server. Socket(int port, int count); // Methods (partial list) public Socket accept(); public void close(); public Inet. Address get. Inet. Address(); public int get. Local. Port(); public String to. String();
Class Server. Socket // Constructors (partial list) public Server. Socket(int port); public Server. Socket(int port, int count); // Methods (partial list) public Socket accept(); public void close(); public Inet. Address get. Inet. Address(); public int get. Local. Port(); public String to. String();
 Class Server. Socket • A Server. Socket waits for requests to come in over the network. It performs some operation based on that request, and then possibly returns a result to the requester. • The actual work of the Server. Socket is performed by an instance of the Socket. Impl class. • The abstract class Socket. Impl is a common superclass of all classes that actually implement sockets. It is used to create both client and server sockets. • A plain socket implements the Socket. Impl methods exactly as described, without attempting to go through a firewall or proxy.
Class Server. Socket • A Server. Socket waits for requests to come in over the network. It performs some operation based on that request, and then possibly returns a result to the requester. • The actual work of the Server. Socket is performed by an instance of the Socket. Impl class. • The abstract class Socket. Impl is a common superclass of all classes that actually implement sockets. It is used to create both client and server sockets. • A plain socket implements the Socket. Impl methods exactly as described, without attempting to go through a firewall or proxy.
 Day. Time. Server import java. net. *; import java. io. *; import java. util. *; public class Day. Time. Server { public static void main(String argv[]) { try { Date today = new Date(); Inet. Address local. Host = Inet. Address. get. Local. Host(); Server. Socket listen = new Server. Socket(0); System. out. println("Listening on port: "+listen. get. Local. Port()); for(; ; ) { Socket clnt = listen. accept(); System. out. println(clnt. to. String()); Print. Writer out = new Print. Writer(clnt. get. Output. Stream(), true); out. println(today); clnt. close(); } } catch(Exception e) {}}}
Day. Time. Server import java. net. *; import java. io. *; import java. util. *; public class Day. Time. Server { public static void main(String argv[]) { try { Date today = new Date(); Inet. Address local. Host = Inet. Address. get. Local. Host(); Server. Socket listen = new Server. Socket(0); System. out. println("Listening on port: "+listen. get. Local. Port()); for(; ; ) { Socket clnt = listen. accept(); System. out. println(clnt. to. String()); Print. Writer out = new Print. Writer(clnt. get. Output. Stream(), true); out. println(today); clnt. close(); } } catch(Exception e) {}}}
 Day. Time. Server in Action The output from the daytime server looks like this: kiev> java Day. Time. Server Listening on port: 36109 Socket[addr=cobalt/129. 21. 37. 176, port=32875, localport=36109] Socket[addr=localhost/127. 0. 0. 1, port=36112, localport=36109] The client output looks like this: cobalt> telnet kiev 36109 Trying 129. 21. 38. 145. . . Connected to kiev. Escape character is '^]'. Fri Feb 06 09: 53: 00 EST 1998 Connection closed by foreign host.
Day. Time. Server in Action The output from the daytime server looks like this: kiev> java Day. Time. Server Listening on port: 36109 Socket[addr=cobalt/129. 21. 37. 176, port=32875, localport=36109] Socket[addr=localhost/127. 0. 0. 1, port=36112, localport=36109] The client output looks like this: cobalt> telnet kiev 36109 Trying 129. 21. 38. 145. . . Connected to kiev. Escape character is '^]'. Fri Feb 06 09: 53: 00 EST 1998 Connection closed by foreign host.
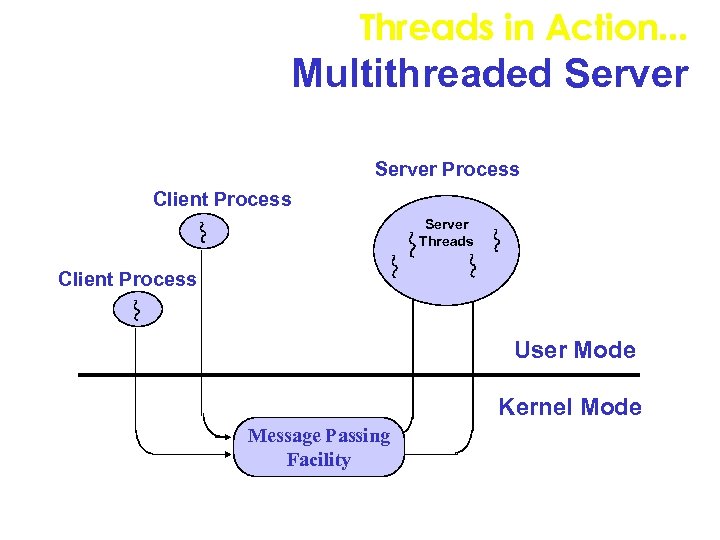 Threads in Action. . . Multithreaded Server Process Client Process Server Threads Client Process User Mode Kernel Mode Message Passing Facility
Threads in Action. . . Multithreaded Server Process Client Process Server Threads Client Process User Mode Kernel Mode Message Passing Facility
 Multi-Threaded Servers • It is quite easy, and natural in Java, to make a server multi-threaded. • In a multi-threaded server a new thread is created to handle each request. • Clearly for a server such as the daytime server this is not necessary, but for an FTP server this is almost required. • The code for the multi-threaded version of the server consists of a new class called Connection. • An instance of this class handles the clients request.
Multi-Threaded Servers • It is quite easy, and natural in Java, to make a server multi-threaded. • In a multi-threaded server a new thread is created to handle each request. • Clearly for a server such as the daytime server this is not necessary, but for an FTP server this is almost required. • The code for the multi-threaded version of the server consists of a new class called Connection. • An instance of this class handles the clients request.
 Multicast Sockets • What is a multicast socket? – unicast sockets provide a point to point connection. There is one sender and one receiver. – Multicast sockets have one sender and many receivers
Multicast Sockets • What is a multicast socket? – unicast sockets provide a point to point connection. There is one sender and one receiver. – Multicast sockets have one sender and many receivers
 Why doesn’t everyone use Mcast sockets? • Not all routers will pass Multicast sockets. • Multicasting may not be supported on your network. • TTLs limit a packets spread. • TTL = max # of routers a packet is allowed to cross.
Why doesn’t everyone use Mcast sockets? • Not all routers will pass Multicast sockets. • Multicasting may not be supported on your network. • TTLs limit a packets spread. • TTL = max # of routers a packet is allowed to cross.
 What are some Applications for Mcast? • appliances can look for a lookup server MCast. – suppose I plug in a PNP printer • MCast is good for discovery • Unicast is good for correspondance. • Etherswitch does a kind of routing that protects net legs from traffic.
What are some Applications for Mcast? • appliances can look for a lookup server MCast. – suppose I plug in a PNP printer • MCast is good for discovery • Unicast is good for correspondance. • Etherswitch does a kind of routing that protects net legs from traffic.
 Etherswitch/mcast • Etherswitch passes all mcast traffic through. • Etherswitch isolates only unicast traffic. • Ethernet 10 mbps – 100 mpbs 1 Gbps 10 Gb/s. • Now we can do VIDEO on the Ethernet.
Etherswitch/mcast • Etherswitch passes all mcast traffic through. • Etherswitch isolates only unicast traffic. • Ethernet 10 mbps – 100 mpbs 1 Gbps 10 Gb/s. • Now we can do VIDEO on the Ethernet.
 Broadcast Video • CCIR-601 Standard Video – 720 -x 480 pixels at 16 bits per PEL at 30 Frames per second. – 160 Mb/s, uncompressed. – Suppose you don’t use a video camera to make video!
Broadcast Video • CCIR-601 Standard Video – 720 -x 480 pixels at 16 bits per PEL at 30 Frames per second. – 160 Mb/s, uncompressed. – Suppose you don’t use a video camera to make video!
 What is video? • • • Image sequences + audio How can I make image sequences? Screen capture…. are almost NOISE FREE. Inter-frame coherence. Difference frames can be coded efficiently.
What is video? • • • Image sequences + audio How can I make image sequences? Screen capture…. are almost NOISE FREE. Inter-frame coherence. Difference frames can be coded efficiently.
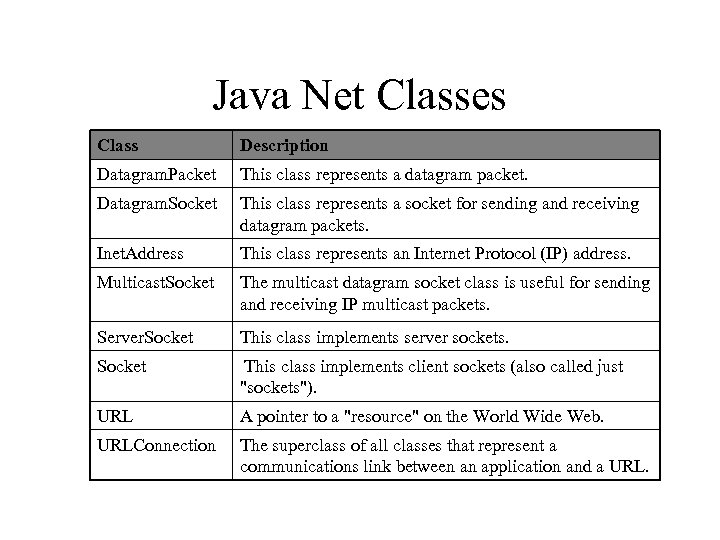 Java Net Classes Class Description Datagram. Packet This class represents a datagram packet. Datagram. Socket This class represents a socket for sending and receiving datagram packets. Inet. Address This class represents an Internet Protocol (IP) address. Multicast. Socket The multicast datagram socket class is useful for sending and receiving IP multicast packets. Server. Socket This class implements server sockets. Socket This class implements client sockets (also called just "sockets"). URL A pointer to a "resource" on the World Wide Web. URLConnection The superclass of all classes that represent a communications link between an application and a URL.
Java Net Classes Class Description Datagram. Packet This class represents a datagram packet. Datagram. Socket This class represents a socket for sending and receiving datagram packets. Inet. Address This class represents an Internet Protocol (IP) address. Multicast. Socket The multicast datagram socket class is useful for sending and receiving IP multicast packets. Server. Socket This class implements server sockets. Socket This class implements client sockets (also called just "sockets"). URL A pointer to a "resource" on the World Wide Web. URLConnection The superclass of all classes that represent a communications link between an application and a URL.
 Connection. java import java. net. *; import java. io. *; import java. util. *; class Connection extends Thread { protected Socket clnt; public Connection(Socket sock) { clnt = sock; this. start(); } public void run() { Date today = new Date(); try { Print. Writer out = new Print. Writer(clnt. get. Output. Stream(), true); out. println(today); client. close(); } catch (IOException e) {}}}
Connection. java import java. net. *; import java. io. *; import java. util. *; class Connection extends Thread { protected Socket clnt; public Connection(Socket sock) { clnt = sock; this. start(); } public void run() { Date today = new Date(); try { Print. Writer out = new Print. Writer(clnt. get. Output. Stream(), true); out. println(today); client. close(); } catch (IOException e) {}}}
 TDay. Time. Server. java import java. net. *; import java. io. *; import java. util. *; public class TDay. Time. Server { public static void main(String argv[]) { try { Inet. Address local. Host = Inet. Address. get. Local. Host(); Server. Socket listen = new Server. Socket(0); System. out. println("Listening on: "+listen. get. Local. Port()); for(; ; ) { Socket clnt = listen. accept(); System. out. println(clnt. to. String()); Connection c = new Connection(client); } } catch(Exception e) { System. out. println("Server terminated"); } } }
TDay. Time. Server. java import java. net. *; import java. io. *; import java. util. *; public class TDay. Time. Server { public static void main(String argv[]) { try { Inet. Address local. Host = Inet. Address. get. Local. Host(); Server. Socket listen = new Server. Socket(0); System. out. println("Listening on: "+listen. get. Local. Port()); for(; ; ) { Socket clnt = listen. accept(); System. out. println(clnt. to. String()); Connection c = new Connection(client); } } catch(Exception e) { System. out. println("Server terminated"); } } }
 UDP Based Applications • UDP provides an unreliable packet based delivery service. An application that uses UDP must deal with the errors that can arise during communication. • The basic unit of transfer is called a Datagrams are small, fixed-length messages. • Datagram based services do have some advantages: – Speed – Message-oriented service.
UDP Based Applications • UDP provides an unreliable packet based delivery service. An application that uses UDP must deal with the errors that can arise during communication. • The basic unit of transfer is called a Datagrams are small, fixed-length messages. • Datagram based services do have some advantages: – Speed – Message-oriented service.
 Datagrams • Datagram packets are used to implement a connectionless, packet based, delivery service. • Each message is routed from one machine to another based solely on information contained within that packet. • Multiple packets sent from one machine to another might be routed differently, and might arrive in any order. • Packets may be lost or duplicated during transit. • The class Datagram. Packet represents a datagram in Java.
Datagrams • Datagram packets are used to implement a connectionless, packet based, delivery service. • Each message is routed from one machine to another based solely on information contained within that packet. • Multiple packets sent from one machine to another might be routed differently, and might arrive in any order. • Packets may be lost or duplicated during transit. • The class Datagram. Packet represents a datagram in Java.
![Class Datagram. Packet //Constructors public Datagram. Packet(byte ibuf[], int ilength); public Datagram. Packet( byte Class Datagram. Packet //Constructors public Datagram. Packet(byte ibuf[], int ilength); public Datagram. Packet( byte](https://present5.com/presentation/f3c69d6eddae3db8ed9f0fe7a47b655b/image-38.jpg) Class Datagram. Packet //Constructors public Datagram. Packet(byte ibuf[], int ilength); public Datagram. Packet( byte ibuf[], int ilength, Inet. Address iaddr, int iport); // Methods public synchronized Inet. Address get. Address(); public synchronized int get. Port(); public synchornized byte[] get. Data(); int get. Length(); void set. Address(Inet. Address iaddr); set. Port(int iport); set. Data(byte ibuf[]); set. Length(int ilength);
Class Datagram. Packet //Constructors public Datagram. Packet(byte ibuf[], int ilength); public Datagram. Packet( byte ibuf[], int ilength, Inet. Address iaddr, int iport); // Methods public synchronized Inet. Address get. Address(); public synchronized int get. Port(); public synchornized byte[] get. Data(); int get. Length(); void set. Address(Inet. Address iaddr); set. Port(int iport); set. Data(byte ibuf[]); set. Length(int ilength);
 Class Datagram. Socket • This class represents a socket for sending and receiving datagram packets. • Addressing information for outgoing packets is contained in the packet header. • A socket that is used to read incoming packets must be bound to an address (sockets that are used for sending must be bound as well, but in most cases it is done automatically). • There is no special datagram server socket class. • Since packets can be lost, the ability to set timeouts is important.
Class Datagram. Socket • This class represents a socket for sending and receiving datagram packets. • Addressing information for outgoing packets is contained in the packet header. • A socket that is used to read incoming packets must be bound to an address (sockets that are used for sending must be bound as well, but in most cases it is done automatically). • There is no special datagram server socket class. • Since packets can be lost, the ability to set timeouts is important.
 Class Datagram. Socket // Constructors Datagram. Socket() Datagram. Socket(int port, Inet. Address iaddr) // Methods void close() Inet. Address get. Local. Address() int get. Local. Port() int get. So. Timeout() void receive(Datagram. Packet p) void send(Datagram. Packet p) set. So. Timeout(int timeout)
Class Datagram. Socket // Constructors Datagram. Socket() Datagram. Socket(int port, Inet. Address iaddr) // Methods void close() Inet. Address get. Local. Address() int get. Local. Port() int get. So. Timeout() void receive(Datagram. Packet p) void send(Datagram. Packet p) set. So. Timeout(int timeout)
 Echo Services • A common network service is an echo server • An echo server simply sends packets back to the sender • A client creates a packet, sends it to the server, and waits for a response. • Echo services can be used to test network connectivity and performance. • There are typically different levels of echo services. Each provided by a different layer in the protocol stack.
Echo Services • A common network service is an echo server • An echo server simply sends packets back to the sender • A client creates a packet, sends it to the server, and waits for a response. • Echo services can be used to test network connectivity and performance. • There are typically different levels of echo services. Each provided by a different layer in the protocol stack.
 UDPEcho. Client. java import java. net. *; import java. io. *; import java. util. *; public class UDPEcho. Client { static int echo. Port = 7; static int msg. Len = 16; static int time. Out=1000; public static void main(String argv[]) { try { Datagram. Socket sock = new Datagram. Socket(); Datagram. Packet pak; byte msg[] = new byte[msg. Len]; Inet. Address echo. Host = Inet. Address. get. By. Name(argv[0]); pak = new Datagram. Packet(msg, msg. Len, echo. Host, echo. Port); sock. send(pak); sock. set. So. Timeout(time. Out); sock. receive(pak); } catch (Interrupted. IOException e) {System. out. println("Timeout"); } catch (Exception e) {} }}
UDPEcho. Client. java import java. net. *; import java. io. *; import java. util. *; public class UDPEcho. Client { static int echo. Port = 7; static int msg. Len = 16; static int time. Out=1000; public static void main(String argv[]) { try { Datagram. Socket sock = new Datagram. Socket(); Datagram. Packet pak; byte msg[] = new byte[msg. Len]; Inet. Address echo. Host = Inet. Address. get. By. Name(argv[0]); pak = new Datagram. Packet(msg, msg. Len, echo. Host, echo. Port); sock. send(pak); sock. set. So. Timeout(time. Out); sock. receive(pak); } catch (Interrupted. IOException e) {System. out. println("Timeout"); } catch (Exception e) {} }}


